Systems and methods for sequential modeling in less than one sequential scan
a sequential model and scan technology, applied in the field of sequential modeling, can solve the problems of increasing the number of data scans for other inductive learners, increasing the difficulty and increasing the difficulty of data mining methods, so as to reduce the complexity of the asymptotic algorithm, the effect of reducing the number of data scans and increasing the accuracy
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
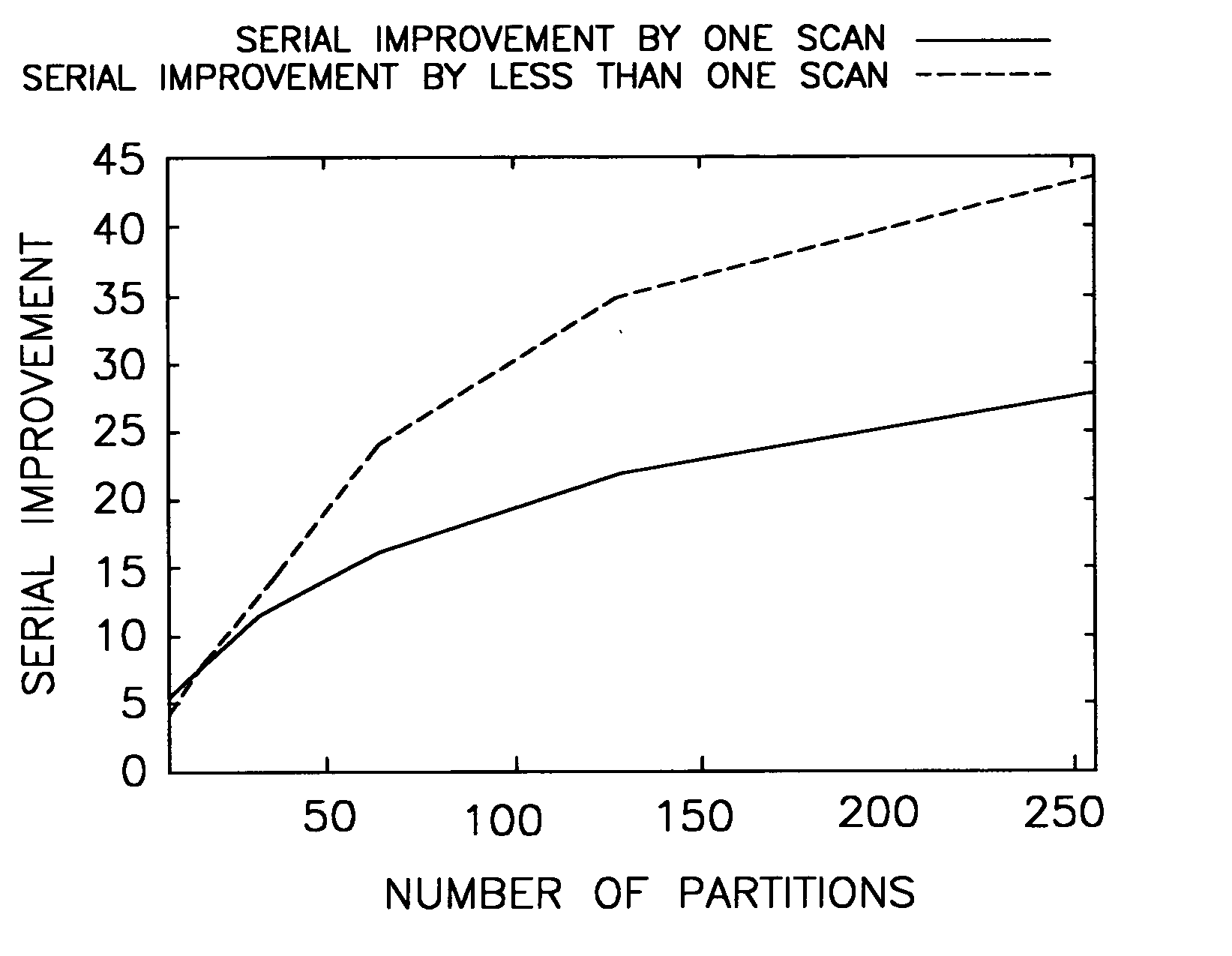
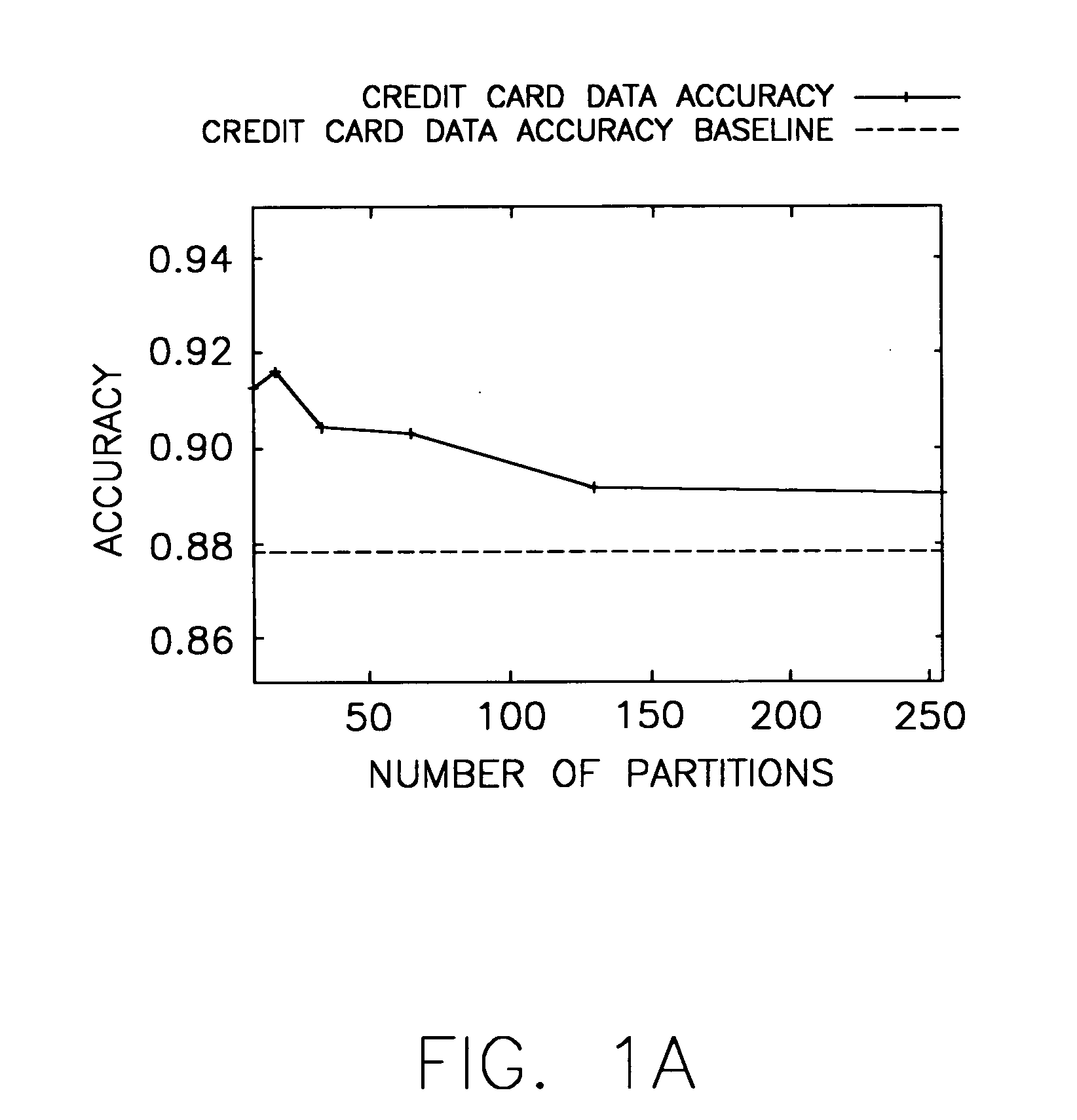
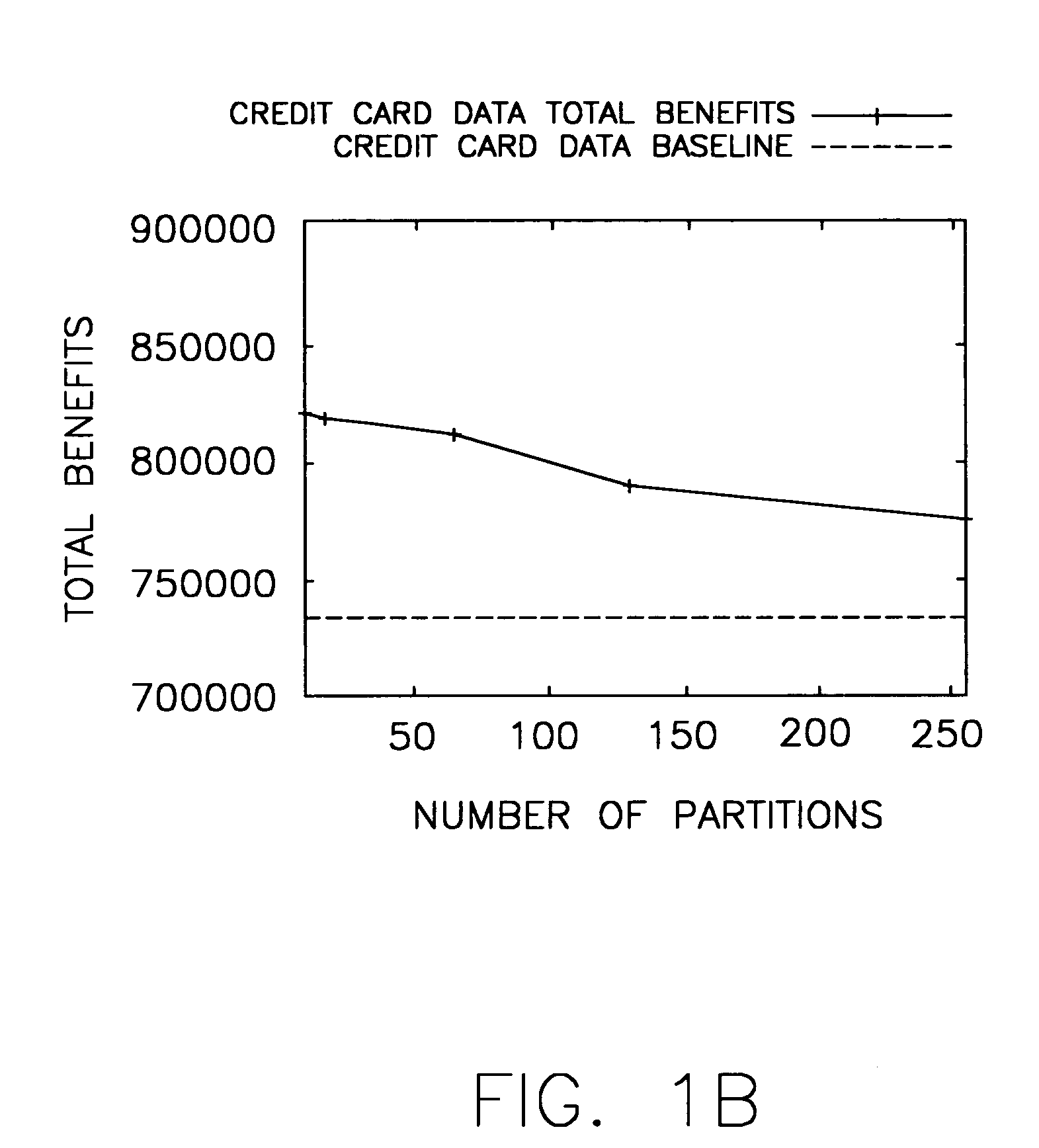
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018] We first describe a strawman algorithm that scans the data set exactly once, then propose the extension that scans the data set less than once. The strawman algorithm is based on probabilistic modeling.
[0019] Suppose p(li|x) is the probability that x is an instance of class li. In addition, we have a benefit matrix b [li′,li] that records the benefit received by predicting an example of class li′ to be an instance of class li. For traditional accuracy-based problems, ∀i,b[li,li]=1 and ∀i′≠i,b[li′, li]=0. For cost-sensitive application such as credit card fraud detection, assume that the overhead to investigate a fraud is $90 and y (x) is the transaction amount, then b[fraud, fraud]=y(x)−$90 and b [fraud, fraud]=−$90. Using benefit matrix and probability, the expected benefit received by predicting x to be an instance of class li is Expected Benefit:e (li❘x)=∑li′ b [li′,li]·p (li′❘x)(1)
[0020] Based on optimal decision policy, the best decision is the label with the ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - Generate Ideas
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com