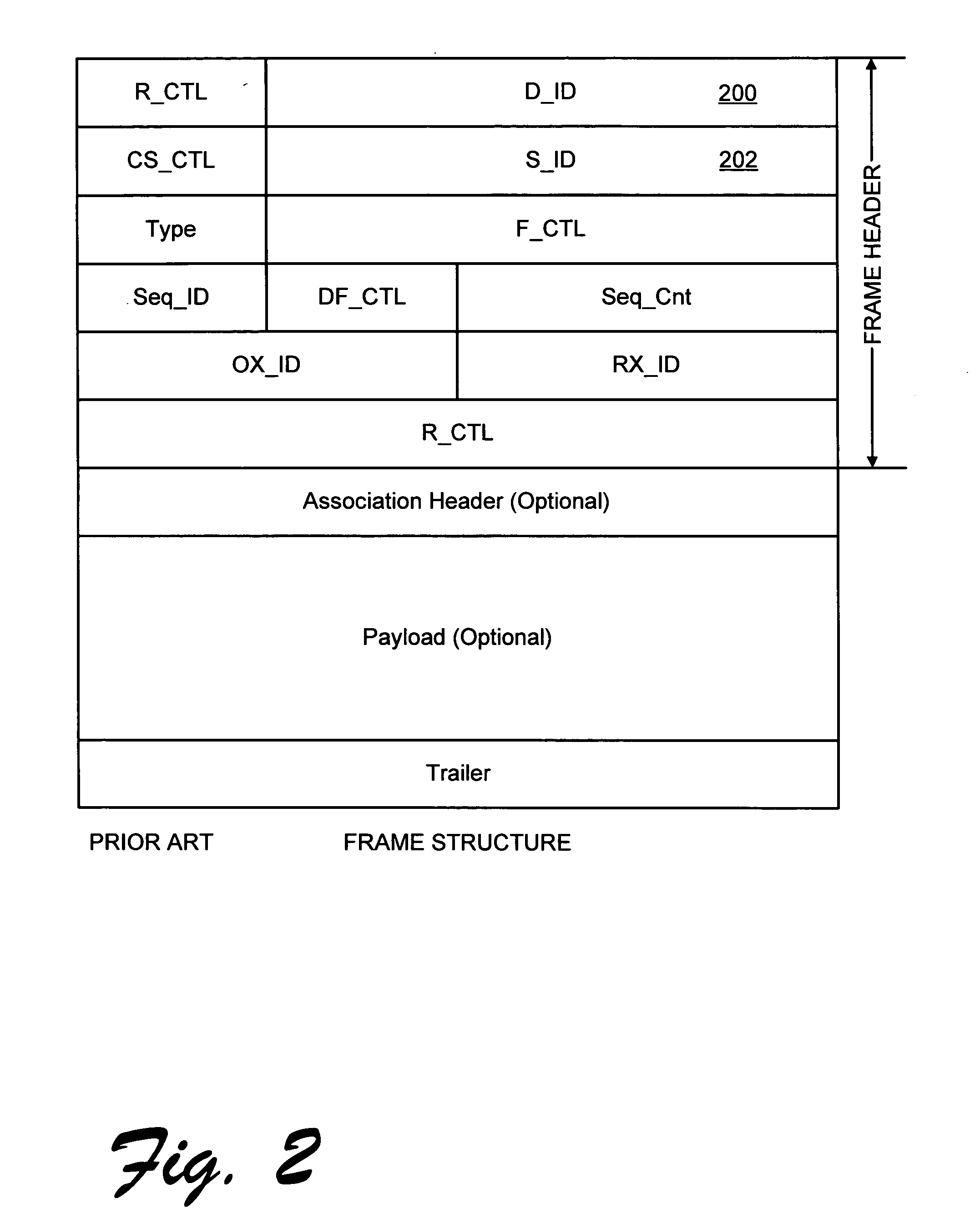
Patents
Literature
151 results about "S/KEY" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
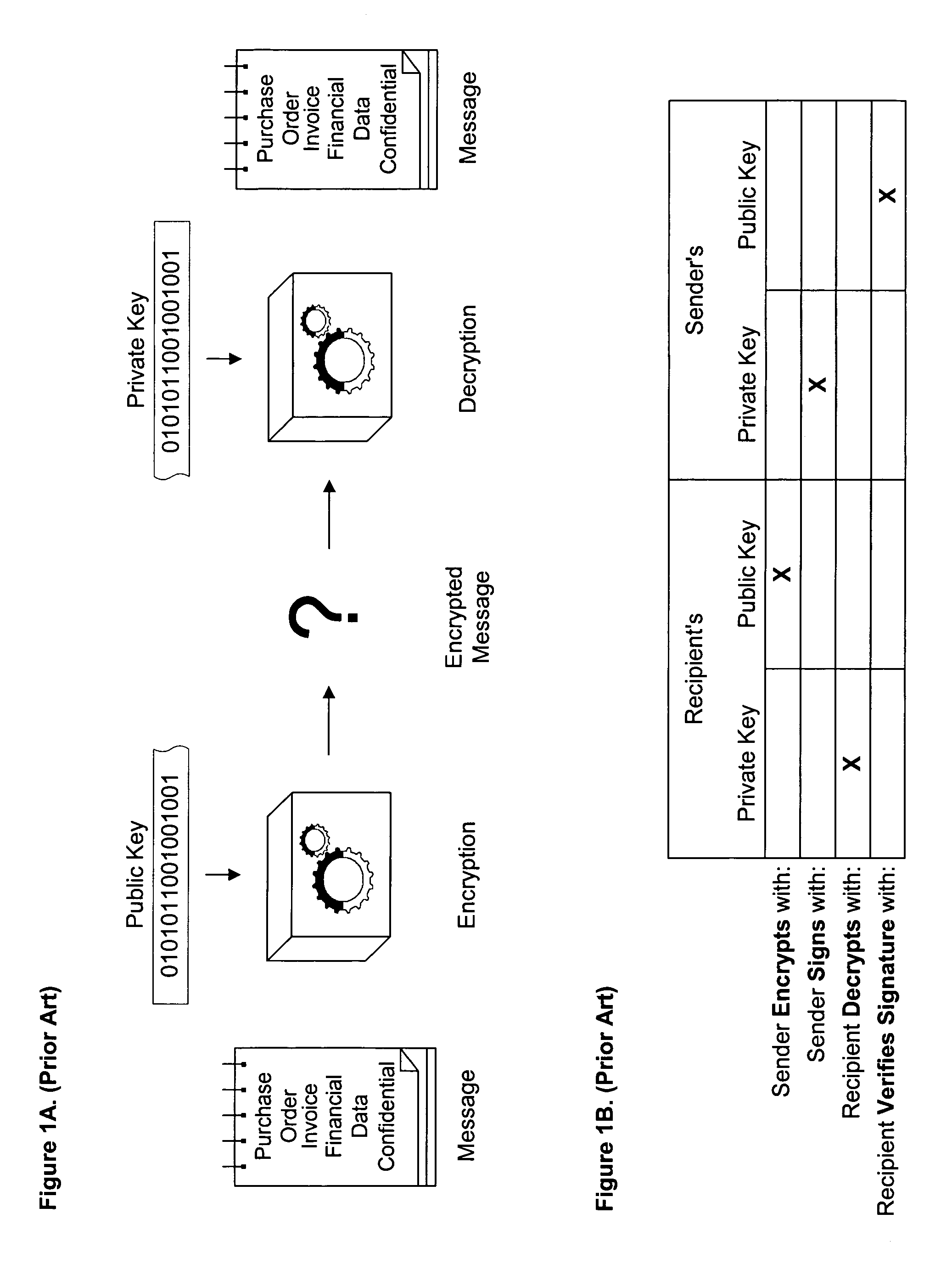
S/KEY is a one-time password system developed for authentication to Unix-like operating systems, especially from dumb terminals or untrusted public computers on which one does not want to type a long-term password. A user's real password is combined in an offline device with a short set of characters and a decrementing counter to form a single-use password. Because each password is only used once, they are useless to password sniffers.
Content security layer providing long-term renewable security
InactiveUS20020141582A1Unparalleled flexibilityIncrease sampling rateTelevision system detailsKey distribution for secure communicationAttackMediaFLO
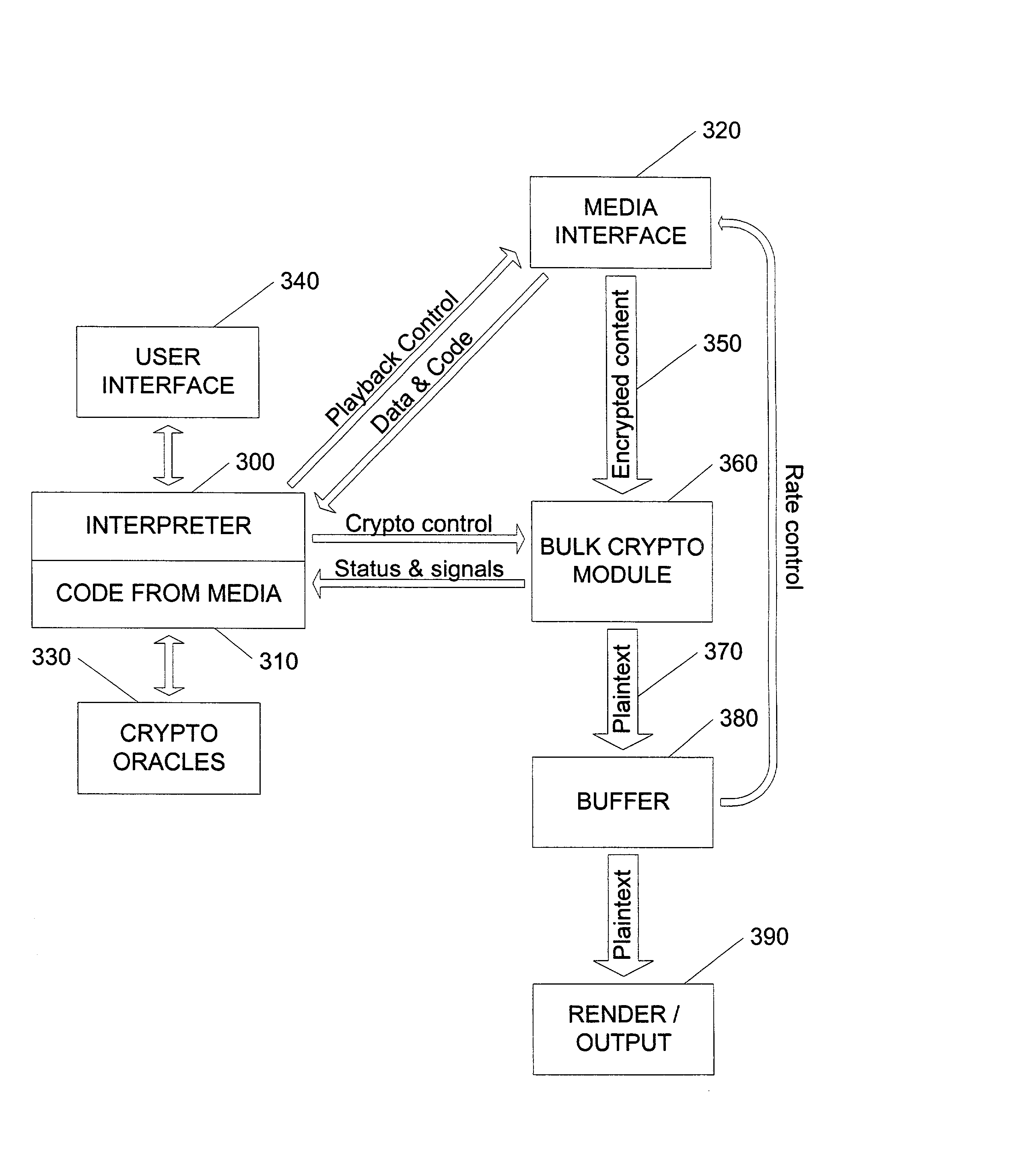
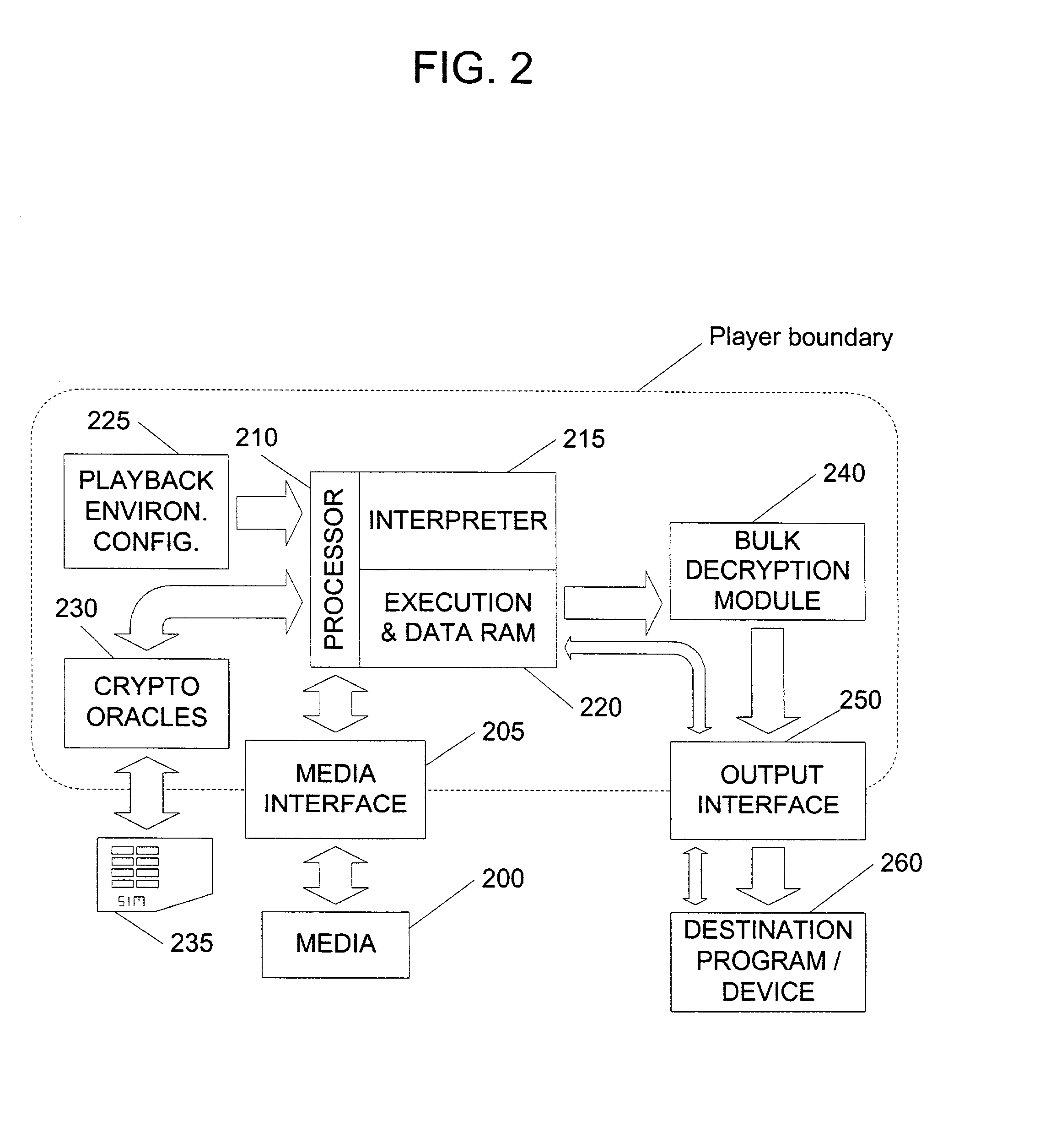
In an exemplary embodiment, digital content is mastered as a combination of encrypted data and data processing operations that enable use in approved playback environments. Player devices having a processing environment compatible with the content's data processing operations are able to decrypt and play the content. Players can also provide content with basic functions, such as loading data from media, performing network communications, determining playback environment configuration, controlling decryption / playback, and / or performing cryptographic operations using the player's keys. These functions allow the content to implement and enforce its own security policies. If pirates compromise individual players or content titles, new content can be mastered with new security features that block the old attacks. A selective decryption capability can also be provided, enabling on-the-fly watermark insertion so that attacks can be traced back to a particular player. Features to enable migration from legacy formats are also provided.
Owner:ROVI SOLUTIONS CORP
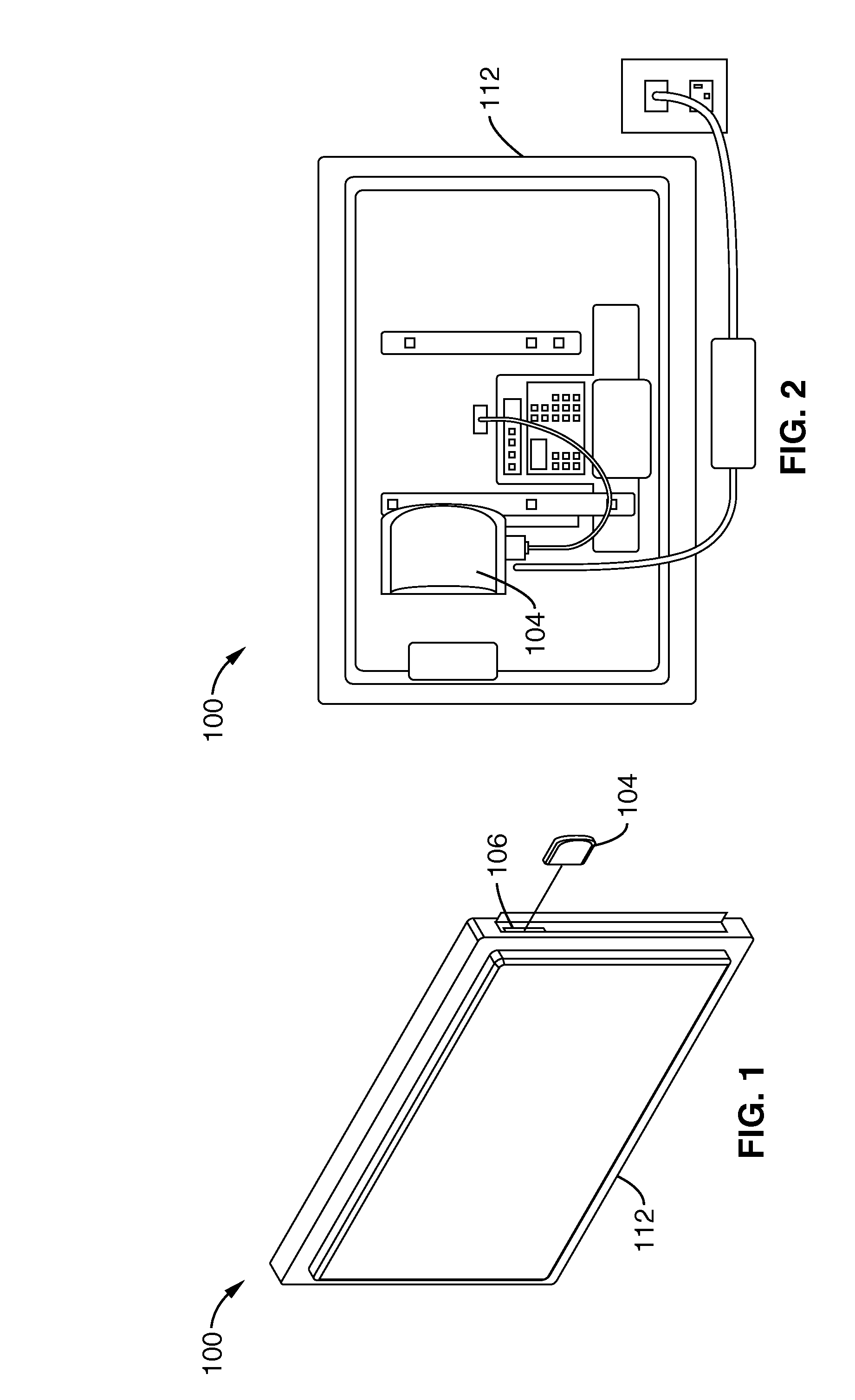
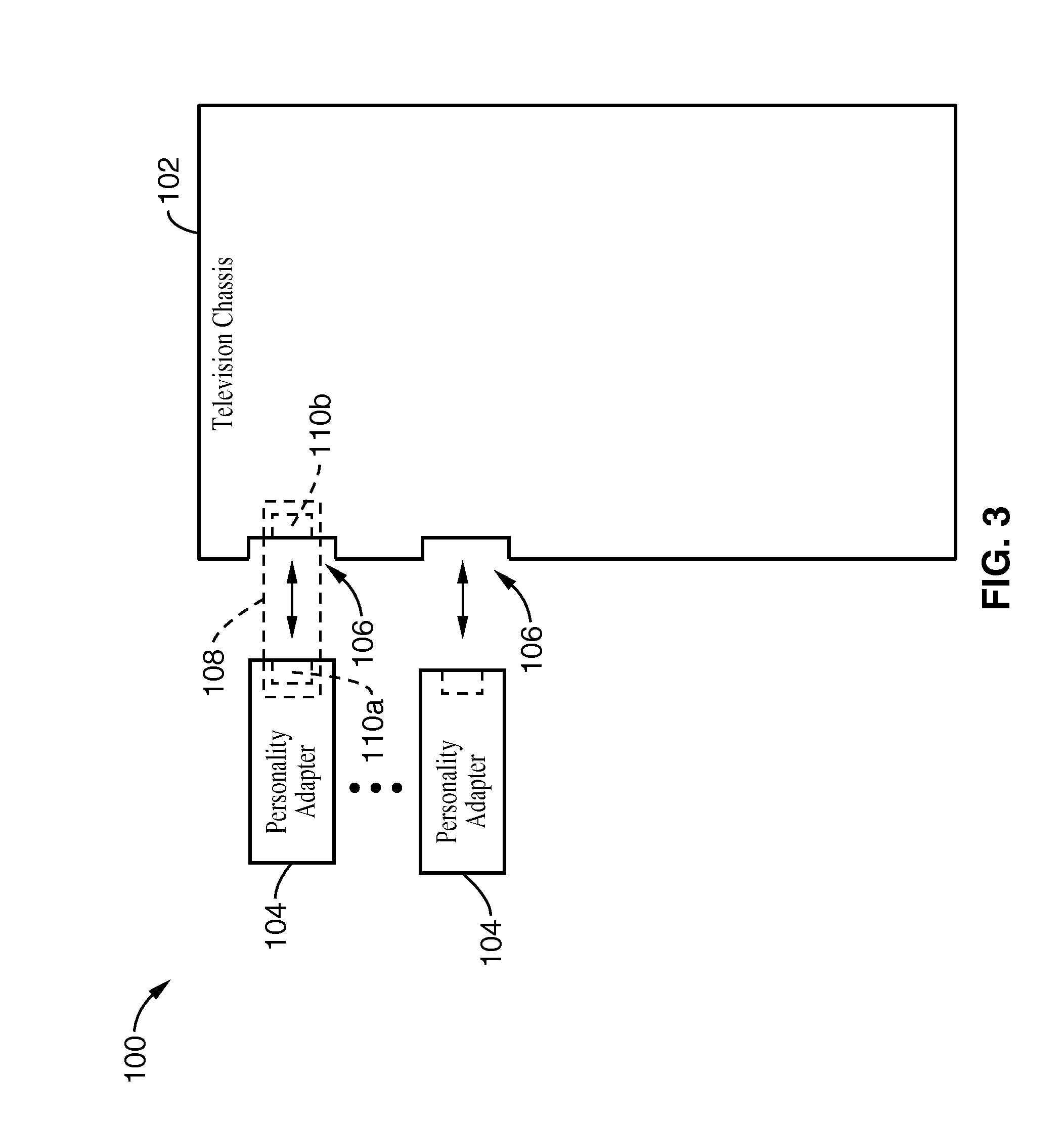
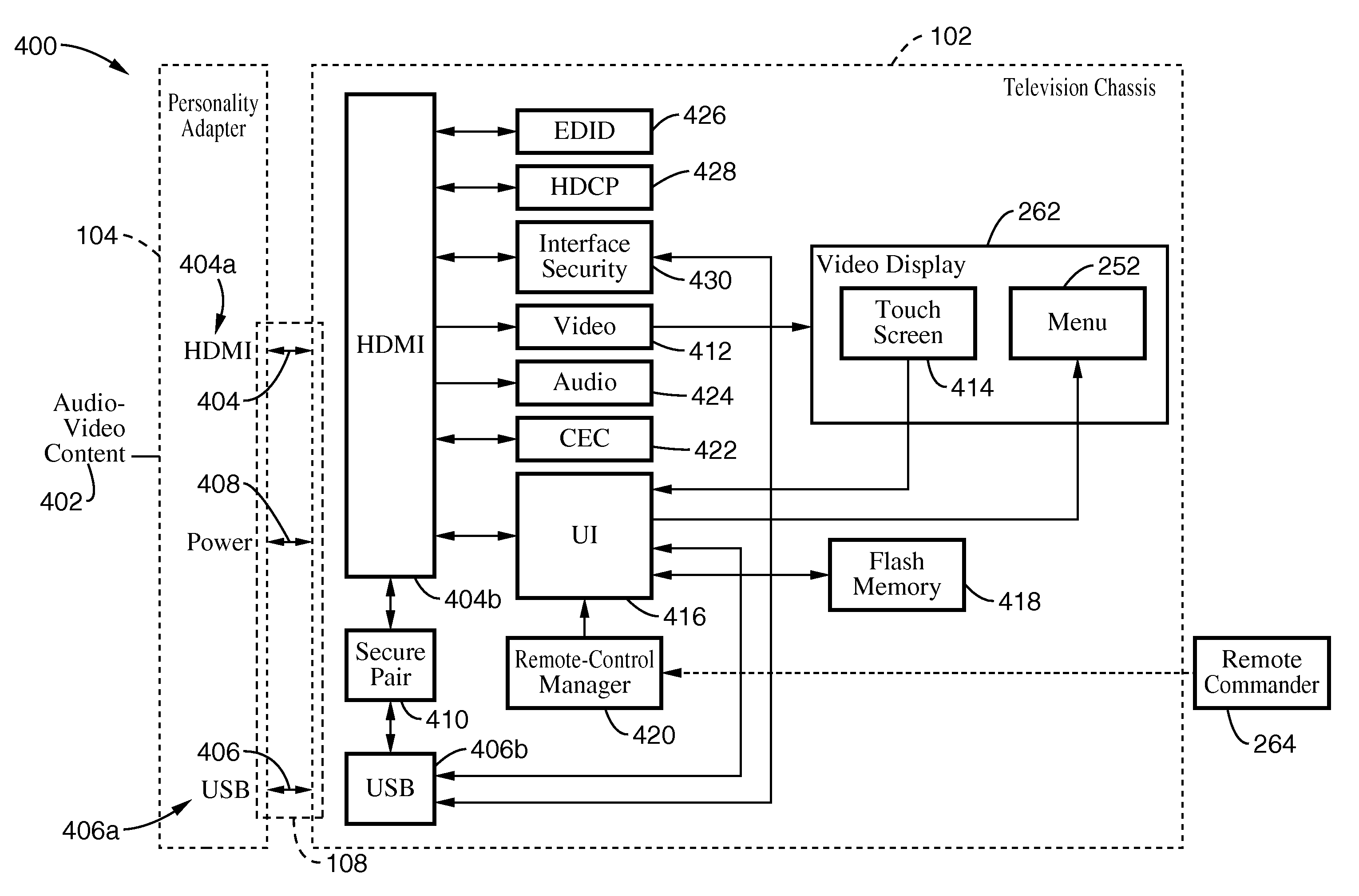
Automatically reconfigurable multimedia system with interchangeable personality adapters
InactiveUS20080134237A1Function increaseTelevision system detailsAnalogue secracy/subscription systemsSoft keyHDMI
Owner:SONY CORP +1
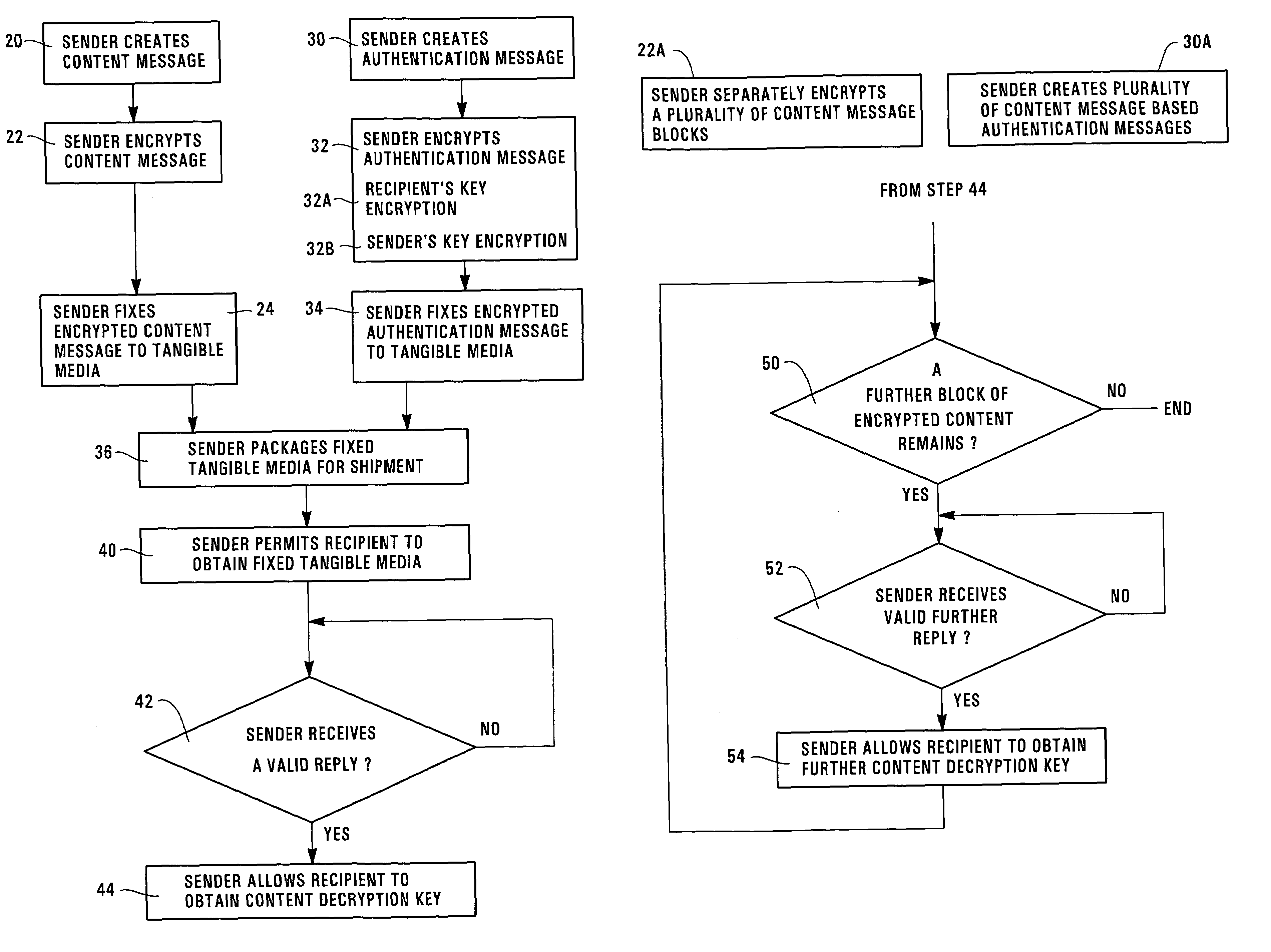
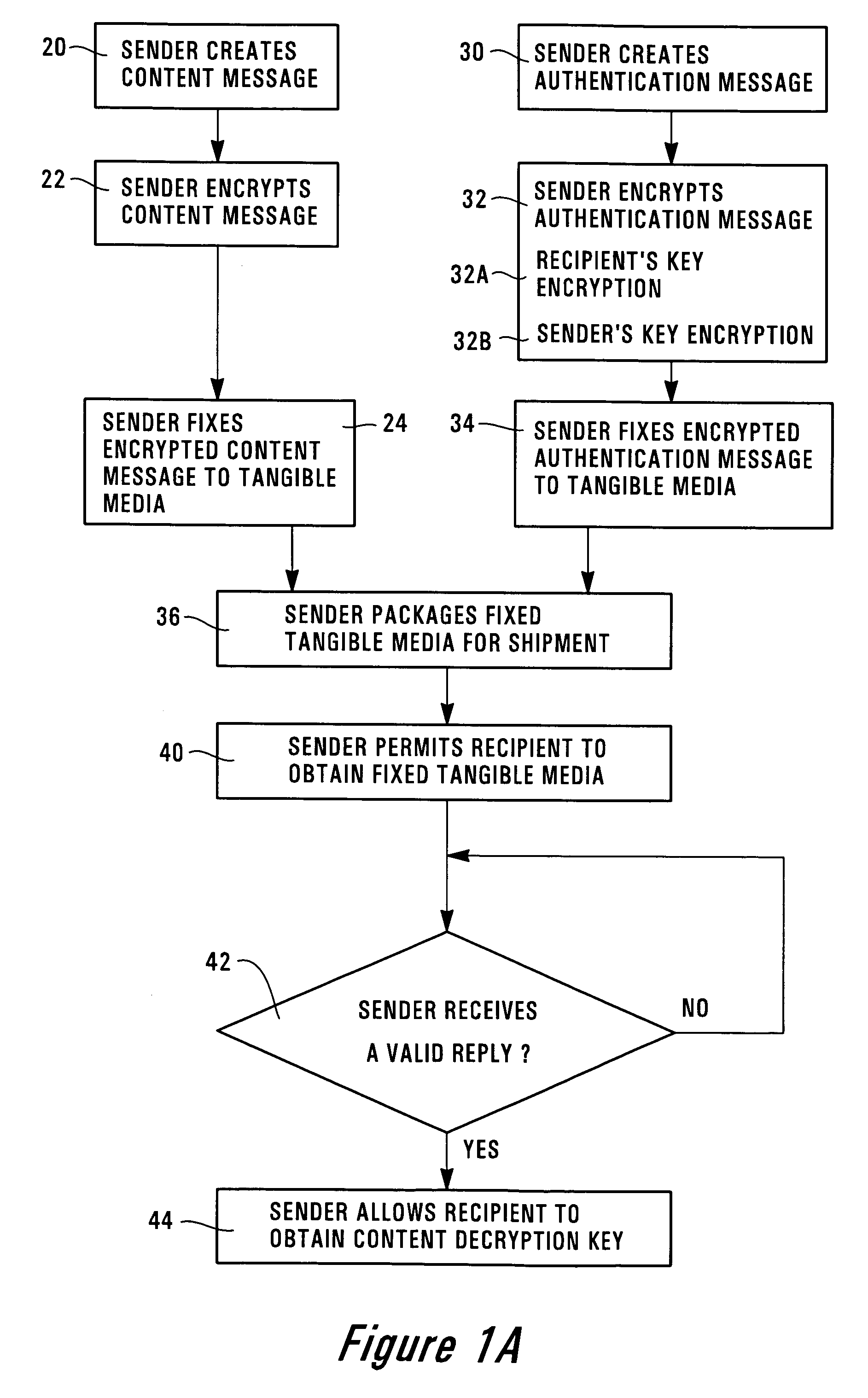
Digital signatures for tangible medium delivery
InactiveUS7165268B1Inhibitory contentDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationDigital signatureS/KEY
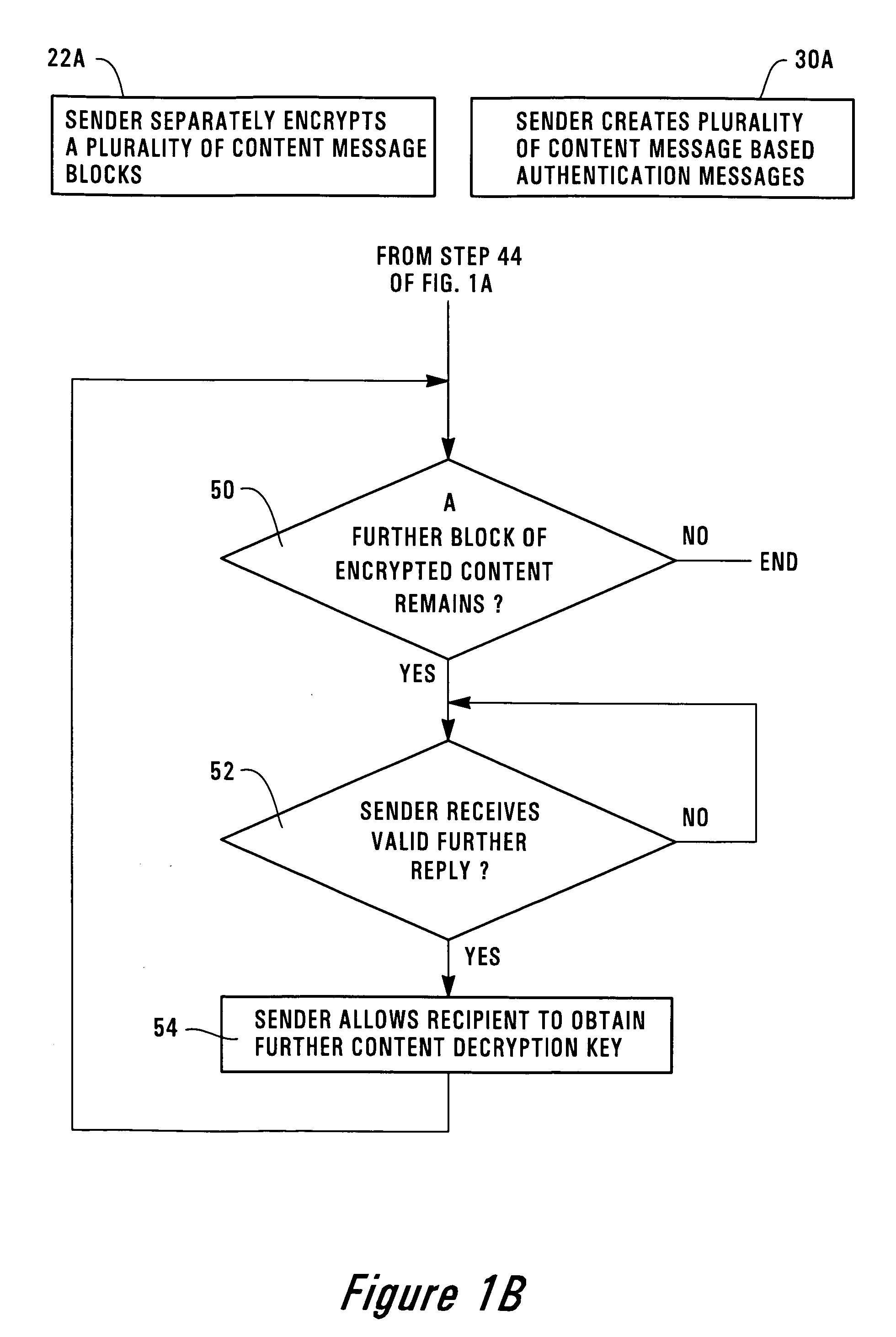
The invention provides a method for a sender to send a message on a tangible medium and ensure that it is privacy protected until verification that the medium has been received by the authorized recipient. The invention provides a method in which a sender creates an encrypted content message that may be decrypted using a content decryption key that is unknown to the authorized recipient. The sender creates an encrypted authentication message that may be decrypted using a recipient's key that is known to the authorized recipient but is unknown to others, except perhaps to the sender. The sender fixes the encrypted content message and the encrypted authentication message onto a tangible medium and then permits the authorized recipient to obtain the tangible medium. The authorized recipient uses the recipient's key to decrypt the encrypted authentication message and then creates a valid reply that is based upon or which uses the decrypted authentication message. The authorized recipient sends the valid reply to the sender and upon verification that the reply is valid the sender allows the authorized recipient to obtain the content decryption key. With the content decryption key, the authorized recipient is able to decrypt the encrypted content message. The invention also includes an article of manufacture for sending an encrypted message from a sender to an authorized recipient using a method, of the invention.
Owner:HEWLETT PACKARD DEV CO LP
Virtual check
ActiveUS8332329B1Sufficient dataCryptography processingCharacter and pattern recognitionComputer hardwareS/KEY
Methods and systems for virtual checking are described. A virtual check is created by a payor's device and then sent to the payee's device. The payee can be another mobile device. The virtual check has many of the same features as a regular, paper check plus additional features only available in digital form. In an example, the data can be encrypted by either the banks key or the payor's key. Further encryption can occur between the payor's device and the payee's device, which can connect on a peer-to-peer network. The check can be an image with tag data. In an example, data can be encoded into the image itself. The virtual check can include populated data that cannot be changed by the payee. In an example, the virtual check application of the payee can automatically perform a funds availability check.
Owner:USAA
Digital content cryptograph and process
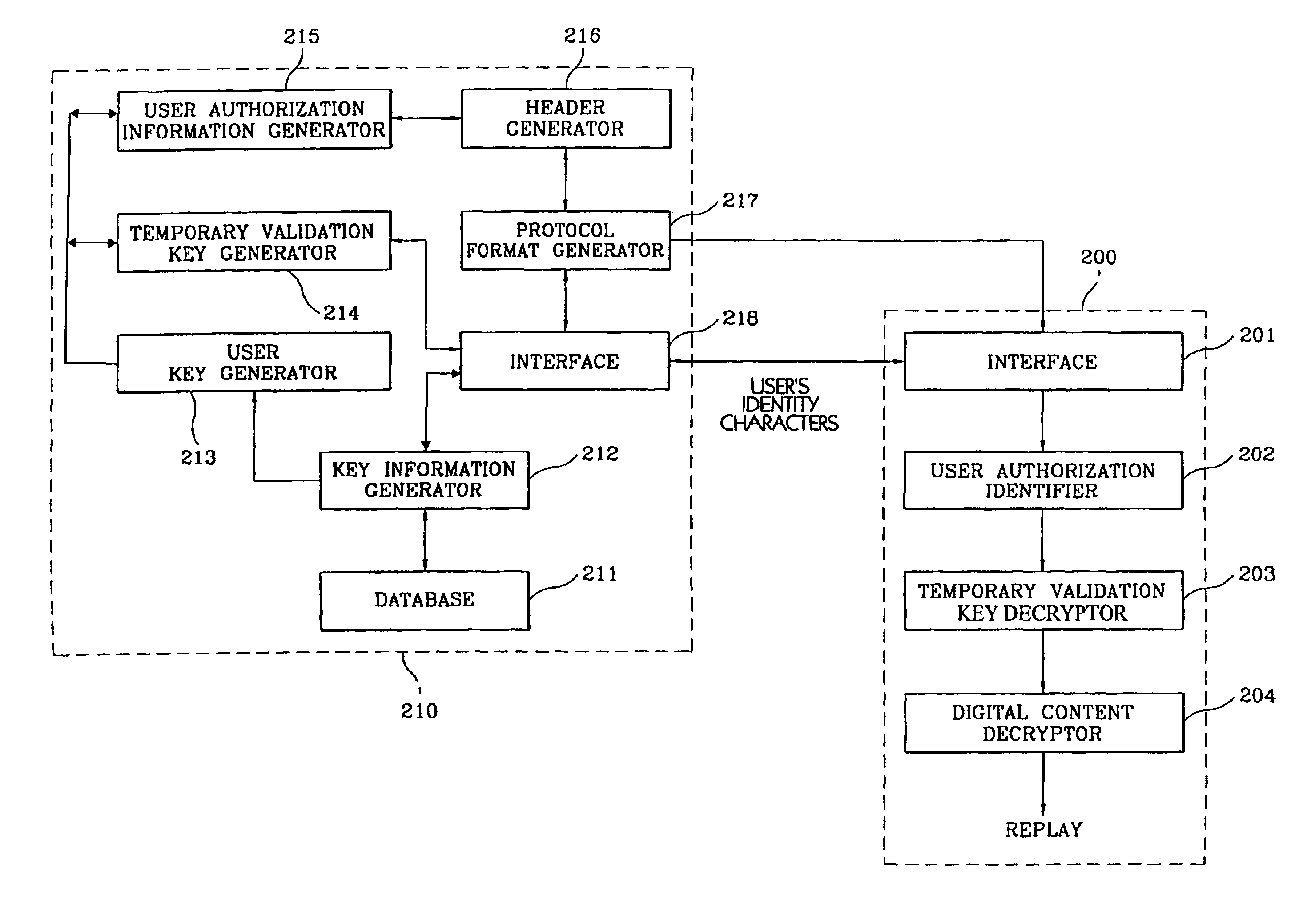
InactiveUS6892306B1Easy to optimizeLimited abilityKey distribution for secure communicationData processing applicationsDigital contentS/KEY
A digital cryptograph and encryption process encrypts and transmits in a digital format specific items of information requested by a user of a digital content transmission system by using key information, a user's key and a temporary validation key, to decrypt and replay the encrypted digital information at the user's terminal by using the key information and the user's authorization information. Each registered subscribing user is provided with unique key information. The user key is generated by applying the key information to a key generation algorithm. The temporary validation key that is created when the registered user accesses the server, is encrypted with the user key. The digital information is encrypted by using the temporary validation key in an encryption algorithm. The decryption algorithm allows the user to decrypt and replay the encrypted digital information upon receipt of the key information that has a one-to-one correspondence to the identity characters of the registered subscribing user.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Systems and methods for file access auditing
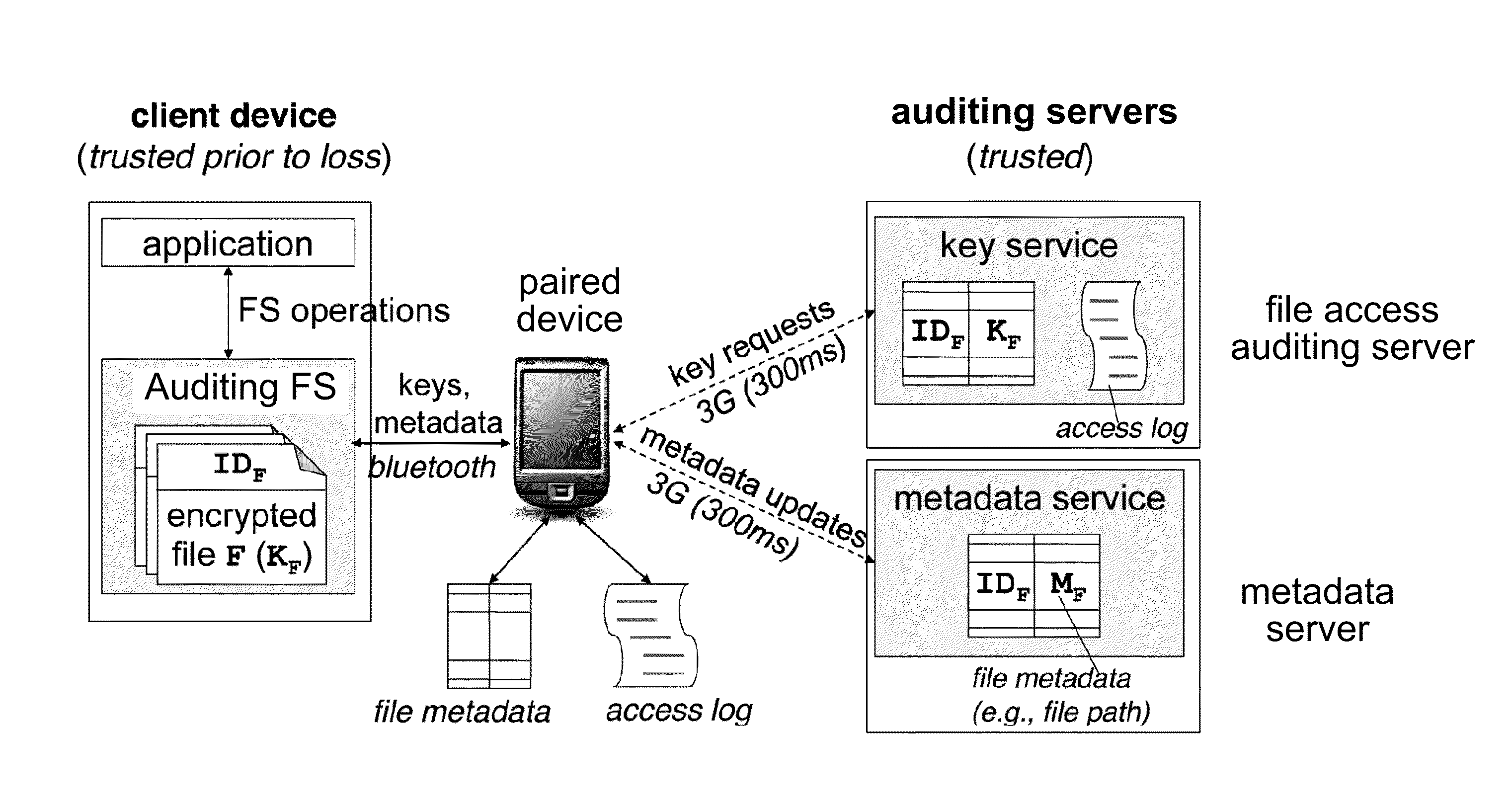
ActiveUS20130198522A1Digital data protectionInternal/peripheral component protectionFile systemS/KEY
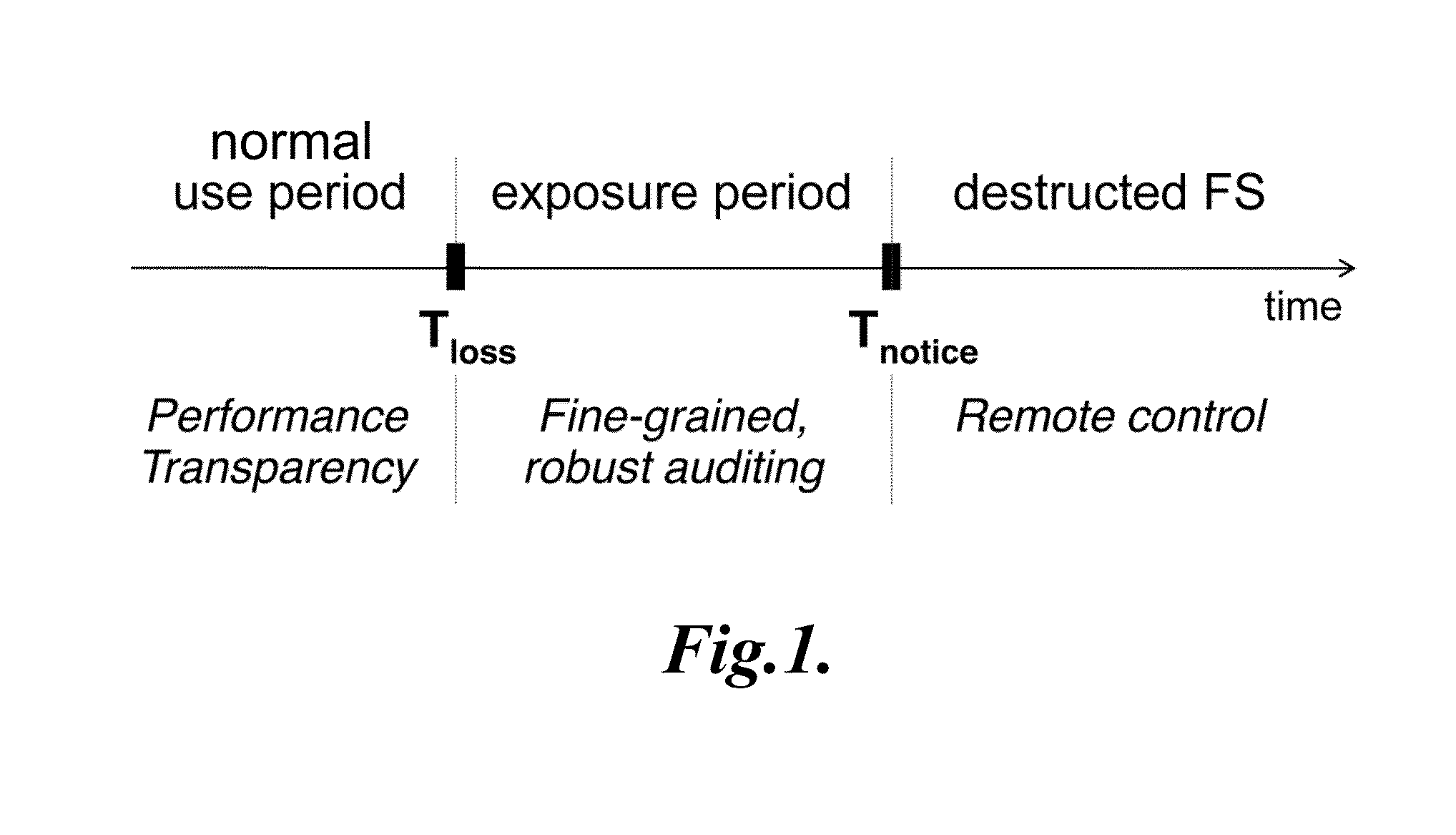
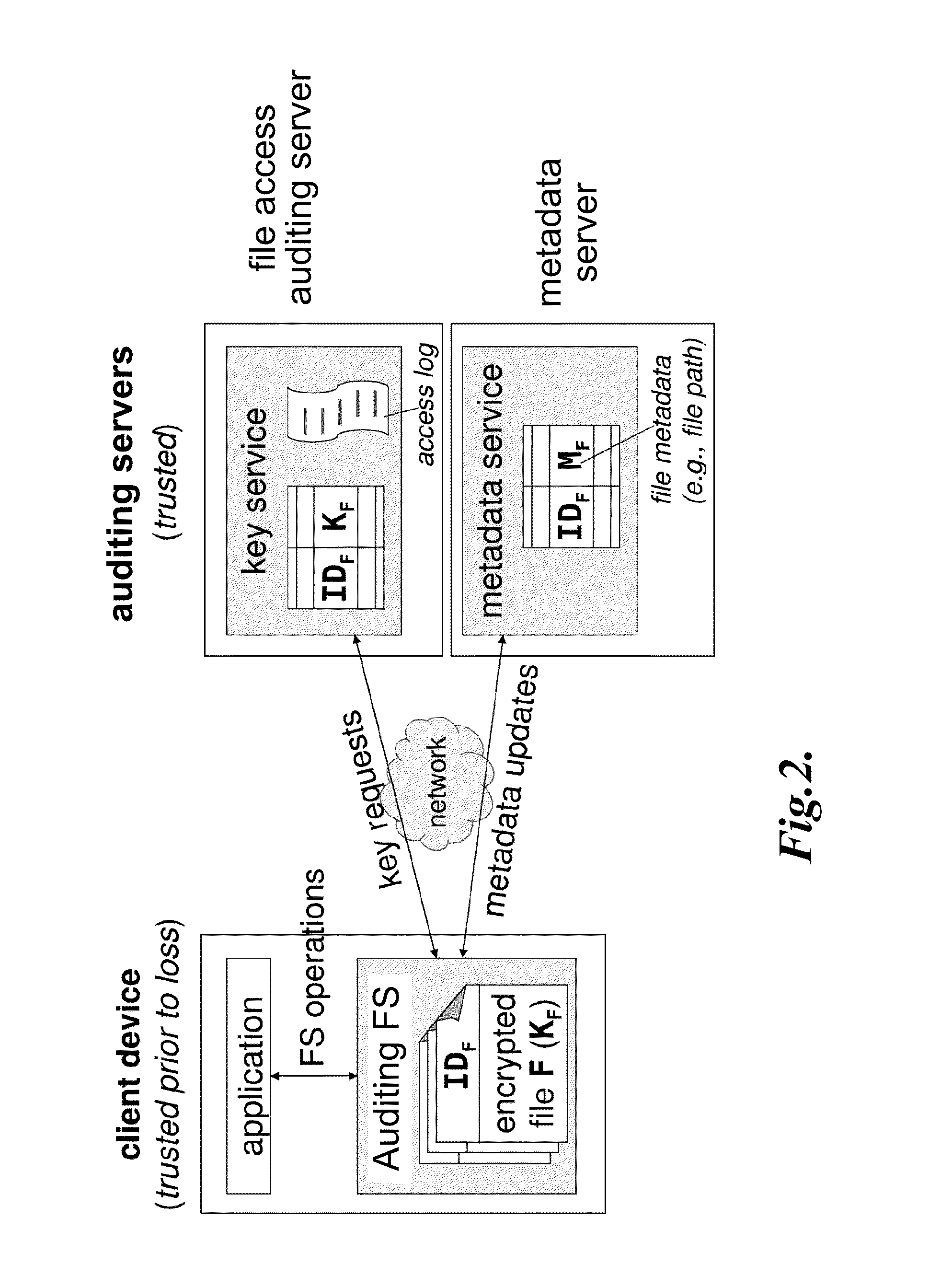
Systems and methods for providing an auditing file system for theft-prone devices are disclosed. The auditing file system supports fine-grained file auditing: a user may obtain reliable, explicit evidence that no files have been accessed after a device's loss. A user may also disable future file access after a device's loss, even in the absence of device network connectivity. In one embodiment, files are encrypted locally but the encryption keys are stored remotely, so that an audit server is queried for encryption keys to access protected files. By configuring the audit server to refuse to return a particular file's key, the user can prevent new accesses after the device is lost.
Owner:UNIV OF WASHINGTON CENT FOR COMMERICIALIZATION
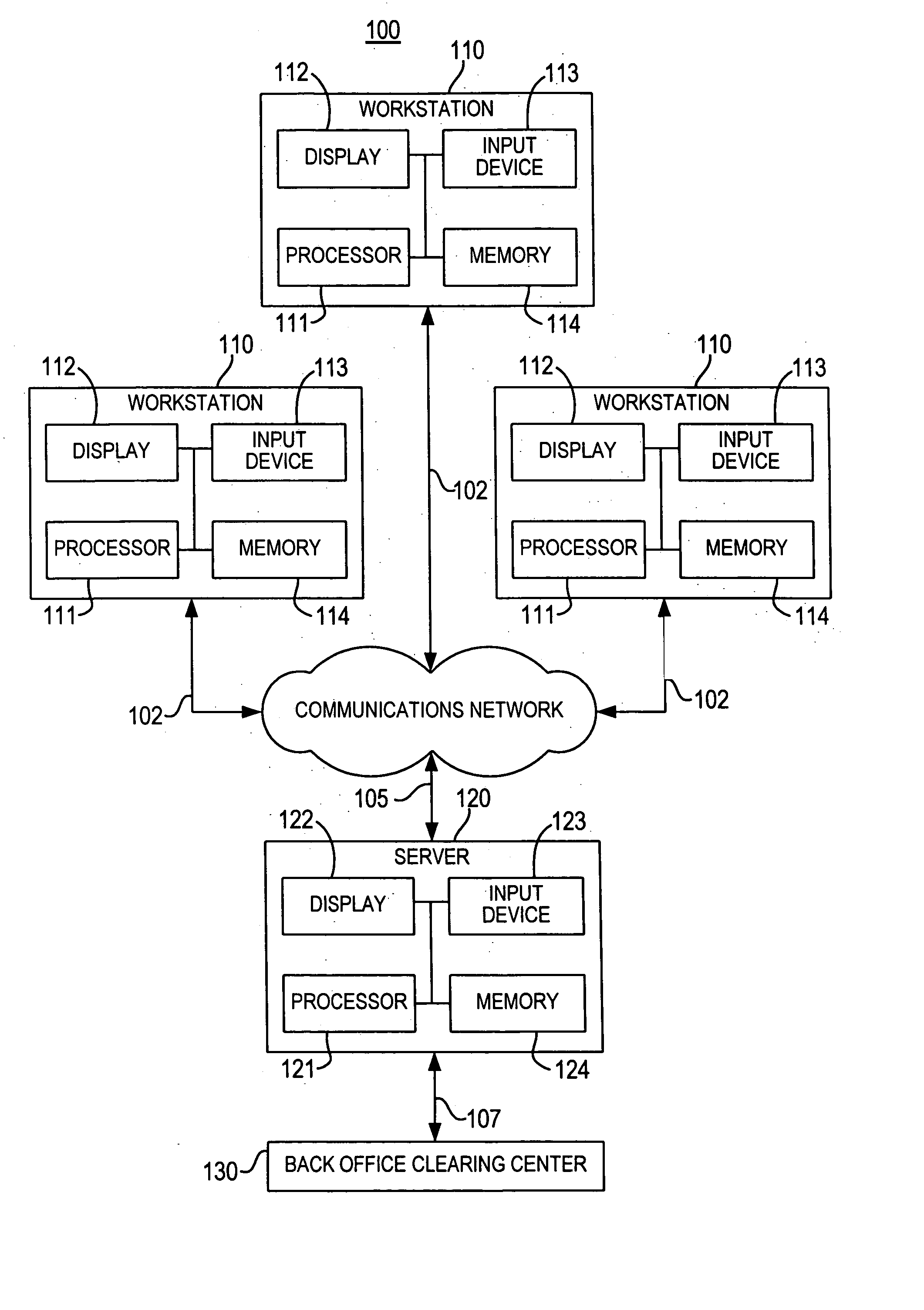
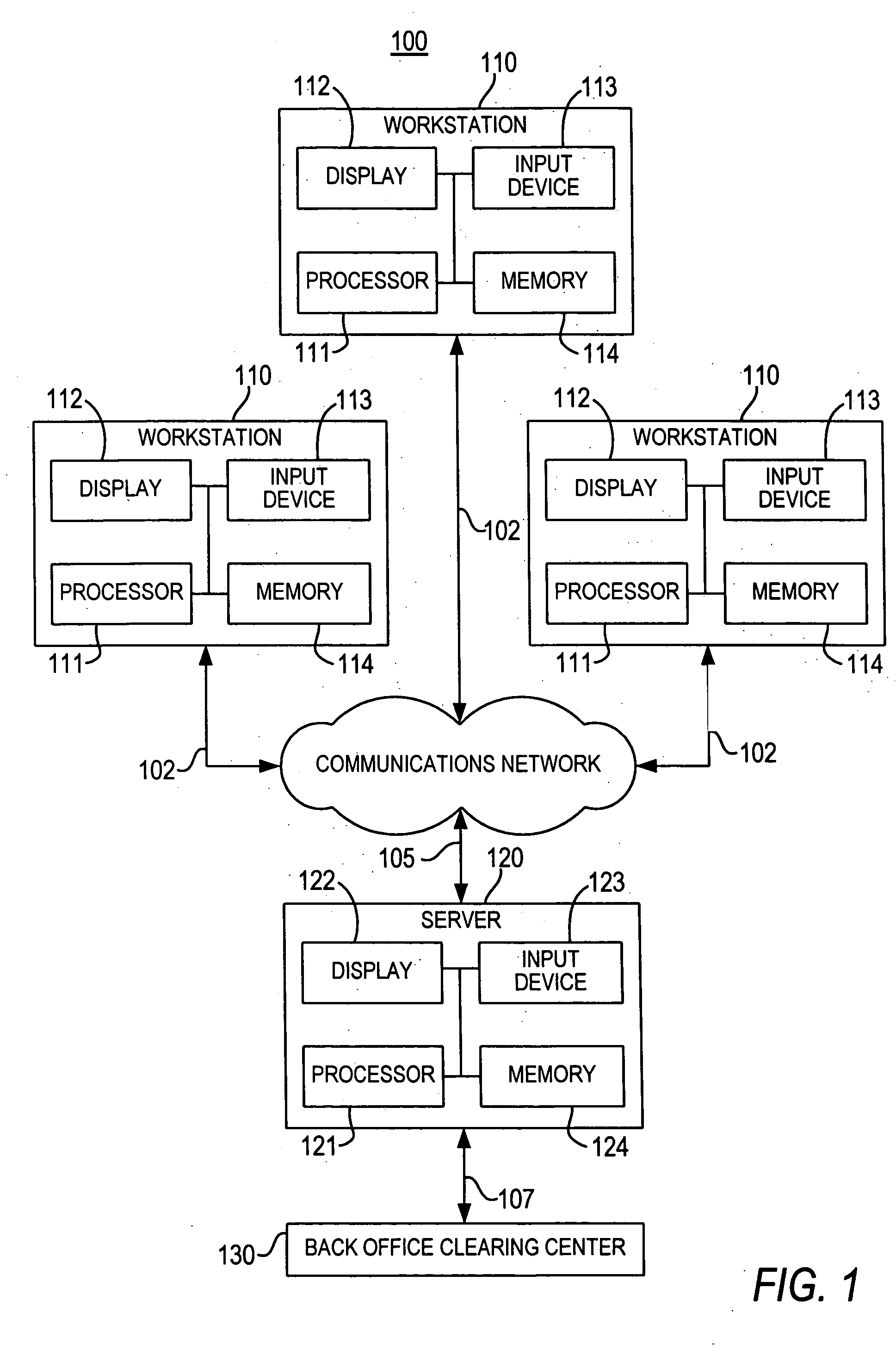
Concurrent server and method of operation having client-server affinity using exchanged client and server keys
InactiveUS6195682B1Eliminate needMultiple digital computer combinationsPayment architectureS/KEYInformation networks
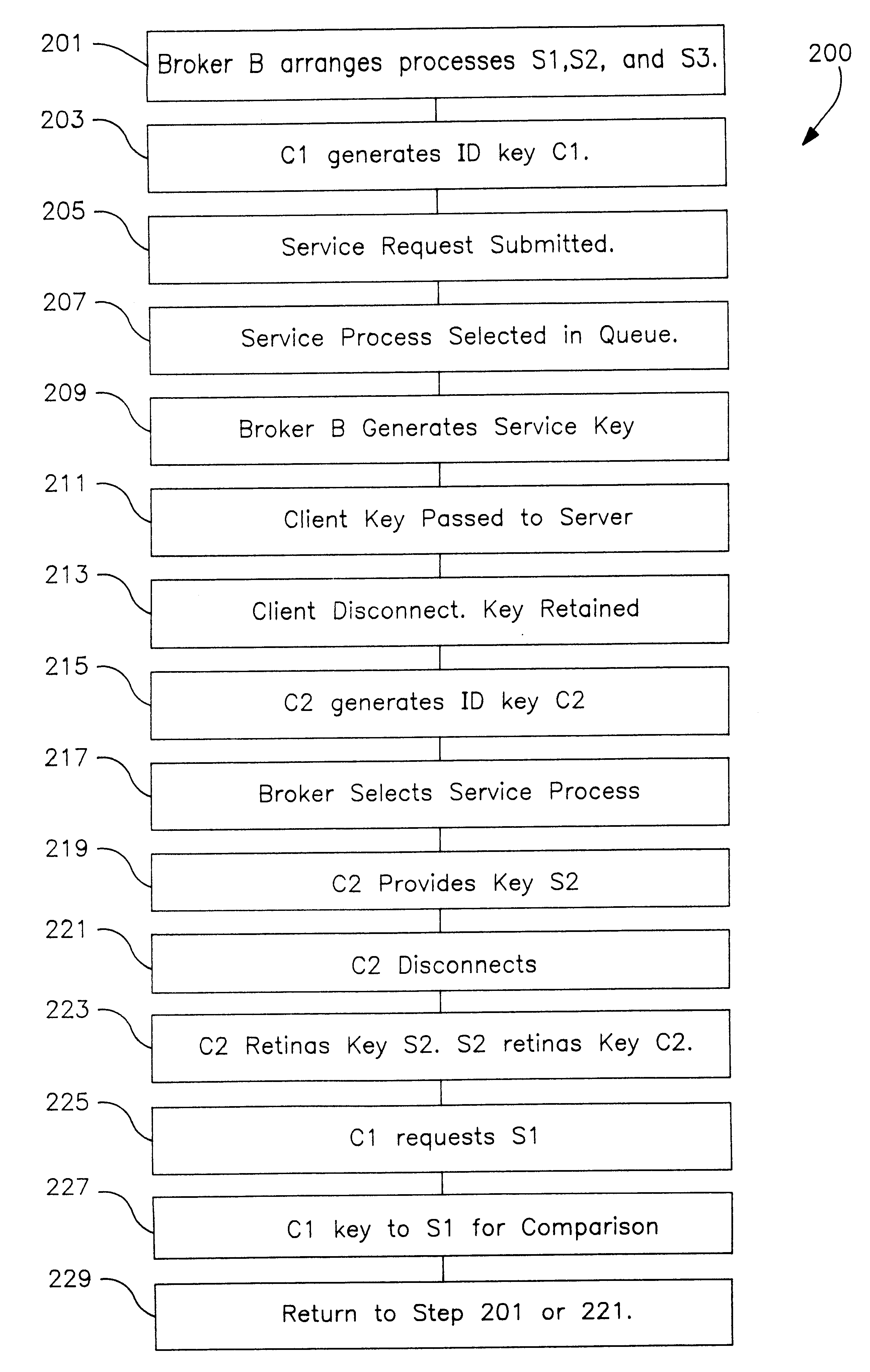
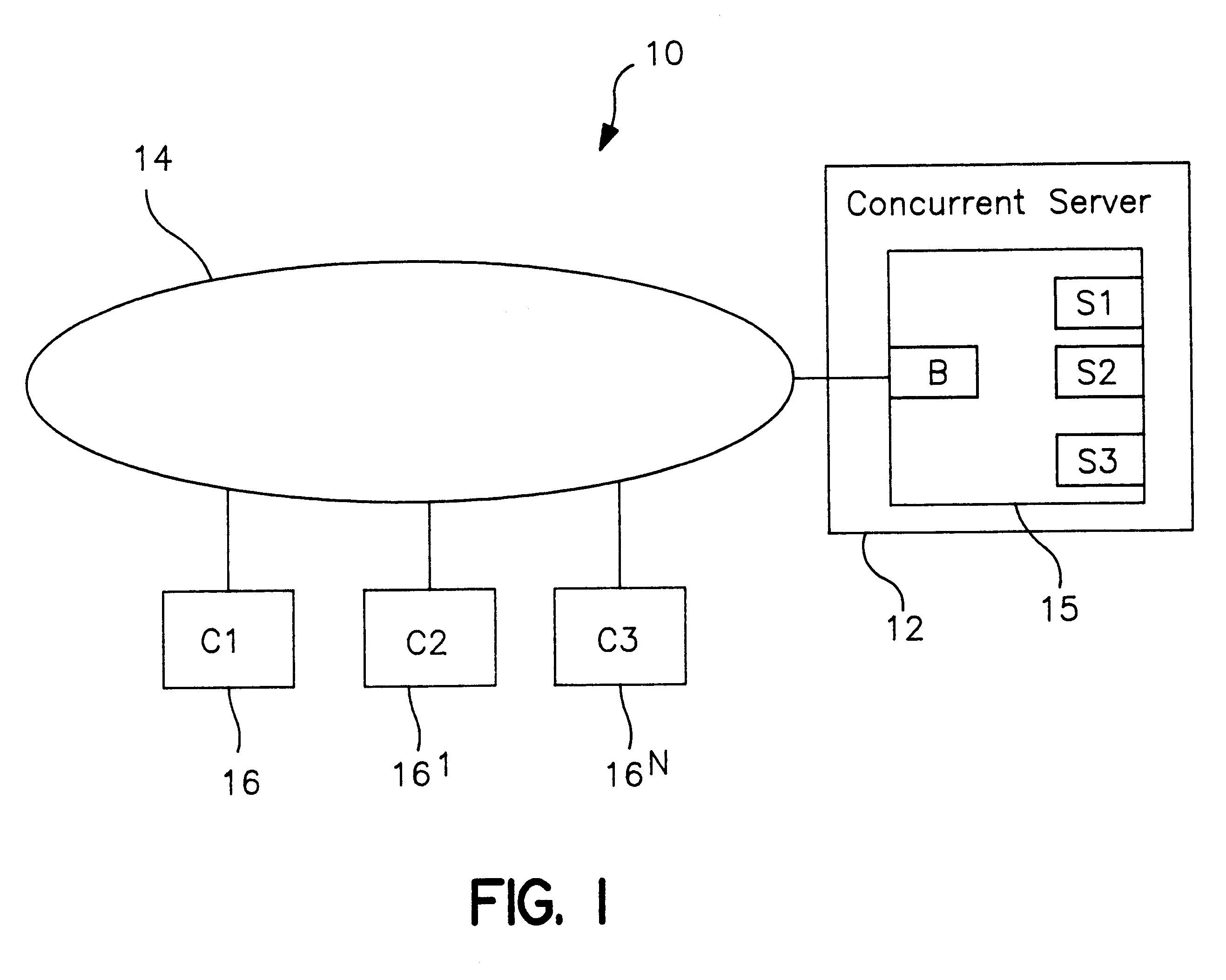
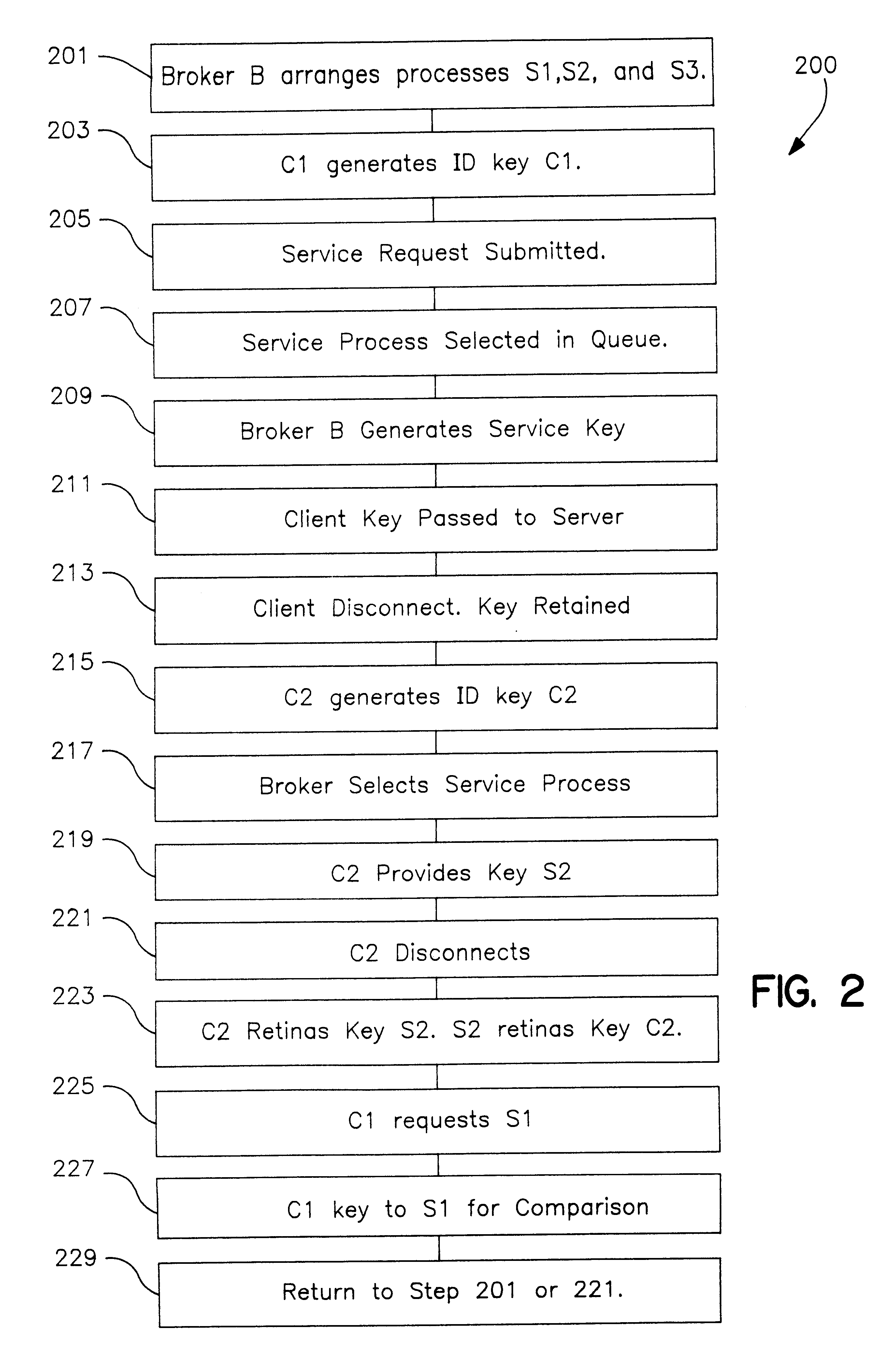
In a distributed information network, a broker server is coupled to a plurality of child servers and to a plurality of clients in the network. The broker server connects clients to a child server in a queue on a FIFO basis and provides the client with a key identifying the child server. The client provides the server with a copy of its key at the time of the initial service request. Both the child server and the client retain a copy of the other's key upon disconnect. The child server returns to the bottom of the queue after disconnect. On a subsequent client service request, the client includes the child server key in the service request and the broker automatically re-connects the client to the child server wherever S1 may be in the queue, provided the child server is not busy serving other clients. When reconnected, the client send its key to the child server which compares the key to the retained copy of the client key. If the keys match, the child server does not refresh and reload the client state data which improves server performance. If the child server is not available, the broker assigns the client to the child server at the top of the queue. The client may also be an intermediate server for other or first tier clients, in which case the intermediate server forwards the server keys to the first tier clients for service requests to the child server.
Owner:IBM CORP
Encryption messaging system
ActiveUS8837739B1Easy to useRaise the level of confidentialityKey distribution for secure communicationPublic key for secure communicationKey exchangeS/KEY
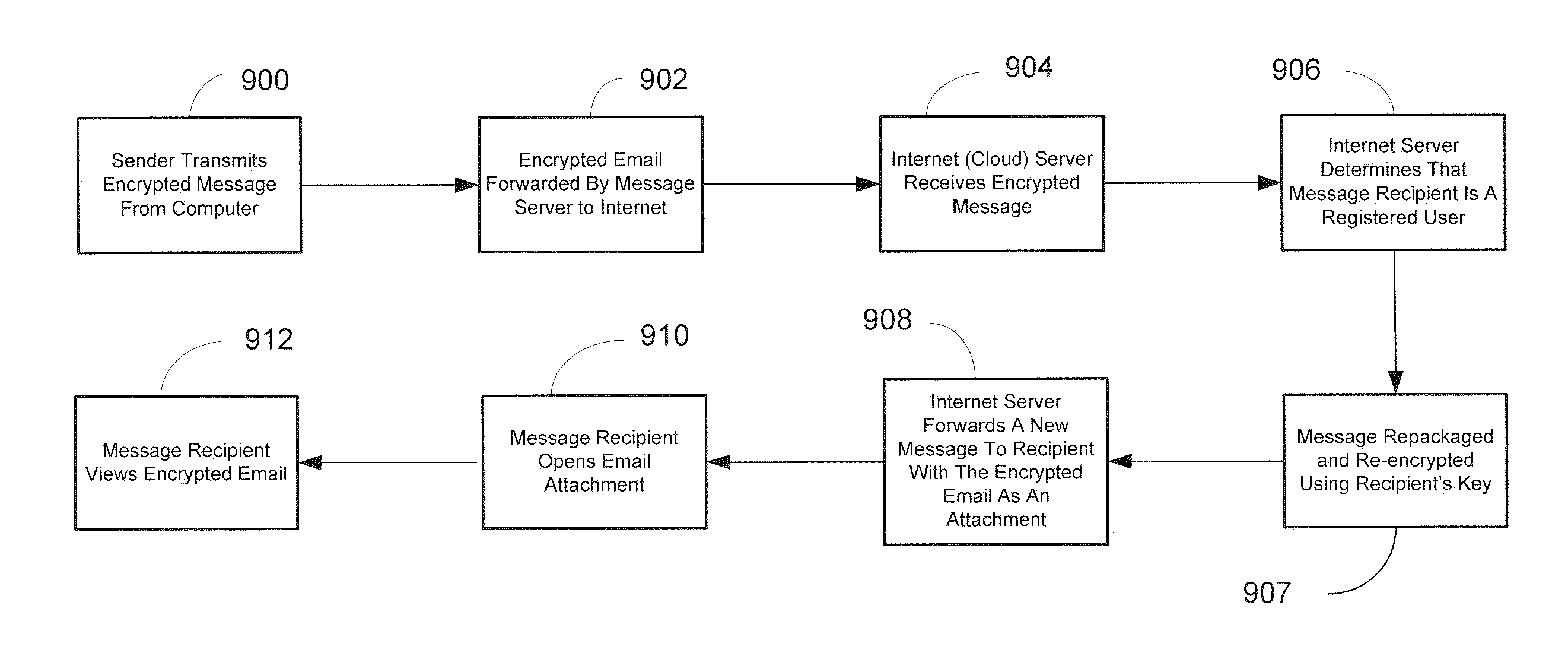
This invention provides a user friendly, email encryption system allowing users to send and receive encrypted messages for registered and unregistered users. Encrypted messages can be sent to registered or non-registered users by transmitting the encrypted message to cloud system servers. The cloud system servers acquire certificates from certificate authorities or any end-to-end exchange of keys between the sender and the recipient of the encrypted message. For registered users, messages sent by senders are encrypted by the sender and sent to the cloud system servers which decrypt the message and re-encrypt the message with the recipient's key. For non-registered users, once the encrypted message is decrypted at the cloud system servers, another message is sent to the non-registered informing them that an encrypted message awaits them if they select a link in the message which allows them to log into the cloud system servers and view the original message.
Owner:IDENTILLECT TECH
Cryptographic system with methods for user-controlled message recovery
InactiveUS7139399B1Storage requirement increaseKey distribution for secure communicationS/KEYCryptosystem
A cryptosystem is described which automatically provides an extra “message recovery” recipient(s) when an encrypted message is generated in the system. The system is typically configured such that the extra recipient or “message recovery agent” (MRA)—an entity which itself has a public key (i.e., a MRA public key)—is automatically added, under appropriate circumstances, as a valid recipient for an encrypted message created by a user. In a corporate setting, for example, the message recovery agent is the “corporate” message recovery agent designated for that company (firm, organization, or other group) and the user is an employee (or member) of that company (or group). In operation, the system embeds a pointer (or other reference mechanism) to the MRA public key into the public key of the user or employee, so that encrypted messages sent to the company's employees from outside users (e.g., those individuals who are not employees of the company) can nevertheless still be recovered by the company. Alternatively, the MRA public key itself can be embedded within the public key of the employee or user (i.e., a key within a key), but typically at the cost of increasing the storage requirement of the user's key. By including in the user's key (e.g., an employee) a pointer to a message recovery agent's key (or the MRA key itself), the system provides a mechanism for assisting a user outside a group (e.g., a user who is outside a particular company) with the task of including in an automatic and non-intrusive manner the key of an additional recipient, such as one intended for message recovery.
Owner:CA TECH INC
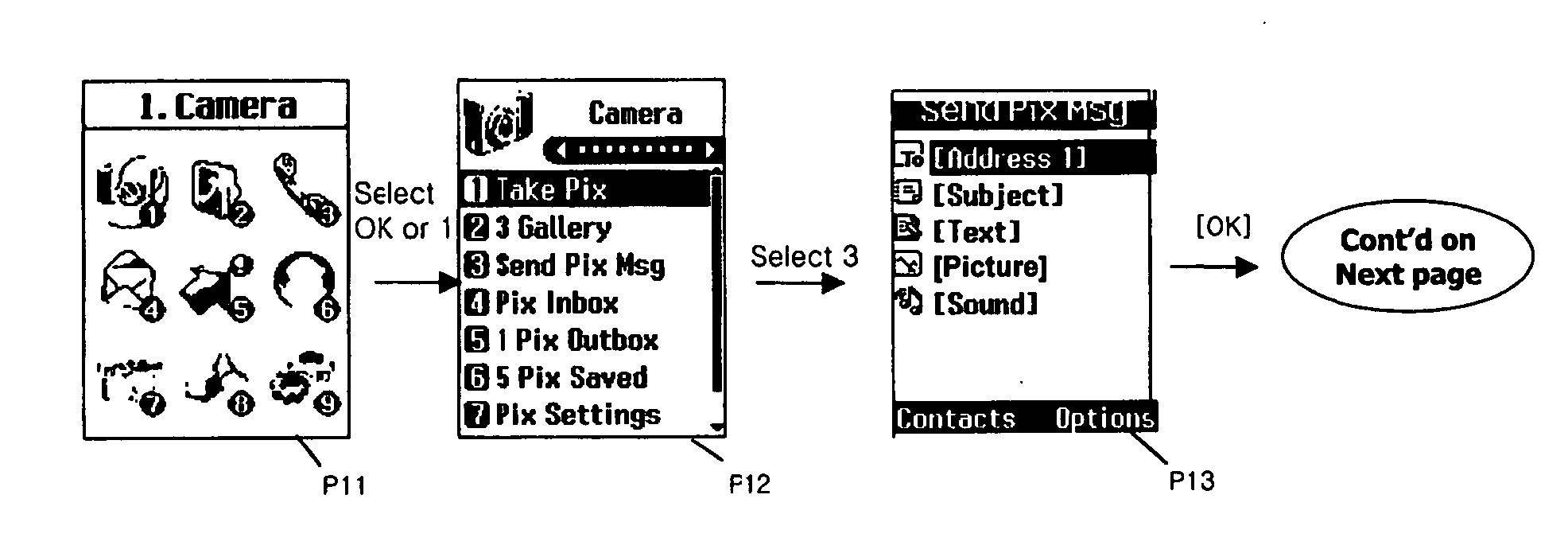
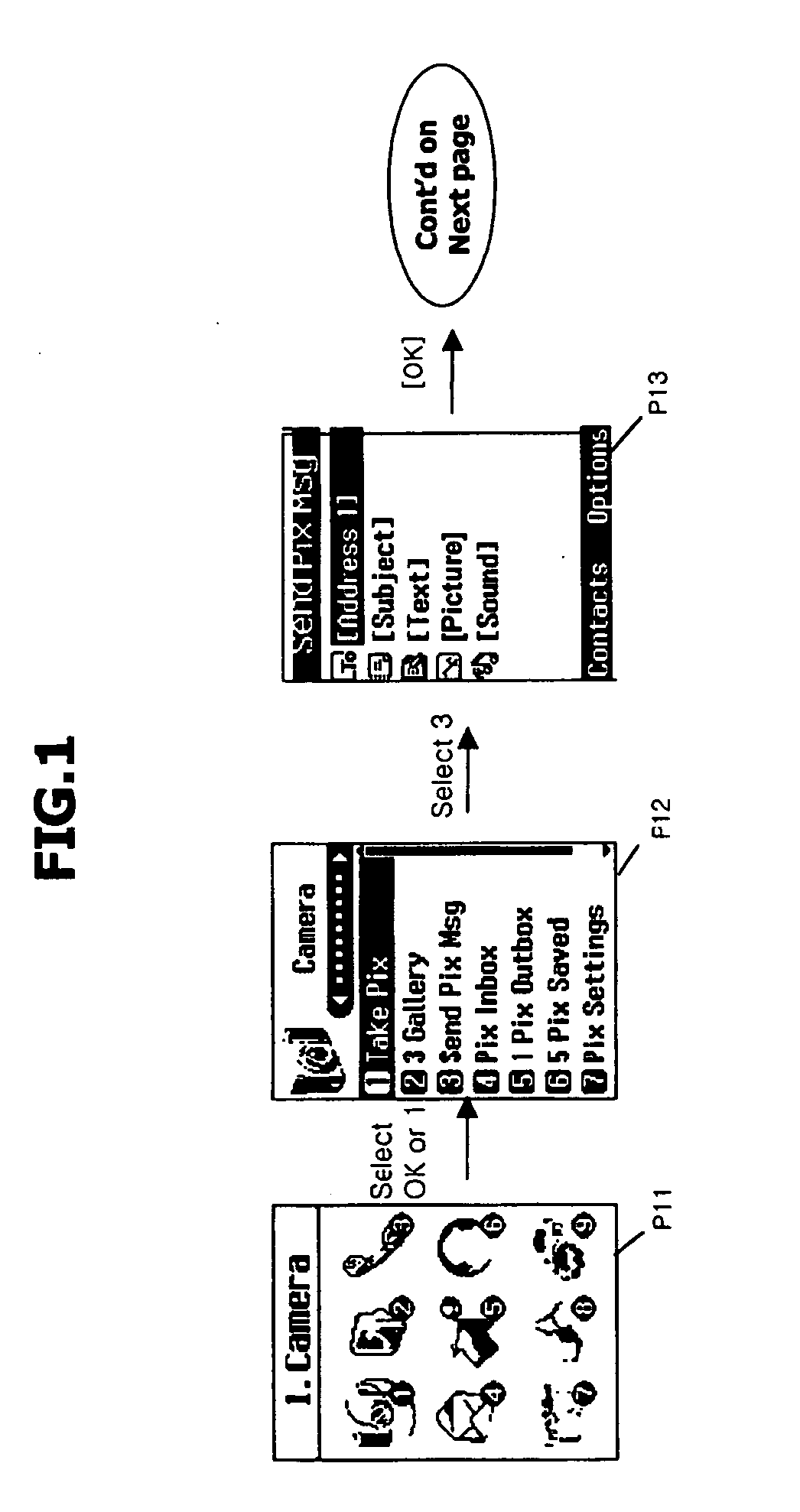
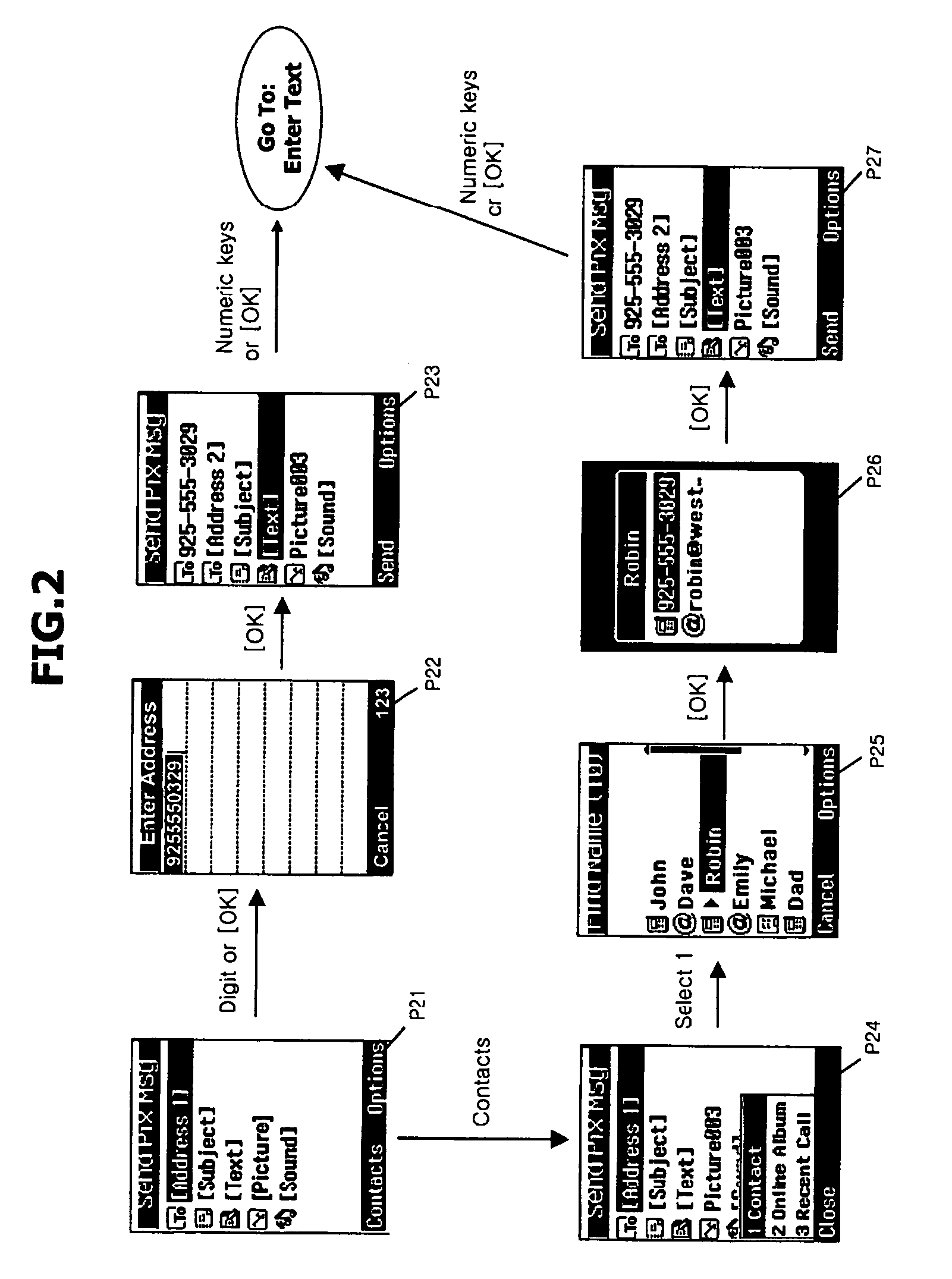
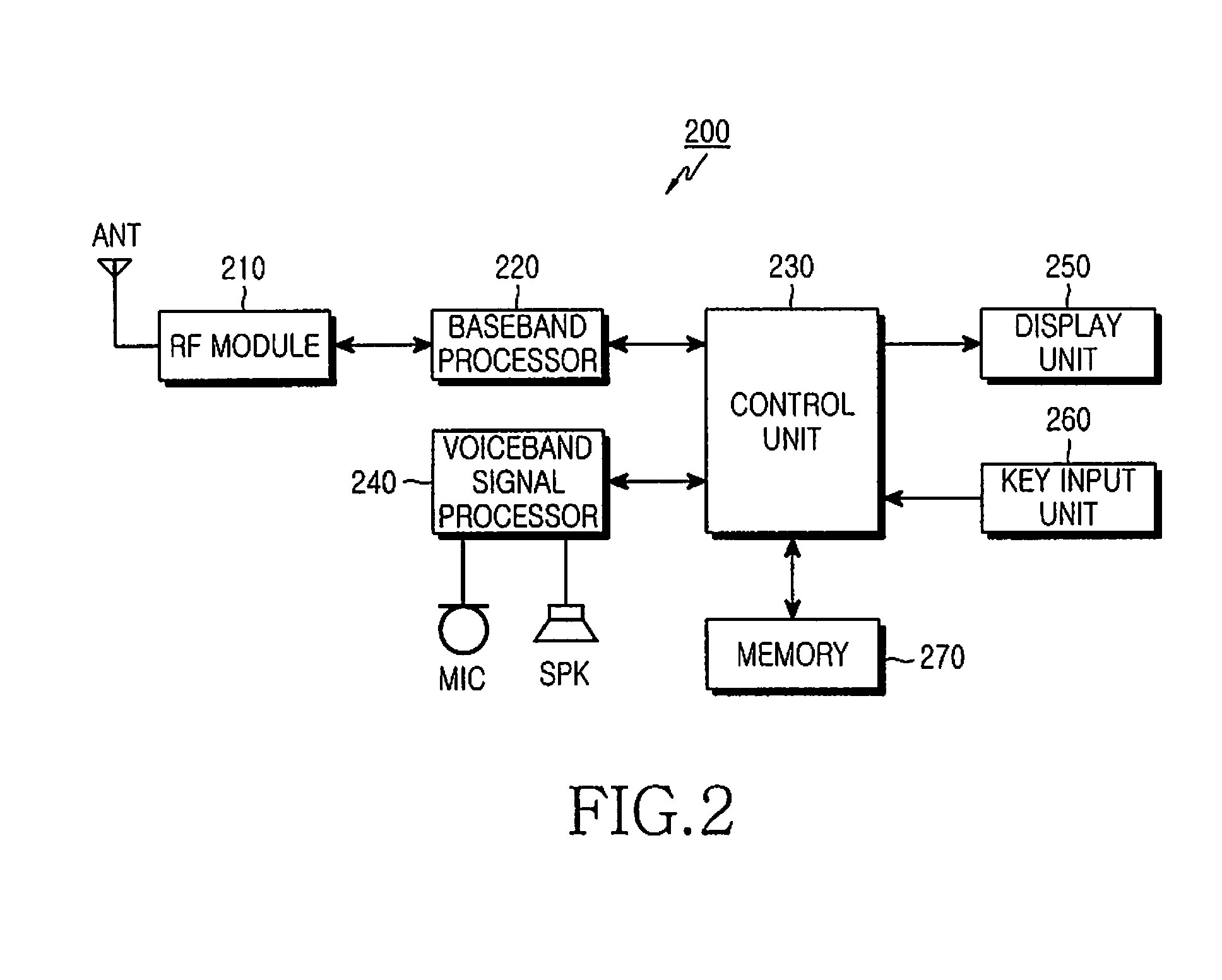
User interface for creating multimedia message of mobile communication terminal and method thereof
ActiveUS20050136953A1Eliminate the problemNatural language data processingData switching by path configurationMenu barKey pressing
A user interface method for creating a multimedia message of a mobile communication terminal is disclosed in which menu fields for creating a multimedia message are displayed in one screen, and when inputting content for each menu field is completed, it is automatically switched to a multimedia message-creating screen in which a selecting bar is positioned at the next field. In addition, while a user is using a multimedia function, a current image can be switched to the multimedia message-creating screen according to a user's need. Thus, the number of user's key manipulations can be reduced in creating the multimedia message, thereby enhancing a user's convenience.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Method and system for efficiently retrieving information from a database
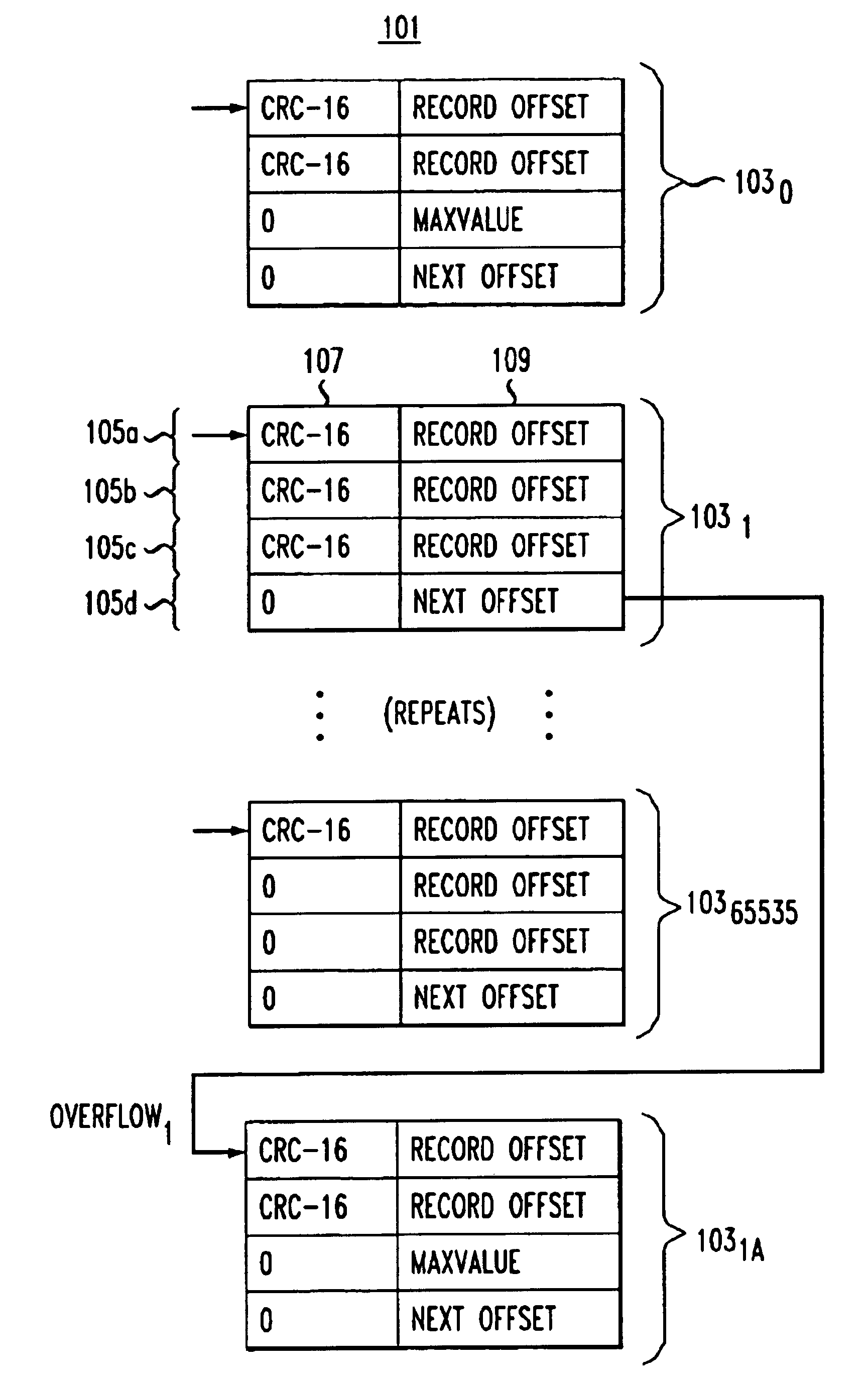
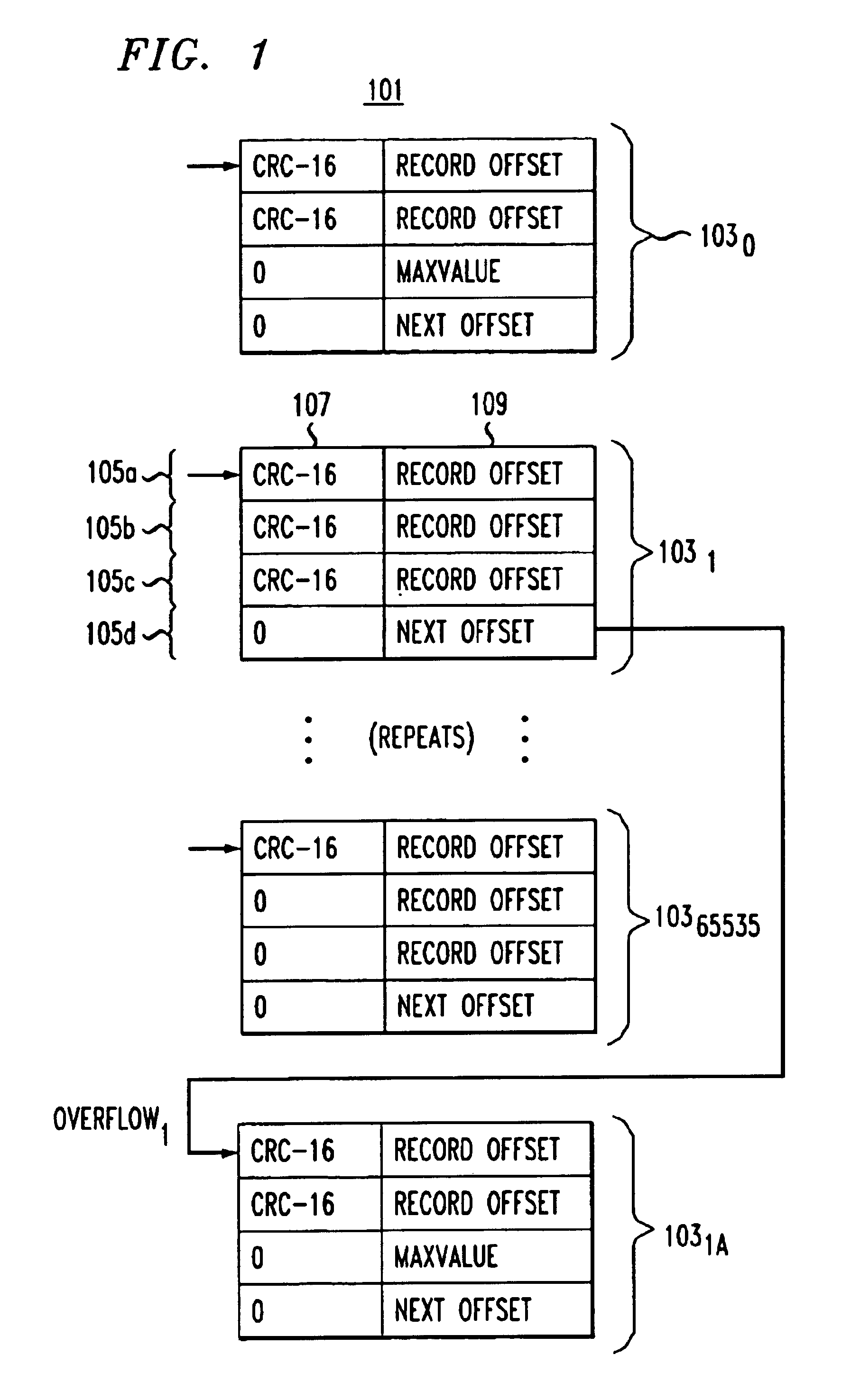
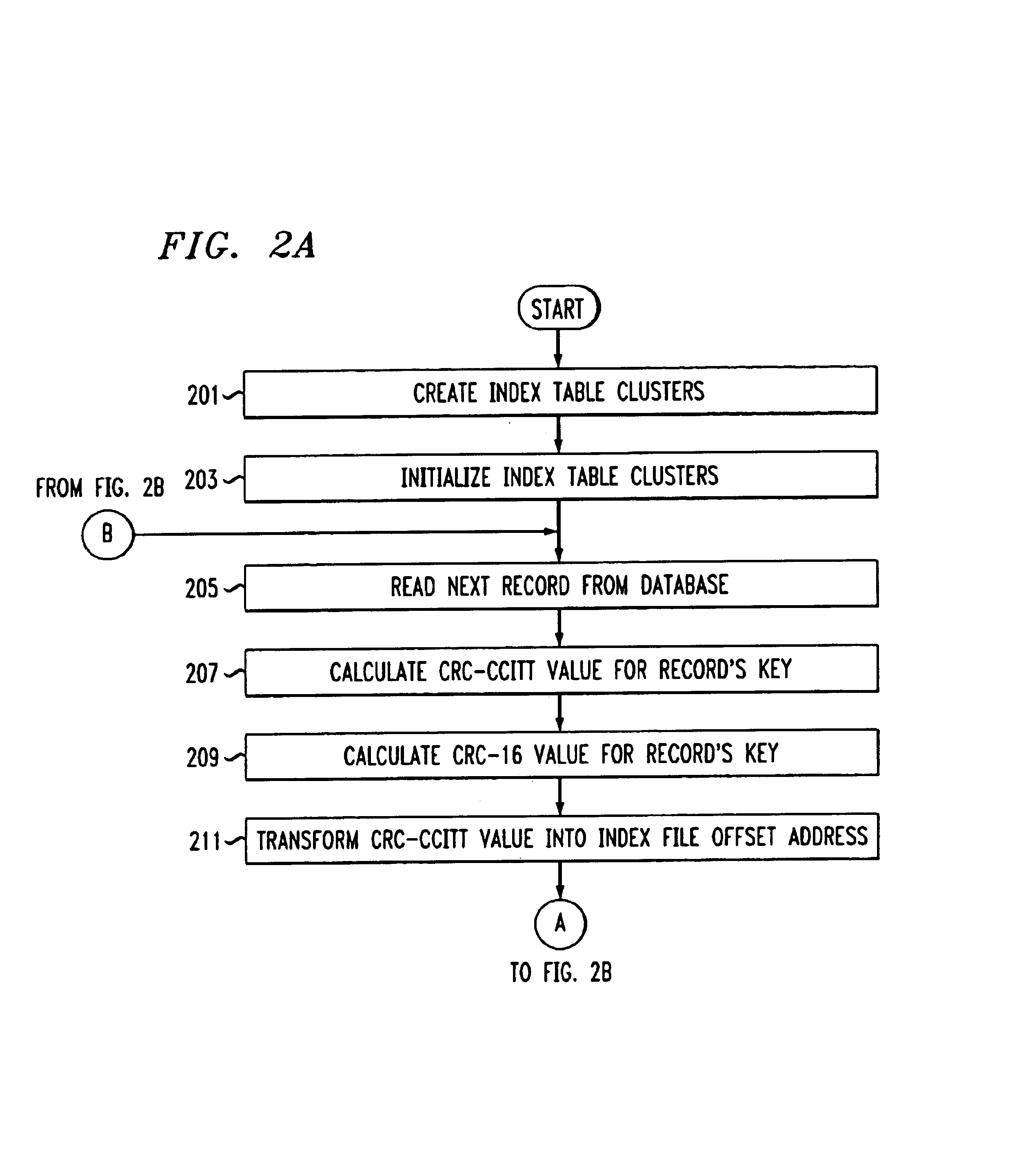
InactiveUS6865577B1Easy to handleSpace minimizationData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalMostly TrueS/KEY
A method for fast and efficient record retrieval in large databases using cyclical redundancy check (CRC) computations as hash functions. Two hash values are computed for each record's key using the CRC-CCITT and CRC-16 generator polynomials. The two CRC values then are combined into a four-byte composite hash value that represents a binary signature of the record's key. Alternately, a single CRC-32 value can be used as a four-byte hash value. In most cases, this four-byte hash value uniquely identifies the record's key. An index file is constructed using a hybrid search method, part hash table and part linear search. The index file is searched to find a match for the four-byte hash value and the record's offset is obtained. The record's offset is used to retrieve the record from the database.
Owner:AMERICAN TELEPHONE & TELEGRAPH CO
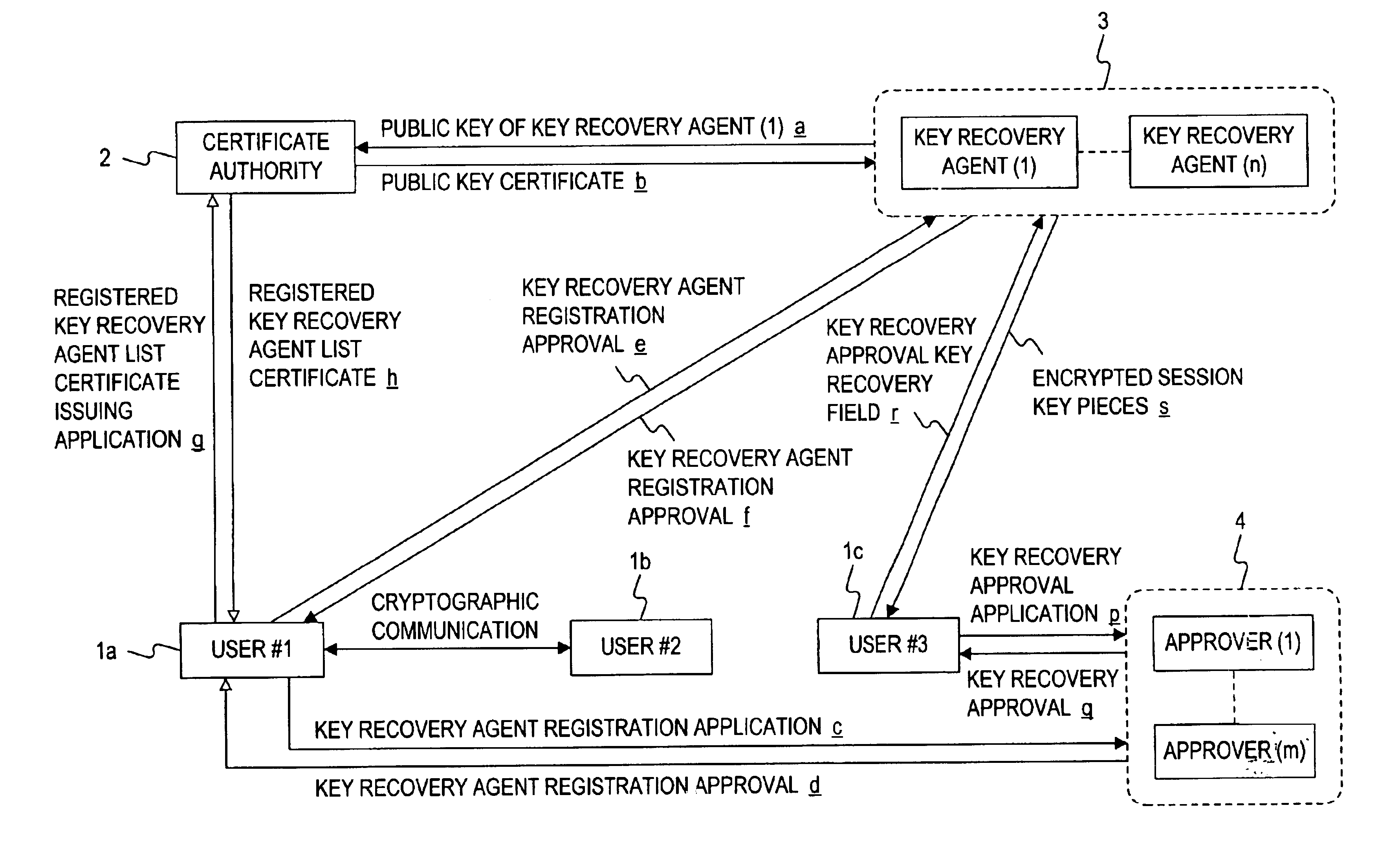
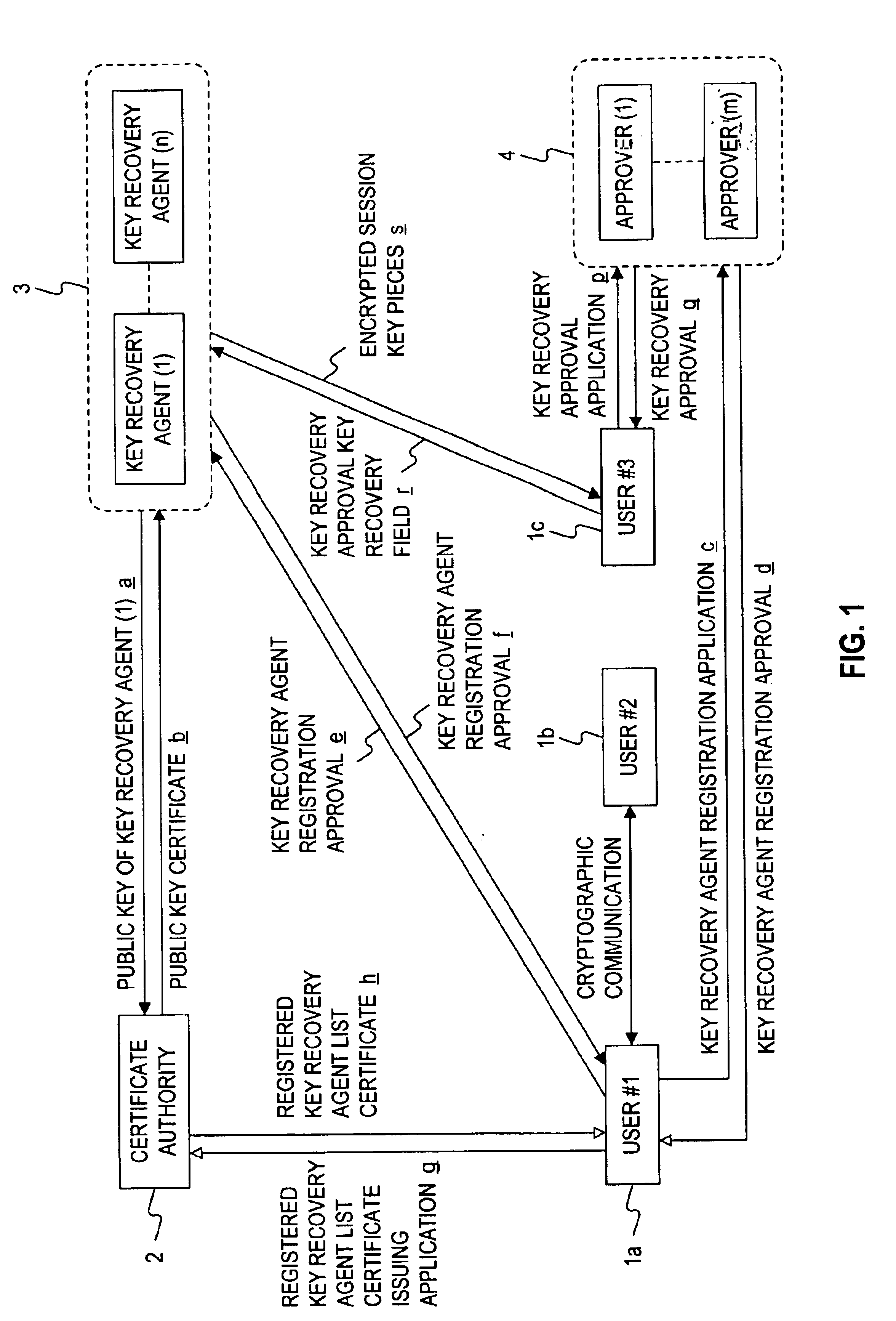
Encryption apparatus, cryptographic communication system, key recovery system, and storage medium
InactiveUS6842523B1Avoid concentrationImprove securityKey distribution for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationCommunications systemS/KEY
In an encryption apparatus for encrypting a data body to contain an encrypted data body in transmission data and transmitting the transmission data to a receiver, the transmission data includes sender's key recovery data obtained by encrypting recovery information for recovering a key for decrypting the encrypted data body to allow a key recovery agent registered by a sender to decrypt the recovery information, and receiver's key recovery data obtained by encrypting the recovery information for recovering the key for decrypting the encrypted data body to allow a key recovery agent registered by a receiver to decrypt the recovery information.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
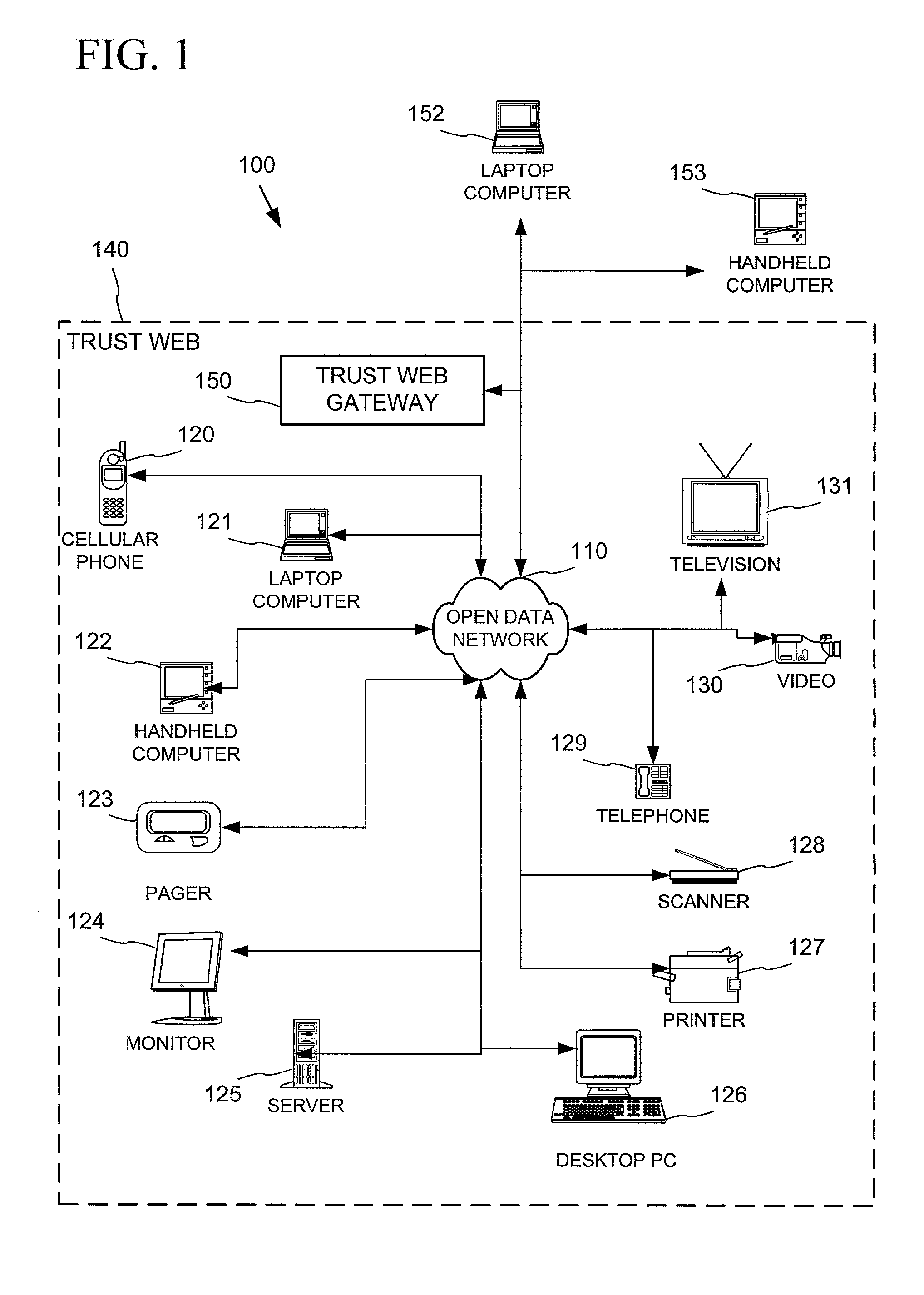
Establishing secure peer networking in trust webs on open networks using shared secret device key
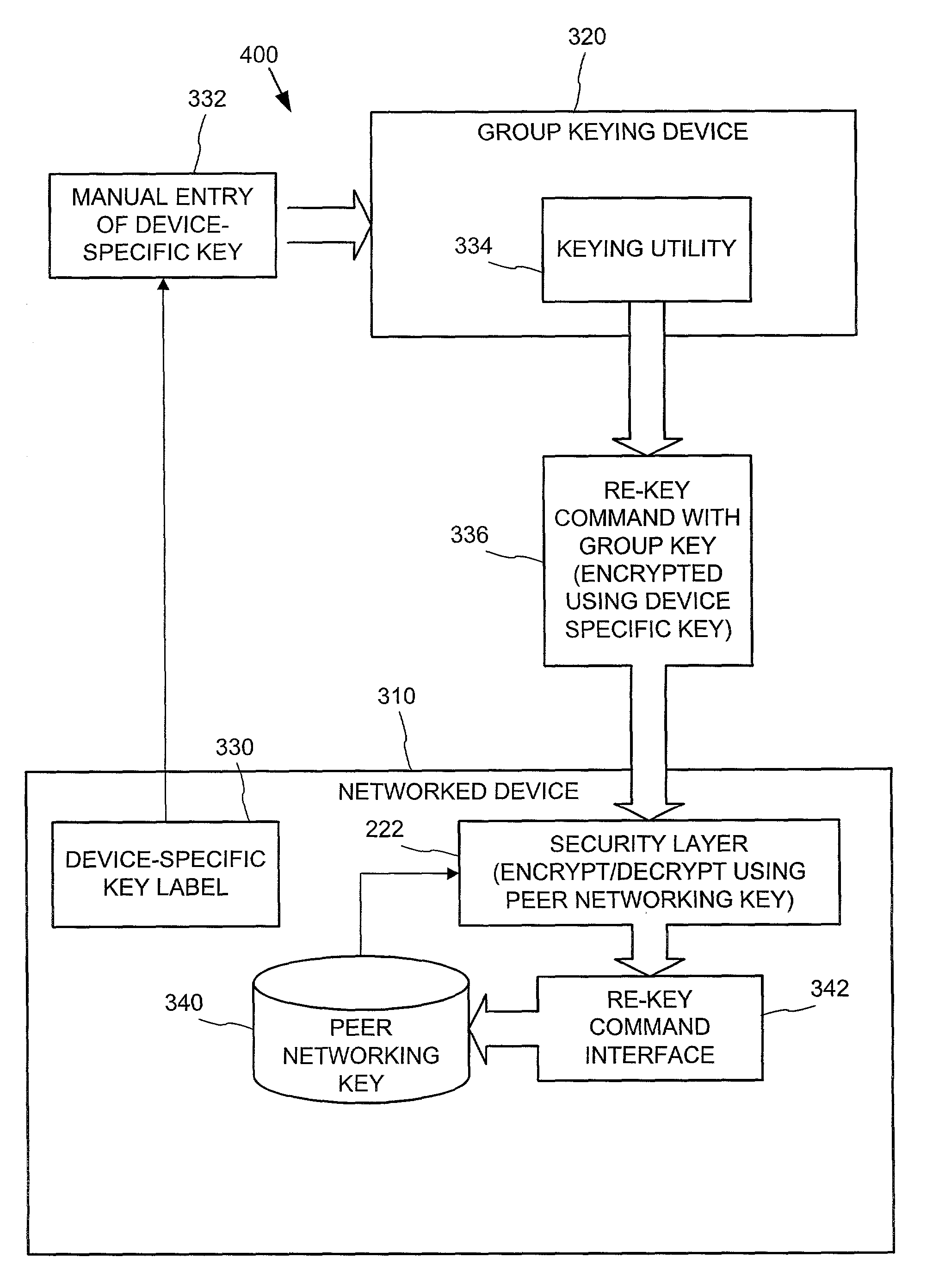
InactiveUS7082200B2CostImprove connectivityKey distribution for secure communicationDigital data processing detailsS/KEYVia device
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
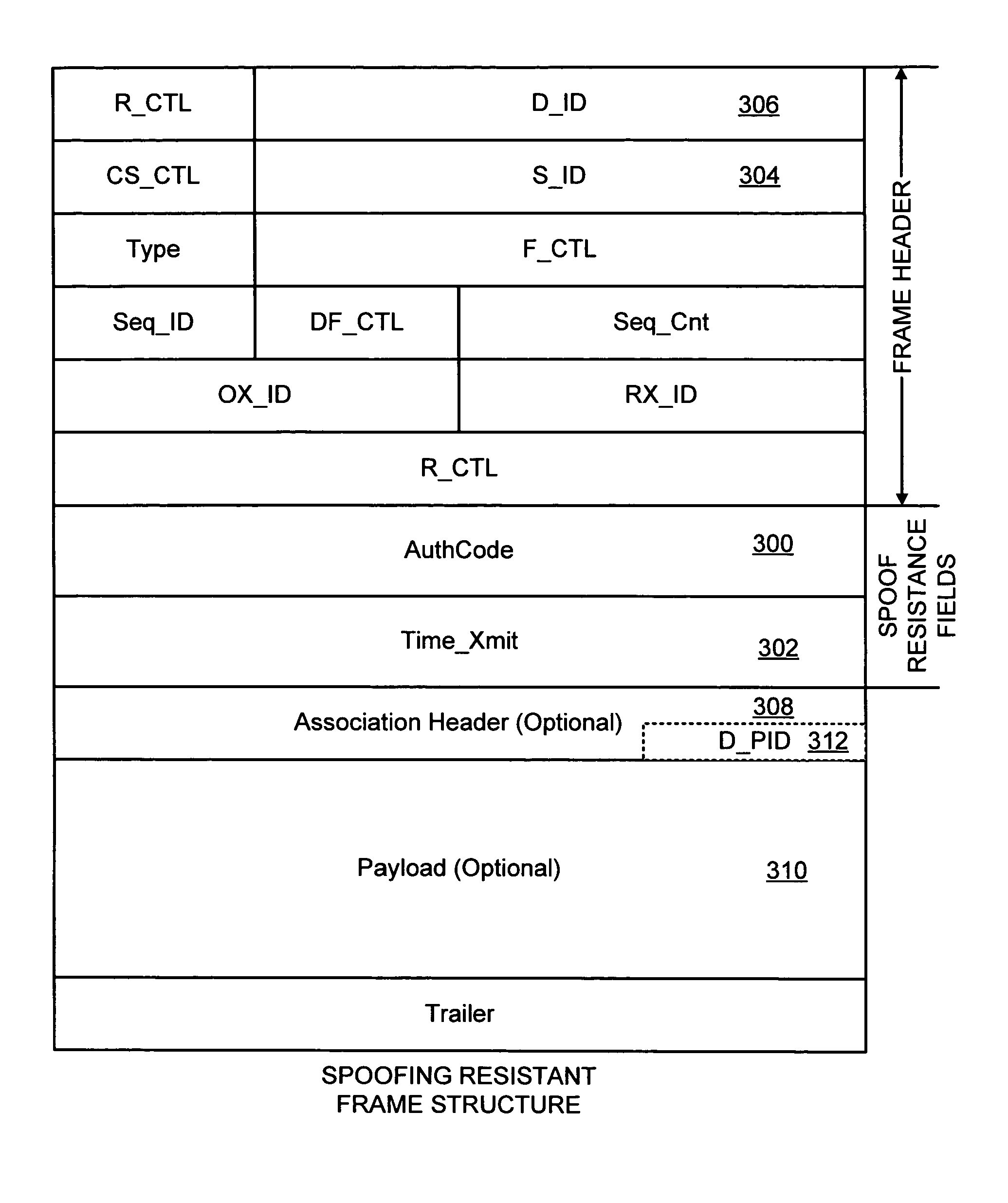
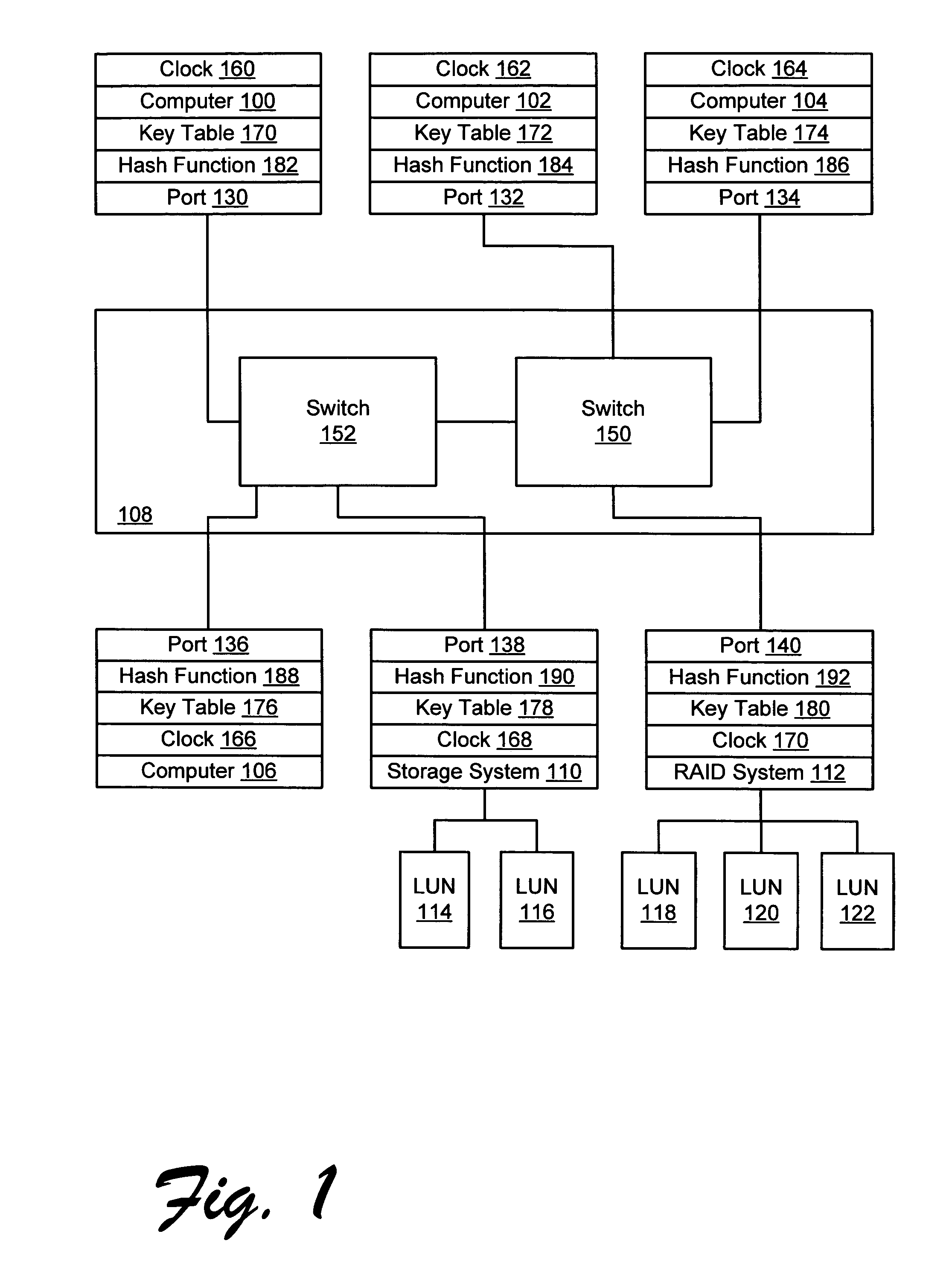
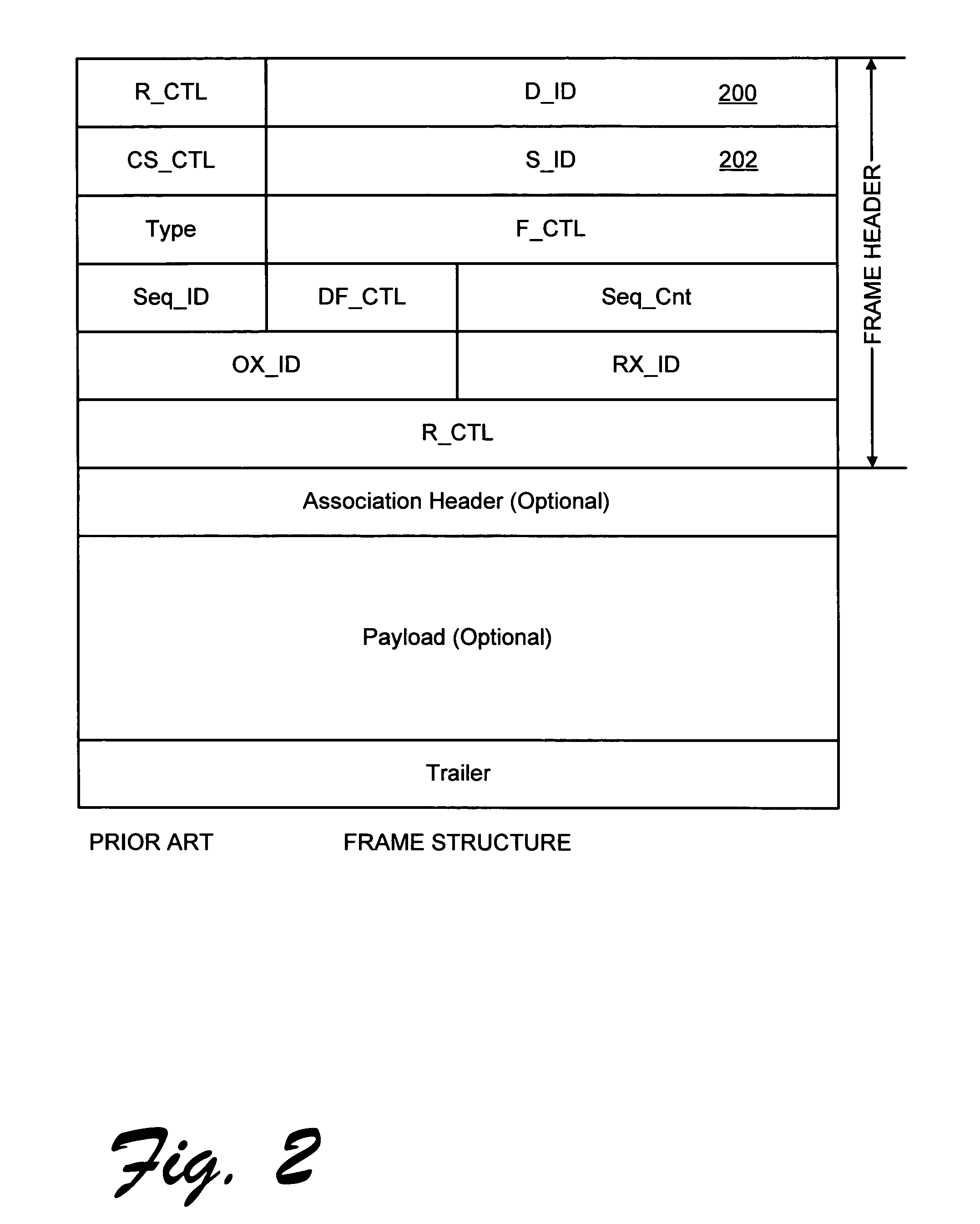
Apparatus and method for implementing spoofing-and replay-attack-resistant virtual zones on storage area networks
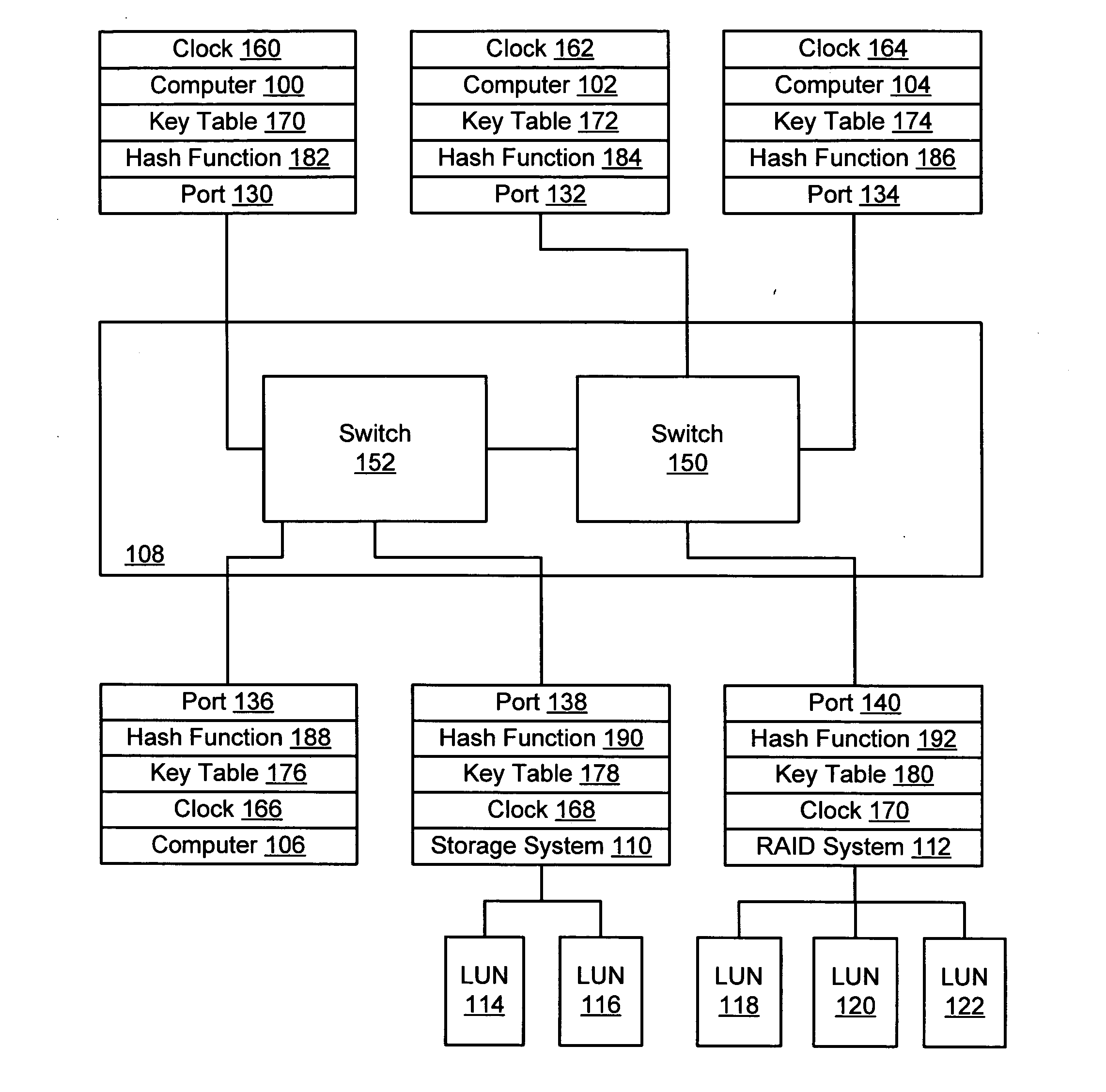
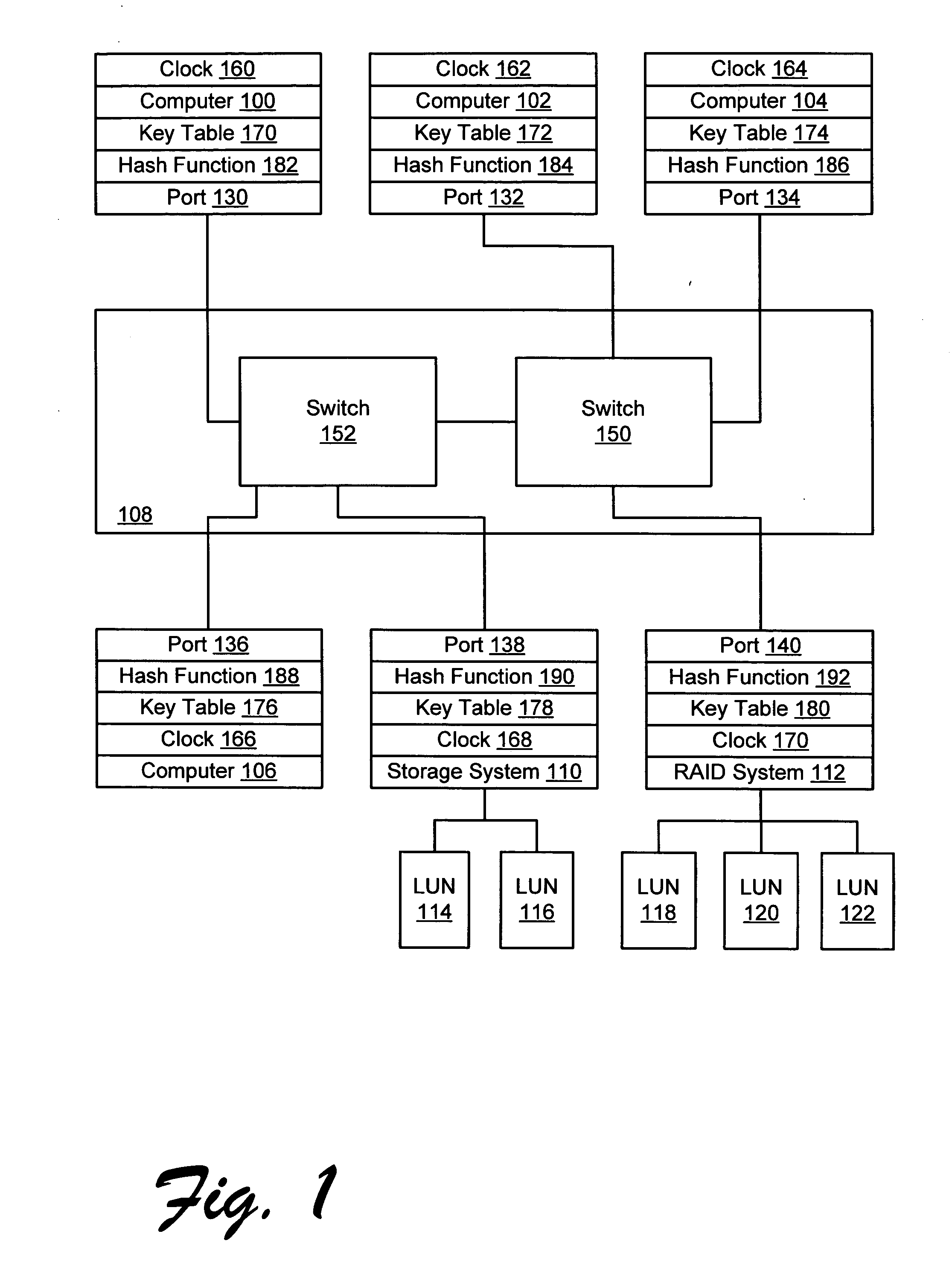
InactiveUS20050044354A1Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationHash functionStorage area network
A storage area network resistant to spoofing attack has several nodes each having a port, and storage area network interconnect interconnecting the ports. Each port is provided with a hash function generator for providing and verifying an authentication code for frames transmitted over the storage area network, and a key table for providing a key to the hash function generator. The authentication code is generated by applying a hash function to the key and to at least an address portion of each frame. In each node, the key is selected from that node's key table according to address information of the frame.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
Decoupling access control from key management in a network
InactiveUS7336790B1Good flexibilityDigital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationPrivate networkS/KEY
Methods and systems consistent with the present invention provide a Supernet, a private network constructed out of components from a public-network infrastructure. Supernet nodes can be located on virtually any device in the public network (e.g., the Internet), and both their communication and utilization of resources occur in a secure manner. As a result, the users of a Supernet benefit from their network infrastructure being maintained for them as part of the public-network infrastructure, while the level of security they receive is similar to that of a private network. The Supernet has an access control component and a key management component which are decoupled. The access control component implements an access control policy that determines which users are authorized to use the network, and the key management component implements the network's key management policies, which indicate when keys are generated and what encryption algorithm is used. Both access control and key management are separately configurable. Thus, the Supernet provides great flexibility by allowing different key management policies to be used with the same access control component.
Owner:ORACLE INT CORP
Automatically reconfigurable multimedia system with interchangeable personality adapters
A TV-set is equipped with HDMI and USB connections that allow it to display and run audio-video content from a variety of conventional consumer devices. The TV-set is further equipped to provide a secure HDMI-USB interface that will allow the transfer of licensed high definition content and Internet subscriber services. Such secure HDMI-USB interface also enables a selection of proprietary application modules to be attached. Downloadable user interface templates, much like XML style sheets, are rendered to a user interface displayed on the screen. These are associated with corresponding thumbnails and URI's that allow a user to surf through lists and catalogs of materials, and then to play them in the appropriate formats and provide the machine with a customized controller. A remote commander is simplified, yet expanded to control all the attached devices through interactions with the user interface. The functions of the remote commander's keys change depending on where the user is navigating and what device is being controlled, similar to so-called soft-keys.
Owner:SONY CORP +1
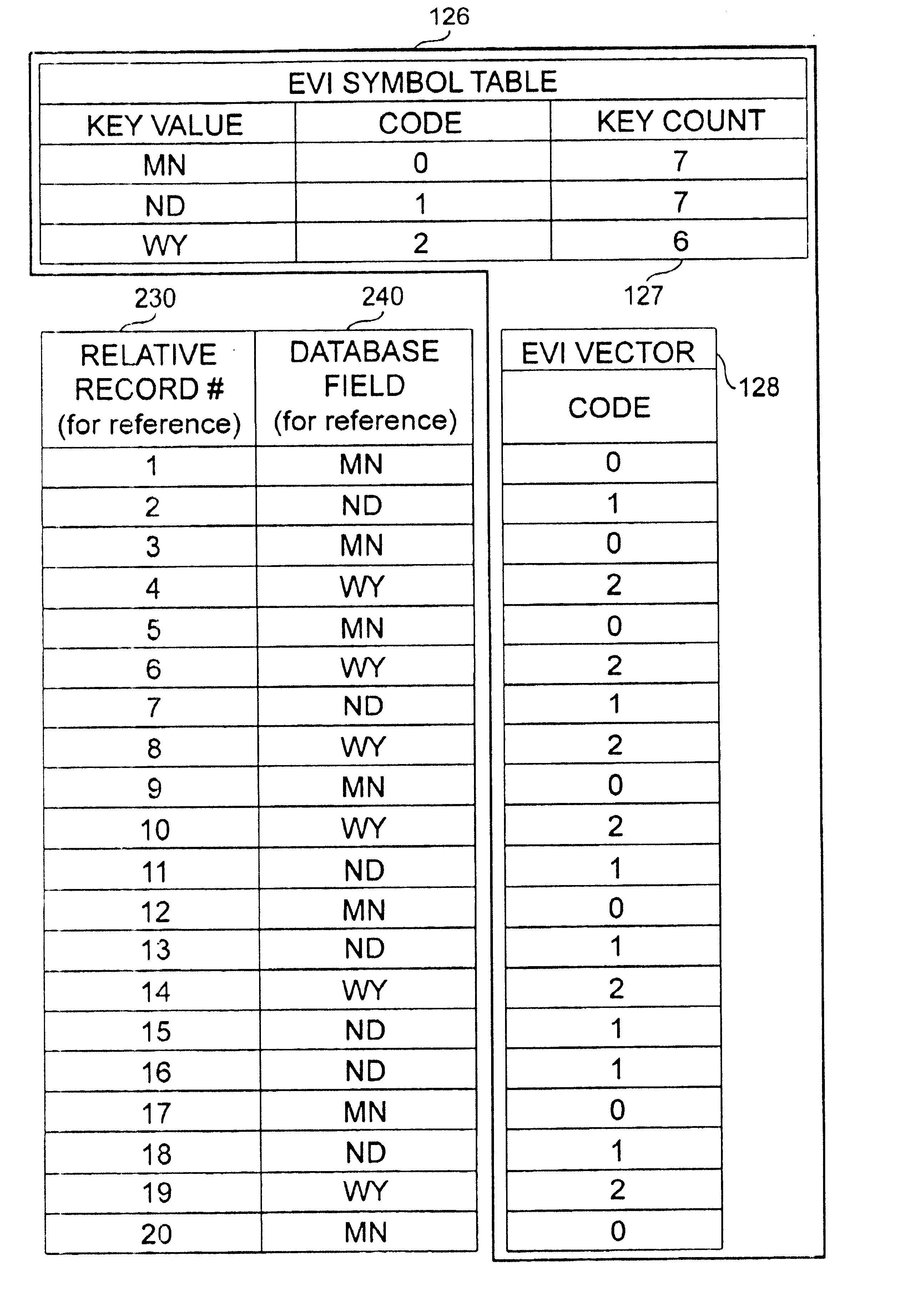
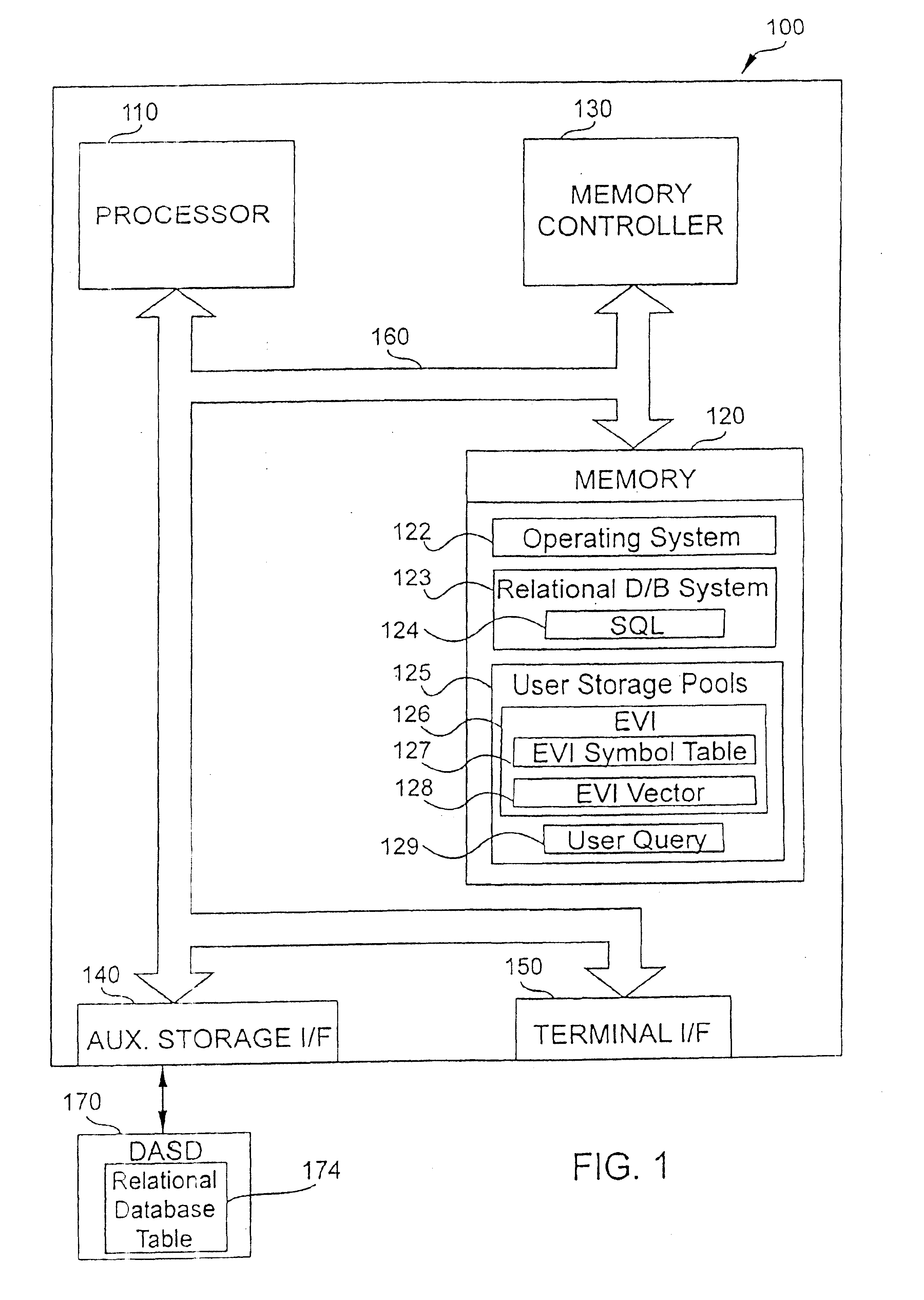
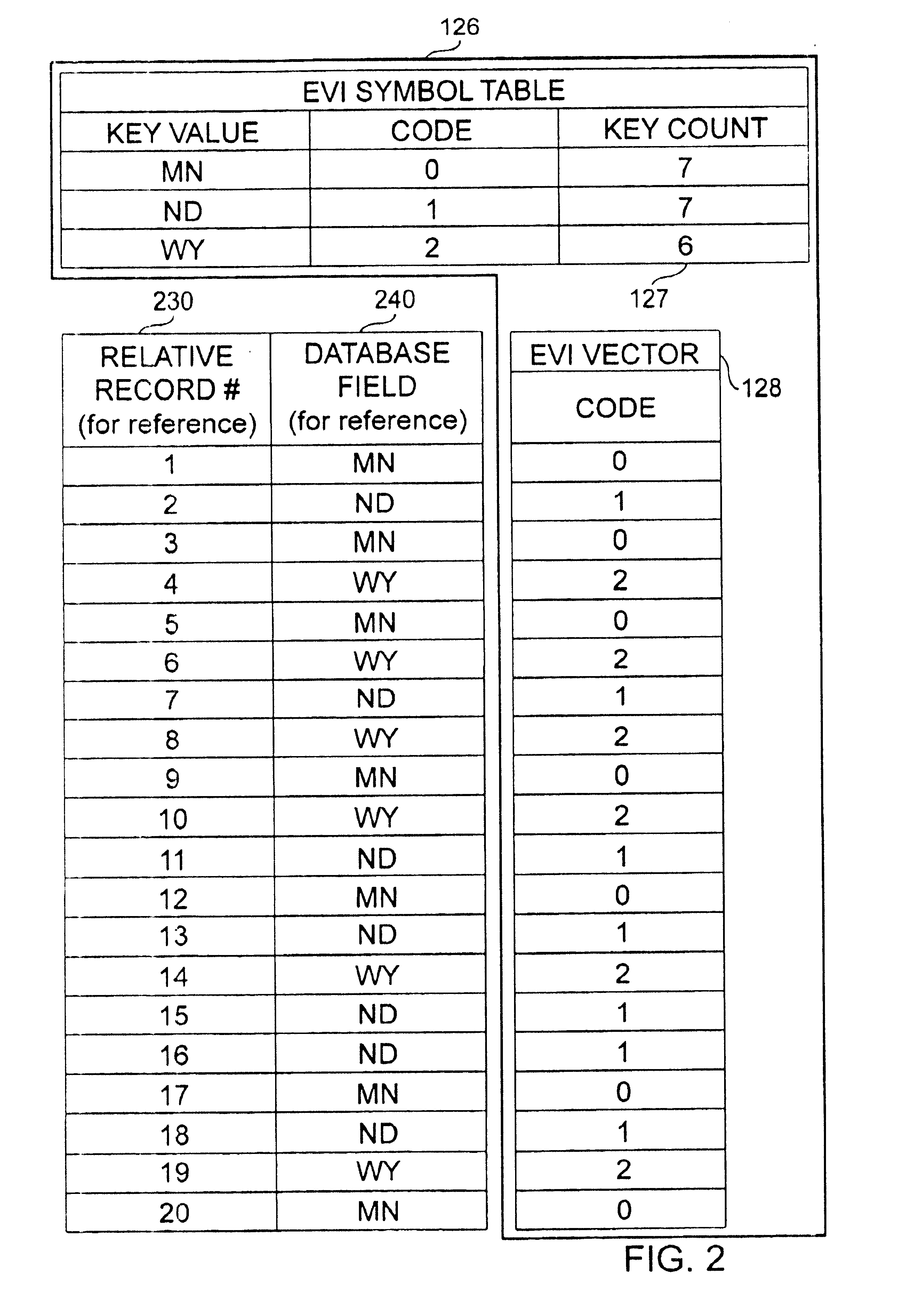
Utilize encoded vector indexing for database grouping
InactiveUS7020647B1Improve performanceQuick buildData processing applicationsDigital data information retrievalS/KEYOperand
An apparatus and method to significantly improve performance of certain group queries using an encoded vector index (EVI) is disclosed. An EVI provides the data necessary to generate query results for COUNT, SUM, MIN, and MAX commands that specify the one or more database fields upon which the EVI is built. Only the EVI symbol table's key count, and the one or more database fields duplicated in the EVI symbol table are necessary to generate the query results.The key count in each EVI symbol table entry contains the number of records in the database having identical values in the EVI fields (that is, the fields upon which the EVI is built). These duplicated database values are called key values in the EVI symbol table entry. The EVI symbol table entry's key count allows quick generation of query results for COUNT and SUM commands that specify one or more EVI fields. SUM command processing of an EVI field is further facilitated by calculating a product of the key count and the key value of that EVI field. The highest or lowest key value in an EVI field provides query results for MAX or MIN commands specifying that EVI field. A HAVING operand specifying a key value delimiter on an EVI field for any of the aforementioned grouping commands is also facilitated using the EVI symbol table.
Owner:IBM CORP
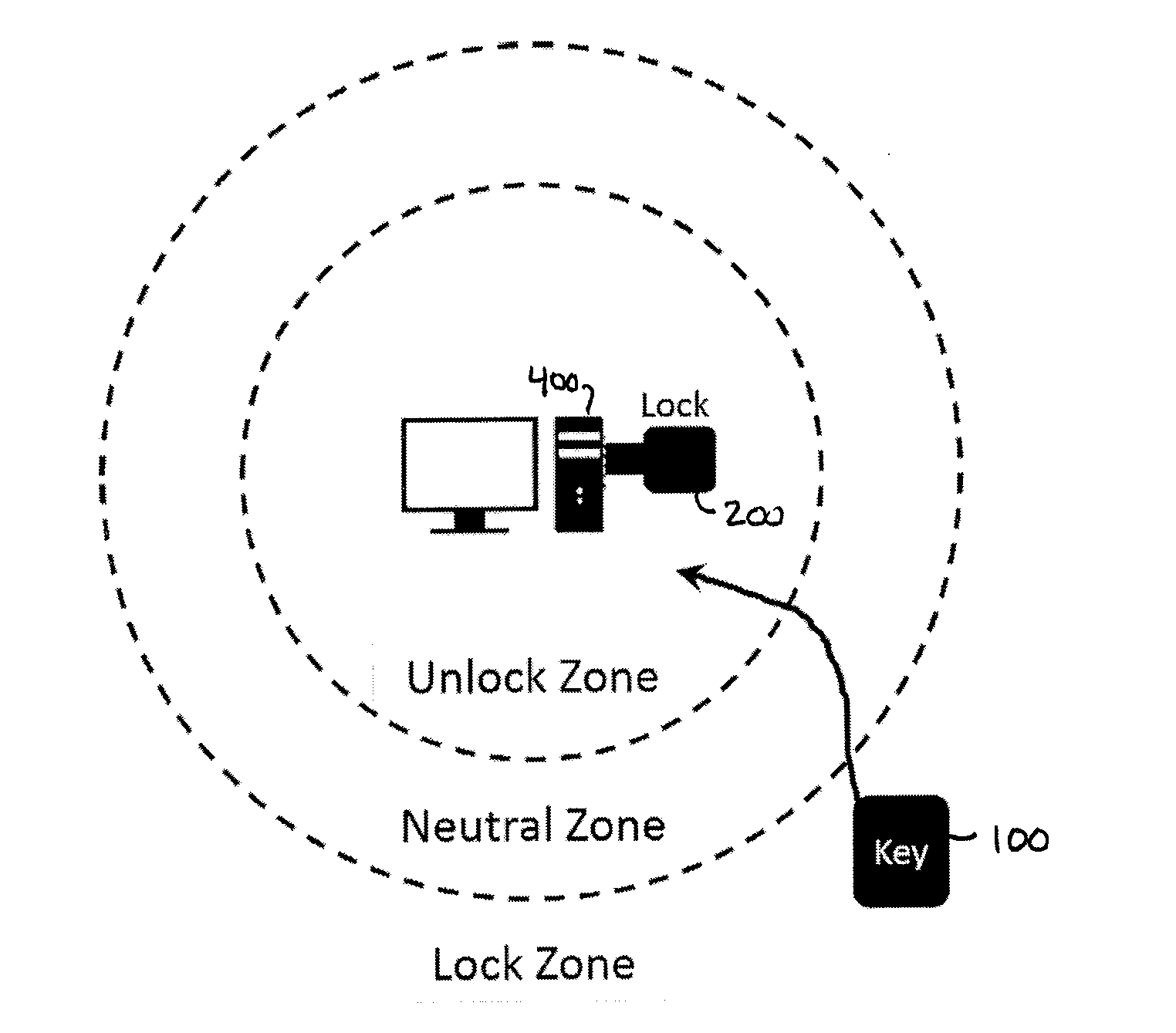
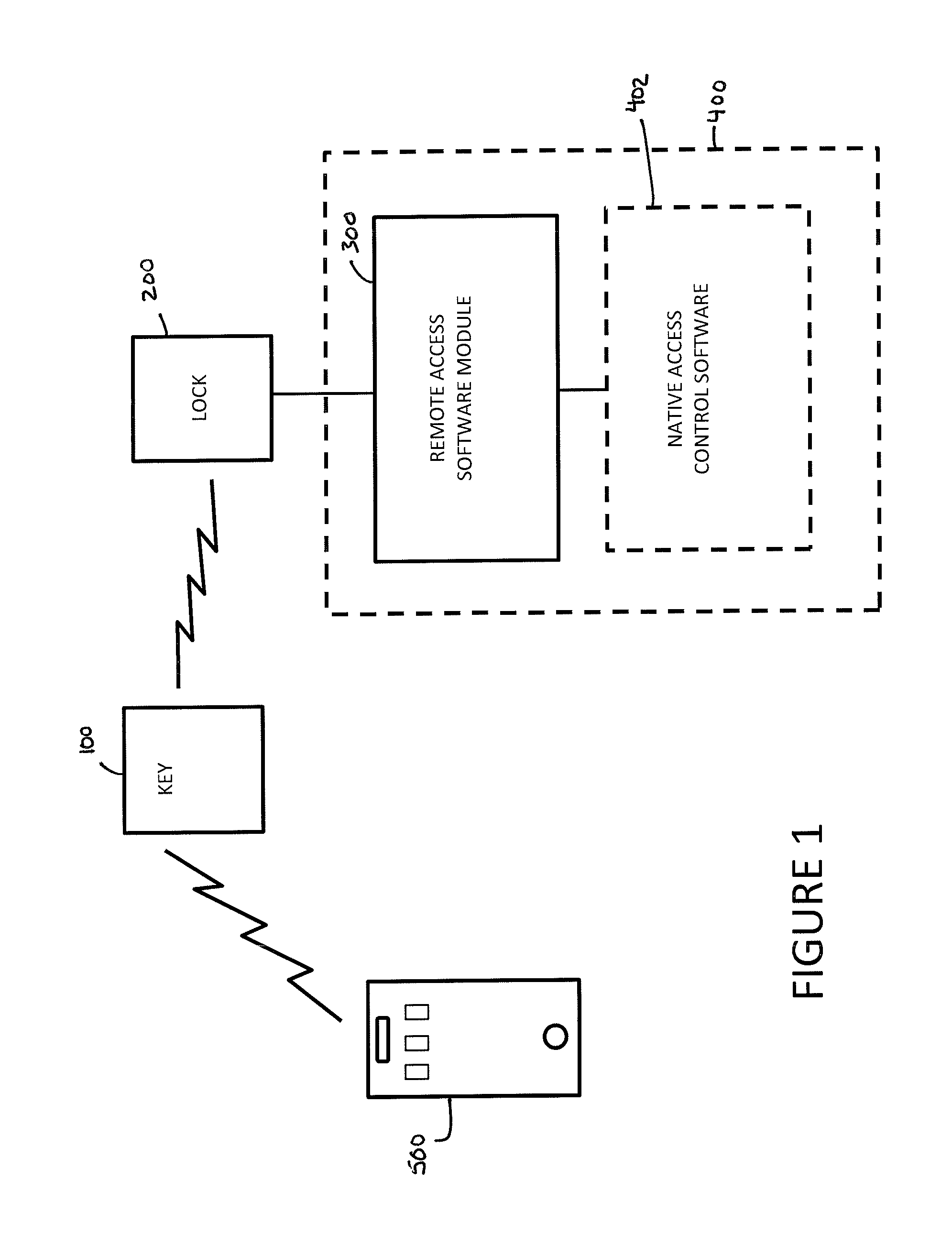
System and method for wireless proximity-based access to a computing device
ActiveUS20150302188A1Avoid accessUser identity/authority verificationDigital data authenticationS/KEYComputer access
Disclosed herein is a system and method for wireless proximity-based access to a computing system, which in accordance with certain aspects of an embodiment of the invention includes a small, portable, person-carried or personal-item-carried (e.g., by attachment to a user's key's, purse, knapsack, etc.) wireless transmitter that serves as a “key,” and a wireless receiver configured for attachment to the computing system that serves as a “lock.” The lock may comprise, for example, a USB device that both wirelessly communicates with the key to detect its physical proximity, and communicates with the computer access software that is native on the computing system (e.g., standard WINDOWS username and password authentication processes) to either allow or disallow such computer access software from allowing access to the computing system based upon the physical proximity of the key to the lock.
Owner:UNTETHERED LABS INC
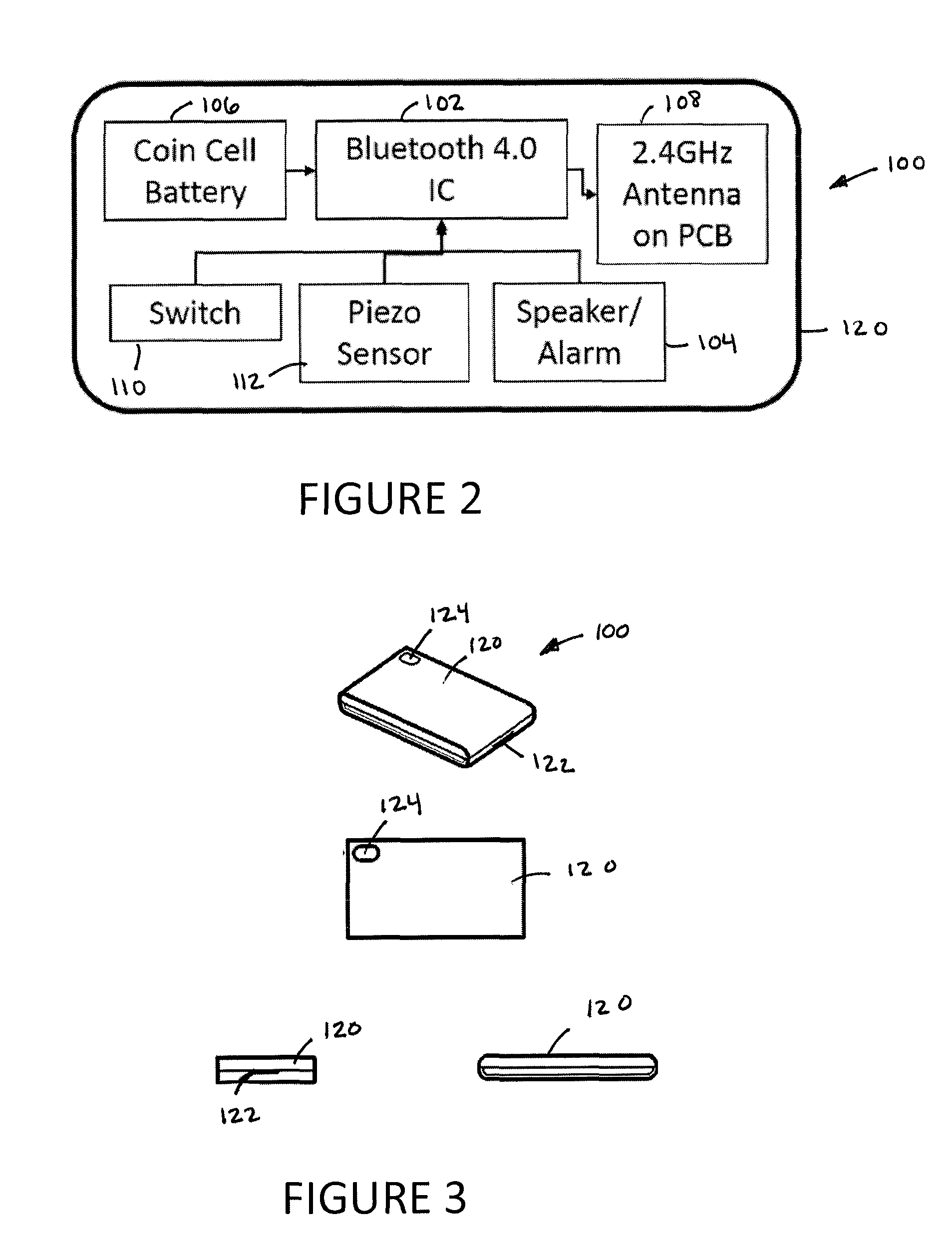
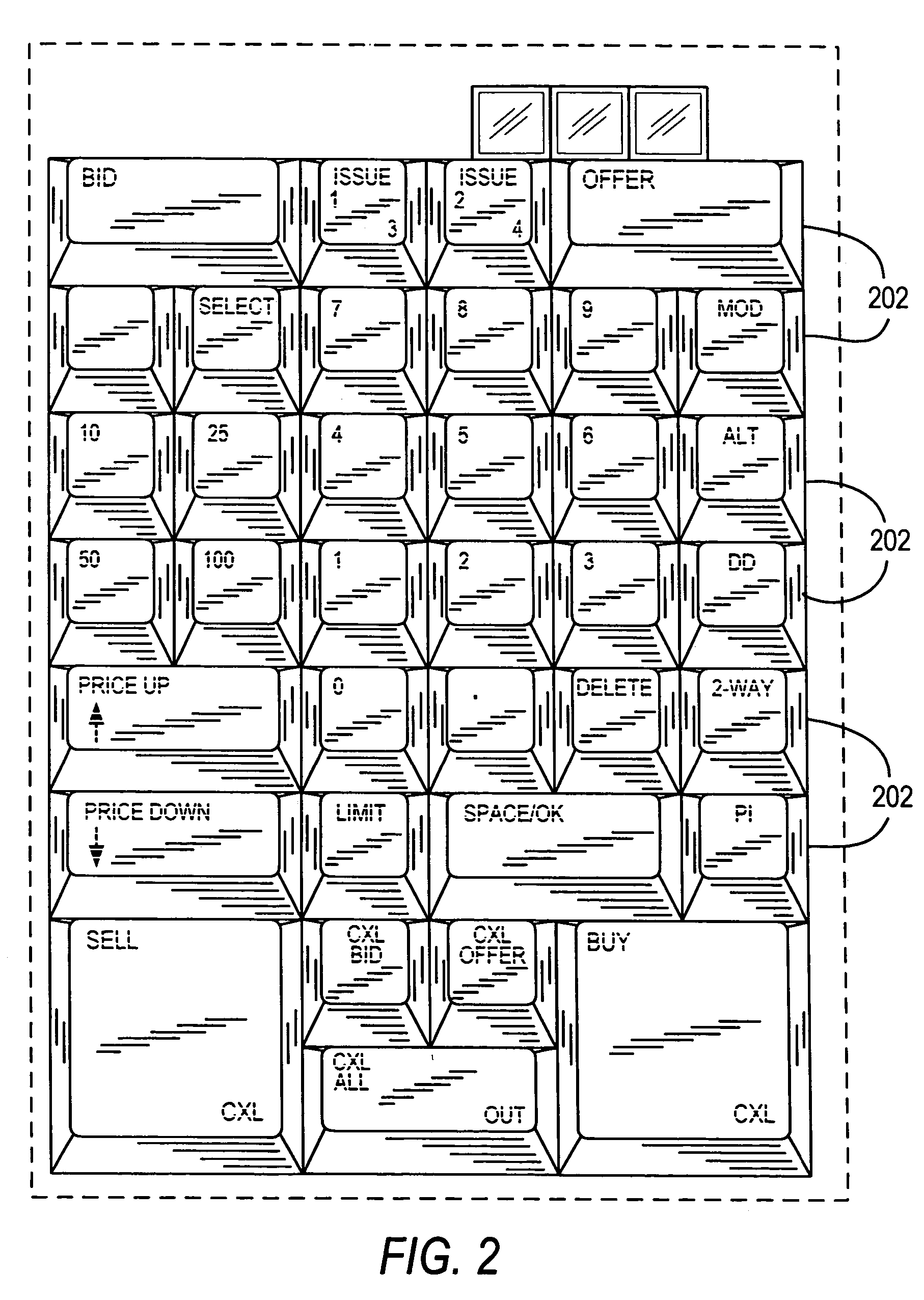
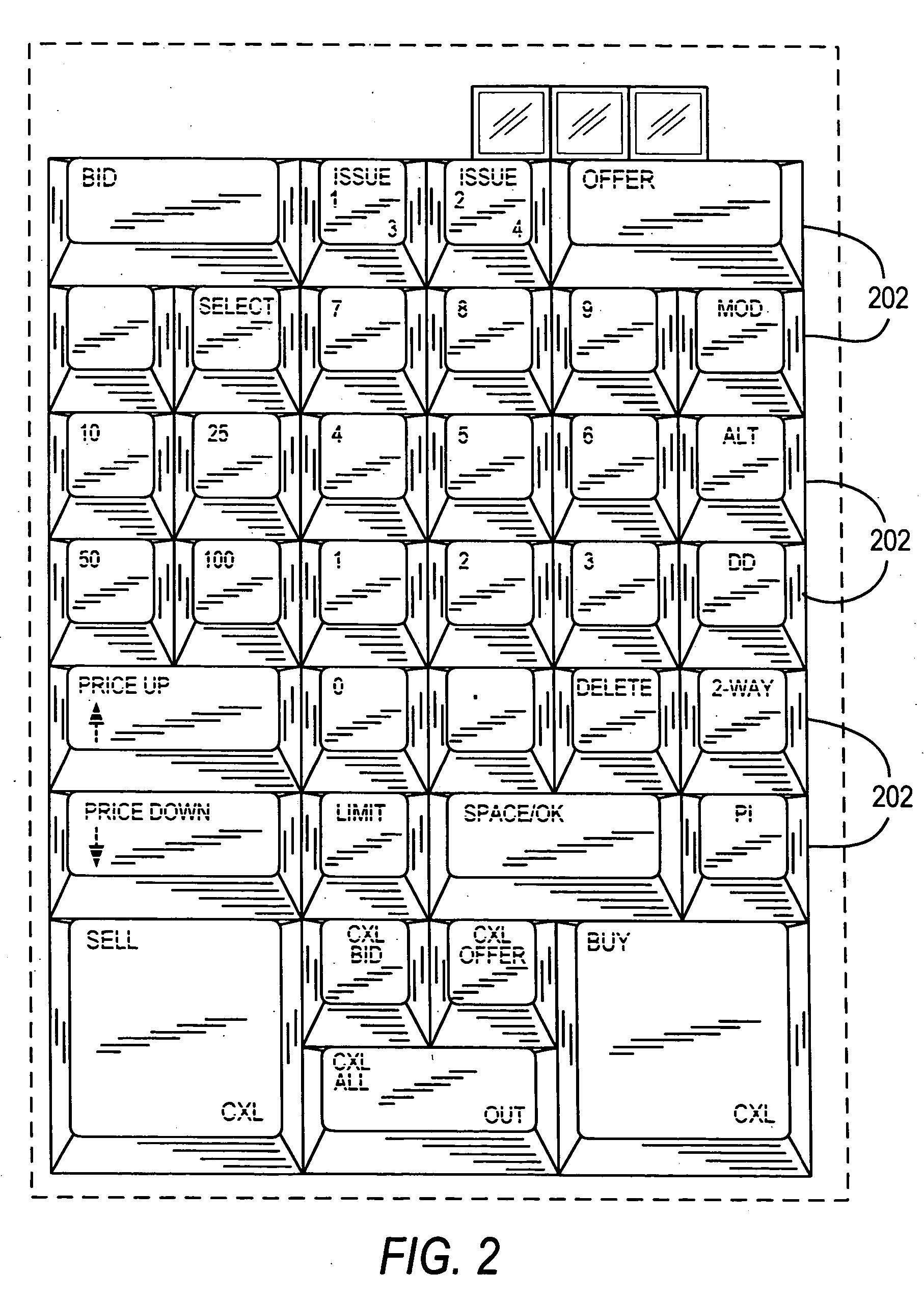
Fully configurable trading keyboard
ActiveUS7283067B2Complete banking machinesInput/output for user-computer interactionS/KEYMode selection
Owner:BGC PARTNERS LP
Apparatus and method for implementing spoofing-and replay-attack-resistant virtual zones on storage area networks
InactiveUS6973568B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationHash functionStorage area network
A storage area network resistant to spoofing attack has several nodes each having a port, and storage area network interconnect interconnecting the ports. Each port is provided with a hash function generator for providing and verifying an authentication code for frames transmitted over the storage area network, and a key table for providing a key to the hash function generator. The authentication code is generated by applying a hash function to the key and to at least an address portion of each frame. In each node, the key is selected from that node's key table according to address information of the frame.
Owner:GOOGLE LLC
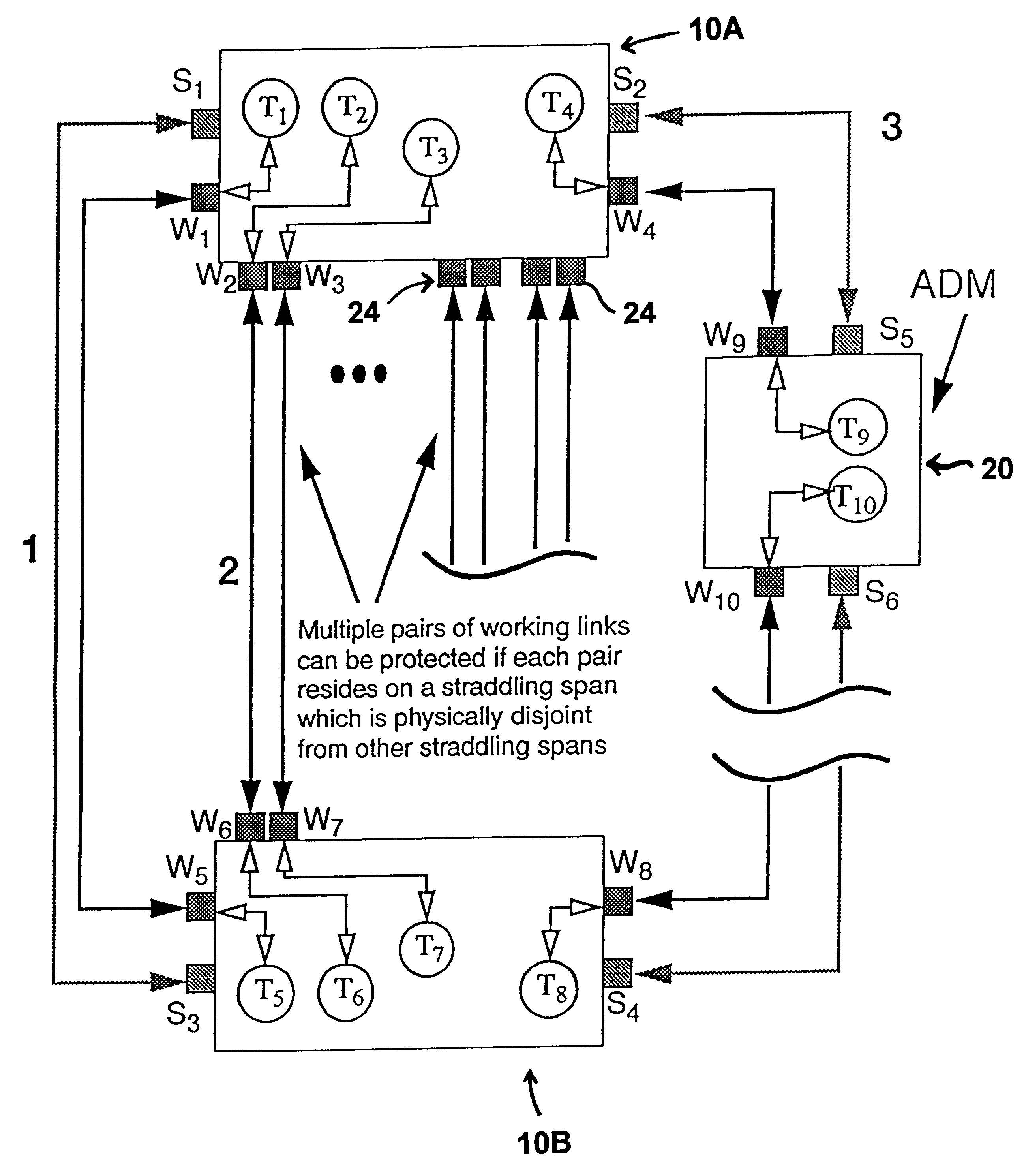
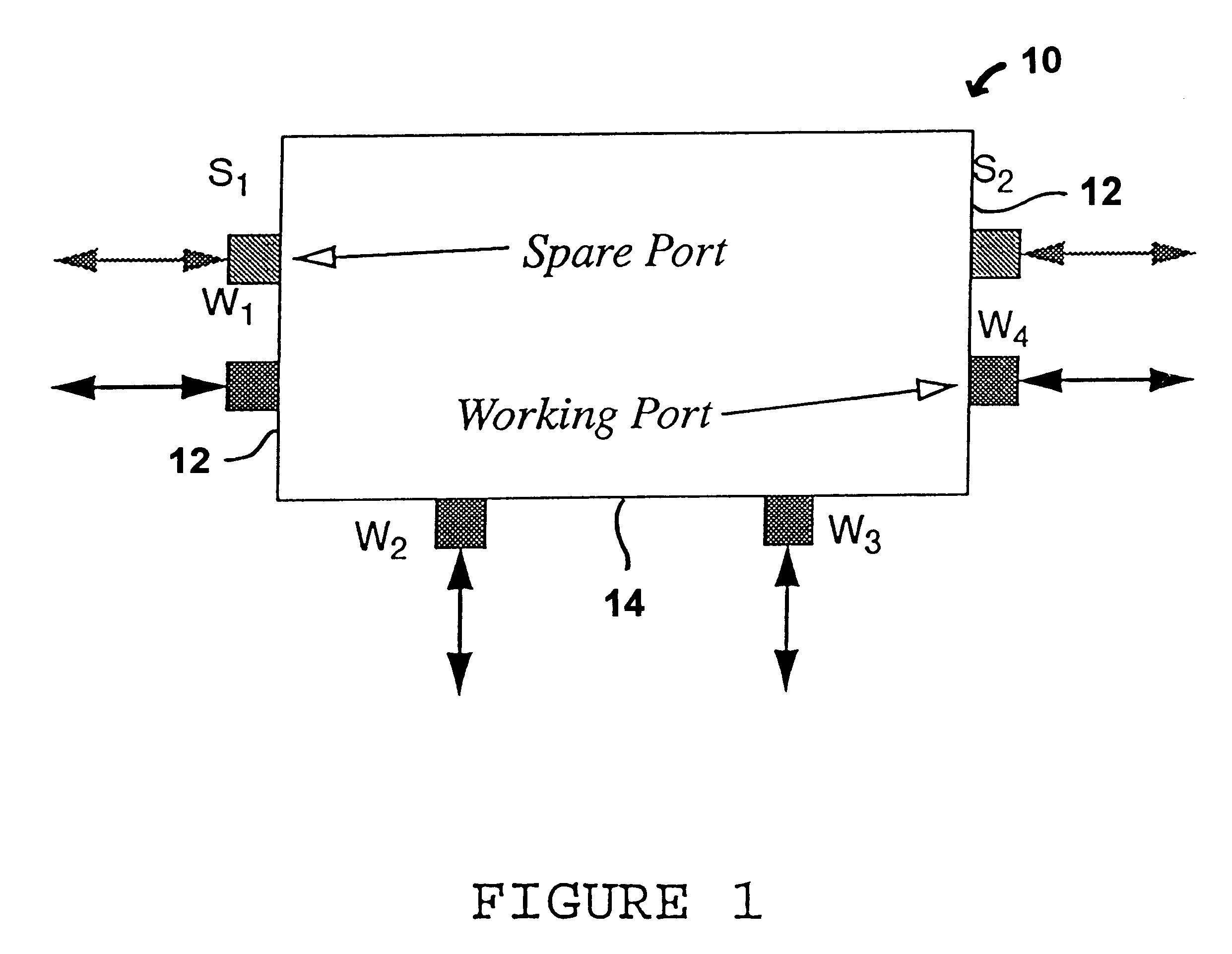
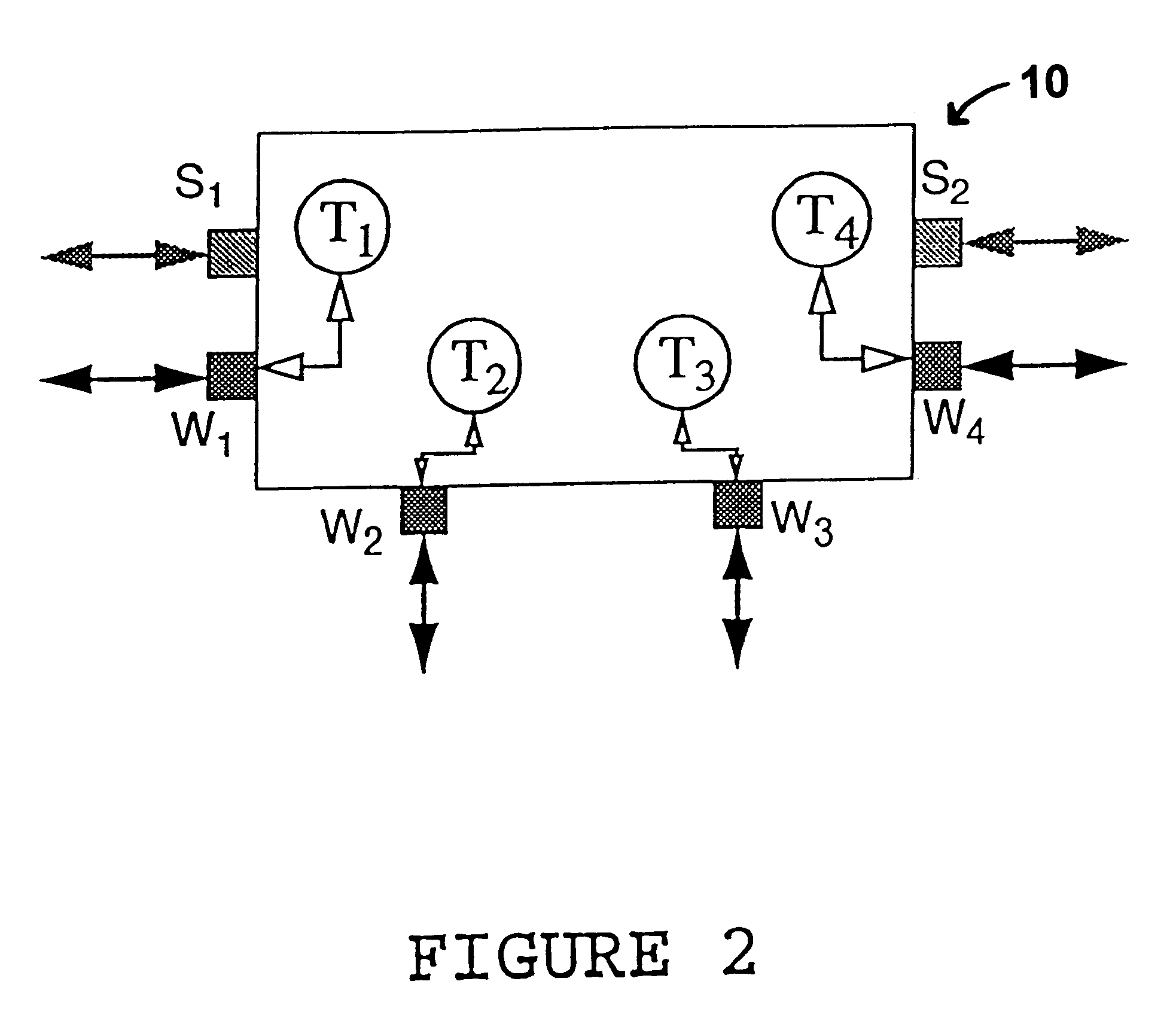
Scalable network restoration device
Tis invention provides a "capacity slice' nodal switching device (in the ADM-like sense) that is designed for deployment under the p-cycle concept. The device's key architectural properties are access, east and west interfaces, with one spare and working port, on each of these interface sides, plus at least two straddling side interfaces. The straddling side interfaces each have equal line capacity to those of east and west interfaces, but all are usable for working capacity. In application, the plug cards in the nodal switching device are supplied to provide up to two line signal units on the straddling side of the p-cycle device, per diverse span arriving at the site. Network level deployment and configuration of the devices requires that they be arranged in p-cycles.
Owner:TELECOMM RES LAB
Method and mobile terminal for rapidly searching for messages received from or sent to same phone number
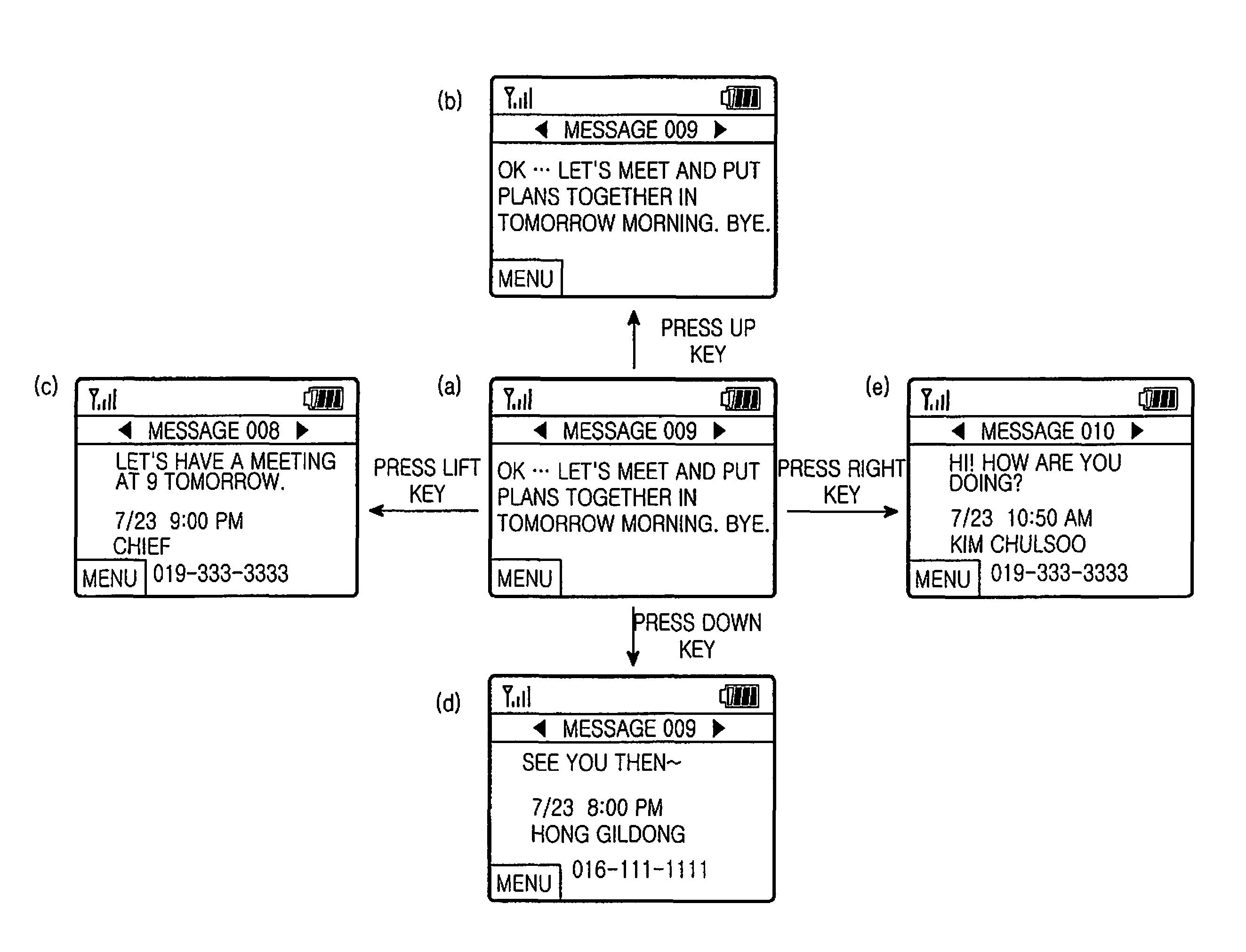
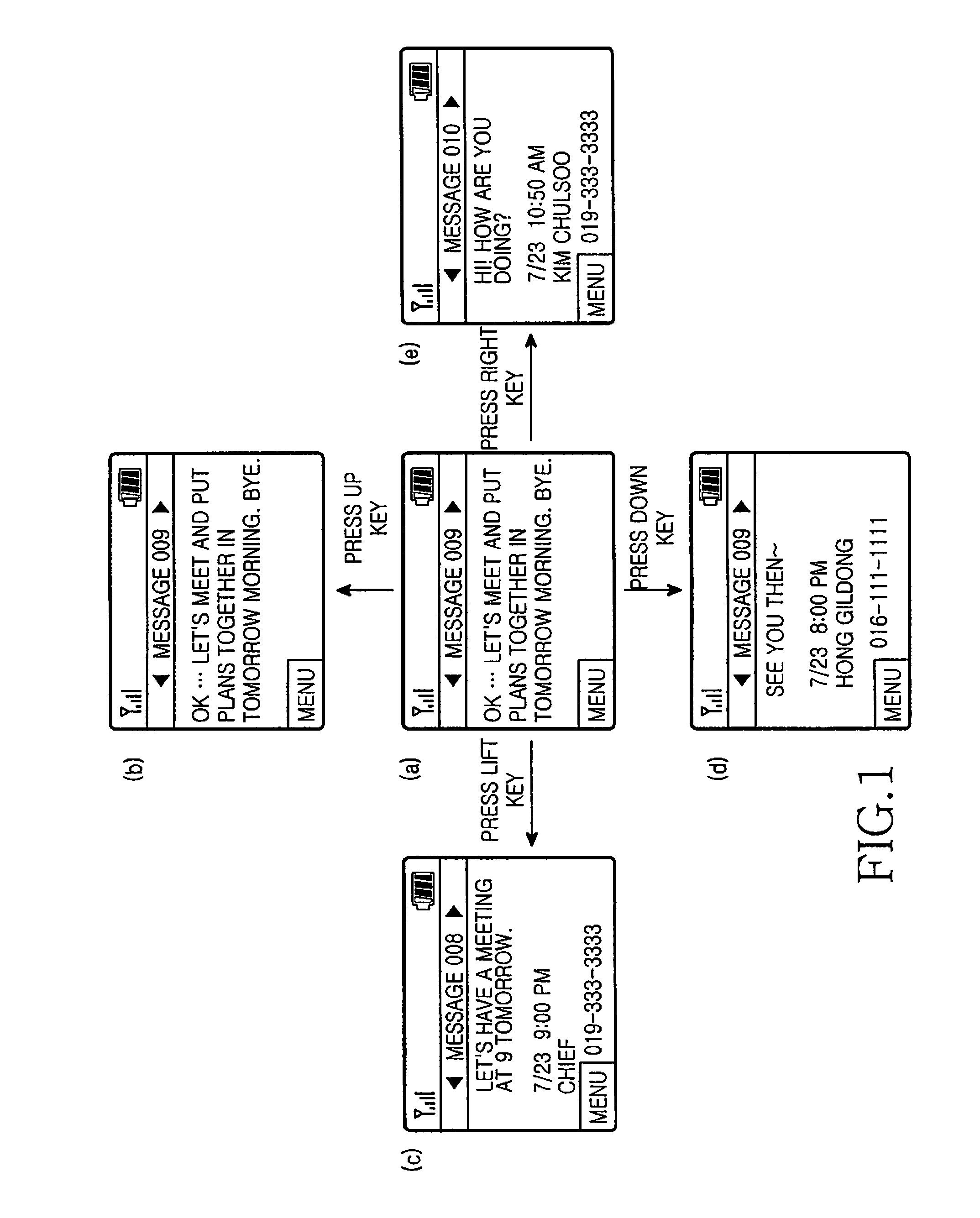
InactiveUS8355700B2Easily and rapidly searchingAutomatic call-answering/message-recording/conversation-recordingData switching networksComputer hardwareUser input
Disclosed are a method and a mobile terminal for easily and rapidly searching for messages received from or sent to the same phone number of a currently displayed message. The method includes a first step of detecting whether a user inputs a key to select a previous or next message received from or sent to the same phone number of a currently displayed message; a second step of searching for the previous or next message received from or sent to the same phone number upon detecting the user's key input; and a third step of displaying the detected message on a display unit of the mobile terminal.
Owner:SAMSUNG ELECTRONICS CO LTD
Fully configurable trading keyboard
ActiveUS20060007160A1Complete banking machinesInput/output for user-computer interactionKey pressingS/KEY
The present invention provides a trading keyboard that can be configured both physically and functionally according to a user's preferences. The trading keyboard preferably includes self-identifying key covers that can be physically arranged on any of the keyboard's key bases. Detection mechanisms included in the key bases detect the commands of the trading application associated with each self-identifying key cover. Therefore, the user may reposition the key covers on the keyboard according to the user's preferences, and yet retain the same functionality for the key covers. The user may also switch between keyboard modes that allow the keyboard to be functionally reconfigured. By selecting different modes, the user can chose between different keyboard mapping configurations that assign the functions of the trading application to the keys in different arrangements. The mode selection mechanism may also be used to select between different commands associated with a single key or key cover.
Owner:BGC PARTNERS LP
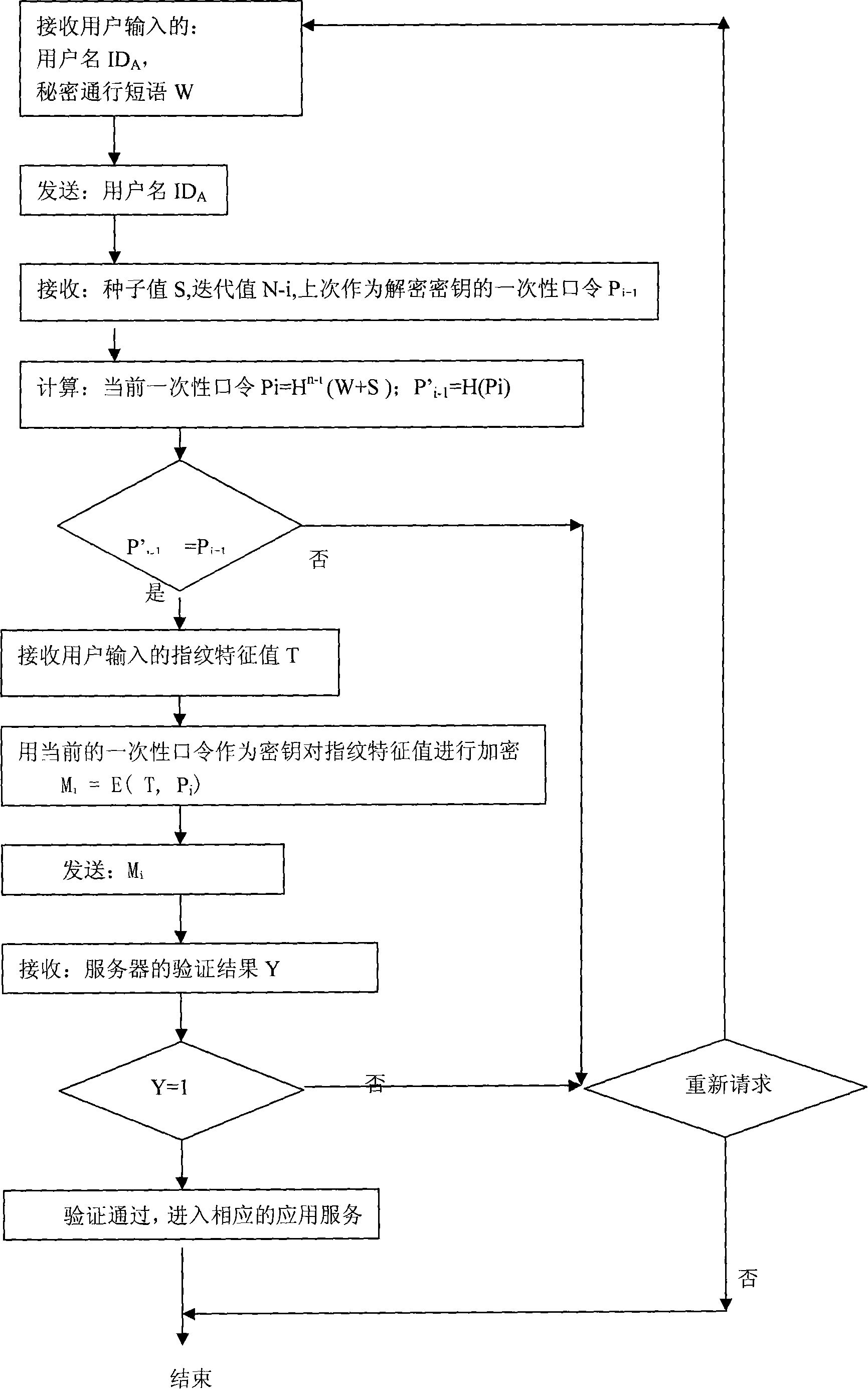
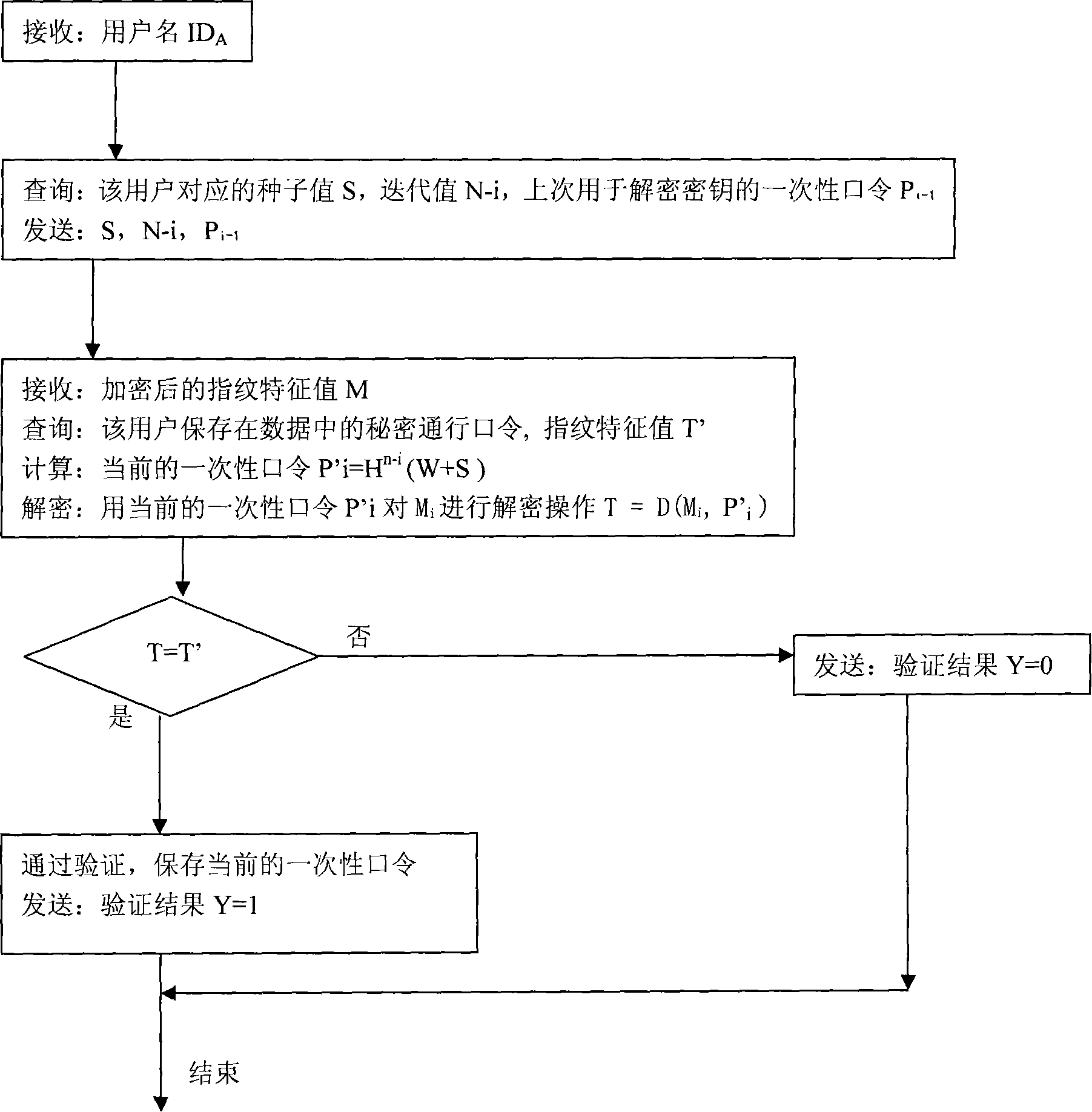
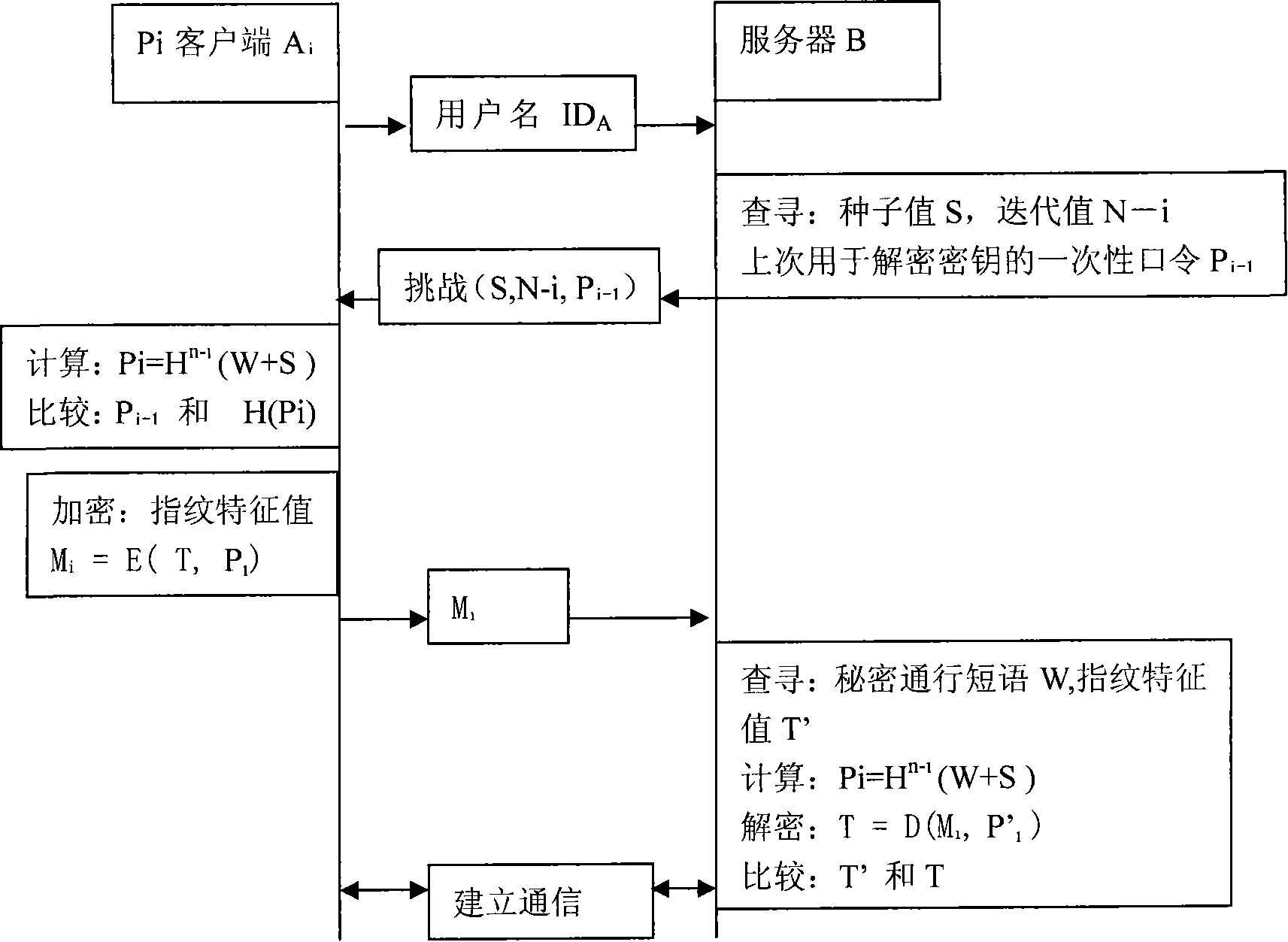
Identity authentication method based on S/Key system
InactiveCN101174953AImprove securityAdd identity authenticationUser identity/authority verificationCharacter and pattern recognitionBiological propertyS/KEY
The present invention relates to an ID identification method based on the S / Key system. The present invention submits the registration data comprising a user name, a code and password, iteration value and the biological property value to an identification server through a user side; the server forms the seed value corresponding to the user and calculates the first one-off password of the password sequence. A duplex identification between the client side and the server which is also the duplex identification of the combination of the one-off password of the registered user and the biological proper value is implemented in the process of user ID identification. .
Owner:LANZHOU UNIVERSITY +1
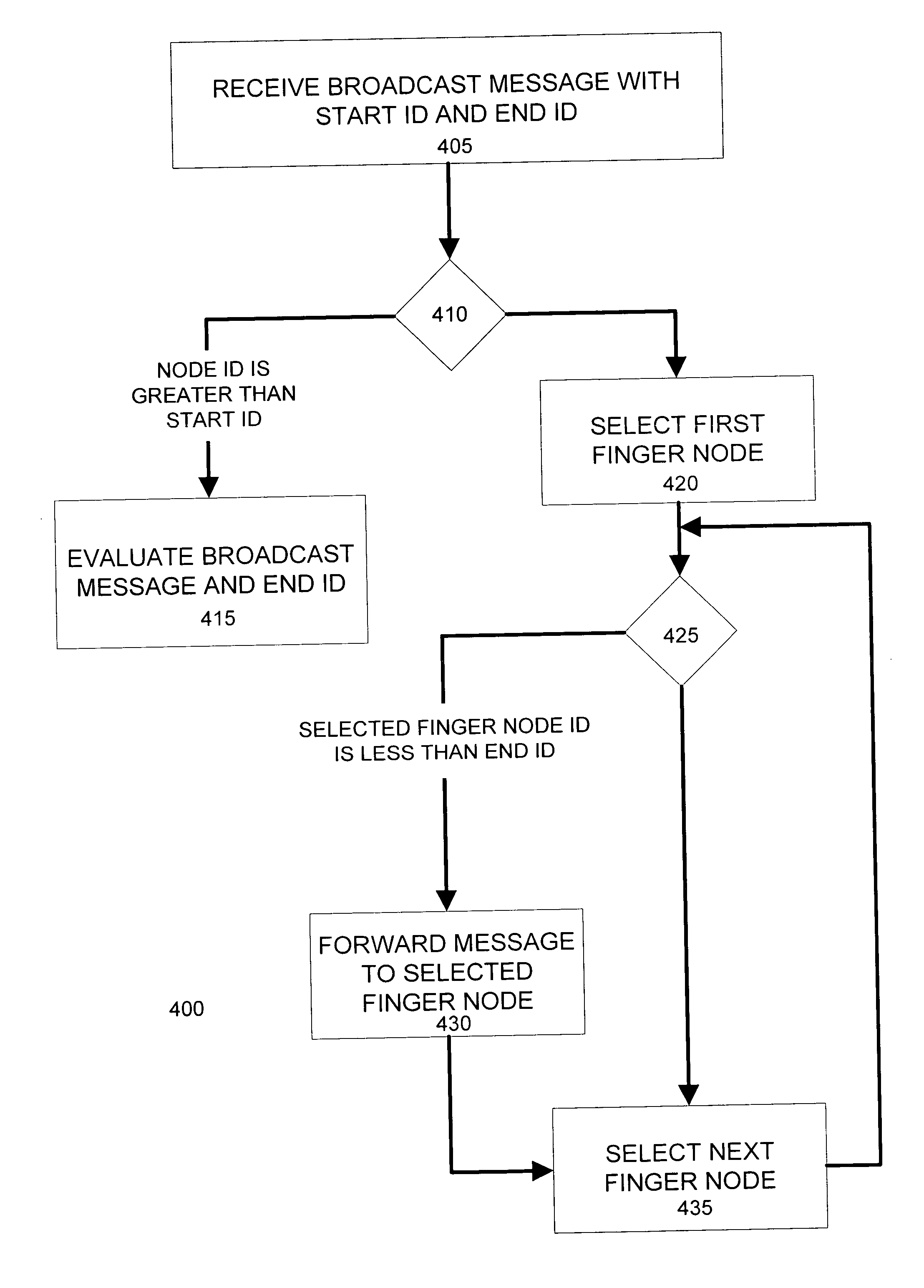
Broadcast messaging in peer to peer overlay network
ActiveUS20070121570A1Without wastingEfficiently directsError preventionFrequency-division multiplex detailsS/KEYPeer to peer overlay networks
Broadcast messages are efficiently directed to nodes of an overlay network. Broadcast messages include an End ID parameter specifying the range of key values for nodes that should receive the broadcast message. Each node of an overlay network maintains a list of finger nodes and their respective key values. Upon receiving a broadcast message, a node assigns a finger node a new End ID value based upon the End ID value of the broadcast message or the key value of an adjacent finger node. The node compares a finger node's new End ID value with the finger node's key value to determine whether to forward the broadcast message to that finger node. A broadcast message forwarded to a finger node includes an End ID parameter equal to the new End ID value determined for the finger node. Nodes can aggregate response messages from its finger nodes.
Owner:SONY COMPUTER ENTERTAINMENT INC
Method of securing files under the semi-trusted user threat model using symmetric keys and per-block key encryption
ActiveUS20150288664A1Rapid and efficientImprove security levelKey distribution for secure communicationMultiple keys/algorithms usageFile systemTrusted client
A computer system and method for securing files in a file system equipped with storage resources that are accessible to an authenticable user operating with an untrusted client device under the semi-trusted client threat model. The file to be secured is stored in one or more blocks belonging to the storage resources along with symmetric per-block key(s) KBi assigned to each of the blocks in the file. The blocks are encrypted with the symmetric per-block keys to obtain encrypted blocks. The user is assigned user key(s) and each per-block key that was used for encryption is in turn encrypted with one of the user's keys to derive wrapped key(s) for each encrypted block. Wrapped key(s) are placed in encrypted block headers and introduce a level of indirection to encrypted file(s) that is appropriate for the semi-trusted client threat model.
Owner:ZETTASET
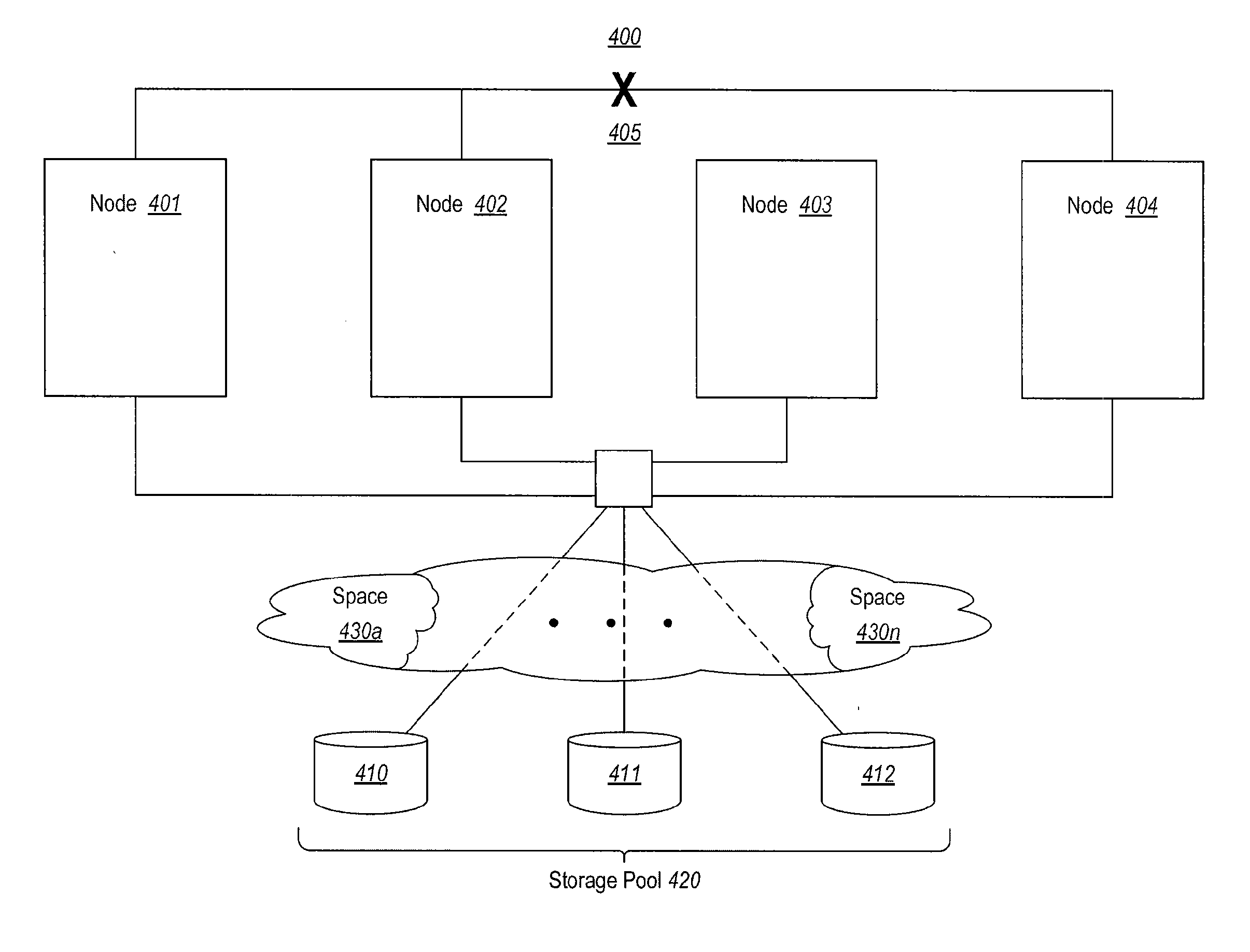
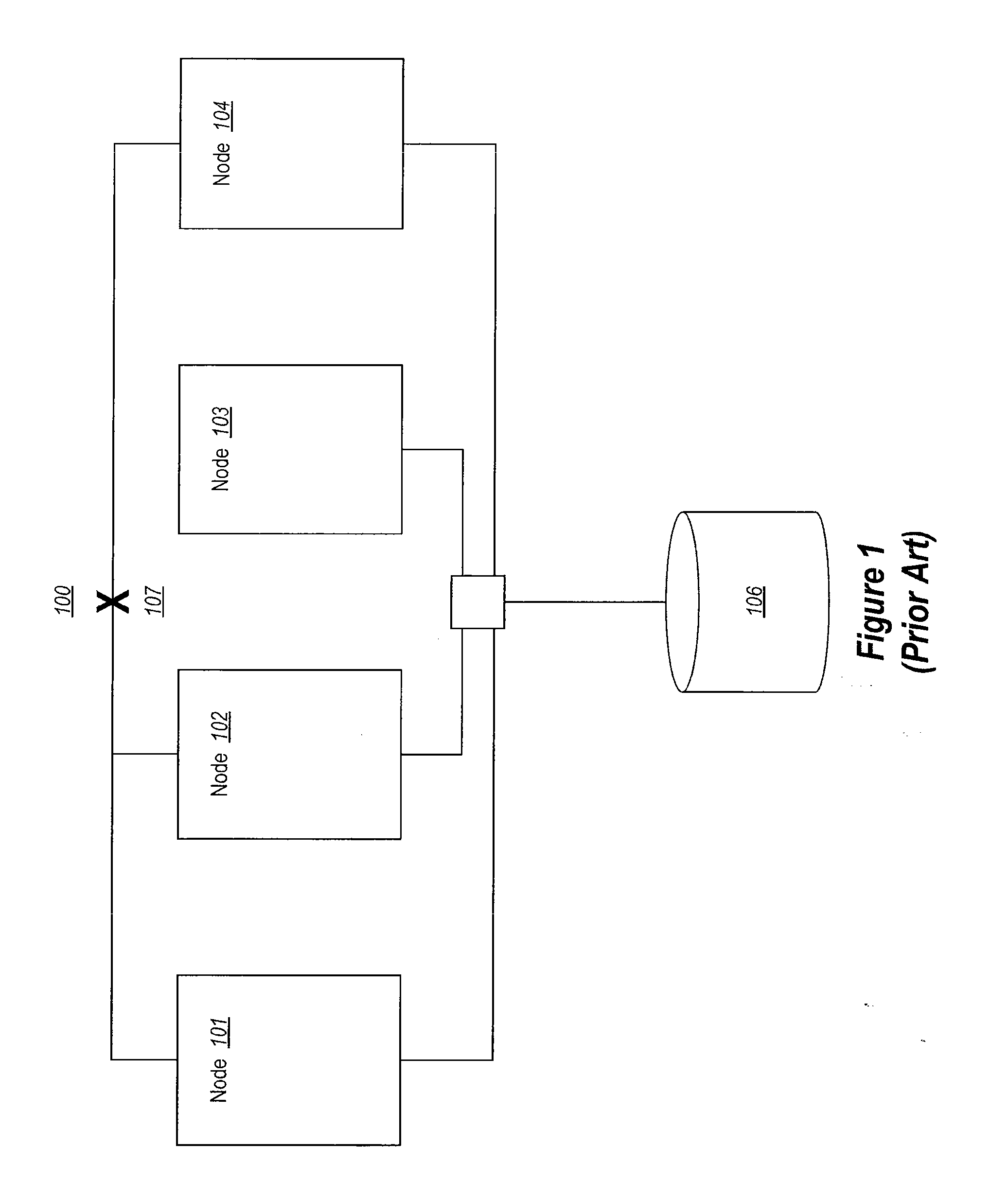
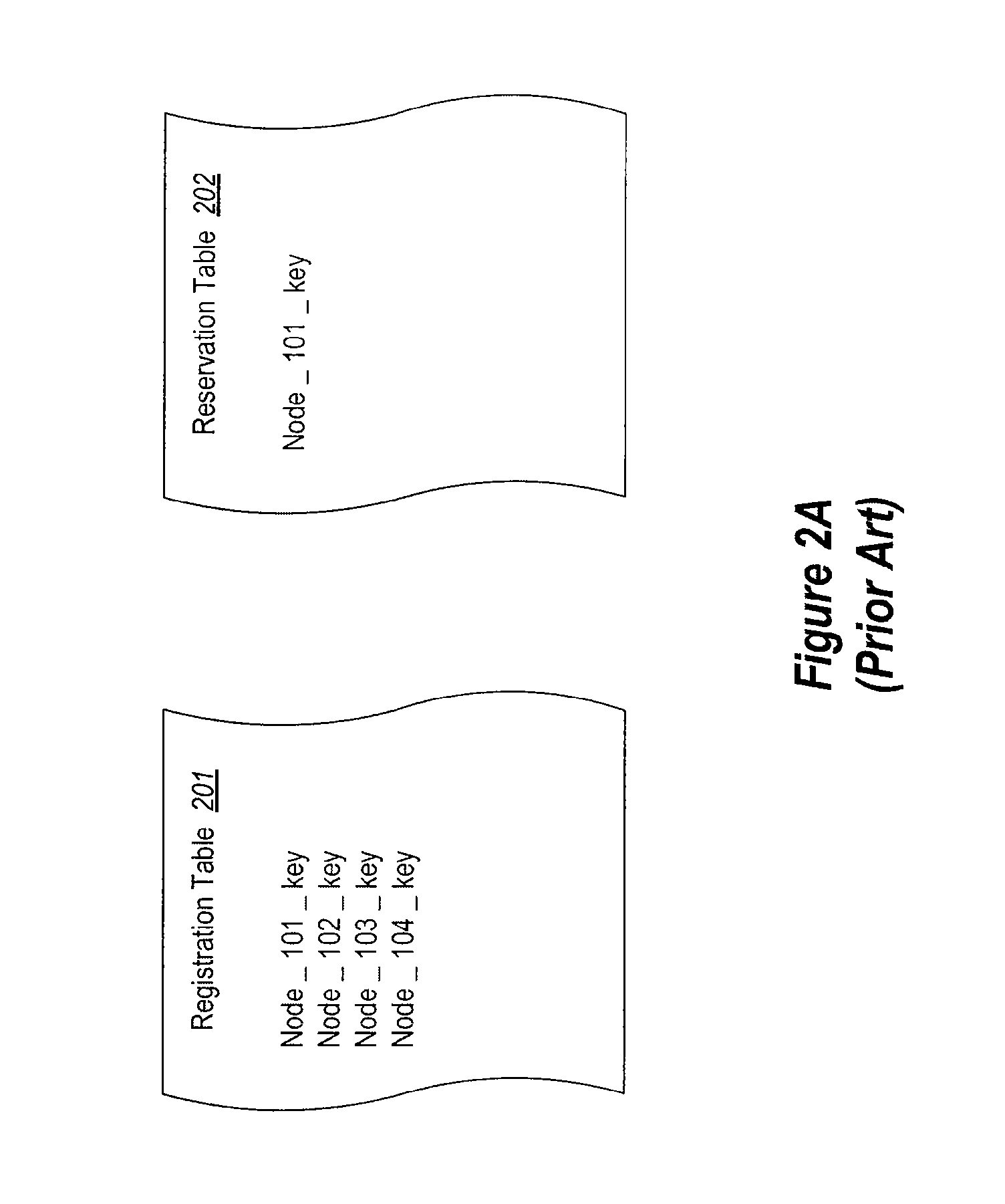
Arbitration of disk ownership in a storage pool
InactiveUS20130227009A1Multiple digital computer combinationsFile access structuresS/KEYStorage pool
The present invention extends to methods, systems, and computer program products for implementing persistent reservation techniques for establishing ownership of one or more physical disks. These persistent reservation techniques can be employed to determine ownership of physical disks in a storage pool as well as in any other storage configuration. Using the persistent reservation techniques of the present invention, when a network partition occurs, a defender of a physical disk does not remove a challenger's registration key until the defender receives notification that the challenger is no longer in the defender's partition. In this way, pending I / O from applications executing on the challenger will not fail due to the challenger's key being removed until the proper ownership of the physical disk can be resolved.
Owner:MICROSOFT TECH LICENSING LLC
Methods for common authentication and authorization across independent networks
ActiveUS7774828B2Digital data processing detailsUser identity/authority verificationS/KEYNetwork Communication Protocols
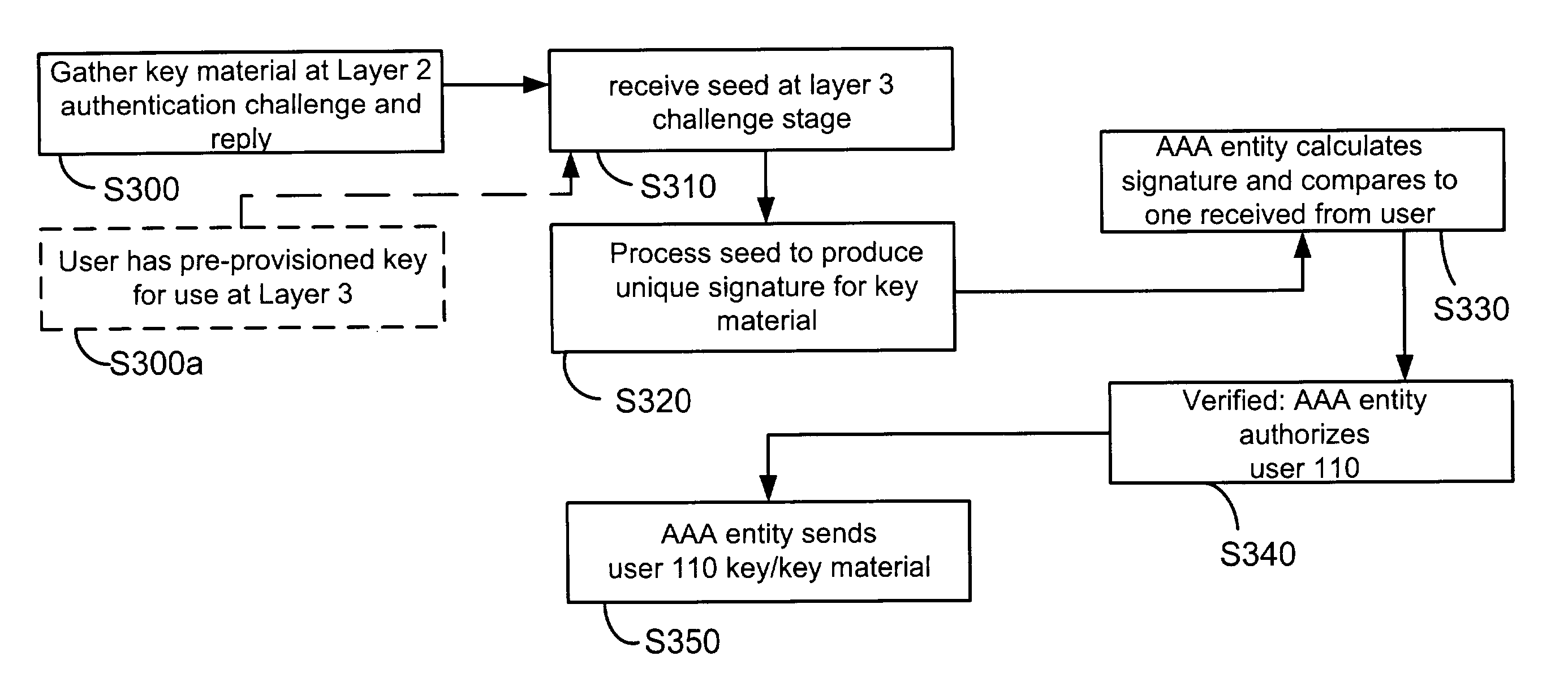
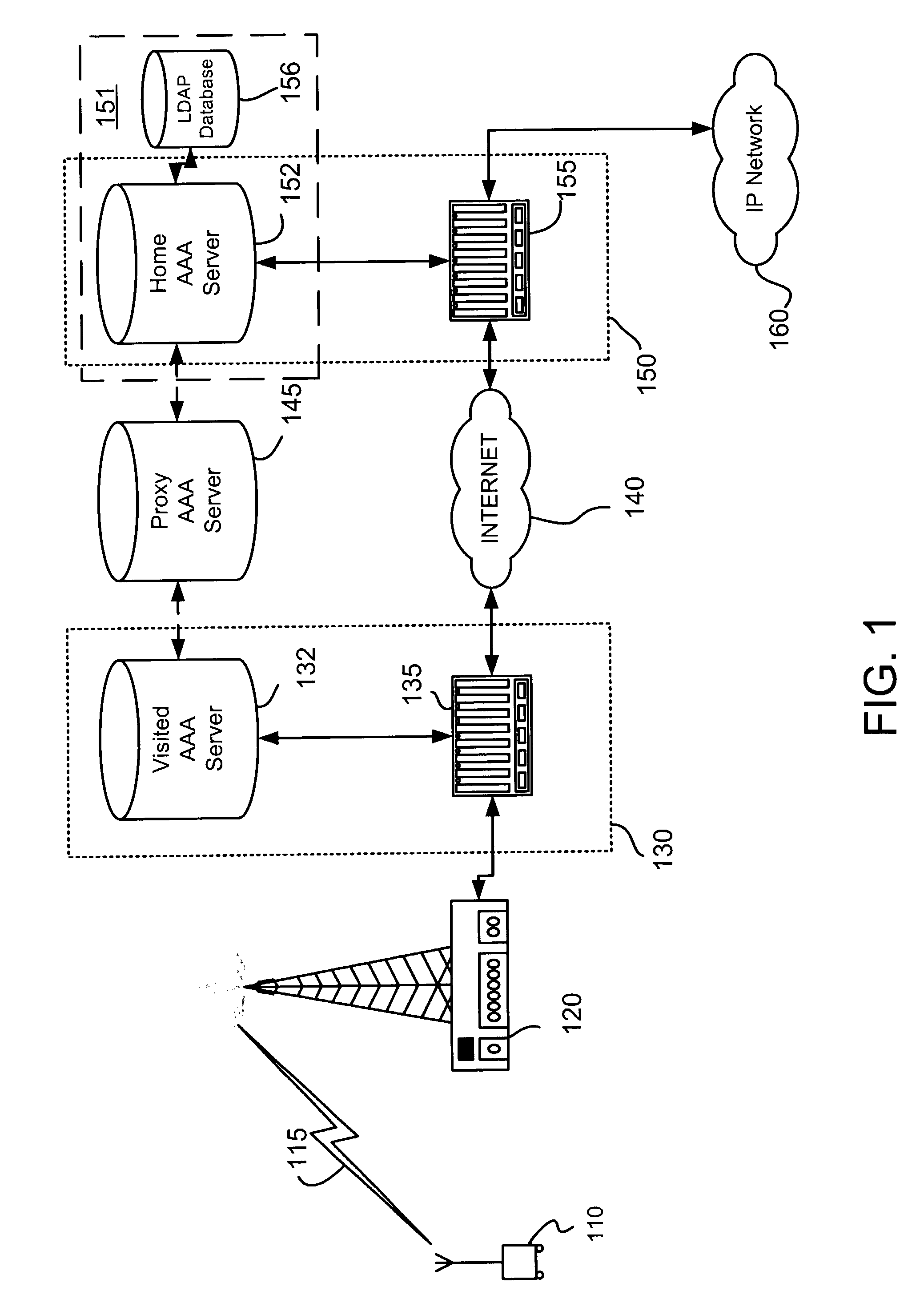
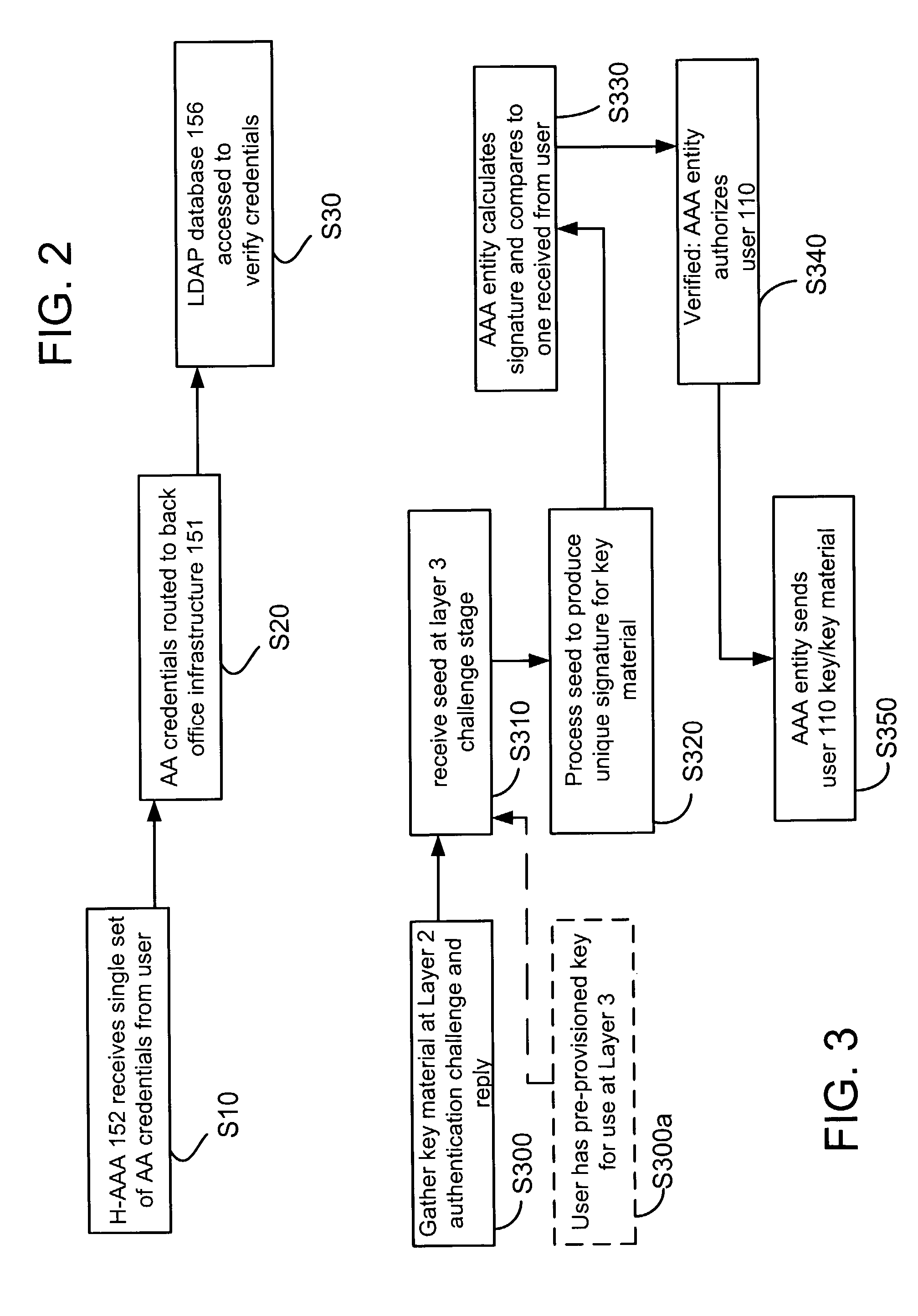
Common authentication and authorization (AA) between networks having disparate access technologies may enable a seamless user transition between the networks. A set of AA credentials from a user attempting to gain access to one of the networks may be received, and a subscriber database of another of the networks may be used to verify the set of AA credentials. A communication protocol common to the networks may be used. Additionally, the user may employ a single set of authentication and authorization (AA) credentials, usable over multiple communication protocol layers. Further, a user may perform a single authentication and authorization (AA) operation when roaming across two or more networks by gathering user's key material during an AA challenge and reply session at a data link layer. The gathered material may be used for an AA challenge at an upper network layer or another network as the user transitions between networks.
Owner:ALCATEL LUCENT SAS
Privacy-enhanced searches using encryption
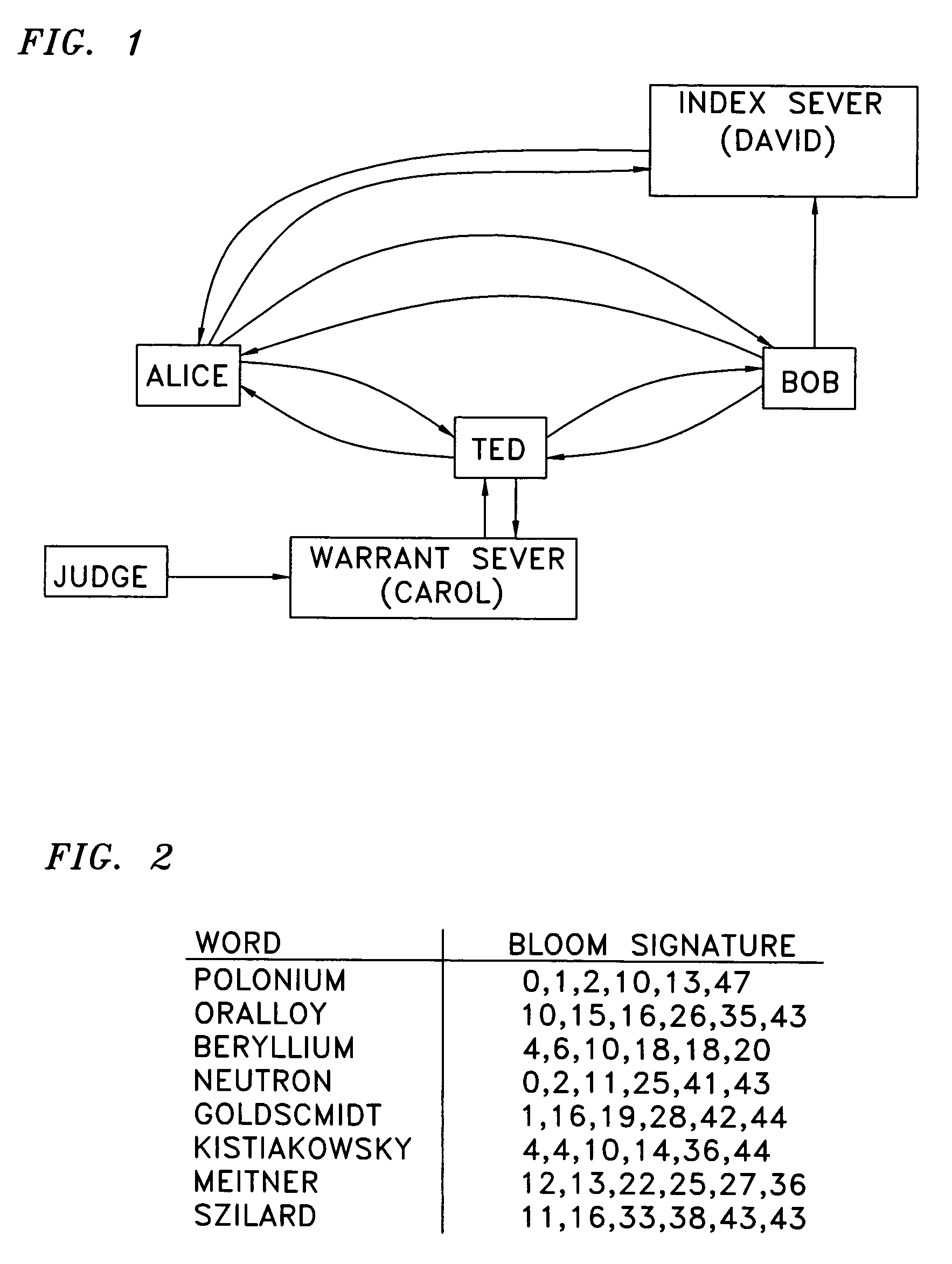
ActiveUS7558970B2Public key for secure communicationUser identity/authority verificationS/KEYBloom filter
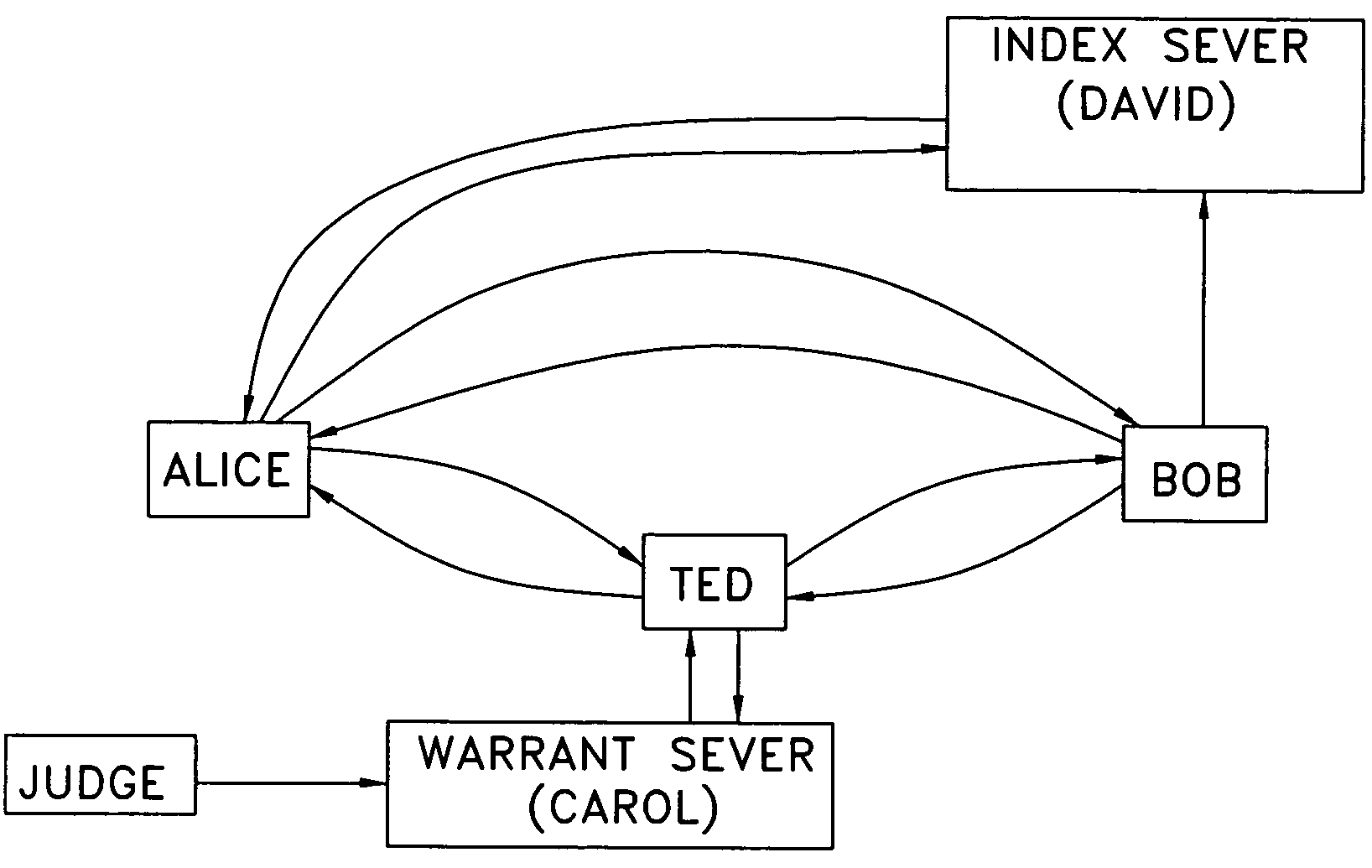
Encryption with keys that form an Abelian group are used in combination with a semi-trusted party that converts queries that are encrypted with the key of a querier to queries that are encrypted with the key of the encrypted database, without knowing the actual keys. In an illustrative embodiment, encryption is done with Bloom filters that employ Pohlig-Hellman encryption. Since the querier's key is not divulged, neither the semi-trusted party nor the publisher of the database can see the original queries. Provision can be made for fourth party “warrant servers”, as well as “censorship sets” that limit the data to be shared.
Owner:AT&T INTPROP II L P
Any-point-to-any-point (AP2AP) quantum key distribution protocol for optical ring network
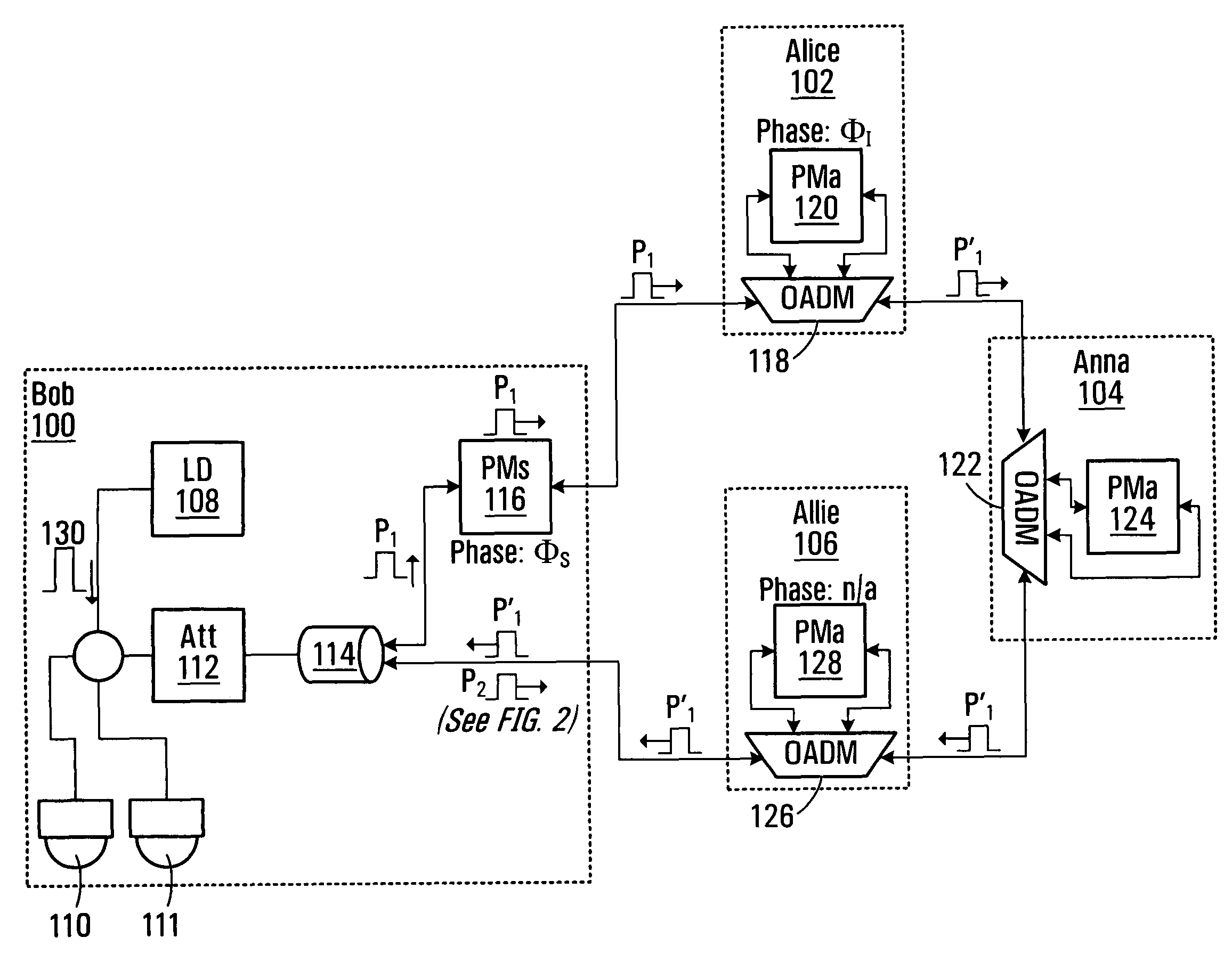
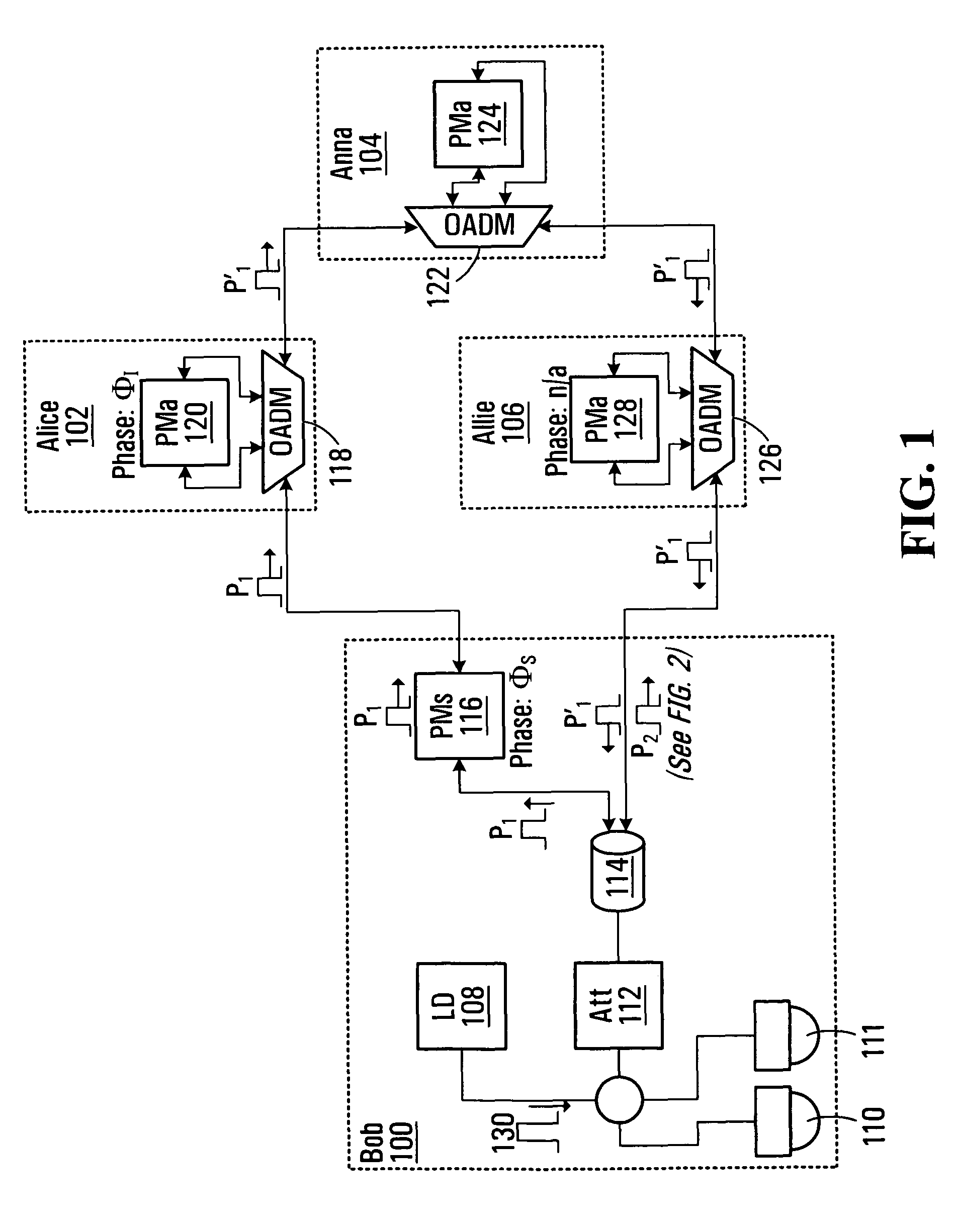
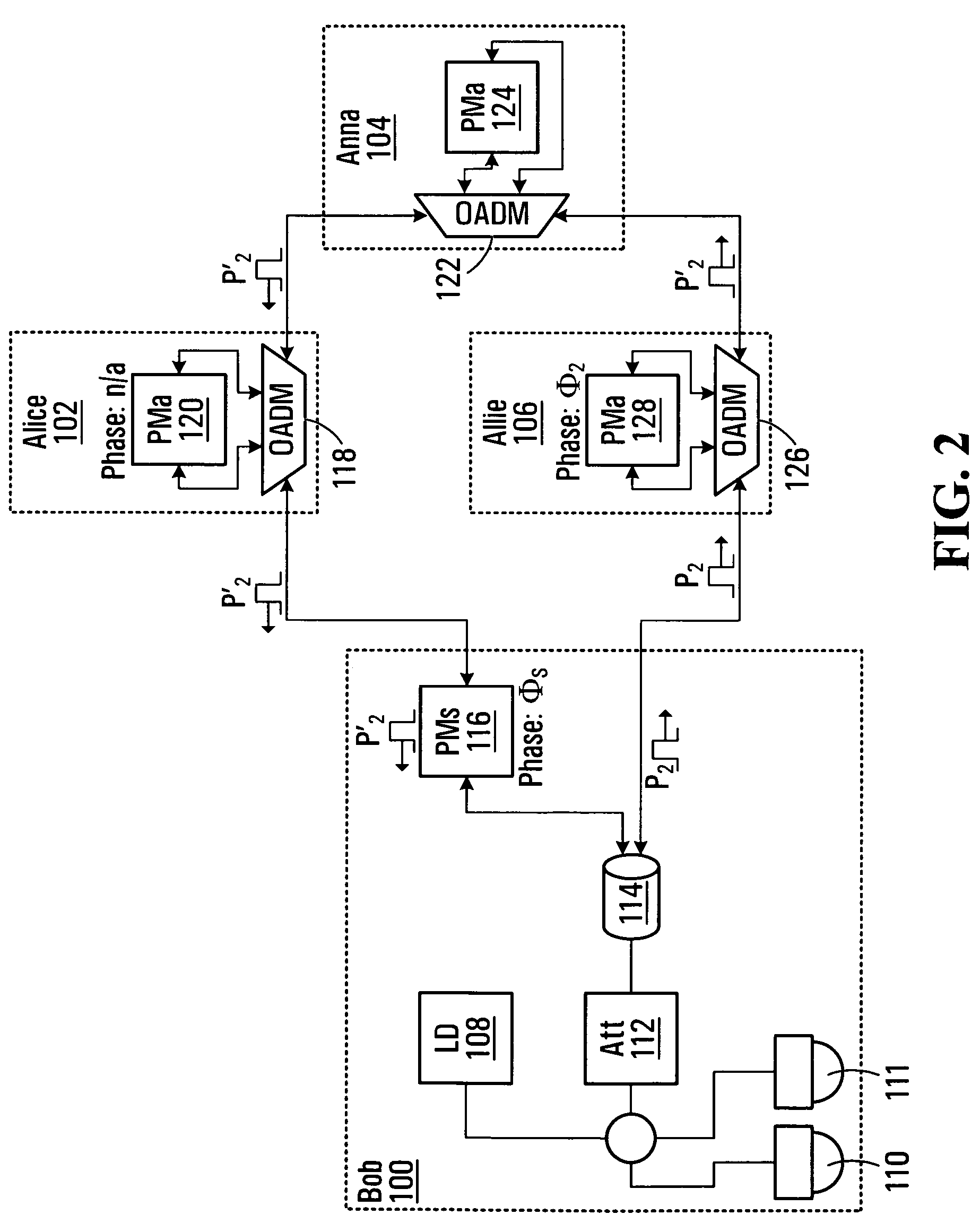
InactiveUS7760883B2Key distribution for secure communicationSecret communicationComputer hardwareS/KEY
Apparatus for distributing a quantum key between nodes Alice and Allie, comprising a coupler that splits generated photon pulses into first and second pulses P1 and P2; and an interface that transmits the P1's and P2's into a network. The P1's are received after modulation by Alice with respective phases selected from two encoding bases and further selected from within the selected encoding basis as a function of a bit value of a respective bit in a key bit string maintained by Alice. The P2's are received after similar modulation by Allie. A detector processes the P1's and P2's upon receipt to produce a sequence of detection outcomes indicative of phase mismatch between the P1's and corresponding P2's. A control unit receives an indication of occurrences of a match between the encoding bases employed by Alice and the encoding bases employed by Allie, derives an XOR bit string from those detection outcomes that are associated with occurrences of a match, and communicates the XOR bit string to Alice and / or Allie. Execution of an XOR between the XOR bit string and either Alice's or Allie's key bit string allows the two participants to form a shifted key.
Owner:RPX CLEARINGHOUSE
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com