Electronic Stitch Length Regulator for Home Sewing Machines
a technology of electronic stitch length and sewing machine, which is applied in the direction of programmed sewing machine, mattress sewing, textiles and papermaking, etc., can solve the problems of uneven stitching, short stitch length, and long stitch length
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
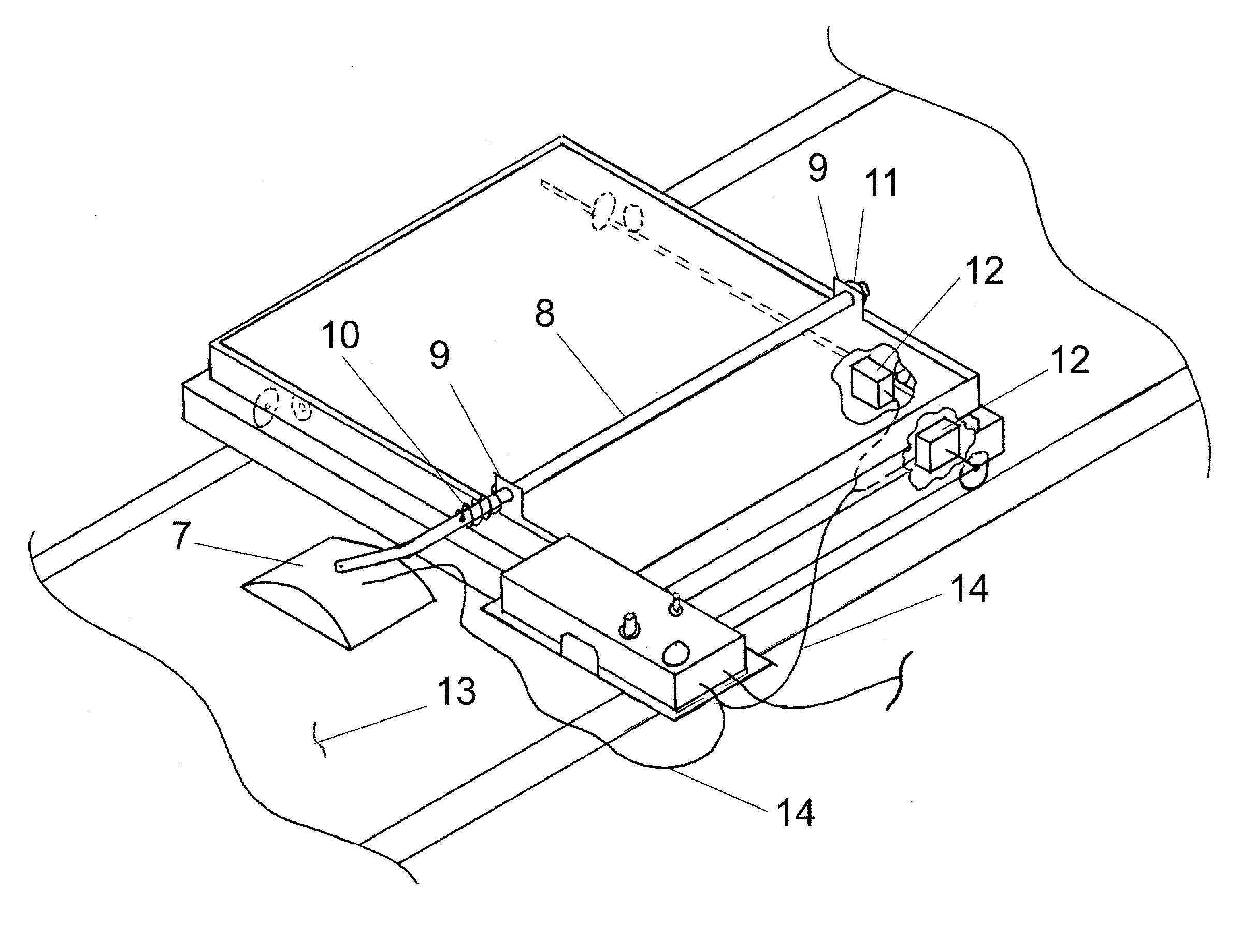
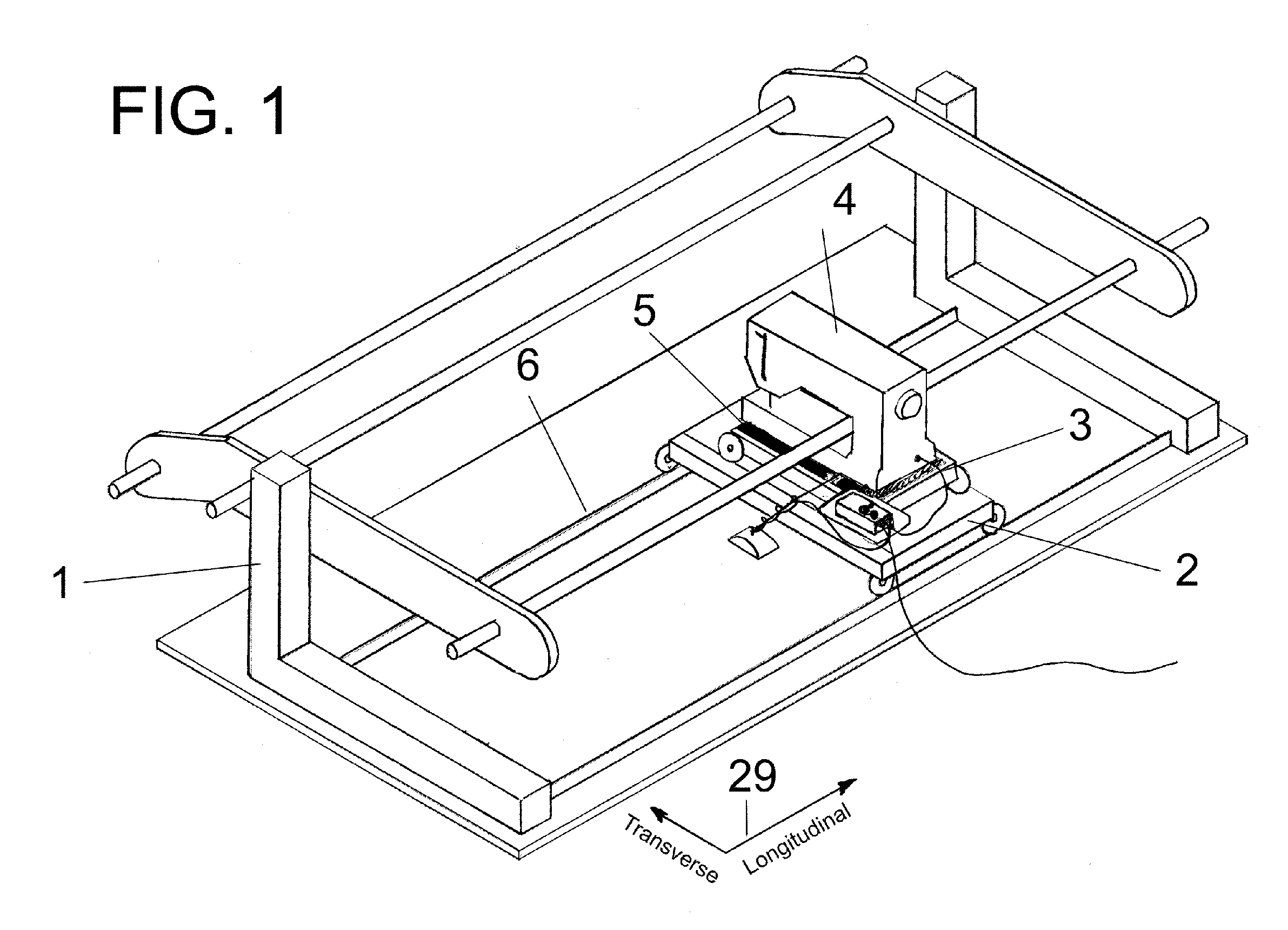
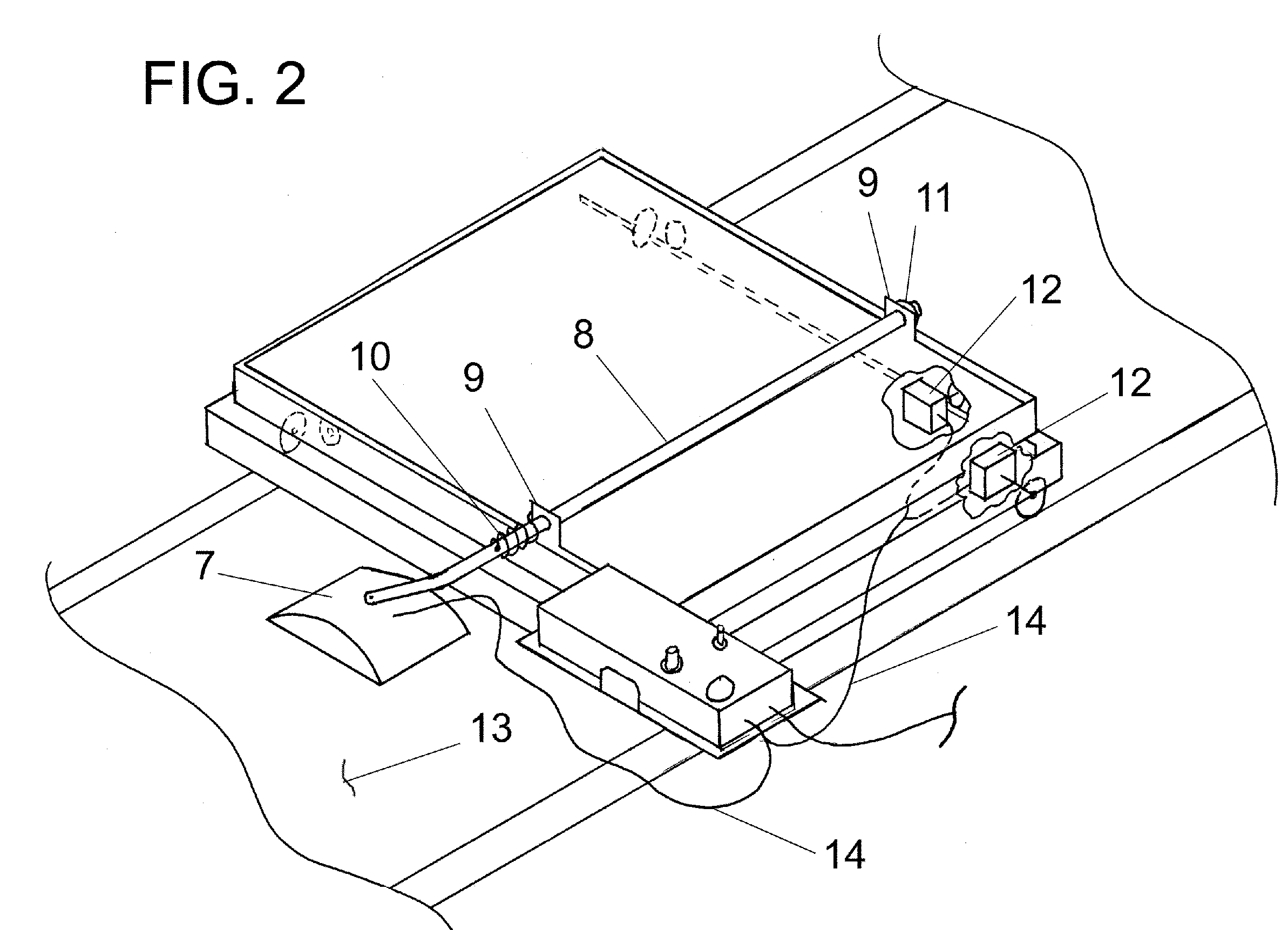
[0008]FIG. 1 illustrates a quilting frame 1 and its components used for reference in this patent. The frame 1 is described in detail in U.S. Pat. No. 6,615,756. The components of frame 1 of interest in this invention are the longitudinal carriage 2 and the transverse carriage 3 with reference to the coordinate system 29. The sewing machine 4 is placed on top of the base plate 5 which is placed on the transverse carriage 3 which is placed on top of the longitudinal carriage 2 which rides on rails 6. The transverse carriage 3 has guide wheels suitably fixed such that only movement in the transverse direction is possible. Similarly, the longitudinal carriage 2 has guide wheels suitably fixed to it such that only longitudinal movement is possible. The sewing machine 4 can move in both the transverse and longitudinal directions using this arrangement. FIG. 2 illustrates the mounting of the position sensor 7 to the sensor arm 8 in one embodiment. The sensor 7 is pivotally mounted to the s...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com