Electronic ballast with feed-forward control
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
)
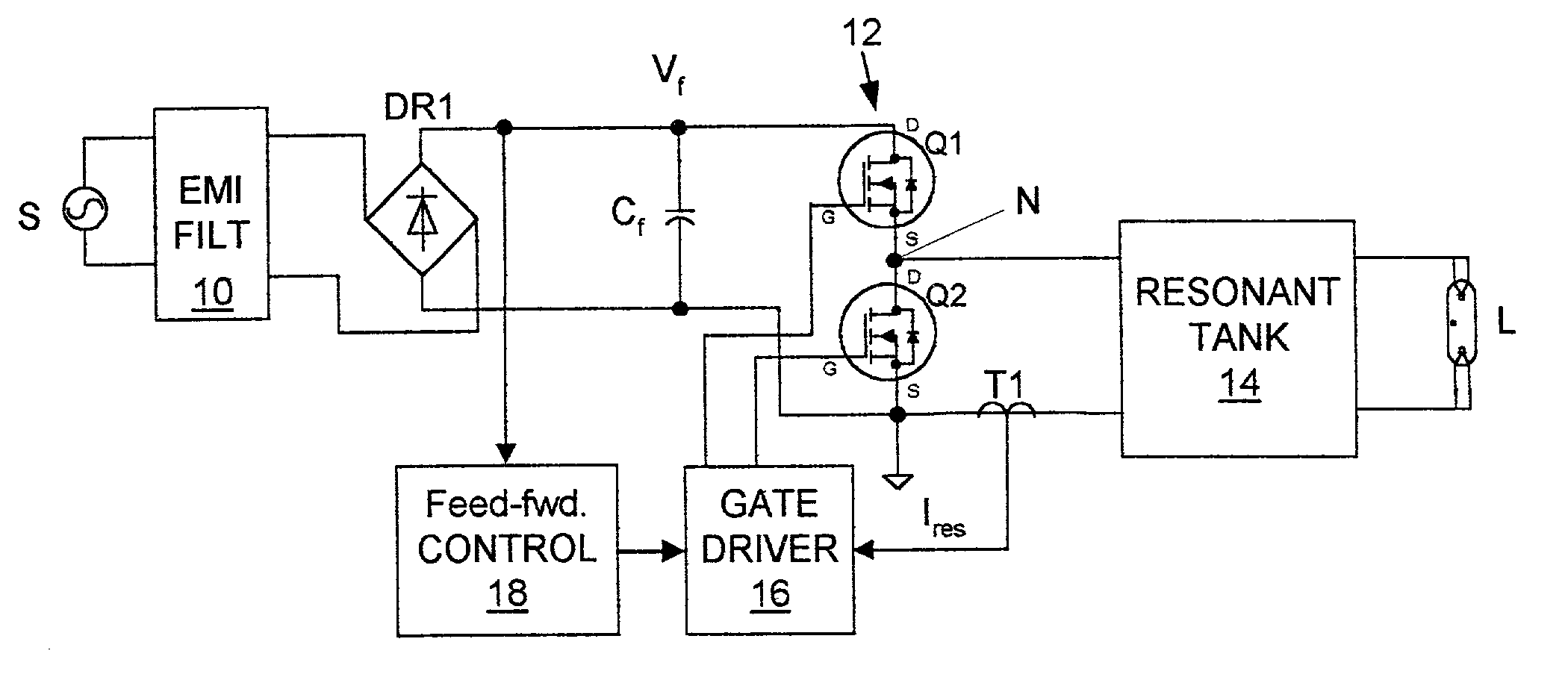
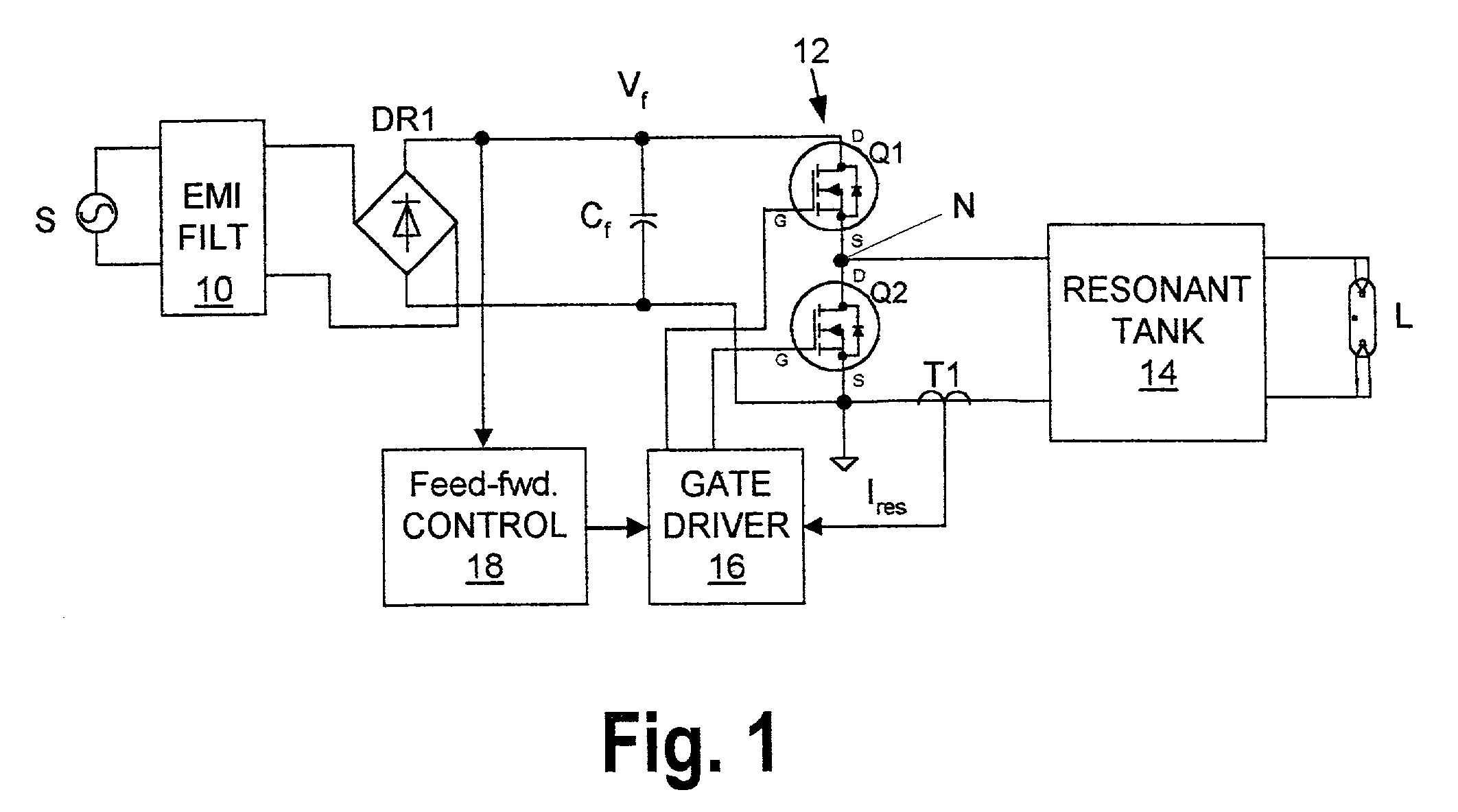
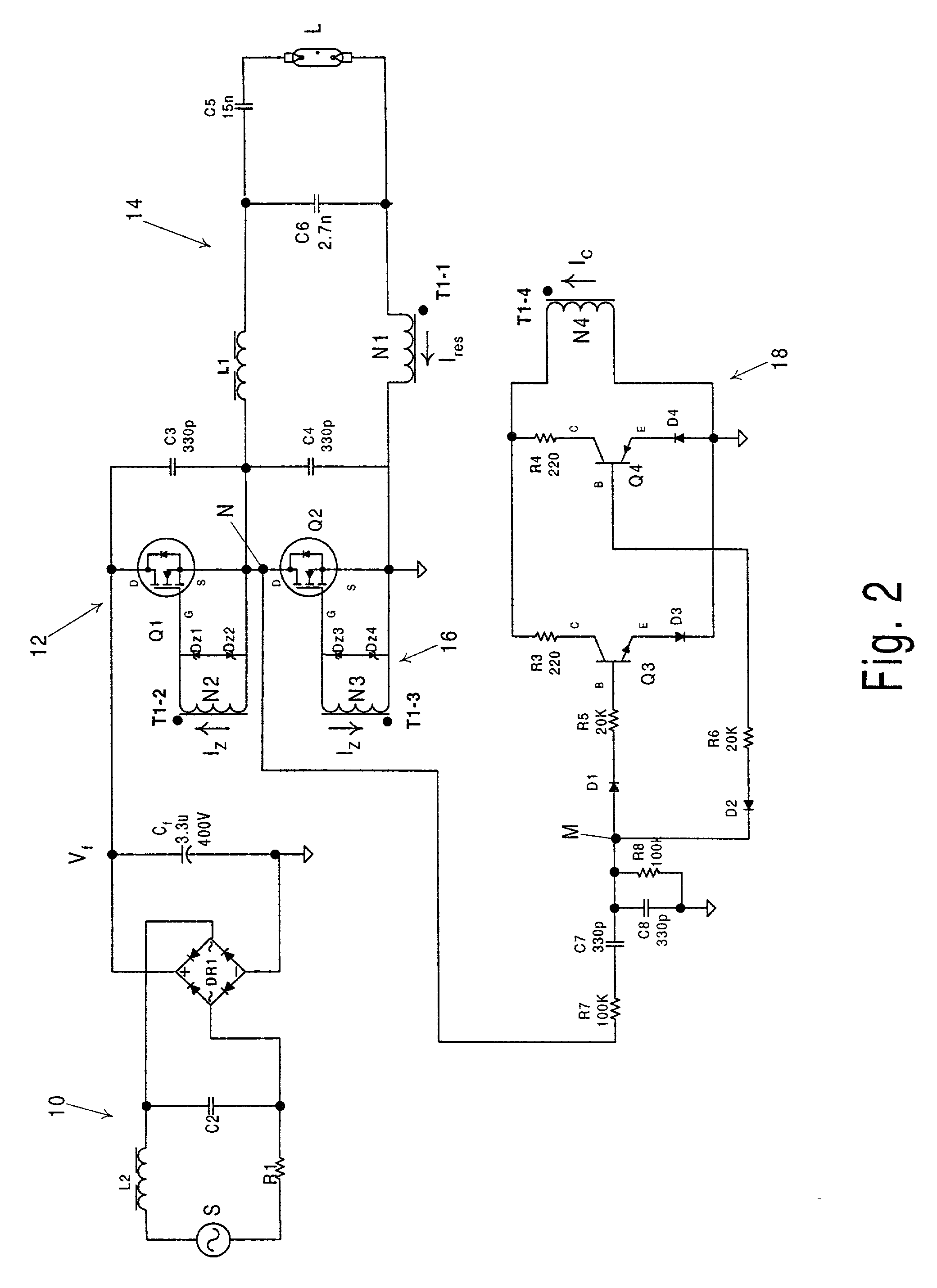
[0014] The exemplary system shown in FIG. 1 includes a source of AC power S, a discharge lamp L (e.g. a fluorescent lamp) and a ballast for controllably passing power to the lamp from the source S. The ballast includes an EMI filter 10, a bridge rectifier DR1, a line-filter capacitor C.sub.f, a half-bridge converter 12, a resonant tank 14, a current transformer T1, a gate driver circuit 16 and a feed-forward control circuit 18.
[0015] The EMI filter 10 serves to isolate the AC power source S from interference signals generated within the ballast (e.g. high-frequency switching signals generated by the converter 12).
[0016] The bridge rectifier DR1 and the filter capacitor C.sub.f convert the AC power from the source S to rectified, but unregulated, DC power having a varying DC voltage V.sub.f. Together, this rectifier and capacitor form a DC power source that is conventional except for its simplicity and the relatively small size of the filter capacitor that is possible because of the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com