Image displaying apparatus
An image display device and image technology, applied in the direction of static indicators, instruments, etc., can solve the problem of improving the effect of dynamic image blurring, and achieve the effect of improving the effect of dynamic image blurring
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
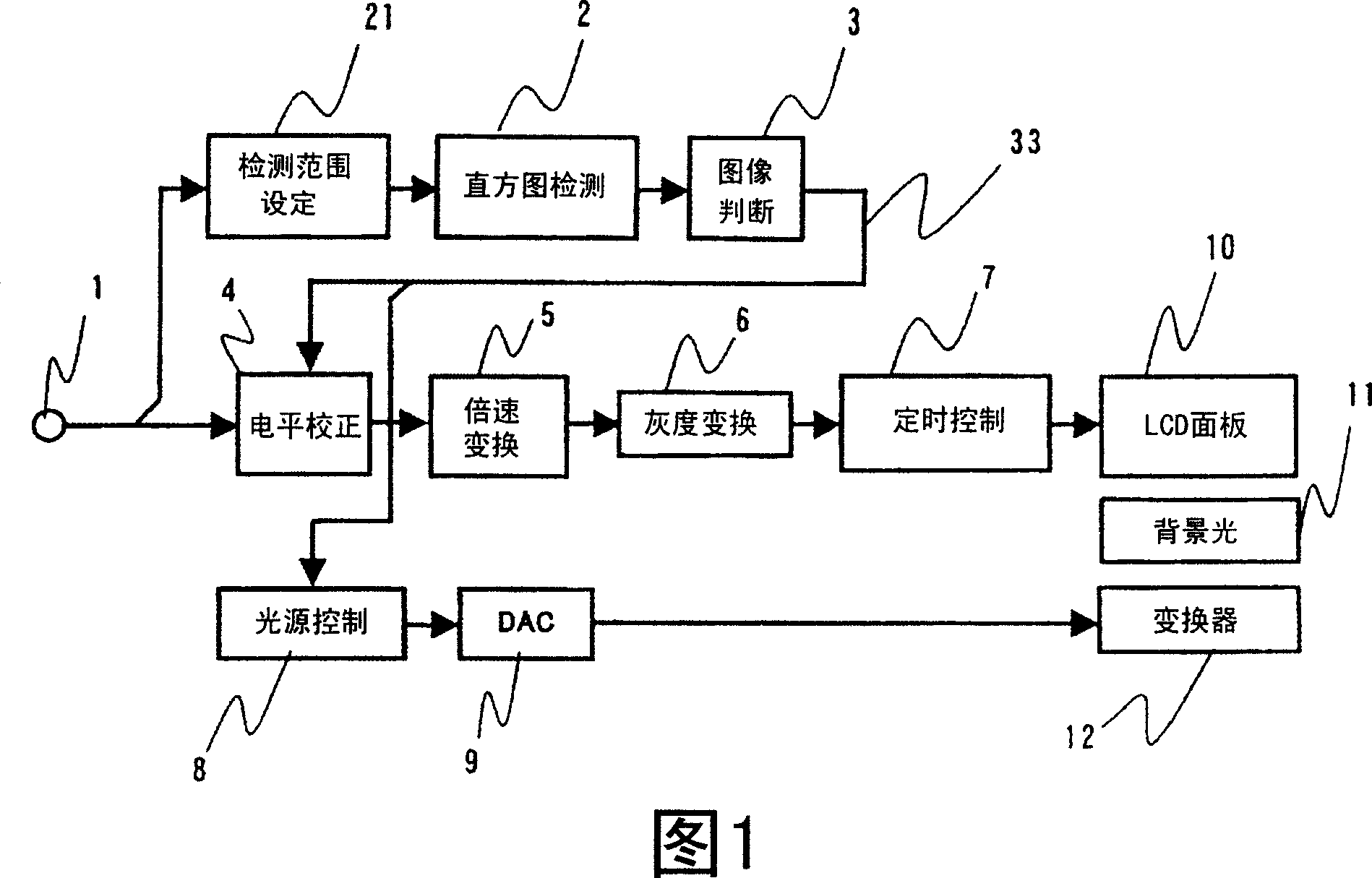
[0032] FIG. 1 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of the first embodiment of the image display device of the present invention. In this embodiment, it is assumed that an image signal in a component format (YcbCr format) having a frame frequency of 60 Hz is input from the input terminal 1 . The image signal input to the input terminal 1 is supplied to the level correction unit 4 . In addition, the input image signal is also supplied to the histogram detection unit 2 via the detection range setting unit 21 . The detection range setting unit 21 sets the range of the brightness histogram detected by the histogram detection unit on the screen of the image 1 (details will be described later). The histogram detection unit 2 detects, for example, a luminance histogram in one frame or one field period from a luminance signal (Y) included in an input image signal. The luminance histogram represents the frequency of appearance of luminance signals corresponding to each o...
Embodiment 2
[0058] Next, a second embodiment of the present invention will be described. This embodiment, as shown in FIG. 8 , is characterized in that a gradation correction unit 21 is newly provided on the level correction circuit 4 , and the gradation correction unit 121 is controlled by a control signal 122 . The structure other than the level correction circuit 4 is the same as that of the first embodiment. Next, details of the present invention will be described. In addition, in FIG. 8, the same code|symbol is attached|subjected to the same component as the component of FIG. 4, and description is abbreviate|omitted.
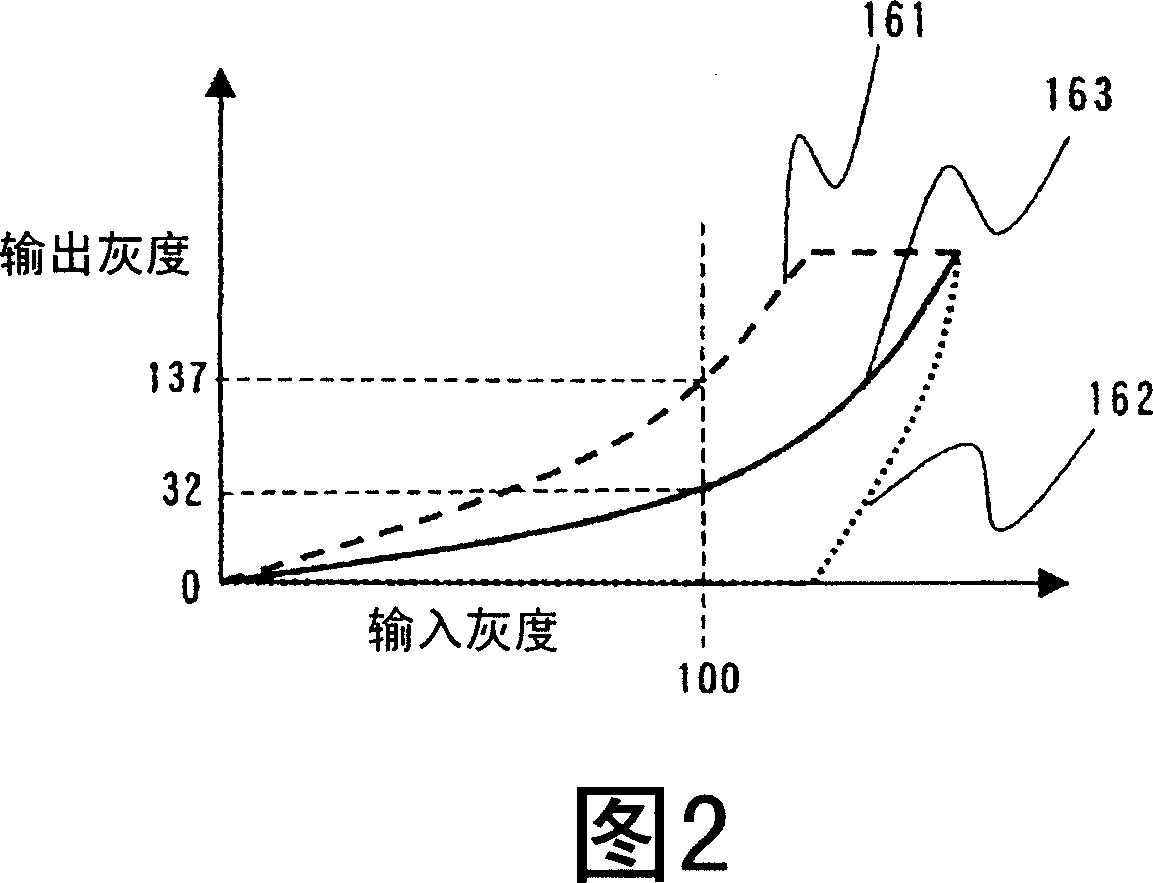
[0059] This embodiment is used to reduce the loss of dark parts through the black level correction performed by the black level correction unit 31 when the amplitude of the input image extends from high grayscale to low grayscale in a wide range. Therefore, the present embodiment provides the gradation correction section 121 for compressing the signal amplitude in th...
Embodiment 3
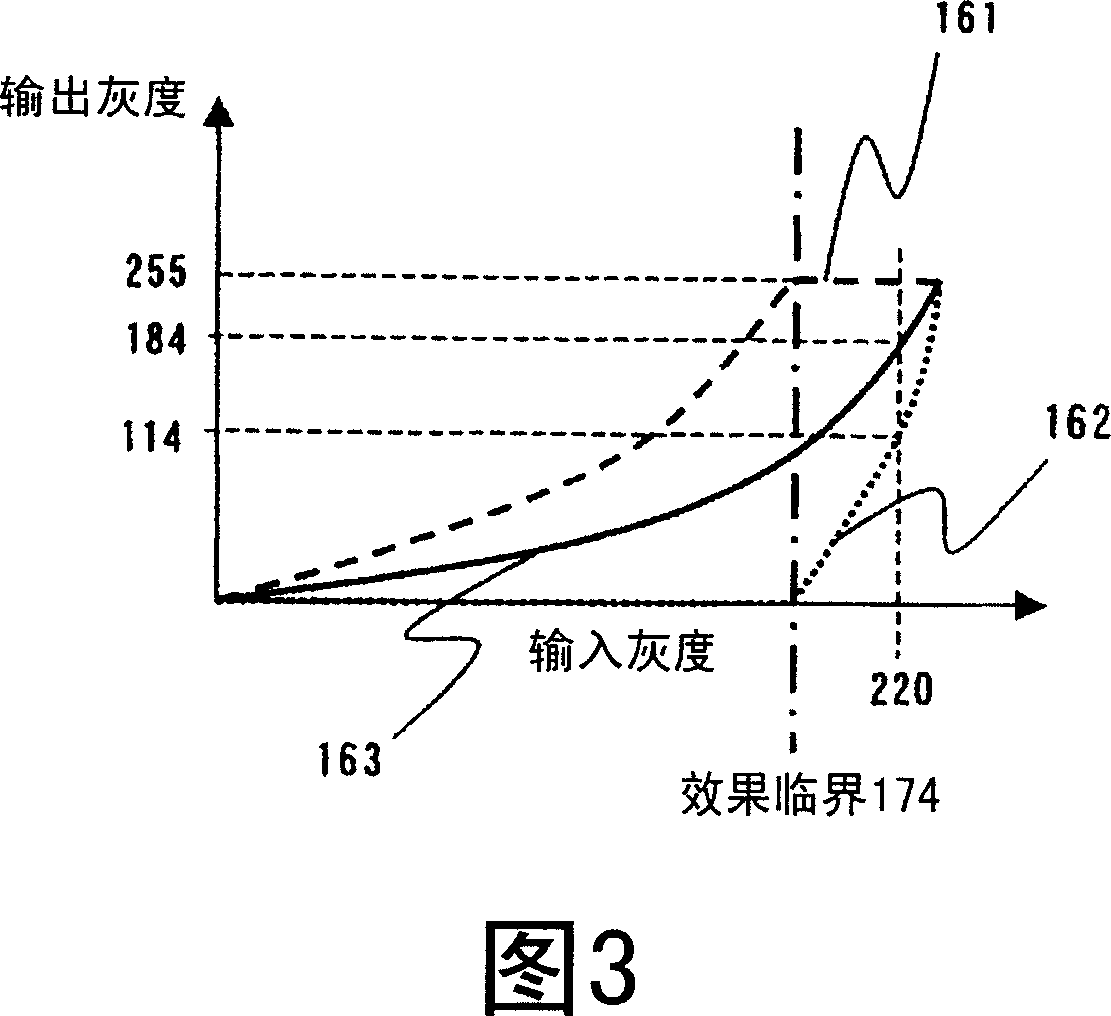
[0066] Next, a third embodiment of the present invention will be described. FIG. 12 is a block diagram showing a configuration example of an image display device according to a third embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 4 , the same reference numerals are assigned to the same components as those of the first embodiment shown in FIG. 1 , and detailed description thereof will be omitted.
[0067] In this embodiment, the signal based on the above-mentioned grayscale division method is suppressed for an image signal after 2-3 pull-down or 2-2 pull-down processing (hereinafter, these are collectively referred to as “pull-down signals”) such as movies, CG, and animation as input images. Handled cases of flickering and jittering. Before describing this embodiment, the reason why flicker and jitter occur when the pull-down signal is subjected to signal processing based on the gradation division method will be described.
[0068] For example, if the signal processing is perfo...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| greyscale | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com