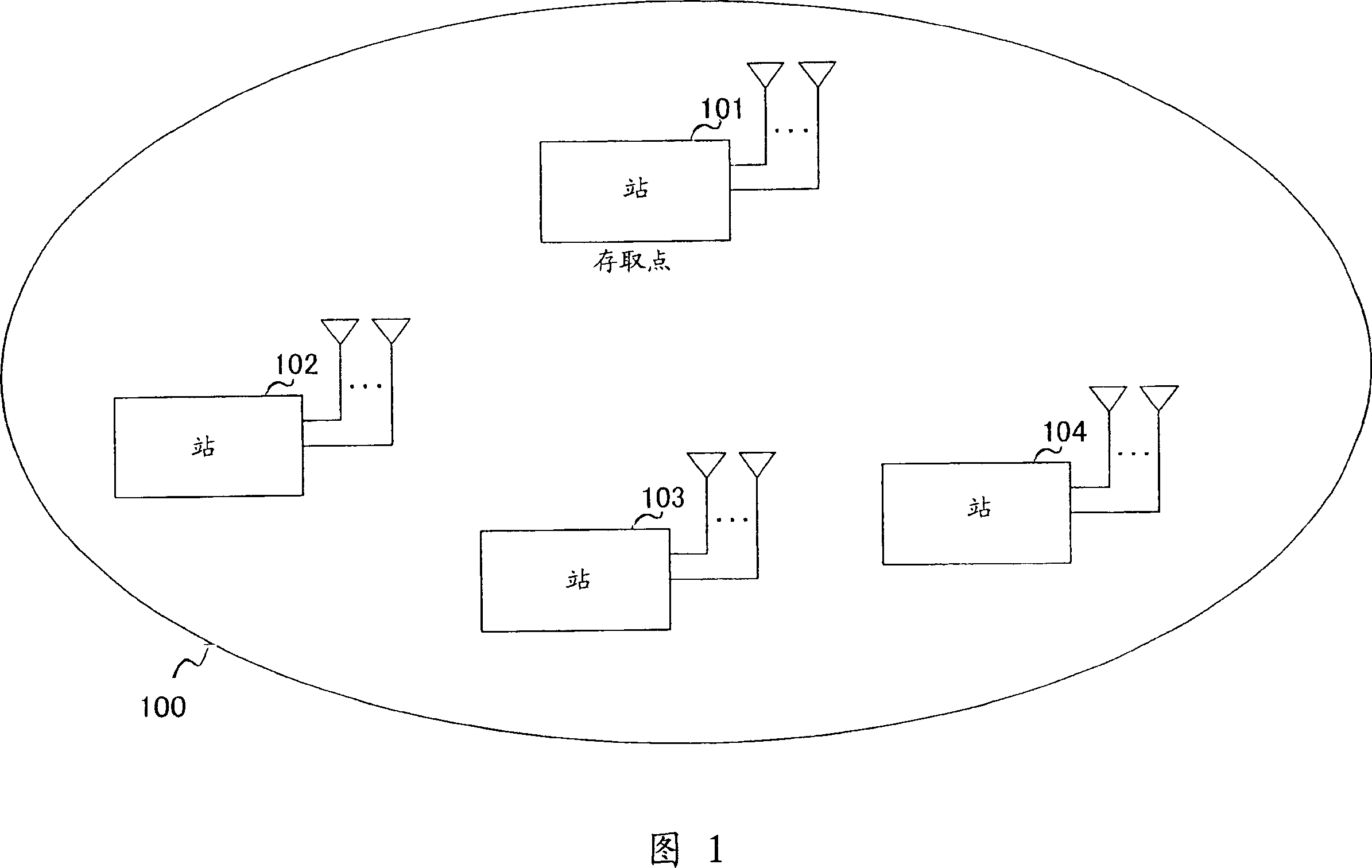
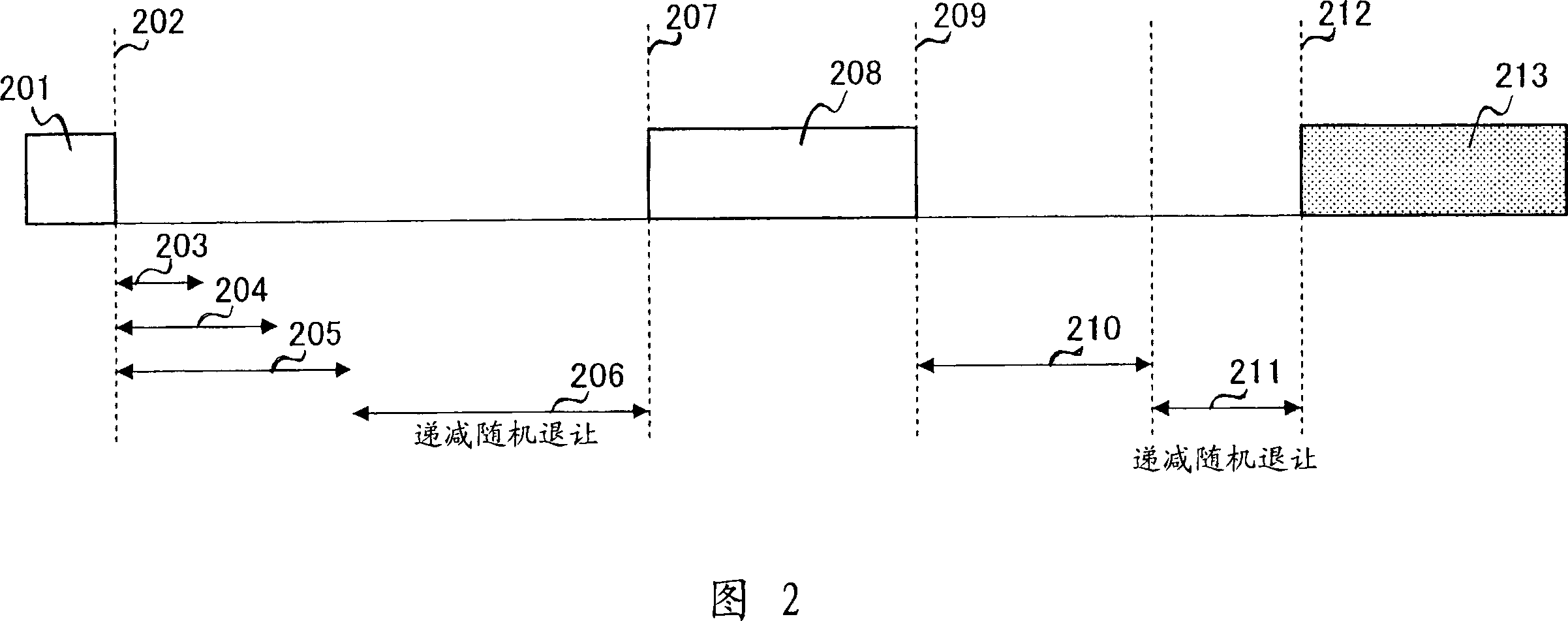
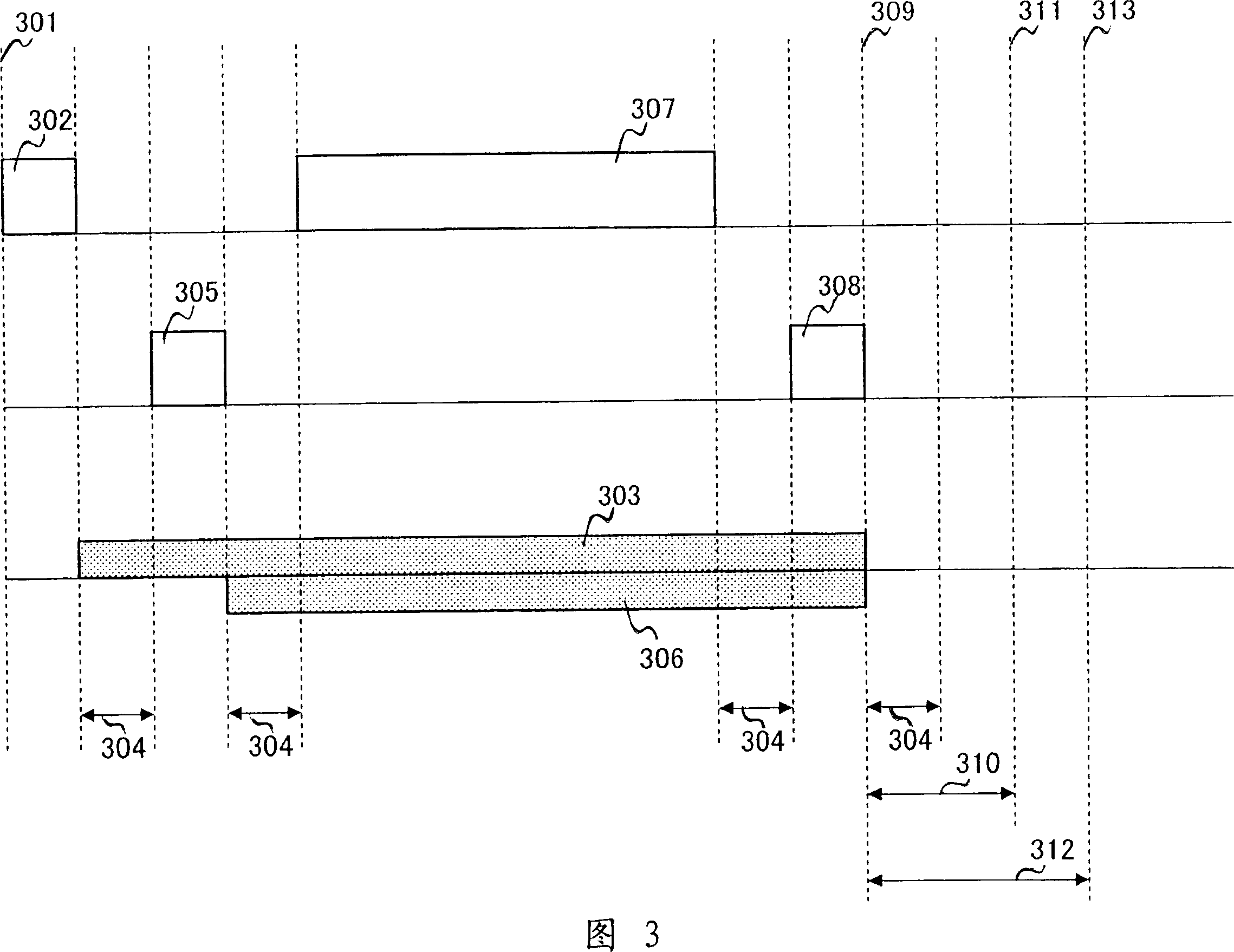
Method for reducing medium access overhead in a wireless network
A media access and wireless network technology, which is applied in the direction of data exchange through path configuration, can solve the problems of expensive bandwidth and unutilized time limit, and achieve the goal of improving media utilization, improving network throughput, and reducing media access overhead Effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
no. 3 example
[0038] A third embodiment, having a similar purpose to the second embodiment, provides that the interpretation of the Interframe Space is signaled at the MAC / PHY boundary sublayer through a field in the preamble in the transmitted frame method.
no. 4 example
[0039] A fourth embodiment, having a similar purpose to the second embodiment, provides a method of signaling the interpretation of the interframe space on the PHY layer by transmission on additional subcarriers during frame transmission.
[0040] The fifth embodiment of the present invention provides a mechanism for dynamically changing the interpretation of the inter-frame space by interpreting the information contained in the media activity indicator (a virtual carrier-aware mechanism) to dynamically change the inter-frame space By way of explanation, this embodiment has a similar intent to the first embodiment.
[0041] The sixth embodiment of the present invention specifies a mechanism for dynamically changing the interpretation of the interframe space at a reset moment in the virtual carrier sensing mechanism, which has a similar intent to the first embodiment.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com