Modifying message data and generating random number digital signature within computer chip
a random number and message data technology, applied in the field of entity authentication, can solve the problems of exposing the secret or biometric value itself to a greater risk of theft, fraudulent use of a private key to generate a digital signature of an ec, and currently cannot be detected
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 200
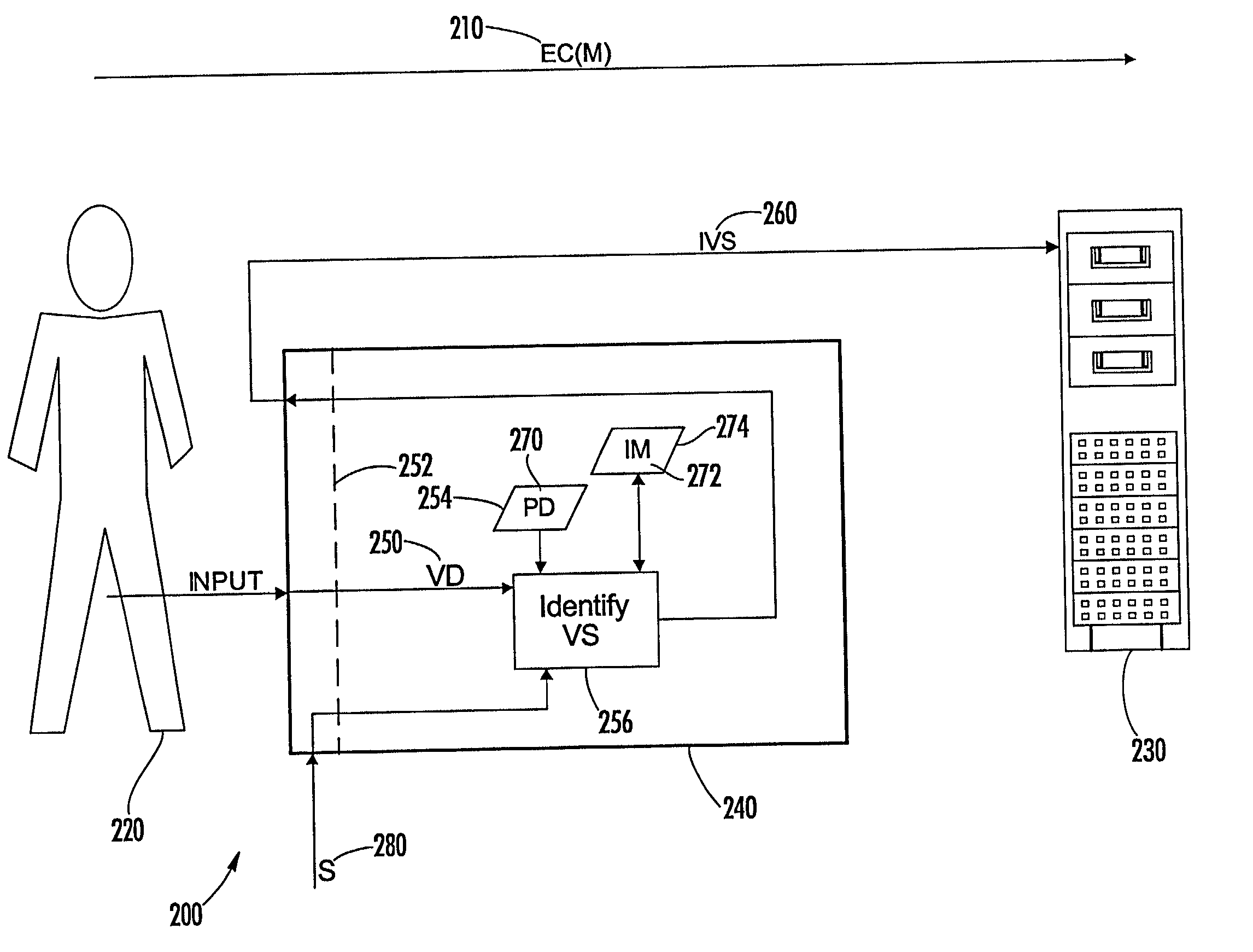
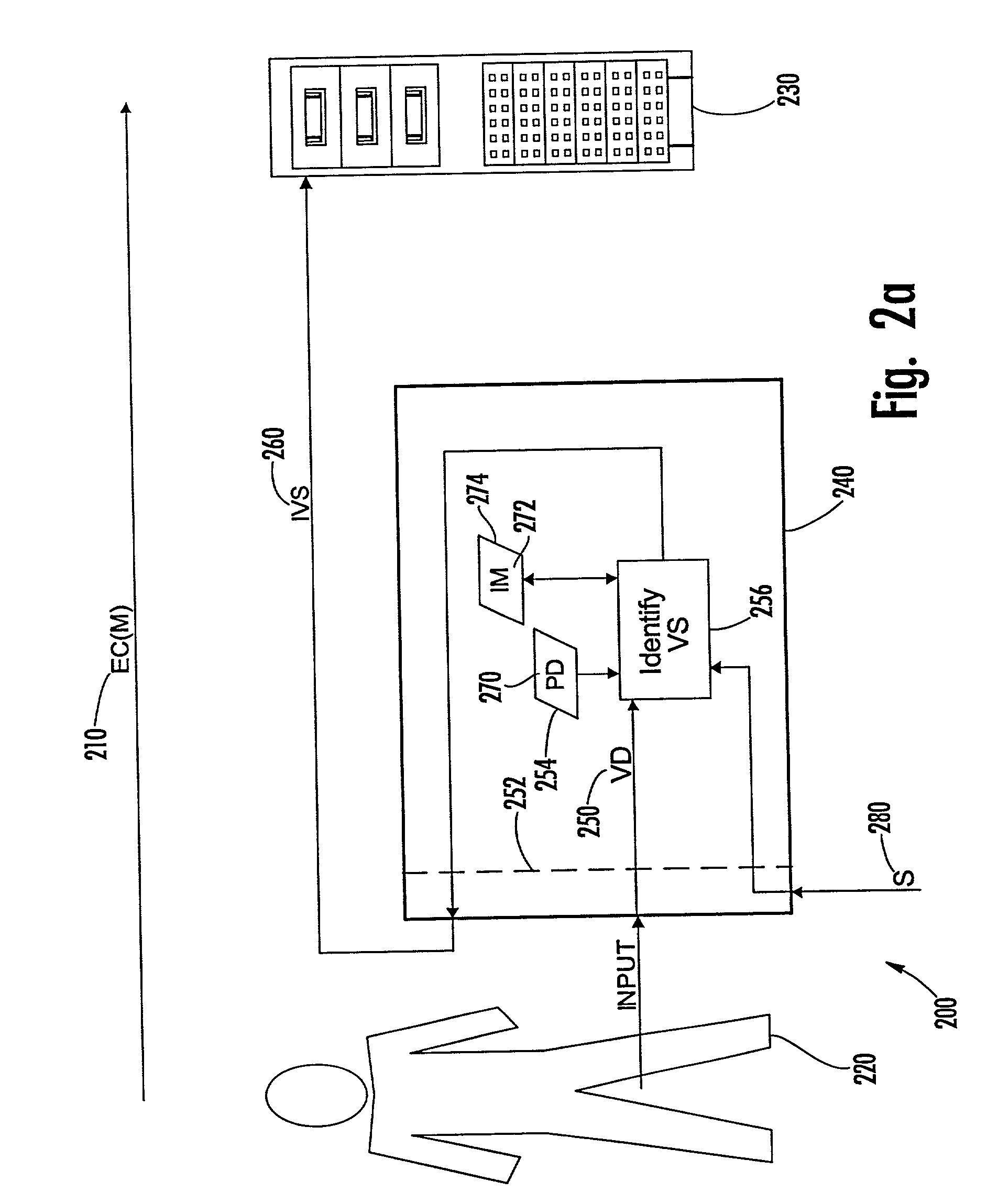
[0132] A first preferred embodiment 200 of the present invention is illustrated in FIG. 2a, wherein an EC 210 including a message from a sender 220 is received by a recipient represented by an electronic apparatus 230, and wherein a device 240 receives input representing verification data (VD) 250 at a device interface 252. The device 240 includes a verification component therein that maintains data (PD) 270 of the sender 220 prestored in memory 254 of the device 240. The verification data 250 and prestored data 270 represent Secret or biometric values.
[0133] The verification component identifies at 256 a current verification status of the device 240 based on a comparison of the verification data 250 with the prestored data 270. Upon receipt of a signal (S) 280, the last identified (i.e., "current") verification status of the device 240 is communicated to the recipient by outputting from the device 240 an indicator 260 that then is transmitted to the recipient in association with th...
embodiment 400
[0144] A second preferred embodiment 400 of the present invention is illustrated in FIG. 4a, wherein an EC 410 including a message from a sender 420 is received by a recipient represented by an electronic apparatus 430, and wherein a device 440 receives input representing verification data (VD) 450 at a device interface 452. The device 440 includes a verification component therein that maintains data (PD) 470 of the sender 420 prestored in memory 454 of the device 440. The verification data 450 and prestored data 470 represent Secret or biometric values.
[0145] The verification component identifies at 456 a current verification status of the device 440 based on a comparison of the verification data 450 with the prestored data 470. Upon receipt of a signal (S) 480, the last identified (i.e., "current") verification status of the device 440 is communicated to the recipient by outputting from the device 440 an indicator 460 that then is transmitted to the recipient in association with t...
embodiment 600
[0158] A third preferred embodiment 600 of the present invention is illustrated in FIG. 6a, wherein an EC 610 including a message from a sender 620 is received by a recipient represented by an electronic apparatus 630, and wherein a device 640 receives input representing verification data (VD) 650 at a device interface 652. The device 640 includes a verification component therein that maintains data (PD) 670 of the sender 620 prestored in memory 654 of the device 640. The verification data 650 and prestored data 670 represent Secret or biometric values.
[0159] The verification component identifies at 656 a current verification status of the device 640 based on a comparison of the verification data 650 with the prestored data 670. Upon receipt of a signal (S) 680, the last identified (i.e., "current") verification status of the device 640 is communicated to the recipient by outputting from the device 640 an indicator 660 that then is transmitted to the recipient in association with th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com