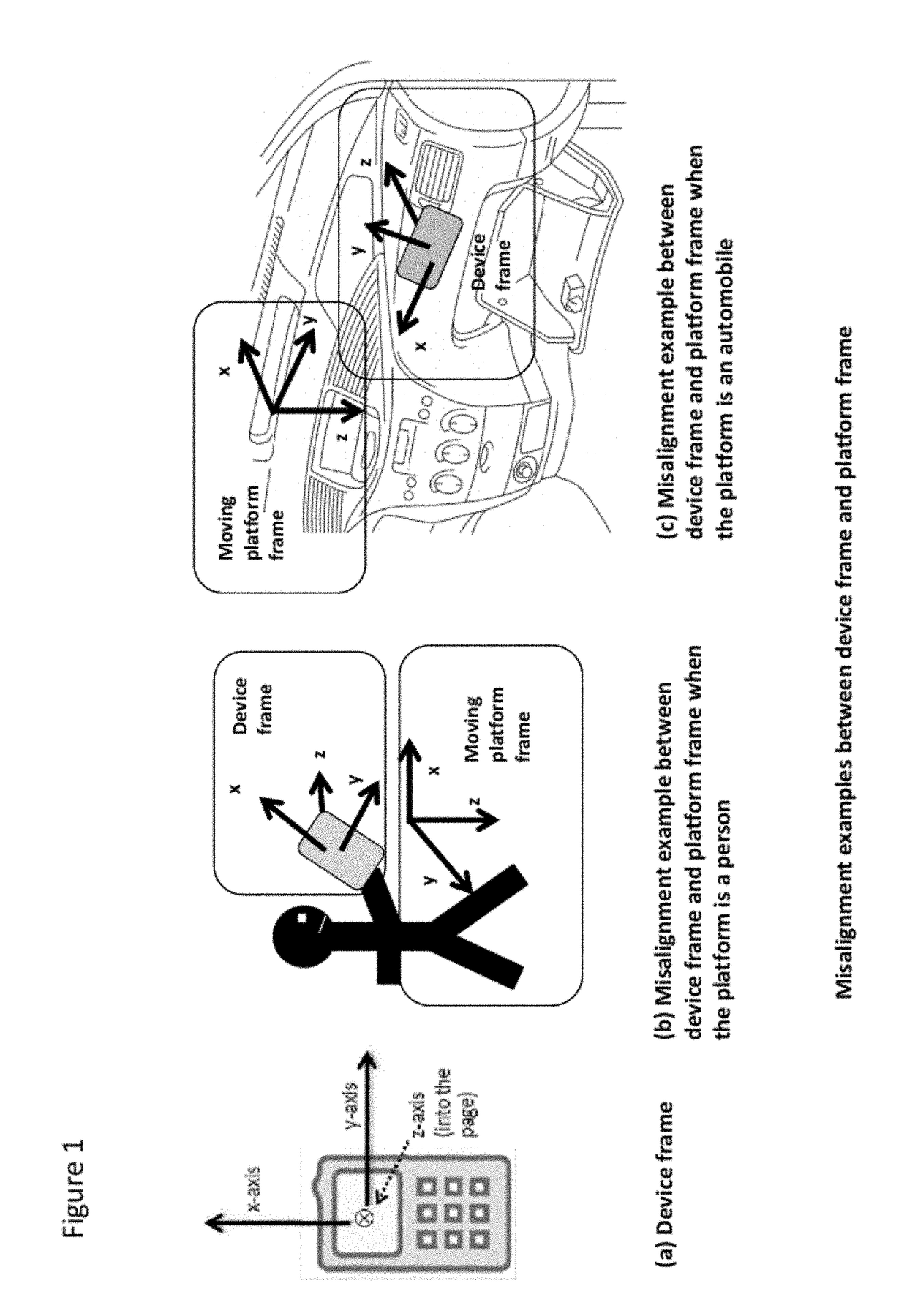
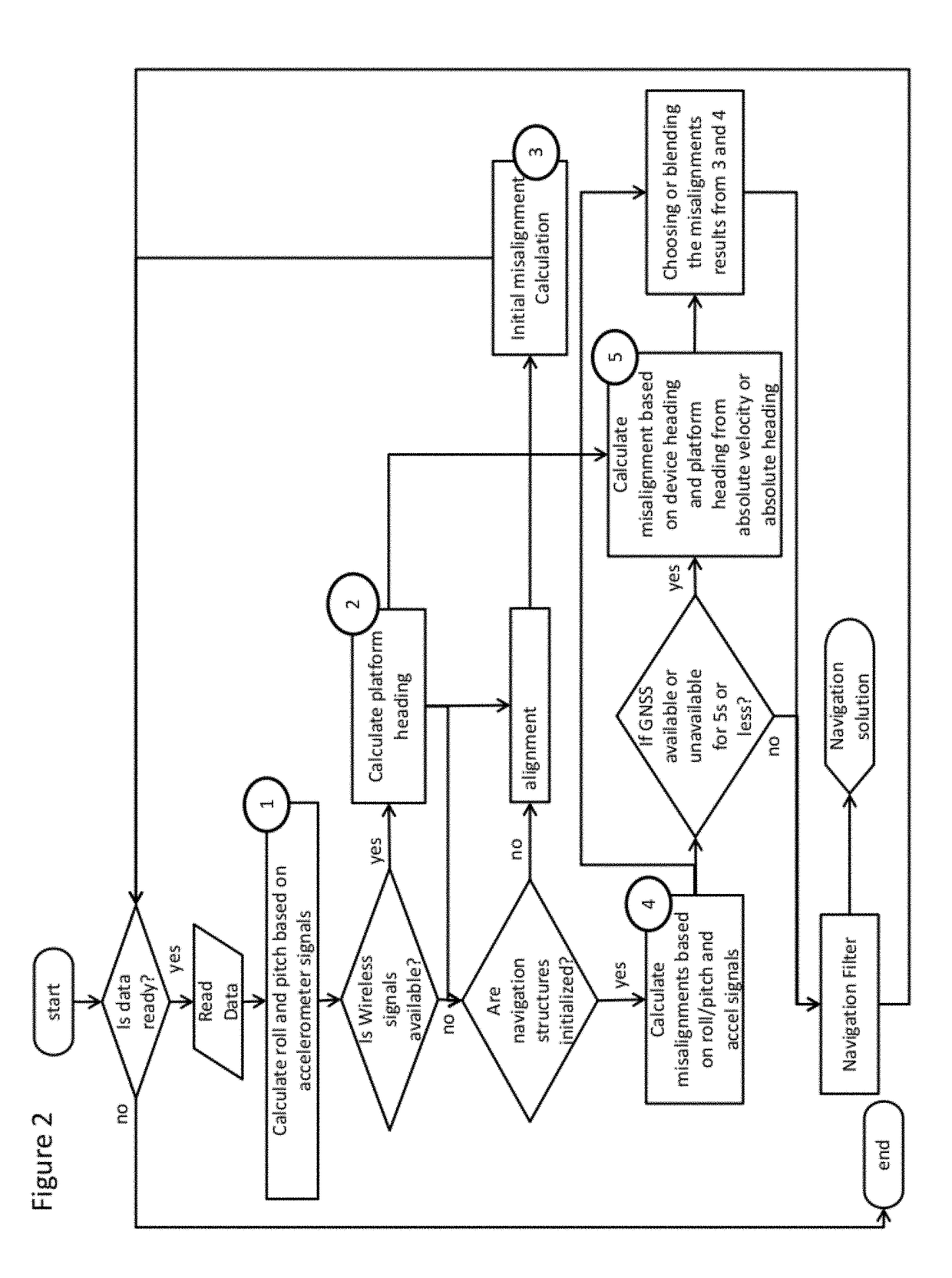
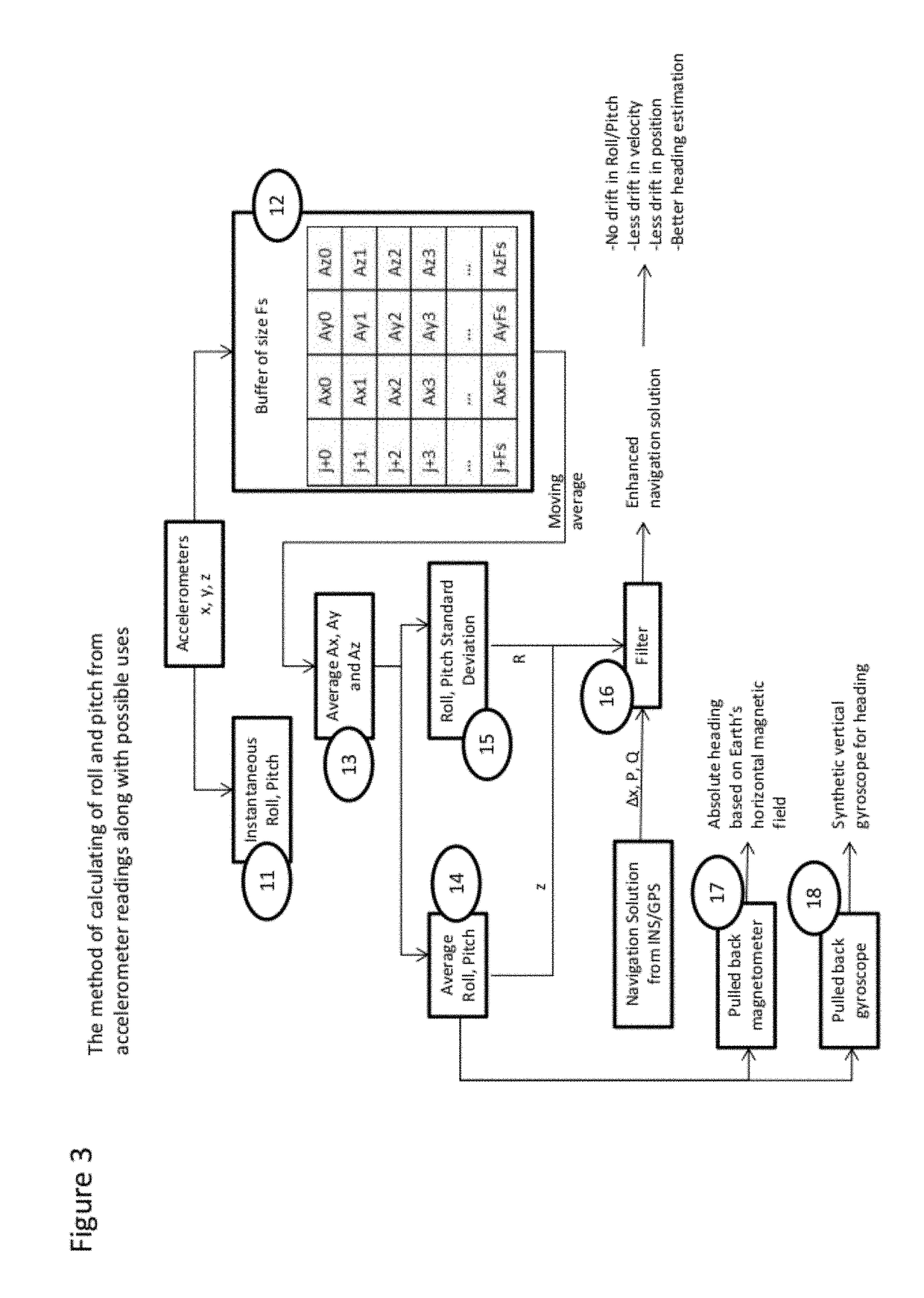
Methods of attitude and misalignment estimation for constraint free portable navigation
a technology of attitude and misalignment estimation, applied in the direction of navigation instruments, speed/acceleration measurement, instruments, etc., can solve the problems of not being able to meet the accuracy demands of location based services (lbs), and not being able to provide the absolute heading of the platform. , to achieve the effect of reducing or eliminating the effects of orientation changes
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 2
[0089]It is known that absolute roll, pitch and heading are required for inertial navigation. Typically, absolute heading of a moving platform is estimated by taking the arctangent of east and north velocities from an absolute velocity source (such as a GNSS receiver). Where GNSS is unavailable (e.g. indoor environment), other known methods of calculating heading may be applied.
[0090]For instance, where a GNSS is unable to provide velocities of the moving platform, or the platform is not moving and the device has a calibrated magnetometer, the absolute device heading can be obtained using the two leveled horizontal components of the earth's magnetic field. Where a digital map is available, the absolute heading of the platform can be calculated from the map. The presence of a radio frequency positioning system other than GNSS can also be used estimate the heading based on the platform changes in position coordinates with respect to time provided that estimated positions are accurate ...
embodiment 4
[0163]The Embodiment 4 of the present method for enhancing the navigation solution for a device and a platform, wherein the mobility of the device is constrained or unconstrained within the platform, the method comprising estimating heading misalignment between the device and the platform, and consequently to provide means for estimating the absolute heading of the platform in the absence of any absolute heading or absolute velocity information for the platform. It is to be noted that the present method can be used as well even when the absolute heading or velocity information for the platform is available, and a better blended version of the heading misalignment and / or the absolute heading of the platform can be obtained.
[0164]The absolute heading of a device can be obtained using the sensors contained within the device, either by integration of the angular measurements starting from an absolute value or deriving the values directly from a sensor (such as a magnetometer). Platform ...
embodiment 5
[0170]This Embodiment 5 of the present method comprises enhancing the navigation solution for a device and a platform, wherein the mobility of the device is constrained or unconstrained within the platform, the method comprising estimating the continued heading misalignment between the device and the platform using a source of absolute velocity of the platform, where said source of absolute velocity may be available or interrupted. Generally, the present Embodiment 5 may be used to determine the heading misalignment between the device and the platform using velocity-derived heading or absolute heading (for the platform) and sensor-derived heading (for the device).
[0171]By way of background, there are three possible sensor derived headings that can be used in device heading estimation. The first sensor-derived device heading comes from aided or unaided mechanization solution if it is available (this method for getting heading needs the initial misalignment to be resolved first using ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com