Start up cascaded fuel cell stack
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
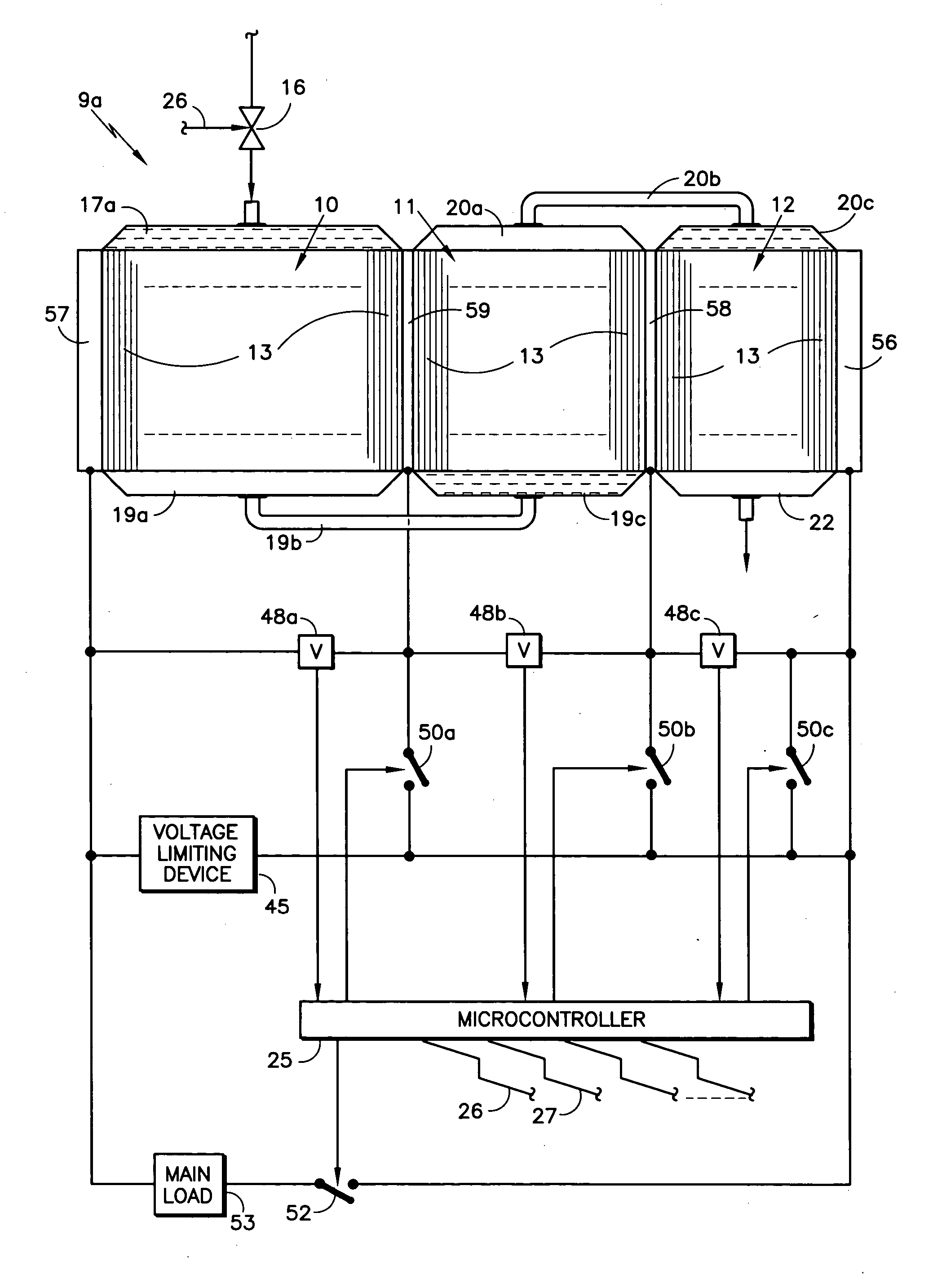
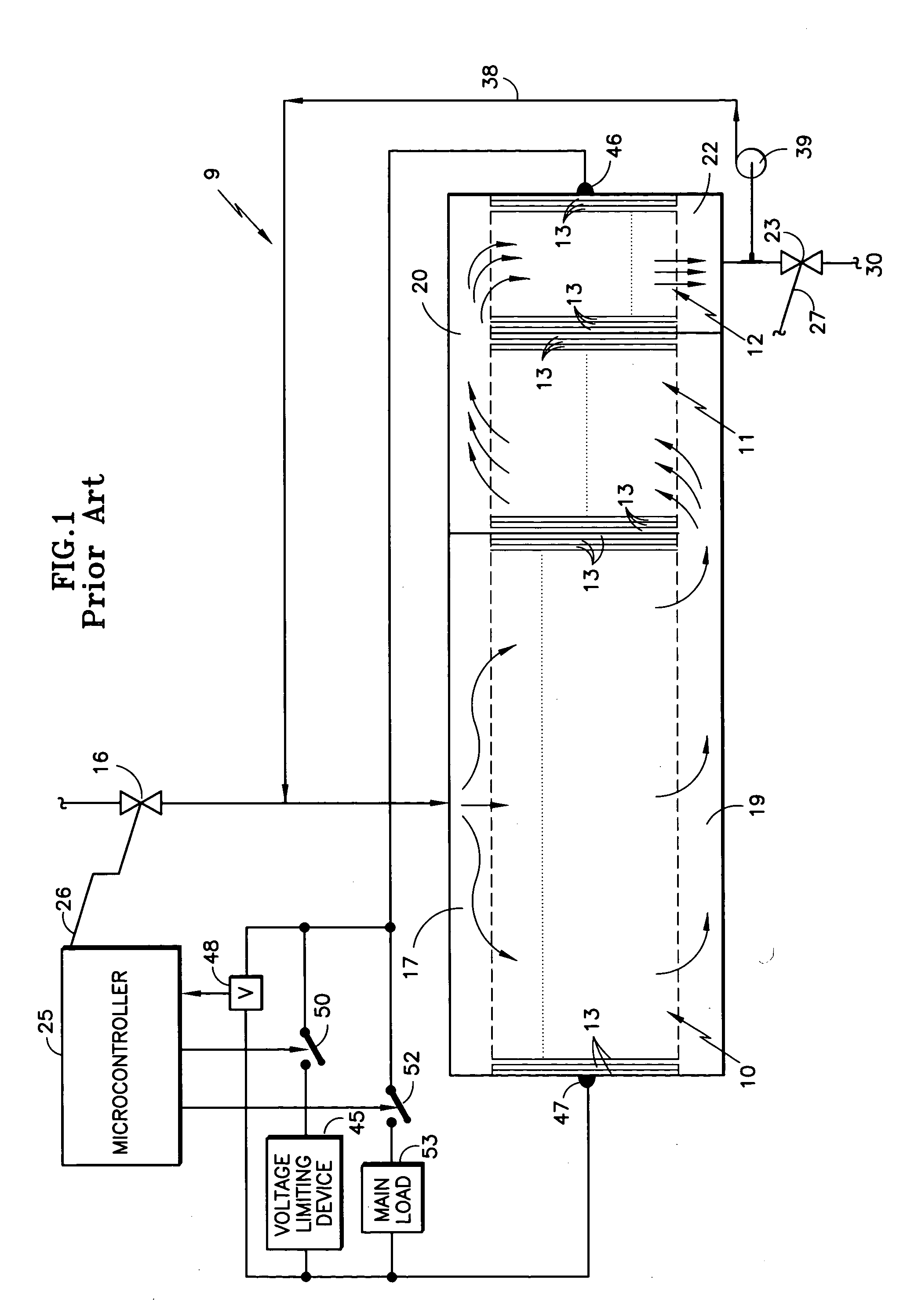
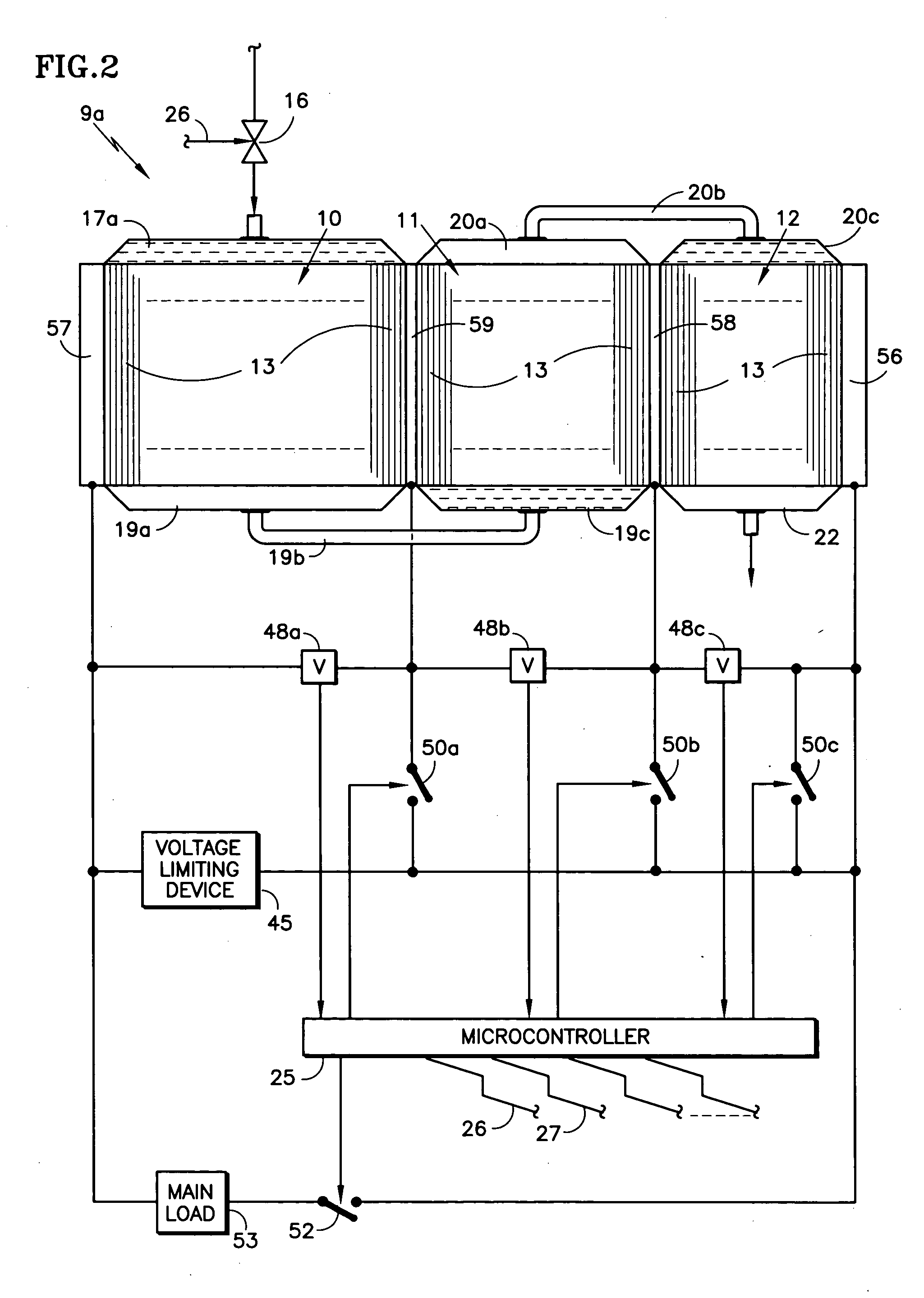
[0021] Referring to FIG. 2, a cascaded fuel cell stack 9a according to the invention includes an inlet fuel distributing fuel inlet manifold 17a at the inlet to the fuel flow fields of the fuel cells 13 in the first group 10. The fuel distributing manifold 17a may be a cascade fuel inlet manifold as described in copending U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10 / 269,654, filed Oct. 10, 2002. The device disclosed therein divides the fuel in half a number of times, such as four times, so that it is evenly distributed across the entire stack of fuel cells, whereby each fuel cell fuel flow field receives a uniform amount of fuel, simultaneously with the fuel flow fields of the other fuel cells. The fuel distributing manifold 17a may also take the form of a permeable baffle inlet fuel gas distributor, as disclosed in copending U.S. patent application Serial No. (Docket No. C-2950), filed Dec. 15, 2003, entitled “Permeable Inlet Fuel Gas Distributor for Fuel Cells”, in which fuel is evenly dis...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com