Data processing apparatus having memory protection unit
a technology for data processing apparatus and protection units, applied in the field of data processing systems, can solve the problems of reducing limiting the number of memory regions, so as to reduce the number of multiplexers, reduce the area of circuitry, and improve the effect of perfromation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
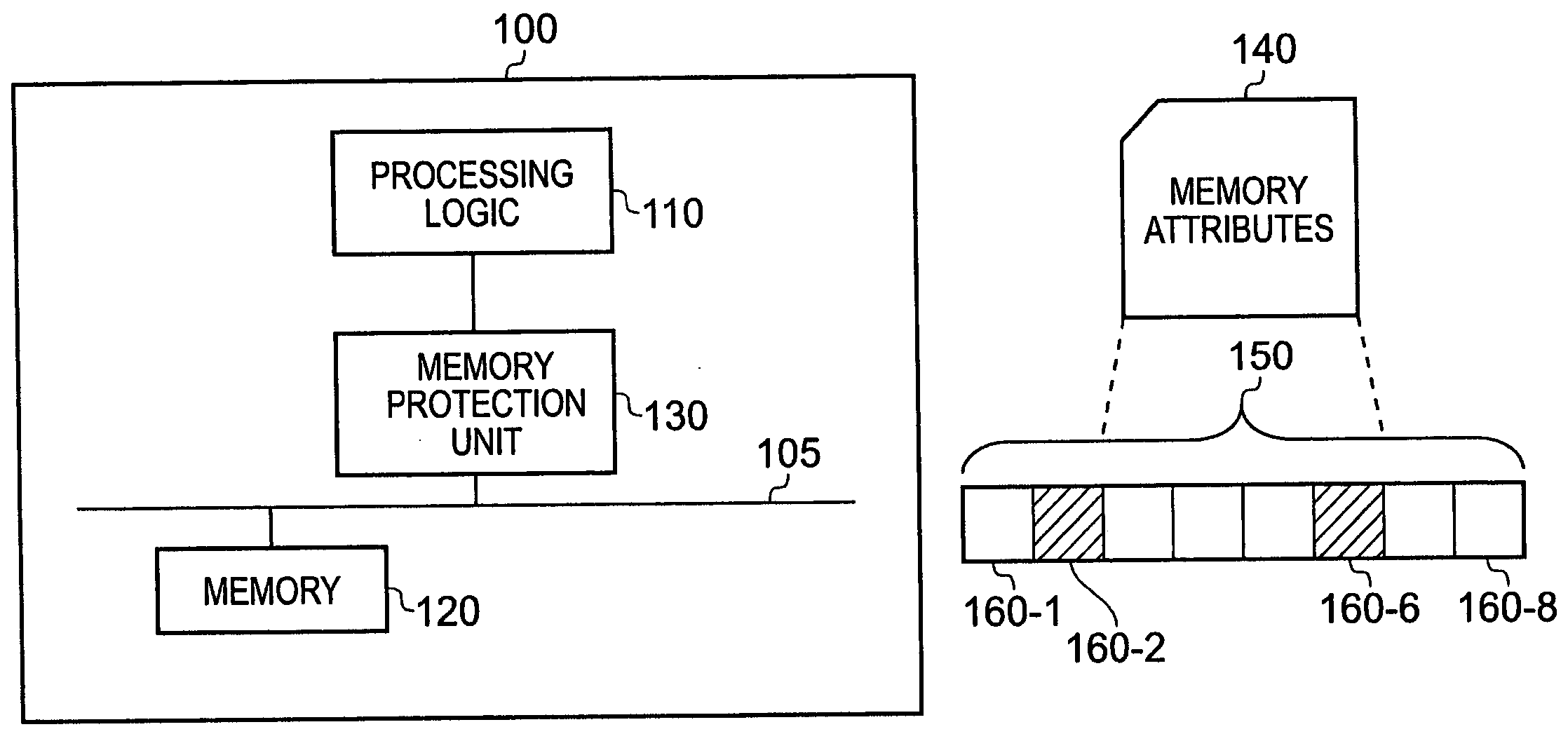
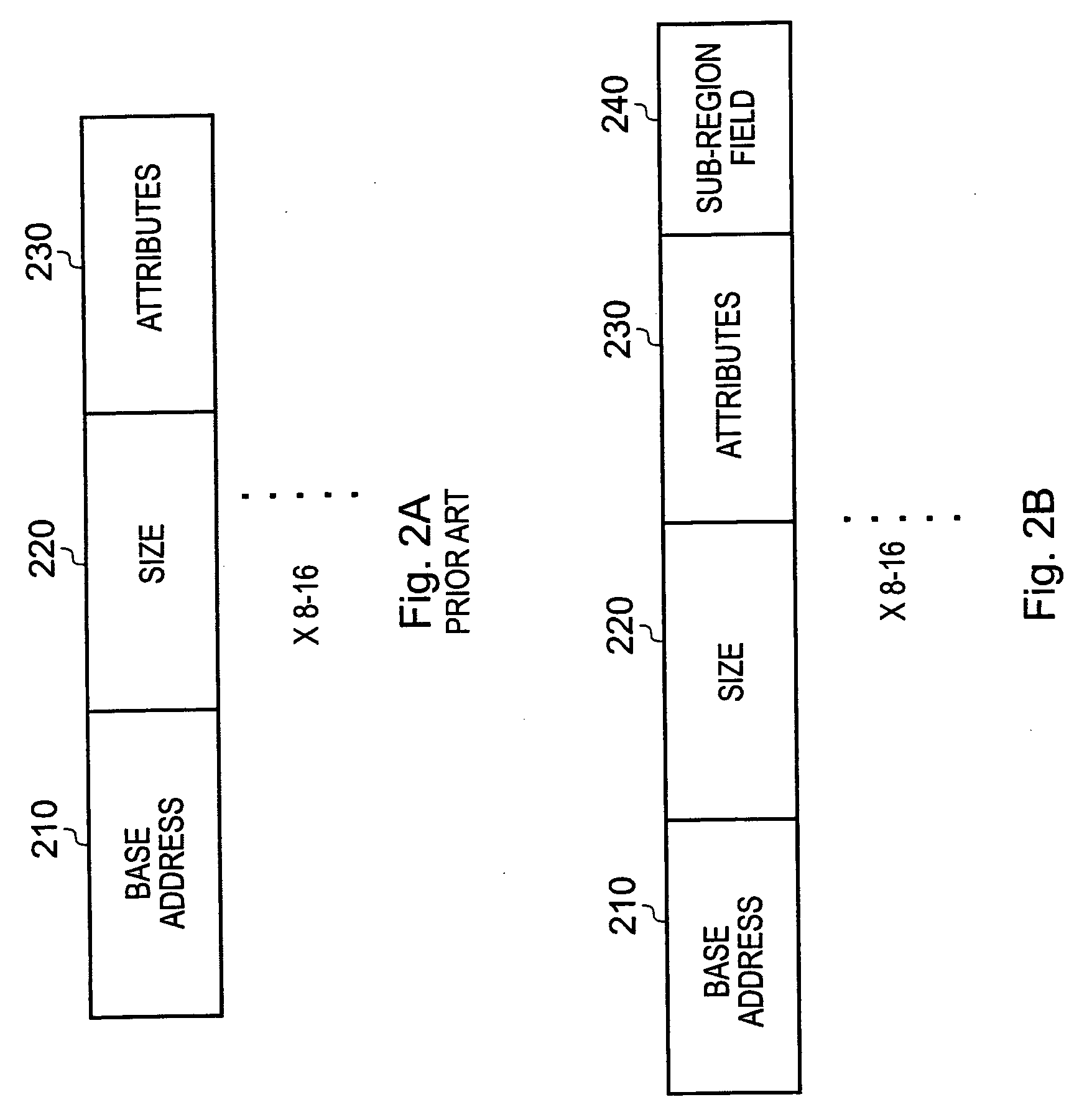
[0049]FIG. 1 schematically illustrates a data processing apparatus according to the present technique. The data processing apparatus 100 comprises processing logic 110, memory 120 operable to store data and / or instructions and a memory protection unit 130. The memory 120 is connected to a bus 105 and the processing logic 110 is connected to the memory protection unit 130, which is in turn connected to the bus. The memory protection unit 130 provides a way of managing the memory 120 and defines a plurality of different memory regions having respective sets of memory attributes 140. The memory protection unit 130 manages the physical memory address space. The memory protection unit 130 defines attributes associated with each of the plurality of protection regions by writing to respective protection unit registers. The size of a memory region is 2n, where n is an integer and can the size range from 4 KB up to 4 GB. The starting address of a memory region is constrained in this embodime...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com