Method and apparatus of on demand business activity management using business performance management loops
a business activity management and business performance technology, applied in the field of business process management, can solve the problems of static processes that cannot adapt to changing needs, slow response to both the problems occurring in the organization and the changes of requirements from customers, and the linear and rigid nature of bpm processes and architectures, and achieve the effect of expanding business performance management capabilities
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
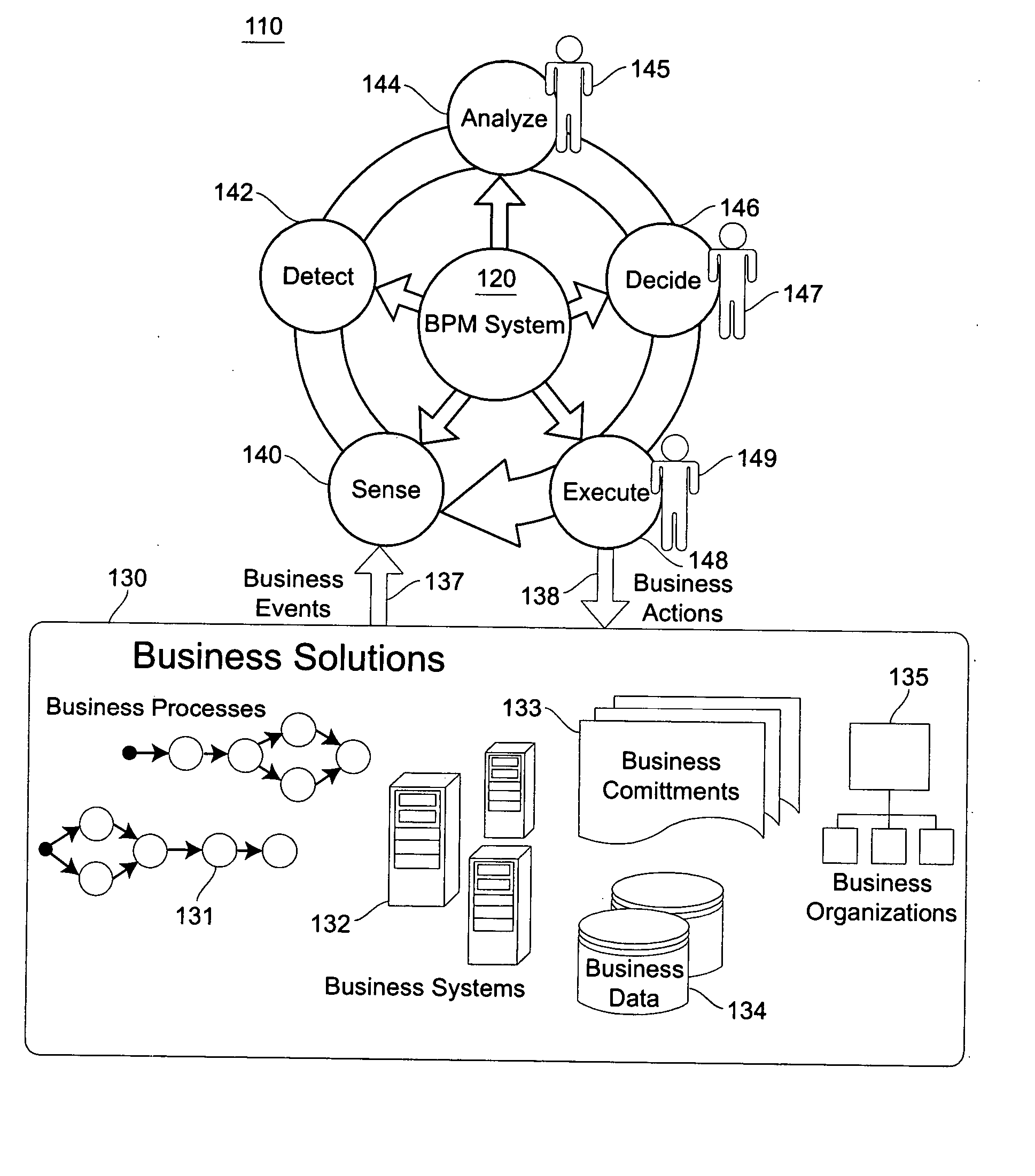
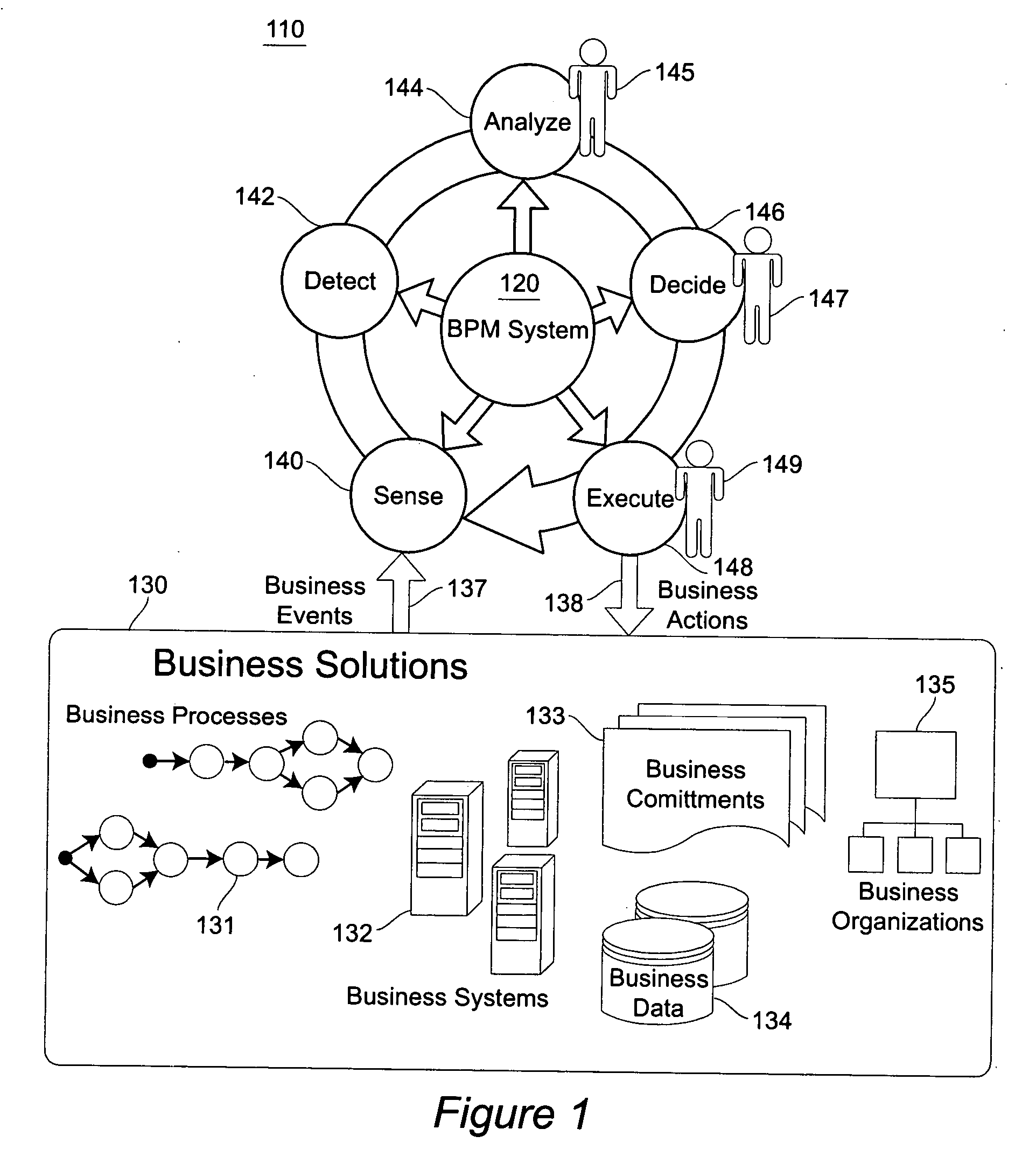
[0027] Referring now to the drawings, and more particularly to FIG. 1, there is shown a business-activity management cycle or “BPM loop”110. A policy based BPM loop structure for a BPM system 120 takes monitored data from target business solutions 130 (e.g. business events 137), invokes BPM services and renders business actions 138 back to target business solutions 130 in a continuous cycle. The business solutions 130 are characterized by one or more business processes 131, business IT systems 132, business commitments 133, business data sets 134, and business organizations 135. In general, there are five representative categories of services in a BPM loop structure 110 for a BPM system 120 according to the invention: Sense 140, Detect 142, Analyze 144, Decide 146 and Execute 148. [0028]“Sense”140 is the stage when a BPM system 120 interacts with business solutions 130 and provides data extraction, transformation, and loading capabilities for the sake of preparing qualified data tha...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com