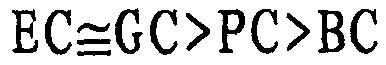Alkylene carbonates as water glass cure accelerants
A kind of alkylene carbonate, ethylene carbonate technology, applied in the curing field of adhesive mixture
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
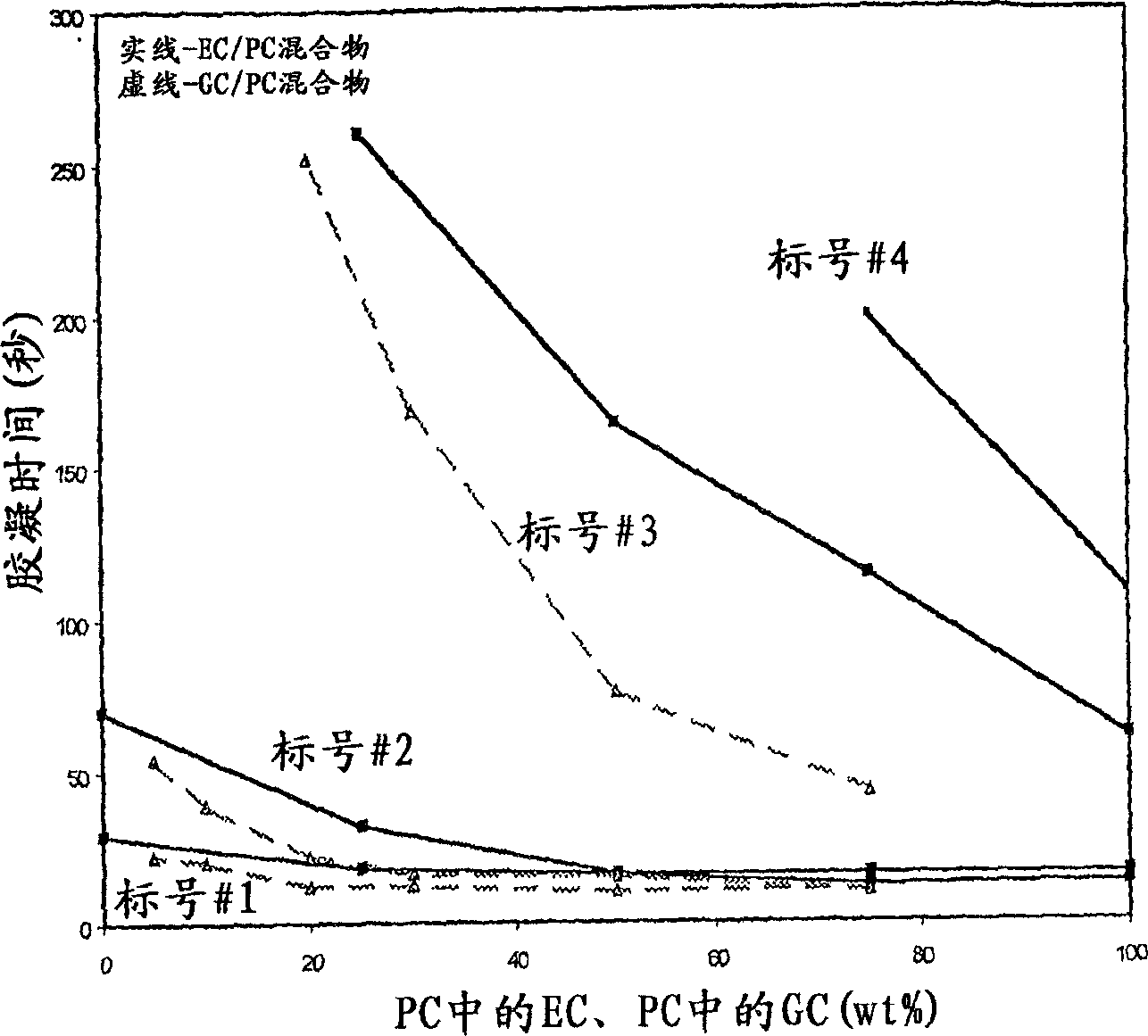
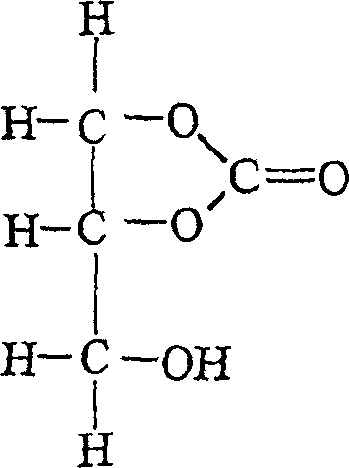
[0008] The problems associated with the use of EC-containing sodium silicate cure accelerators stemming from the relatively high freezing point of EC are alleviated by the present invention, i.e., the combination of PC with another ethylene carbonate known as glycerol carbonate (hereinafter "GC") A mixture of alkyl esters accelerates the cure of the sodium silicate to about the same extent as pure ethylene carbonate. However, unlike EC, GC does not disadvantageously freeze above -40°C. Accordingly, the present invention provides a blend of GC and PC that provides a wide range of commercial cure times while remaining liquid over a wider temperature range than prior art cure accelerators.
[0009] It is known that the order of reactivity between alkylene carbonate and amine is EC>PC>BC. Therefore, the prior art teaches that the reactivity of carbonates with amines decreases with the size of the substituents attached to the carbonate ring, so that, given its molecular structure,...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| freezing point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com