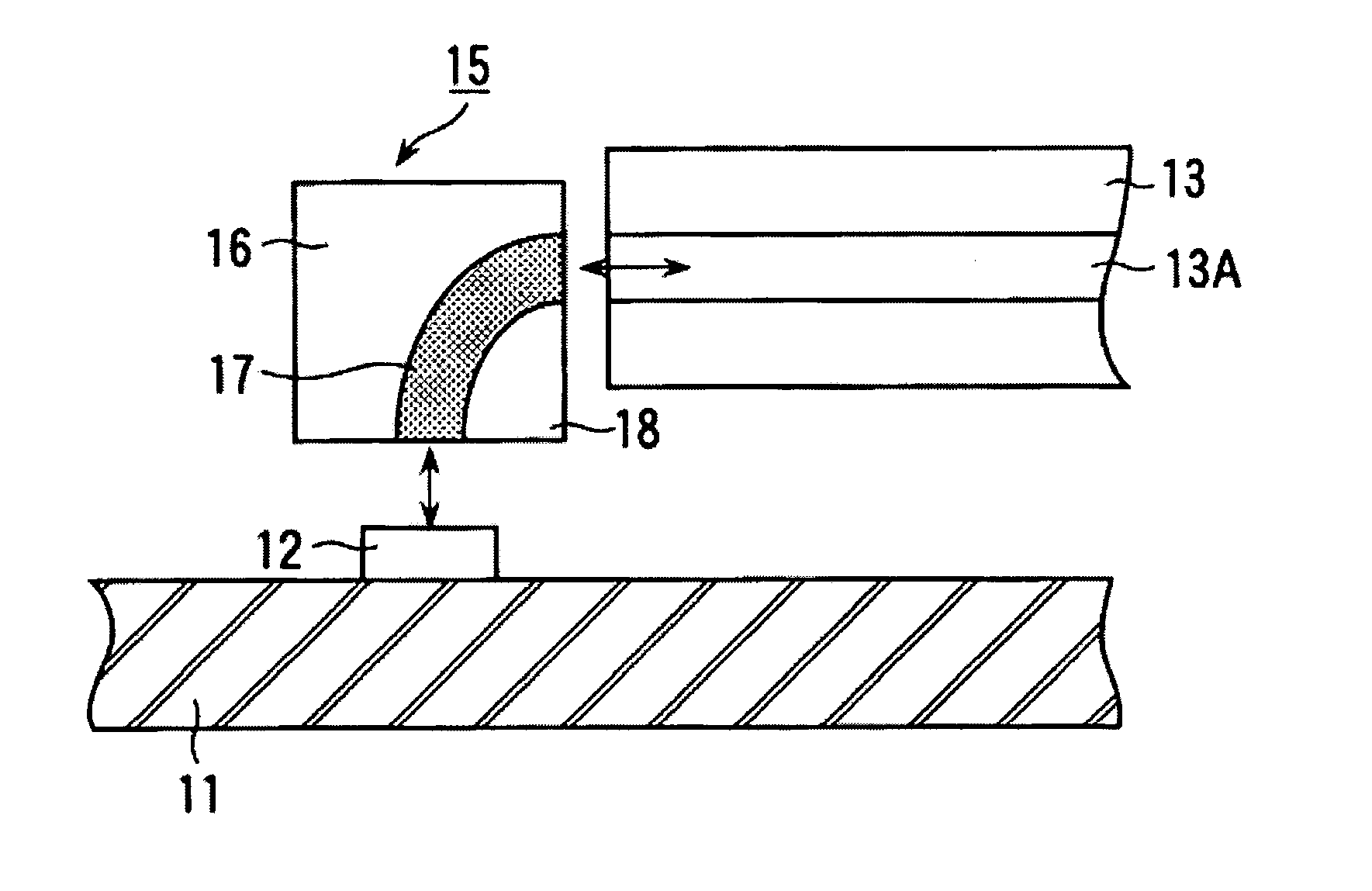
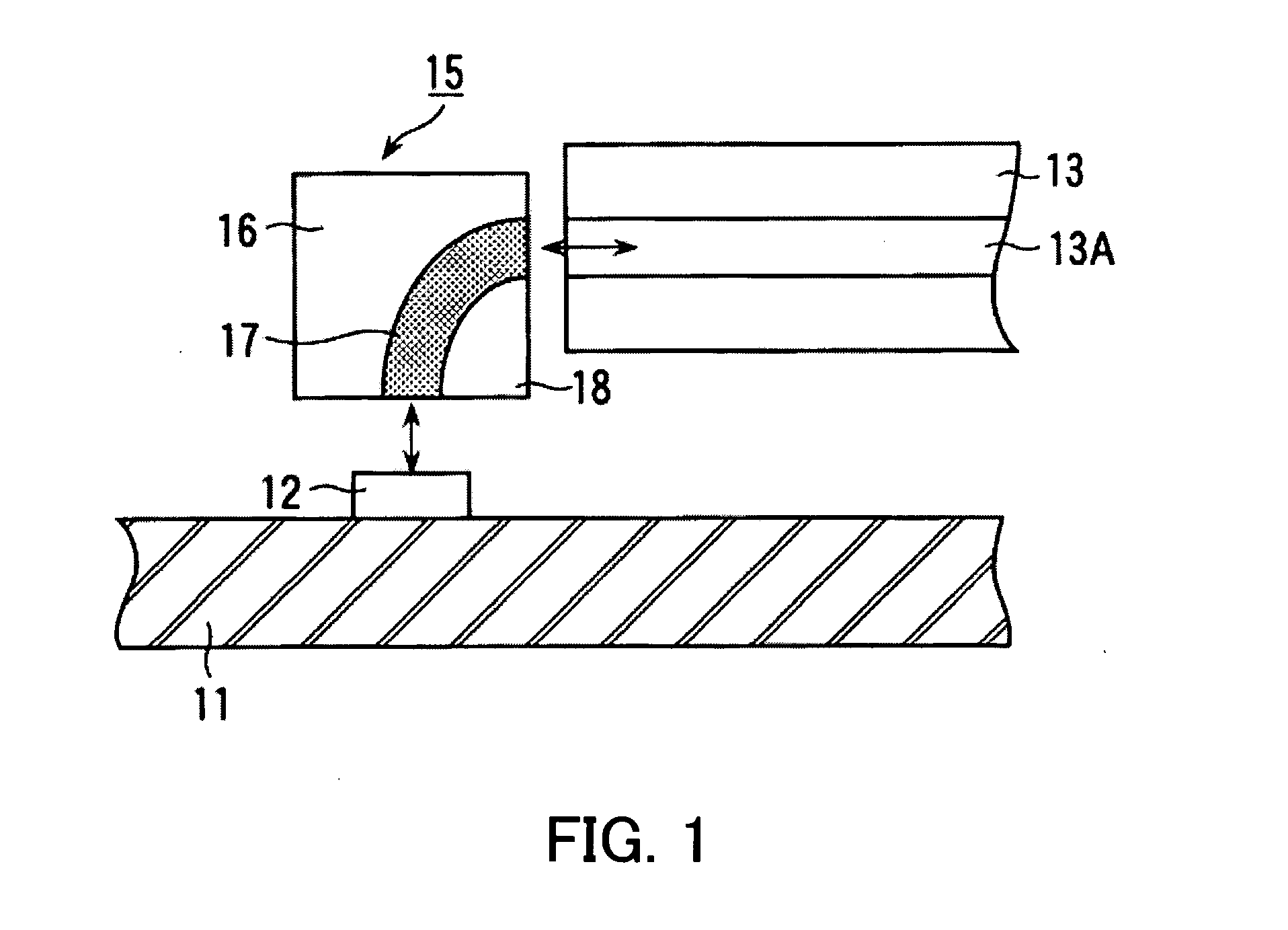
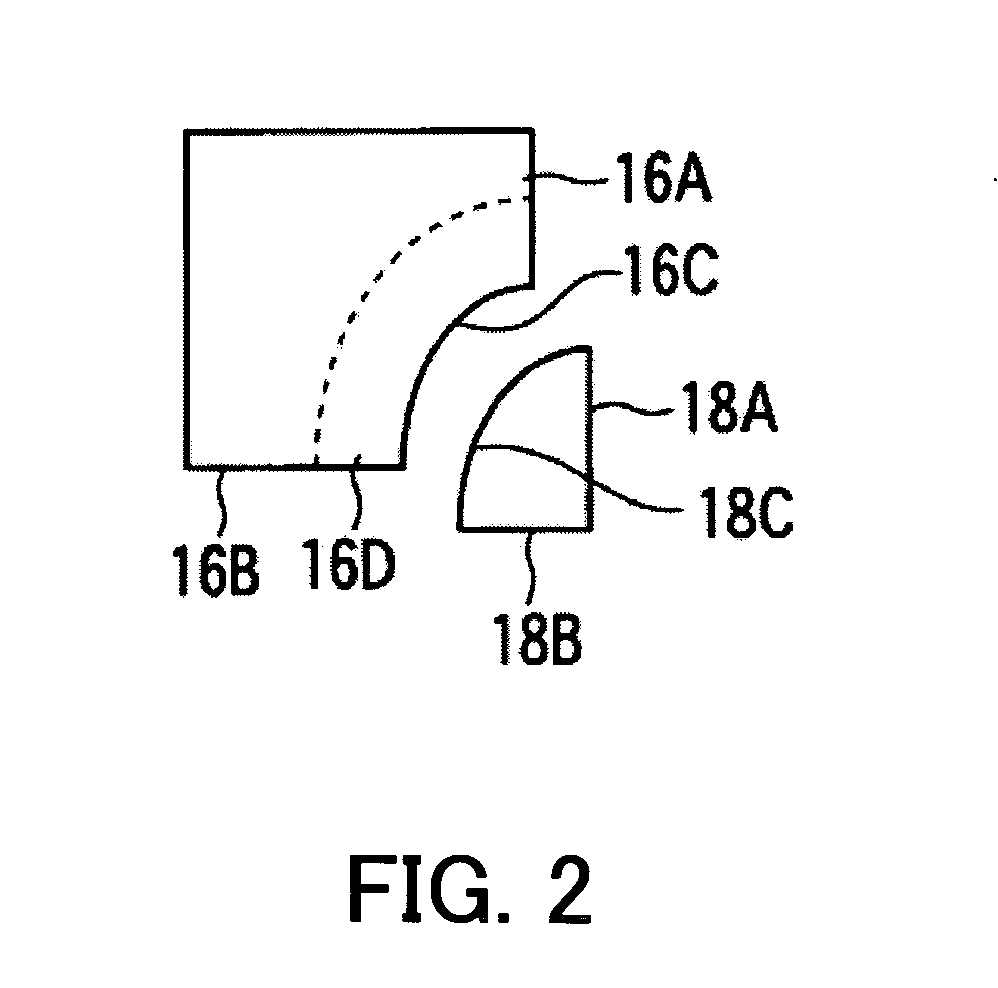
Optical waveguide structure and optical module
a technology of optical modules and waveguides, applied in the direction of optical waveguide light guides, instruments, optical light guides, etc., can solve the problems of troublesome work and inconvenient structure for realizing flat optical modules
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
[0095]FIG. 19 is a sectional view of a feature of an optical module for describing an example of the first embodiment of the present invention. In FIG. 19, a printed circuit board 41, a surface type optical device 42, such as a surface emitting laser diode or a photodiode, mounted on the printed circuit board 41, a first clad section 43, a curved surface 43A for turning the course of light gradually and squarely, a lens 43B, a concavity 43C formed in the under surface of the first clad section 43 to cover the surface type optical device 42, a second clad section 45, an optical fiber ribbon 46, and a mechanically transferable (MT) optical connector 47 are shown. A plurality of grooves (not shown) are formed in the direction in which light travels in the curved surface 43A and core sections are formed in these grooves.
[0096]FIG. 20 is an enlarged sectional view of a portion enclosed by a dashed line in FIG. 19. The same symbols that are used in FIG. 19 indicate the same components or...
second embodiment
[0140]FIGS. 39 through 44 are views for roughly describing processes for fabricating an optical waveguide structure into which lenses are integrated. FIG. 39 is a front view of a feature for roughly describing a first process performed for fabricating an optical waveguide structure into which lenses are integrated. FIG. 40 is a sectional view of the feature for roughly describing the first process performed for fabricating the optical waveguide structure into which the lenses are integrated. FIG. 41 is a front view of a feature for roughly describing a second process performed for fabricating the optical waveguide structure into which the lenses are integrated. FIG. 42 is a sectional view of the feature for roughly describing the second process performed for fabricating the optical waveguide structure into which the lenses are integrated. FIG. 43 is a front view of a feature for roughly describing a third process performed for fabricating the optical waveguide structure into which t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com