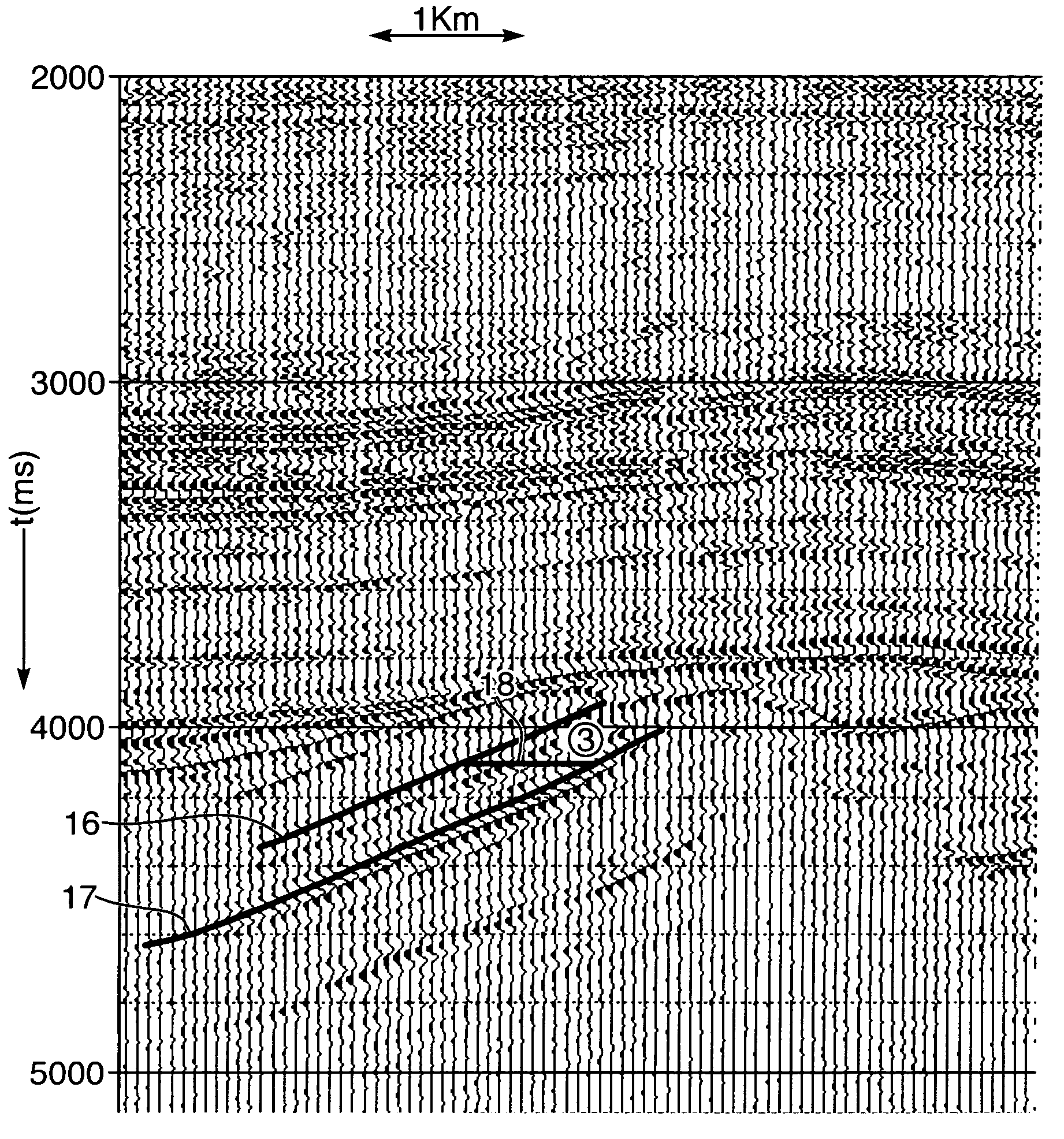
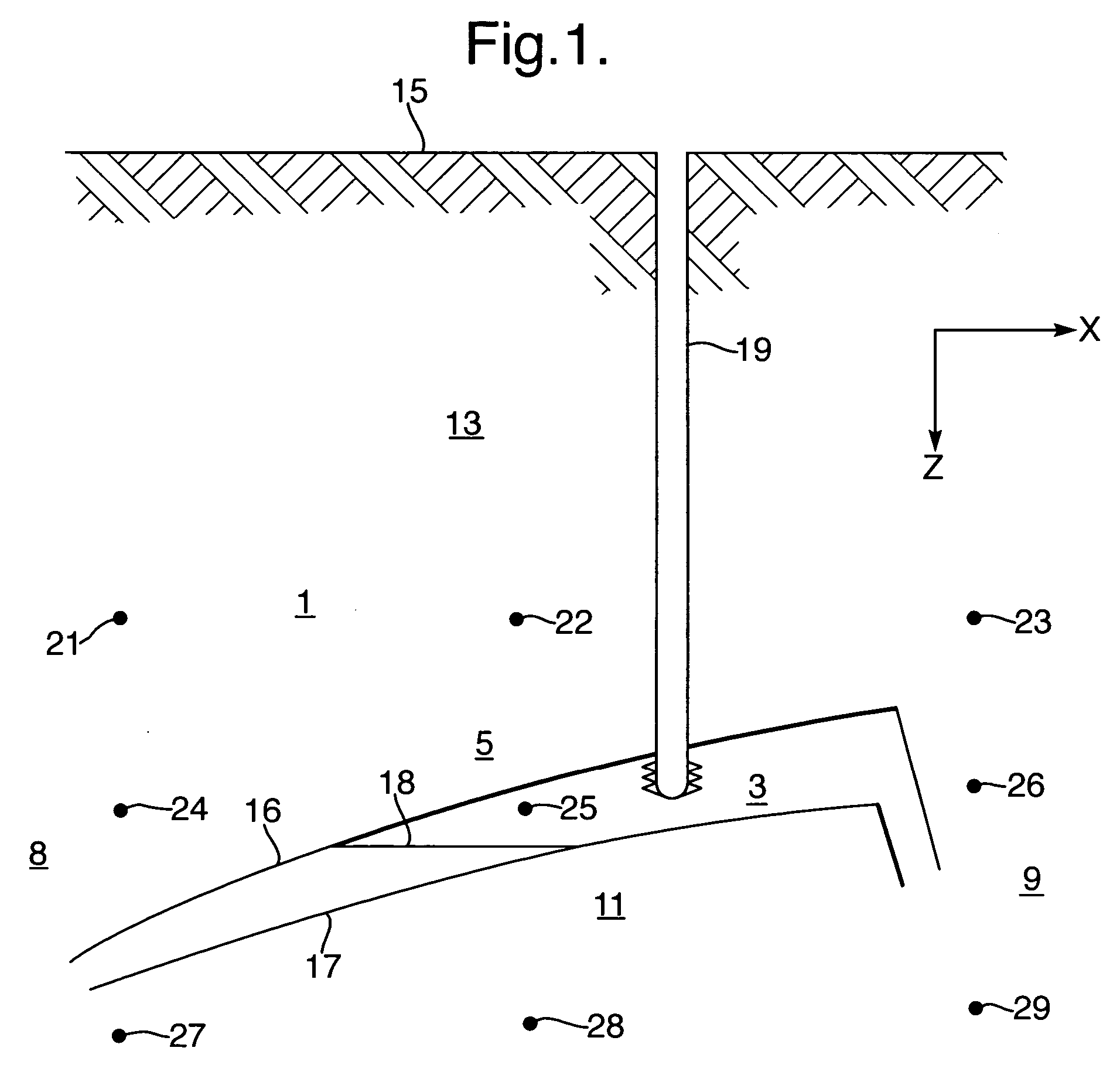
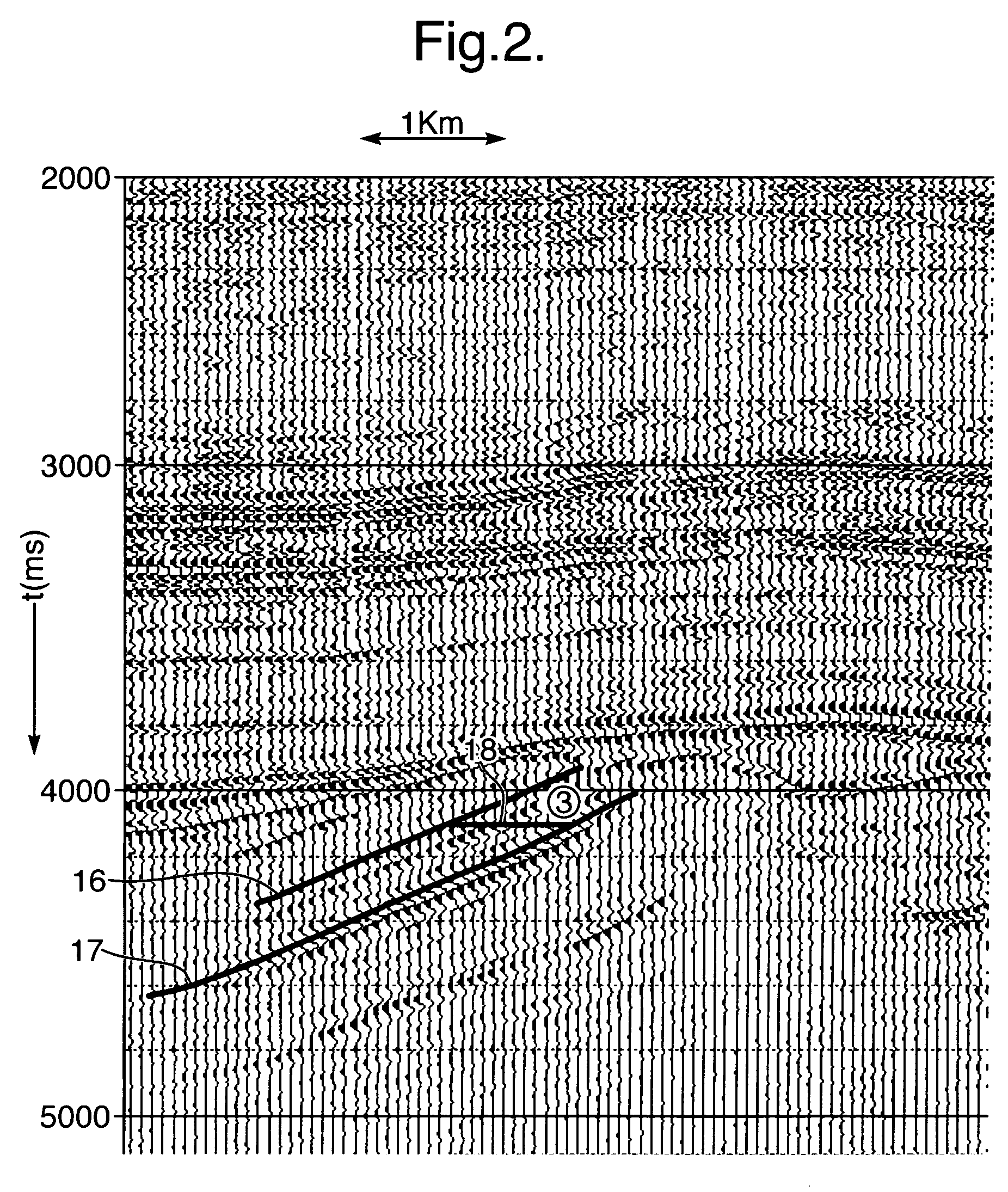
Time-lapse seismic survey of a reservoir region
a reservoir region and time-lapse seismic technology, applied in the field of time-lapse seismic survey of the reservoir region, can solve the problems of reducing the accuracy of seismic data processing, affecting the resolution of seismic data in the reservoir region, and comparatively small thickness of the reservoir region or layer, so as to improve the estimation of the change in pore pressure
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0032] The total stress at a certain location in the subsurface formation is counteracted to some degree by the pore pressure. This leads to the definition of an effective stress that is the difference between the total stress and a term proportional to the pore pressure.
[0033] When the fluid pressure in a reservoir region is reduced, the effective stress field in and around the reservoir region changes, and the reservoir rock undergoes some degree of compaction. The change in the effective stress can be described by the equation:
Δσeff=Δσ−αΔP, (1)
wherein σeff is the effective stress tensor, σ is the total stress tensor, αis the so-called Biot alpha coefficient and is generally in the order of one, and P is the fluid pressure. The sign Δ is used to refer to a difference between a later and a first point in time. The sign convention used in equation 1 is that compressive stresses are negative. Biot showed that the composite properties could be determined from the porosity and the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com