Level shift circuit
a level shift circuit and level shift technology, applied in electronic switching, pulse automatic control, pulse technique, etc., can solve the problems of increasing power dissipation and difficulty in performing the intended operation of the level shift circuit, and achieve the effect of reliable performing the desired level shift operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
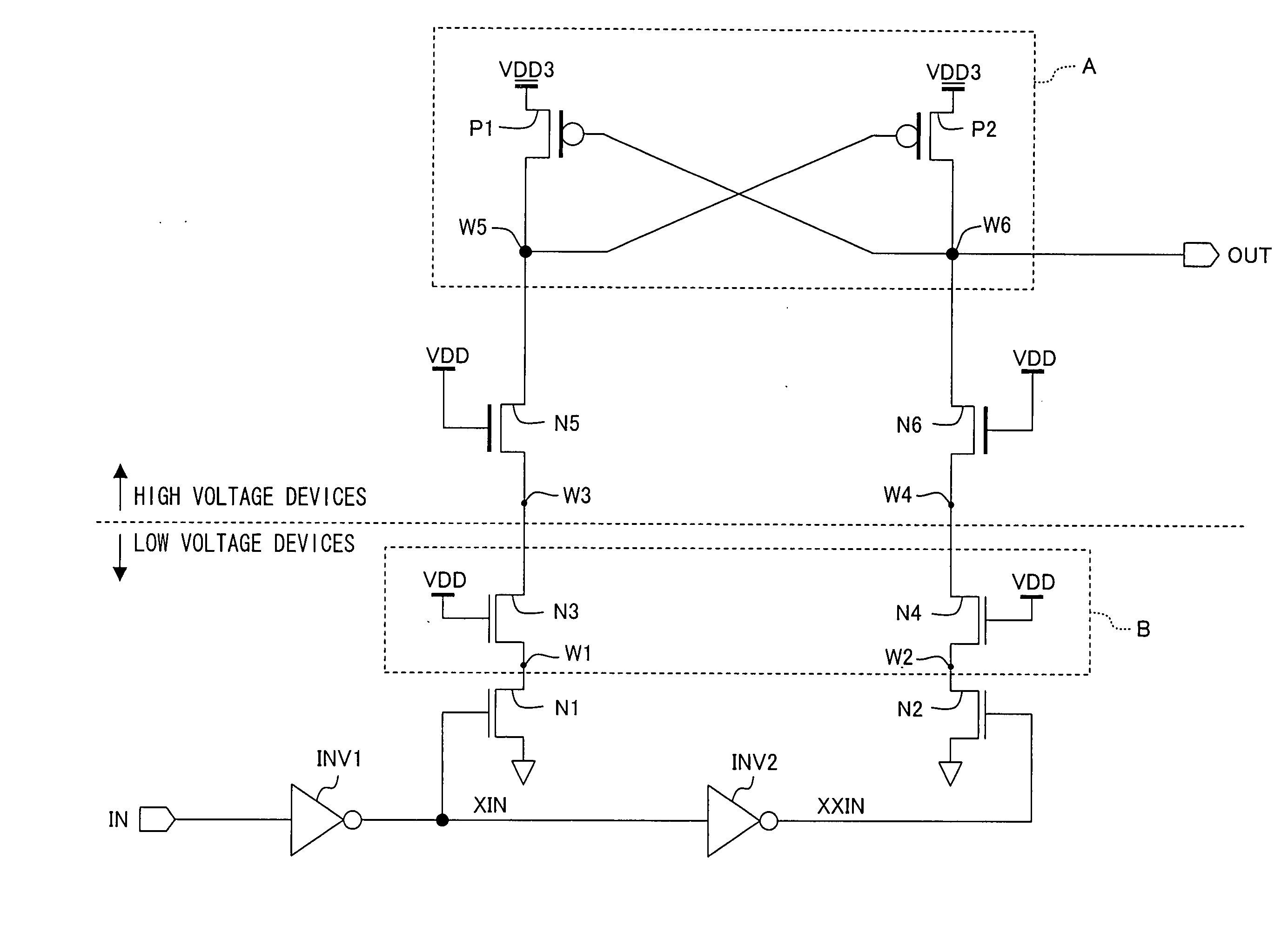
[0076]FIG. 1 is a view illustrating the specific configuration of a level shift circuit in accordance with this embodiment.
[0077] In FIG. 1, the reference mark IN denotes a signal input terminal, the reference mark INV1 denotes an inverter for inverting a signal input to the input terminal IN, and the reference mark INV2 denotes an inverter which inverts a signal output from the inverter INV1. The inverters INV1 and INV2 operate at a voltage of 1.5 V, for example, supplied from a low-voltage supply VDD.
[0078] In FIG. 1, the reference marks N1 and N2 denote N-type low-voltage transistors which receive a pair of complementary signals and are capable of withstanding only low voltage (which will be hereinafter refereed to as “N-type complementary-signal-receiving low-voltage transistors.) The N-type complementary-signal-receiving low-voltage transistors N1 and N2 have their respective sources grounded. A signal XIN (which is one of first and second signals serving as the complementary...
first modified example
of the First Embodiment
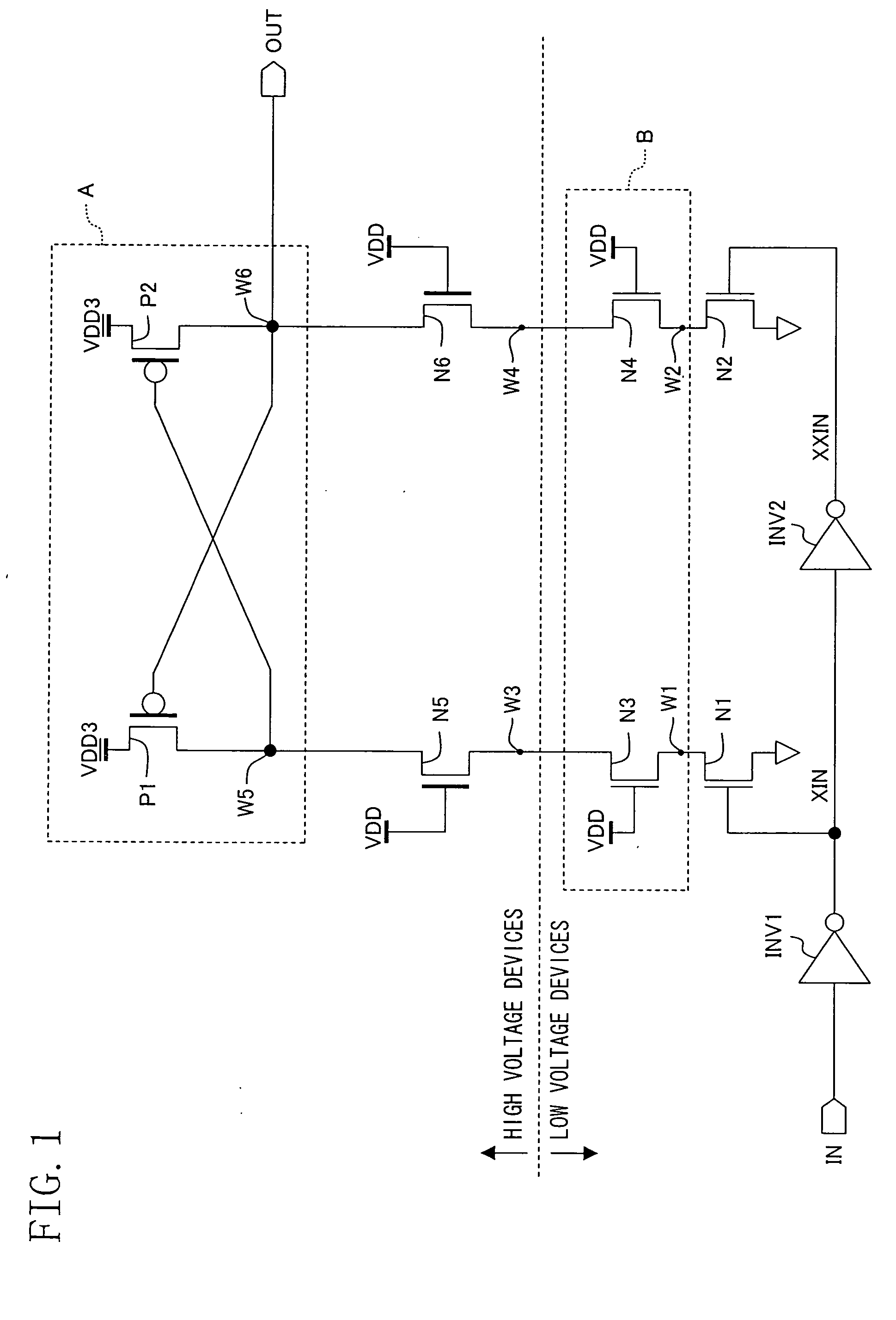
[0094]FIG. 2 illustrates a first modified example of the first embodiment.
[0095] This modified example is obtained by making modifications to the internal configuration of the power supply circuit A of the first embodiment. More specifically, in the power supply circuit A shown in FIG. 2, the reference marks P1 and P2 denote a pair of P-type transistors. The sources of the P-type transistors P1 and P2 are connected to a high-voltage supply VDD3, while the gate of each P-type transistor is cross-coupled to the drain of the other. And their respective drains are connected to the drains of N-type transistors N5 and N6. The connecting point, at which the P-type transistor (i.e., a first P-type transistor) P1 and the N-type transistor N5 are connected together, is a fifth node W5, and the connecting point, at which the other P-type transistor (i.e., a second P-type transistor) P2 and the N-type transistor N6 are connected together, is a sixth node W6.
[0096] The r...
second modified example
of the First Embodiment
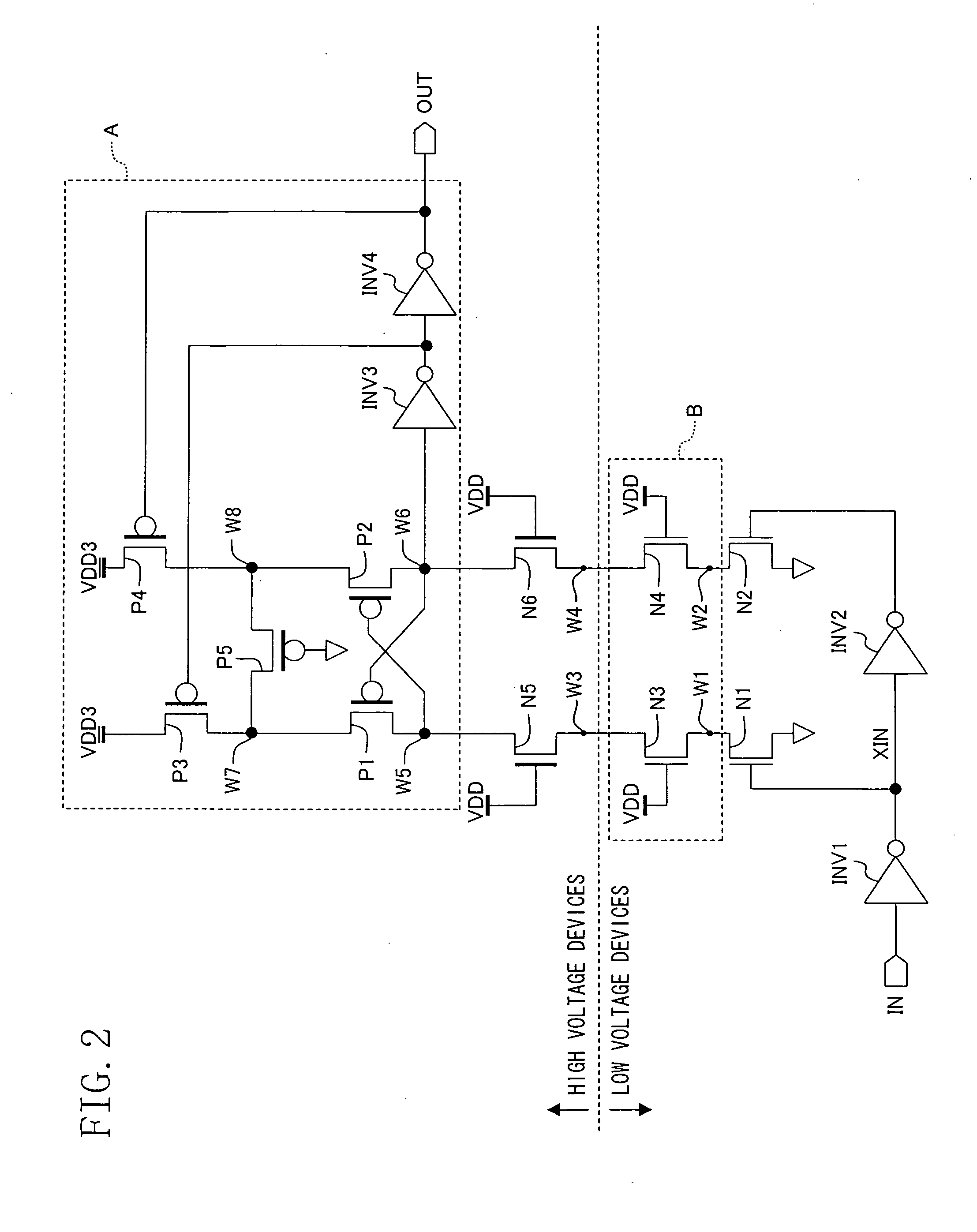
[0098]FIG. 3 illustrates a second modified example of the first embodiment.
[0099] This modified example is obtained by making other modifications to the internal configuration of the power supply circuit A of the first embodiment.
[0100] More specifically, the power supply circuit A of FIG. 3 includes a precharge circuit composed of: a supply circuit consisting of a pair of P-type transistors P6 and P7; a disconnecting circuit consisting of a pair of N-type transistors N7 and N8; and a P-type transistor P8 operating as a resistor. The P-type transistor P6 has its source connected to a high-voltage supply VDD3 and its drain to a fifth node W11. The other P-type transistor P7 has its source connected to the high-voltage supply VDD3 and its drain to a sixth node W12. In the precharge circuit shown in FIG. 3, the N-type transistor N7 is disposed between the fifth node W11 and an N-type transistor N5, while the other N-type transistor N8 is disposed between the si...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com