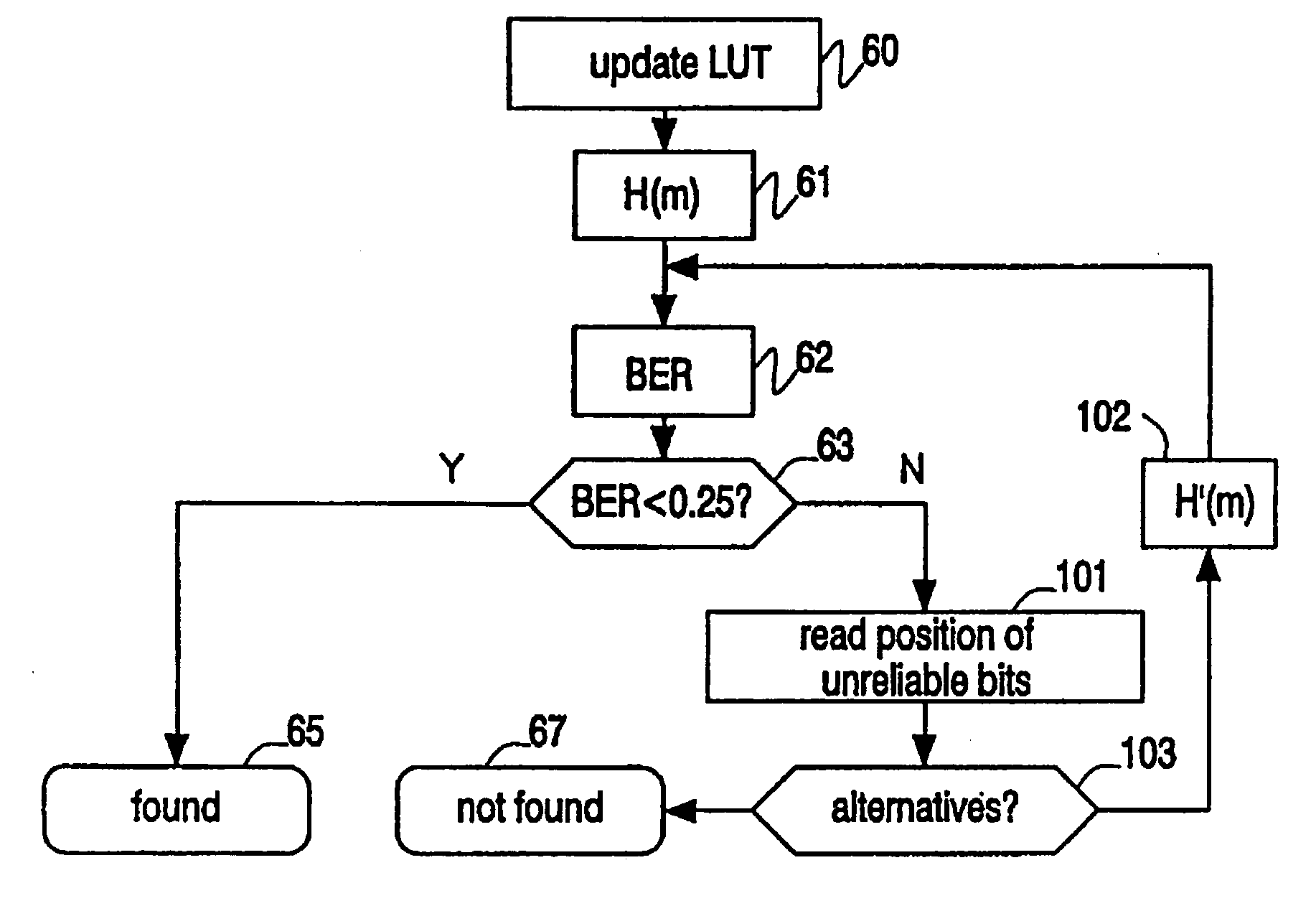
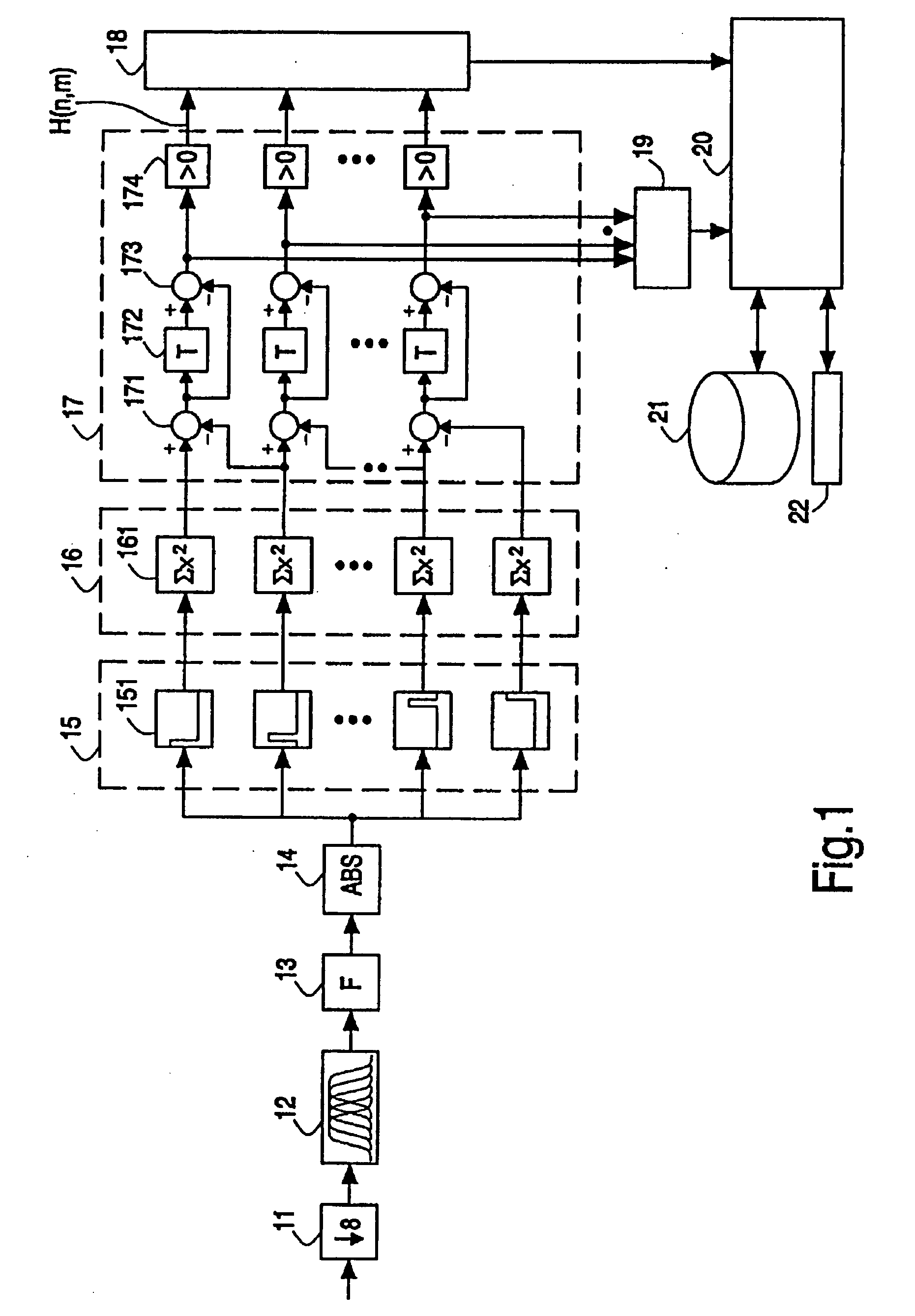
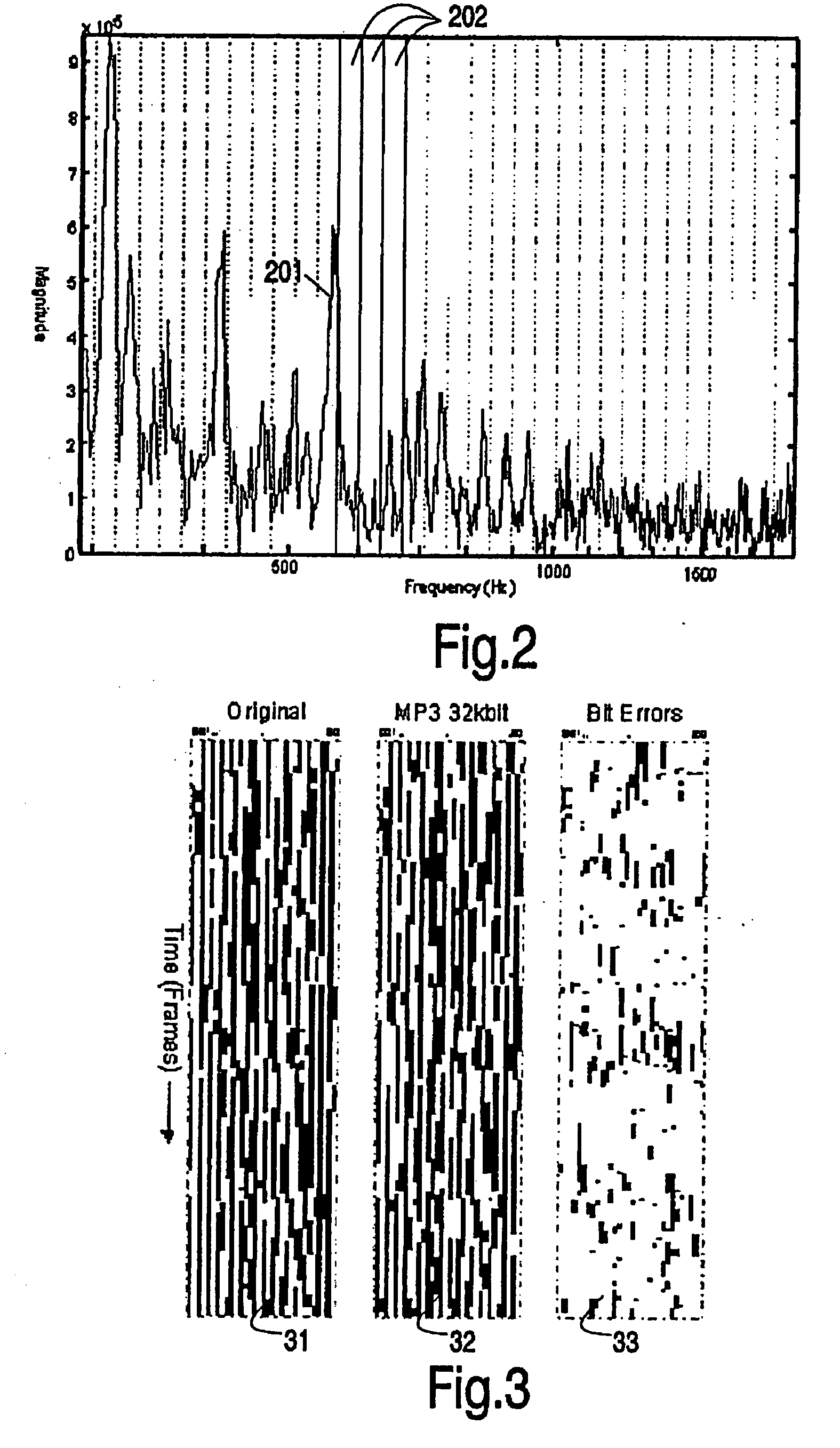
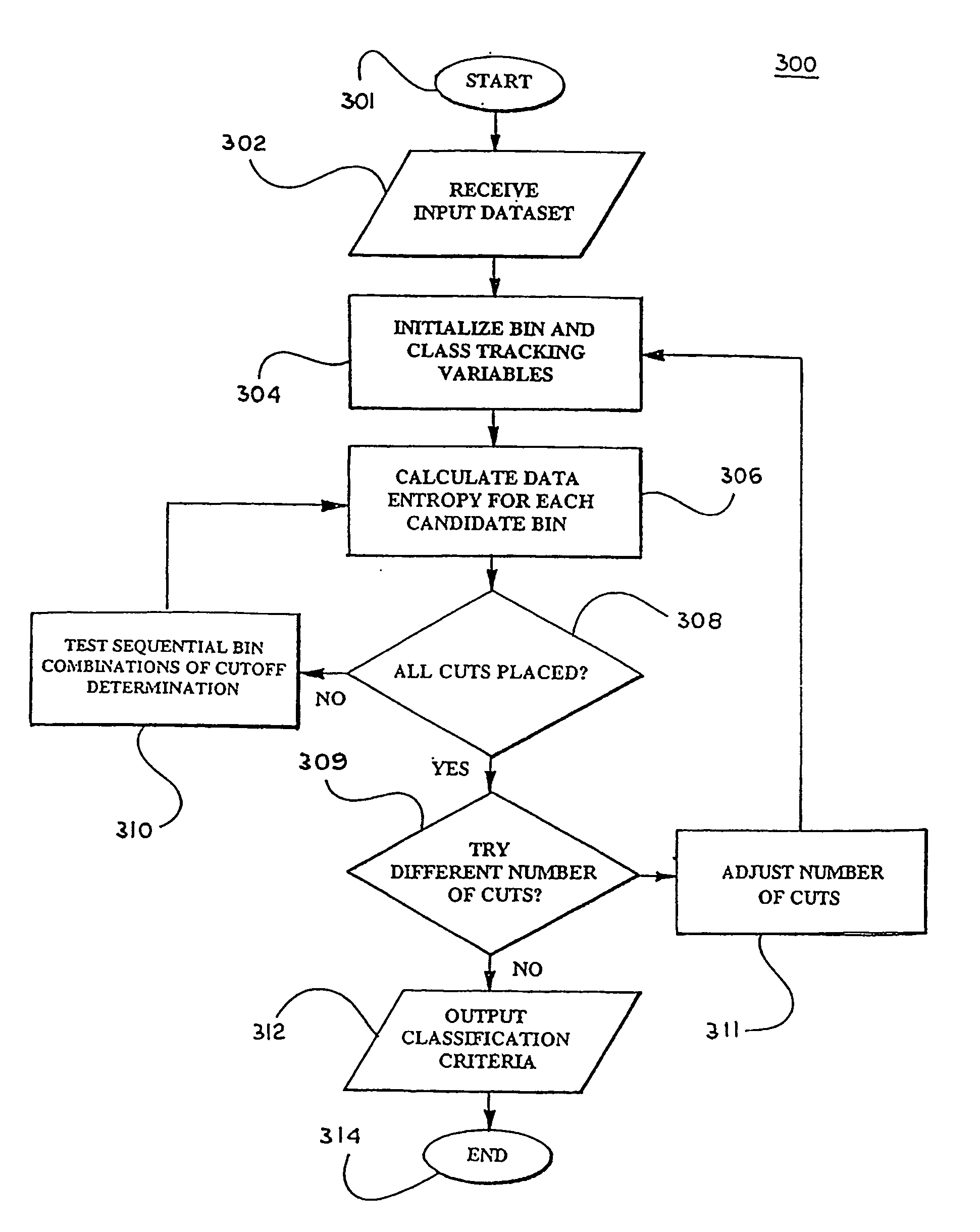
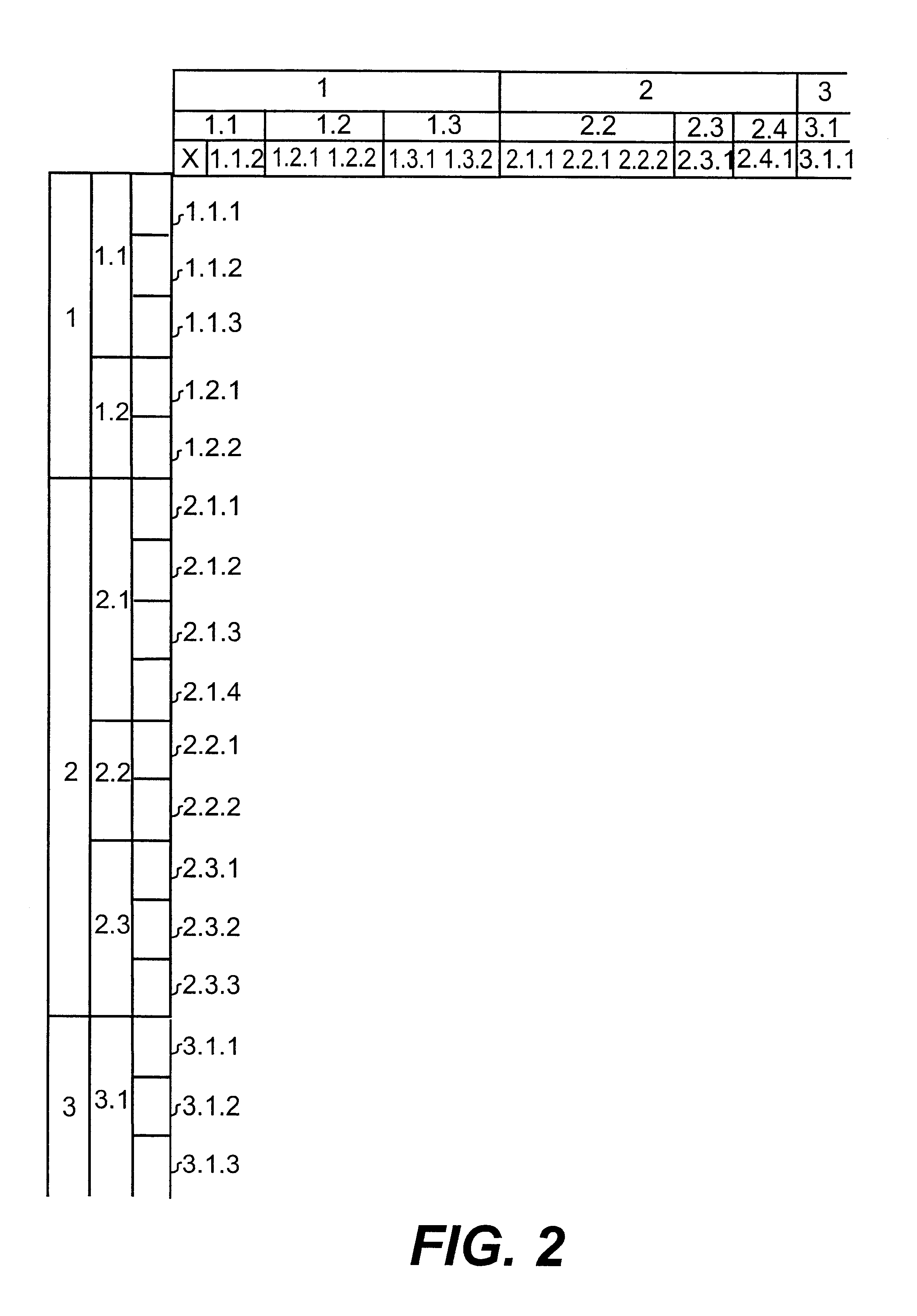Patents
Literature
207 results about "Very large database" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
A very large database, (originally written very large data base) or VLDB, is a database that contains a very large amount of data, so much that it can require specialized architectural, management, processing and maintenance methodologies .
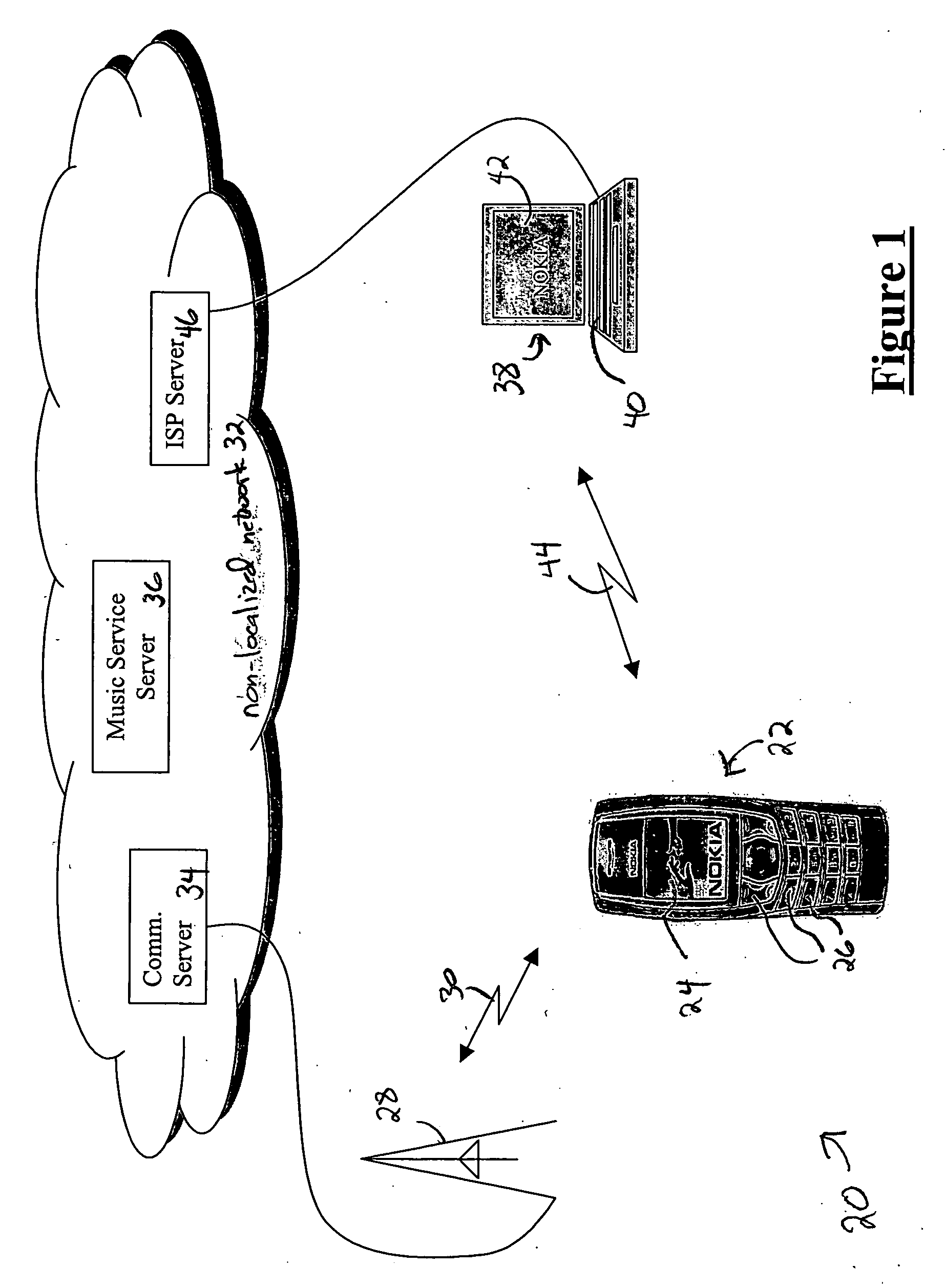
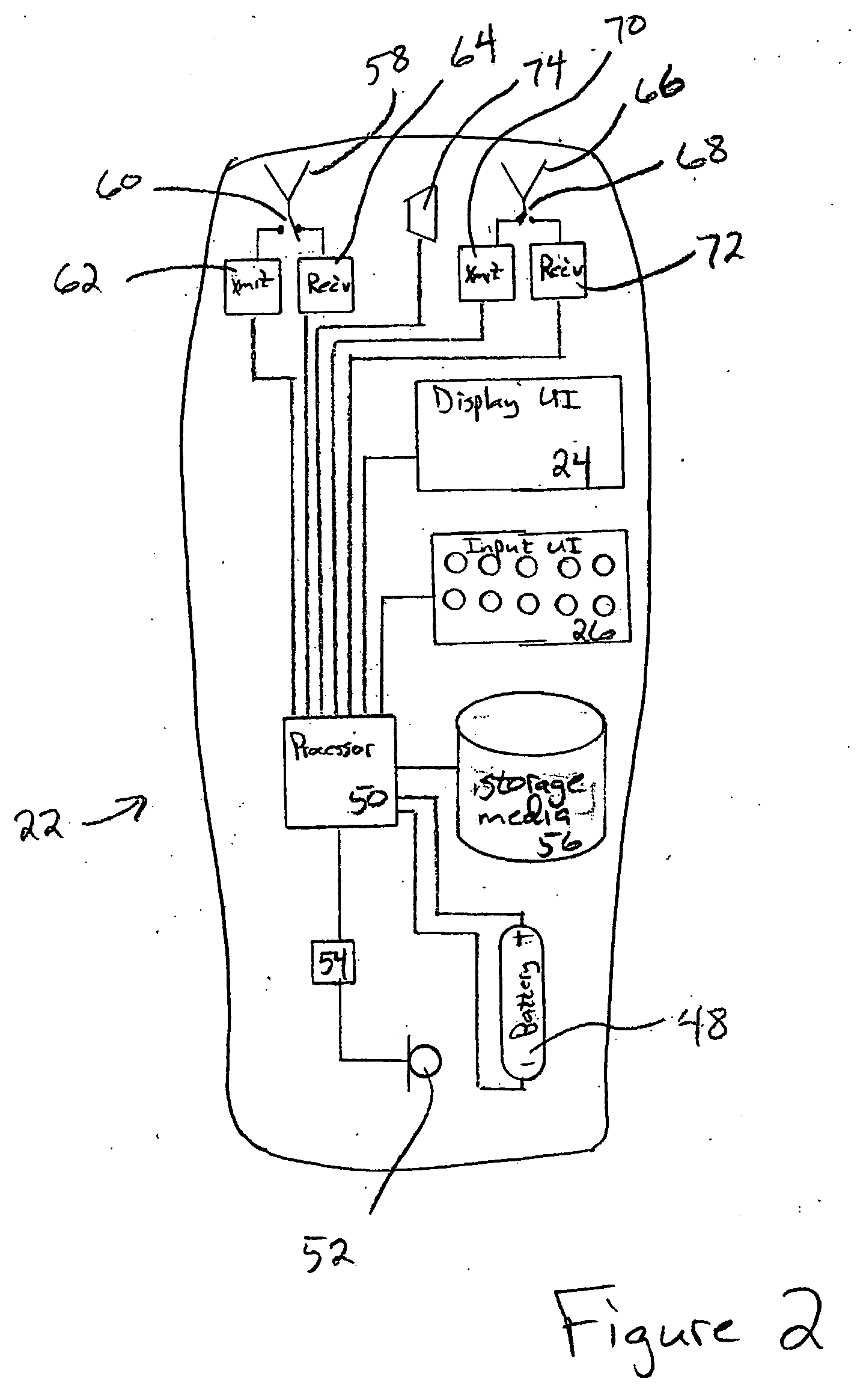
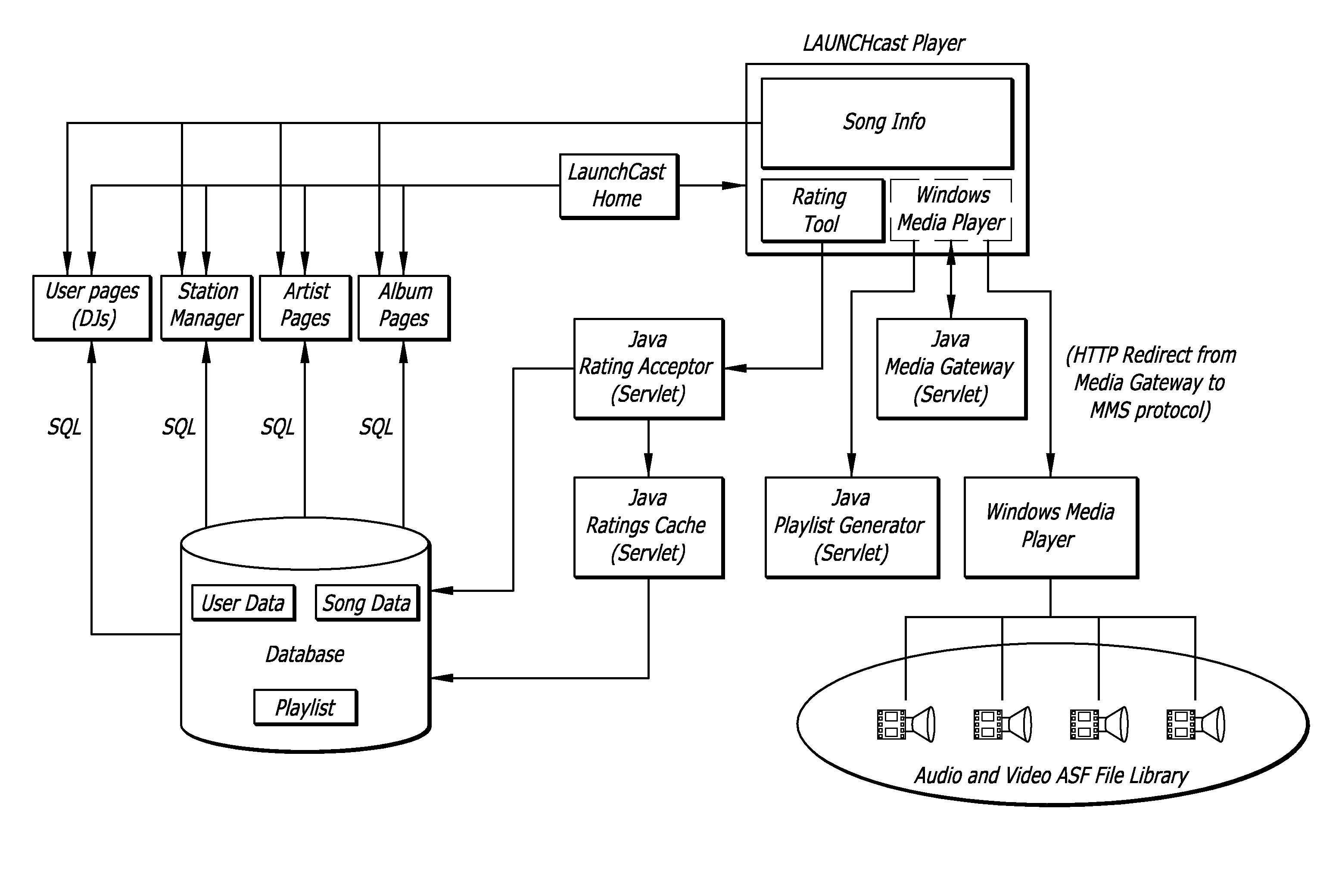
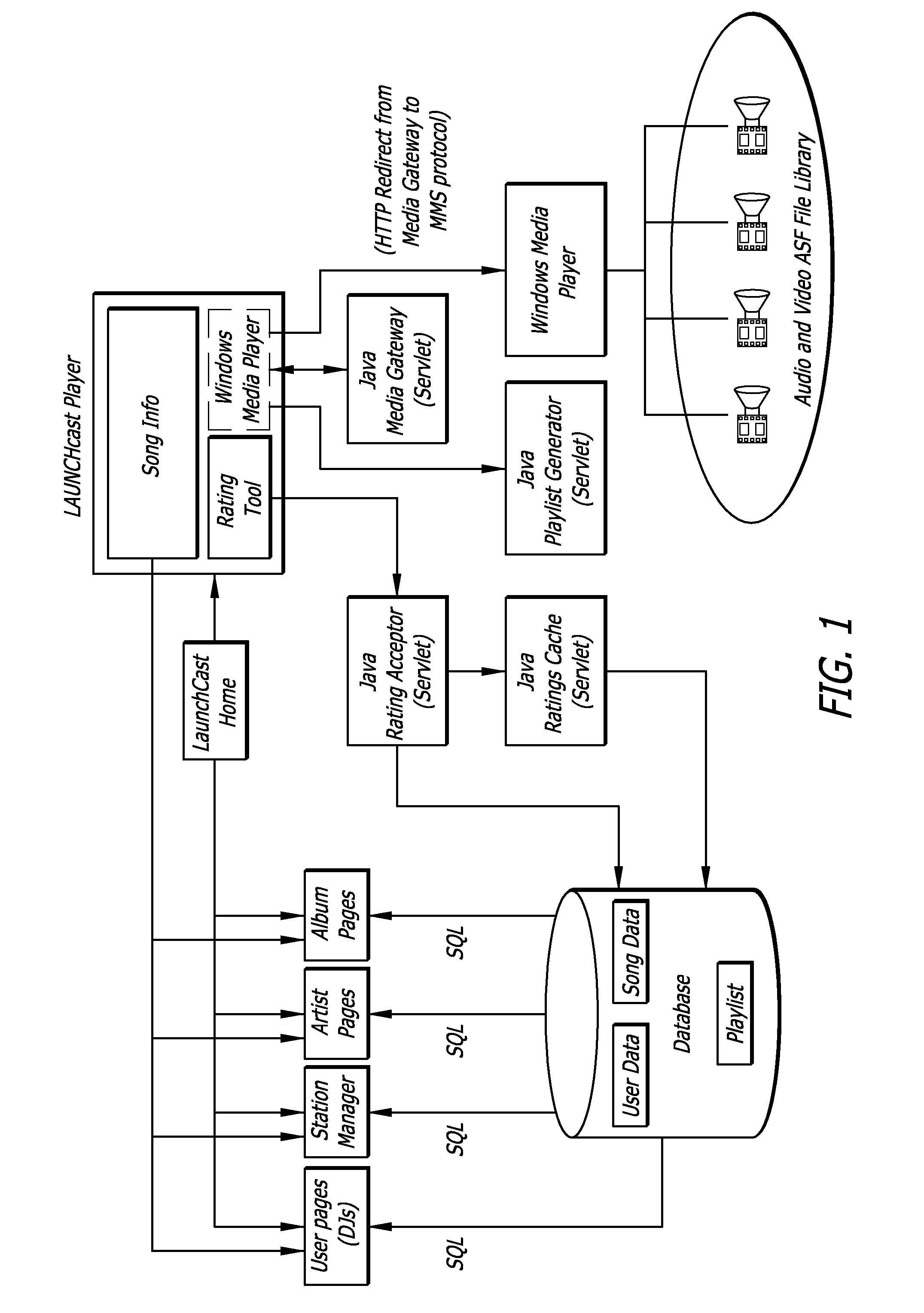
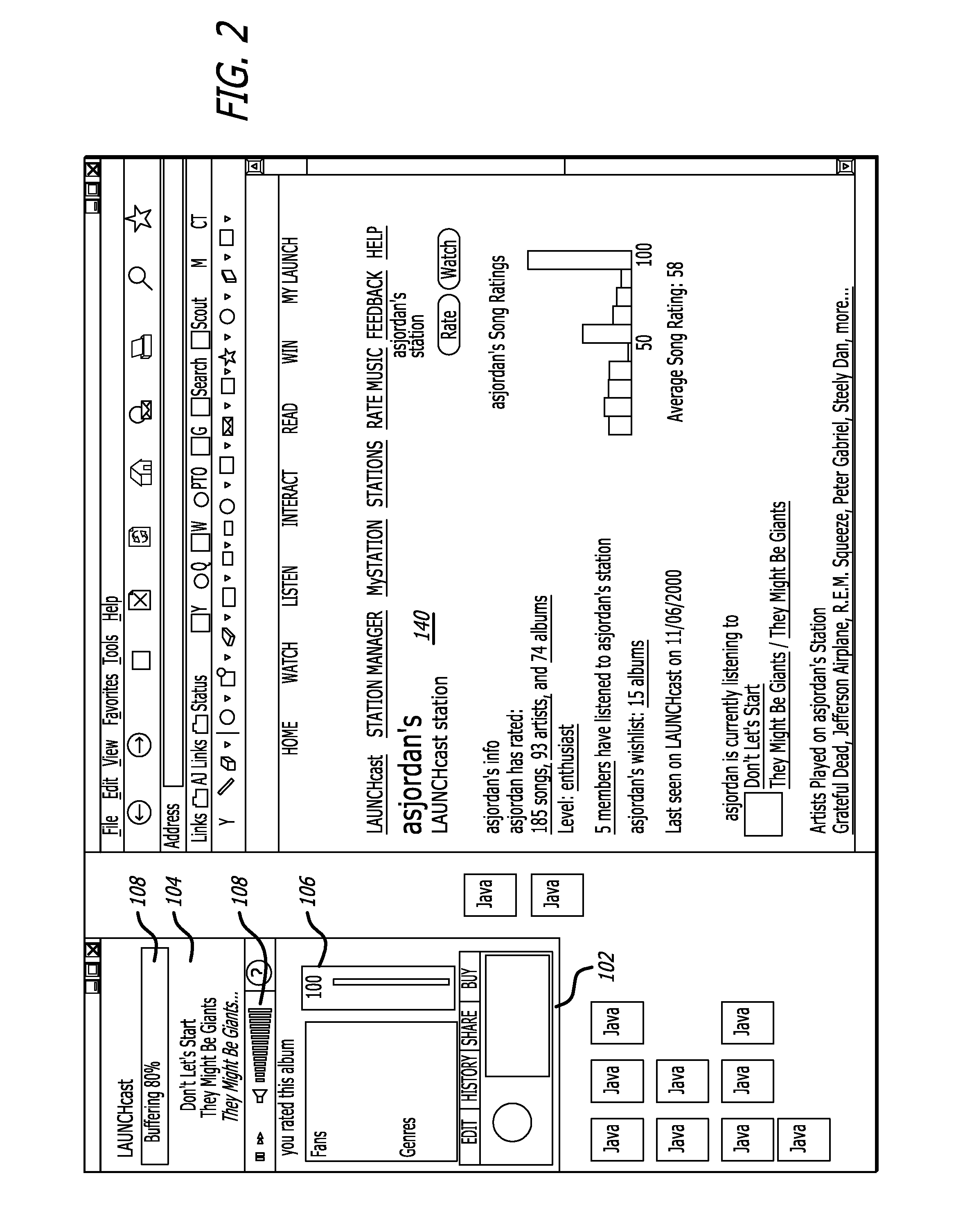
System and method for music synchronization in a mobile device
ActiveUS20050216855A1Multimedia data indexingSpecial service for subscribersMobile stationMobile device
A computer program embodied in a computer readable medium in a mobile station MS includes instructions to display a first identifier, such as a song title, associated with a first media (music or video) file and a second identifier identified with a second media file. The first identifier indicates that the first media file is stored in the MS and the second identifier indicates that the file is not stored within the MS. Five such identifiers are disclosed, with functionality to up / download the media files one or more at a time from a PC or a networked server. Playlists and albums may be similarly indicated in their identifiers. The user is enabled to create and edit playlists on the MS without regard to what media files are stored on the MS. The MS may store file identifiers for the database maintained on the PC, a large-scale database maintained at a media service server, or a portion thereof. A mobile station is also described.
Owner:RPX CORP
System And Methods For Clustering Large Database of Documents
InactiveUS20090043797A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsData setComputerized system
In a computerized system, a method of organizing a plurality of documents within a dataset of documents, wherein a plurality of documents within a class of the dataset each includes one or more citations to one or more other documents, comprising creating a set of fingerprints for each respective document in the class, wherein each fingerprint comprises one or more citations contained in the respective document, creating a plurality of clusters for the dataset based on the sets of fingerprints for the documents in the class, assigning each respective document in the dataset to one or more of the clusters, creating a descriptive label for each respective cluster, and presenting one or more of the labeled clusters to a user of the computerized system or providing the user with access to documents in at least one cluster.
Owner:SPARKIP
Systems and methods for object recognition using a large database
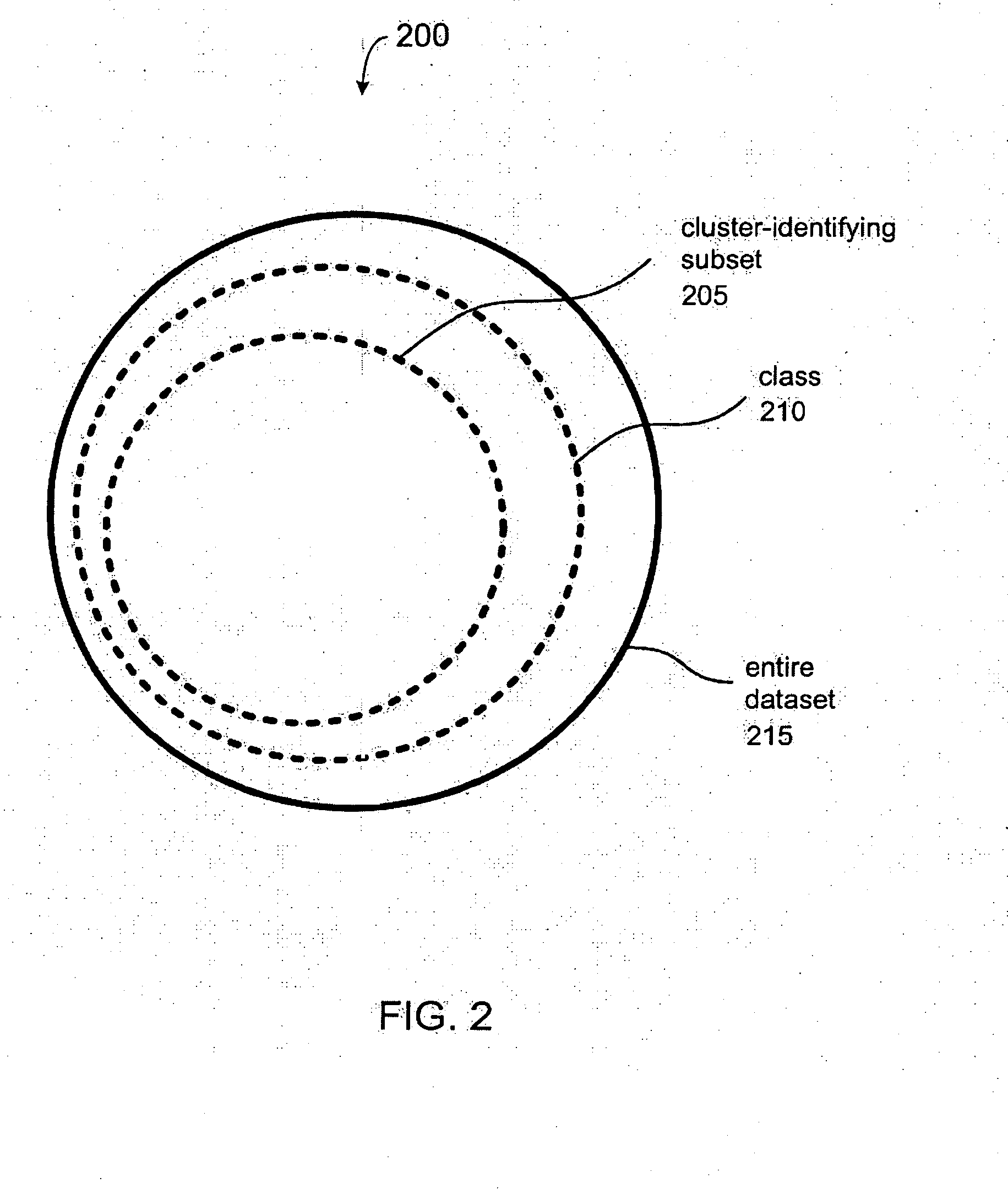
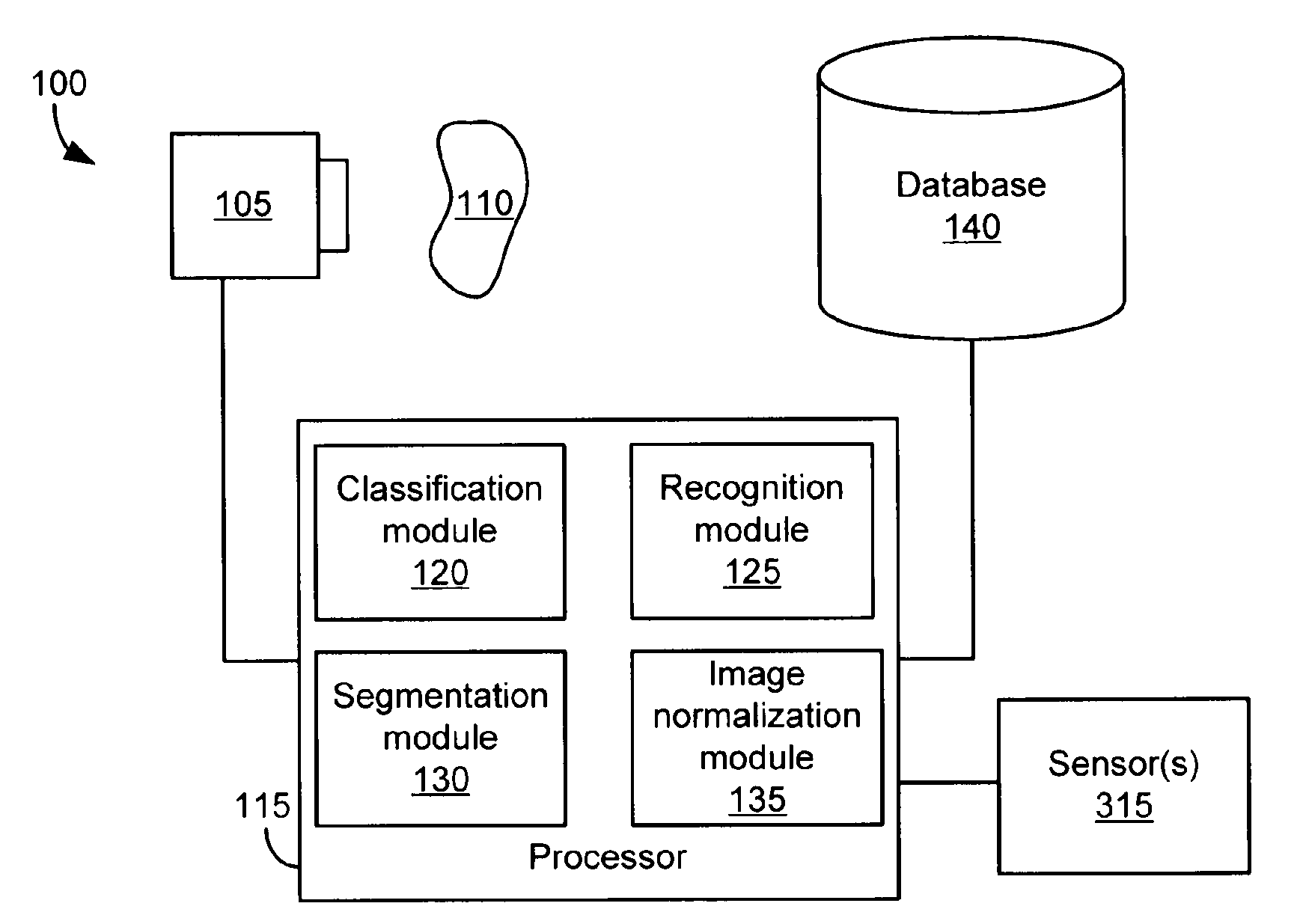
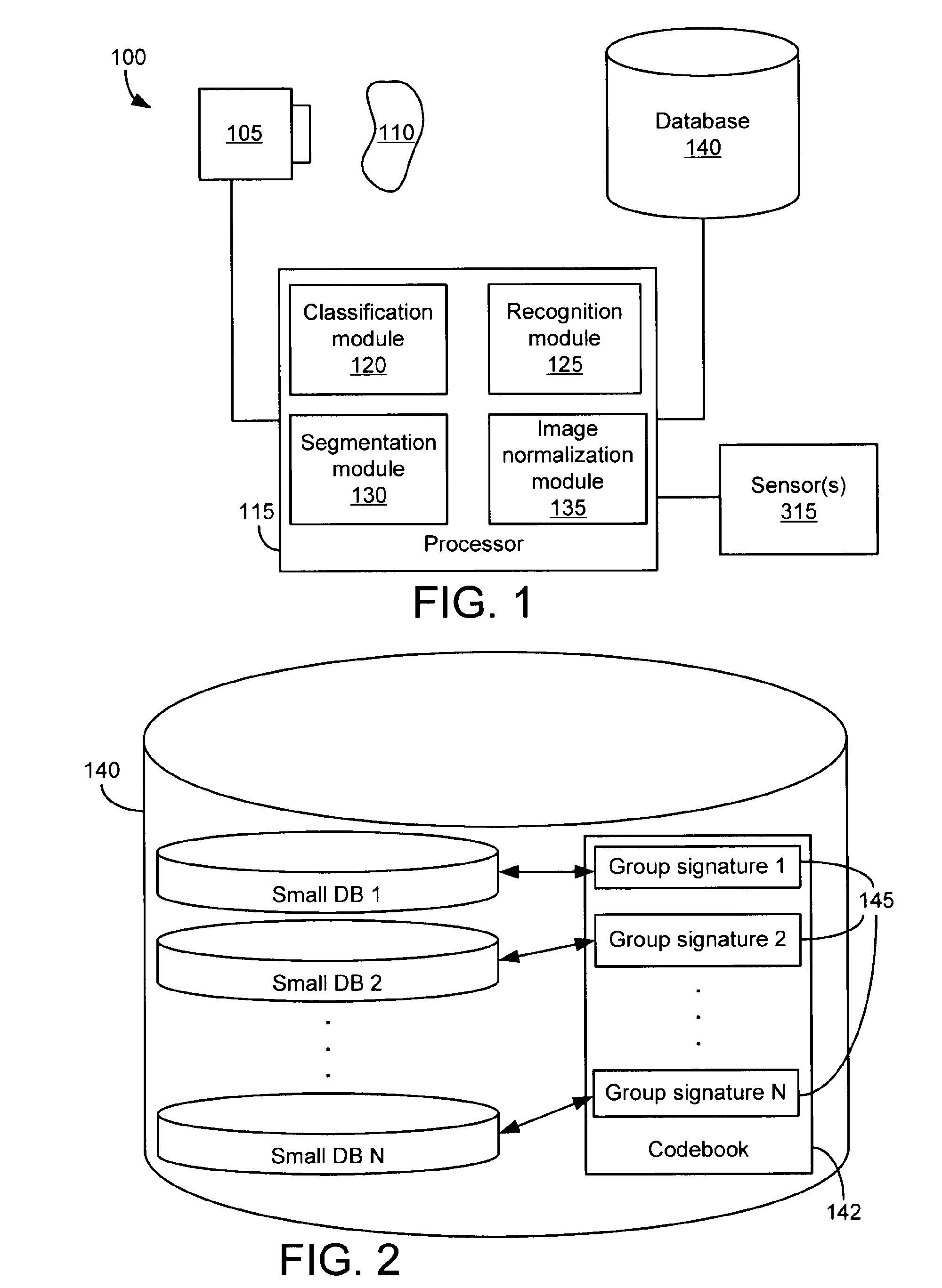
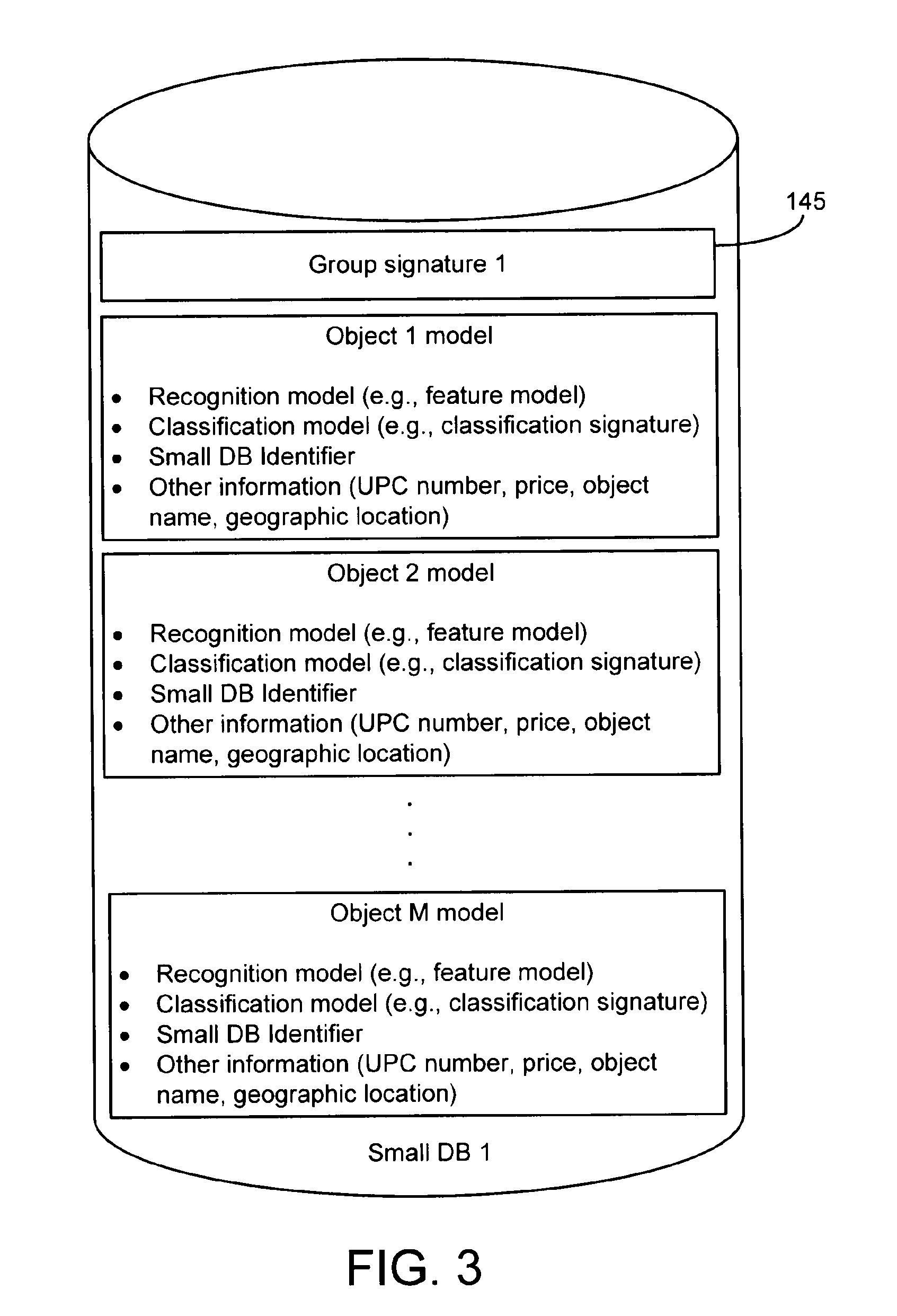
InactiveUS20110286628A1Digital data information retrievalCharacter and pattern recognitionObject storeVery large database
A method of organizing a set of recognition models of known objects stored in a database of an object recognition system includes determining a classification model for each known object and grouping the classification models into multiple classification model groups. Each classification model group identifies a portion of the database that contains the recognition models of the known objects having classification models that are members of the classification model group. The method also includes computing a representative classification model for each classification model group. Each representative classification model is derived from the classification models that are members of the classification model group. When a target object is to be recognized, the representative classification models are compared to a classification model of the target object to enable selection of a subset of the recognition models of the known objects for comparison to a recognition model of the target object.
Owner:DATALOGIC ADC
Method and system for sleep monitoring, regulation and planning
InactiveUS20110230790A1Accurately determineGood user interfaceAcoustic time signalsPerson identificationActigraphyAnalysis data
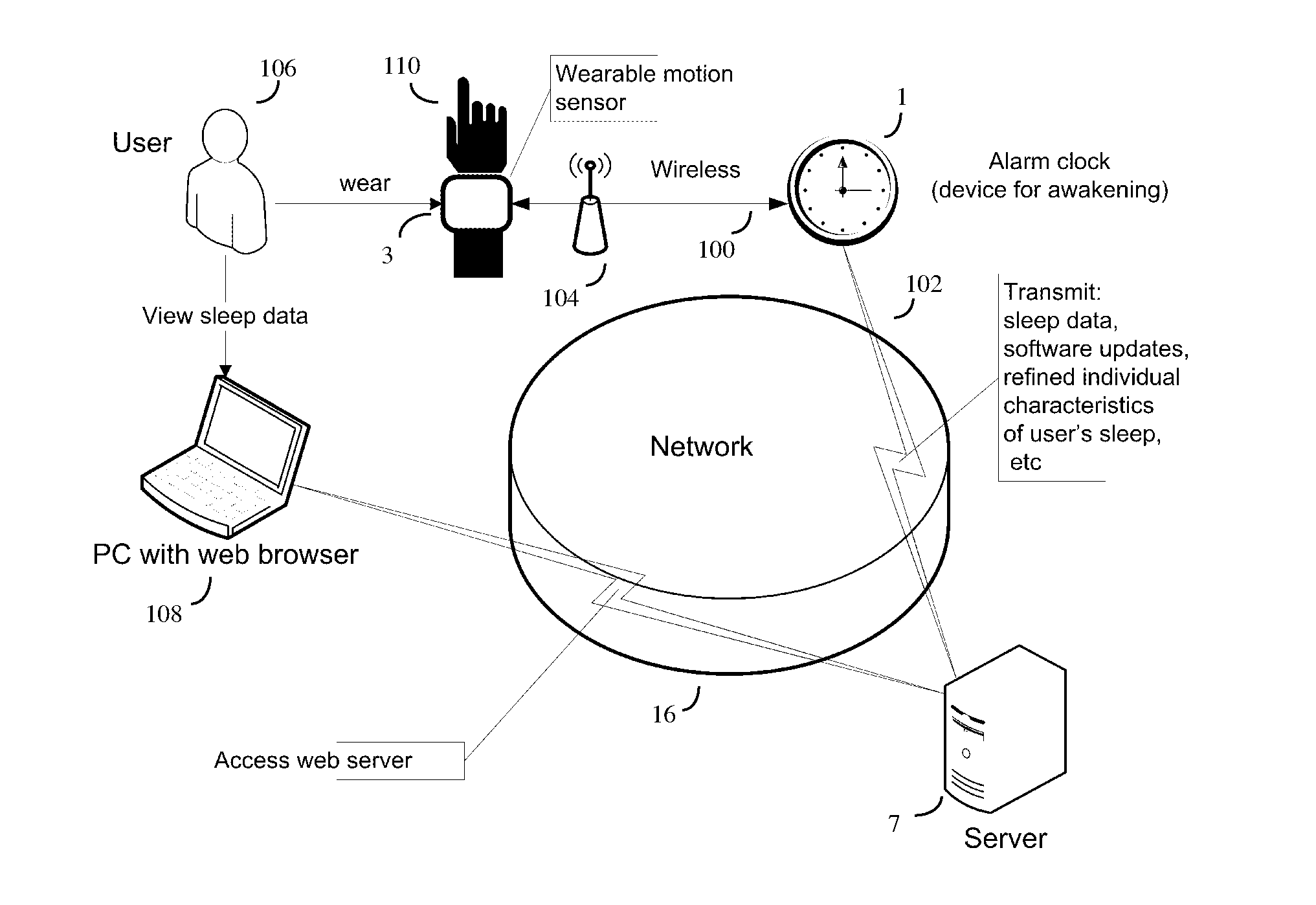
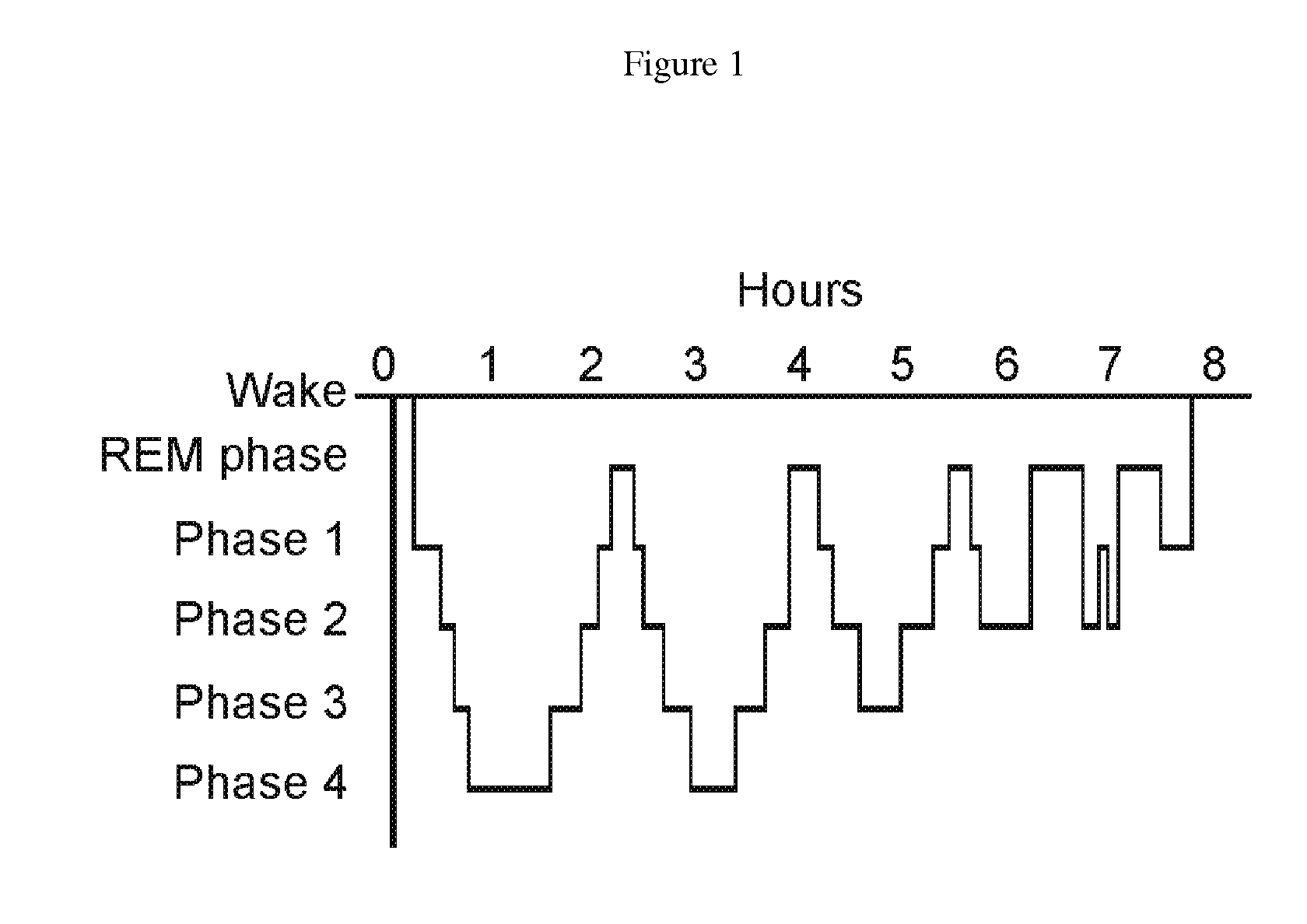
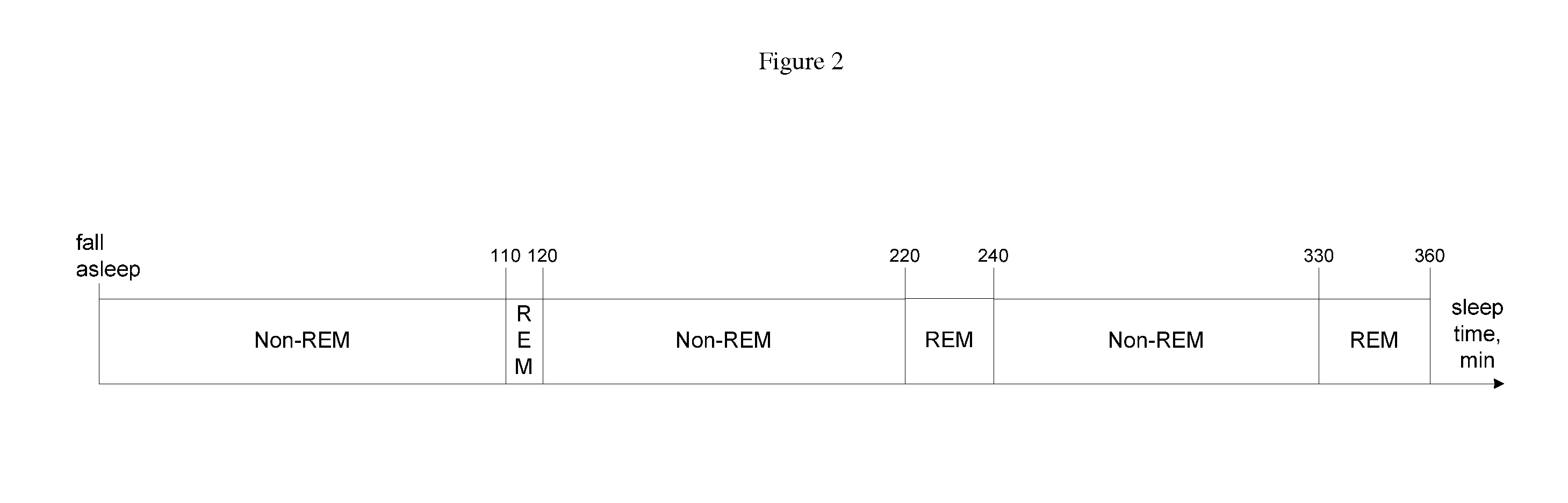
A method for operating a sleep phase actigraphy synchronized alarm clock that communicates with a remote sleep database, such as an internet server database, and compares user physiological parameters, sleep settings, and actigraphy data with a large database that may include data collected from a large number of other users with similar physiological parameters, sleep settings, and actigraphy data. The remote server may use “black box” analysis approach by running supervised learning algorithms to analyze the database, producing sleep phase correction data which can be uploaded to the alarm clock, and be used by the alarm clock to further improve its REM sleep phase prediction accuracy.
Owner:KOZLOV VALERIY
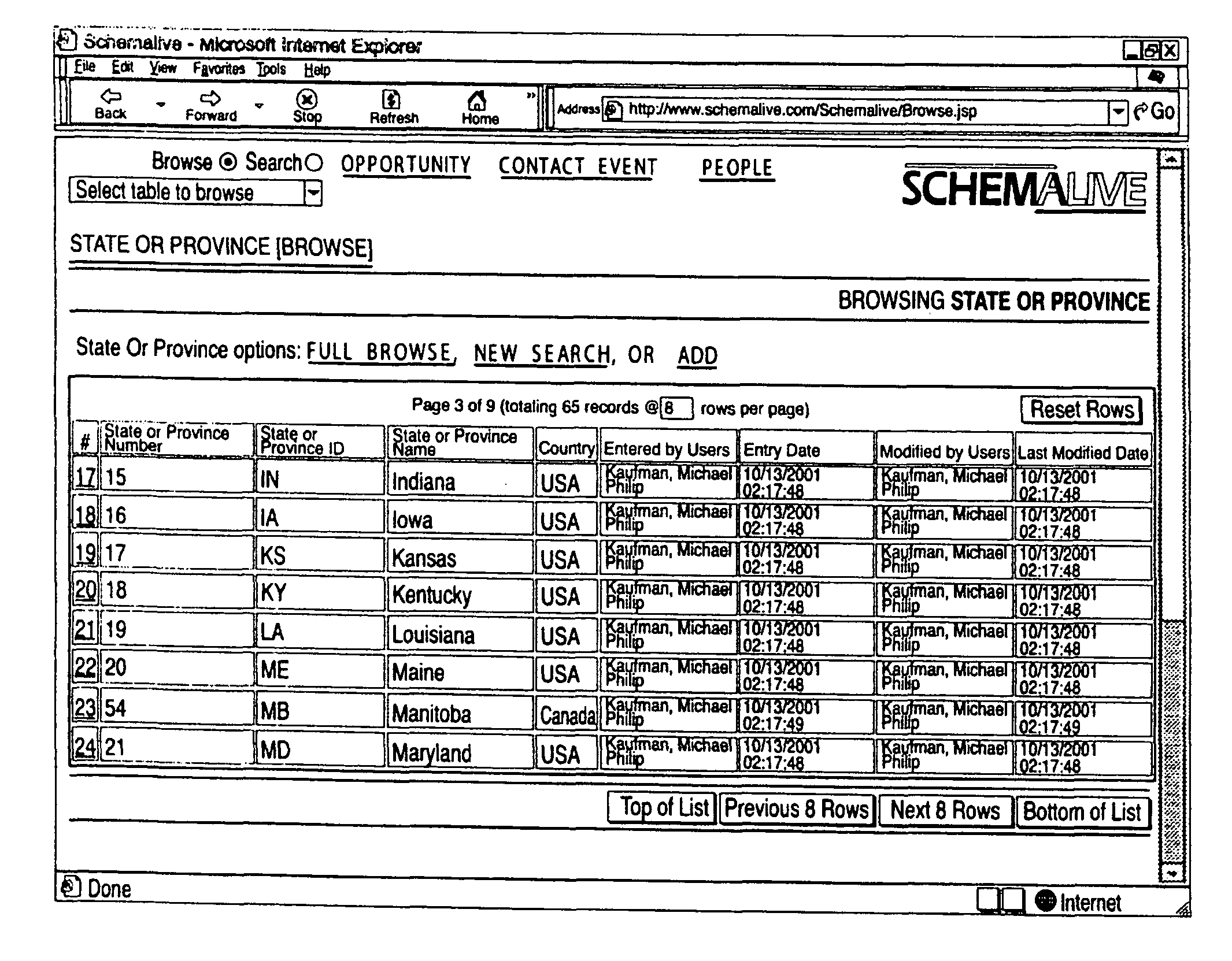
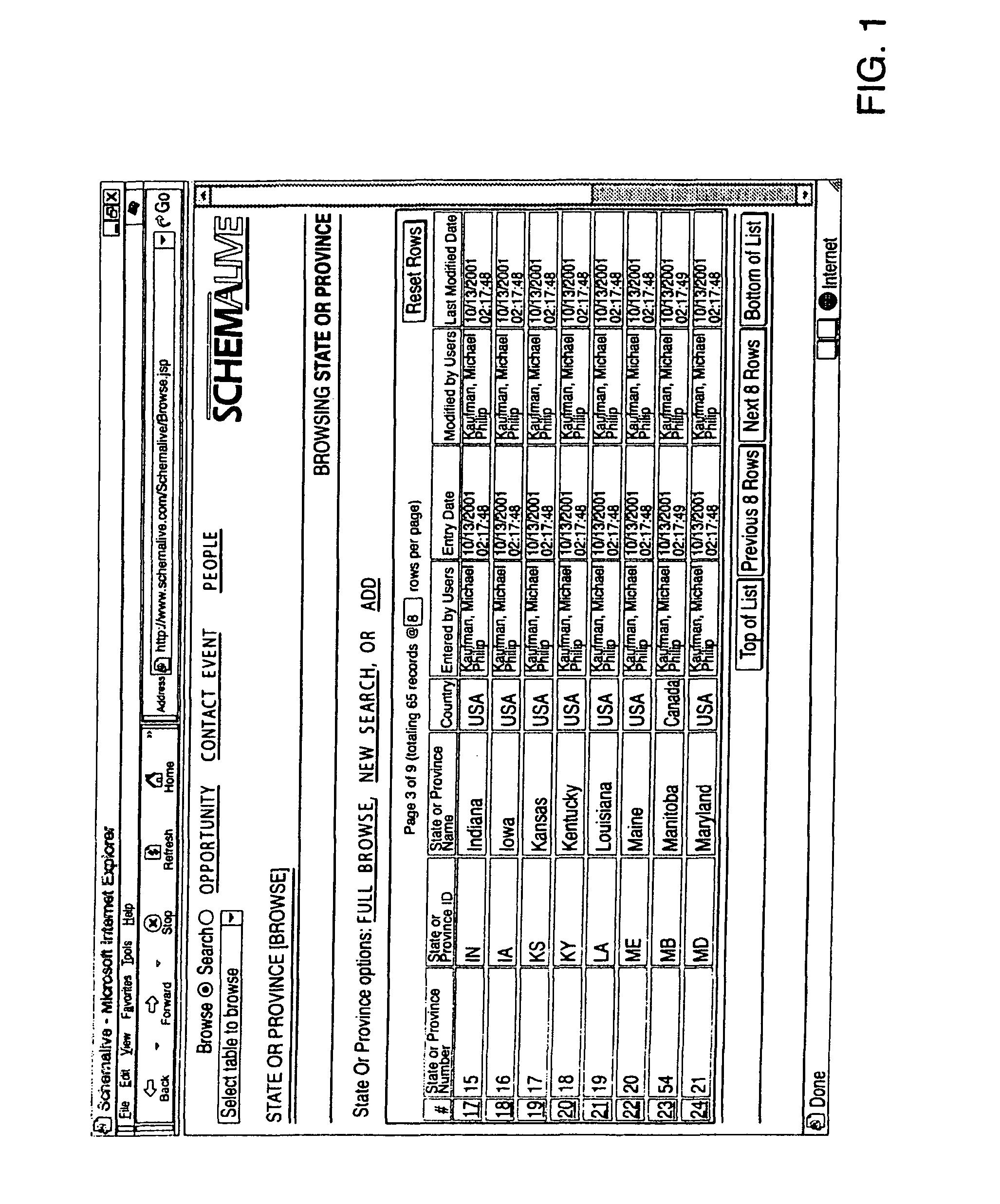
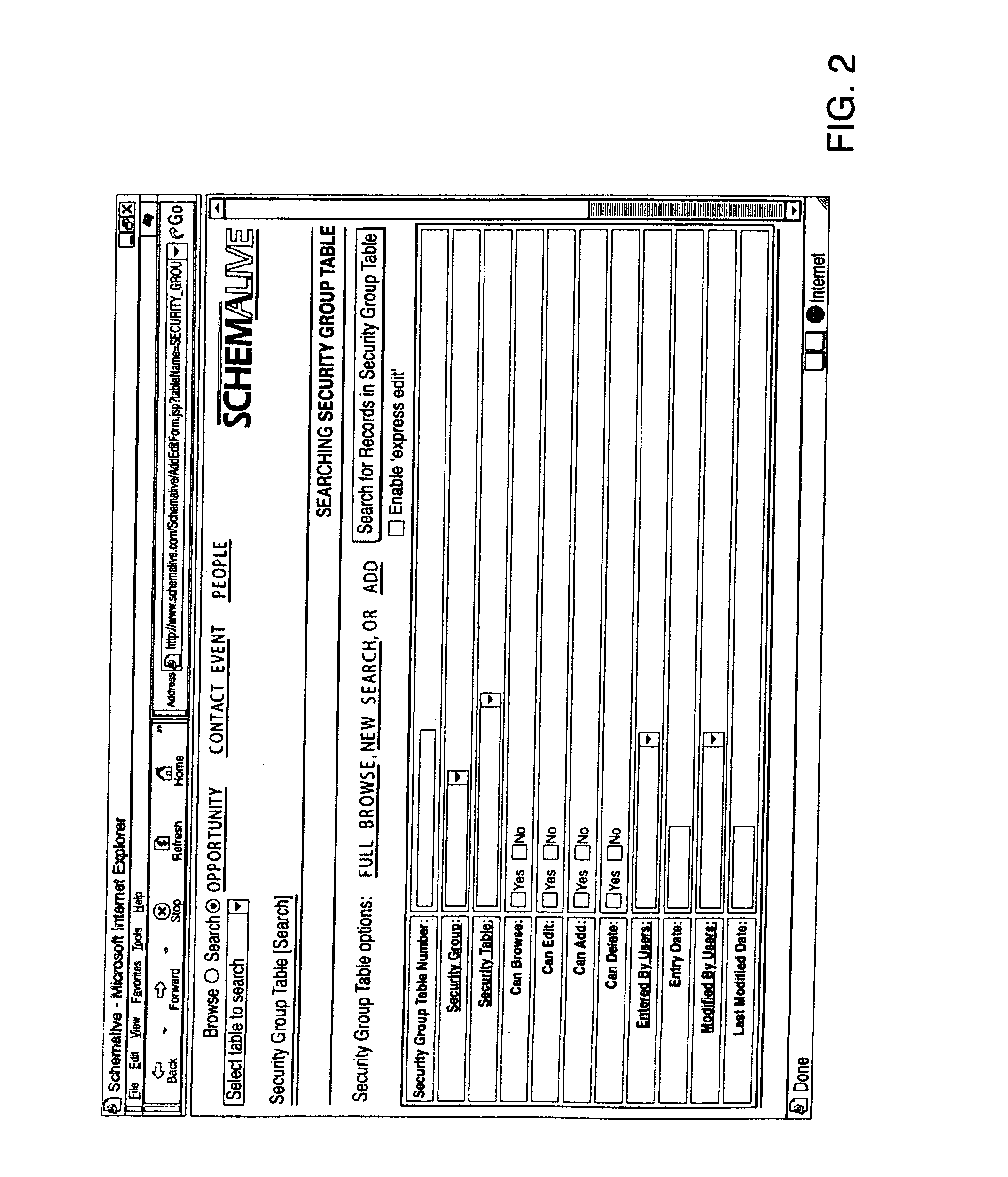
System and Method for Generating Automatic User Interface for Arbitrarily Complex or Large Databases
InactiveUS20080046462A1Natural, powerful, and easy-to-useData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDrill downSoftware system
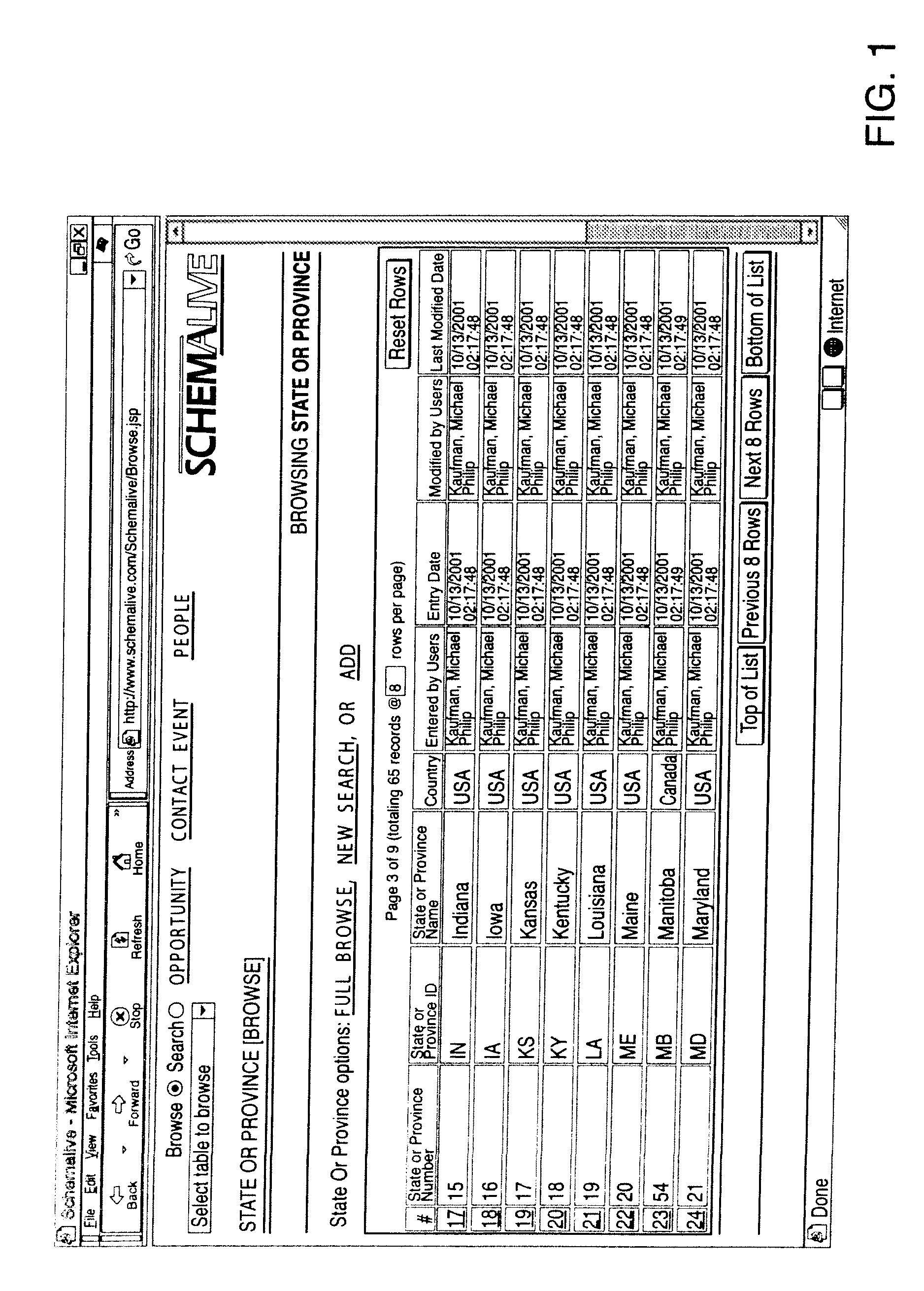
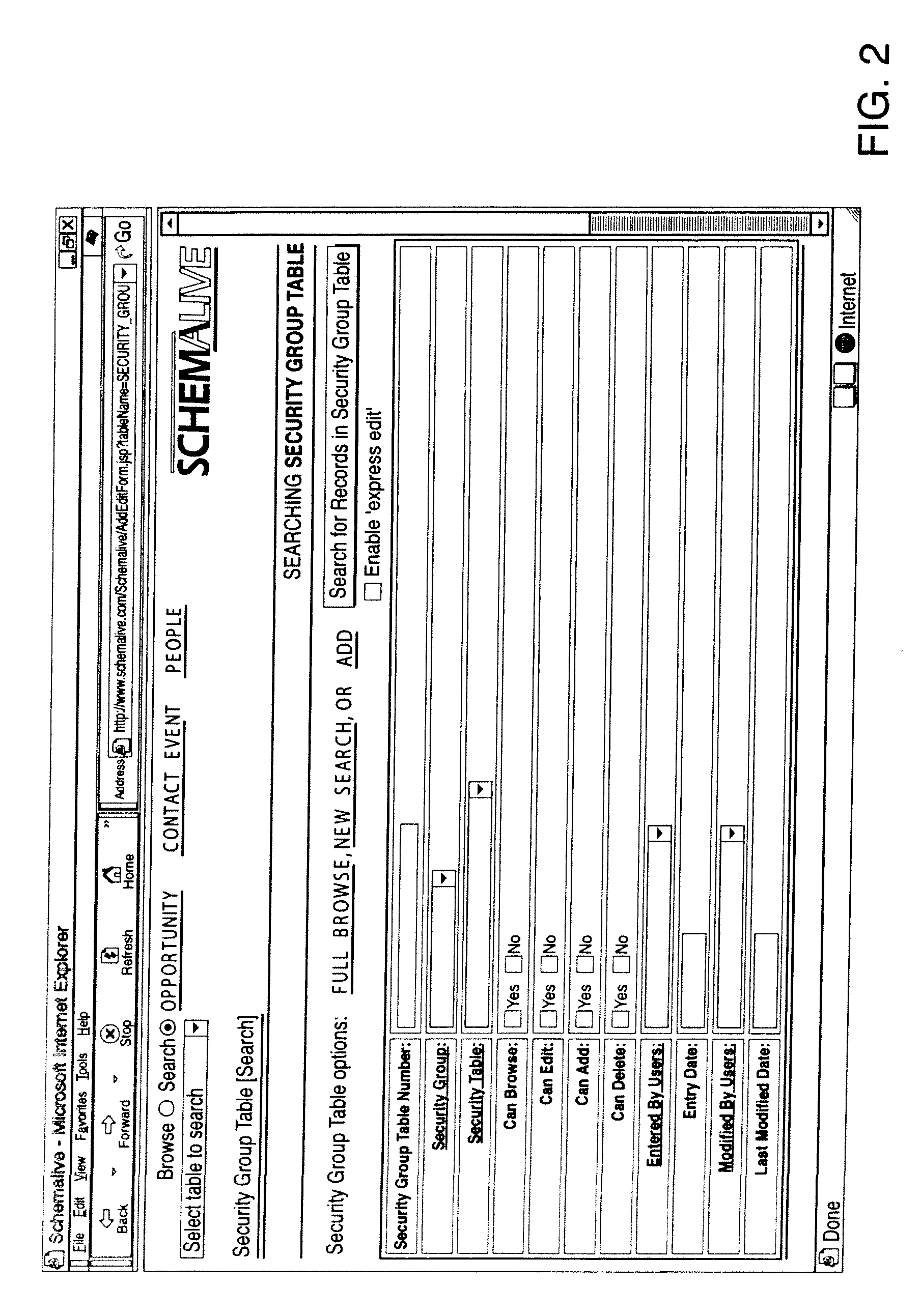
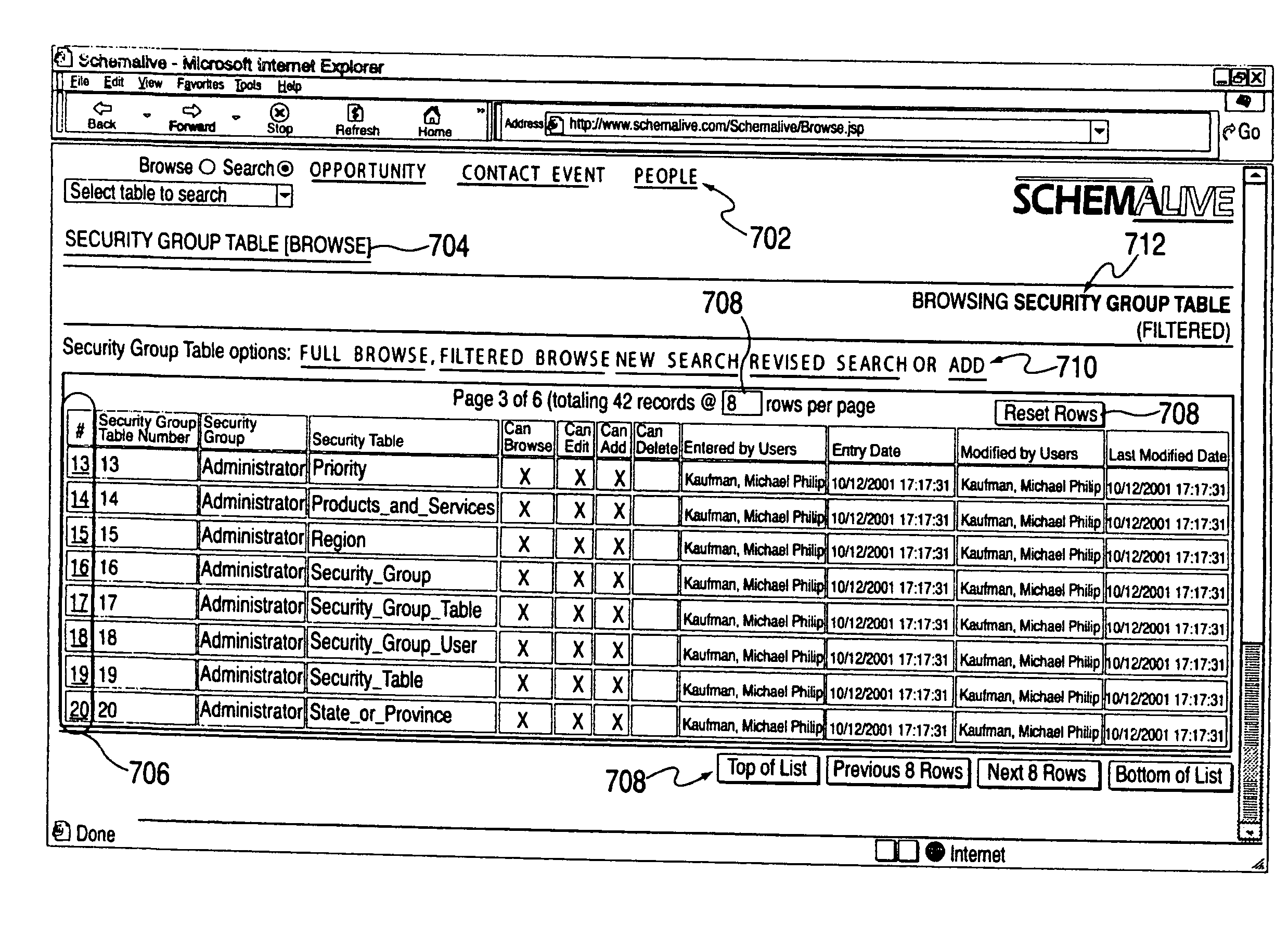
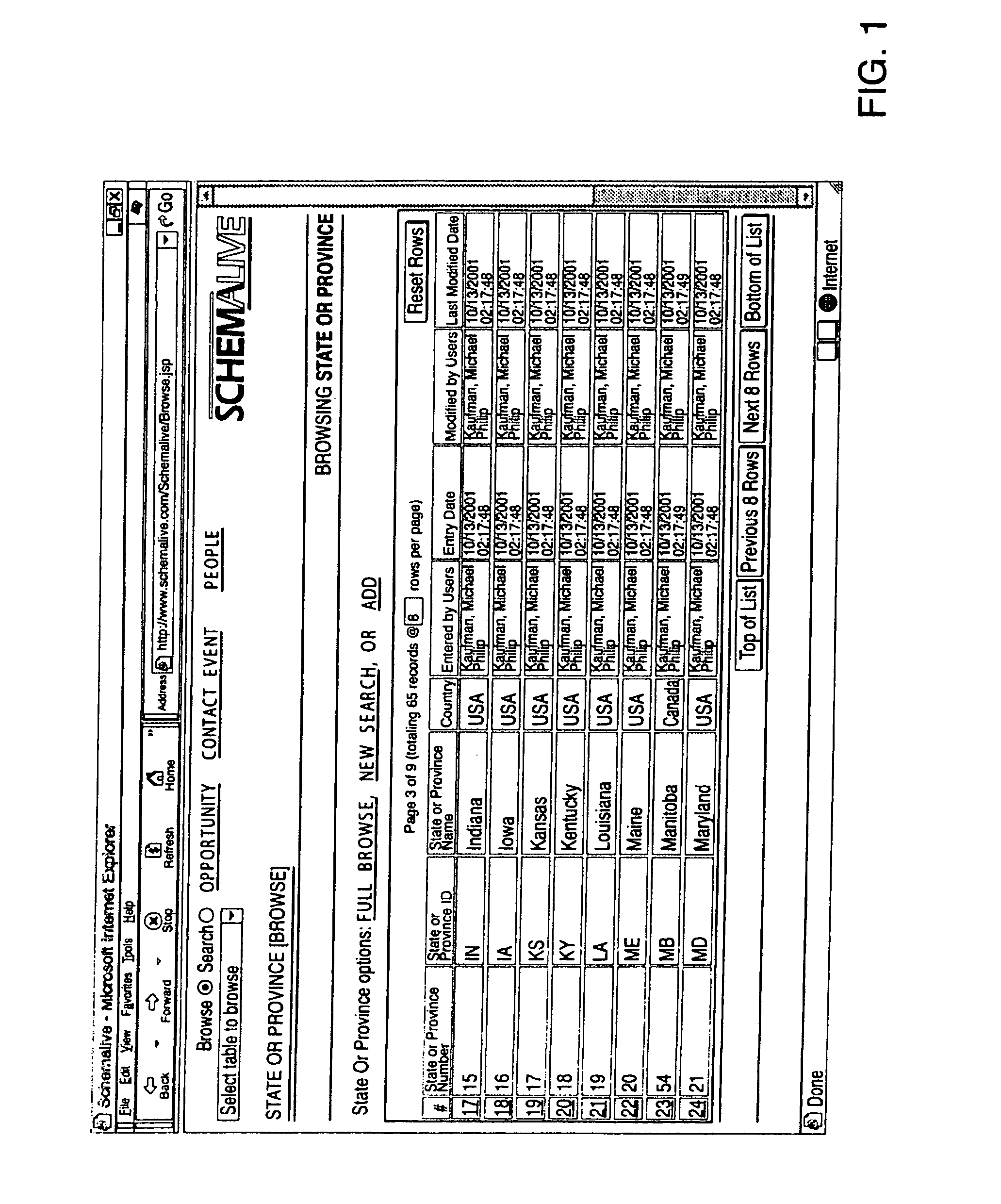
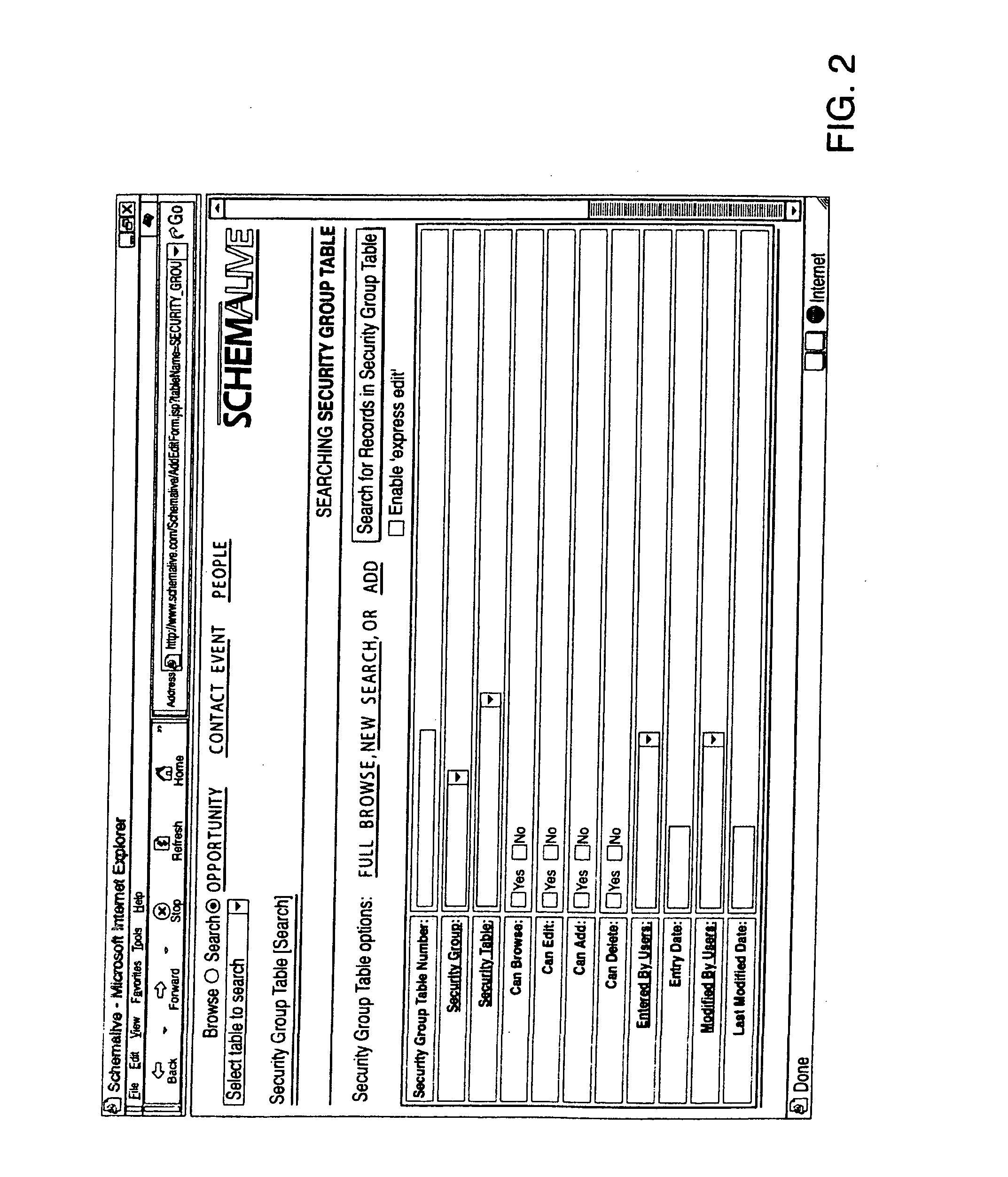
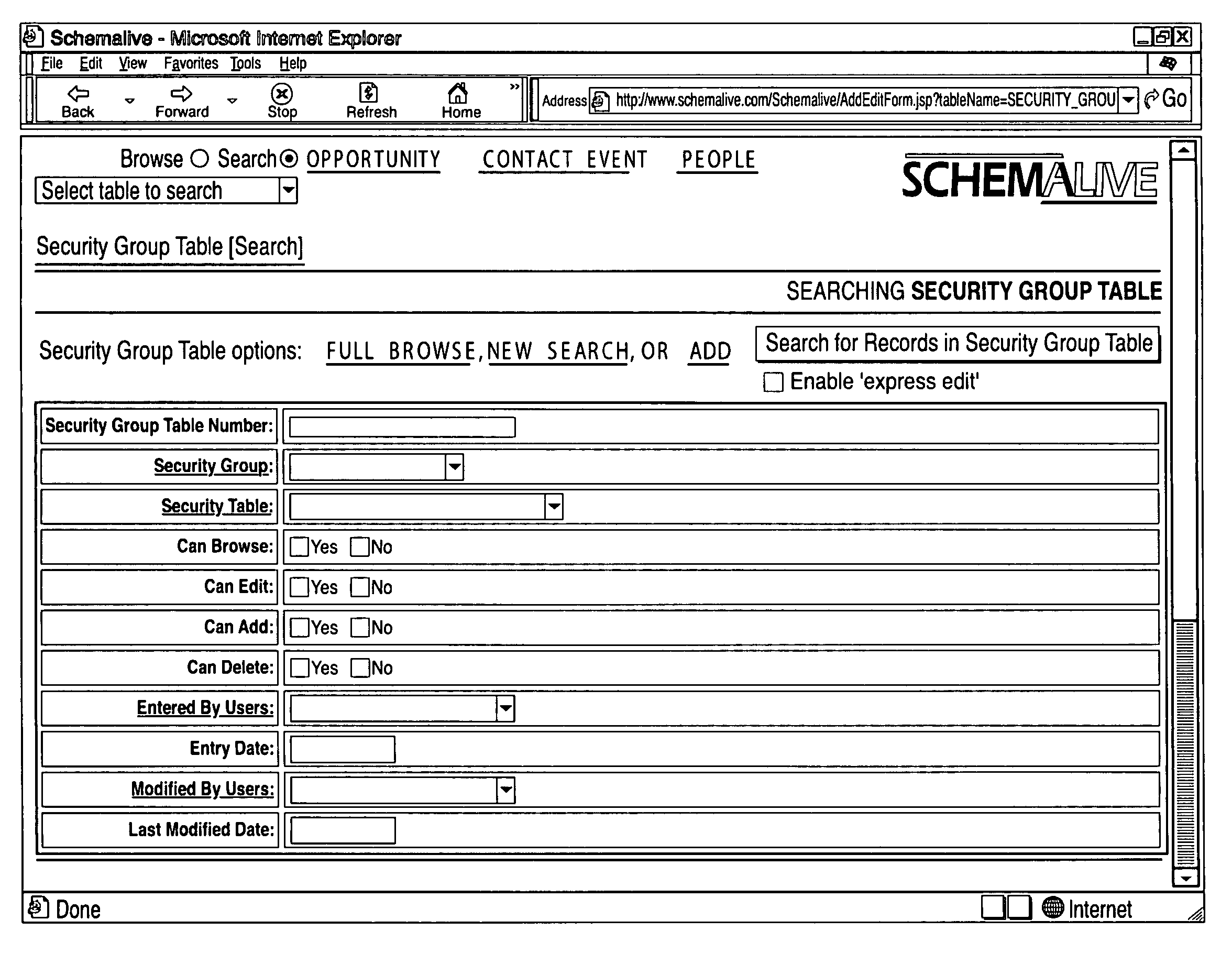
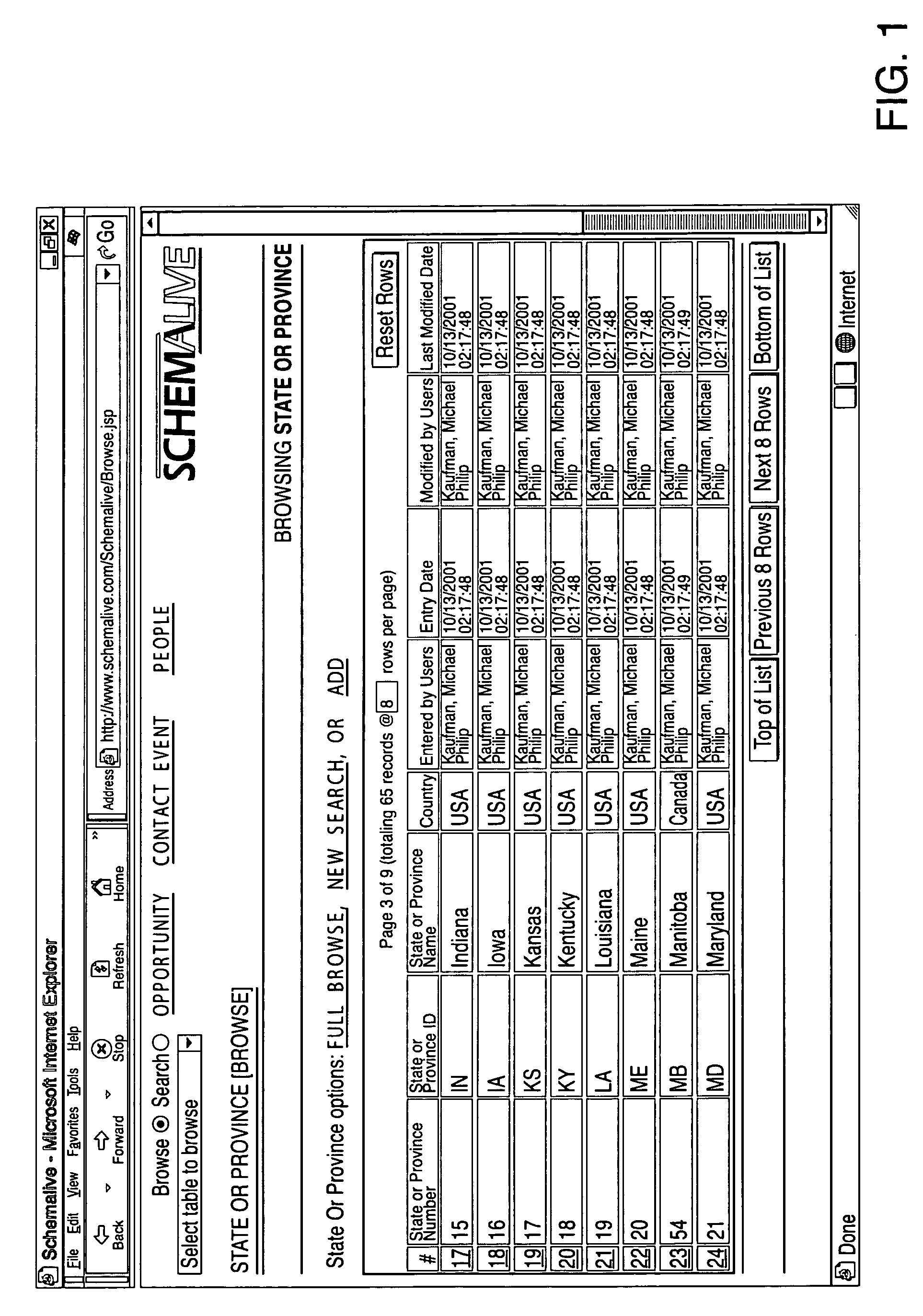
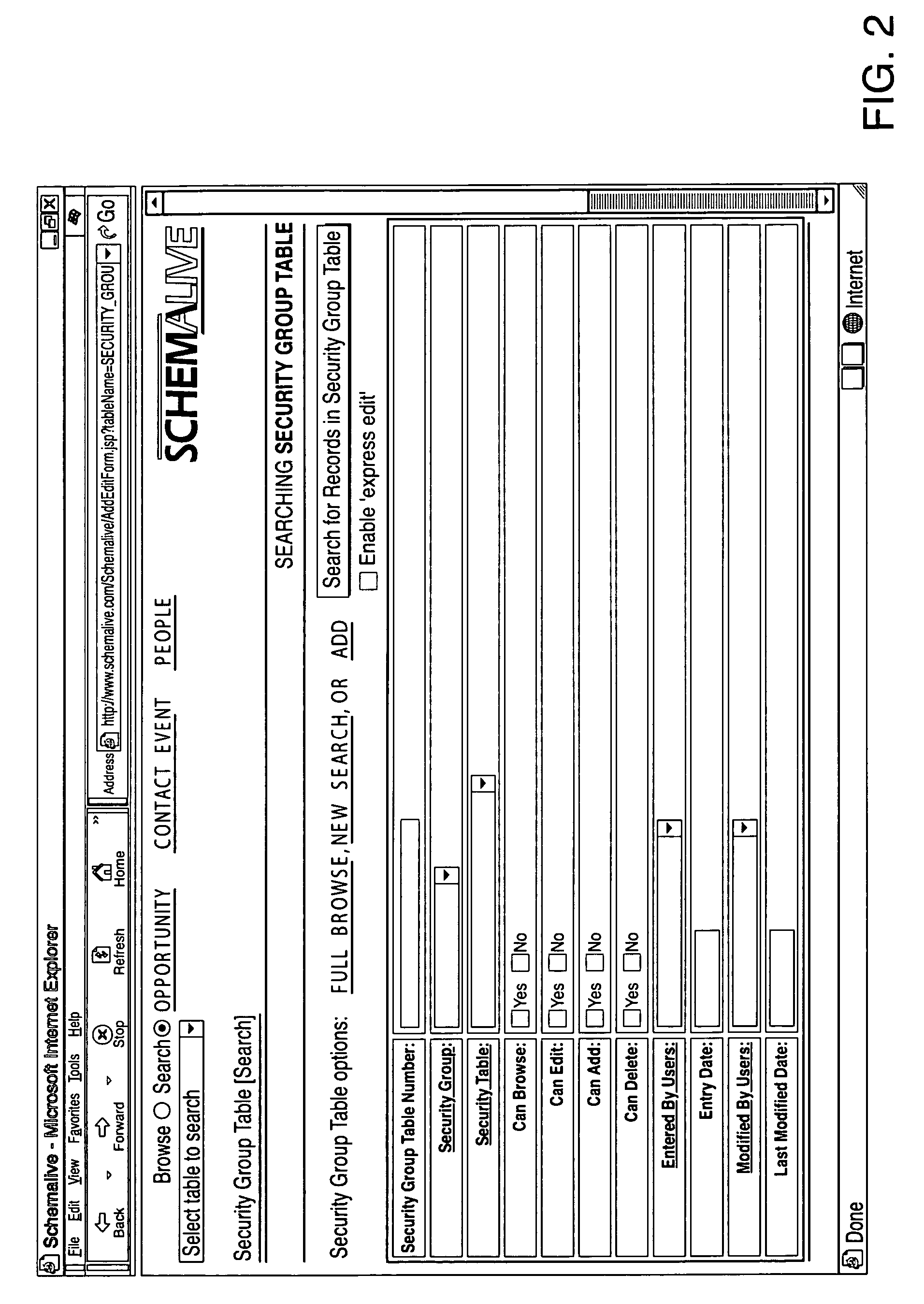
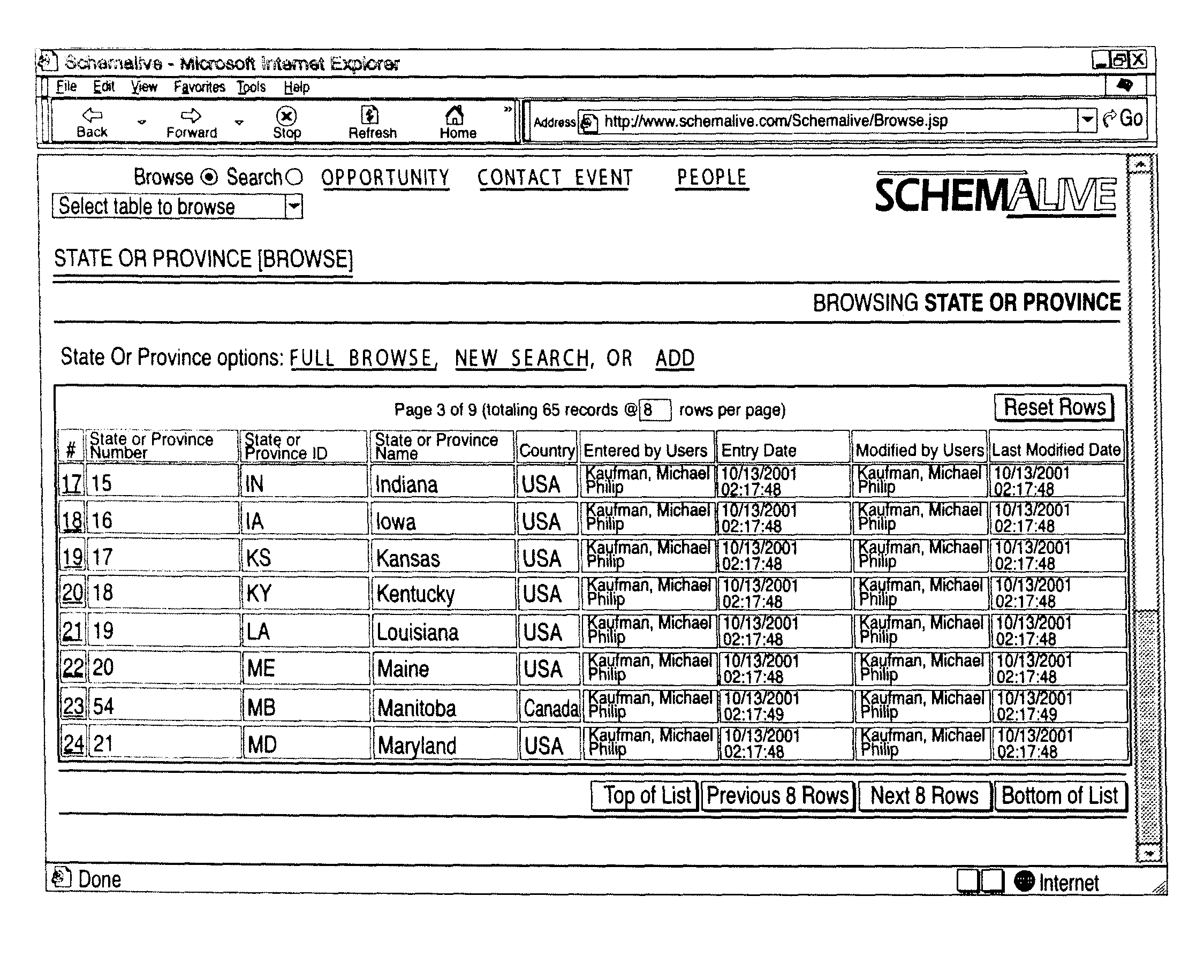
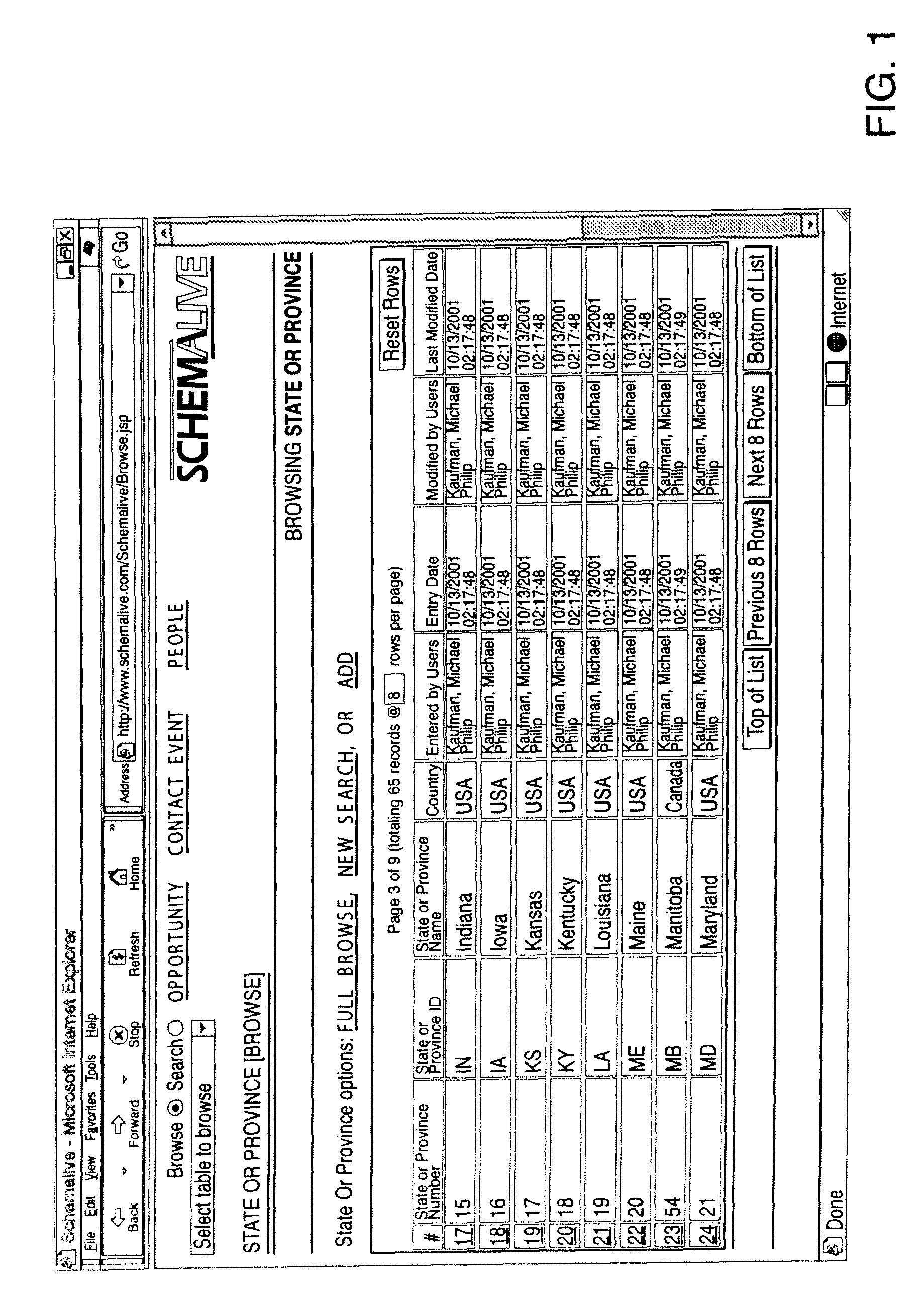
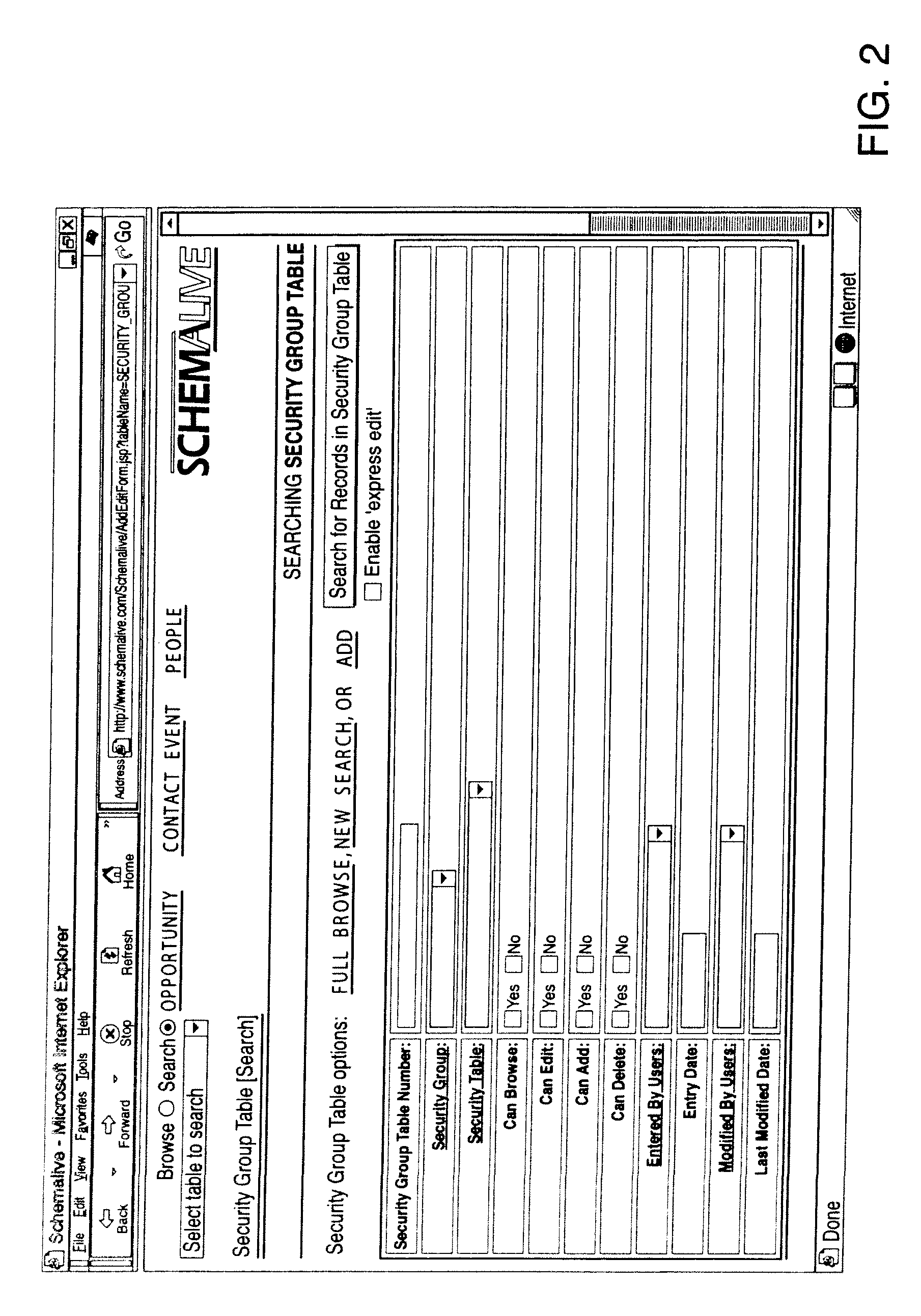
A software system automatically and dynamically generates a fully functional user interface (UI) based upon, and connected directly to, an underlying data model (as instantiated within a relational database management system (RDBMS)). The UI derives from an automated interrogation of the RDBMS, and comprises all mode displays (e.g., browse, search, edit, add) for all tables, and a full complement of mechanisms—integrated directly into the mode displays—for representing, navigating, and managing relationships across tables, regardless of the complexity of the underlying RDBMS schema. It utilizes a hierarchical “context stack” for suspending the working state of a particular table while “drilling down” to work with related-table information and return relevant changes to the base table. The embodiment further provides methods to enhance and extend the internal representation of table structures, constraints, relationships, and—special requirements (“business rules”) for improved revelation of the schema structure through external interrogation.
Owner:KAUFMAN MICHAEL PHILIP
System and method for generating automatic user interface for arbitrarily complex or large databases
InactiveUS20110191303A1Natural, powerful, and easy-to-useData processing applicationsWeb data indexingDrill downSoftware system
A software system automatically and dynamically generates a fully functional user interface (UI) based upon, and connected directly to, an underlying data model (as instantiated within a relational database management system (RDBMS)). The UI derives from an automated interrogation of the RDBMS, and comprises all mode displays (e.g., browse, search, edit, add) for all tables, and a full complement of mechanisms—integrated directly into the mode displays—for representing, navigating, and managing relationships across tables, regardless of the complexity of the underlying RDBMS schema. It utilizes a hierarchical “context stack” for suspending the working state of a particular table while “drilling down” to work with related-table information and return relevant changes to the base table. The embodiment further provides methods to enhance and extend the internal representation of table structures, constraints, relationships, and—special requirements (“business rules”) for improved revelation of the schema structure through external interrogation.
Owner:KAUFMAN MICHAEL PHILIP
System and method for generating automatic user interface for arbitrarily complex or large databases
InactiveUS7318066B2Natural, powerful, and easy-to-useData processing applicationsVisual data miningDrill downSoftware system
A software system automatically and dynamically generates a fully functional user interface (UI) based upon, and connected directly to, an underlying data model (as instantiated within a relational database management system (RDBMS)). The UI derives from an automated interrogation of the RDBMS, and comprises all mode displays (e.g., browse, search, edit, add) for all tables, and a full complement of mechanisms—integrated directly into the mode displays—for representing, navigating, and managing relationships across tables, regardless of the complexity of the underlying RDBMS schema. It utilizes a hierarchical “context stack” for suspending the working state of a particular table while “drilling down” to work with related-table information and return relevant changes to the base table. The embodiment further provides methods to enhance and extend the internal representation of table structures, constraints, relationships, and special requirements (“business rules”) for improved revelation of the schema structure through external interrogation.
Owner:KAUFMAN MICHAEL PHILIP
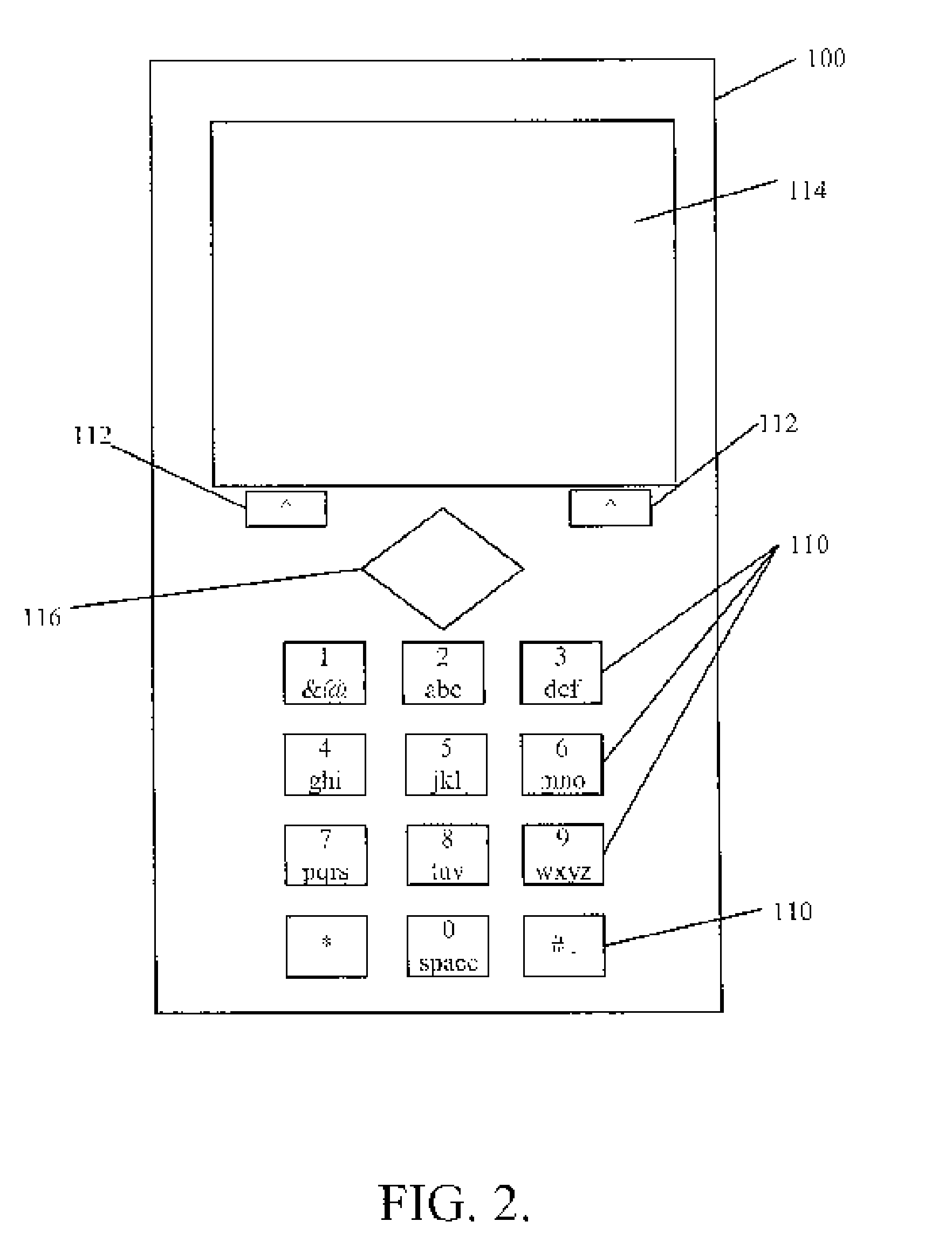
A method and apparatus for searching large databases via limited query symbol sets
InactiveUS20050192944A1Digital data information retrievalSpecial data processing applicationsOutput deviceVery large database
Methods and systems for searching a database that includes a plurality of records. Each record includes one or more tokens. The one or more tokens include one or more letters, numbers, or symbols. The system includes a user interface that when activated by a user generates at least one of a query symbol or a string of query symbols. A processing device compares the generated query symbol or string of query symbols to the stored records. An output device presents the record or records having tokens that match the generated query symbol or a string of query symbols based on the comparison. The user interface includes two or more input keys. Each input key is associated with a query symbol and the number of input keys is less than the number of distinct letters, characters, and symbols.
Owner:MELODEO
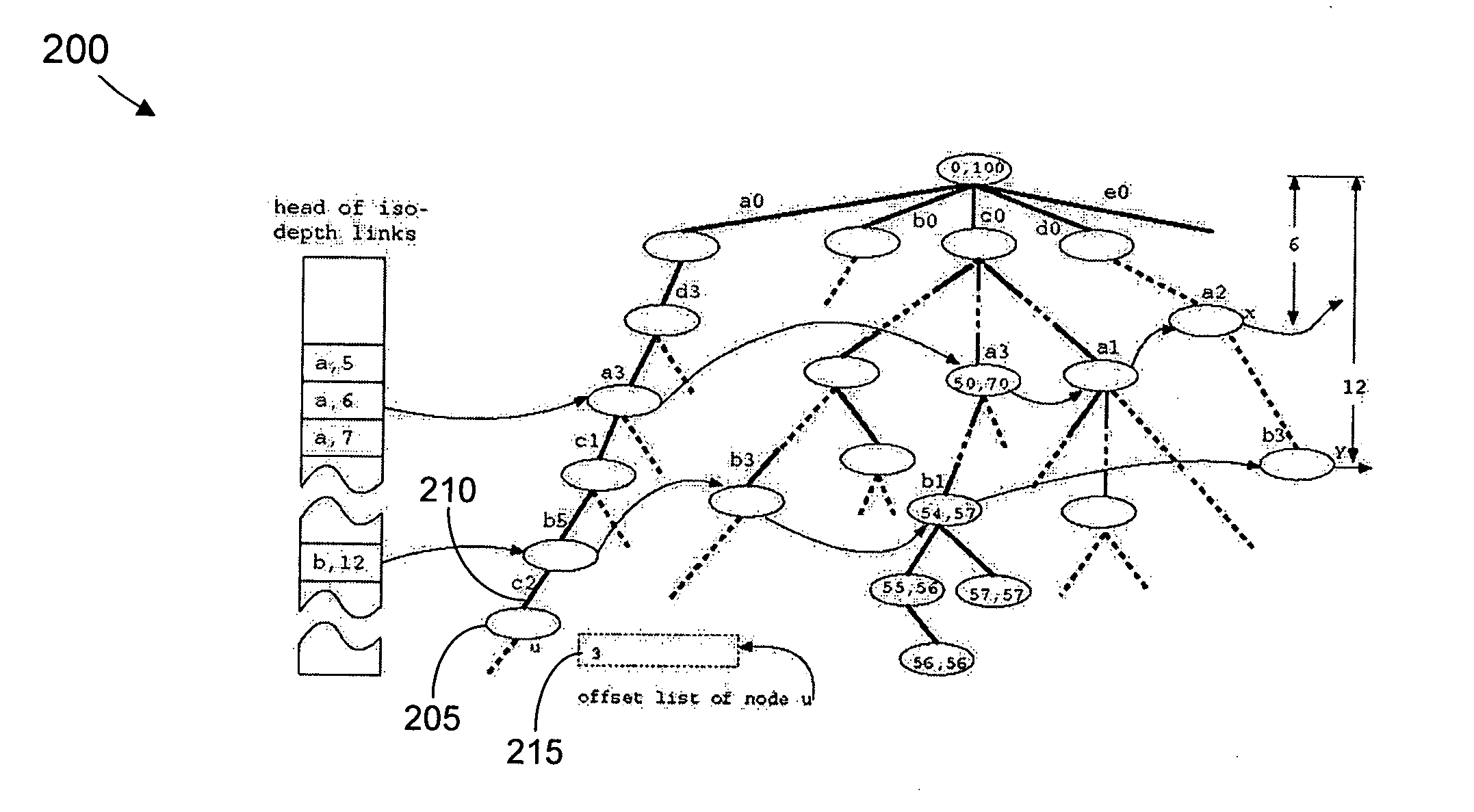
System and method for indexing weighted-sequences in large databases
ActiveUS20050114298A1Data processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalTimestampSequence database
The present invention provides an index structure for managing weighted-sequences in large databases. A weighted-sequence is defined as a two-dimensional structure in which each element in the sequence is associated with a weight. A series of network events, for instance, is a weighted-sequence because each event is associated with a timestamp. Querying a large sequence database by events' occurrence patterns is a first step towards understanding the temporal causal relationships among the events. The index structure proposed herein enables the efficient retrieval from the database of all subsequences (contiguous and non-contiguous) that match a given query sequence both by events and by weights. The index structure also takes into consideration the nonuniform frequency distribution of events in the sequence data.
Owner:SAP AG
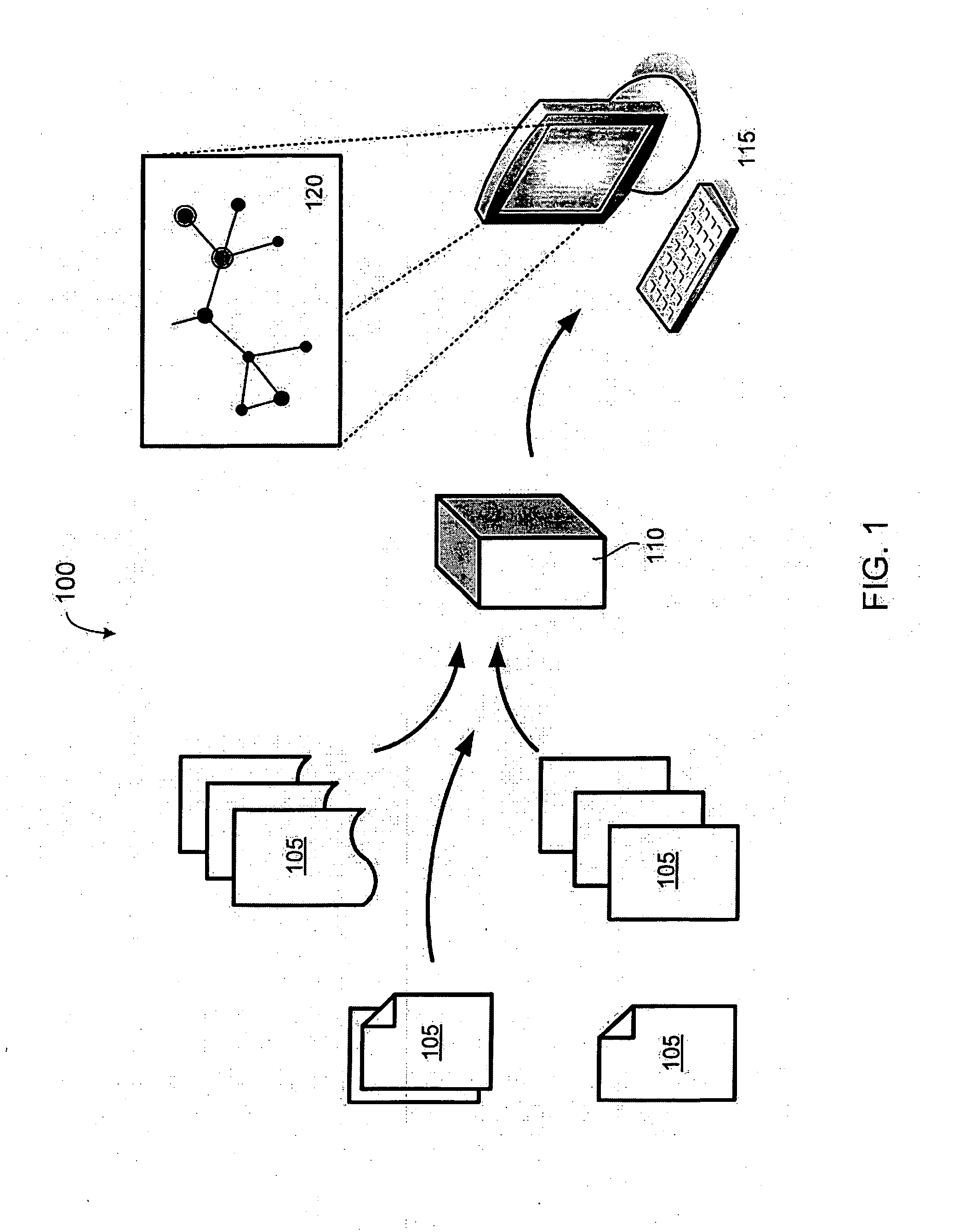
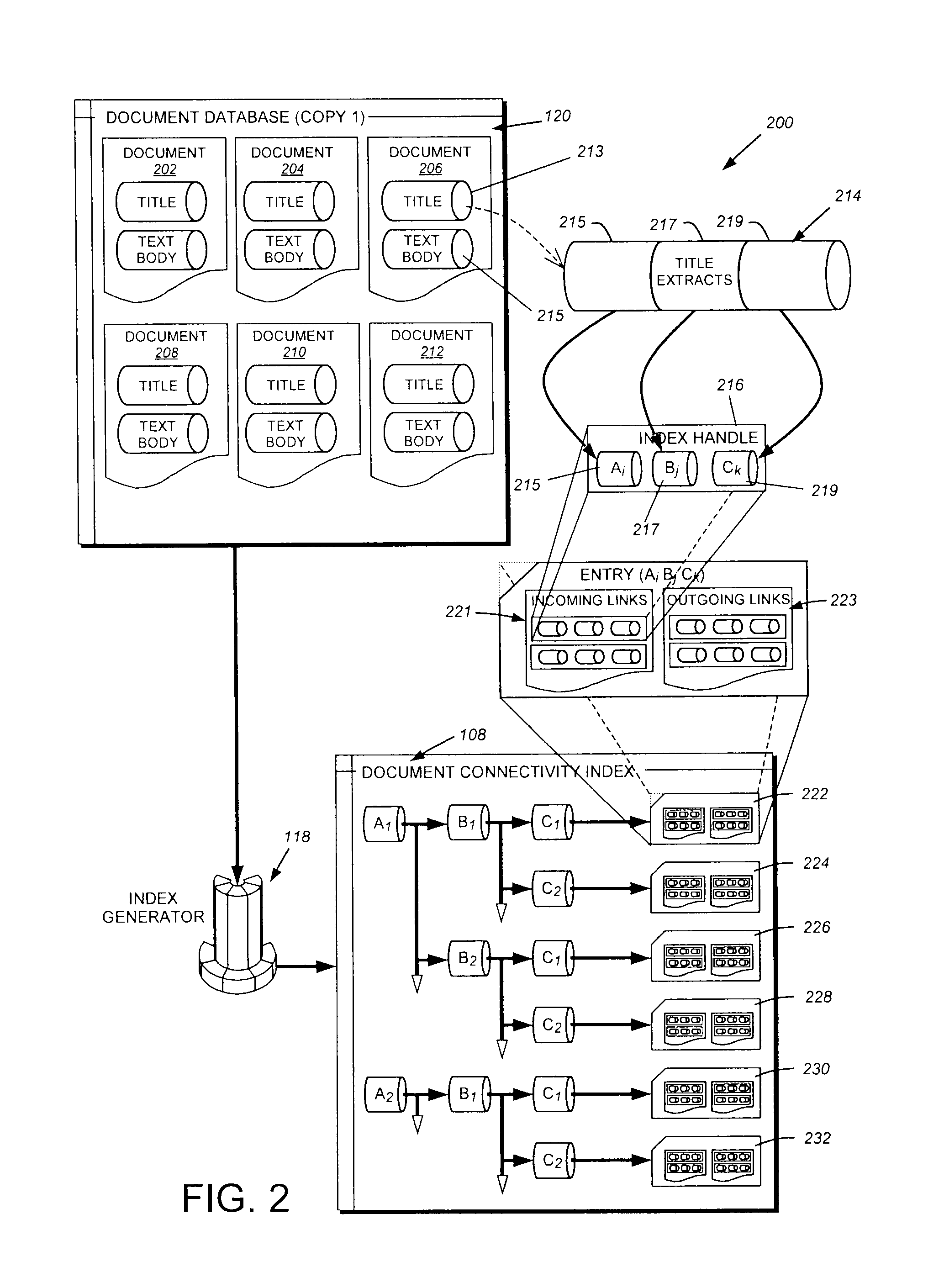
System and method for searching and displaying text-based information contained within documents on a database
InactiveUS20080263022A1Improve search efficiencyOvercome disadvantagesWeb data indexingDigital data processing detailsGraphicsUser input
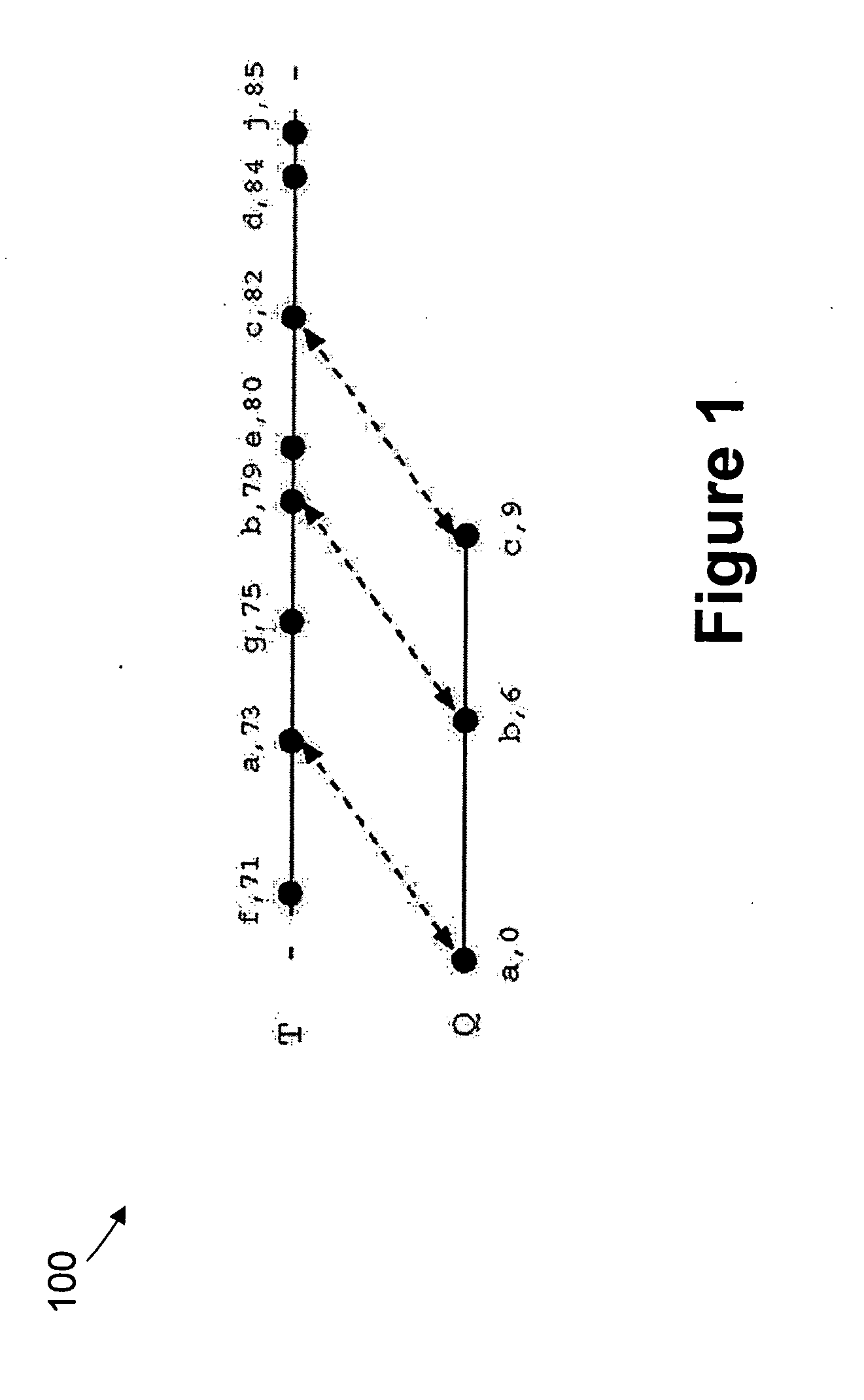
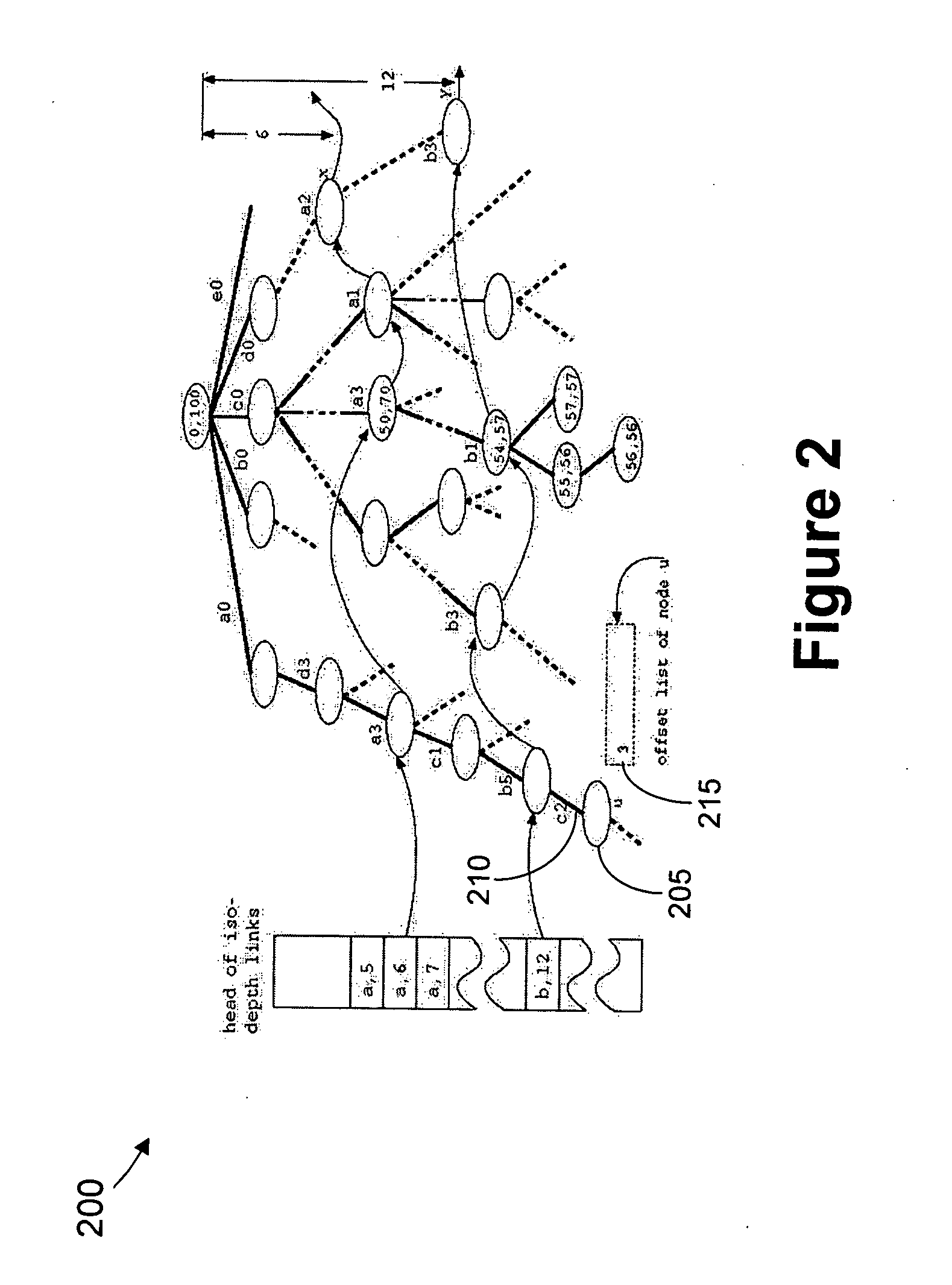
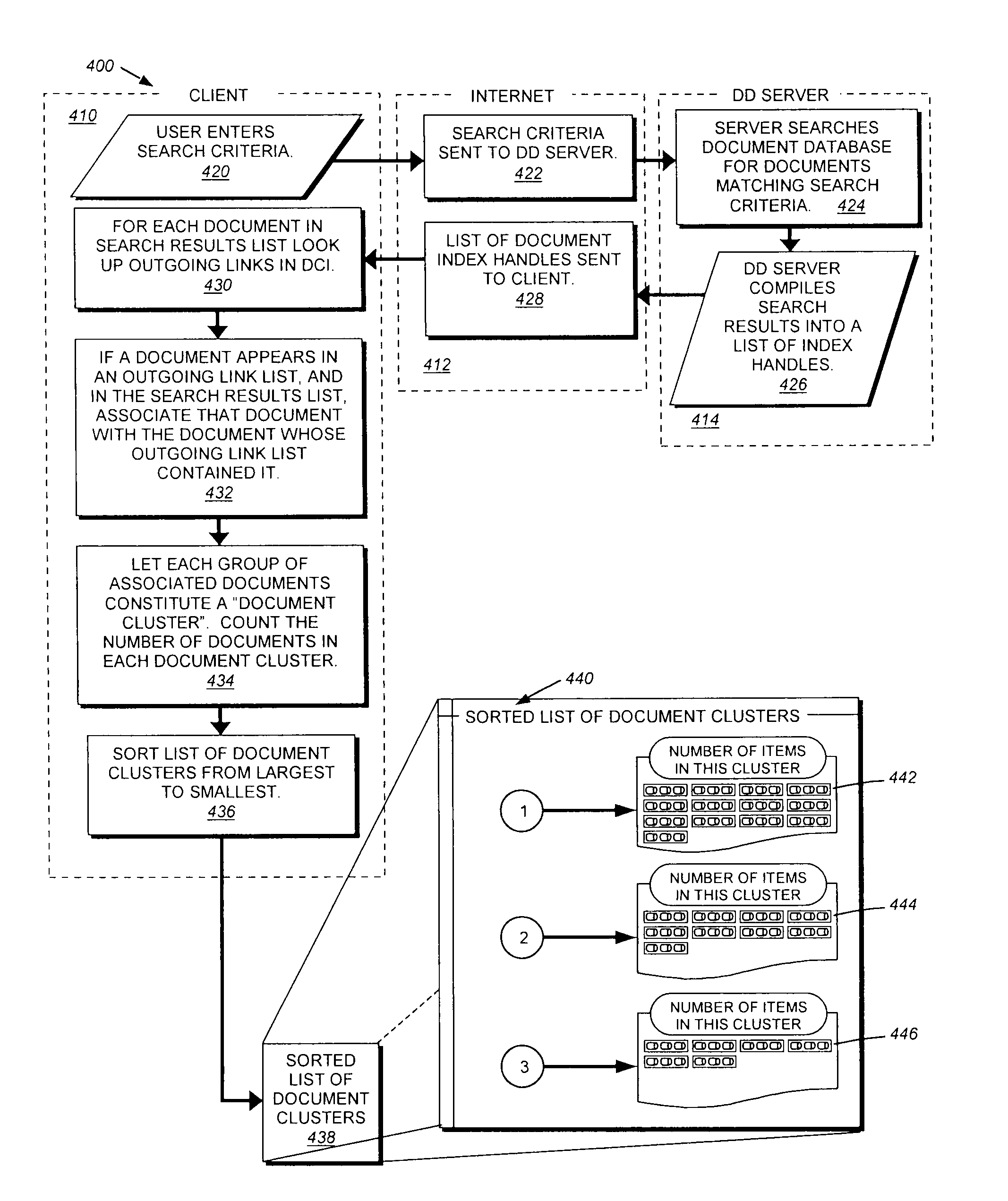
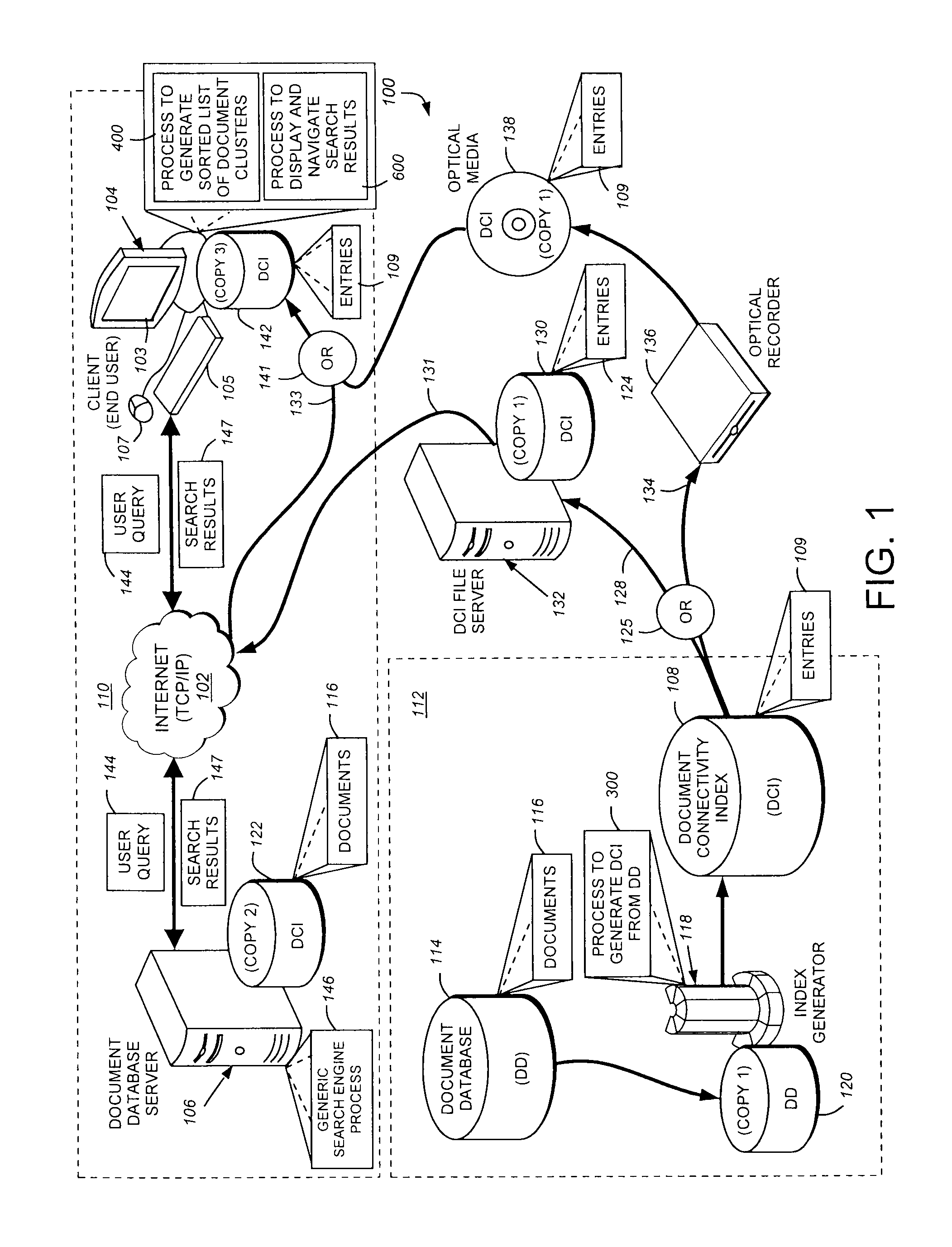
This invention provides a system method for search and displaying text-based documents, based upon user-input search terms that organizes and displays documentary search results in a series of clusters of documents that have been sorted in a manner that relates to the general relevance of those documents to the search terms. In particular, this system and method allows for the searching of large databases of related documents by utilizing citations between those documents to improve search efficiency as well as visualization of search results. The document databases (DD) are used to generate a document connectivity index (DCI), of which a copy is stored on (or remotely accessed by) the client computer. The client issues a search request to a DD server, which returns a list of matching documents. The client compares this list against the DCI to generate a sorted list of document clusters. Using a graphical interface, the user can view and navigate these clusters to identify and view documents of interest. The clusters can be displayed as nodes in which each document is a node and the selected (or, by default, highest ranking) document / node is centered on the screen with linked documents placed around it with appropriate link lines (the surrounding node-and-link display). Each node can be activated to re-centered the nod-and-link display and show the underlying document text body.
Owner:BLUESHIFT INNOVATIONS
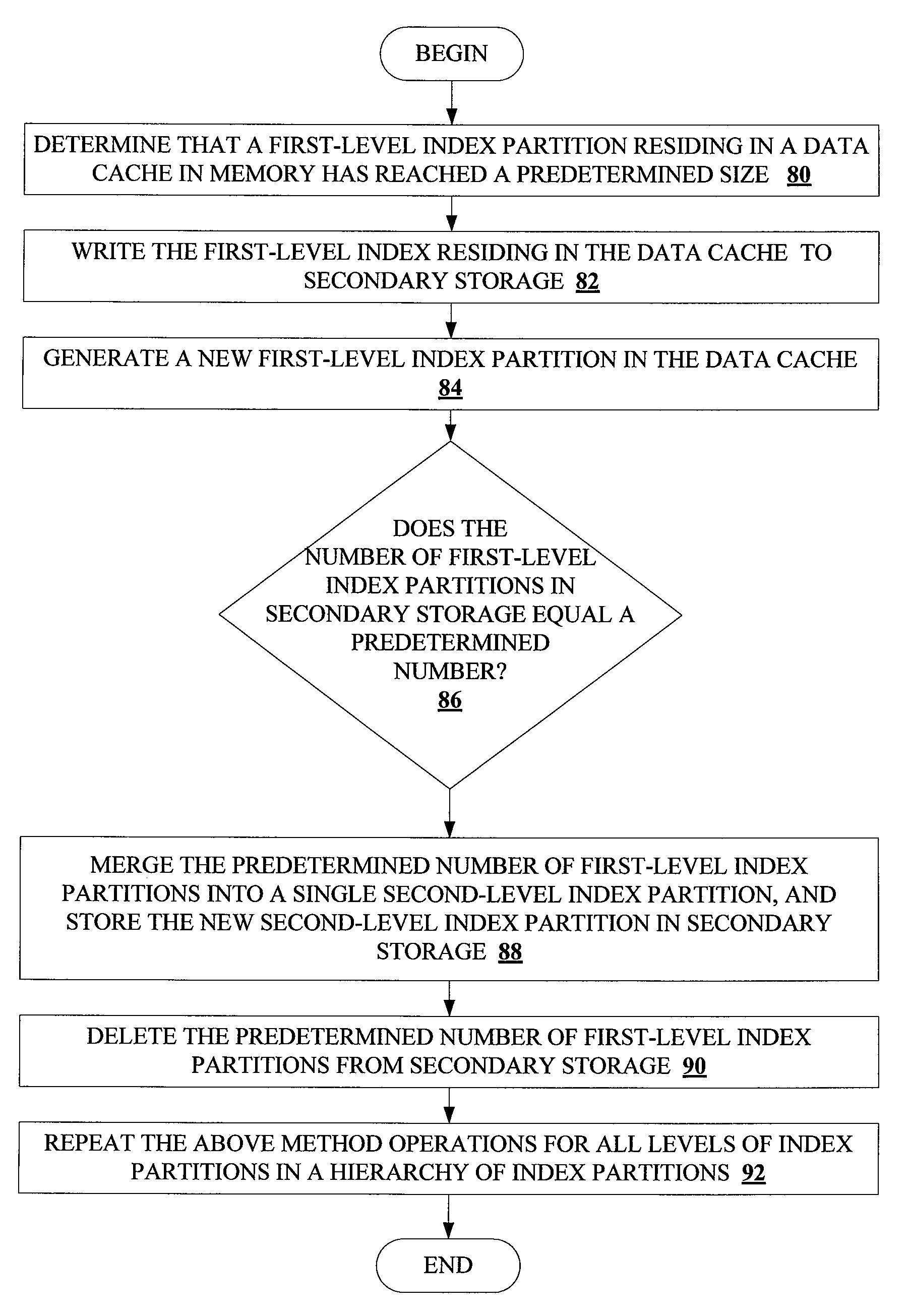
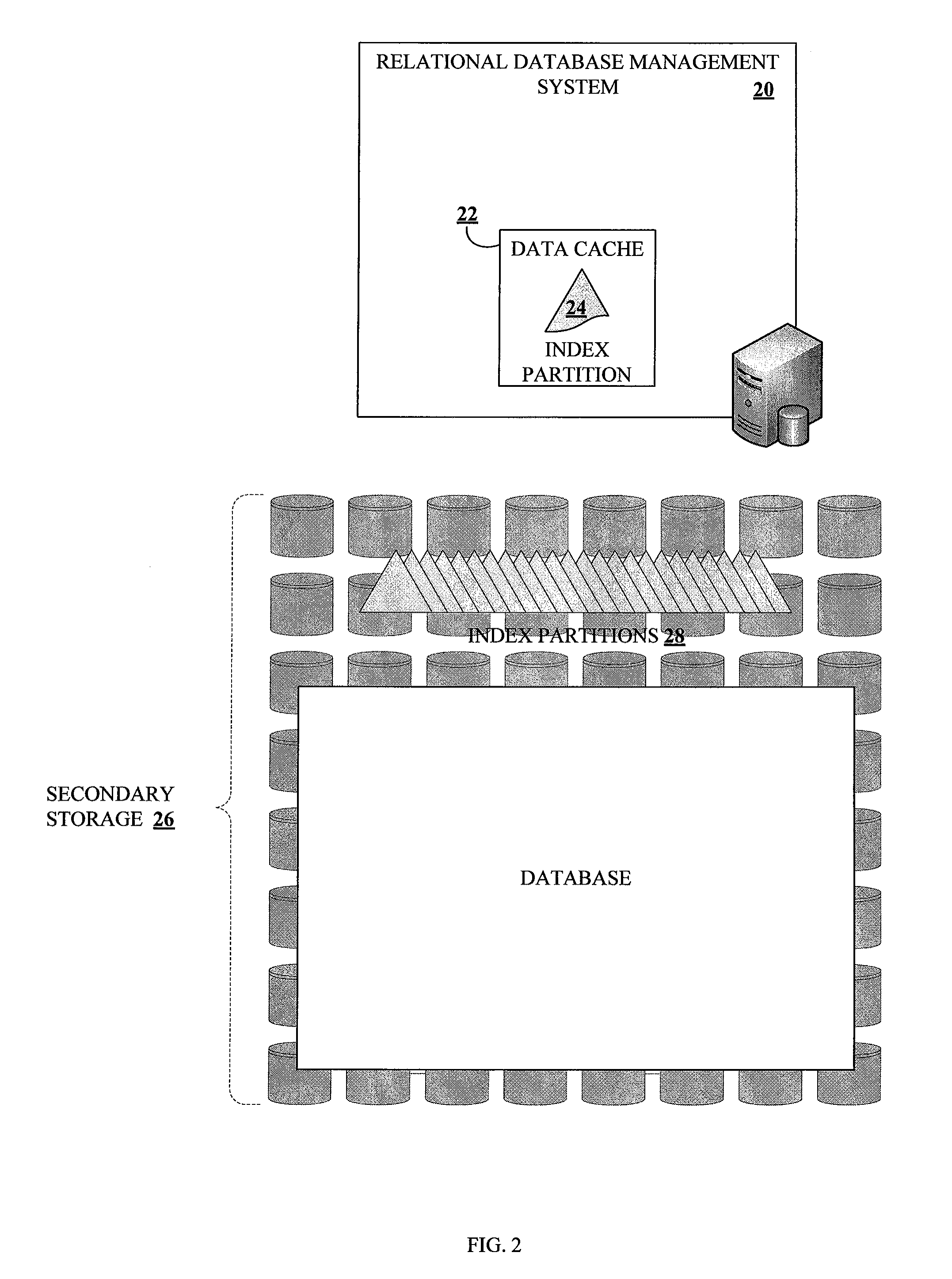
Method and system for dynamically partitioning very large database indices on write-once tables
ActiveUS20100161569A1Increase in sizeAvoid performance degradationDigital data processing detailsRelational databasesDatabase indexIncrease size
Methods and systems for partitioning and dynamically merging a database index are described. A database index includes a single first-level index partition stored in a data cache. As the first-level index partition in the data cache reaches a predetermined size, it is copied to secondary storage and a new index partition is generated in the data cache. When the number of index partitions in secondary storage reaches some predetermined number, the index partitions are merged to create a single index partition of a higher level in a hierarchy of index partitions having an exponentially increasing size with each increase in level within the hierarchy.
Owner:SAP AG
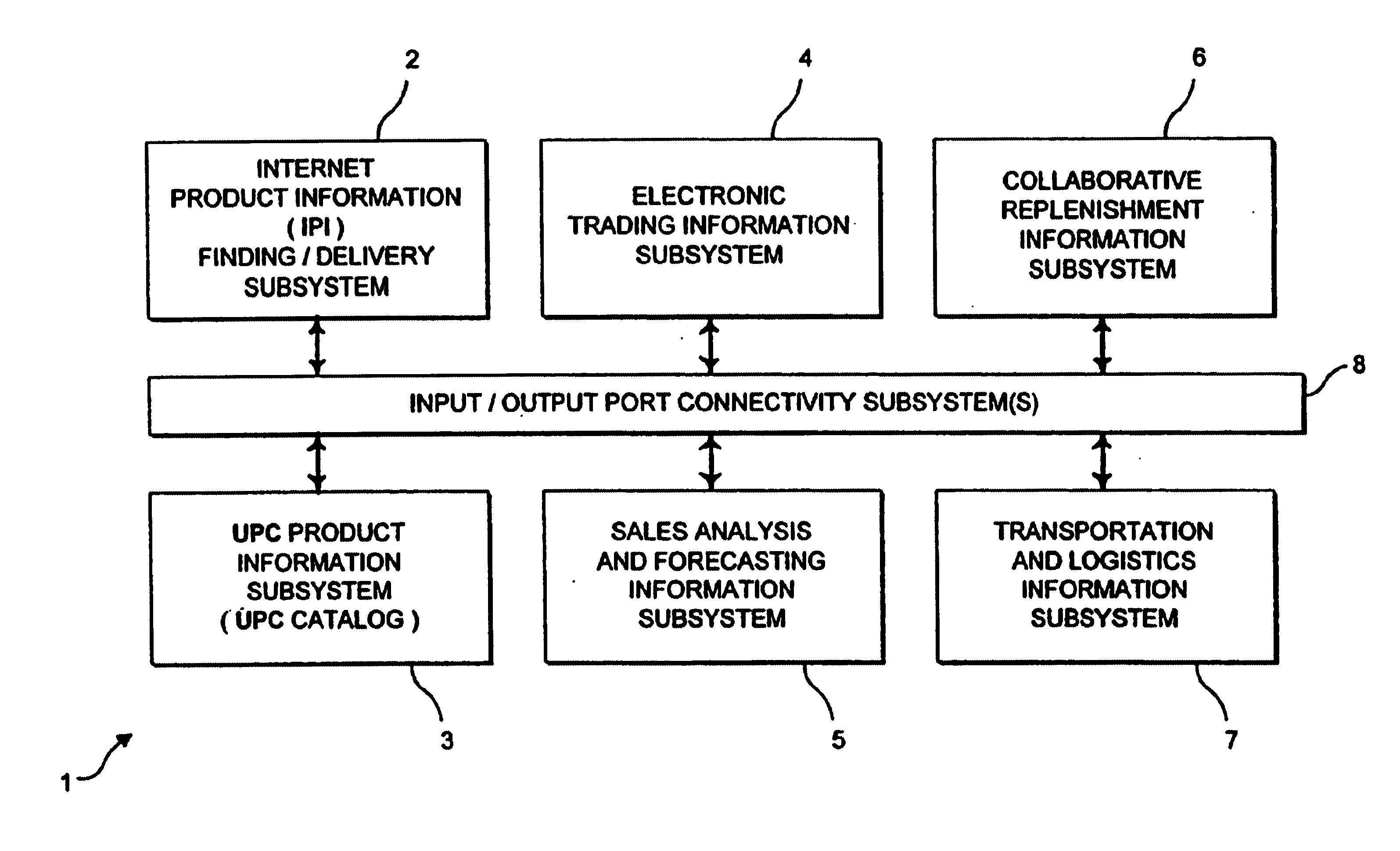
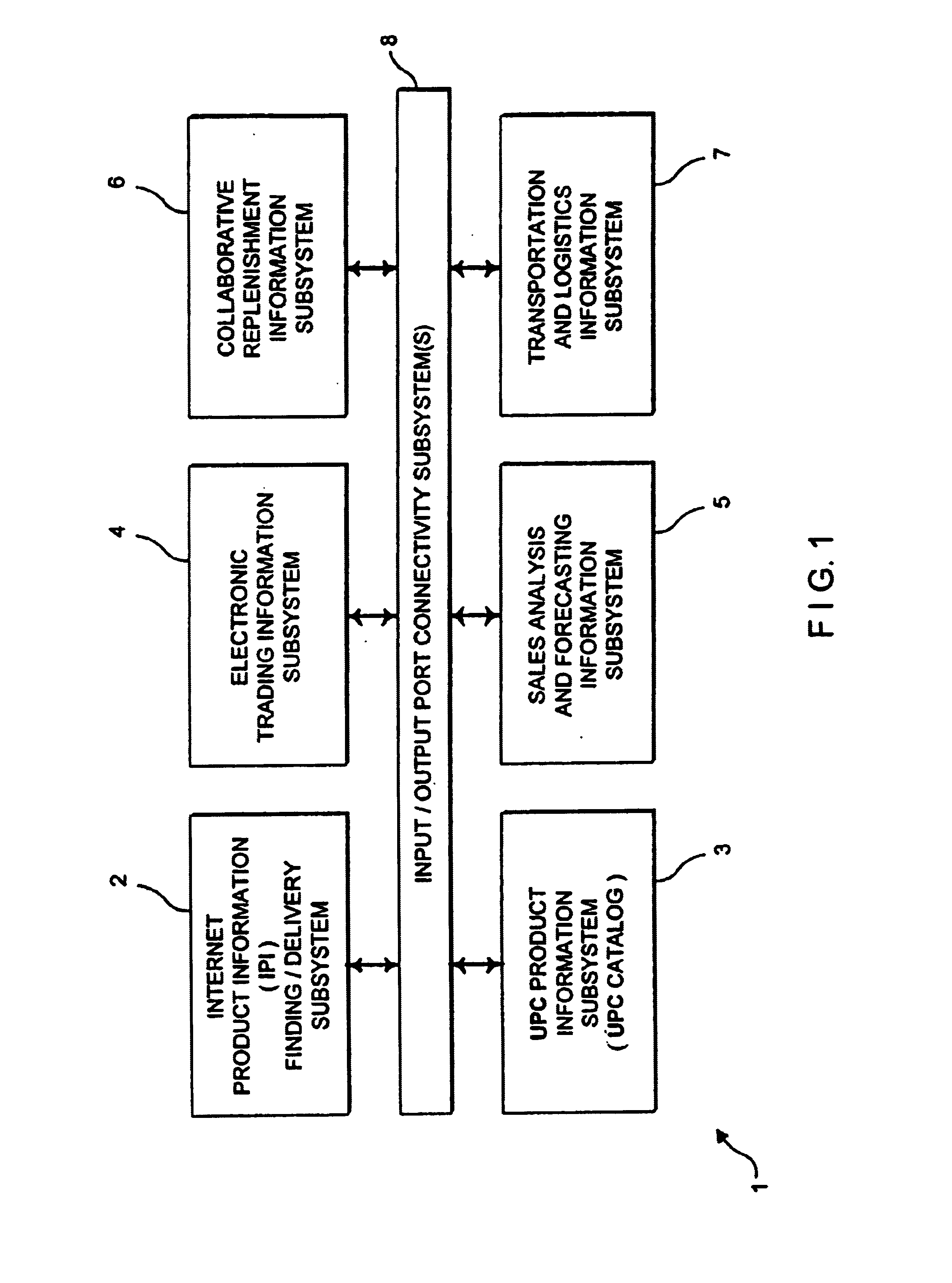
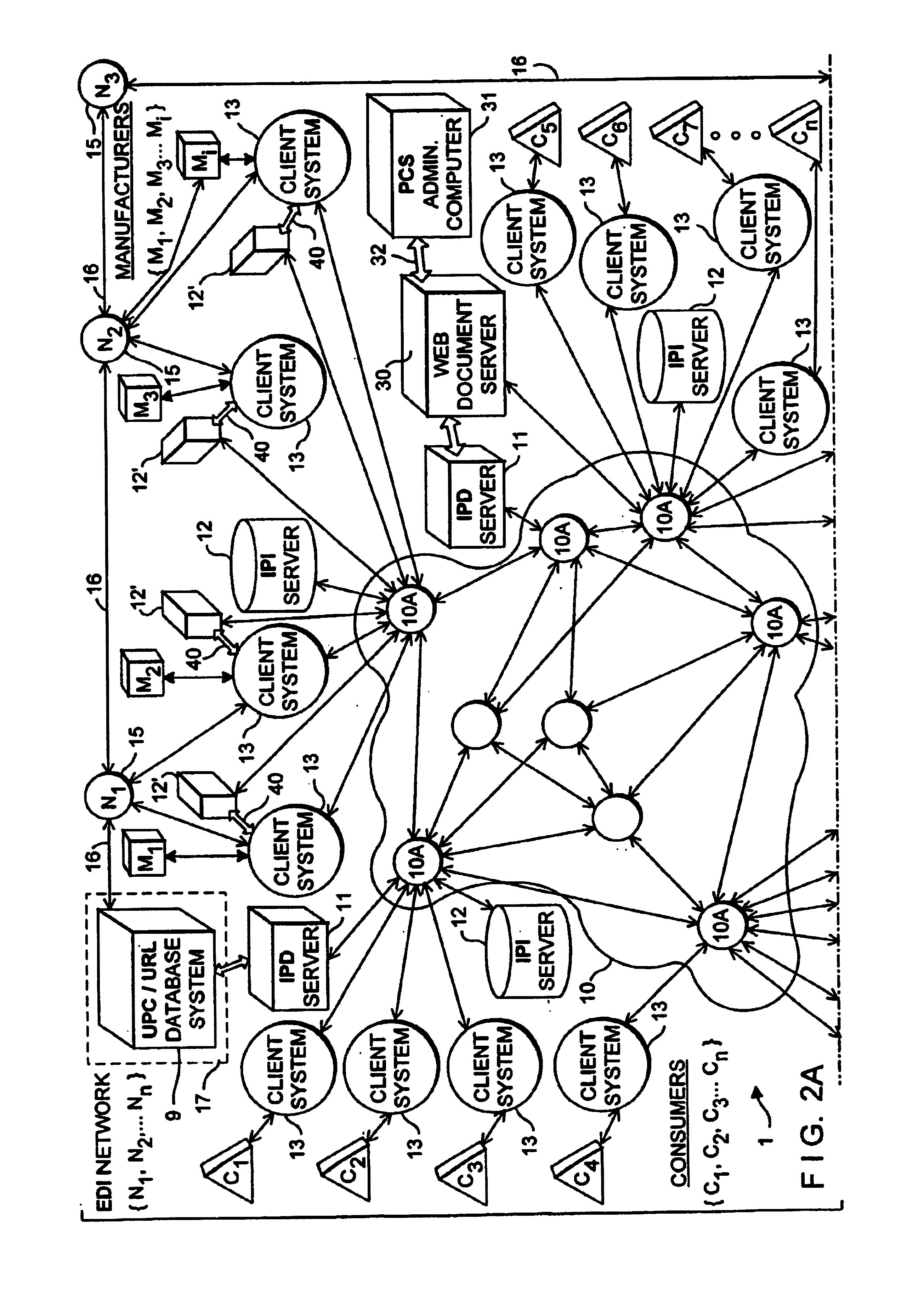
Internet-based system for collecting, managing and serving consumer product-related information over the internet using trademarks and universal resource locators (URLS) symbolically-linked by manufacturers of consumer products and/or their agents
An Internet-based system for collecting, managing and serving consumer product-related information over the Internet. The system comprises a database management subsystem for storing and managing information representative of (i) a plurality of trademarks placed on or used in connection with a plurality of consumer products, and (ii) a plurality of Uniform Resource Locators (URLs) symbolically linked to the trademarks and specifying the location of a plurality of Web documents stored in one or more Internet-based information servers, by manufacturers, their agents and / or third parties, and contain particular kinds of information related to consumer products on which the trademarks are placed and used in commerce. A trademark / URL information server accesses one or more URLs from the database management subsystem in response to a request placed therewith by a consumer-operated client computer subsystem. Each manufacturer uses a manufacturer-managed client computer subsystem to transmit to the database management subsystem, information representative of a plurality of symbolically linked trademarks and URLs. Each consumer uses a consumer-operated client computer subsystem to access one or more URLs from the database management subsystem in response to a request transmitted to the trademark / URL information server. The accessed URLs are then used to access and display Web documents specified by the URLs and containing consumer product related information. Using the present invention, large databases containing symbolically linked trademarks and URLs can be created and managed, so that corresponding consumer product related information on the World Wide Web (WWW) can be reliably accessed and displayed by consumers using trademarks.
Owner:PERKOWSKI THOMAS J
Signature generation for multimedia deep-content-classification by a large-scale matching system and method thereof
ActiveUS20090043818A1Broadcast information characterisationBroadcast information switching/replacementApplication softwareComputer vision
Content-based clustering, recognition, classification and search of high volumes of multimedia data in real-time. The invention is dedicated to real-time fast generation of signatures to high-volume of multimedia content-segments, based on relevant audio and visual signals, and to scalable matching of signatures of high-volume database of content-segments' signatures. The invention can be implemented in any applications which involve large-scale content-based clustering, recognition and classification of multimedia data, such as, content-tracking, video filtering, multimedia taxonomy generation, video fingerprinting, speech-to-text, audio classification, object recognition, video search and any other application requiring content-based signatures generation and matching for large content volumes such as, web and other large-scale databases.
Owner:CORTICA LTD
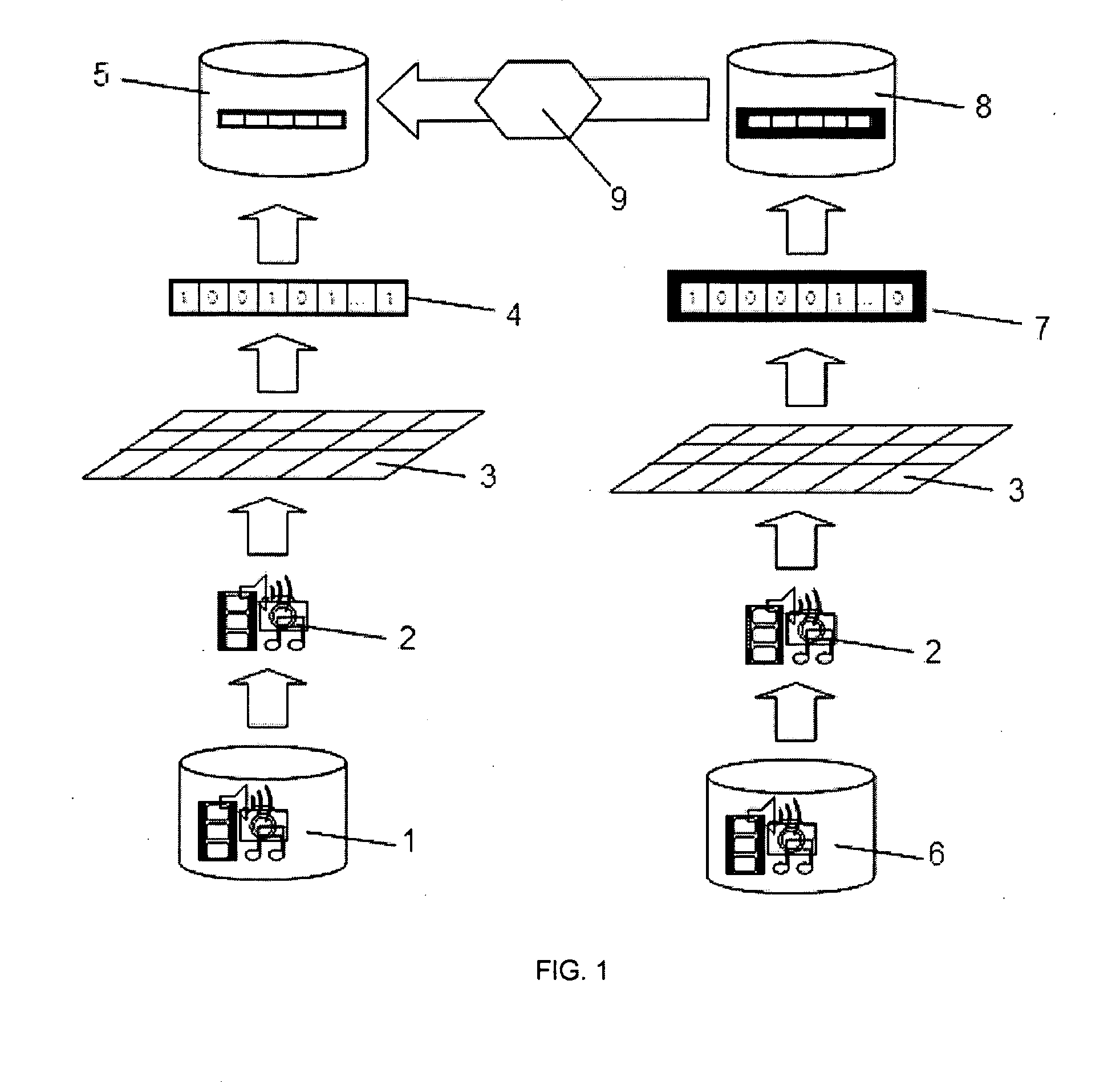
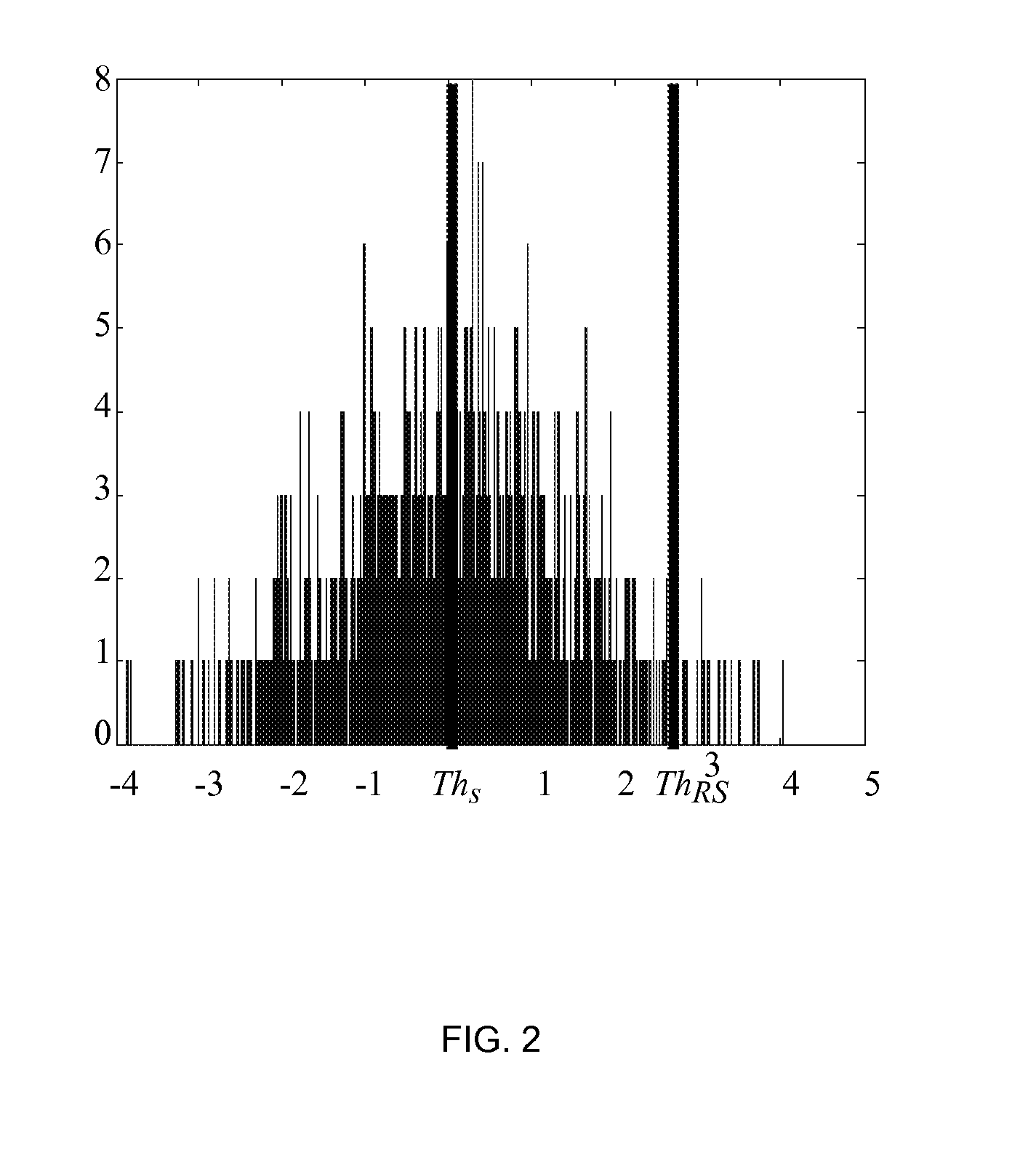
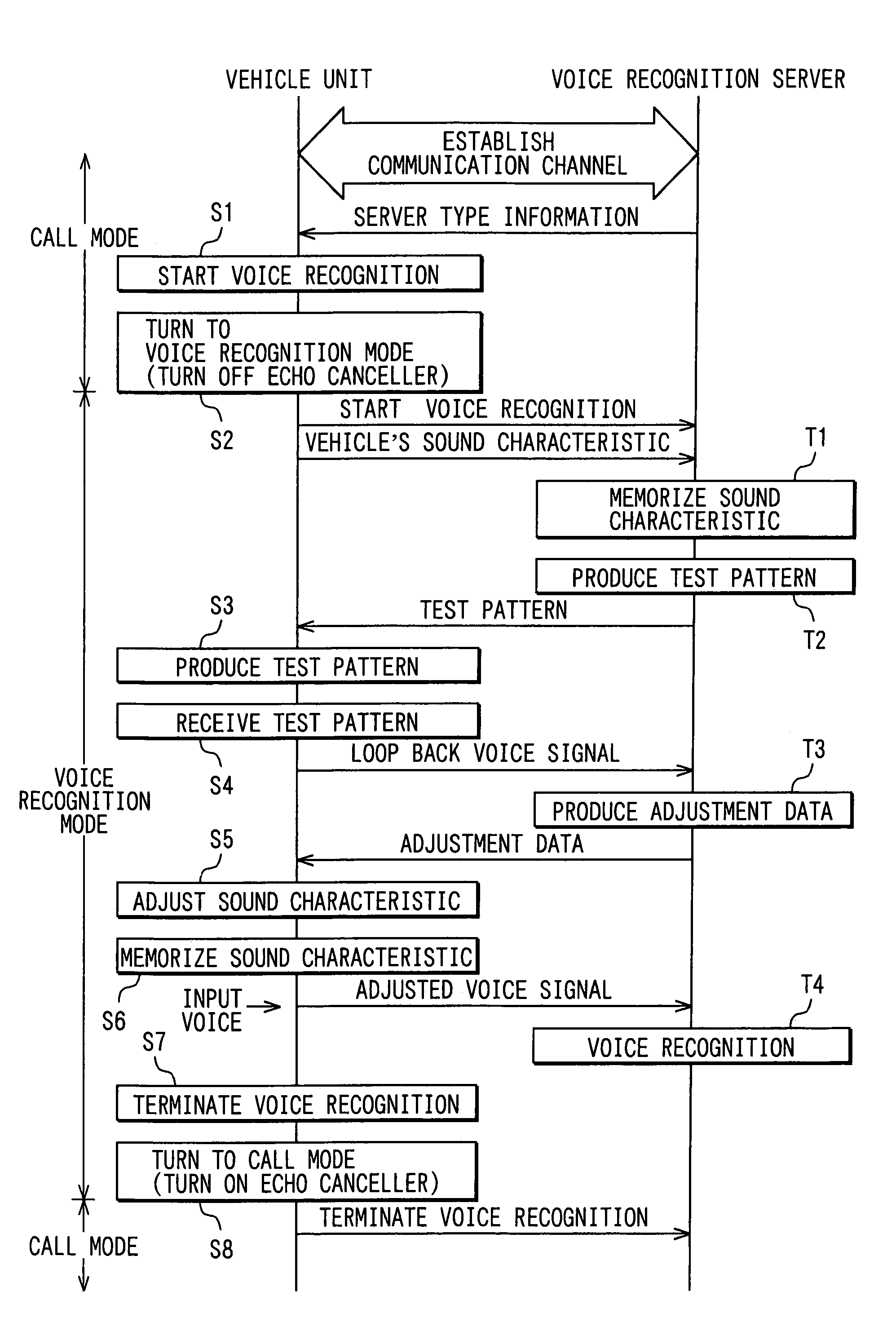
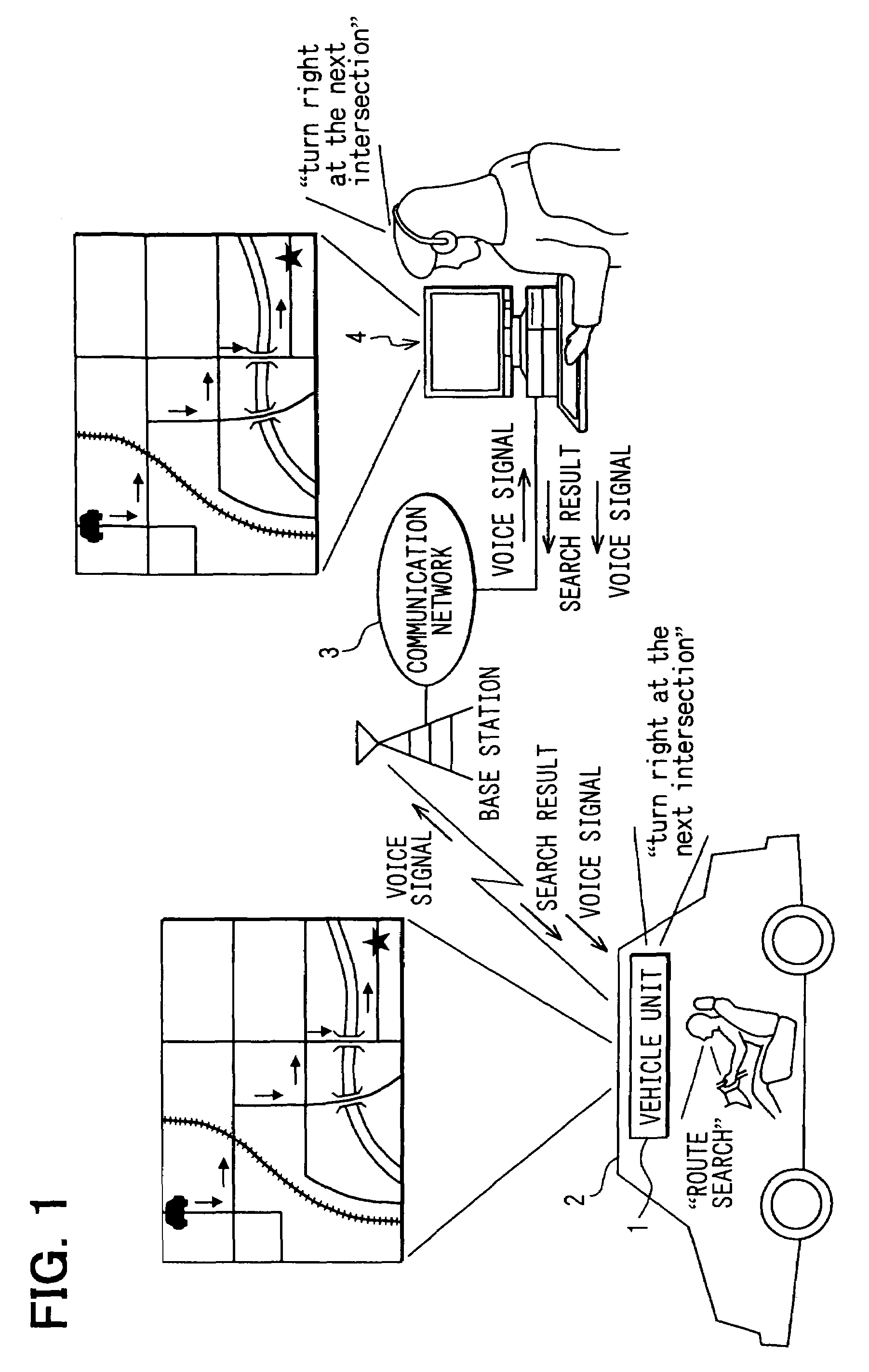
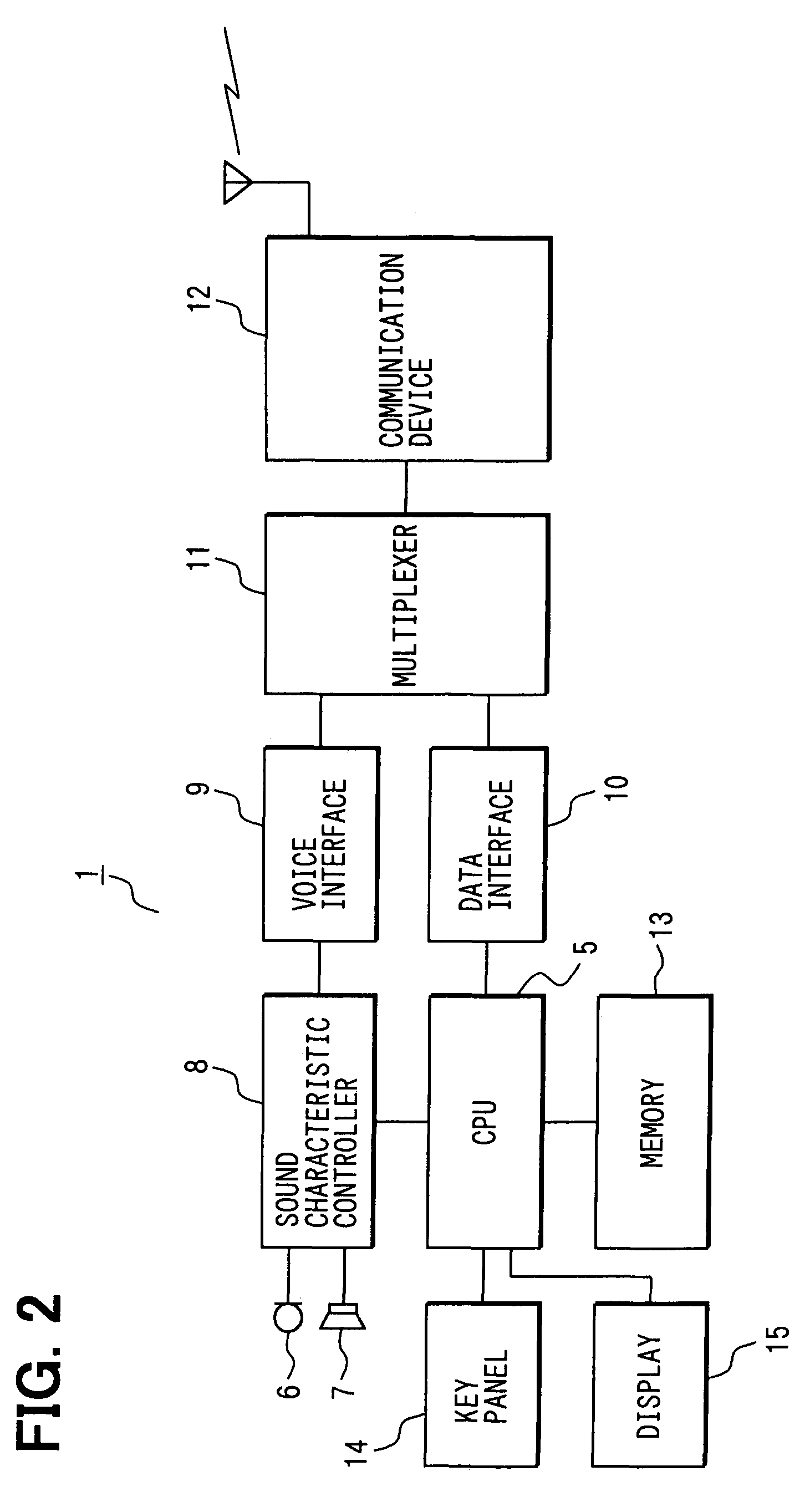
Adjusting sound characteristic of a communication network using test signal prior to providing communication to speech recognition server
InactiveUS7356471B2Reduce the burden onImprove reliabilitySpecial service for subscribersSupervisory/monitoring/testing arrangementsComputer terminalSpeech identification
Owner:DENSO CORP
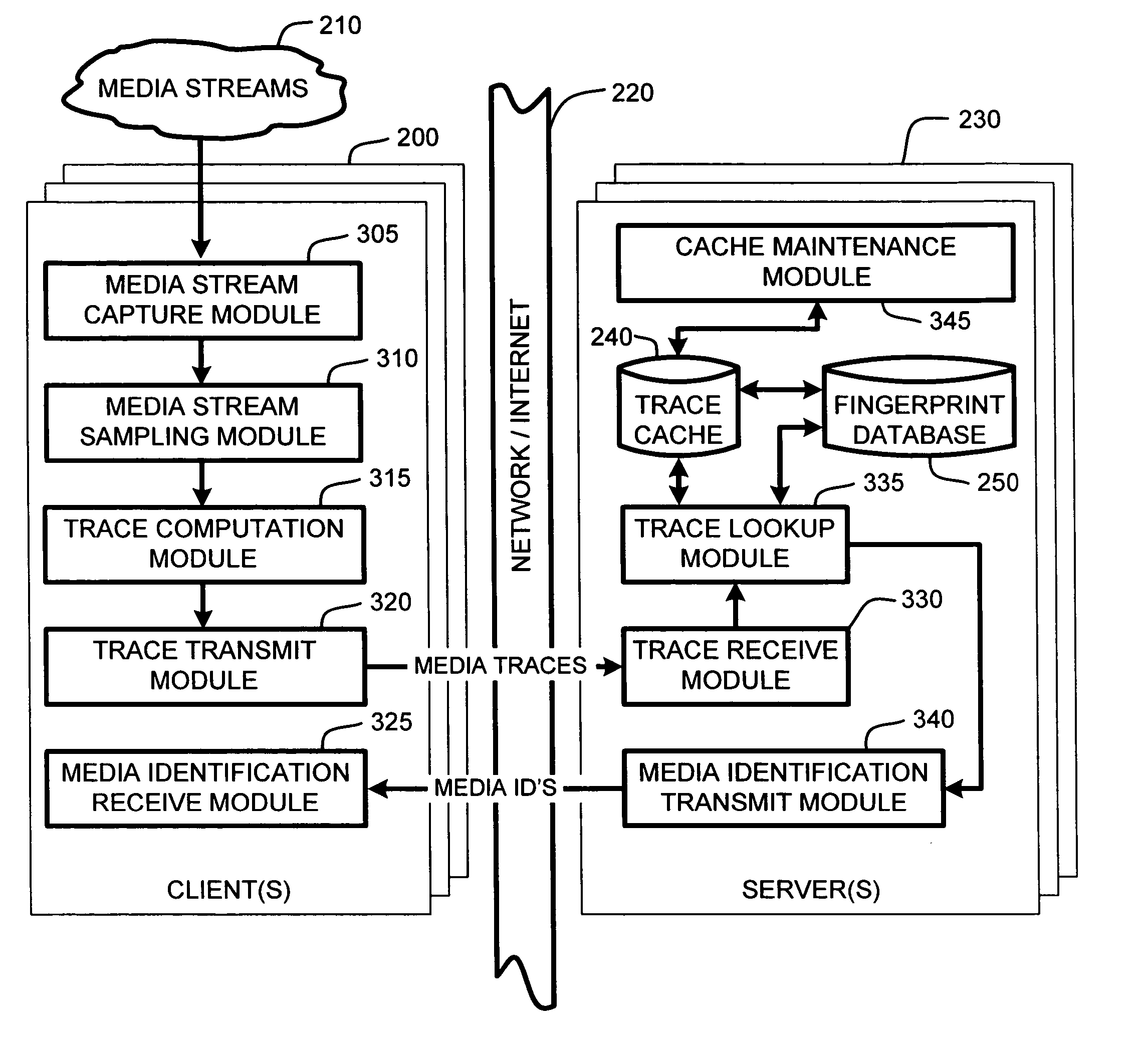
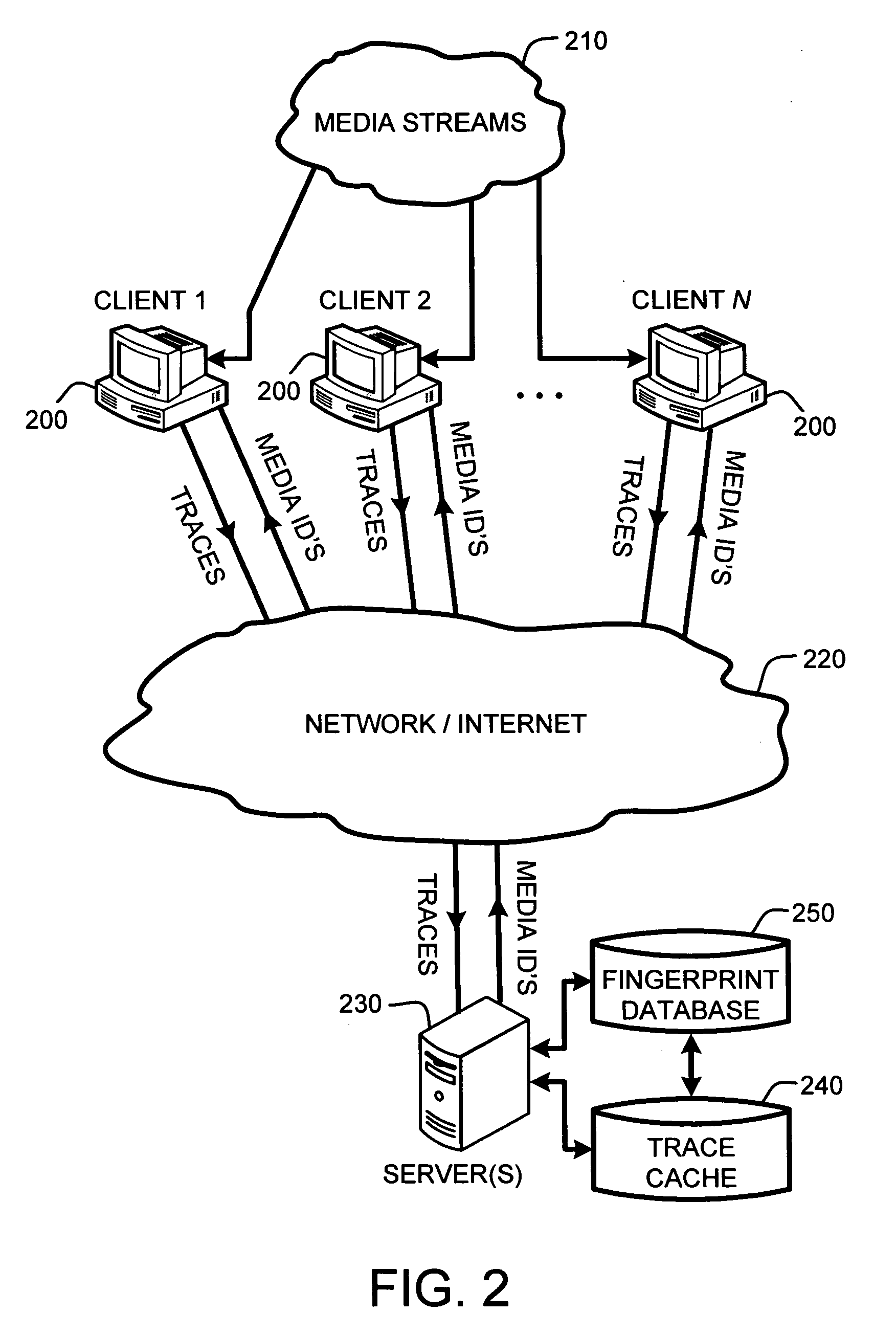
System and method for speeding up database lookups for multiple synchronized data streams
InactiveUS20060106867A1Increase loadImprove accuracyData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalData streamReal time services
A “Media Identifier” operates on concurrent media streams to provide large numbers of clients with real-time server-side identification of media objects embedded in streaming media, such as radio, television, or Internet broadcasts. Such media objects may include songs, commercials, jingles, station identifiers, etc. Identification of the media objects is provided to clients by comparing client-generated traces computed from media stream samples to a large database of stored, pre-computed traces (i.e., “fingerprints”) of known identification. Further, given a finite number of media streams and a much larger number of clients, many of the traces sent to the server are likely to be almost identical. Therefore, a searchable dynamic trace cache is used to limit the database queries necessary to identify particular traces. This trace cache caches only one copy of recent traces along with the database search results, either positive or negative. Cache entries are then removed as they age.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Internet radio and broadcast method
InactiveUS20100205166A1Television system detailsDigital data processing detailsData streamInternet radio
Owner:PANDORA MEDIA
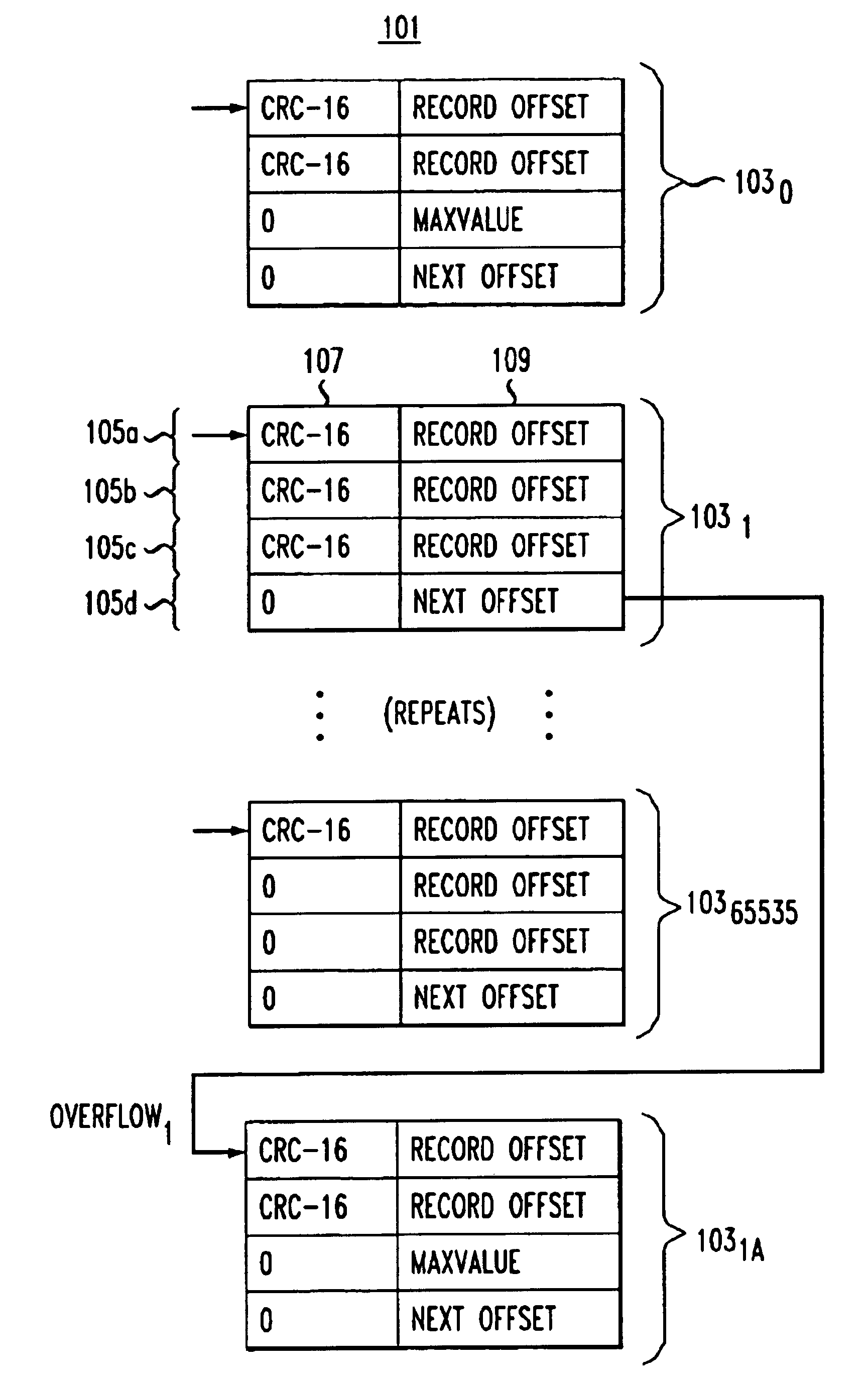
Method and system for efficiently retrieving information from a database
InactiveUS6865577B1Easy to handleSpace minimizationData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalMostly TrueS/KEY
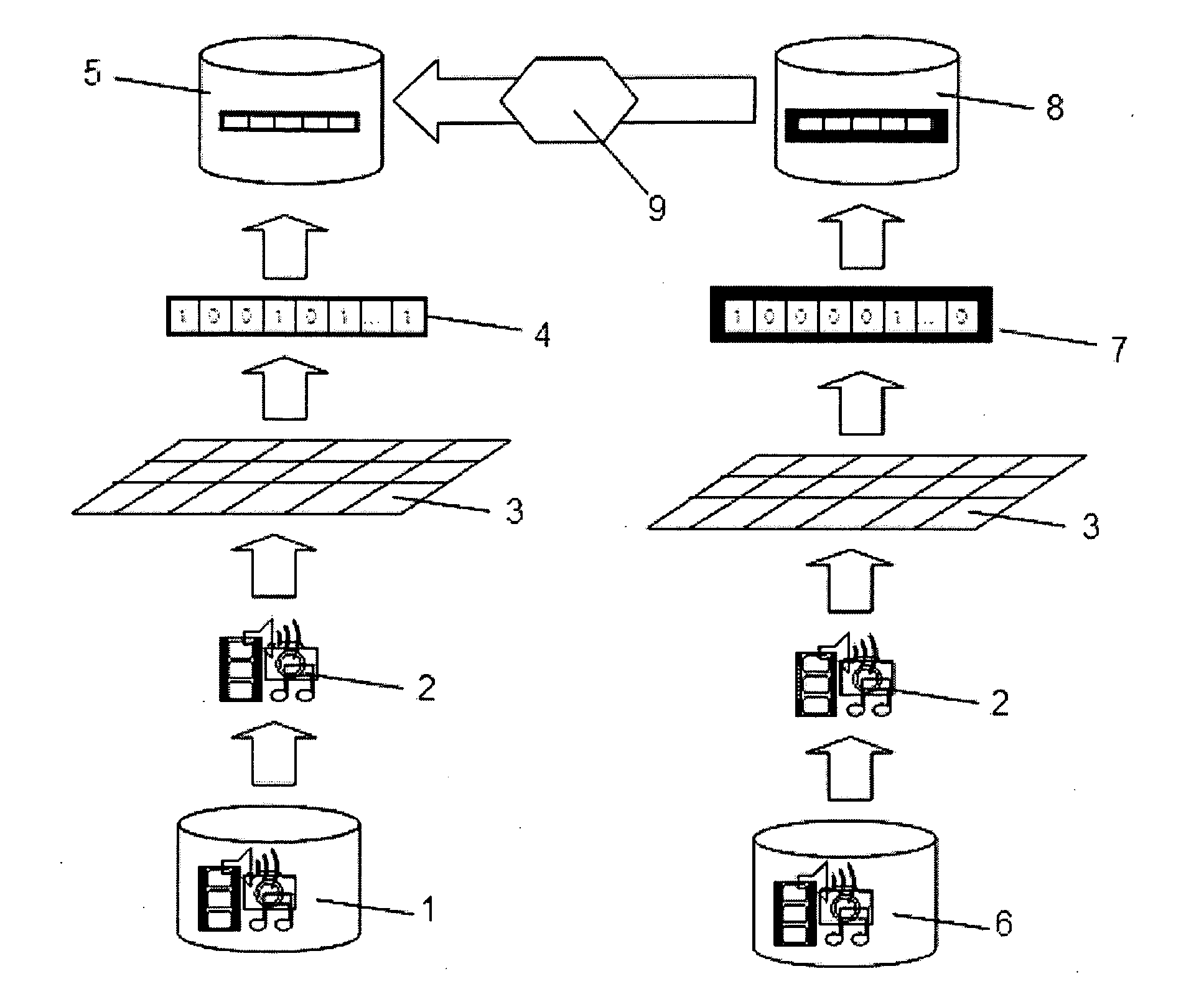
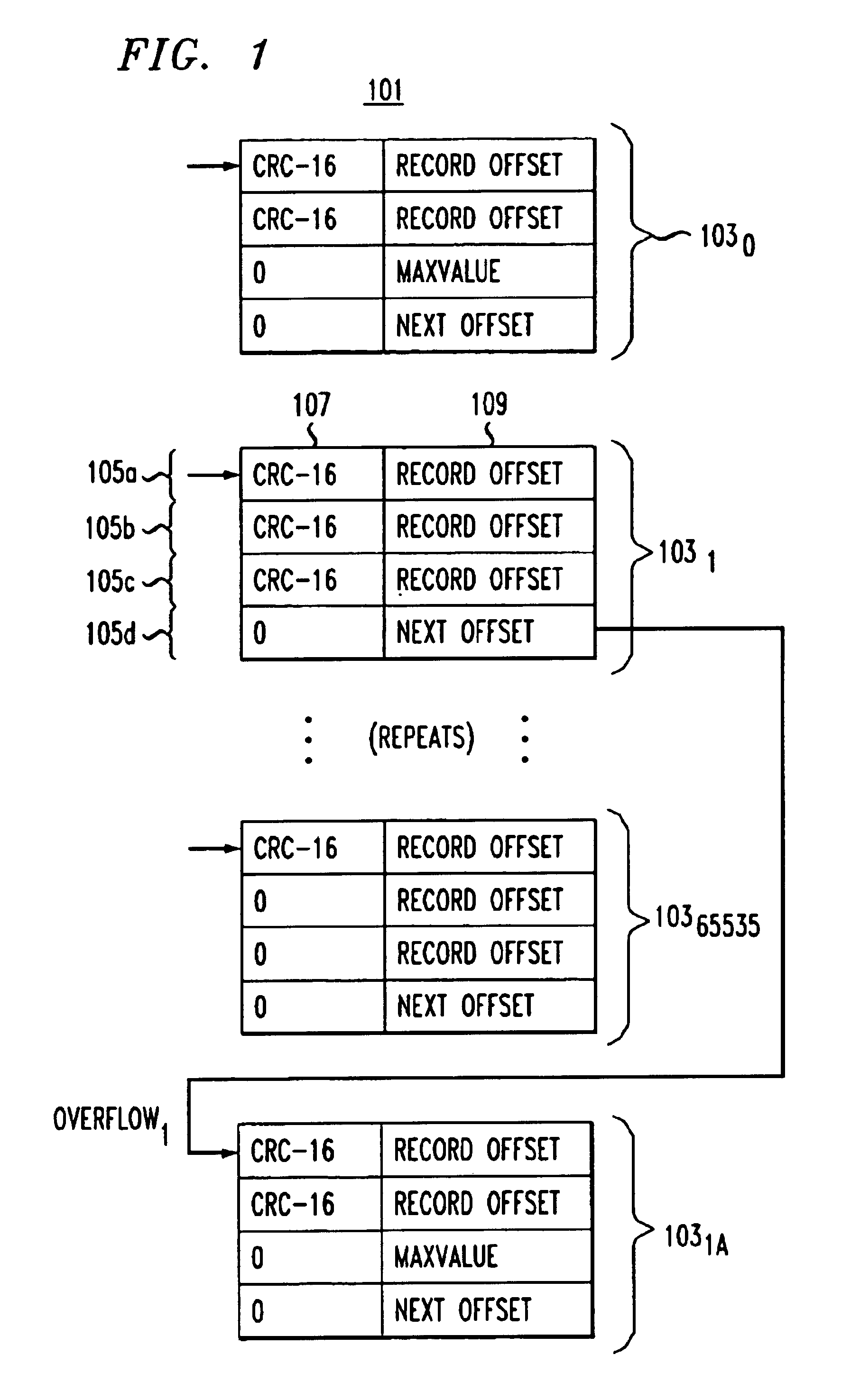
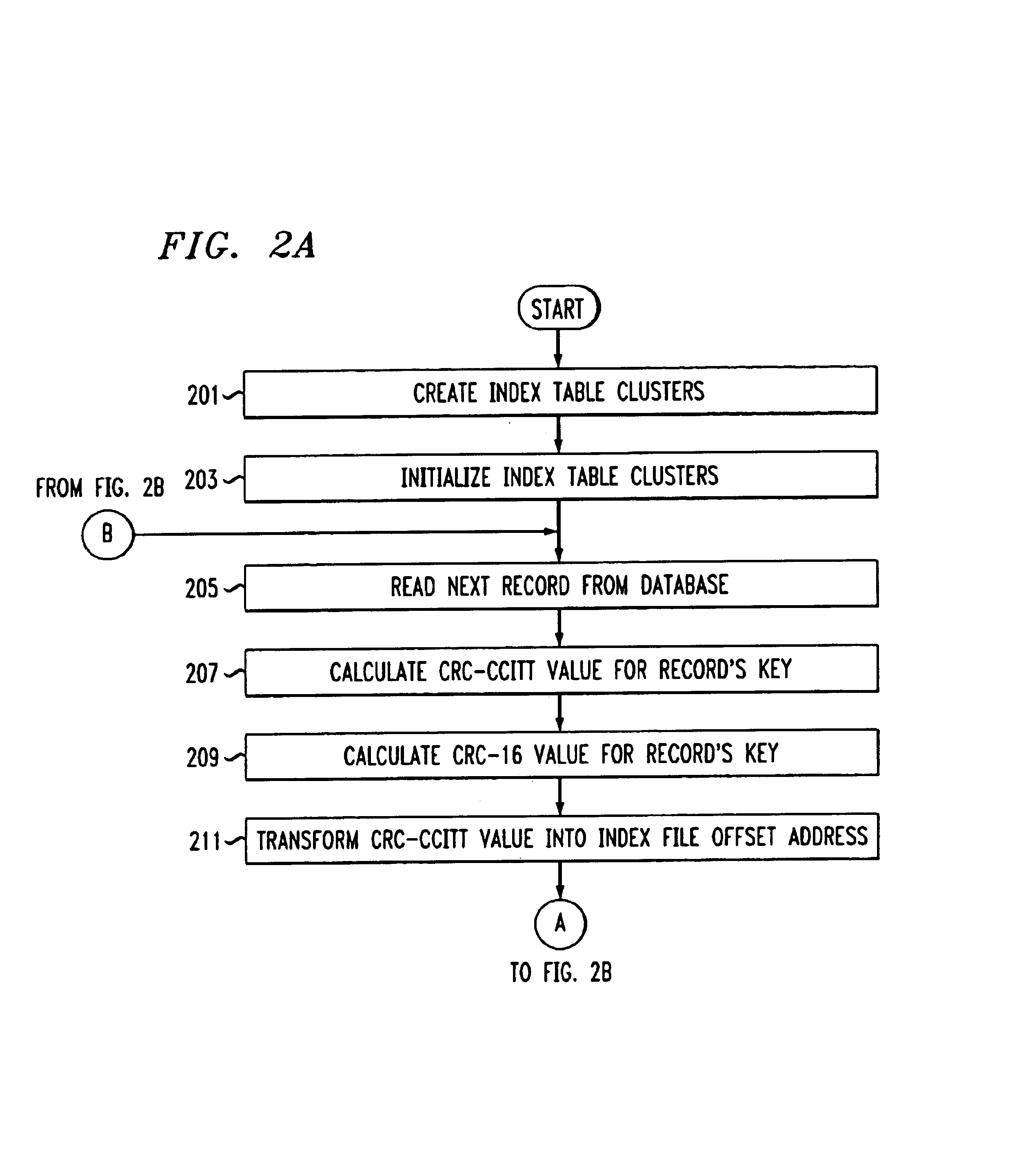
A method for fast and efficient record retrieval in large databases using cyclical redundancy check (CRC) computations as hash functions. Two hash values are computed for each record's key using the CRC-CCITT and CRC-16 generator polynomials. The two CRC values then are combined into a four-byte composite hash value that represents a binary signature of the record's key. Alternately, a single CRC-32 value can be used as a four-byte hash value. In most cases, this four-byte hash value uniquely identifies the record's key. An index file is constructed using a hybrid search method, part hash table and part linear search. The index file is searched to find a match for the four-byte hash value and the record's offset is obtained. The record's offset is used to retrieve the record from the database.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
System and method for limiting disclosure in hippocratic databases
InactiveUS20060248592A1Digital data information retrievalDigital data processing detailsCost effectivenessInternet privacy
A tool for enforcing limited disclosure rules in a software application, typically an unmodified database. The invention enables individual queries to respect data subjects' preferences and choices by storing privacy semantics, classifying data items into categories, rewriting incoming queries to reflect stored privacy semantics, and masking prohibited values. Privacy semantics include individual data subject choices and privacy policies comprise rules describing authorized data recipients and authorized data access purposes. Privacy policies may require specific consent from data subjects. The invention assigns each (purpose, recipient) pair a view over each database table, so entire tuples and individual cells can have particular privacy semantics. Purposes and recipients are inferred based on the application issuing the query. Masking is performed at the individual cell level, and may employ NULL or other predetermined indicia for prohibited values. The invention is cost-efficient and scalable to large databases.
Owner:IBM CORP
System and method for obtaining keyword descriptions of records from a large database
InactiveUS7363308B2Reduction of informationData processing applicationsWeb data indexingReference databasePredictive modelling
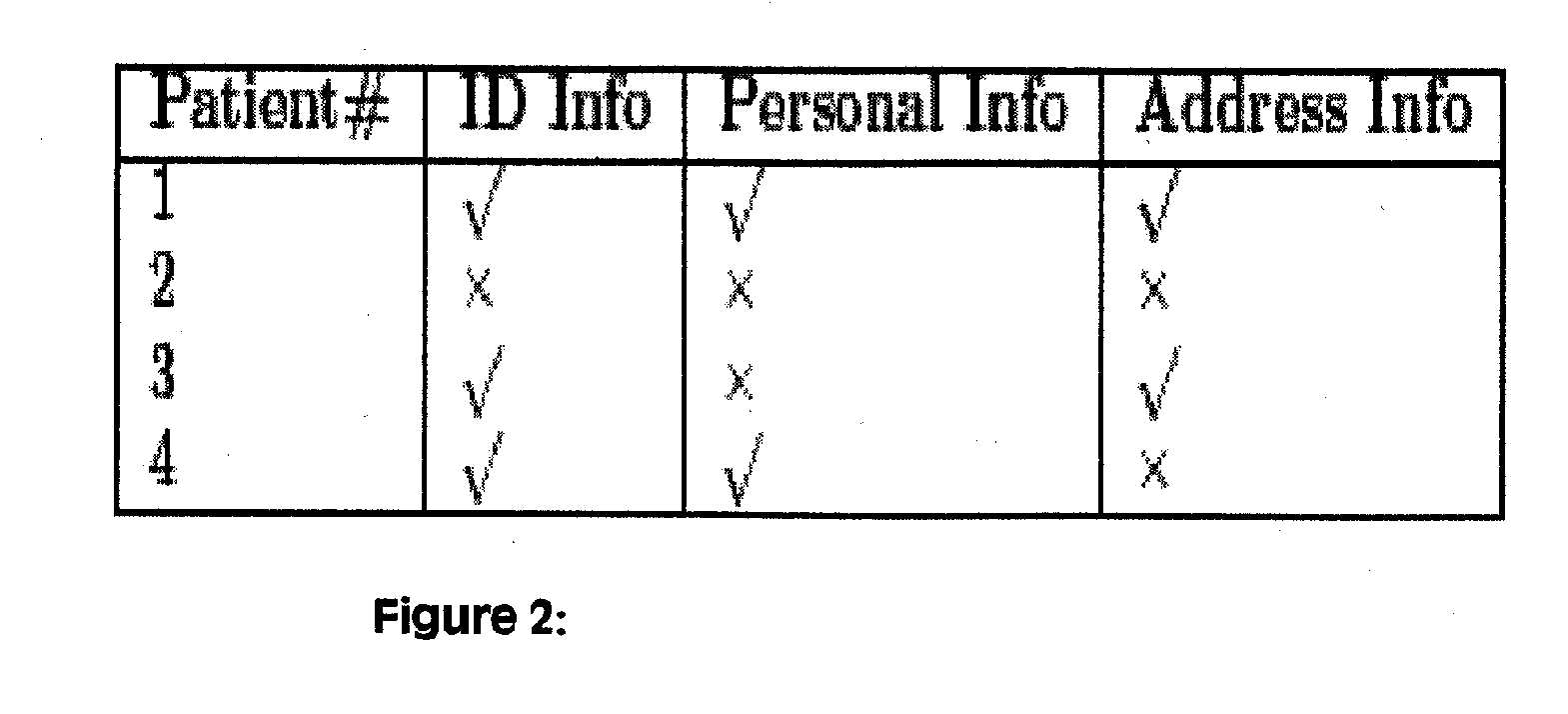
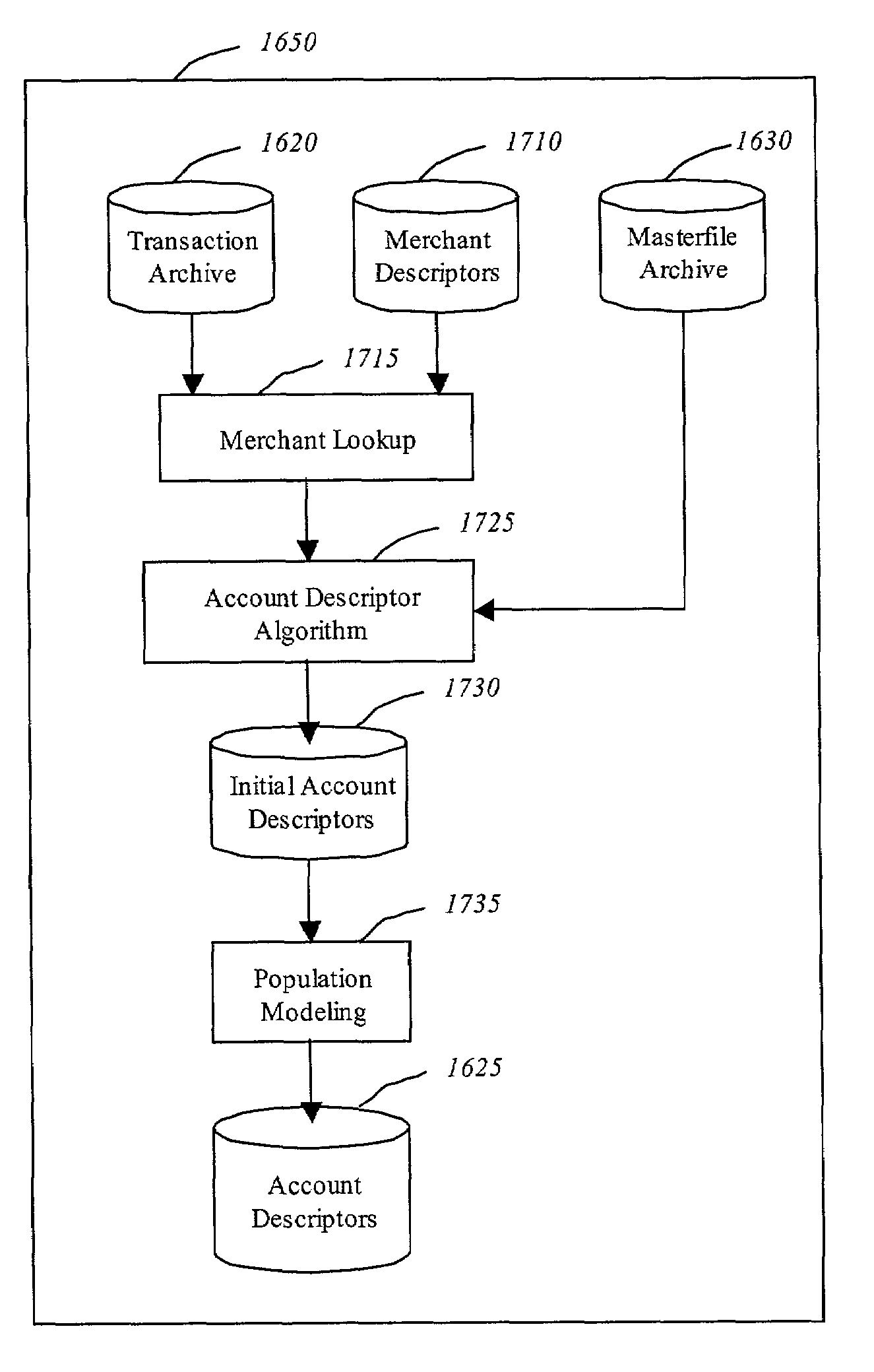
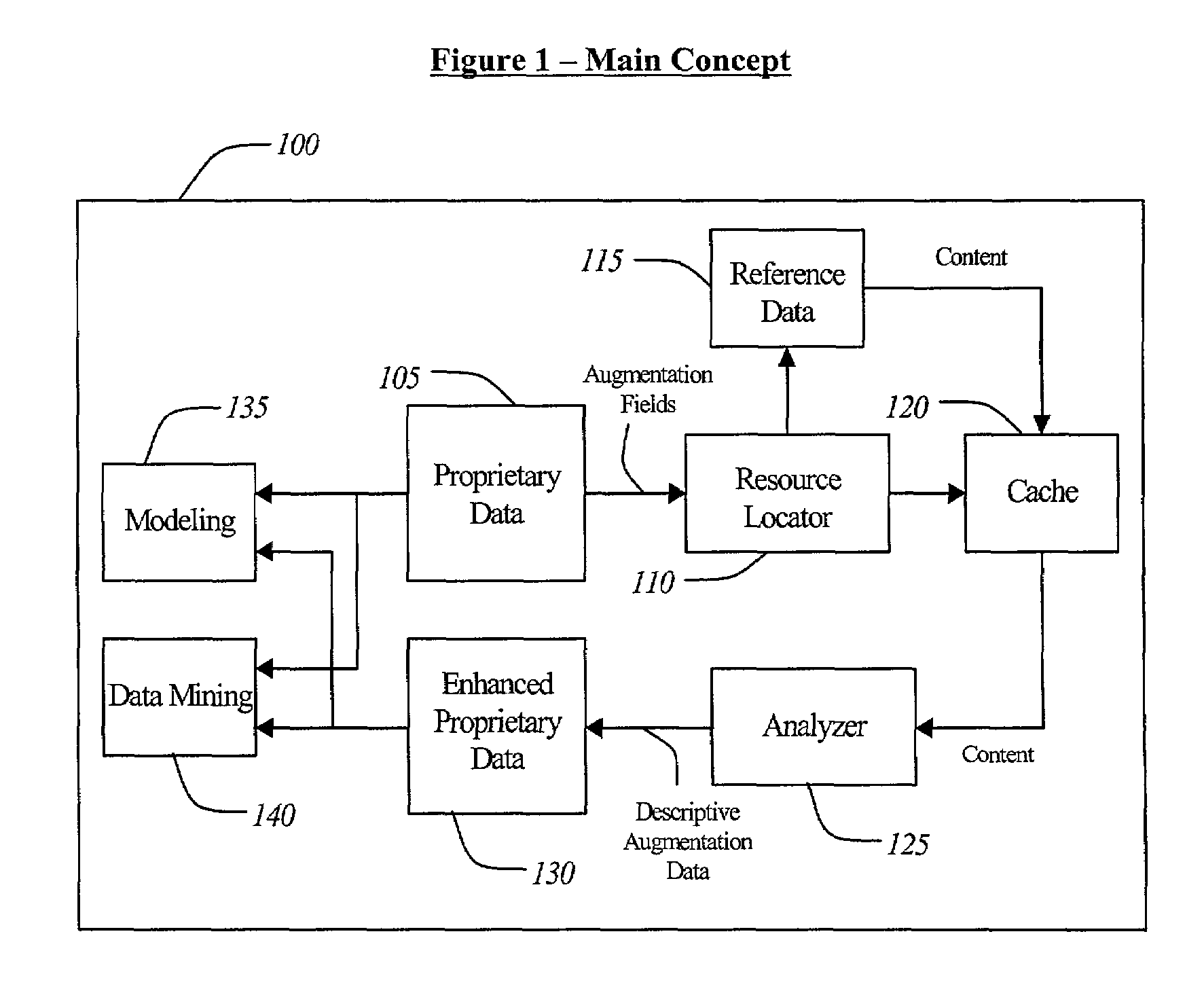
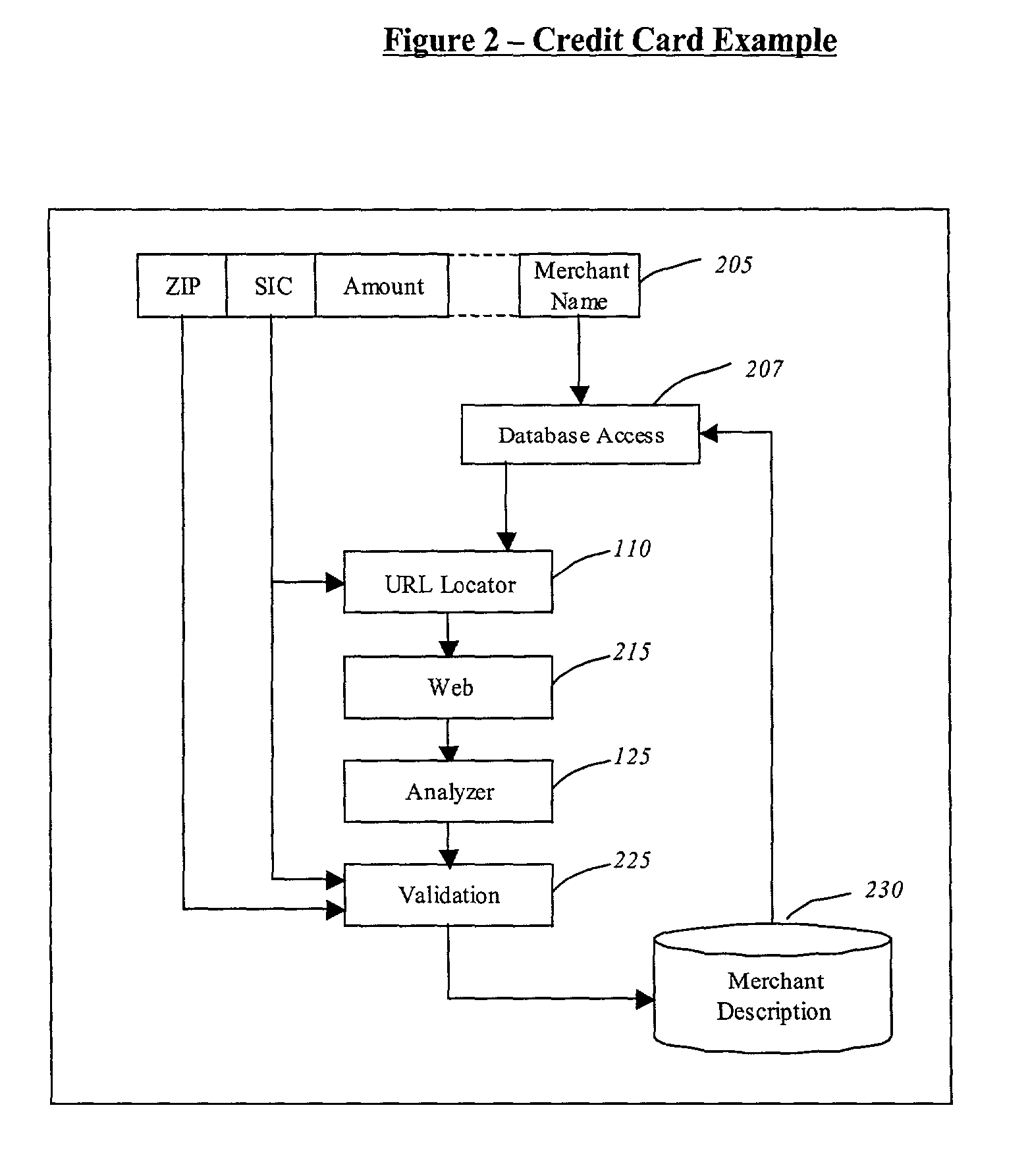
A computerized system for augmenting data from a source database with data from a reference database to generate an augmented database that can be used for predictive modeling is disclosed. The present invention includes a method for using the Internet to obtain information, including, reading a data record stored in a field of data, searching a database for information describing the data record, condensing the information describing the data record into a value description, associating the value description with the data record, and augmenting the field of data with the value description associated with the data. The present invention also includes a computerized system for augmenting data from a source database with data from a reference database to generate an augmented database that can be used for predictive modeling and data mining to conduct searches of data in the augmented database.
Owner:FAIR ISAAC & CO INC
Generating and matching hashes of multimedia content
ActiveUS20080263360A1Overcomes this NP-complete search complexityElectrophonic musical instrumentsEncryption apparatus with shift registers/memoriesComputer hardwareFrequency spectrum
Hashes are short summaries or signatures of data files which can be used to identify the file. Hashing multimedia content (audio, video, images) is difficult because the hash of original content and processed (e.g. compressed) content may differ significantly. The disclosed method generates robust hashes for multimedia content, for example, audio clips. The audio clip is divided (12) into successive (preferably overlapping) frames. For each frame, the frequency spectrum is divided (15) into bands. A robust property of each band (e.g. energy) is computed (16) and represented (17) by a respective hash bit. An audio clip is thus represented by a concatenation of binary hash words, one for each frame. To identify a possibly compressed audio signal, a block of hash words derived therefrom is matched by a computer (20) with a large database (21). Such matching strategies are also disclosed. In an advantageous embodiment, the extraction process also provides information (19) as to which of the hash bits are the least reliable. Flipping these bits considerably improves the speed and performance of the matching process.
Owner:GRACENOTE
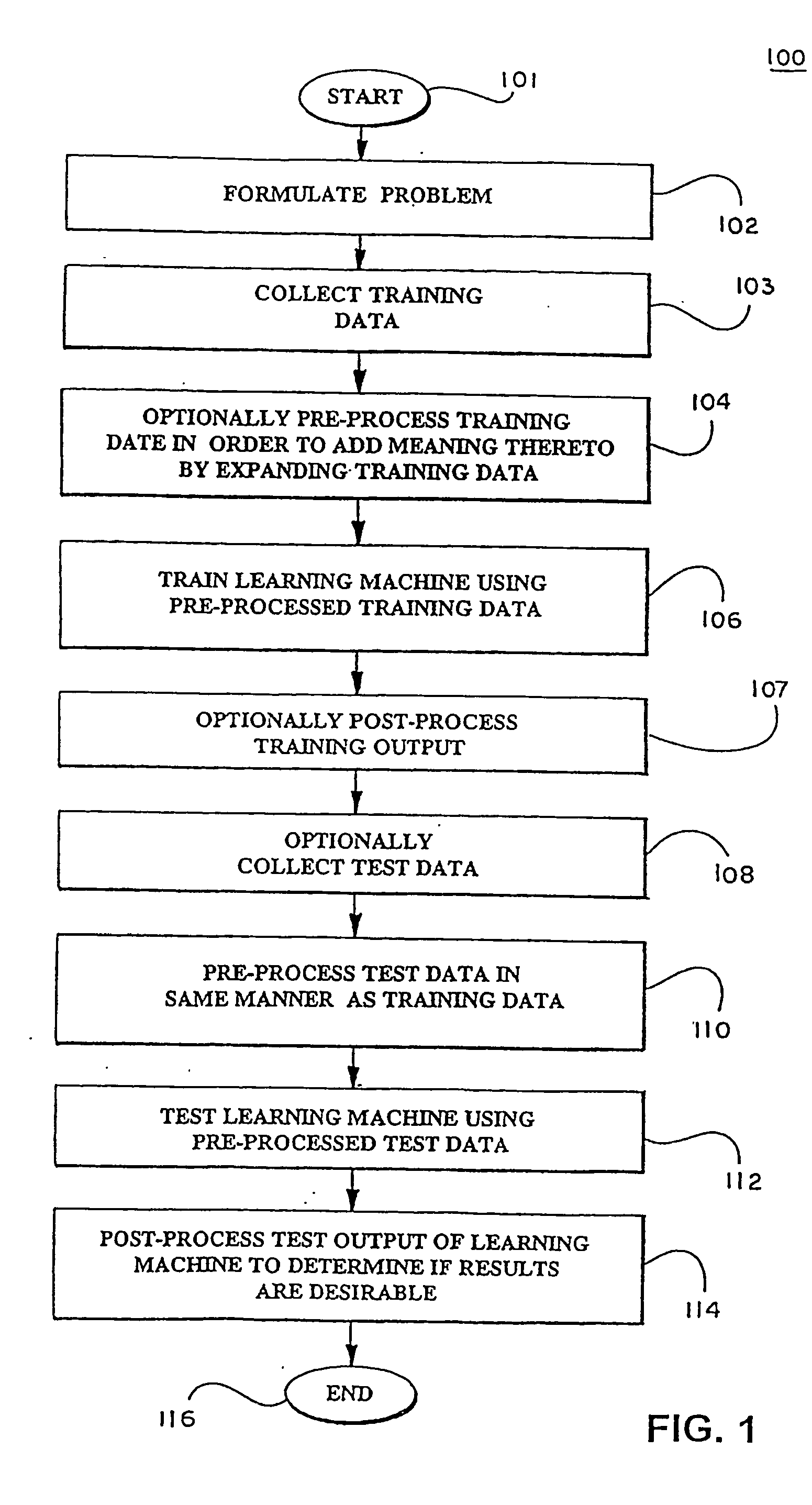
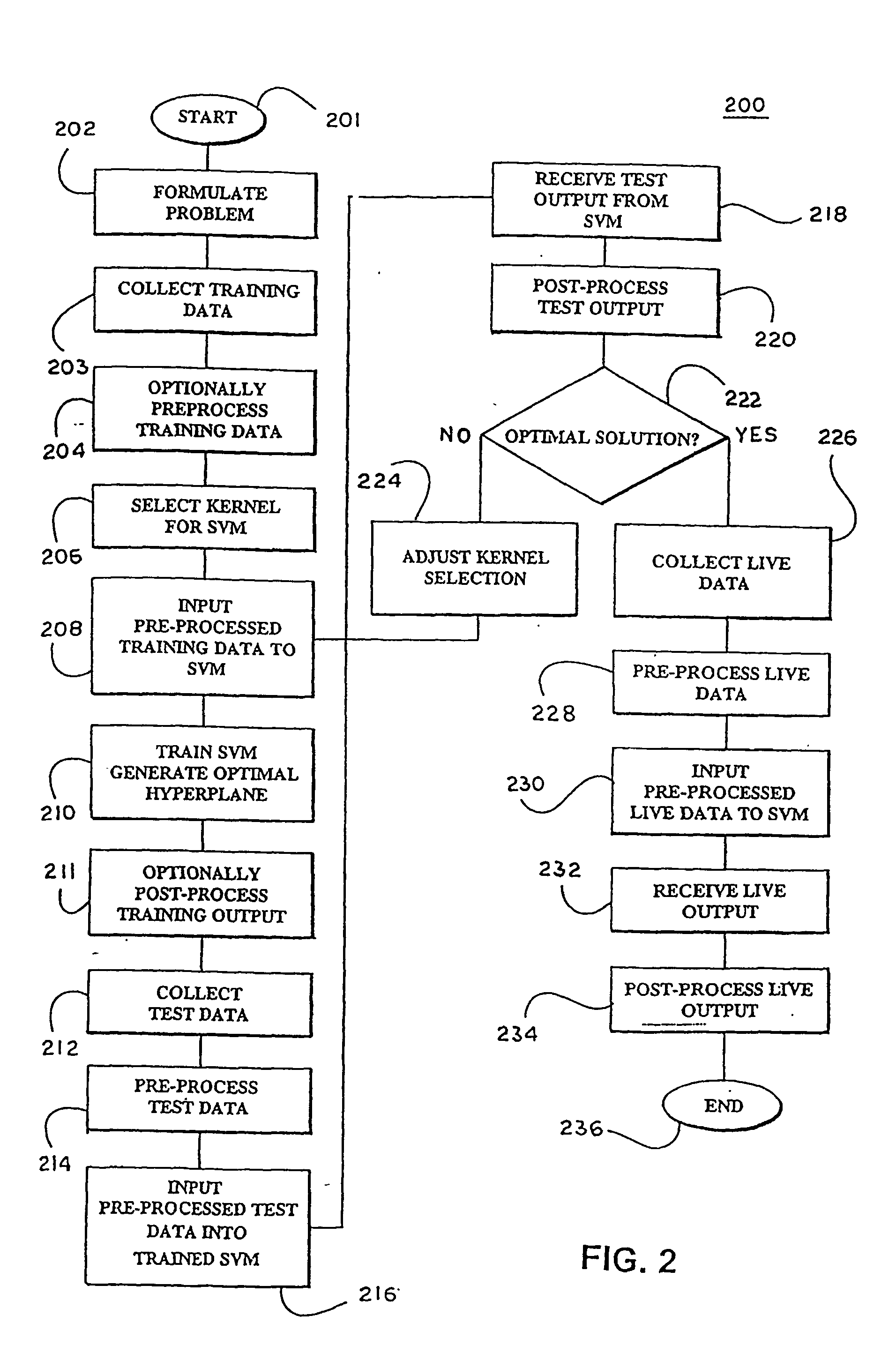
Pre-processed feature ranking for a support vector machine
InactiveUS20050131847A1Reduce in quantityBroaden applicationKernel methodsDigital computer detailsLearning machineFeature ranking
Features are preprocessed (204) to minimize classification error in a Support Vector Machines (200) used to identify patterns in large databases. Pre-processing (204) is performed to constrain features used to train (210) the SVM learning machine. Live data (226) is collected and processed (232) with SVM.
Owner:BIOWULF TECH +1
Diagnostic and predictive system and methodology using multiple parameter electrocardiography superscores
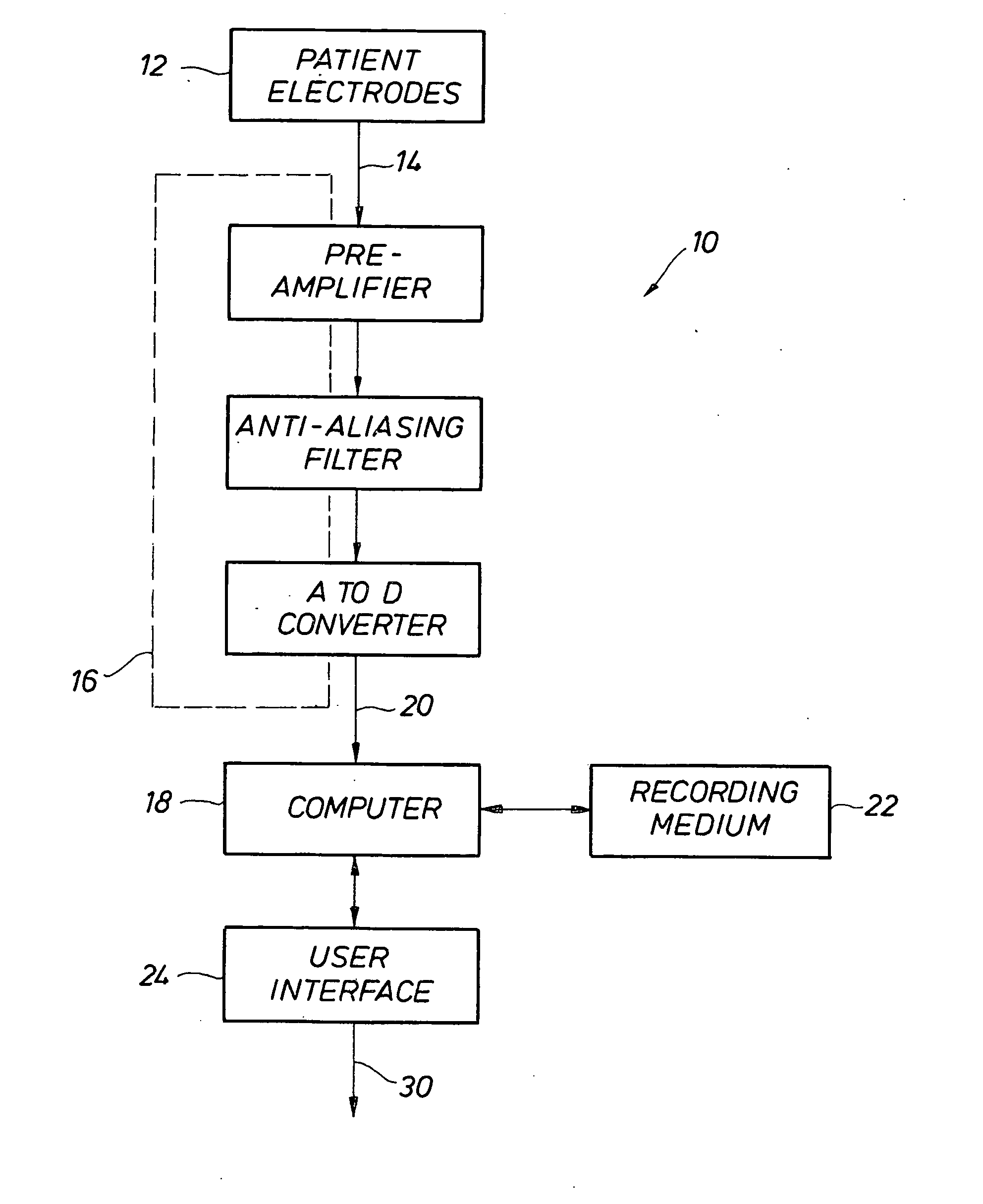
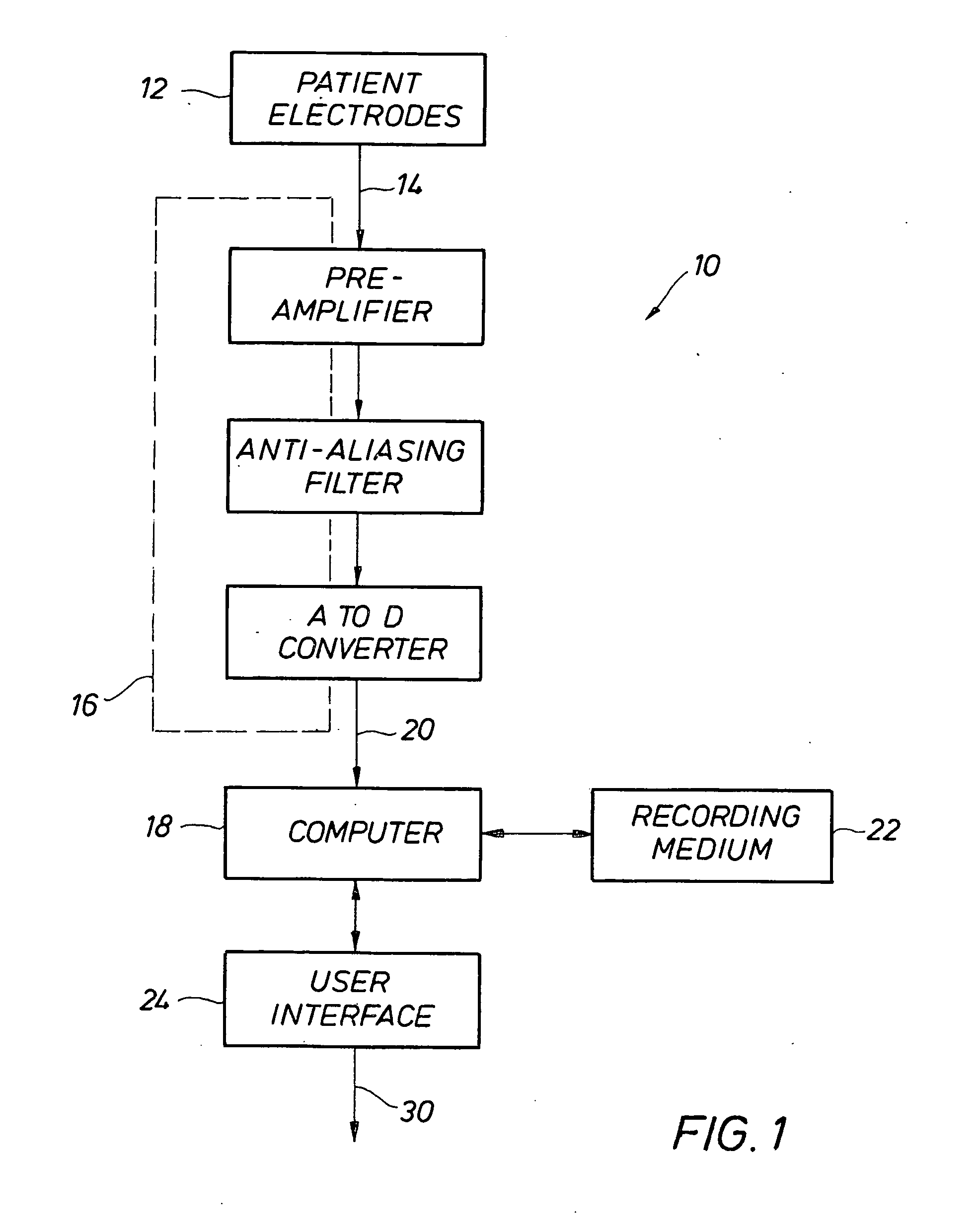
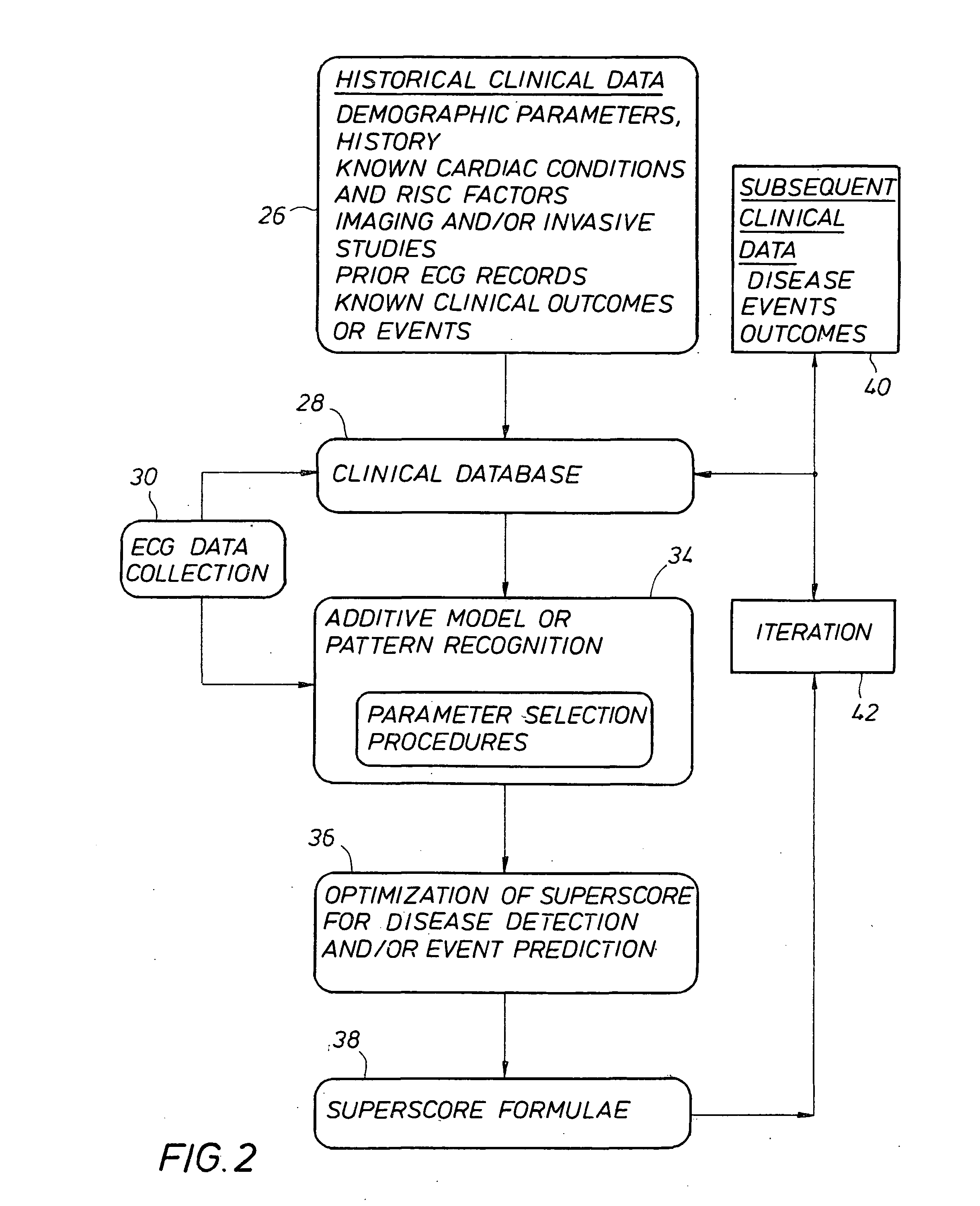
InactiveUS20100217144A1Easy to detectGreat riskElectrocardiographyHealth-index calculationPredictive systemsWeight coefficient
A plurality of ECG Superscore formulae, created from multiple parameter ECG measurements including those from advanced ECG techniques, can be optimized using additive multivariate statistical models or pattern recognition procedures, with the results compared against a large database of ECG measurements from individuals with known cardiac conditions and / or previous cardiac events. Superscore formulae utilize multiple ECG parameters and accompanying weighting coefficients and allow data obtained from any given patient to be used in calculating that patient's ECG Superscore results. ECG Superscores have retrospectively optimized accuracy for identifying and screening individuals for underlying heart disease and / or for determining the risk of future cardiac events. They thus have greater predictive value than that of any conventional or advanced ECG measurement alone or of any non-optimized combinations of conventional or advanced ECG measurements that have been used in the past. Ongoing optimization of ECG Superscore diagnostic and predictive accuracy may be realized through the iterative adjustment of Superscore formulae based on the incorporation of data from new patients into the database and / or from longitudinal follow-up of the disease and cardiac event status of existing patients.
Owner:BRIAN ARENARE
Method and system for persisting and managing computer program clippings
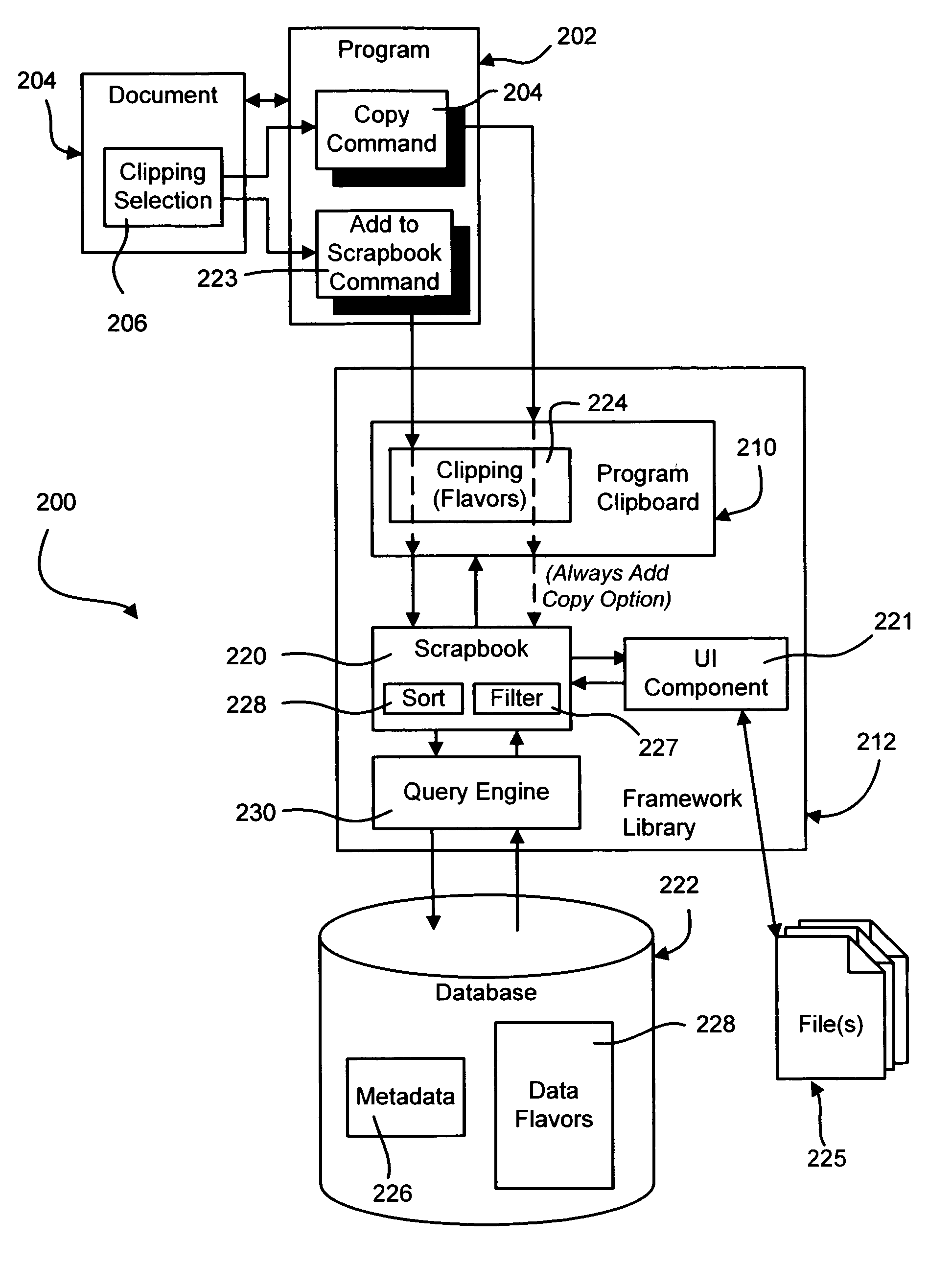
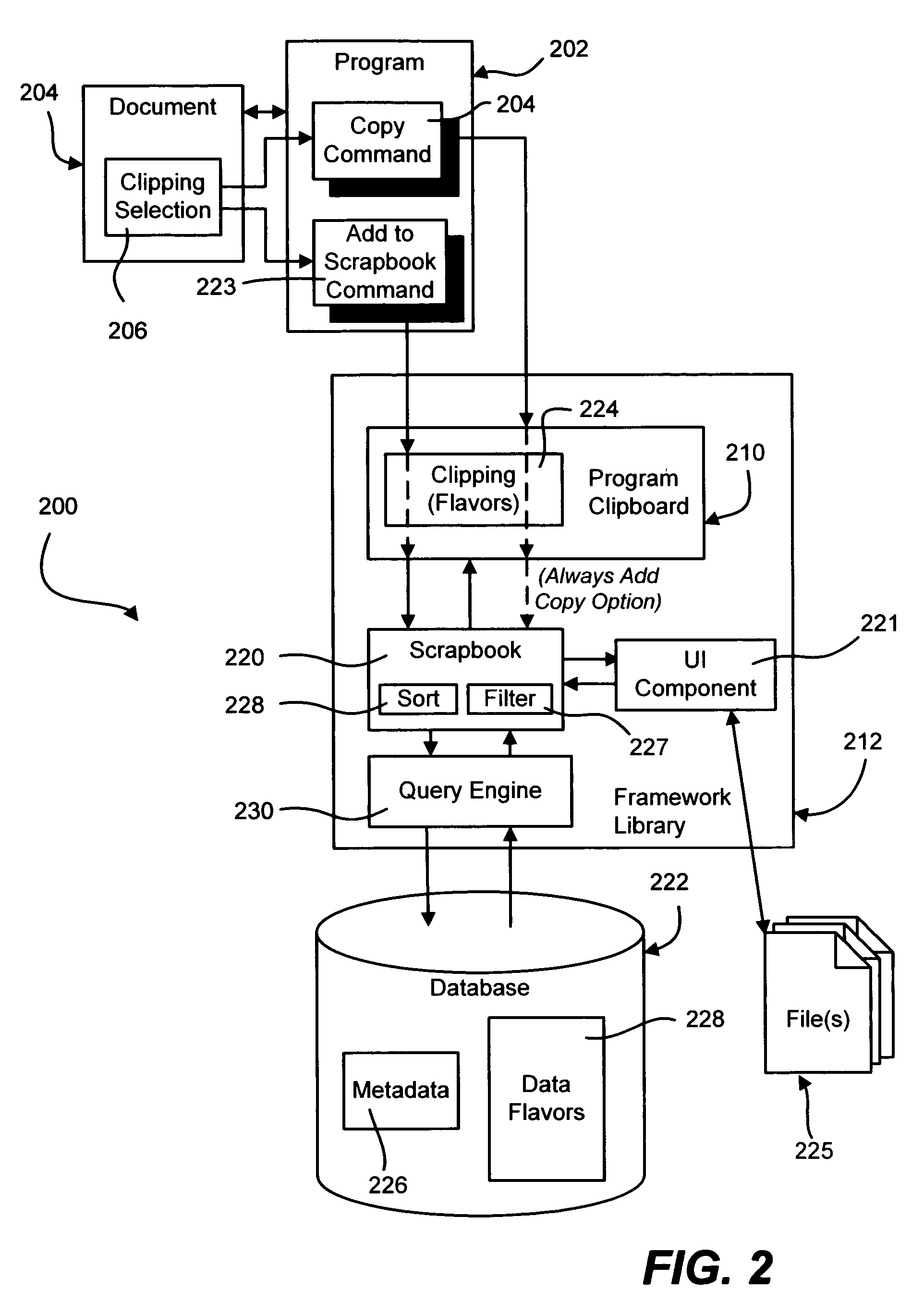
InactiveUS20060075353A1Easy to optimizeData processing applicationsNatural language data processingOriginating applicationPaper document
Described is a system and method that provide an organized view of computer content clippings including text, documents, pictures, and other file types. The clippings are persisted with associated metadata that enables the users to access the clippings in a managed manner via filtering and sorting mechanisms that allow the user to view clippings sorted and / or filtered based on the metadata. The metadata includes originating application information, originating document information, and date and size information. The user can assign categories or projects to the clippings to organize various clippings for a future project to be created from the clippings, assign keywords, and give the clipping a title. The present invention thus allows users to maintain a large database of useful clippings that can be reused in different documents.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
System and method for generating automatic user interface for arbitrarily complex or large databases
InactiveUS7885981B2Natural, powerful, and easy-to-useData processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsDrill downSoftware system
A software system automatically and dynamically generates a fully functional user interface (UI) based upon, and connected directly to, an underlying data model (as instantiated within a relational database management system (RDBMS)). The UI derives from an automated interrogation of the RDBMS, and comprises all mode displays (e.g., browse, search, edit, add) for all tables, and a full complement of mechanisms—integrated directly into the mode displays—for representing, navigating, and managing relationships across tables, regardless of the complexity of the underlying RDBMS schema. It utilizes a hierarchical “context stack” for suspending the working state of a particular table while “drilling down” to work with related-table information and return relevant changes to the base table. The embodiment further provides methods to enhance and extend the internal representation of table structures, constraints, relationships, and-special requirements (“business rules”) for improved revelation of the schema structure through external interrogation.
Owner:KAUFMAN MICHAEL PHILIP
Device and method for multidimensional pattern analysis
InactiveUS6282532B1Data processing applicationsDigital data processing detailsGraphicsVery large database
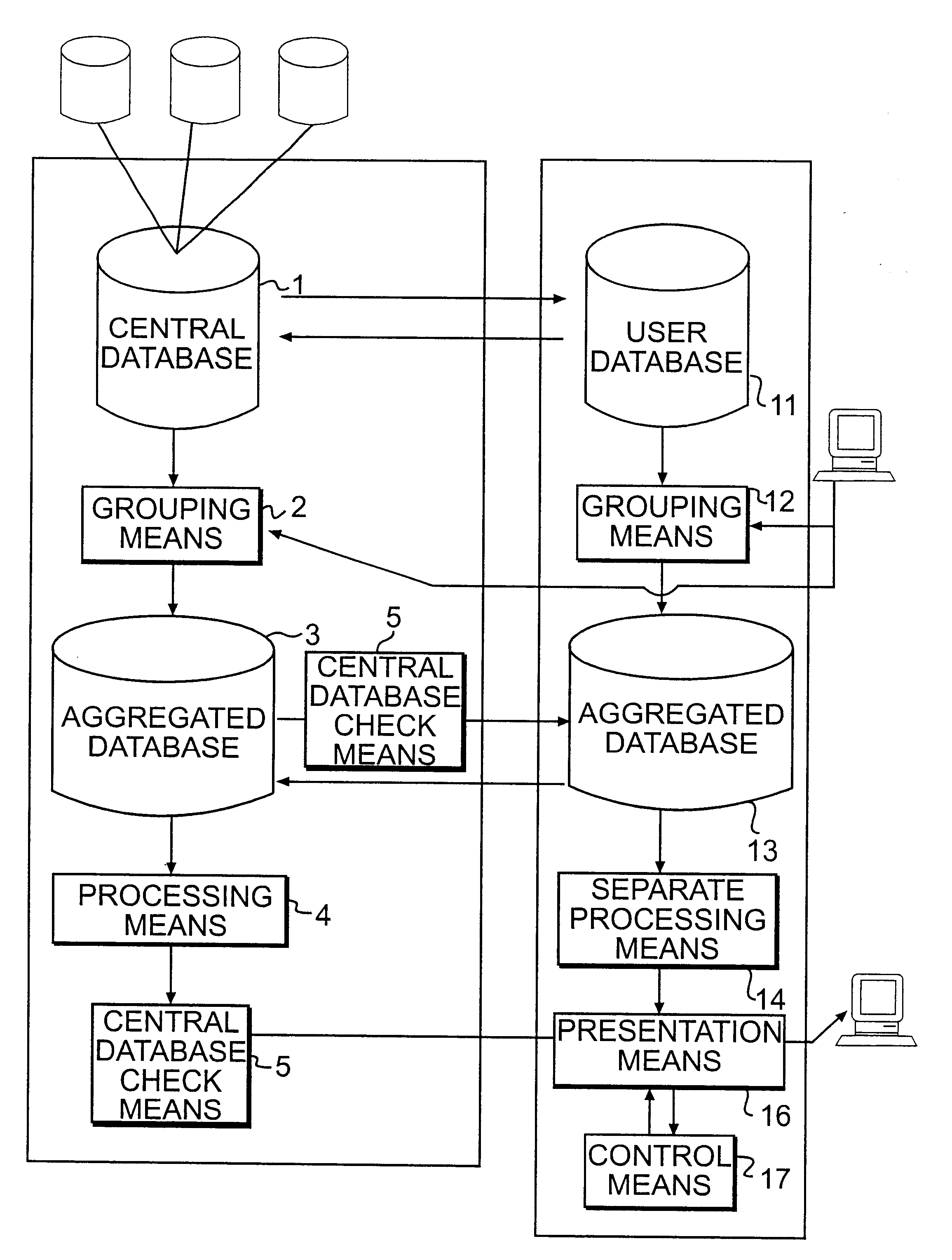
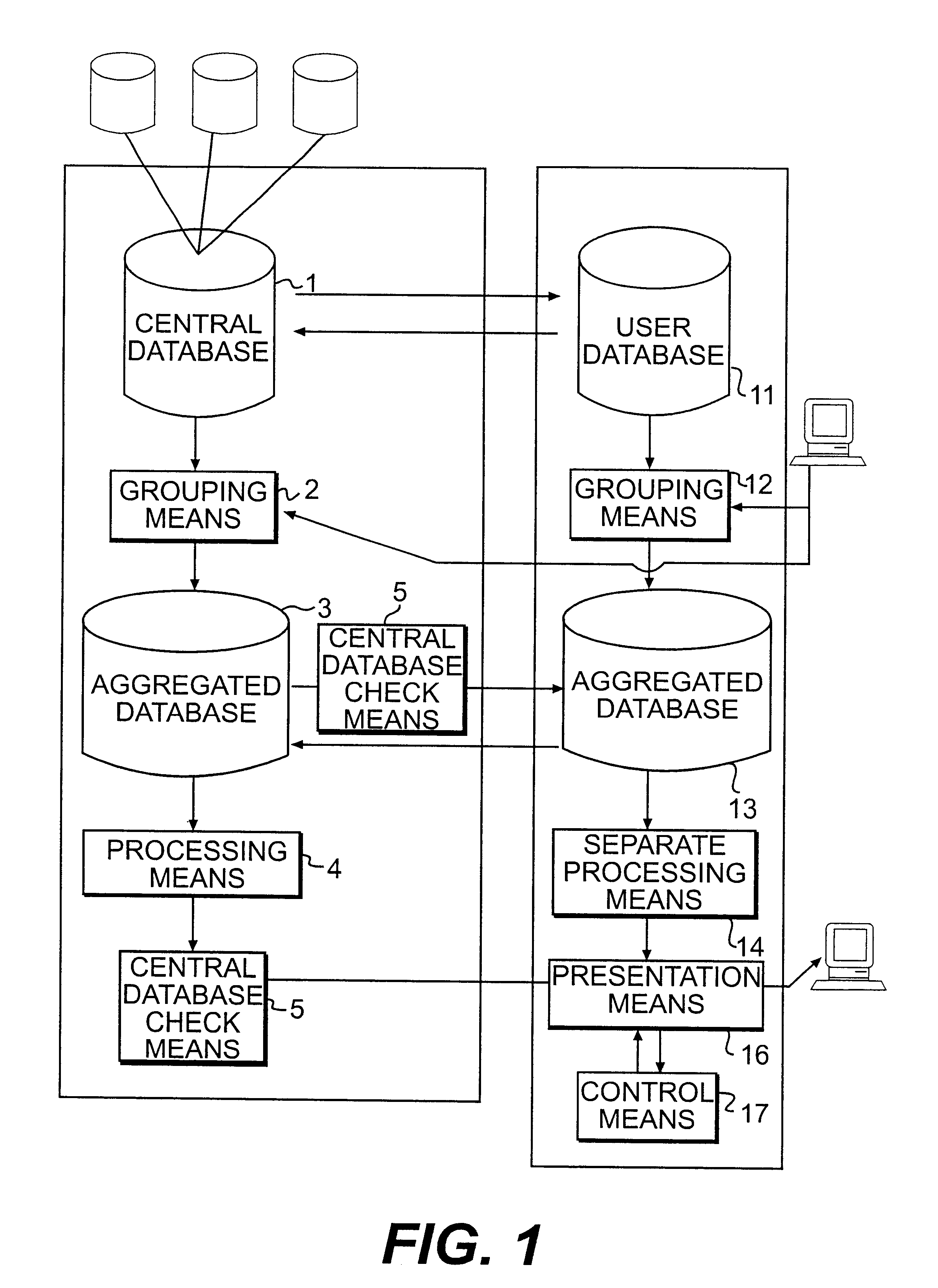
The present invention concerns a device and a method for pattern analysis of large volumes of data in order to make it possible to distinguish tendencies to co-variations and developments in time from one large database, preferably one composed by a number of smaller databases. The data in the database is divided into on the one hand objects and on the other variables. The method is characterized by first grouping the volume of data, whereby the variables are grouped to dimensions and objects to categories based on a variable or a dimension, by thereafter storing the aggregated database thus formed, by sorting the database with respect to dimensions and categories in order to position similar dimensions and categories in proximity to one another and by graphically presenting the volume of data, the grouping parameters, the sorting parameters, and the presenting parameters being controlled by the user, and by repeating the method the desired number of times while changing one or several of the parameters mentioned.
Owner:SHAMROCK INNOVATIONS N AMER
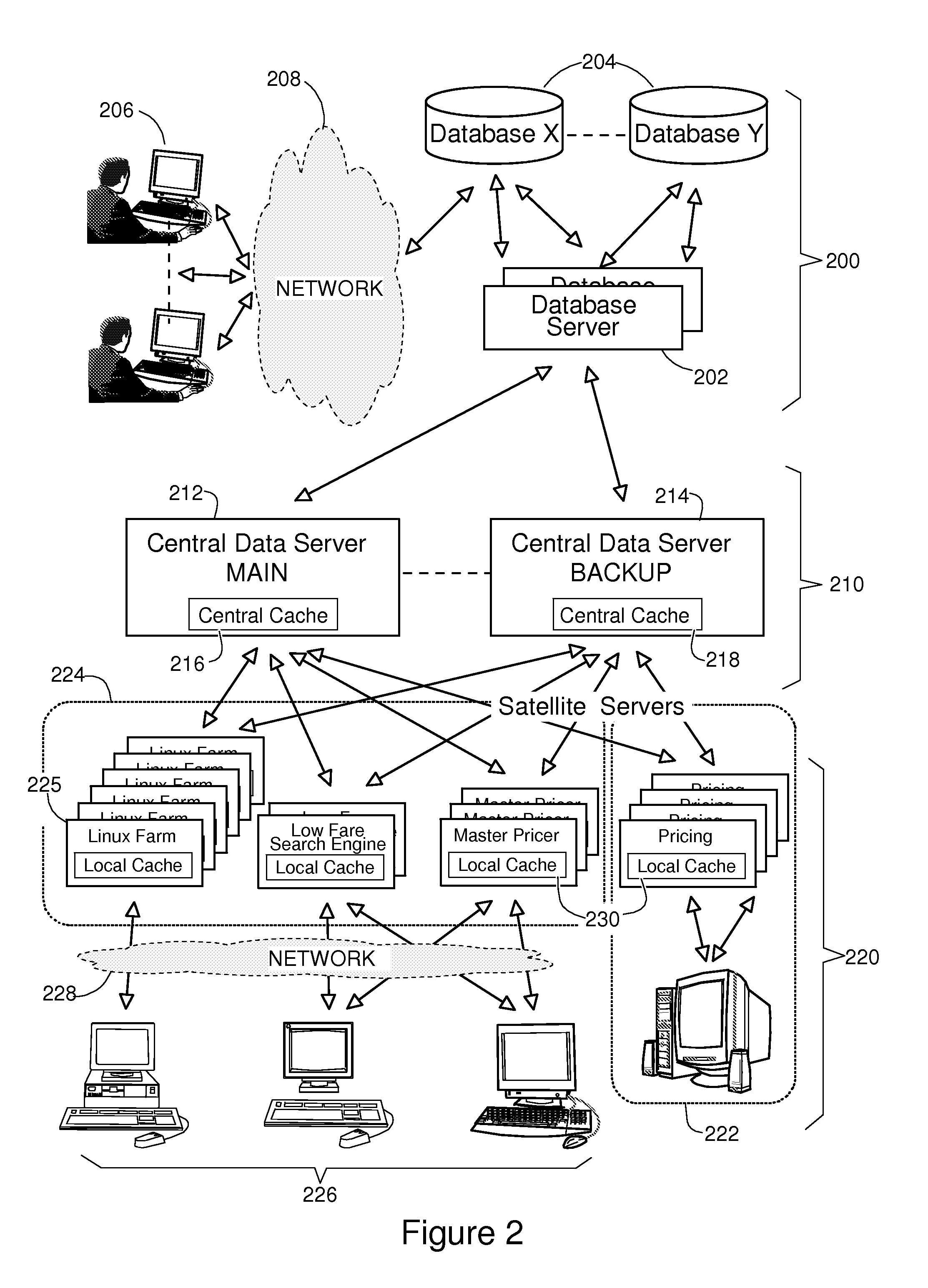
System and Method to Maintain Coherence of Cache Contents in a Multi-Tier System Aimed at Interfacing Large Databases
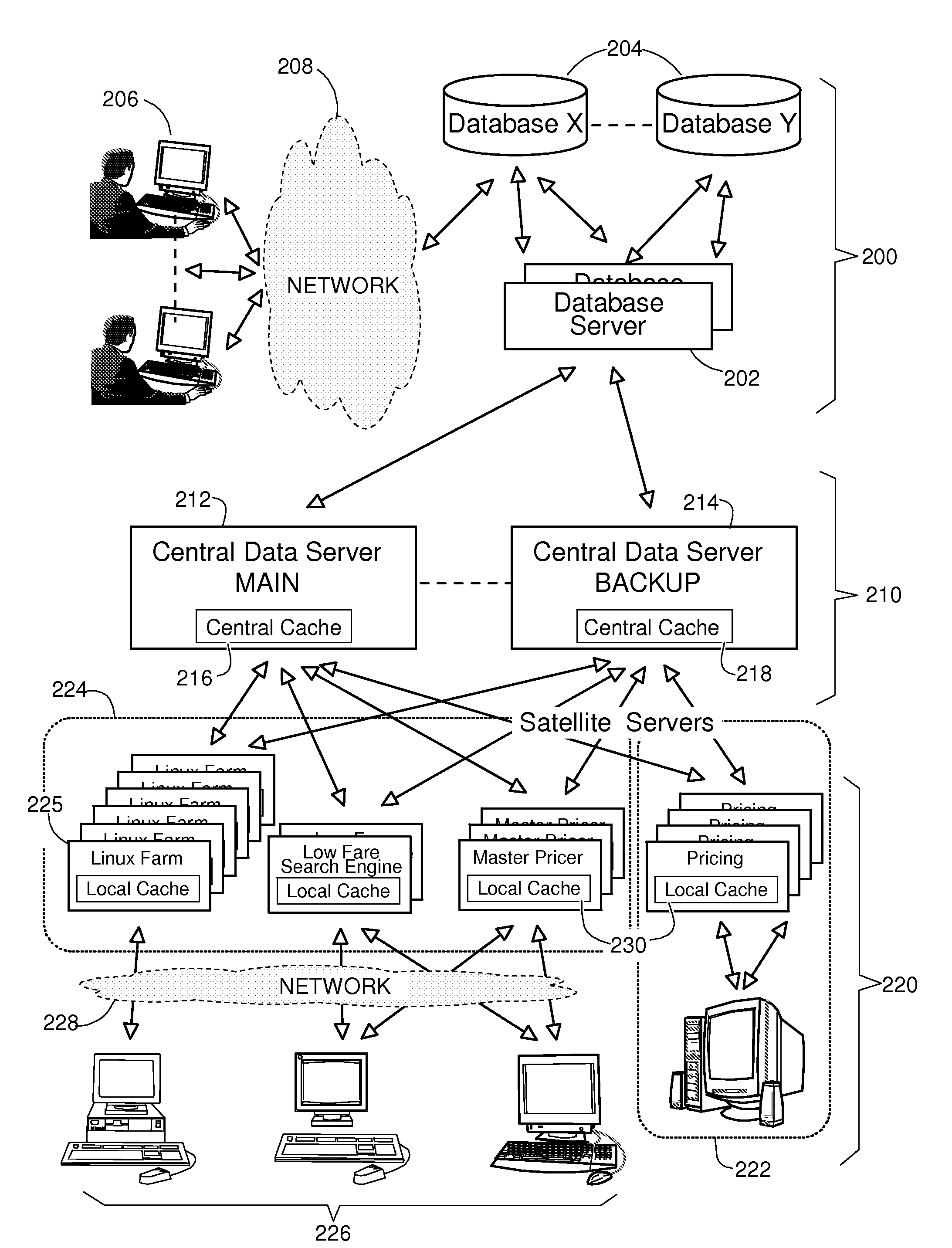
ActiveUS20080235292A1Improve the level ofFrequent updateDigital data processing detailsDatabase distribution/replicationDatabase serverApplication software
A method and a system for maintaining coherence of cache contents in a multi-tiered architecture of servers are described. This includes a front tier of satellite servers, each operating a local cache, and a middle tier of central servers each operating a central cache. Central servers interface with databases through database servers to retrieve the data elements used to construct objects and store them in central caches. Once constructed, objects are attributed a time-to-live (TTL) and stored in central caches then, forwarded to the satellite servers where they are stored in local caches before being delivered to the software applications that have requested them. They are invalidated when outdated and reconstructed from a central server from where they are forwarded to all central caches and to the local caches where they are needed.
Owner:AMADEUS S
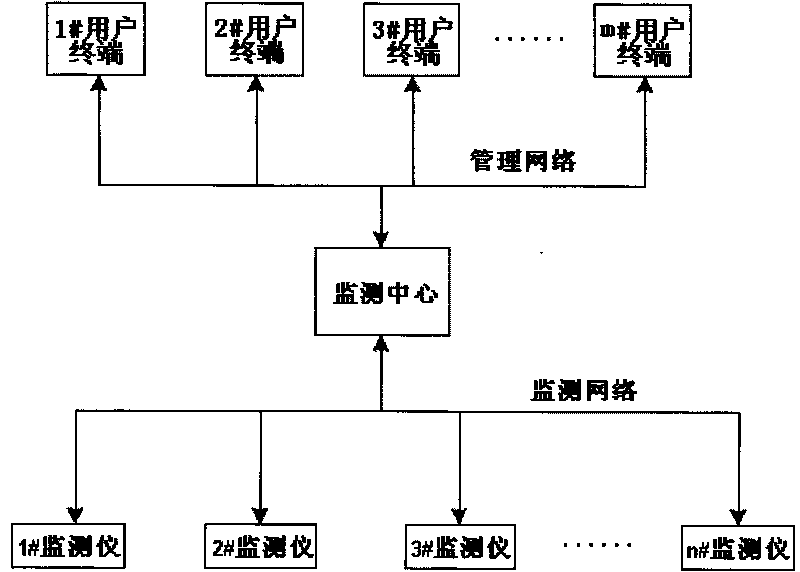
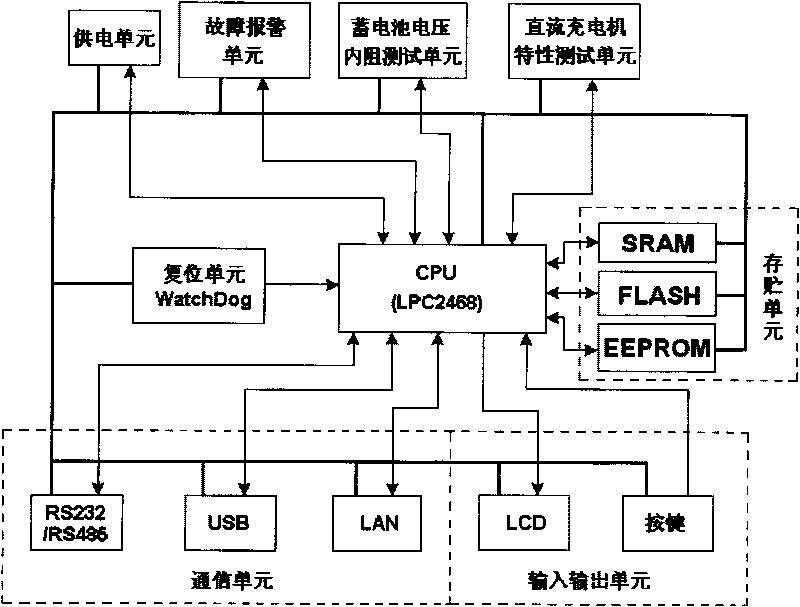
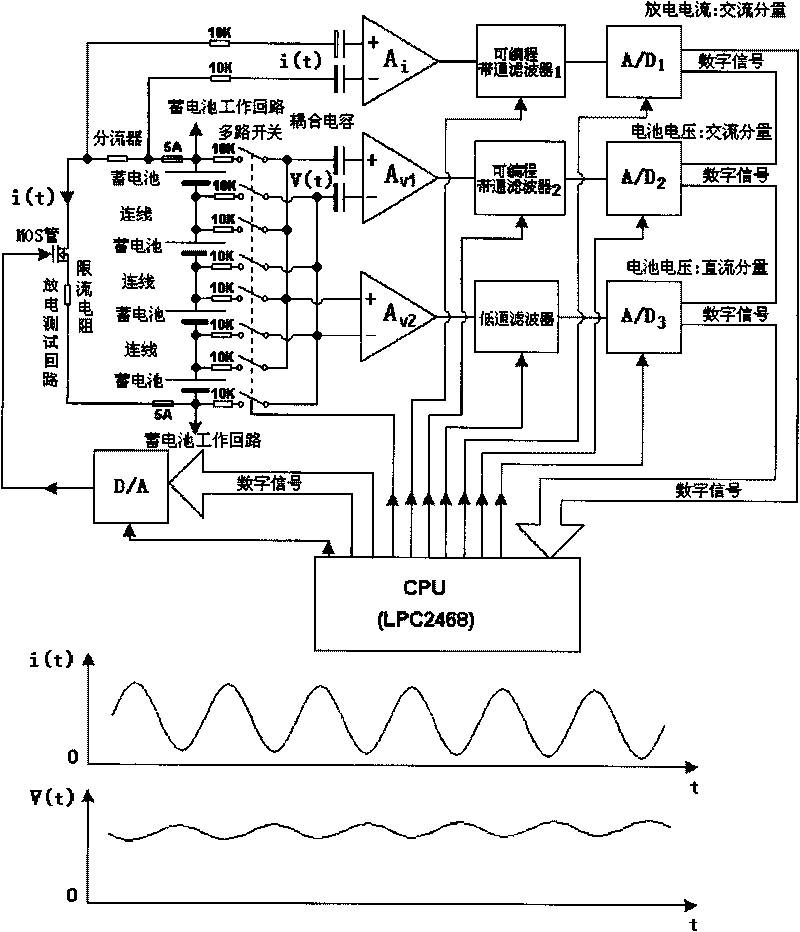
On-line monitoring system for direct-current power supply and storage battery
ActiveCN101706558AImprove securityImprove reliabilityPower supply testingCommunication unitInternal resistance
The invention discloses an on-line monitoring system for a direct-current power supply and a storage battery, which comprises an on-line monitor, a monitoring centre, a user terminal, a monitoring network and a management network, wherein the on-line monitor consists of a CPU, a storage battery voltage and internal resistance test unit, a direct-current charger characteristic test unit, a power supply unit, a communication unit, an input-output unit, a fault alarm unit, a reset unit and a storage unity, monitors a field storage battery and the direct-current charger online and transmits monitoring data to the monitoring centre through the monitoring network; the monitoring centre is a large-scale server, which receives the monitoring data transmitted from the on-line monitor and performs storage management on the monitoring data in a large-scale database mode; the system responses various commands of the user terminal, and receives the commands of the user terminal to perform various controls on the on-line monitor installed on-site.
Owner:PLUKE TECH
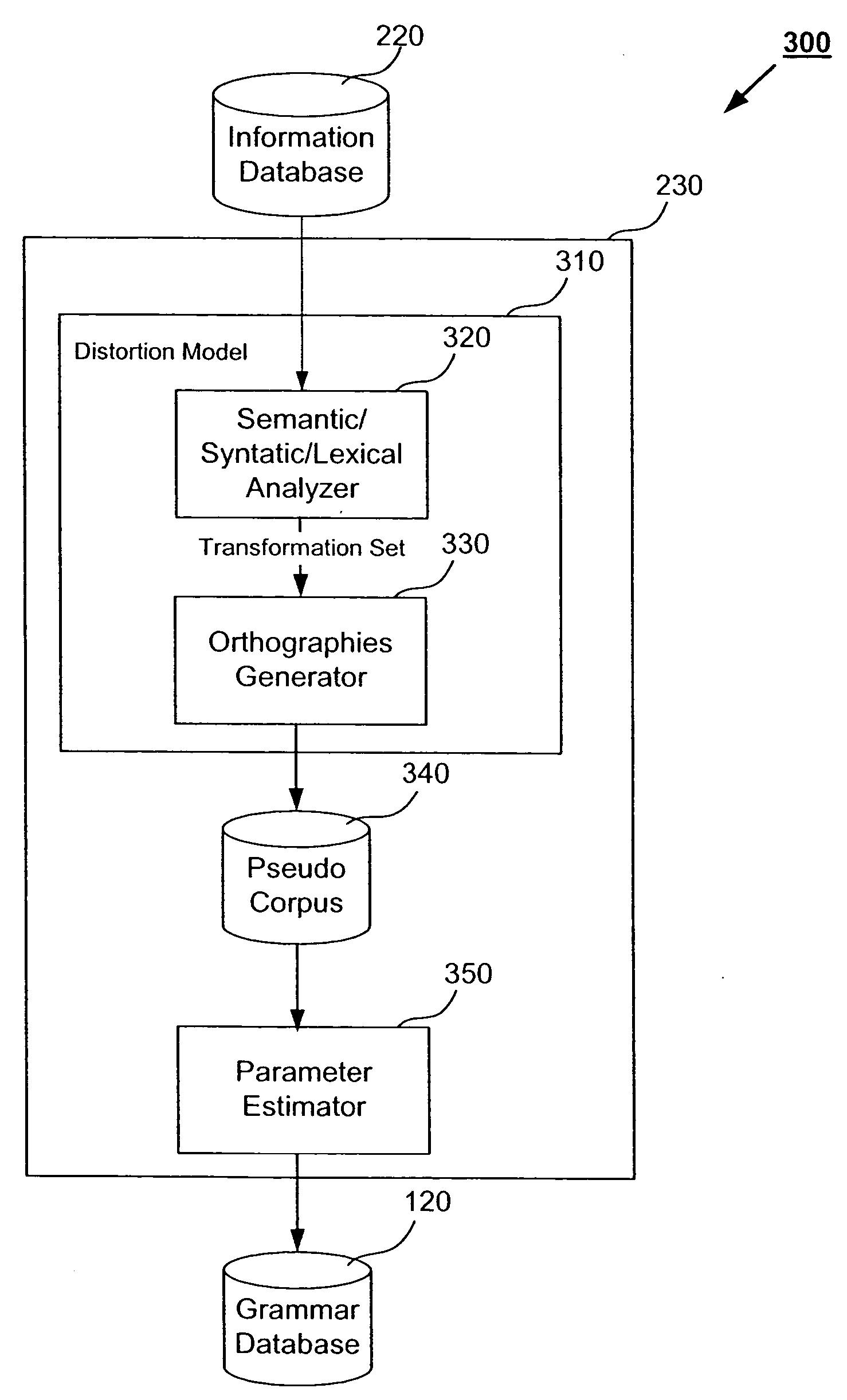
System and method for a spoken language interface to a large database of changing records
Embodiments of the present invention provide a spoken language interface to an information database. A plurality of word N-grams from each entry in the information database may be generated. A corresponding probability score for each word N-gram included in the plurality of word N-grams may also be generated. Any one word N-gram from the plurality of word N-grams may be included in a distorted version of the entry generated based on a transformation rule. Duplicate word N-grams from the plurality of word N-grams generated from each entry in the information database may be identified. Corresponding probability scores for the identified duplicate word N-grams may be accumulated. One of the duplicate word N-grams and the corresponding accumulated probability score may be stored in a grammars database.
Owner:TELELOGUE
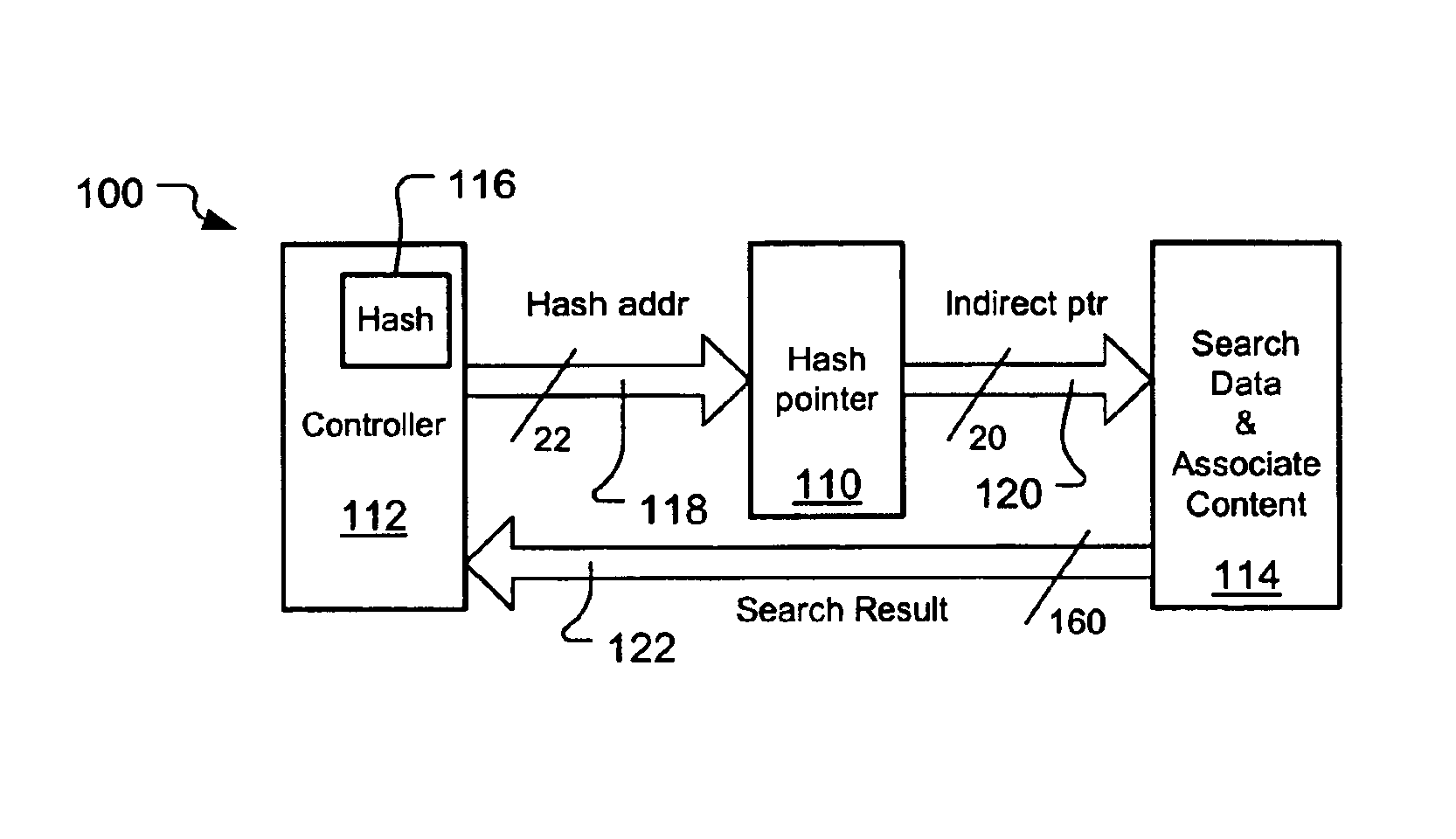
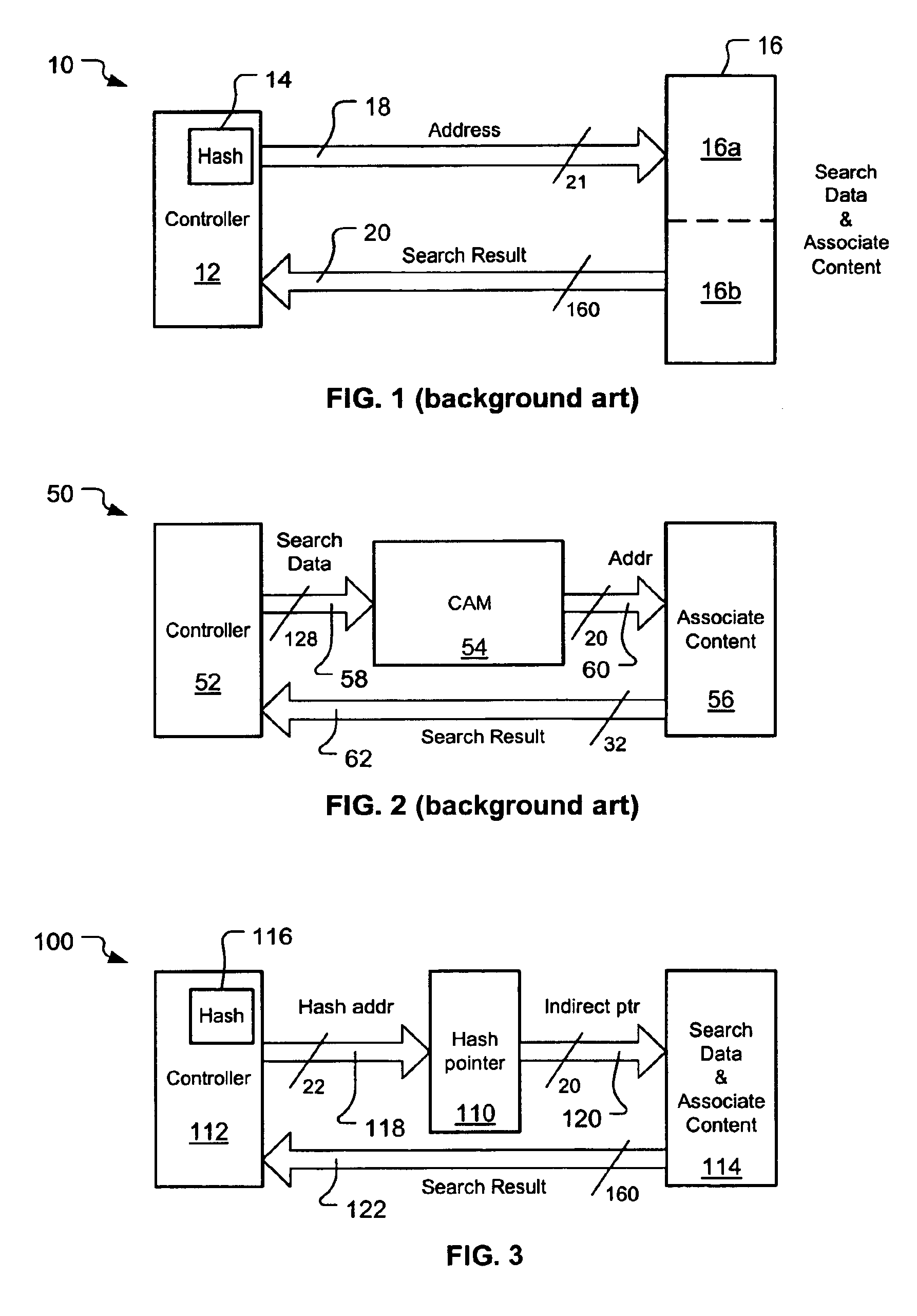
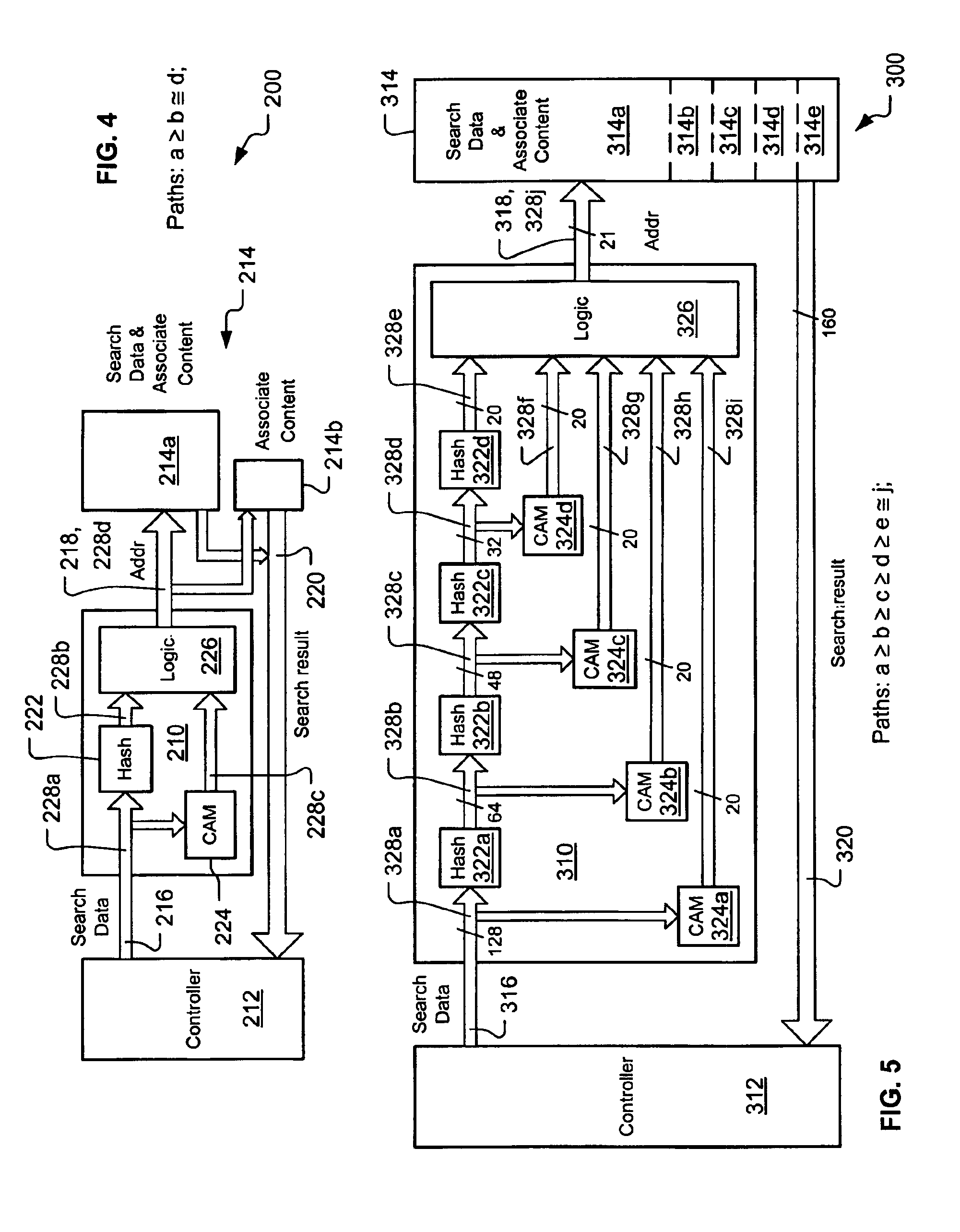
Large database search using content addressable memory and hash
InactiveUS6889225B2Improve memory utilizationReduce bus widthData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalLogic cellTheoretical computer science
A hash-CAM (H-CAM) which may work with a controller and a memory containing a database of either search values and associate content or associate content by itself The H-CAM includes at least one set of paired hash units and CAM units and at least one logic unit. The CAM units hold values known to cause hash collisions in the respectively paired hash units, and the logic unit prioritizes the hash and CAM unit outputs to a single address value usable to access the memory and obtain a search result at the controller that is not the result of a hash collision. The H-CAM may optionally include a search data storage to store the search values, so that they need not be stored in the memory, and a comparator to determine and handle newly determined hash collisions.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
System and method for generating automatic user interface for arbitrarily complex or large databases
InactiveUS8161081B2Natural, powerful, and easy-to-useData processing applicationsWeb data indexingDrill downSoftware system
A software system automatically and dynamically generates a fully functional user interface (UI) based upon, and connected directly to, an underlying data model (as instantiated within a relational database management system (RDBMS)). The UI derives from an automated interrogation of the RDBMS, and comprises all mode displays (e.g., browse, search, edit, add) for all tables, and a full complement of mechanisms—integrated directly into the mode displays—for representing, navigating, and managing relationships across tables, regardless of the complexity of the underlying RDBMS schema. It utilizes a hierarchical “context stack” for suspending the working state of a particular table while “drilling down” to work with related-table information and return relevant changes to the base table. The embodiment further provides methods to enhance and extend the internal representation of table structures, constraints, relationships, and—special requirements (“business rules”) for improved revelation of the schema structure through external interrogation.
Owner:KAUFMAN MICHAEL PHILIP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com