Prediction and control of mass unbalance and high speed uniformity
a technology of mass unbalance and high speed, applied in the direction of vehicle testing, way, structural/machine measurement, etc., can solve the problem of potentially large fx, and achieve the effect of relatively small stiffness variation effect on fz
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
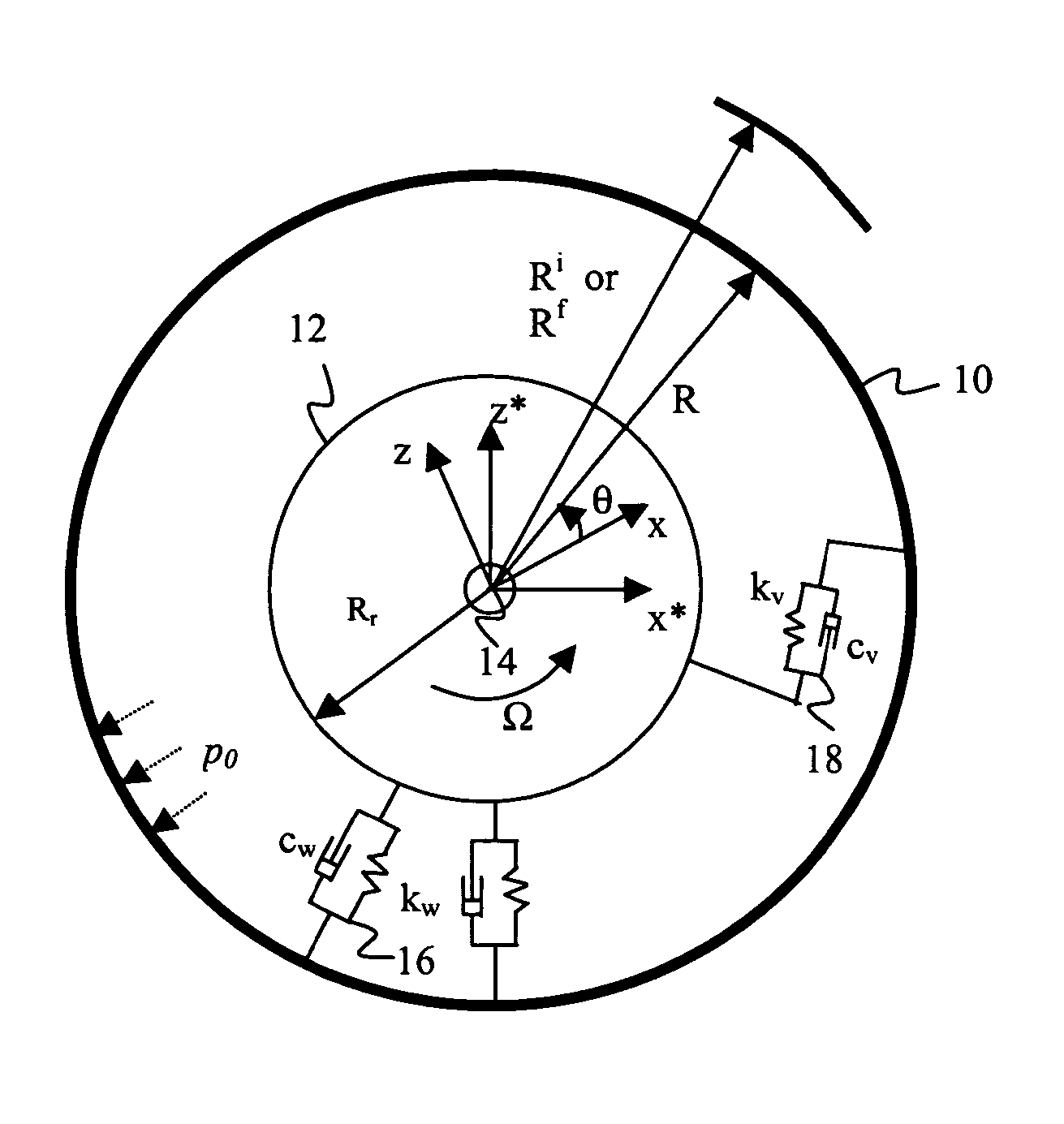
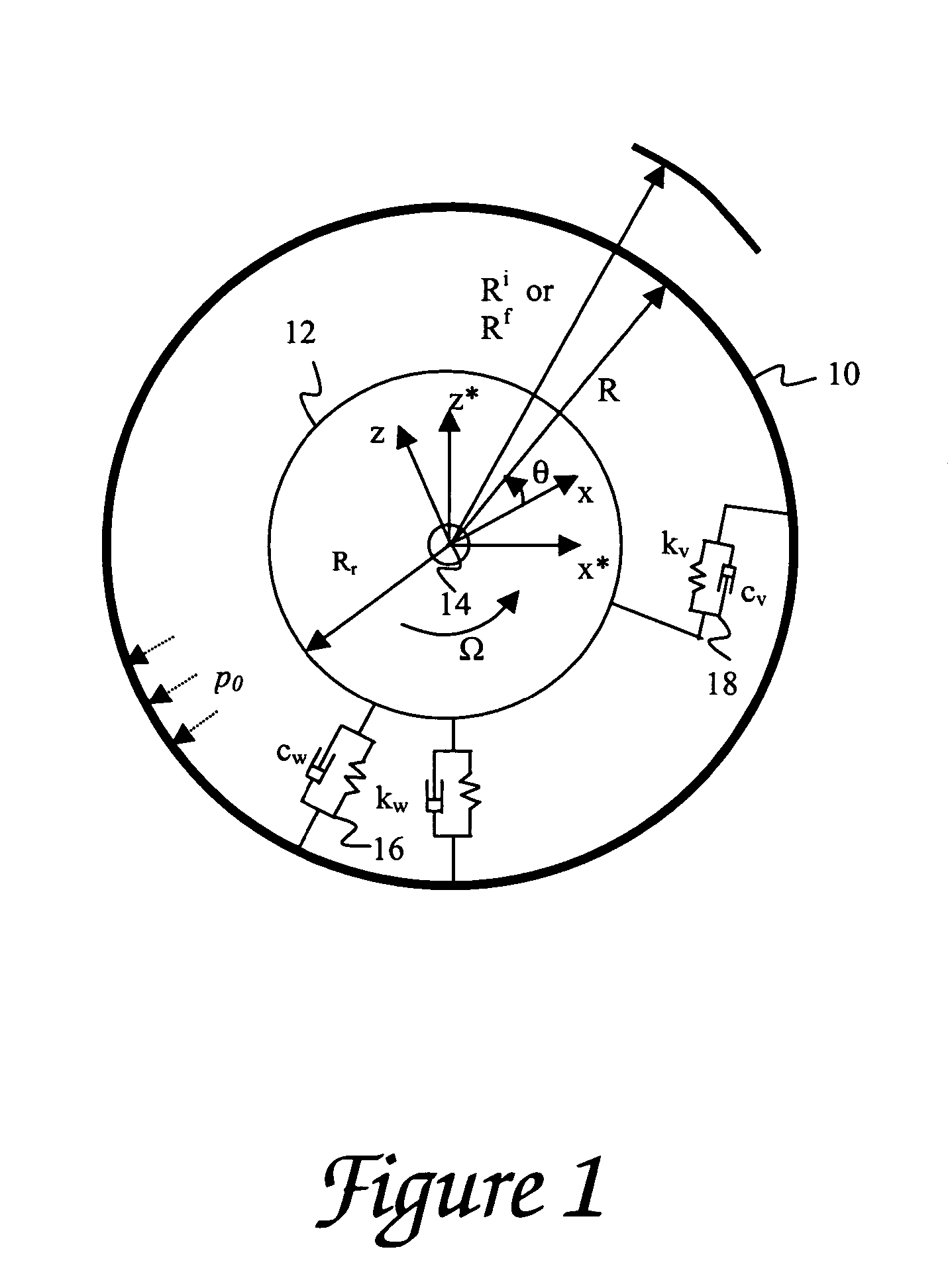
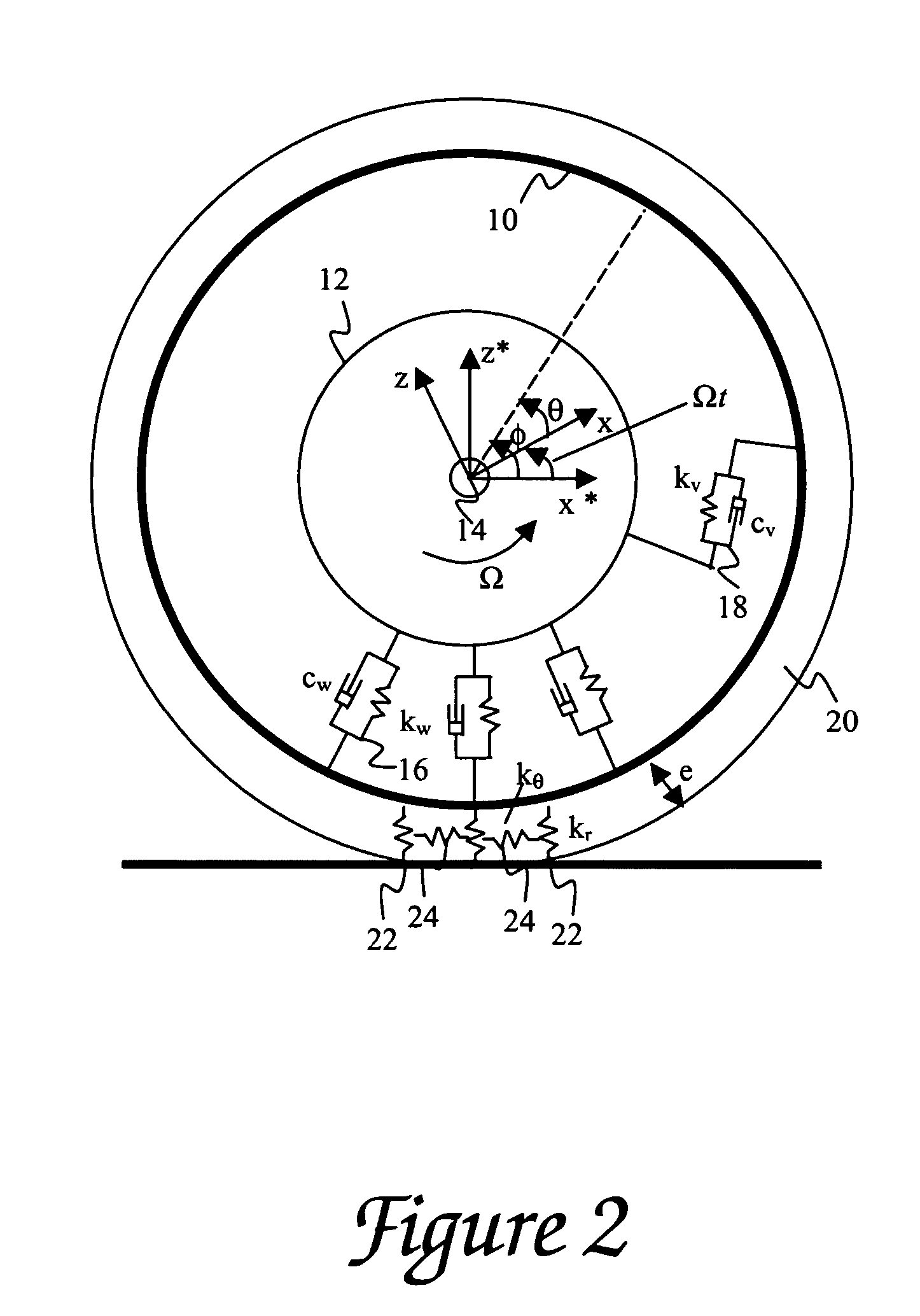
[0039] As discussed in the Summary of the Invention section, the present subject matter concerns aspects of characterizing low and high speed uniformity aspects of a tire. Respective contributions of radial run out and stiffniess variations (e.g., radial, tangential, bending, and extensional stiffniess variations) to radial and tangential force variations are determined. Characterization of such tire parameters can be further applied to tire sorting and / or grading processes and improvements to tire manufacturing, for example in control and optimization of process reference angles.
[0040] Aspects of tire modeling and numerical analysis that provide initial basis for the process applications and methodology of the present subject matter are presented hereafter with respect to FIGS. 1-8D, respectively. More particularly, discussion with respect to FIGS. 1-4, respectively, corresponds to tire modeling and formulation of equations for calculating radial run out as well as high-speed spin...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com