Metrology device for videoendoscopic probe
a technology of endoscope and probe, which is applied in the field of videoendoscope, can solve the problems of preventing the use of the entire sensitive surface of the ccd sensor connected to the lens, affecting the accuracy of the measurement, and only being used for repetitive measurements
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
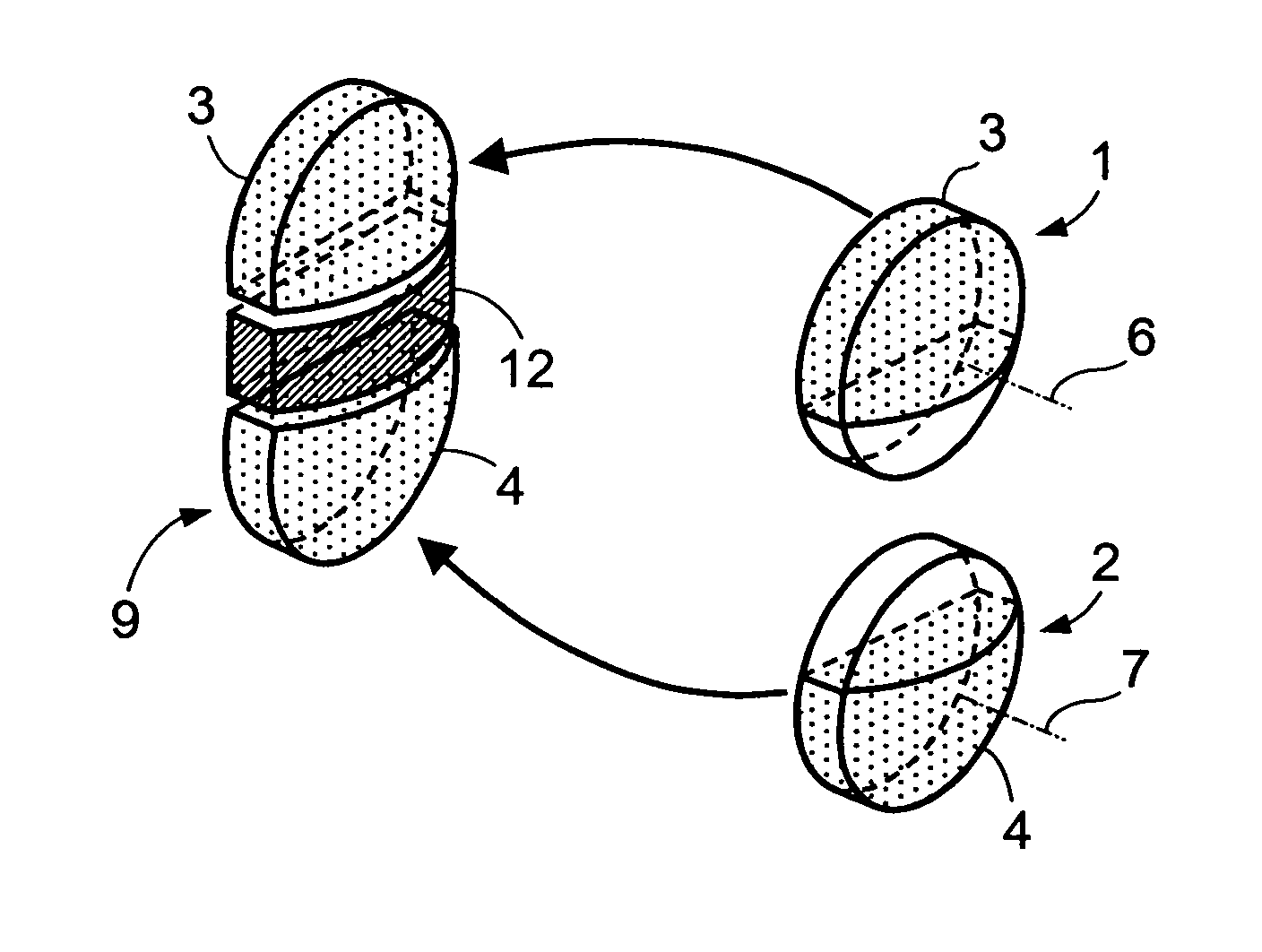
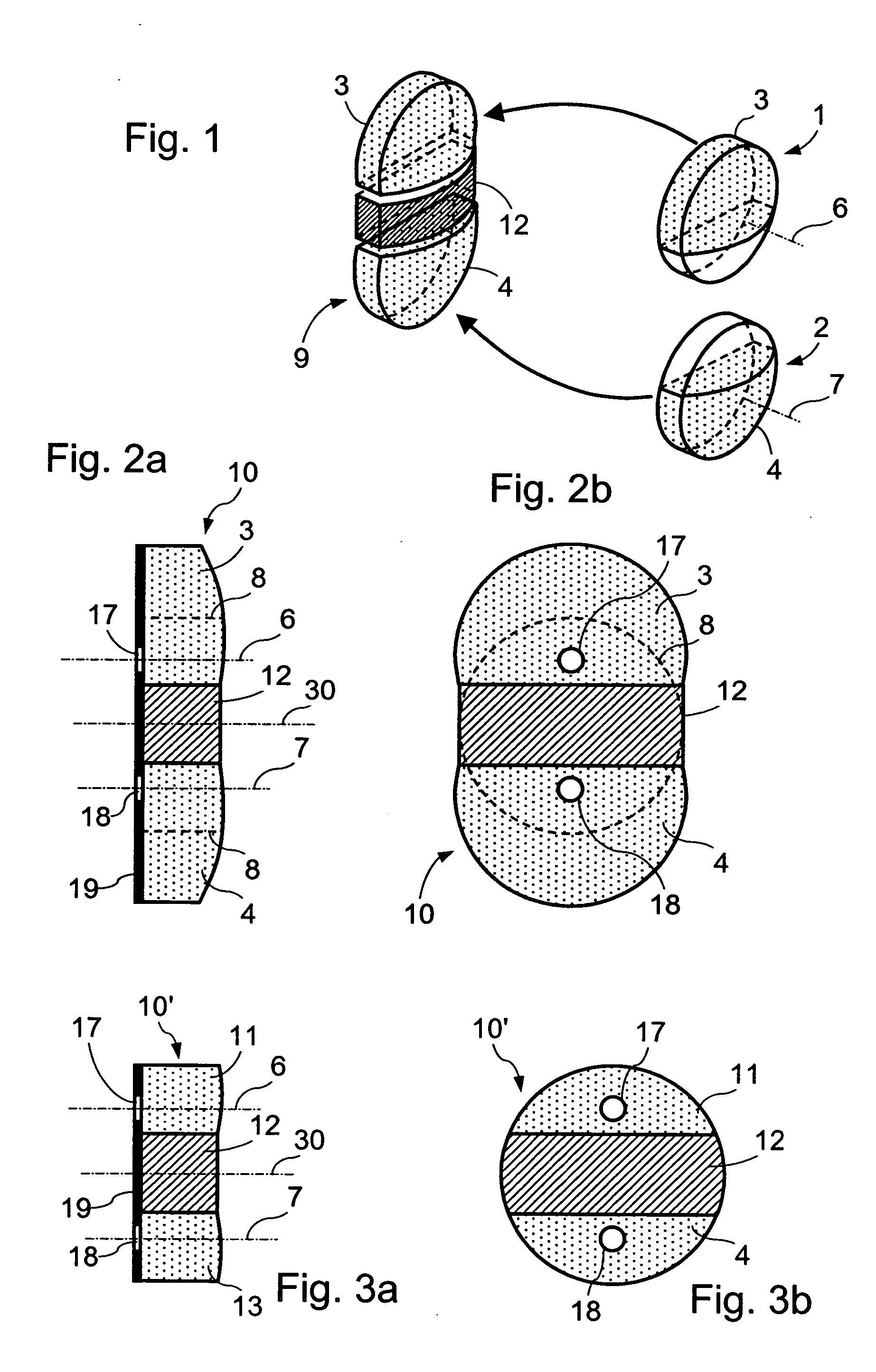
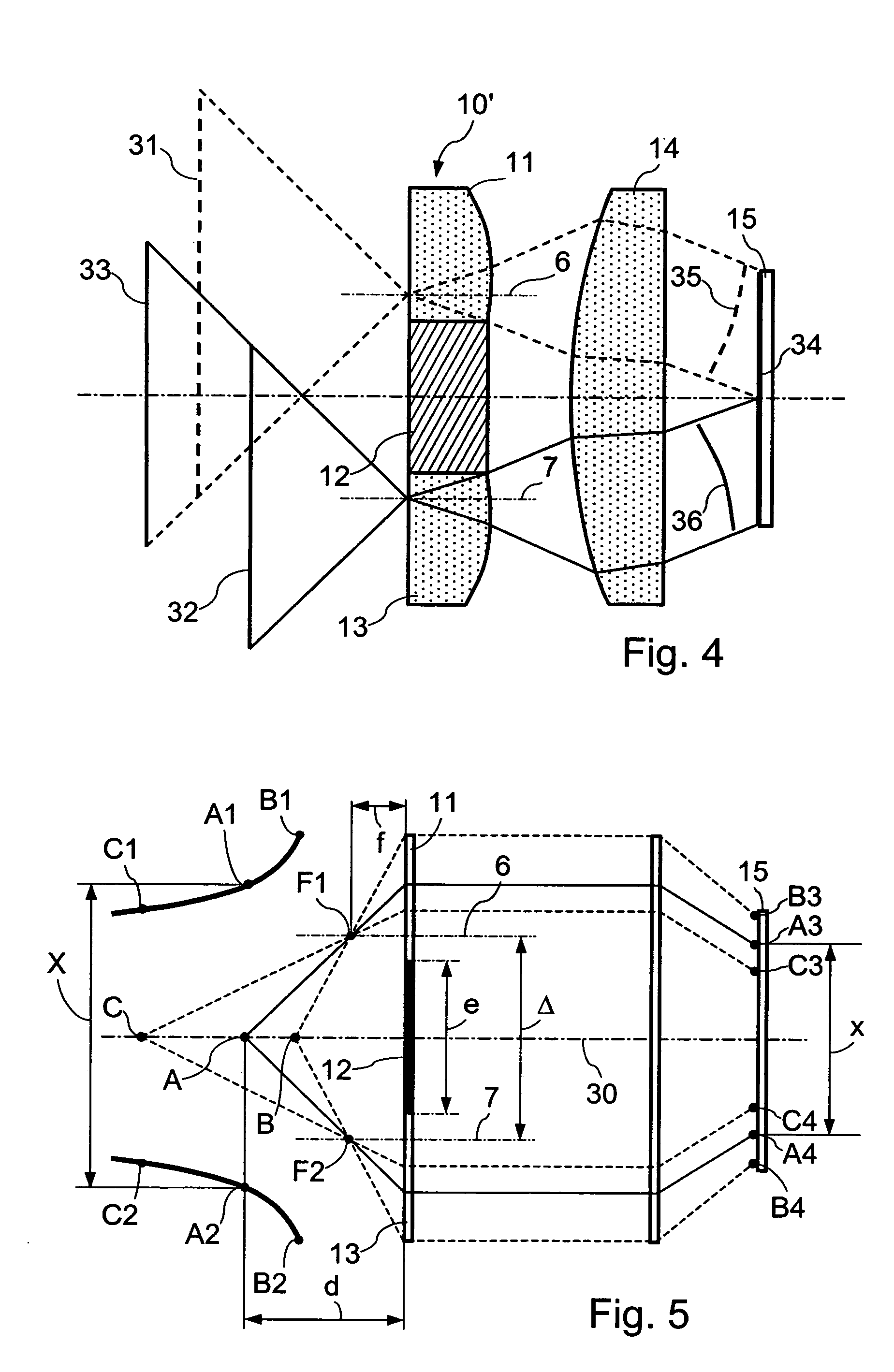
[0079]FIG. 1 schematically represents the structure of an image splitting optical component 10 according to the invention.
[0080] The optical component 9 shown on this figure is obtained by bringing together an opaque central element 12 and two identical side sections 3, 4 of lenses 1, 2 larger than a half-lens or half-moon in order to include the optical axes 6, 7 of the lenses 1, 2. Each of these lens sections is obtained by cutting a convergent lens 1, 2, for example according to a cutting plane parallel to the optical axis of the lens, the convergent lens having a flat face and a convex face. The optical component 9 shown in FIG. 1 thus presents two perpendicular symmetry planes, namely, a mediator plane of the central element 13 dividing each of the two lens sections and the central element into two symmetrical parts and a mediator plane of the central element on either side of which the two lens sections are placed symmetrically.
[0081]FIGS. 2a and 2b show a front and profile ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com