Heating apparatus and method
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
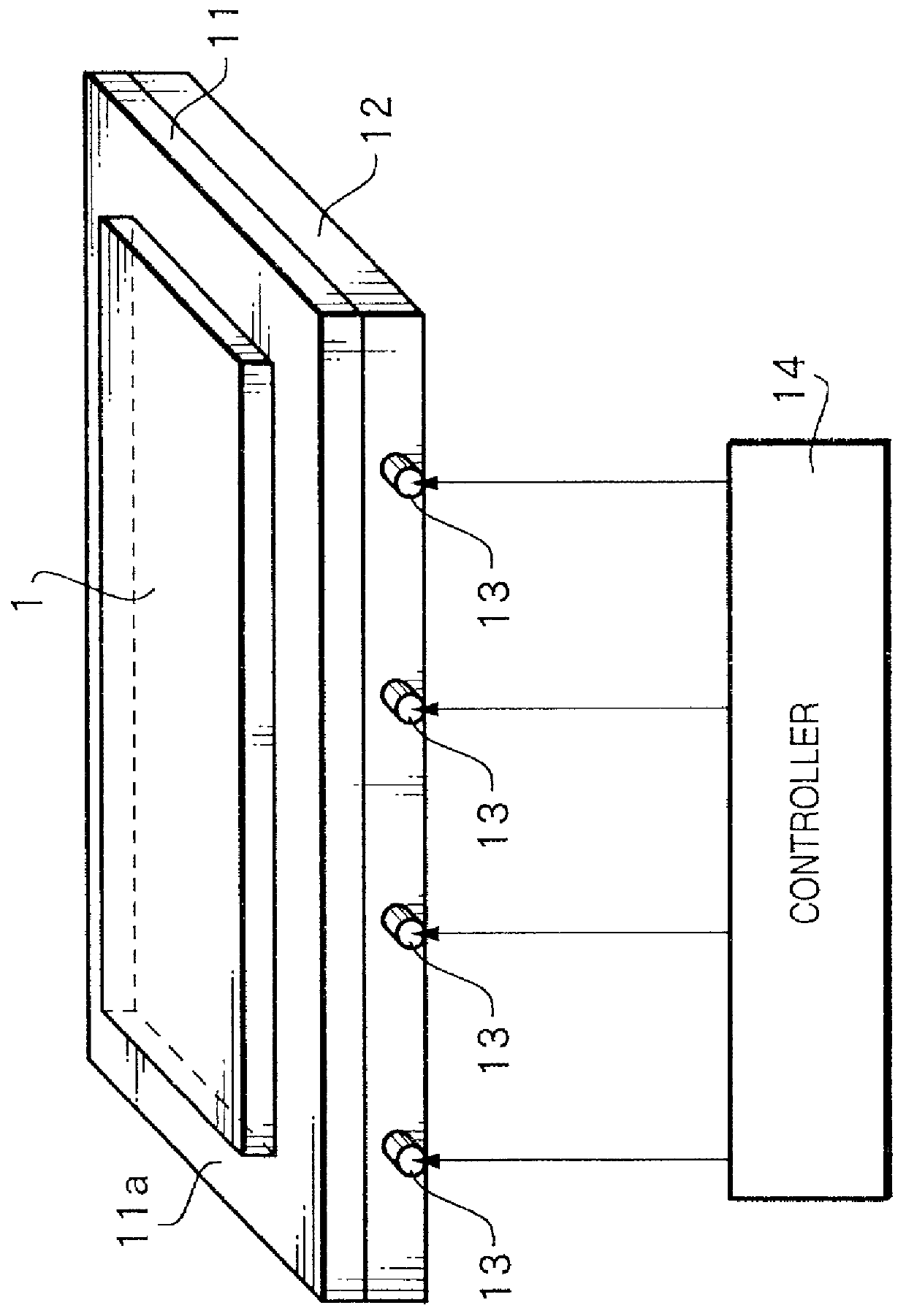
[0074] FIG. 1 is a view explaining a heating apparatus according to the present invention.
[0075] The heating apparatus of this embodiment is formed by stacking a base plate 11 on a heat transfer plate 12 in which rod heaters 13 controlled by a controller 14 are inserted, and heats an object 1 to be heated placed on the base plate 11.
[0076] The base plate 11 is made of stainless steel or the like having smaller creep than the heat transfer plate 12. The base plate 11 is fixed with a support member (not shown). The heat transfer plate 12 is made of aluminum or the like having a larger thermal conductivity than the base plate 11. The heat value of the rod heaters 13 is controlled by the controller 14 on the basis of a signal from at least one temperature sensor (not shown) placed on the base plate 11 or heat transfer plate 12. The object 1 to be heated is placed on a heating surface 11a of the base plate.
[0077] The heat transfer process from the rod heaters 13 to the object 1 to be hea...
second embodiment
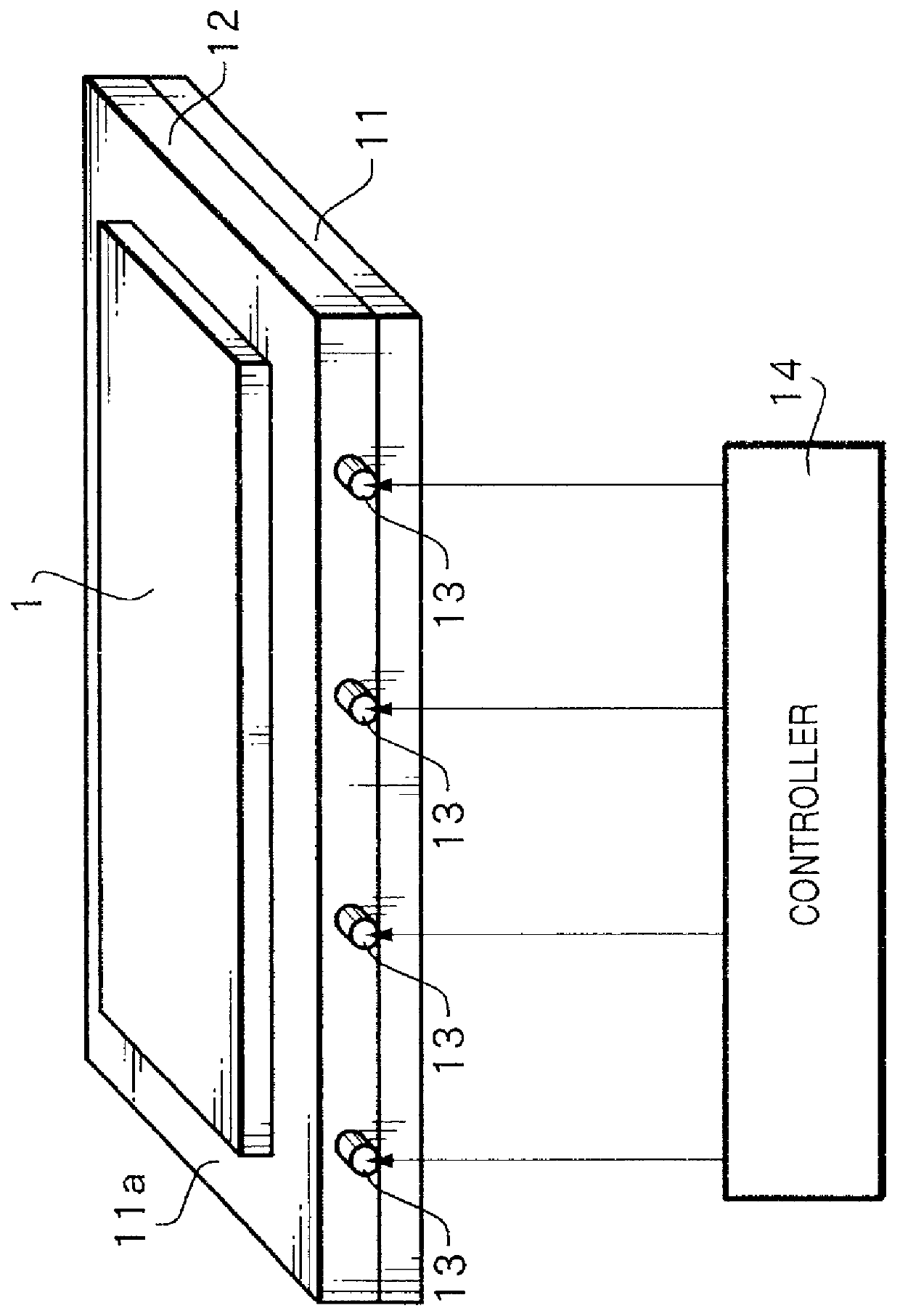
[0083] FIG. 2 is a view explaining a heating apparatus according to the present invention.
[0084] In the second embodiment, a heat transfer plate 12 in which rod heaters 13 are inserted directly heats an object 1 to be heated, and a base plate 11 is placed on the lower surface of the heat transfer plate 12, as shown in FIG. 2, i.e., the base plate 11 and heat transfer plate 12 are stacked in the reverse order. The second embodiment is different from the first embodiment described above in this respect.
[0085] Other than that, the second embodiment is similar to the first embodiment in, e.g., the materials of the base plate 11 and heat transfer plate 12, the fact that the heat value of the rod heaters 13 is controlled by a controller 14 on the basis of a signal from at least one temperature sensor (not shown) provided to the base plate 11 or heat transfer plate 12, and the like.
[0086] The heat transfer process from the rod heaters 13 to the object 1 to be heated in this embodiment will...
fourth embodiment
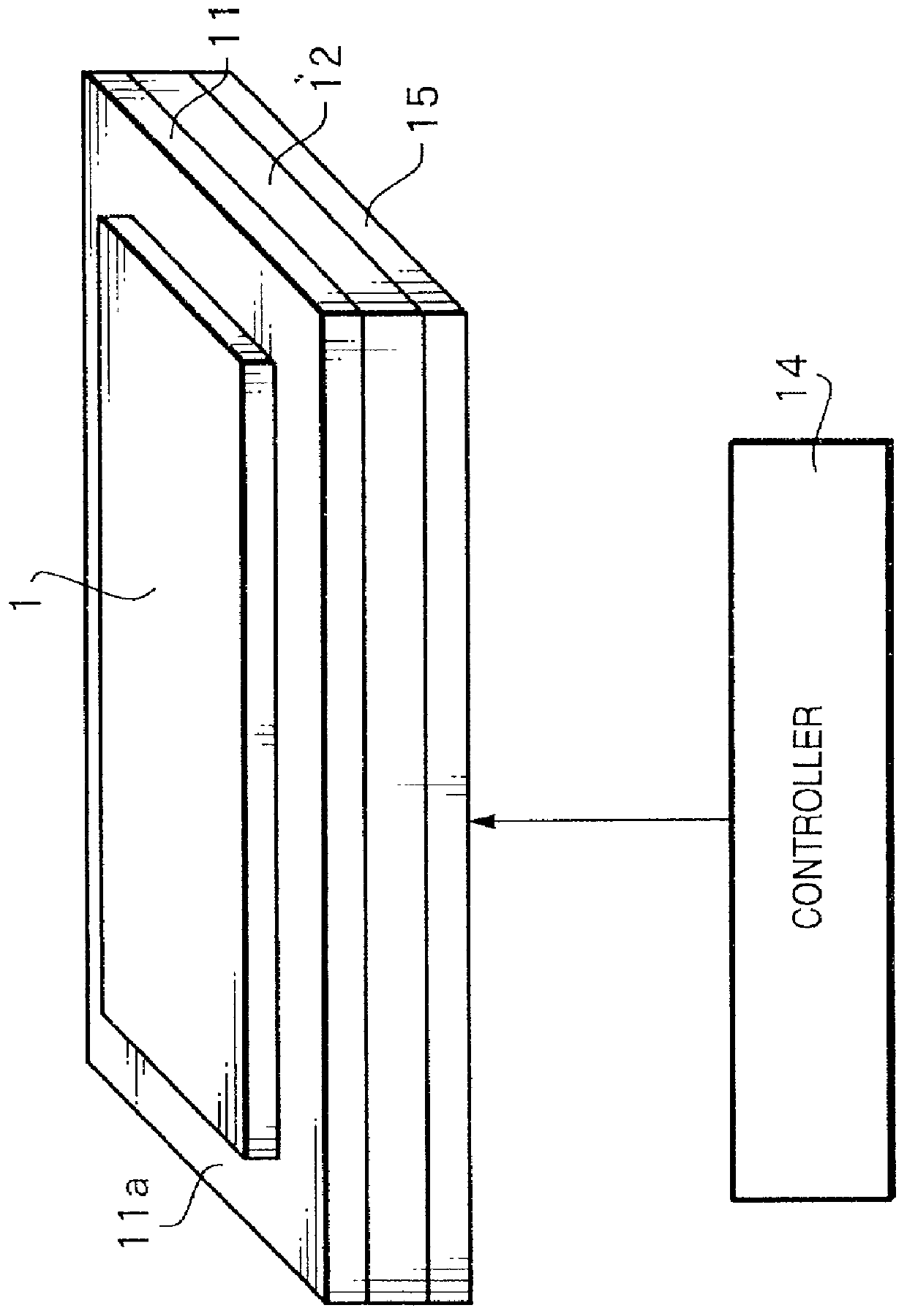
[0094] FIG. 4 is a view explaining a heating apparatus according to the present invention.
[0095] In the fourth embodiment, an auxiliary plate 16 is placed on the lower surface of a heat transfer plate 12. The fourth embodiment is different from the first embodiment in this respect. The auxiliary plate 16 is made of a material having a thermal conductivity and creep closer to those of a base plate 11 than those of the heat transfer plate 12. The auxiliary plate 16 may be made of the same material as that of the base plate 11.
[0096] Other than that, the fourth embodiment is similar to the first embodiment in, e.g., the materials of the base plate 11 and heat transfer plate 12, the fact that the heat value of rod heaters 13 is controlled by a controller 14 on the basis of a signal from at least one temperature sensor (not shown) provided to the base plate 11 or heat transfer plate 12, and the like.
[0097] In the fourth embodiment, in addition to the effect of the first embodiment, even ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Melting point | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com