Patents
Literature
68 results about "Memory protection unit" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
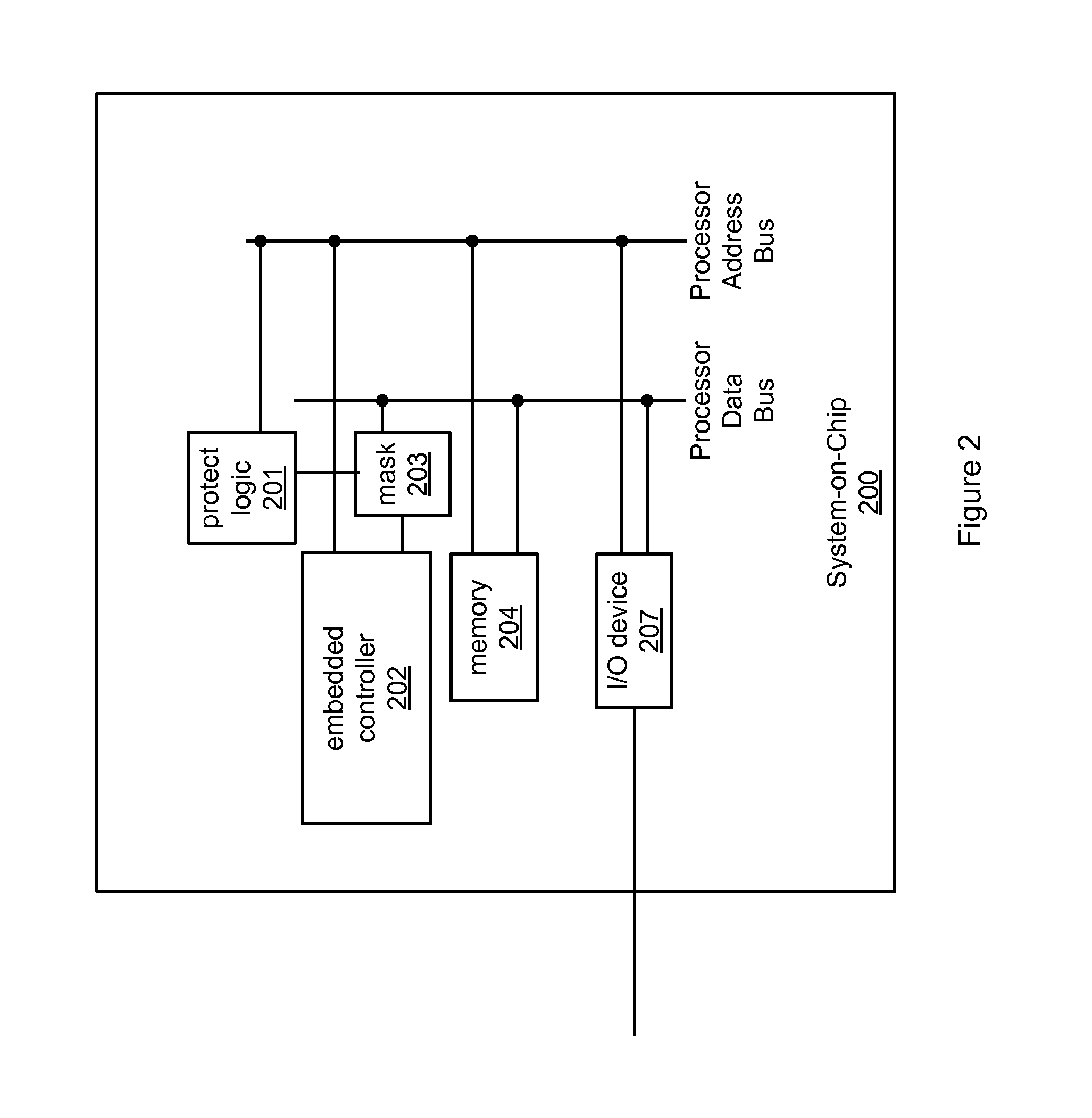
Memory protection unit. A memory protection unit (MPU), is a computer hardware unit that provide memory protection.
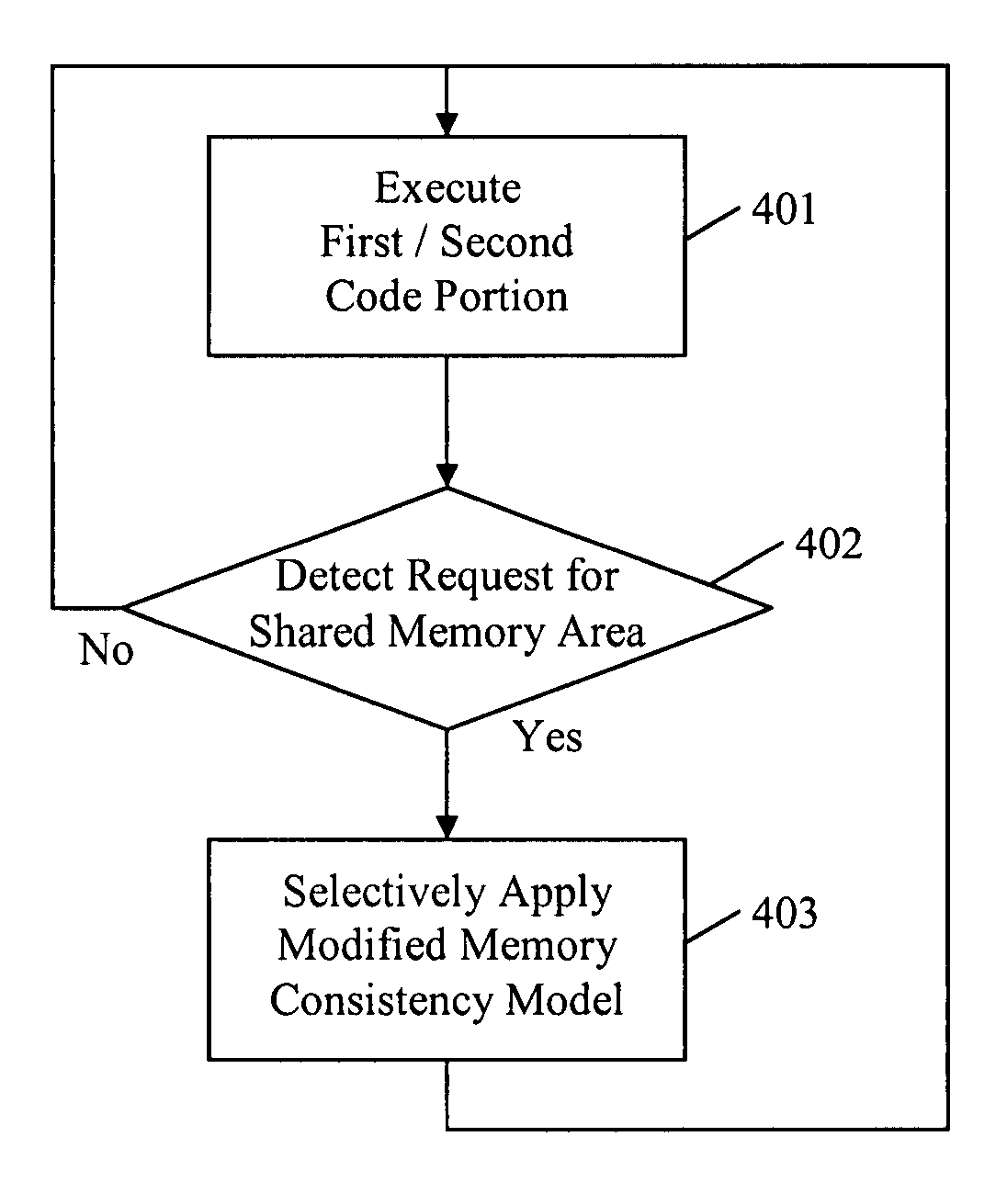
Memory consistency protection in a multiprocessor computing system
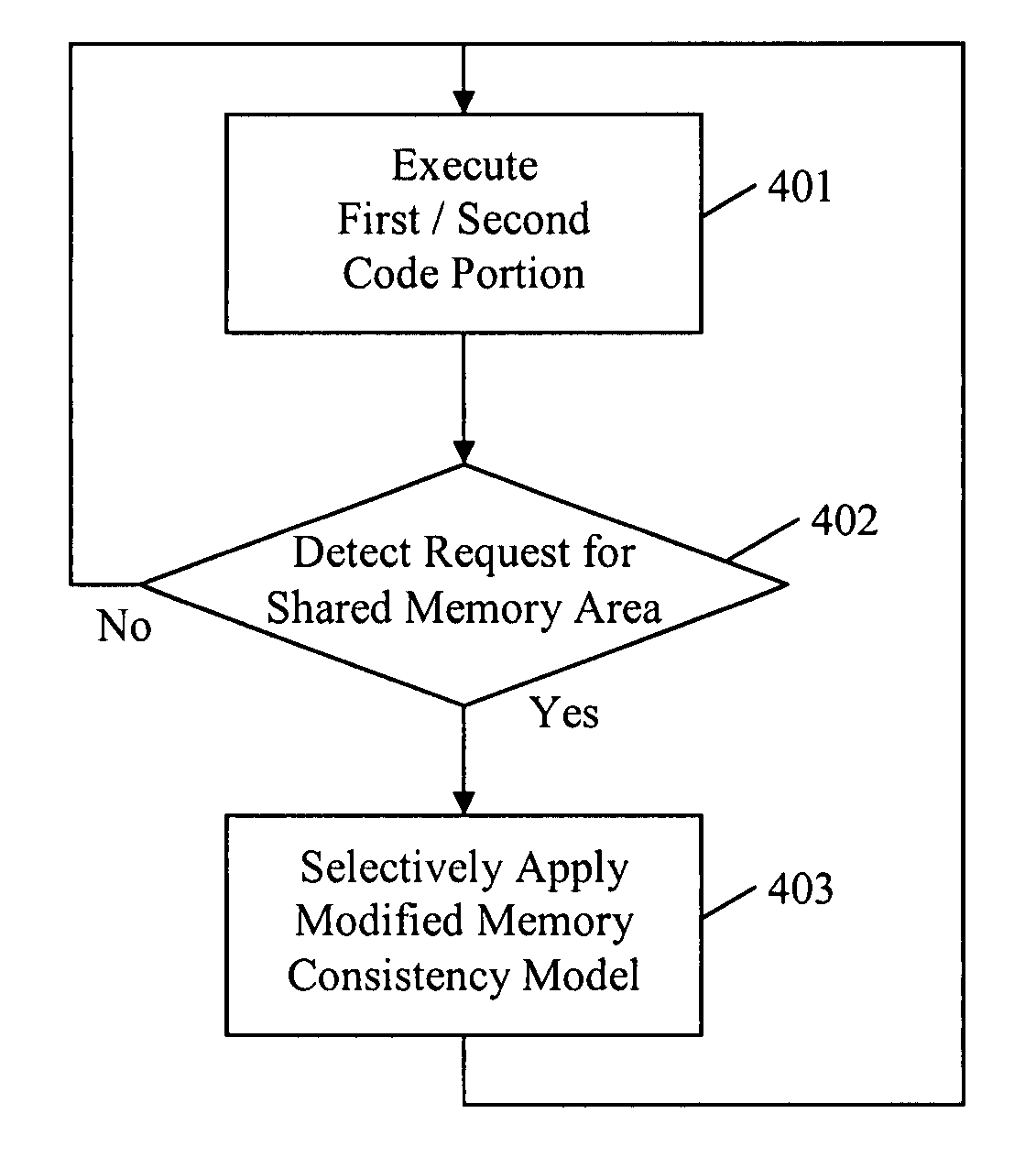
InactiveUS20080140971A1Low-cost and effectiveImproved memory consistencyResource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMulti processorObject code
A method and apparatus to protect memory consistency in a multiprocessor computing system are described, in particular relating to program code conversion such as dynamic binary translation. The exemplary system provides a memory, processors and a controller / translator unit (CTU) arranged to convert subject code into at least first and second target code portions executable on the processors. The CTU comprises an address space allocation unit to provide virtual address space regions and direct the target code portions to access the memory therethough; a shared memory detection unit to detect a request to access a shared memory area, accessible by both target code portions, and to identify at least one group of instructions in the first target code portion which access the shared memory area; and a memory protection unit to selectively apply memory consistency protection in relation to accesses to the shared memory area by the identified group of instructions.
Owner:IBM CORP
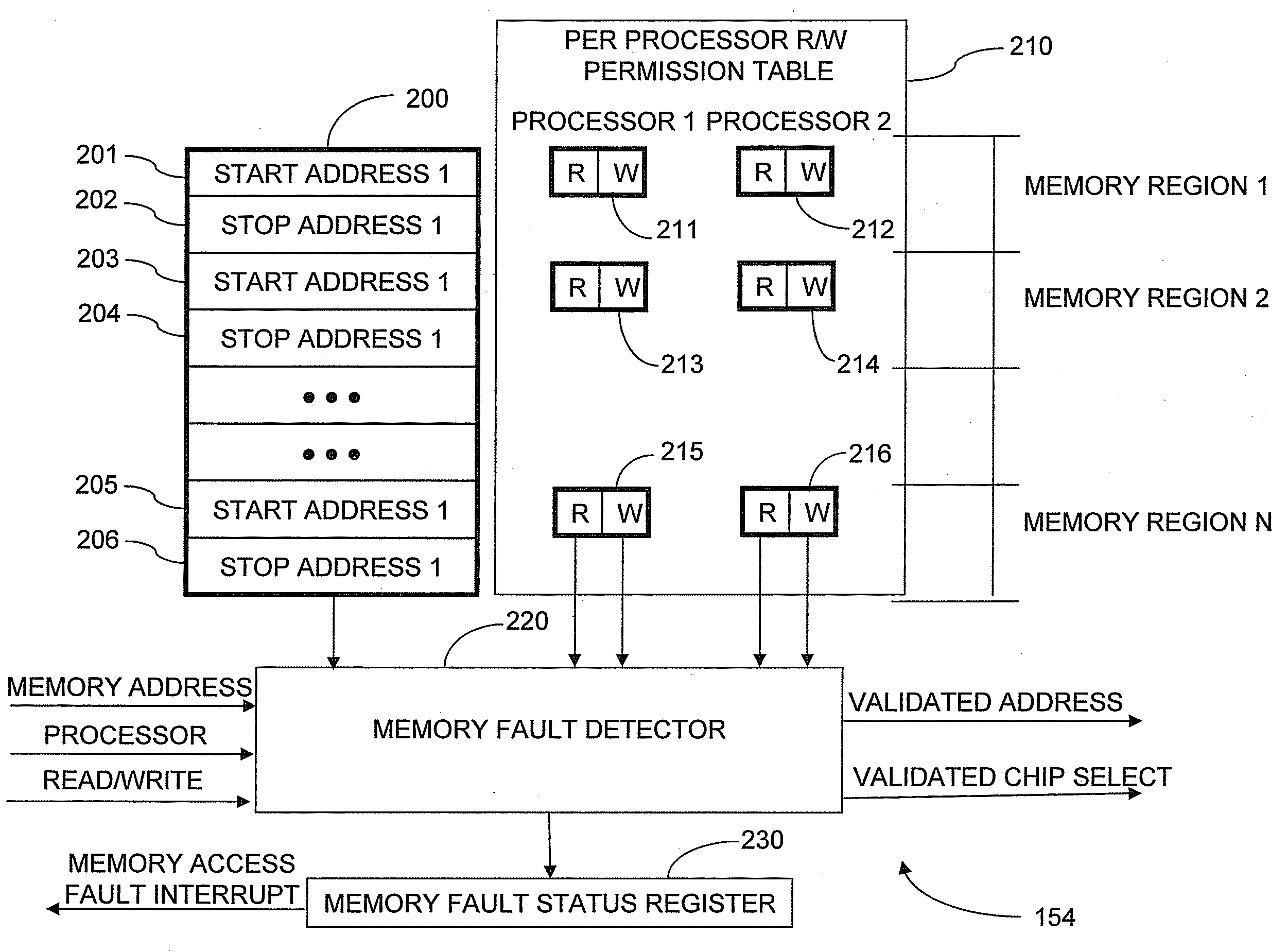
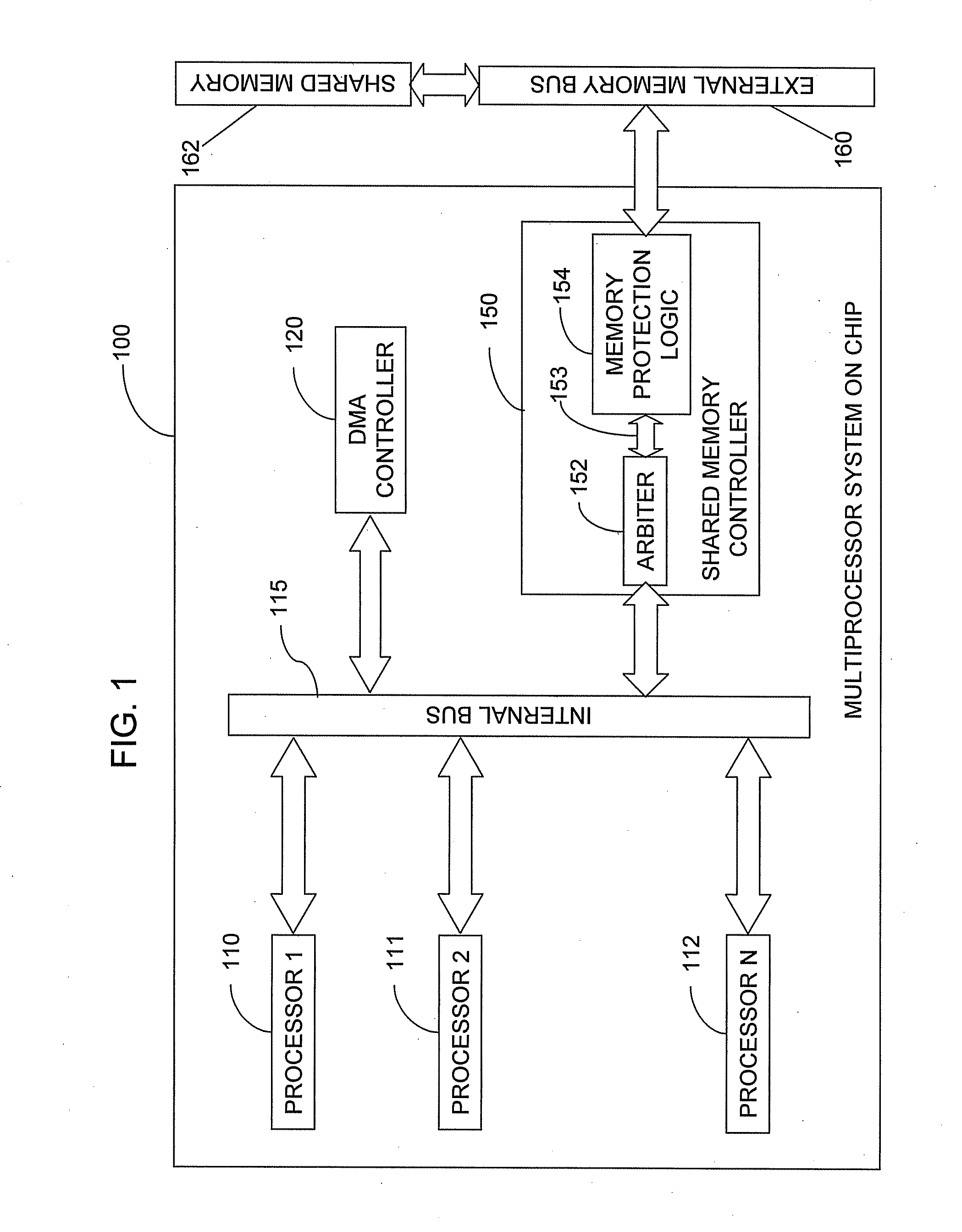
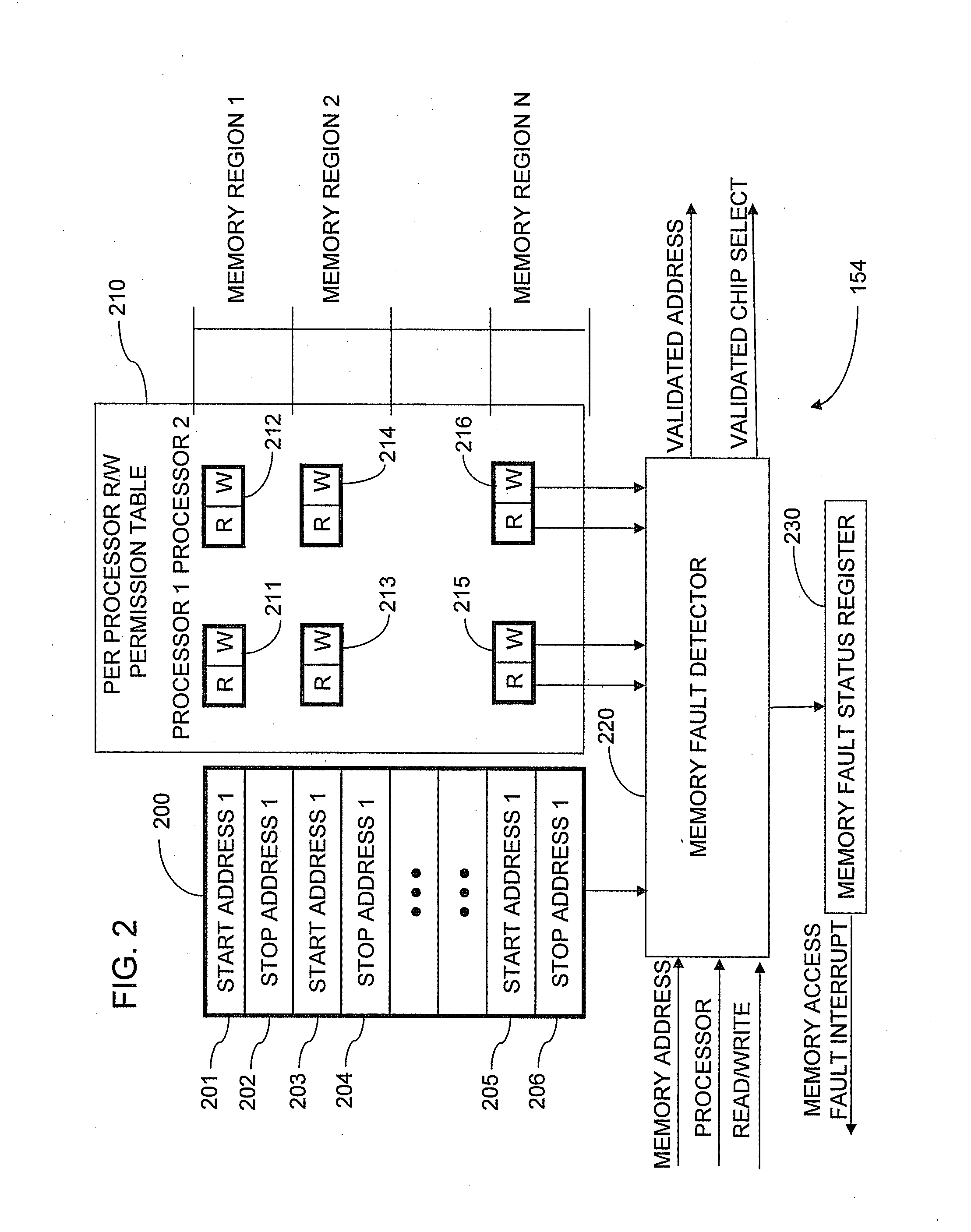
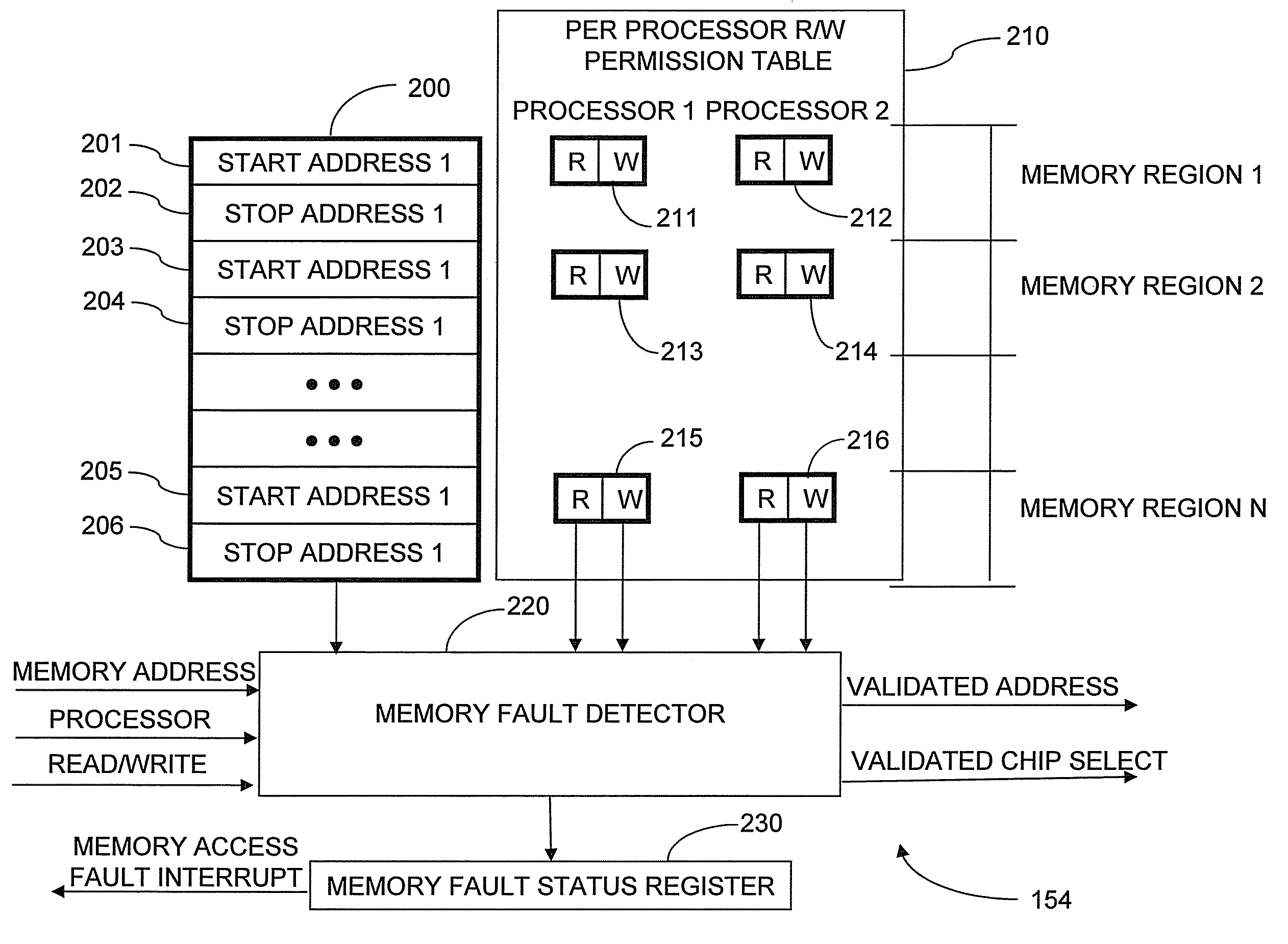
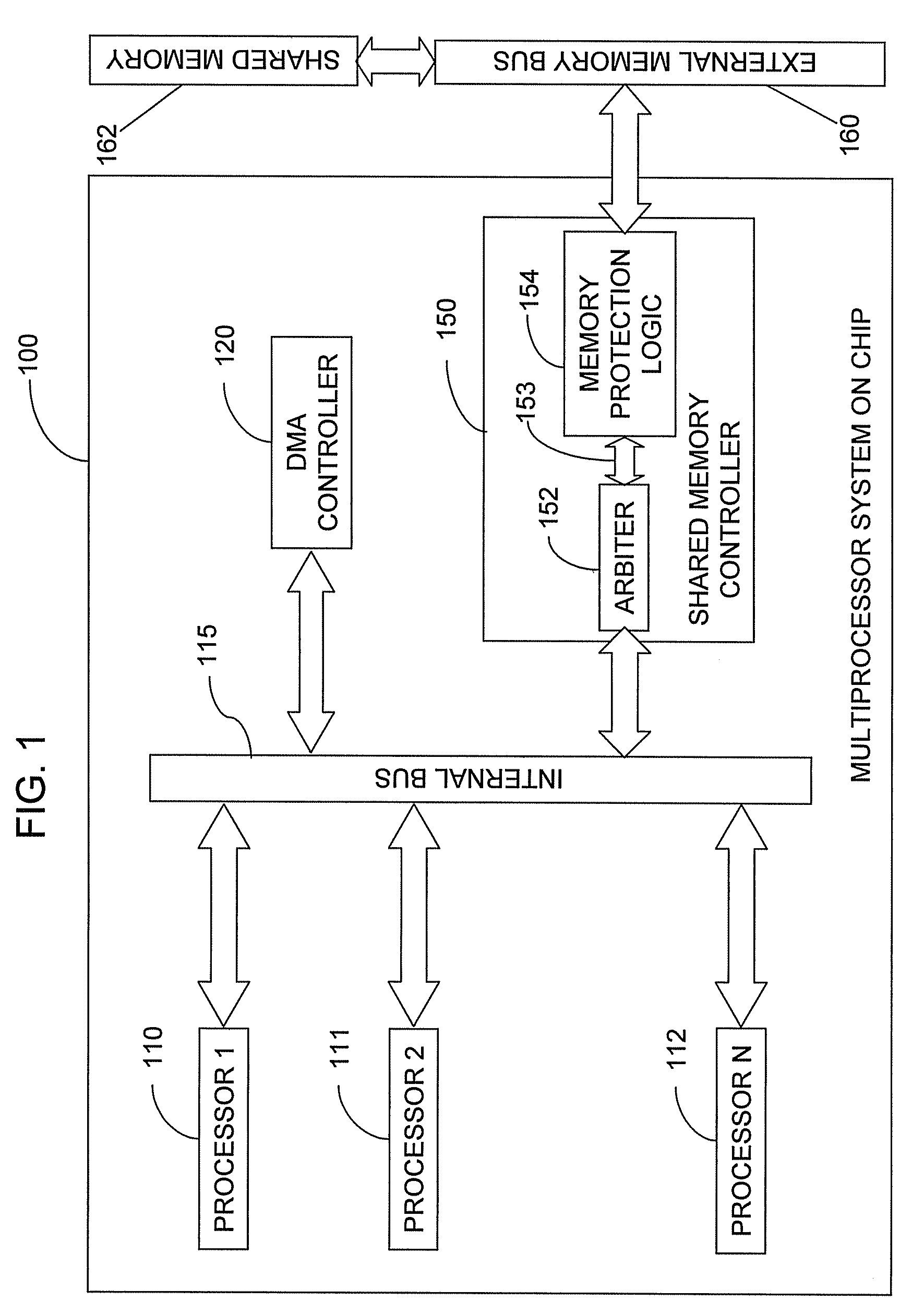
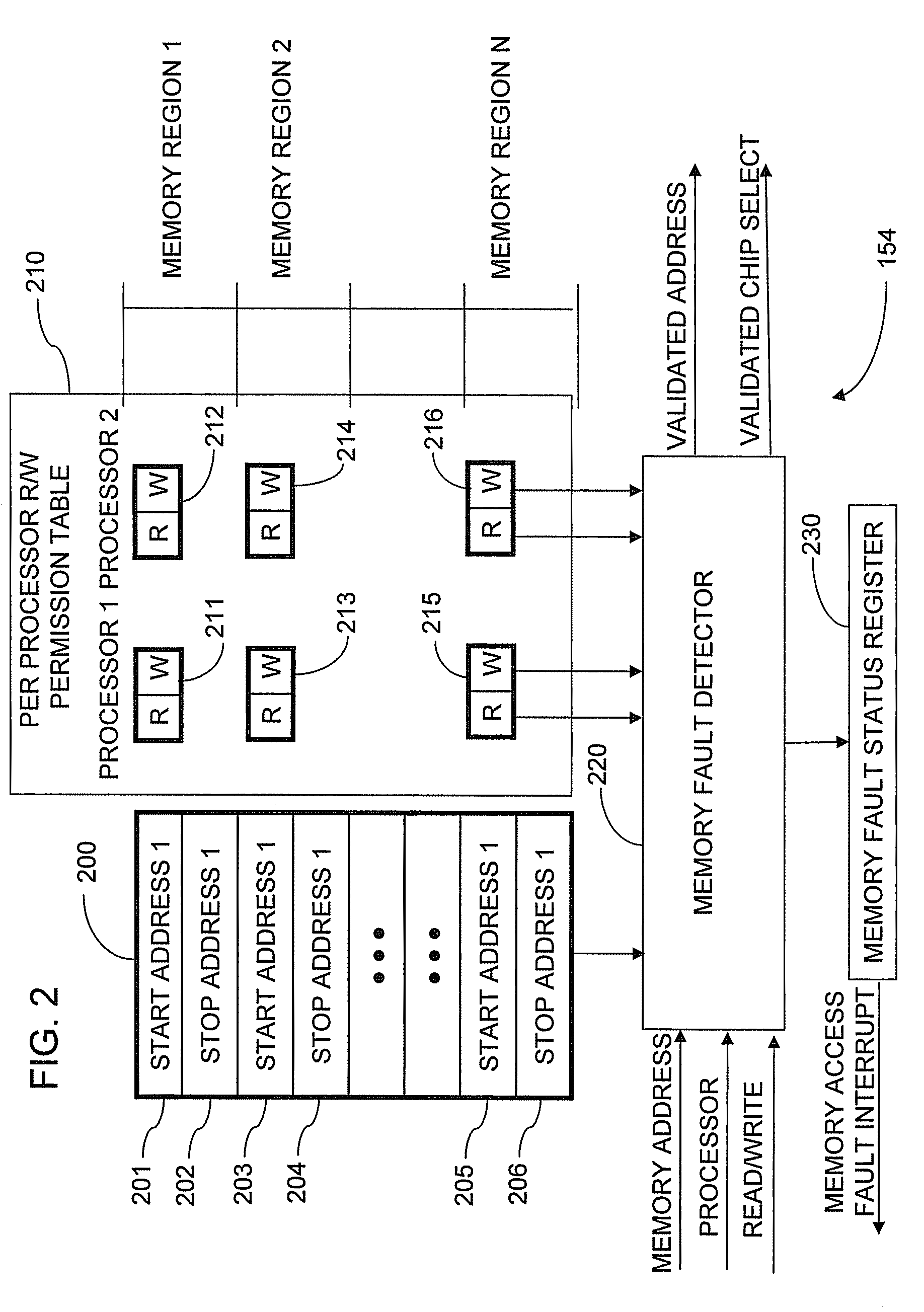
Memory protection system and method
A shared memory controller is provided for controlling access to a shared memory by a plurality of processors. At least one device includes a storage area for storing a respective address range for each of a plurality of memory regions. The at least one device further includes a permission table containing, for each of the plurality of memory regions, read and write permission data for each of the plurality of processors. A memory fault detector is coupled to the at least one device and has an input for receiving a memory access request including a memory address, a processor identification and a read / write indicator. The memory fault detector includes logic for determining whether a memory access according to the memory access request would conflict with the read and write permission data in the permission table.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
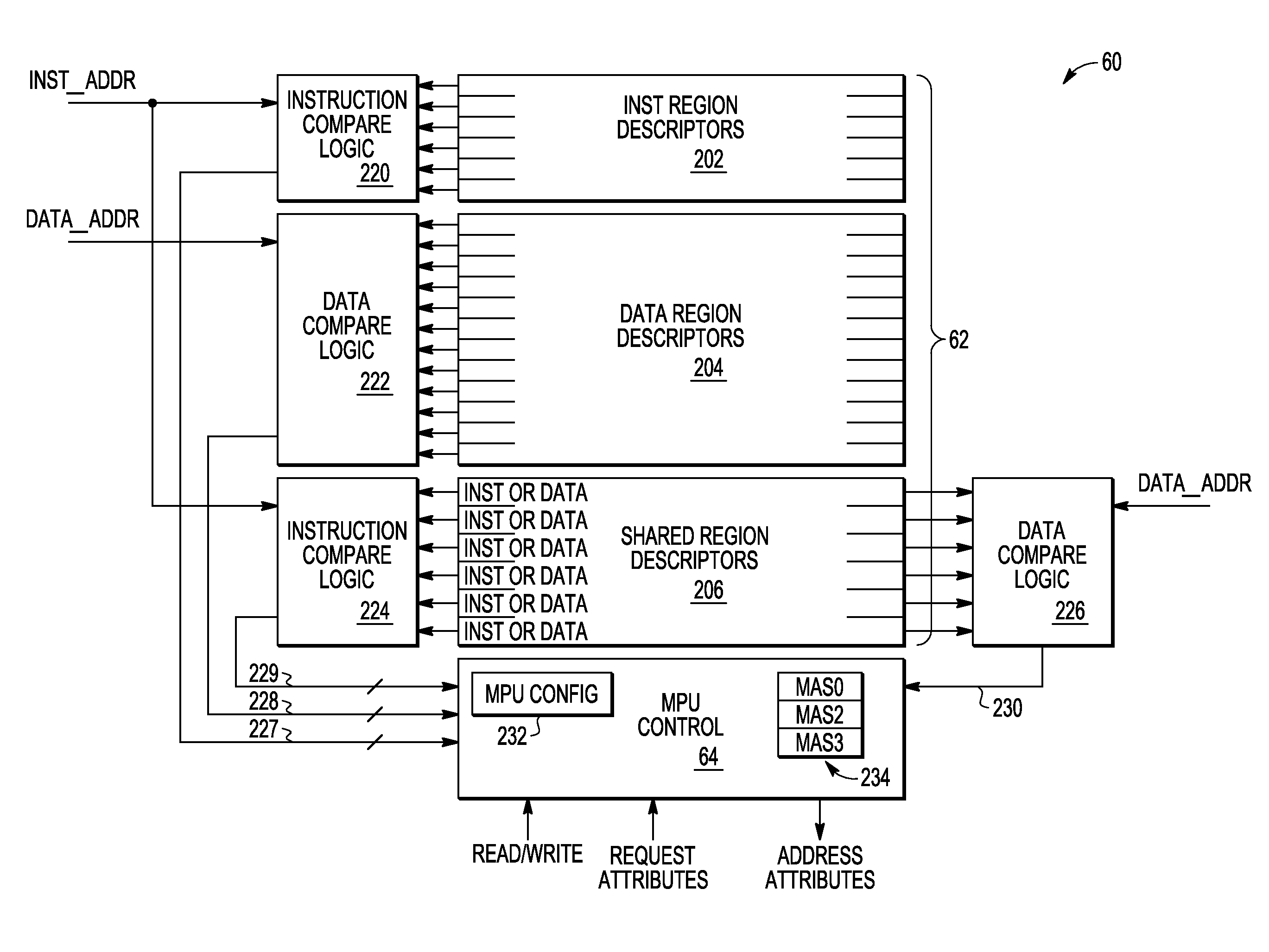
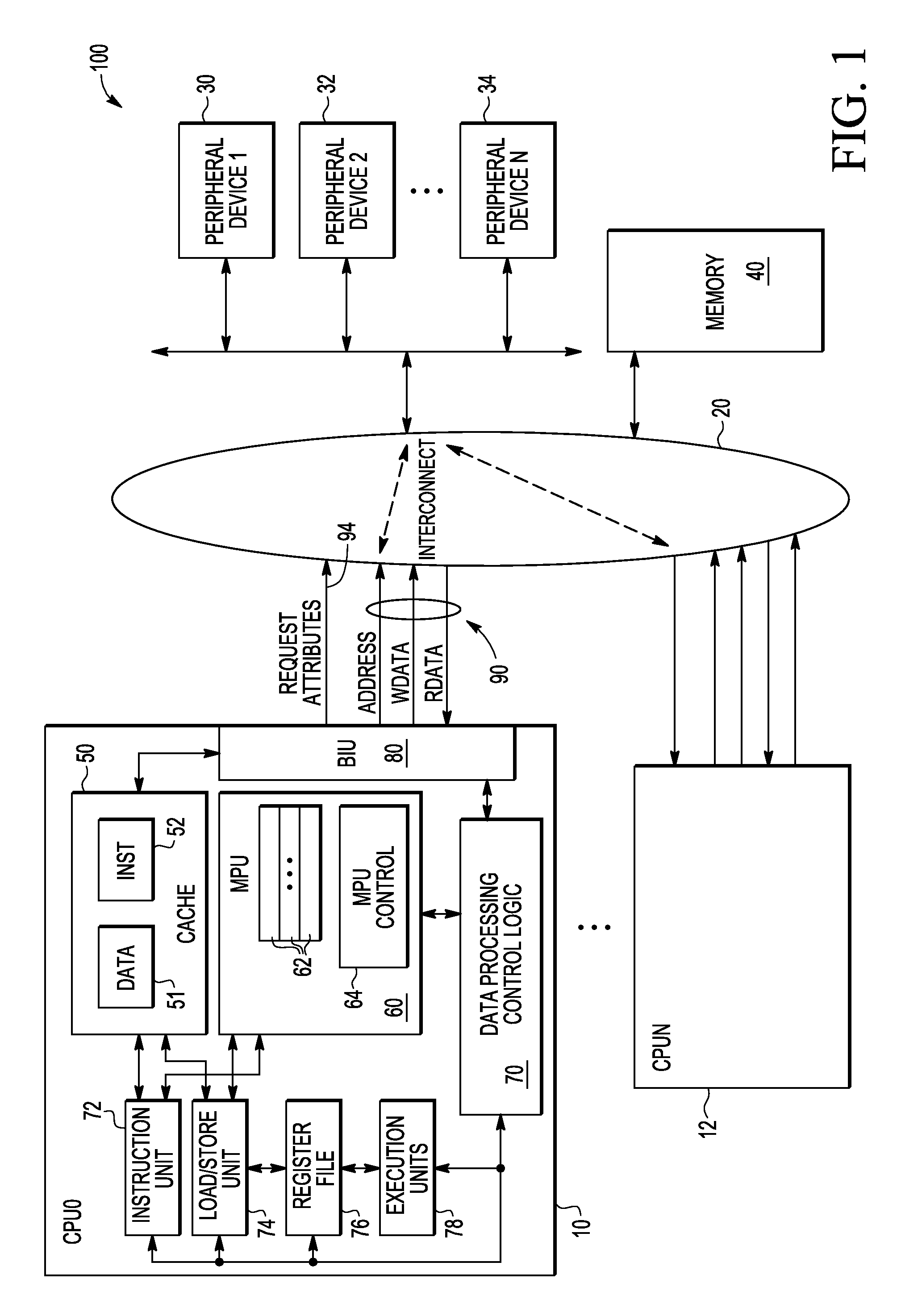
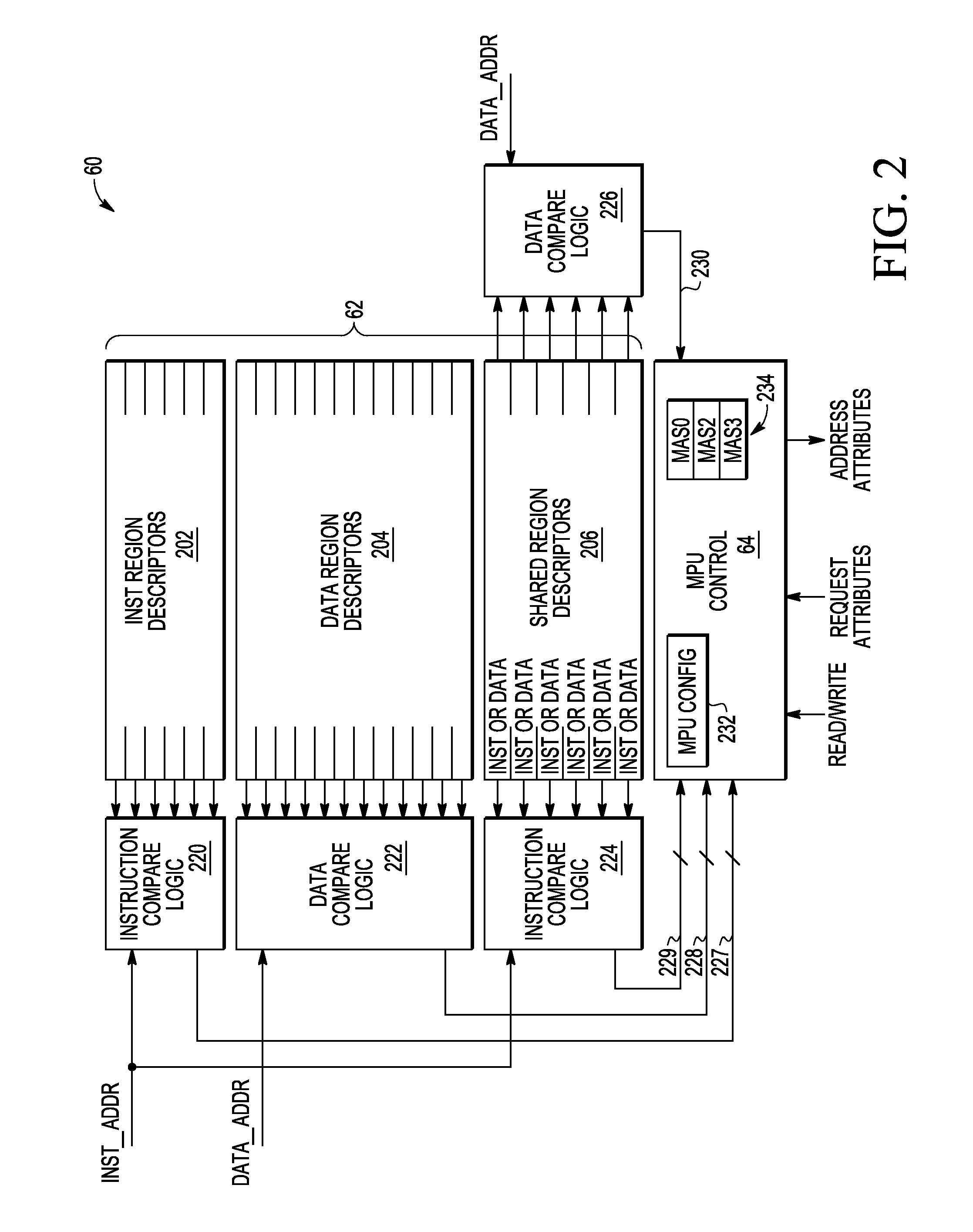
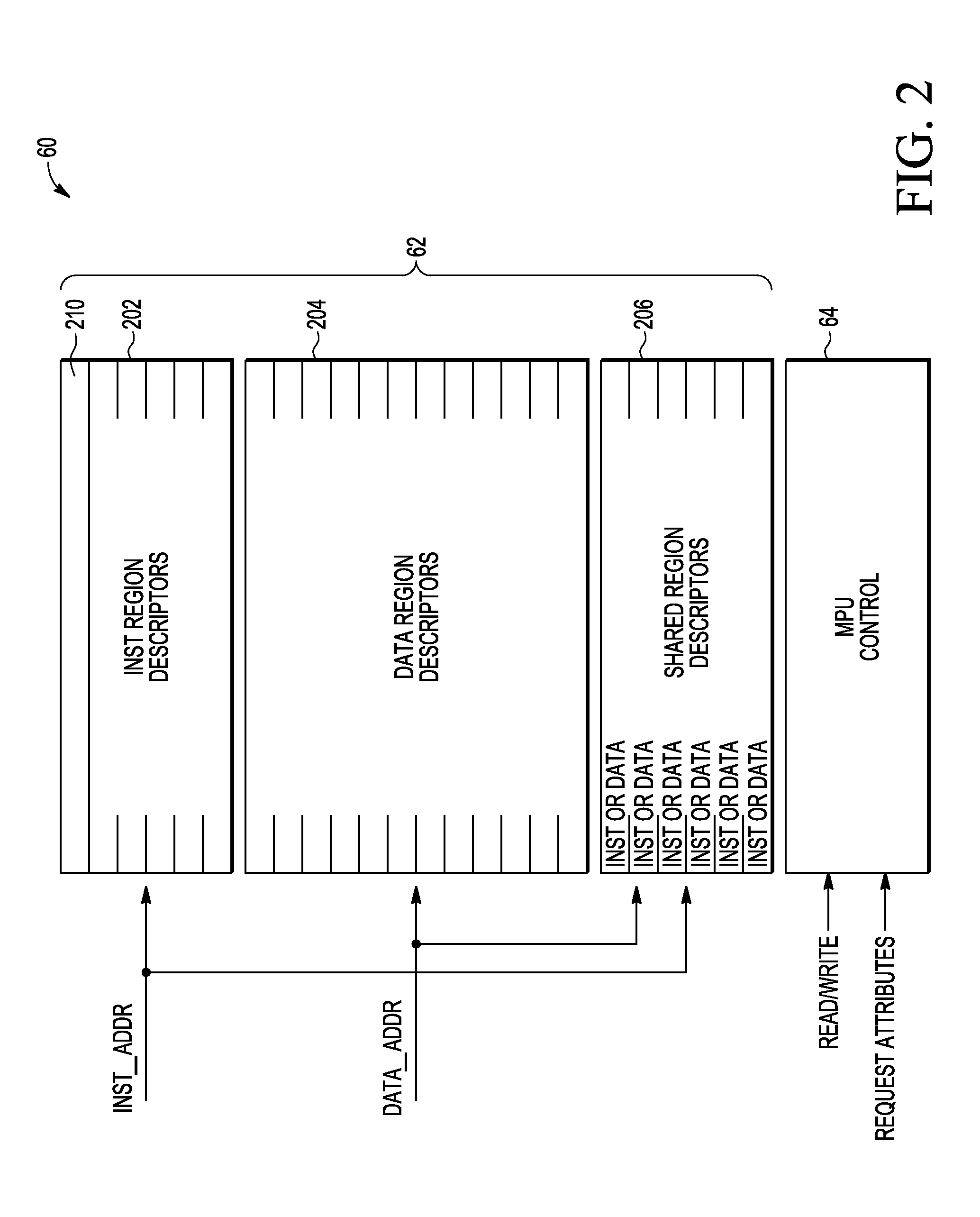
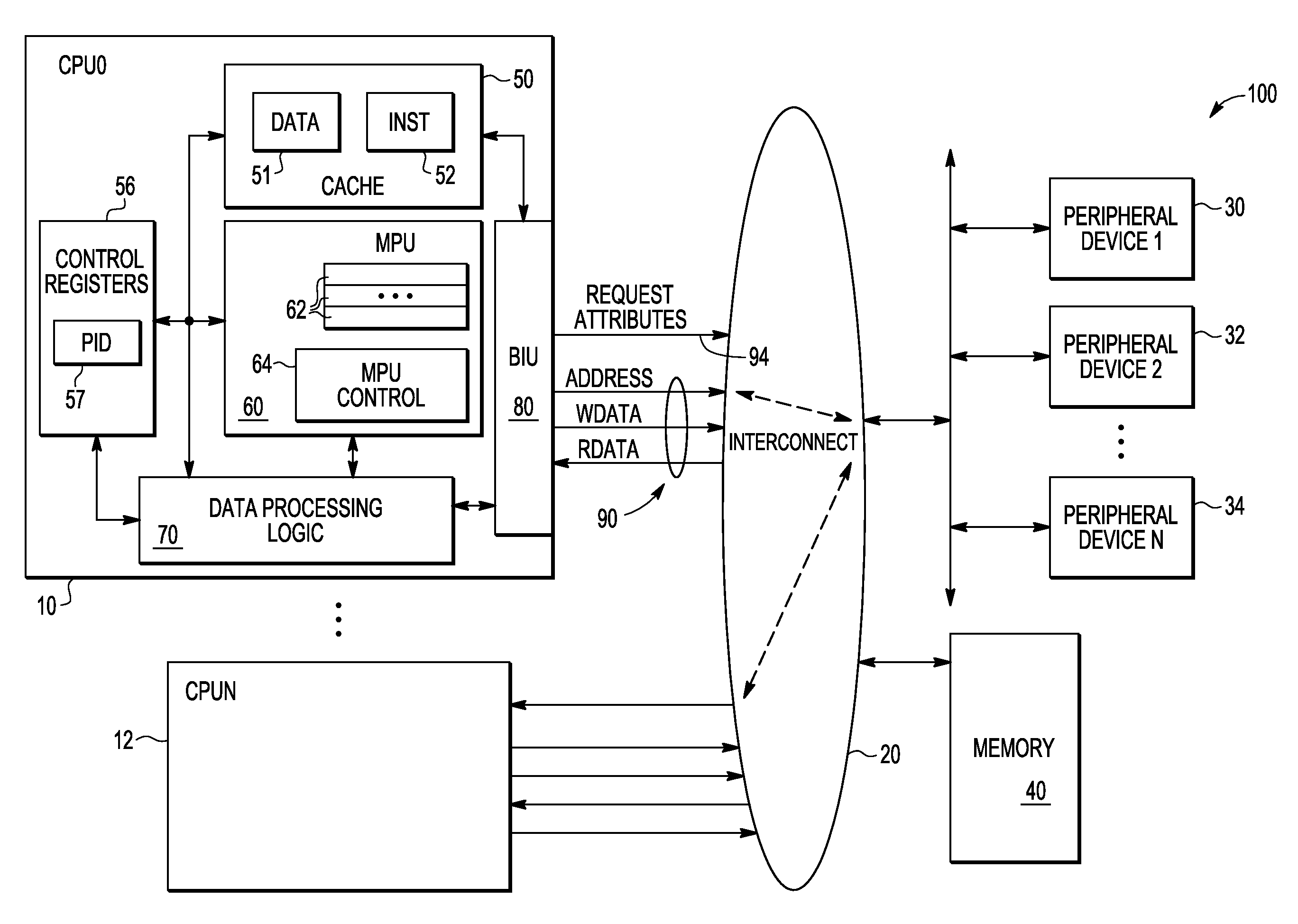
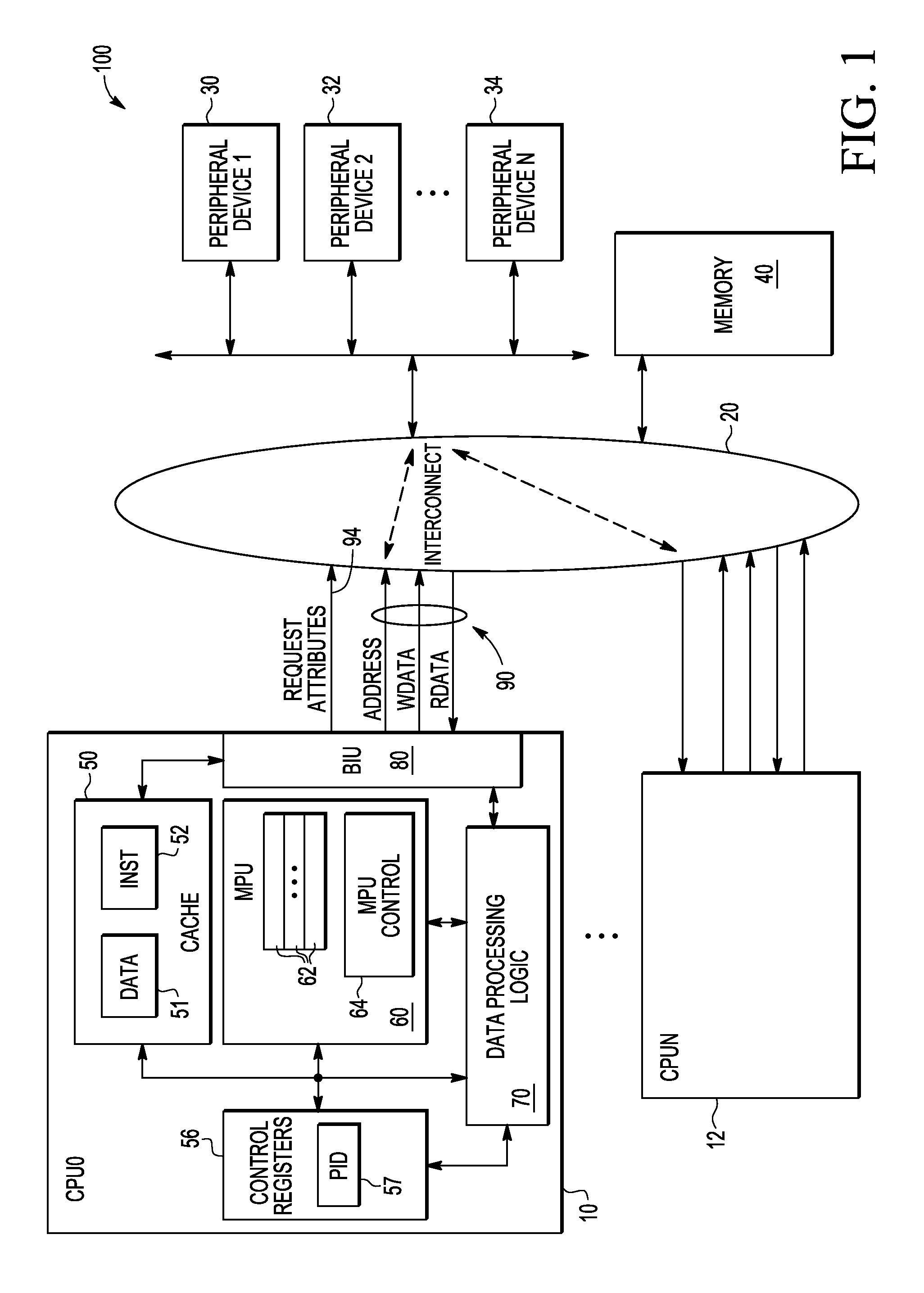
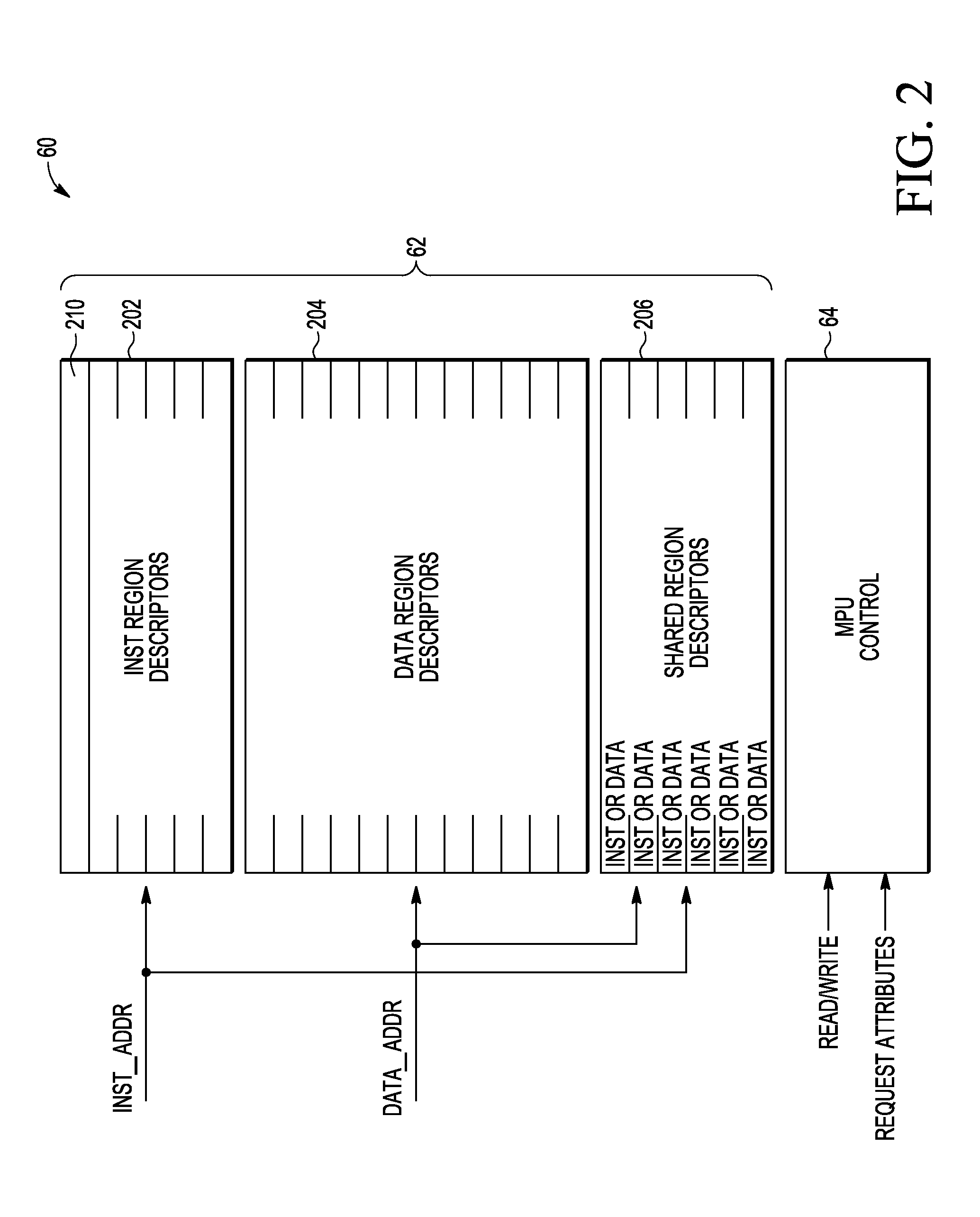
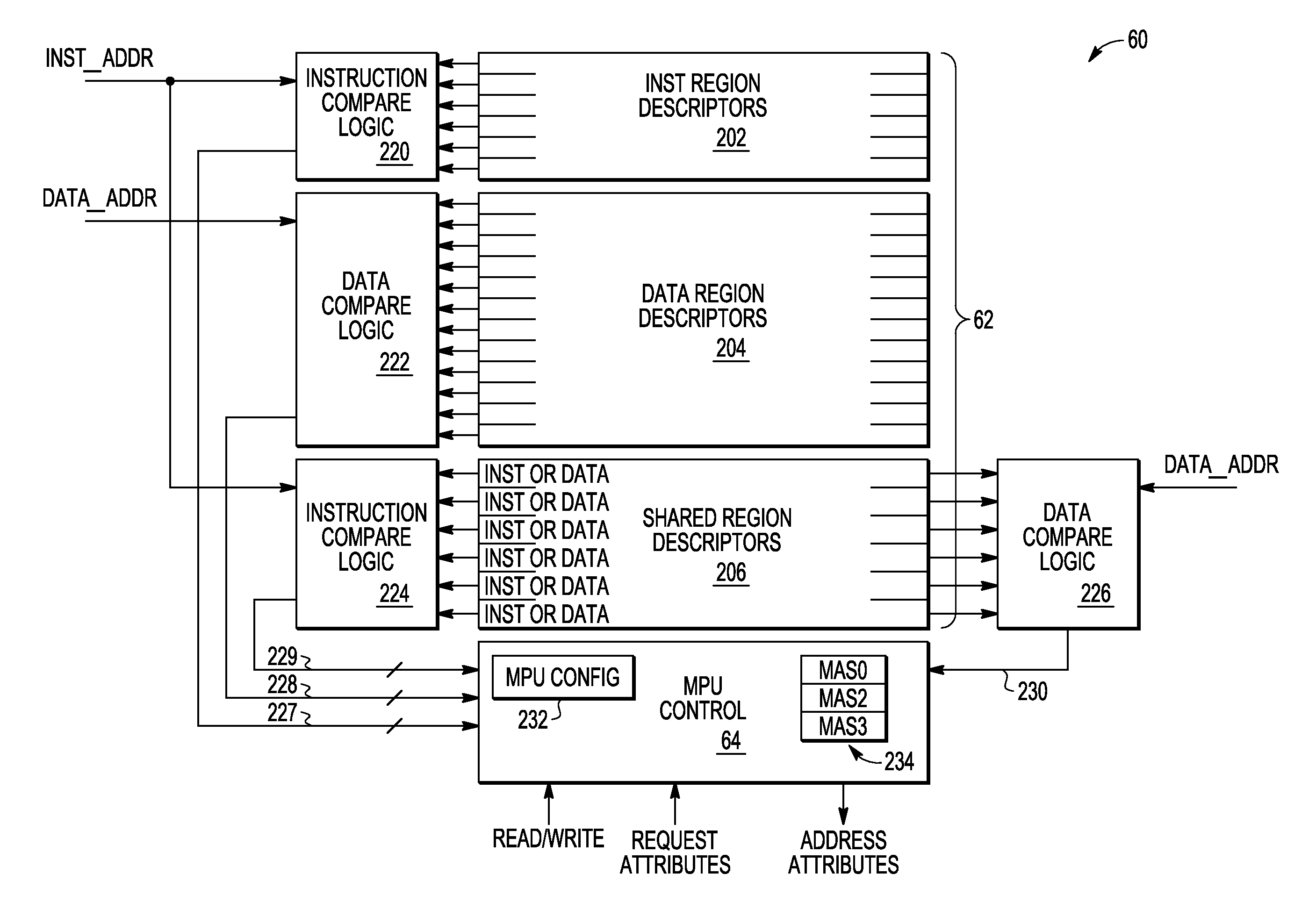
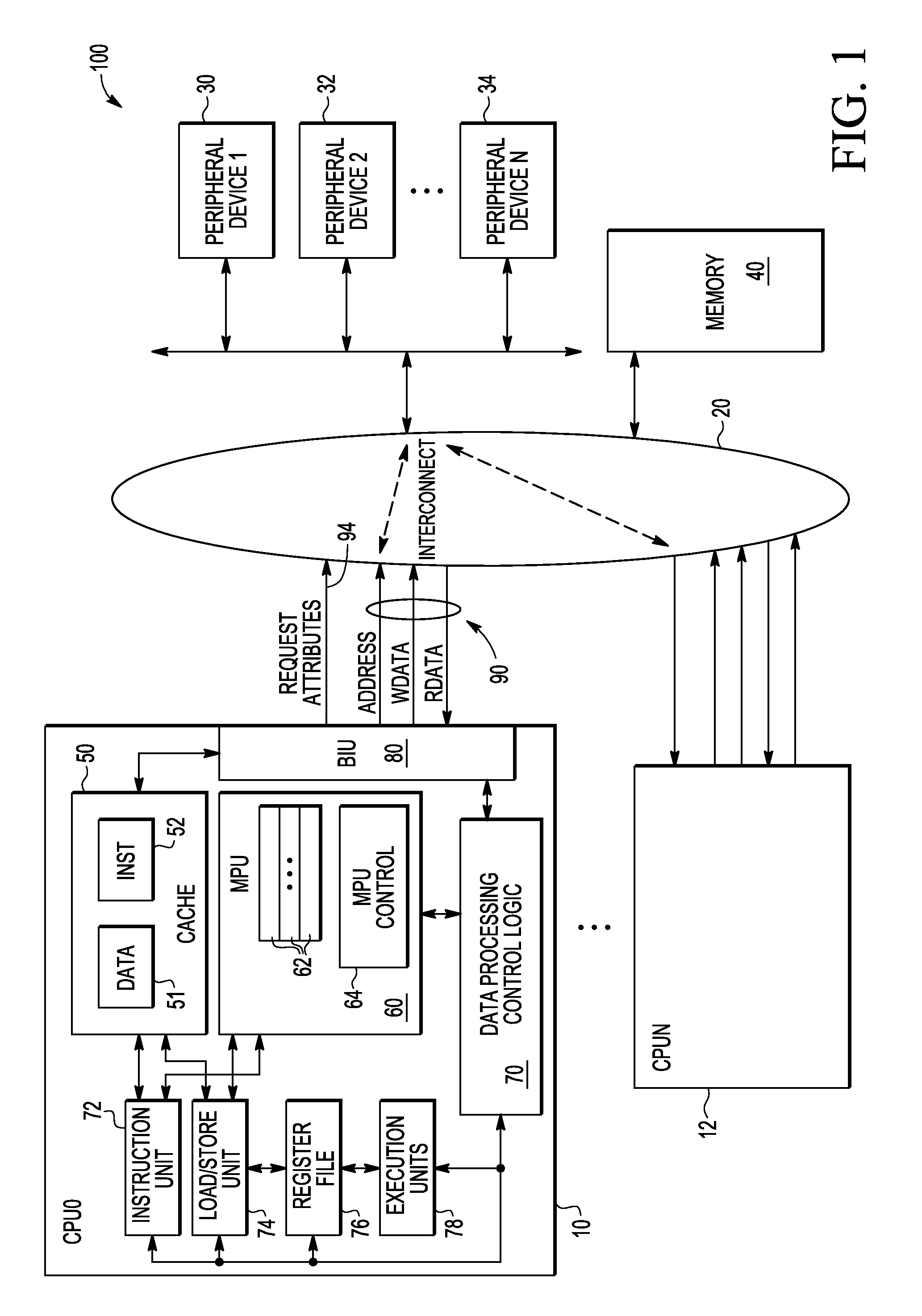
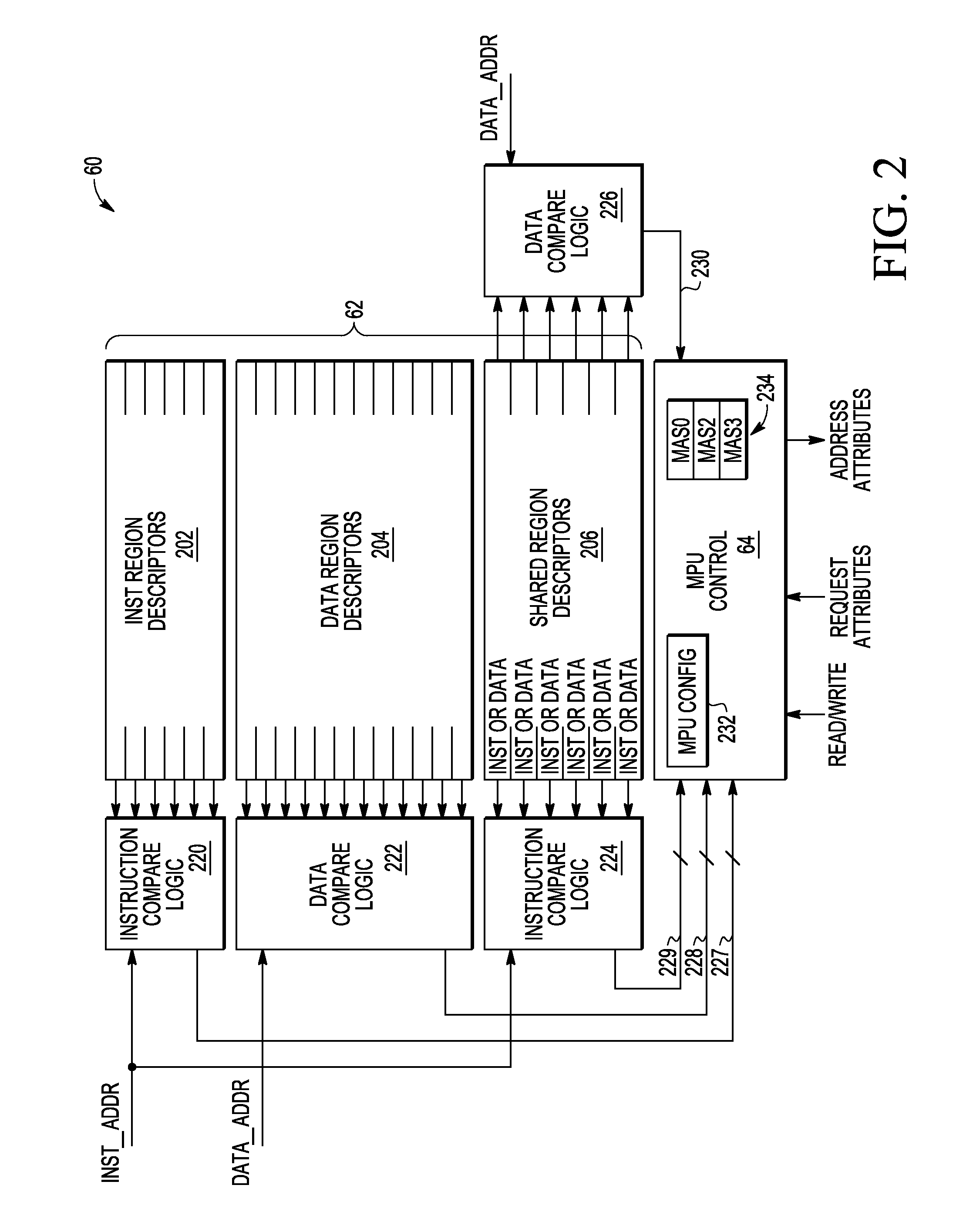
Memory protection unit (MPU) having a shared portion and method of operation
In a disclosed embodiment, a data processing system comprises a memory protection unit (MPU); and a plurality of region descriptors associated with the MPU. Each region descriptor is associated with one of multiple subsets of the region descriptors and includes an address range, protection settings, and attributes for a respective region of memory. The subsets include data-only region descriptors, instruction-only region descriptors, and shared region descriptors. The shared region descriptors are used to access memory regions for data and instruction memory requests.
Owner:NXP USA INC
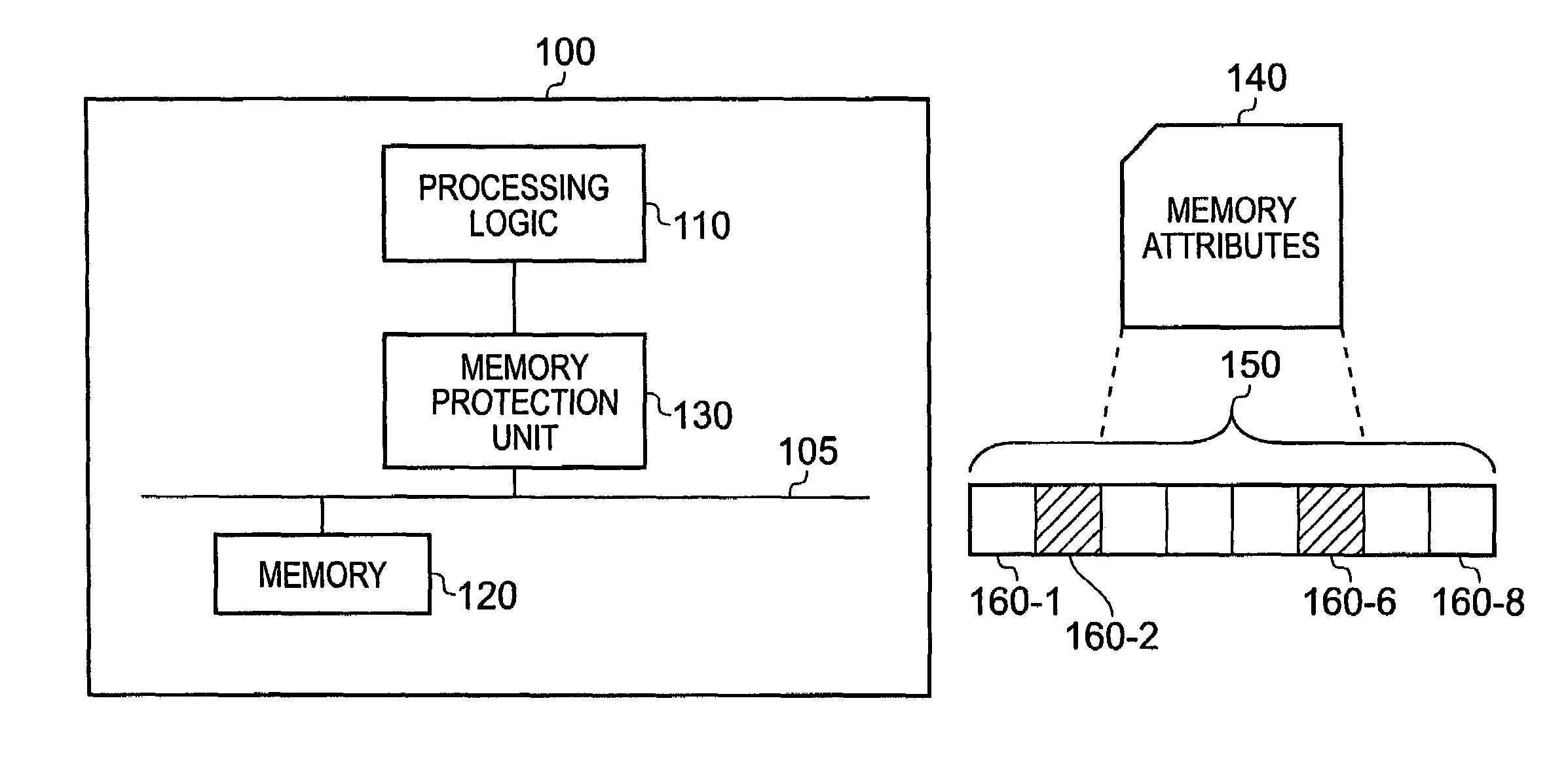
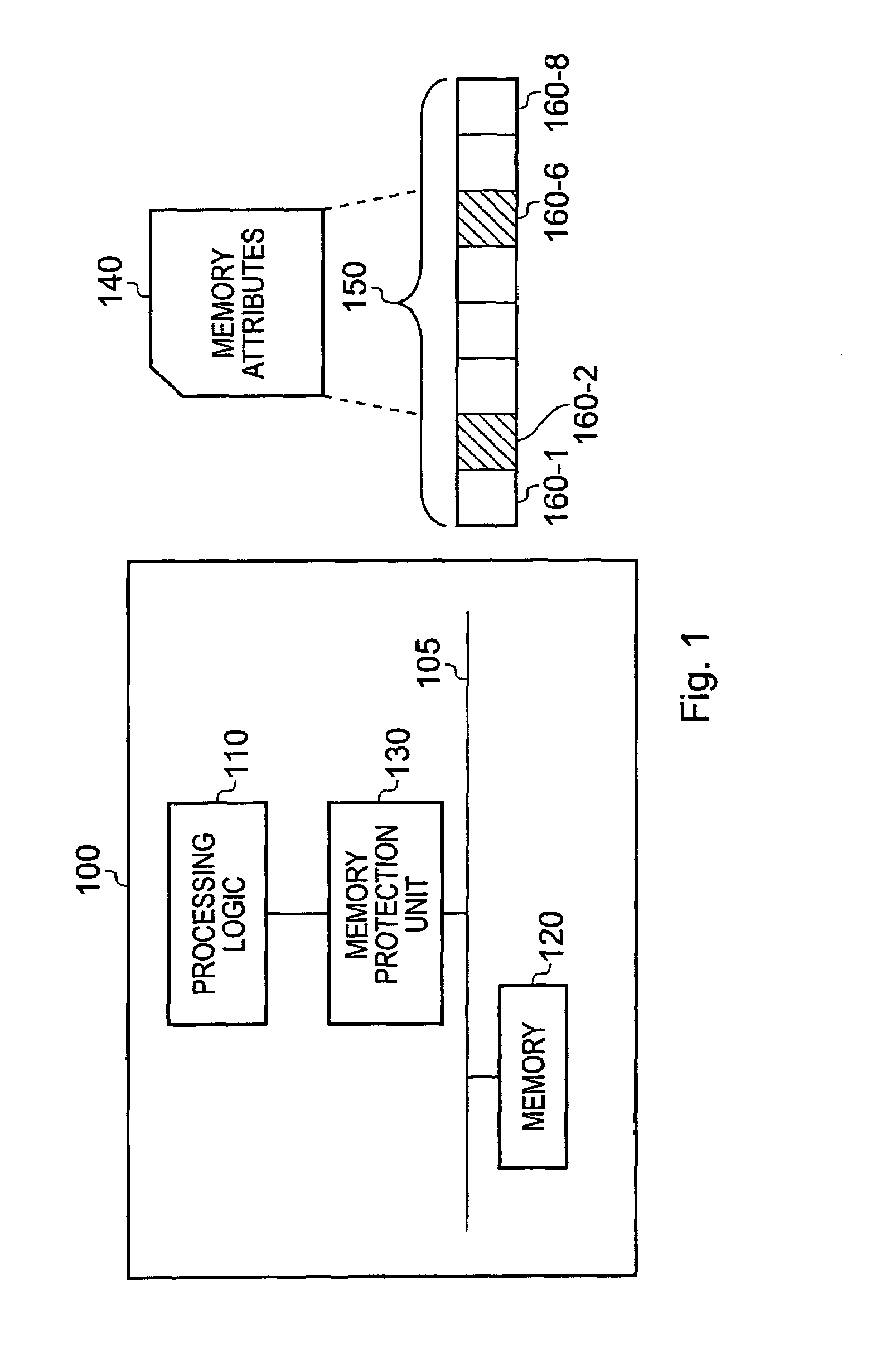
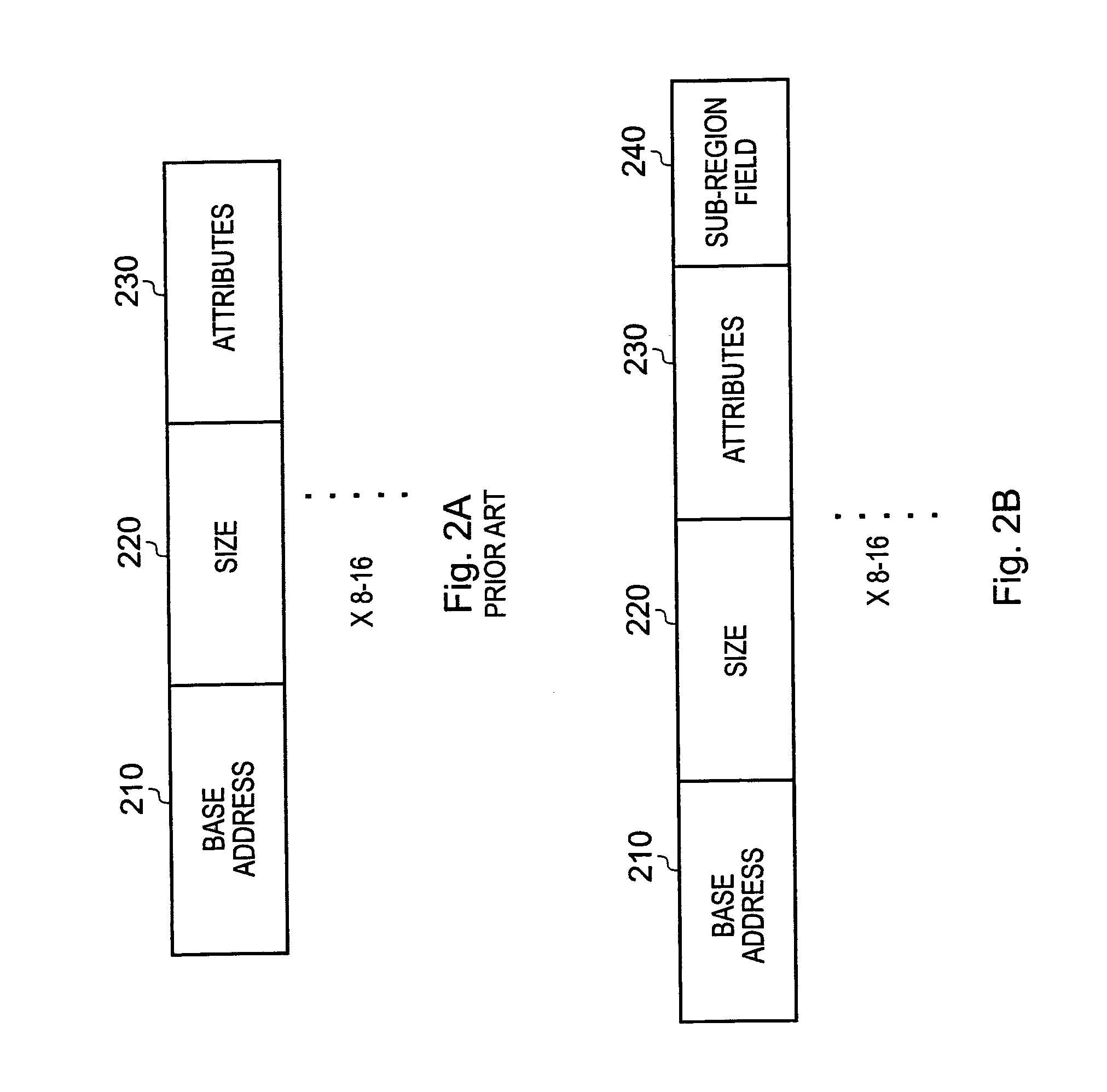
Data processing apparatus having memory protection unit
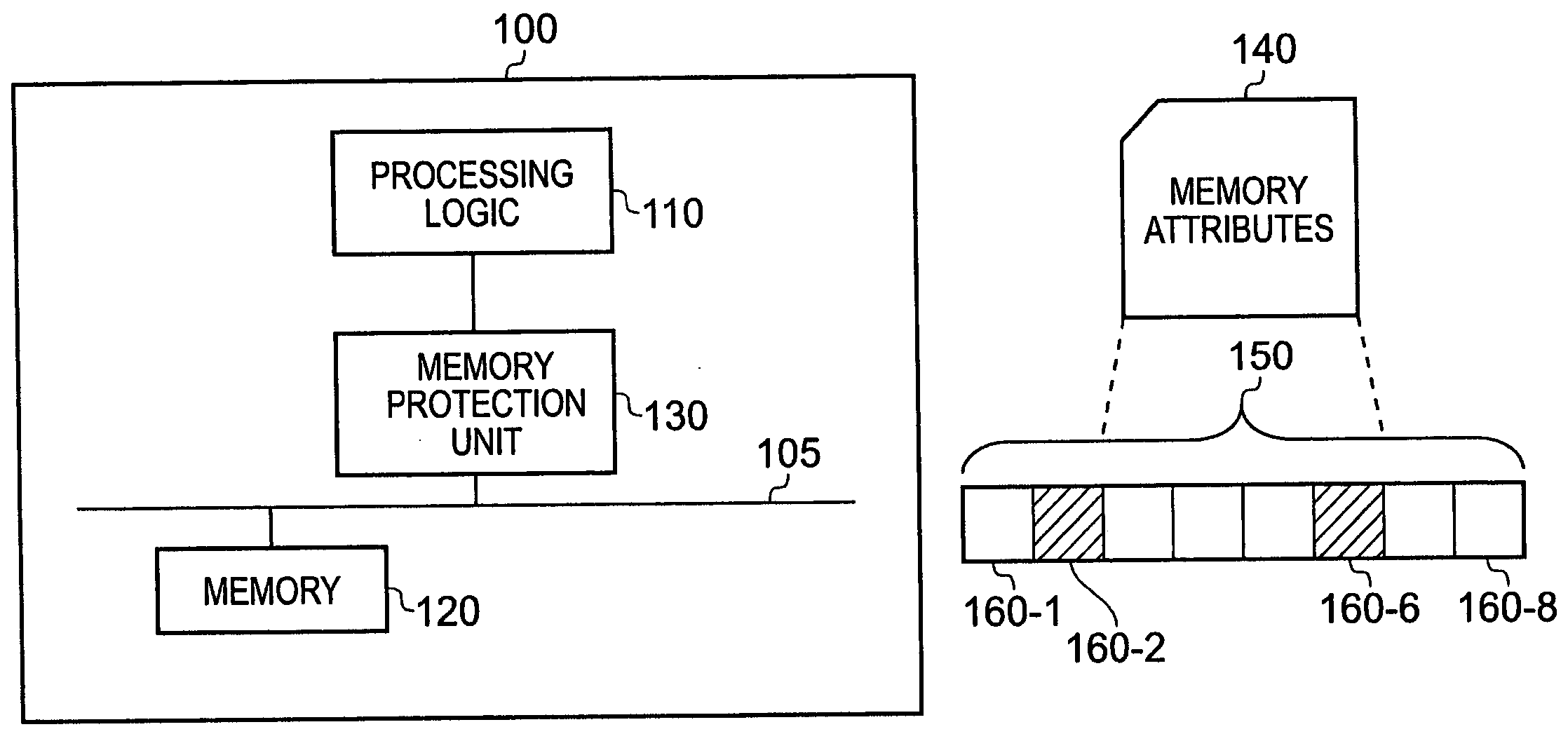
ActiveUS7068545B1Reduce amountUnauthorized memory use protectionDigital storageComputer hardwareData value
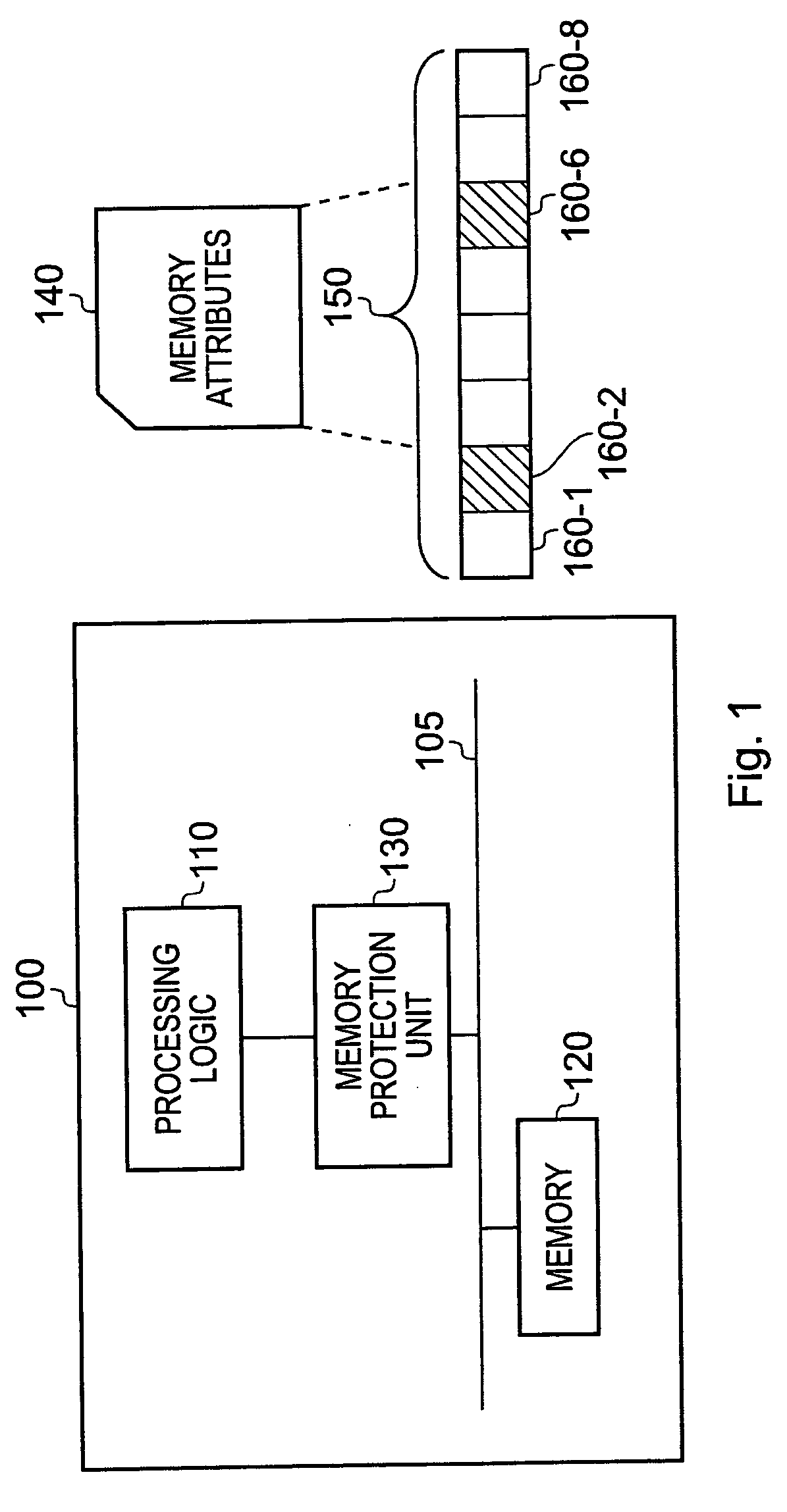
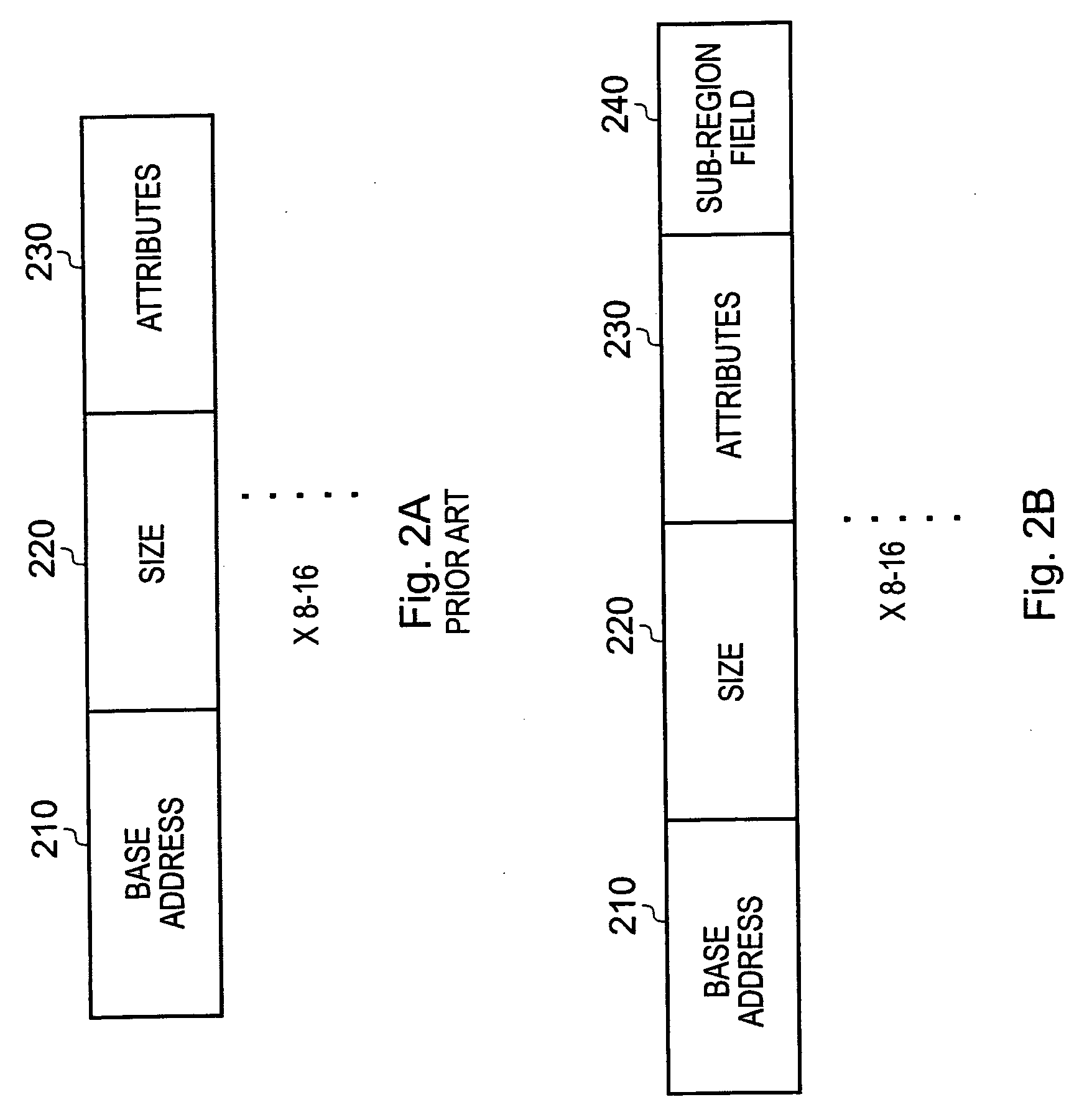
A data processor (100) has a memory operable to store data values; a memory protection unit (130) operable to associate memory attributes with portions of said memory and to identify a plurality of memory regions corresponding to respective address ranges of said memory. The memory protection unit is operable to associate with at least one of the plurality of memory regions (150) a respective memory region specifier comprising an attributes field (230) for defining a set of memory attributes associated with said memory region and a sub-region field (240) for holding a sub-region membership value. The sub-region membership value specifies, for each of a plurality of sub-regions of the memory region, whether respective sub-regions (160-1 to 160-8) are member sub-regions or non-member sub-regions such that said memory attributes are applied to said member sub-regions but are not applied to said non-member sub-regions.
Owner:ARM LTD
Method for technically controlling secure access to embedded system memory
ActiveCN105787360ARealize dynamic switchingEnsure legitimate accessInternal/peripheral component protectionPlatform integrity maintainanceWrite bufferOperational system
The invention discloses a method for technically controlling secure access to an embedded system memory. The method includes the following steps of initially designing a system of a memory secure access mechanism, wherein an MPU memory protection unit is introduced, domain attributes of different grades are distributed, and an access attribute and a system initiating progress are set; secondly, designing the secure access to the memory for switching of embedded operation system process context, wherein a domain control module is set, the system process context is set, and switching of the system process content is achieved in the domain control module. The illegal access of all address space resources are detected and limited through a processor MPU hardware mechanism, the boundary control and context switching of any task of the embedded real-time multi-task operation system for accessing resources of other tasks is achieved, distributing and designing of cache, writing buffer and MPU attributes of different storage spaces in the system are achieved, and the control over secure access to all background domains in the memory is ensured.
Owner:HANGZHOU BYTE INFORMATION TECH CO LTD
Data processing apparatus having memory protection unit
ActiveUS20060149911A1Reduce amountUnauthorized memory use protectionDigital storageParallel computingTerm memory
A data processor (100) has a memory operable to store data values; a memory protection unit (130) operable to associate memory attributes with portions of said memory and to identify a plurality of memory regions corresponding to respective address ranges of said memory. The memory protection unit is operable to associate with at least one of the plurality of memory regions (150) a respective memory region specifier comprising an attributes field (230) for defining a set of memory attributes associated with said memory region and a sub-region field (240) for holding a sub-region membership value. The sub-region membership value specifies, for each of a plurality of sub-regions of the memory region, whether respective sub-regions (160-1 to 160-8) are member sub-regions or non-member sub-regions such that said memory attributes are applied to said member sub-regions but are not applied to said non-member sub-regions.
Owner:ARM LTD
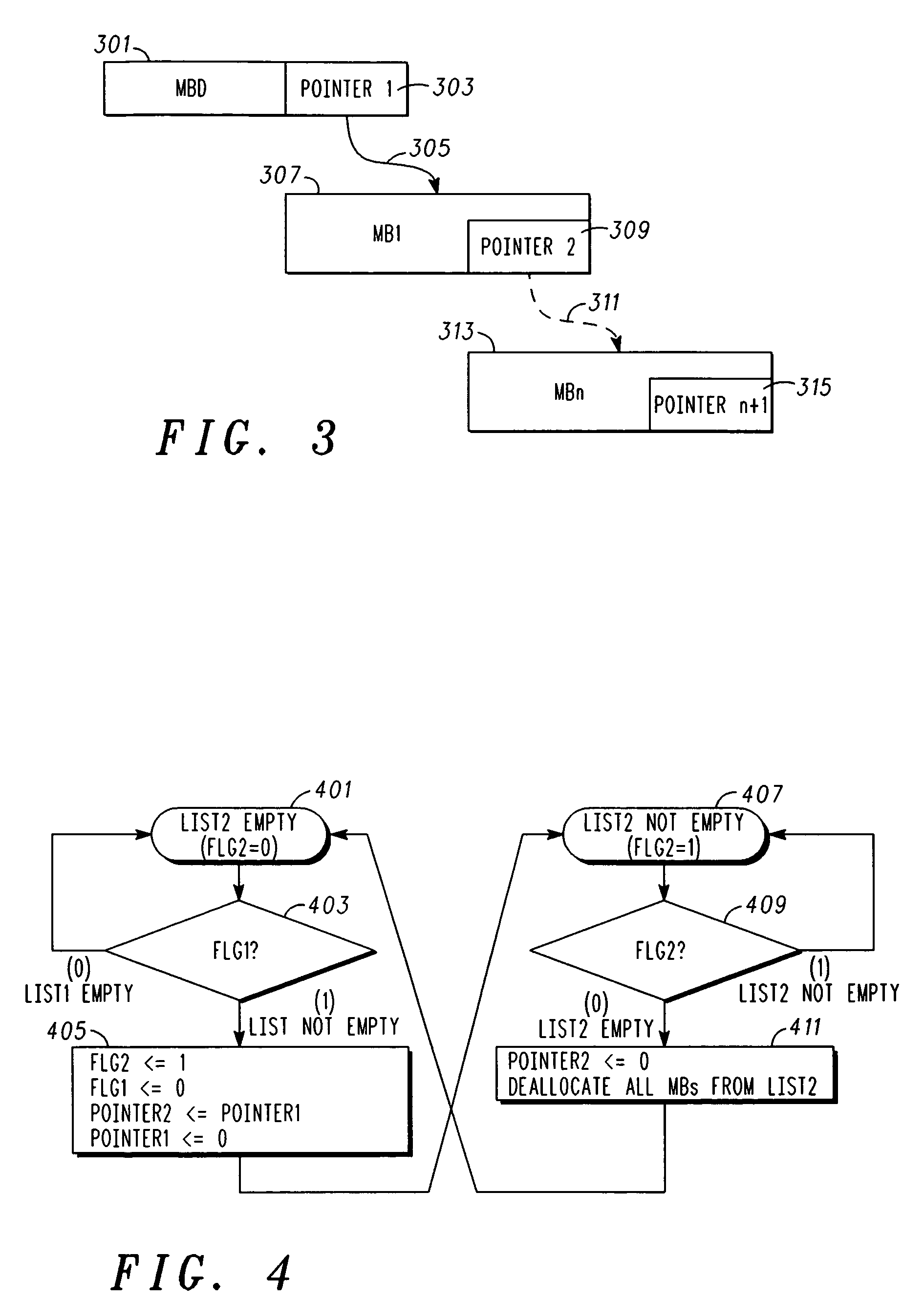
Dynamic allocation of message buffers
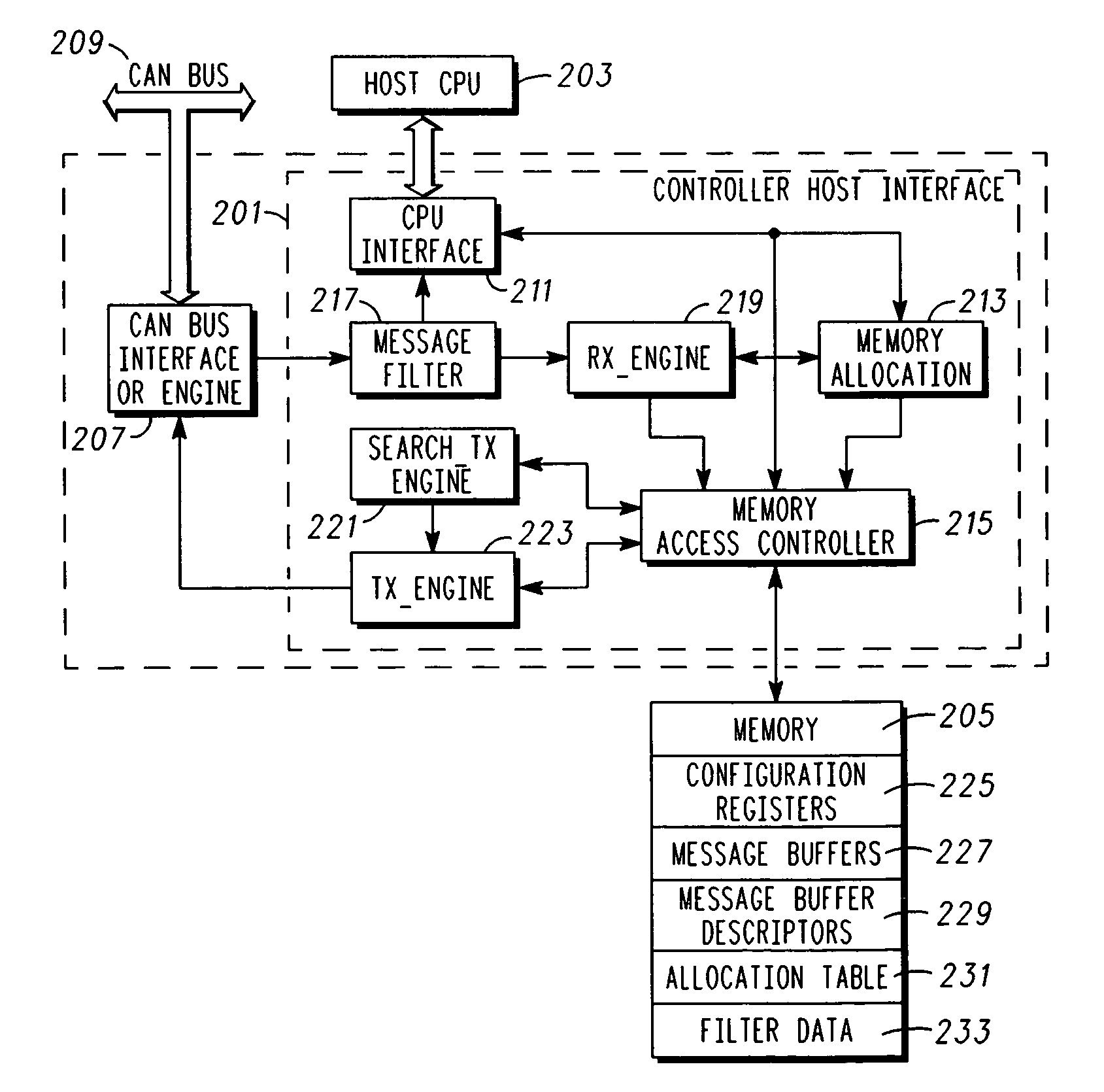
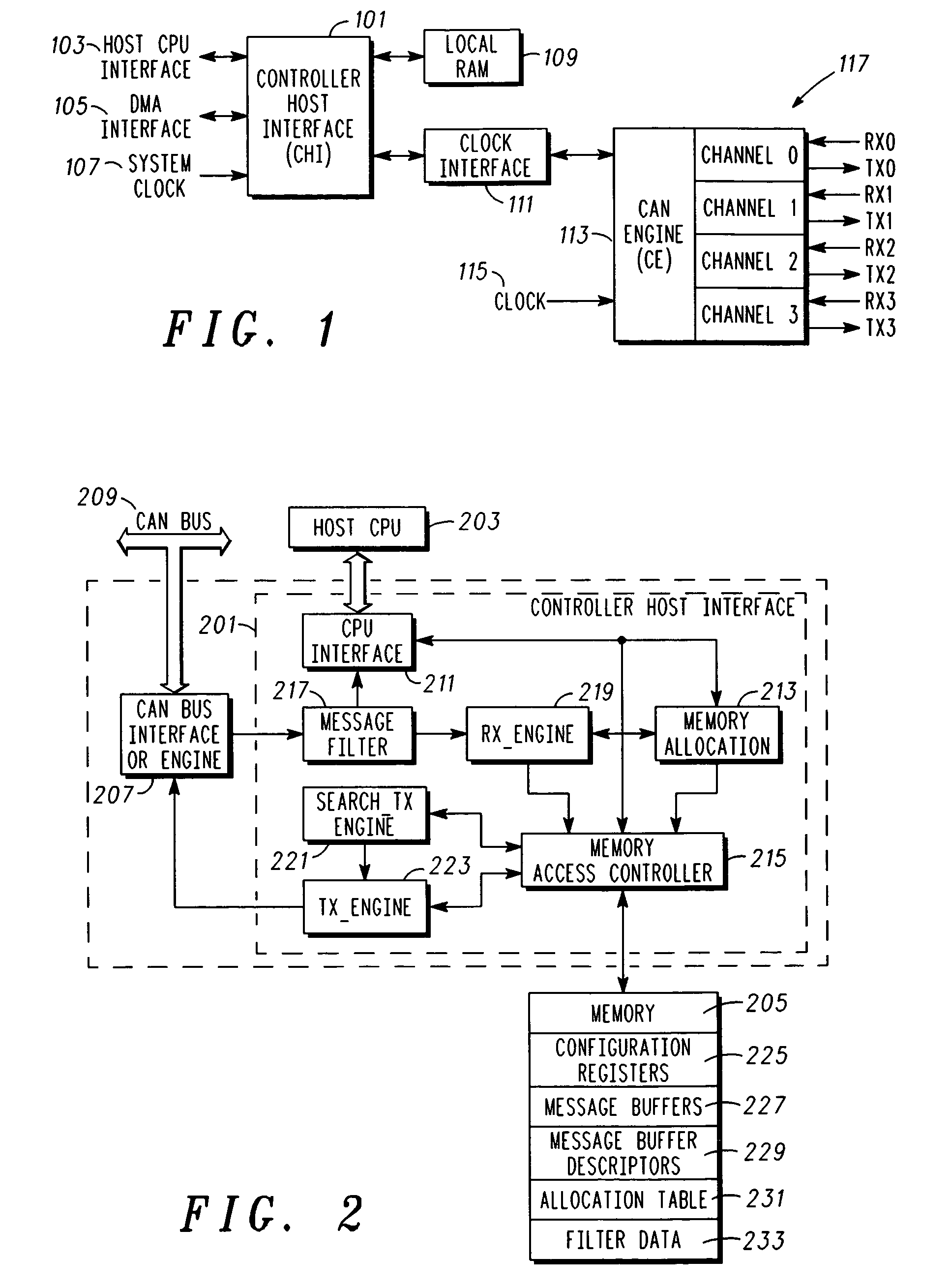
A method for allocating memory that is associated with a CAN (controller area network) controller, comprises receiving a data frame comprising an identifier (ID) and data; dynamically allocating a message buffer (MB) within the memory for queuing the data frame; and generating a pointer that points to the MB, where the pointer is accessed via a static location in the memory. A corresponding host interface for the CAN controller can be implemented in IC circuitry, is configured to be coupled to a host CPU and a CAN bus interface, and includes a memory allocation unit for dynamic memory allocation and a memory access controller, coupled to the memory allocation unit and the memory, that is configured to control access to the memory to facilitate transmitting and receiving a multiplicity of data frames over a CAN bus.
Owner:NORTH STAR INNOVATIONS
Method And Computer System For Providing Remote Direct Memory Access
InactiveUS20090024714A1Costly adaptationSimple methodMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDirect memory accessComputerized system
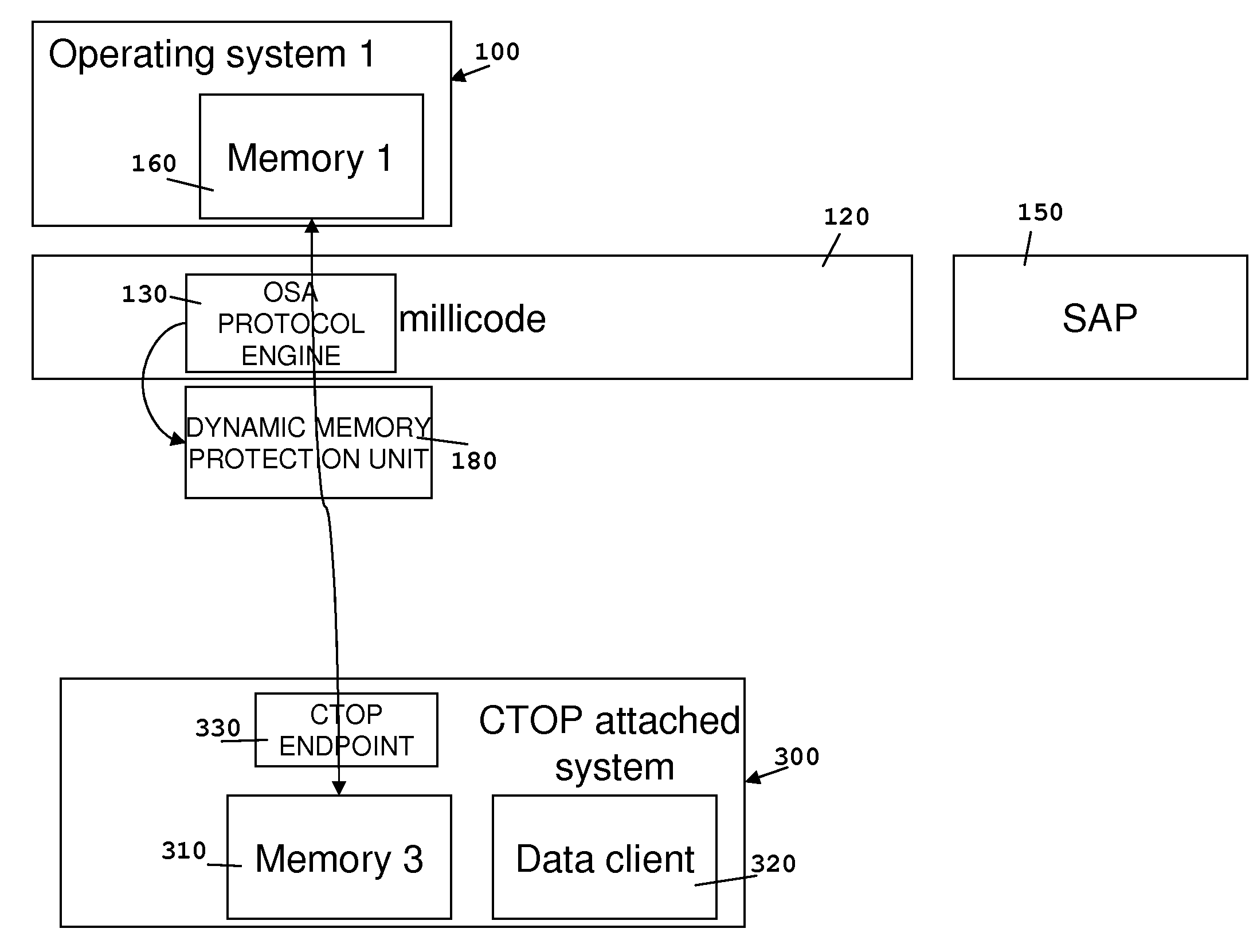
A method for providing remote direct memory access (RDMA) between two computers, preferably between central processing units (CPUs) and a functional subsystem of a computer system as part of their network communication, e.g. using TCP / IP. Tasks of analyzing network protocol data and the actual RDMA operations can be offloaded to the functional subsystem with this method. Further, the functional subsystem cannot compromise the status of the first computer system as only access to certain allowed memory locations is granted by a memory protection unit during phases of actual data transfer between the functional subsystem and the CPUs.
Owner:IBM CORP
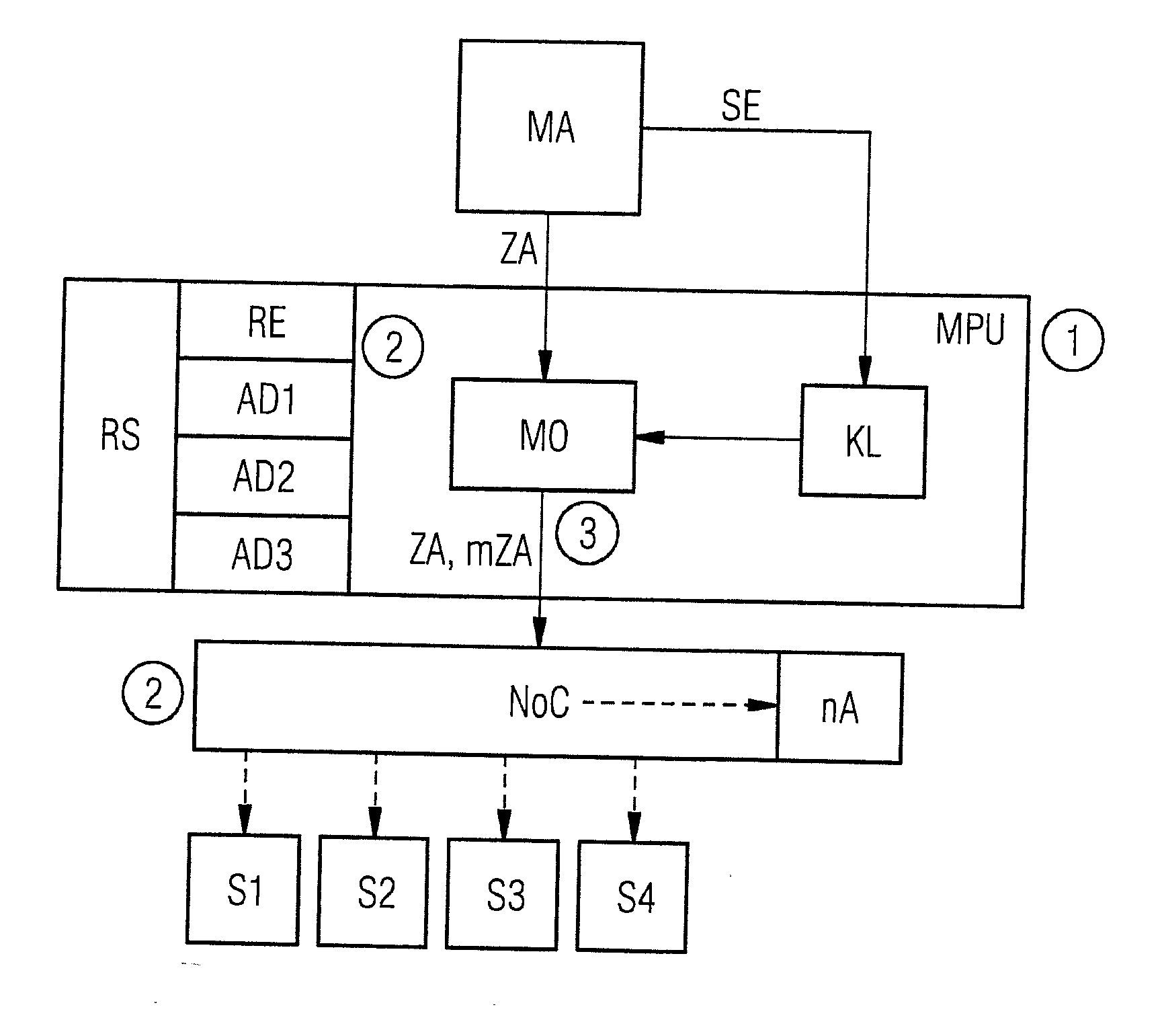
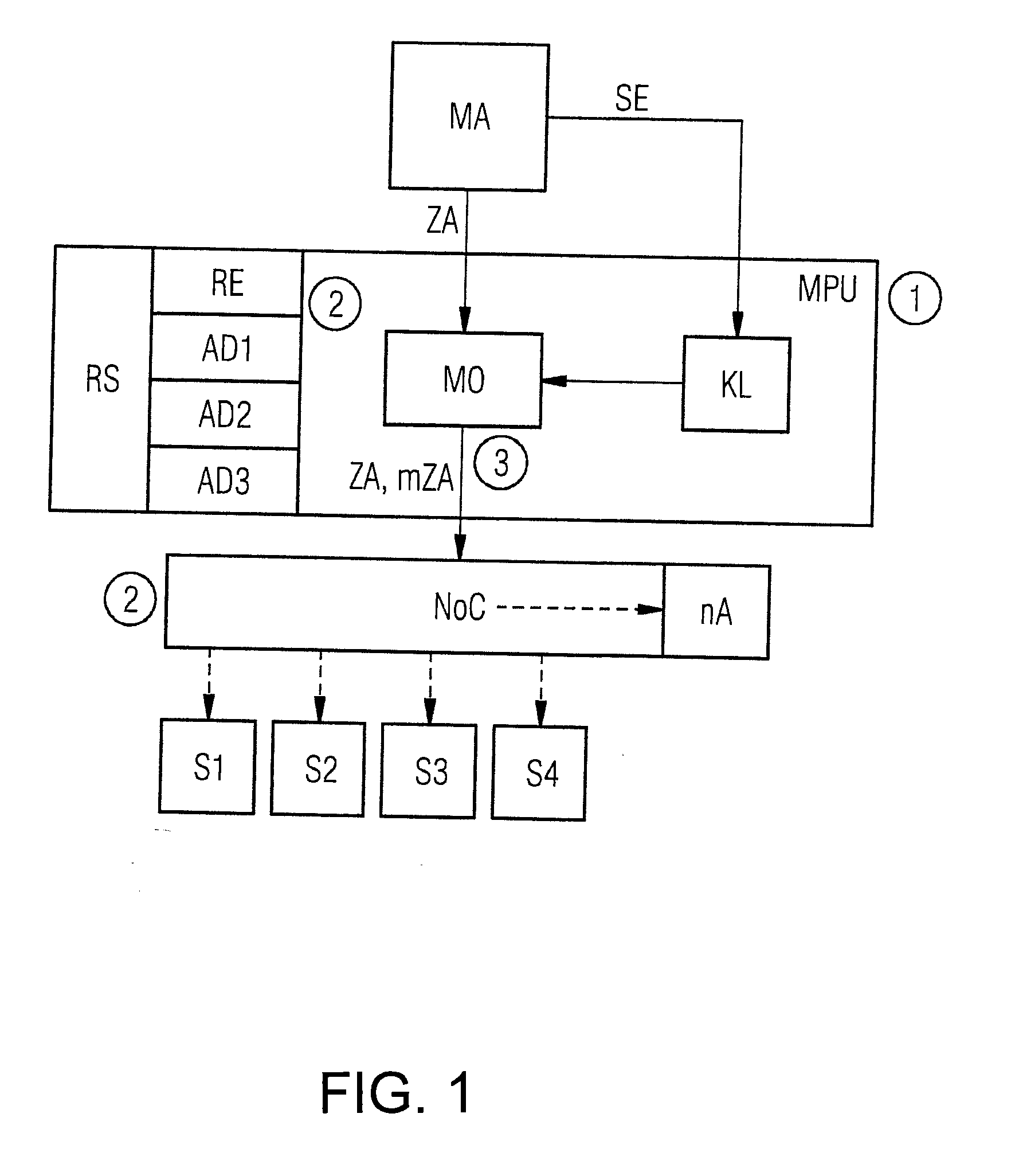
Method and circuit arrangement for accessing slave units in a system on chip in a controlled manner
InactiveUS20160004647A1Simple wayIncrease overheadMemory architecture accessing/allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionControl mannerNetworks on chip
A circuit arrangement and method for accessing slave units in a system on chip in a controlled manner, wherein an access of a master unit of the system on chip to one of the slave units is performed via a network-on-chip bus system using an access address, where a memory protection unit is integrated between the at least one master unit and the network-on-chip bus system, and access authorization of the master unit to a slave unit is checked by the memory protection unit by comparing the access address with specified address sections, and when an unauthorized access of the master unit to a slave unit is identified, the access address is modified by the memory protection unit such that the unauthorized access is terminated in the network-on-chip bus system.
Owner:SIEMENS AG
Memory protection system and method
A shared memory controller is provided for controlling access to a shared memory by a plurality of processors. At least one device includes a storage area for storing a respective address range for each of a plurality of memory regions. The at least one device further includes a permission table containing, for each of the plurality of memory regions, read and write permission data for each of the plurality of processors. A memory fault detector is coupled to the at least one device and has an input for receiving a memory access request including a memory address, a processor identification and a read / write indicator. The memory fault detector includes logic for determining whether a memory access according to the memory access request would conflict with the read and write permission data in the permission table.
Owner:AVAGO TECH WIRELESS IP SINGAPORE PTE
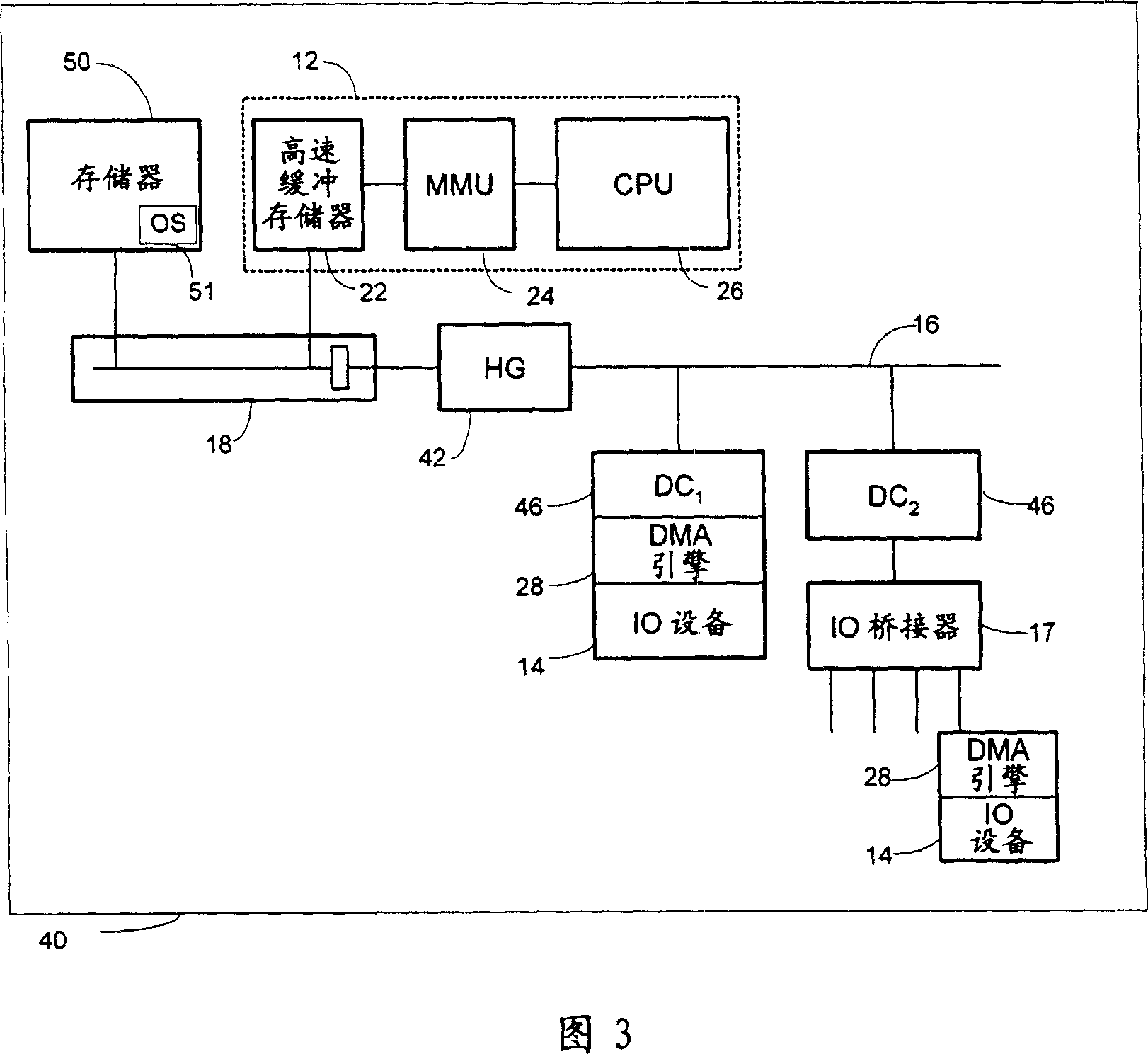
Method and system for memory protection and security using credentials
ActiveCN101004717AUnauthorized memory use protectionComputer security arrangementsDirect memory accessOperating system
A computer-implemented system and method for protecting a memory are provided. The system includes a memory section with privileged and non-privileged sections, a host gateway (HG) to generate a capability credential, a device controller (DC) to append the credential to data transmitted to the memory, and at least one IO device enabled to do direct memory access (DMA) transactions with the memory.
Owner:IBM CORP
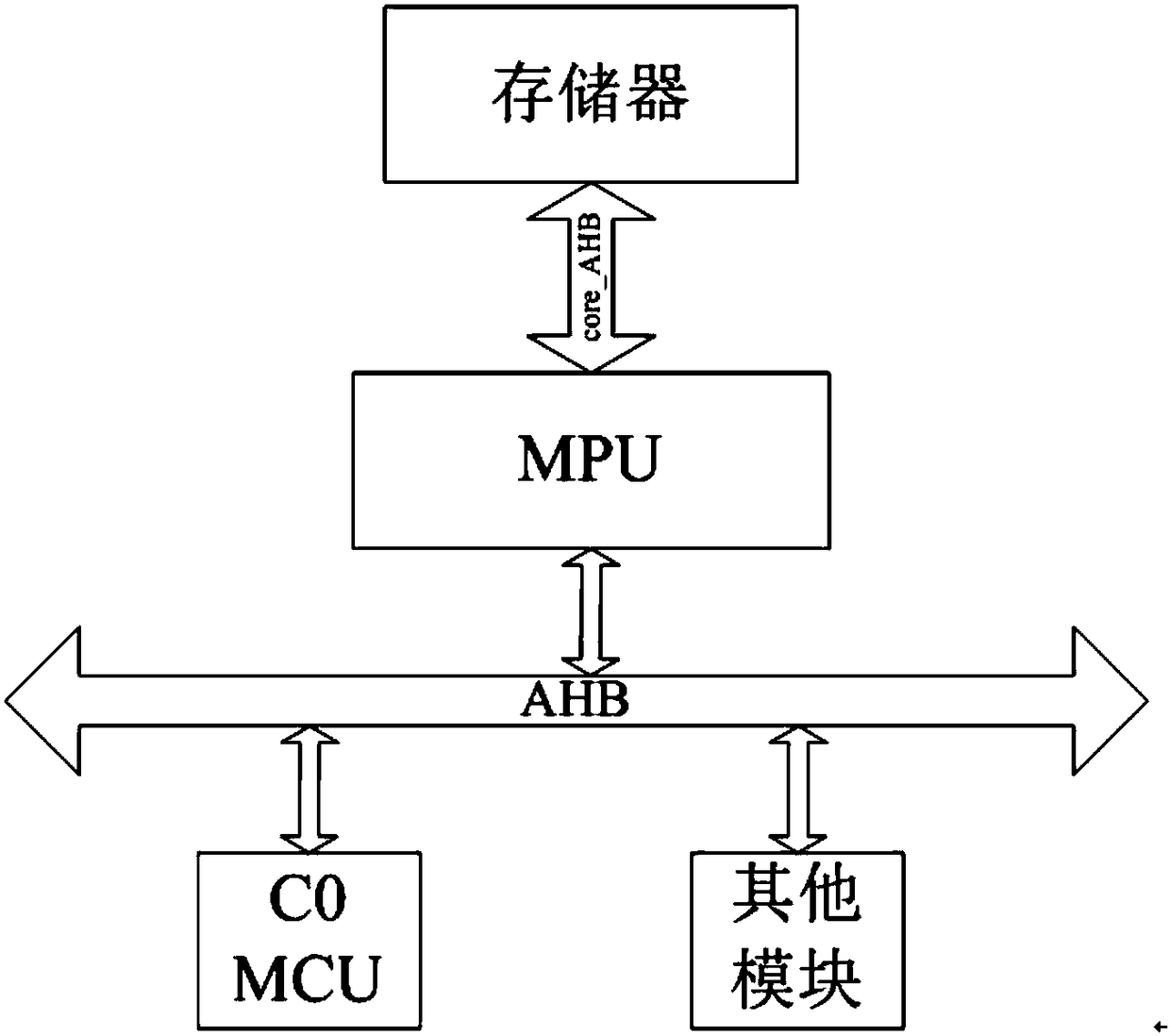
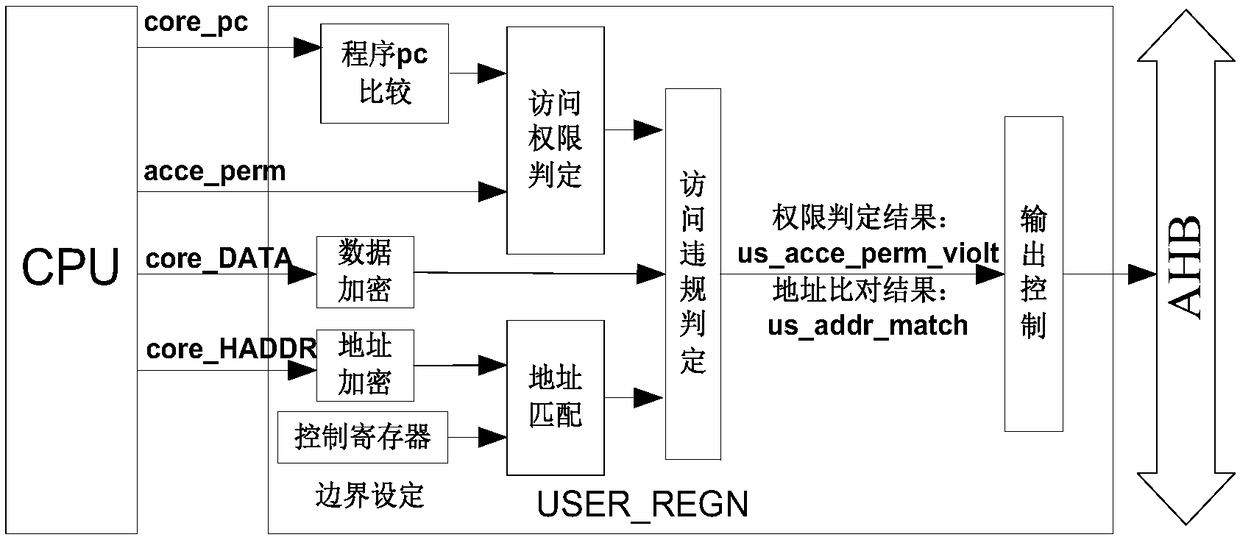
Division method of user control area in memory protection unit and memory protection system
InactiveCN108460287AAchieve protectionImprove confidentialityDigital data protectionEmbedded systemMemory protection unit
The invention discloses a division method of a user control area in a memory protection unit. The division method includes: on the basis of a SoC system developed for a core by a C0 MCU, setting areaauthority management of chip inside storer FLASH; establishing correlation between users and corresponding areas of the FLASH according to setting of the users to form areas with user attributes; setting independent access authority for each area; when receiving user access authority, if the areas are unmatched with corresponding authority of the users, returning wrong information to the C0 MCU tostop unmatched access. The division method has the advantages that ownership of system resources is ensured from hardware, a good mechanism is provided for preventing illegal access to the resources,and protection of the chip inside storer is realized effectively.
Owner:NANTONG UNIVERSITY
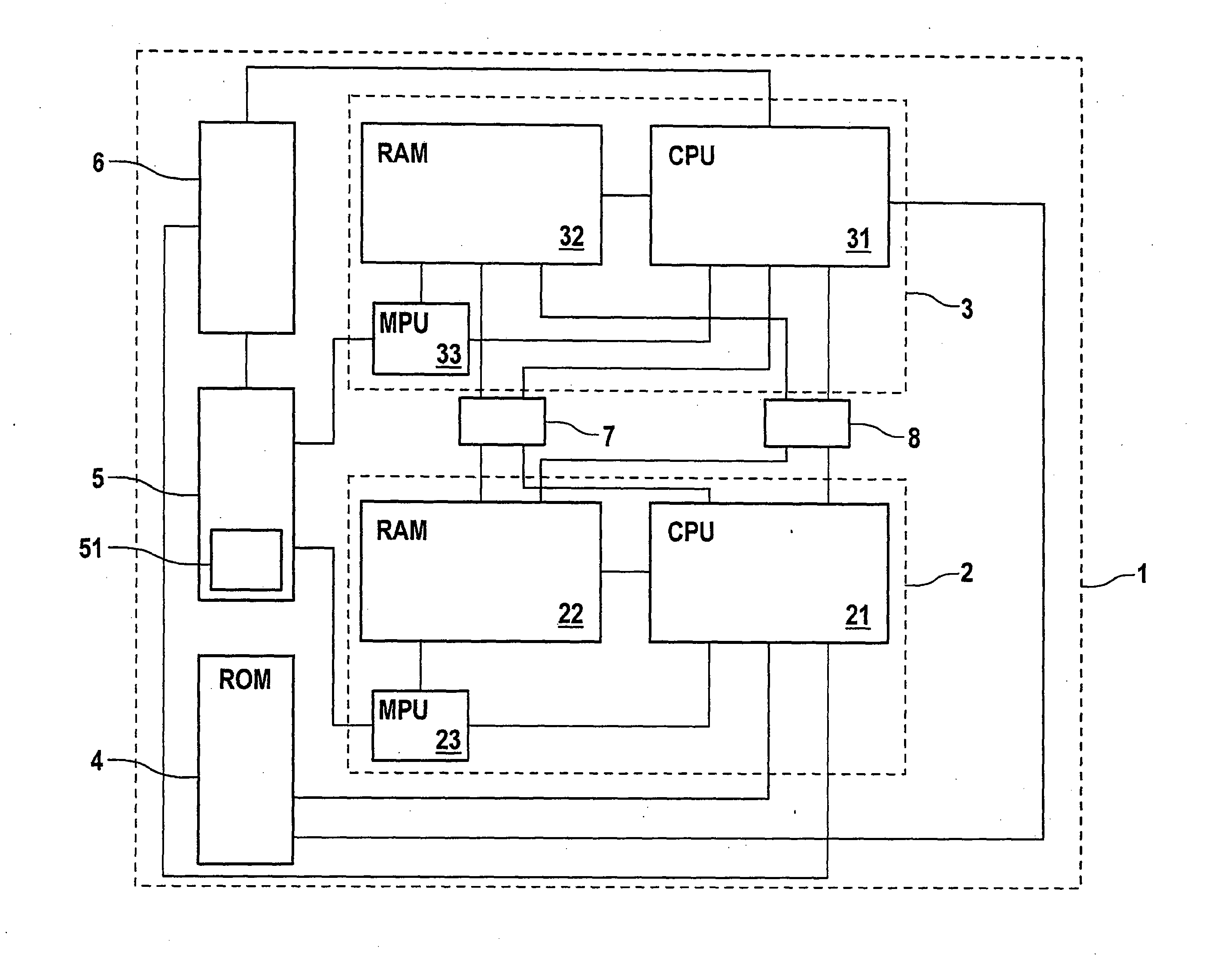
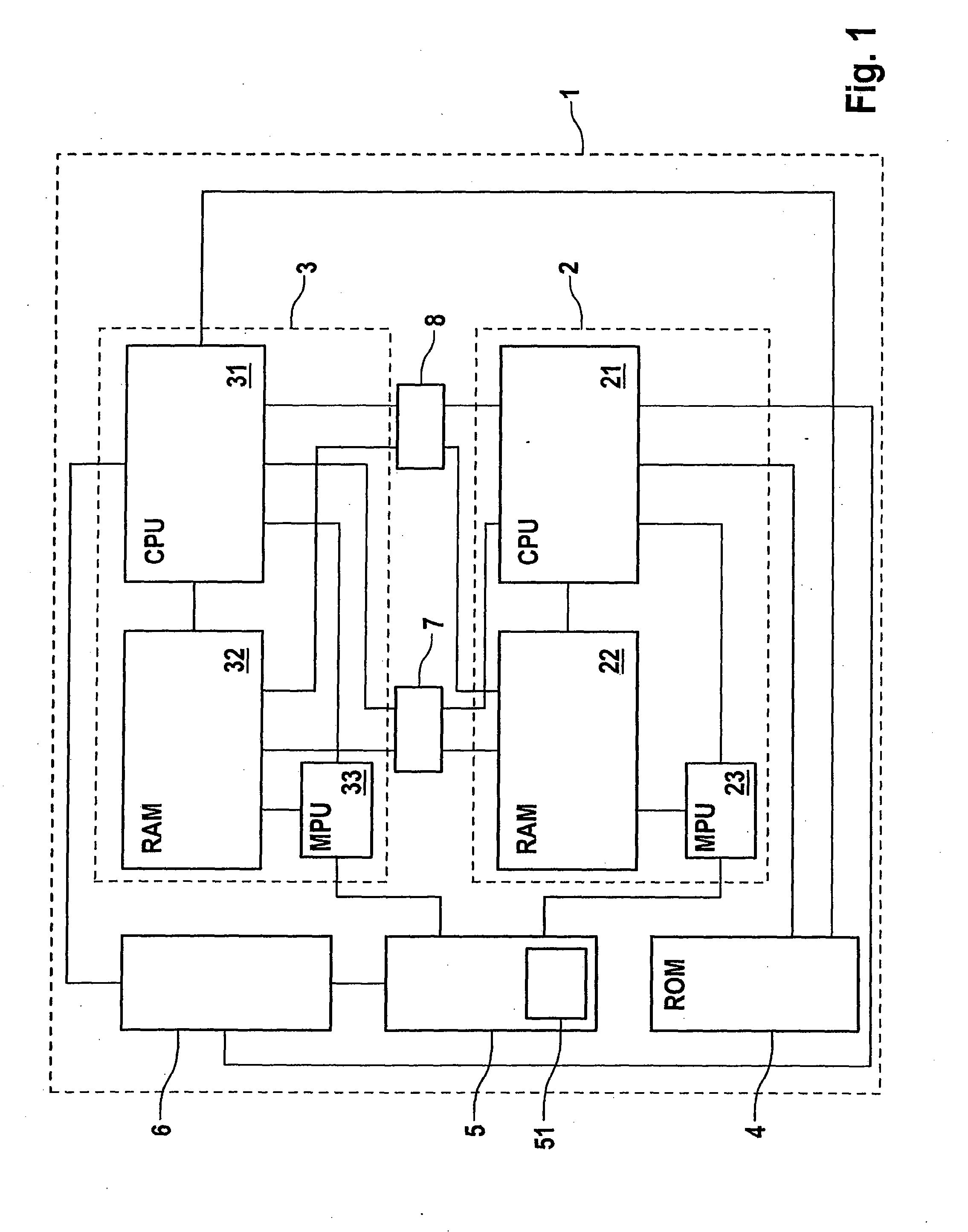
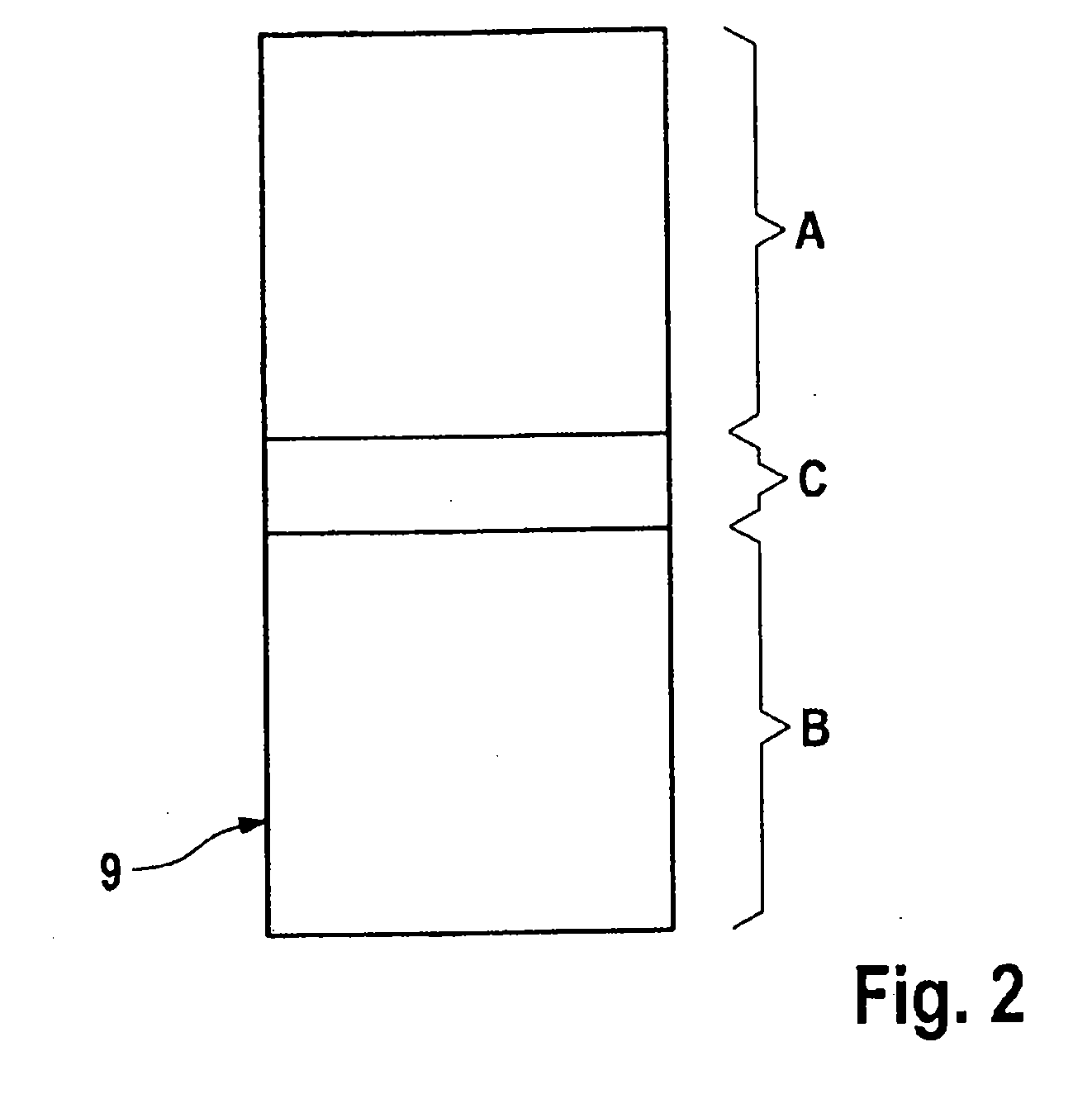
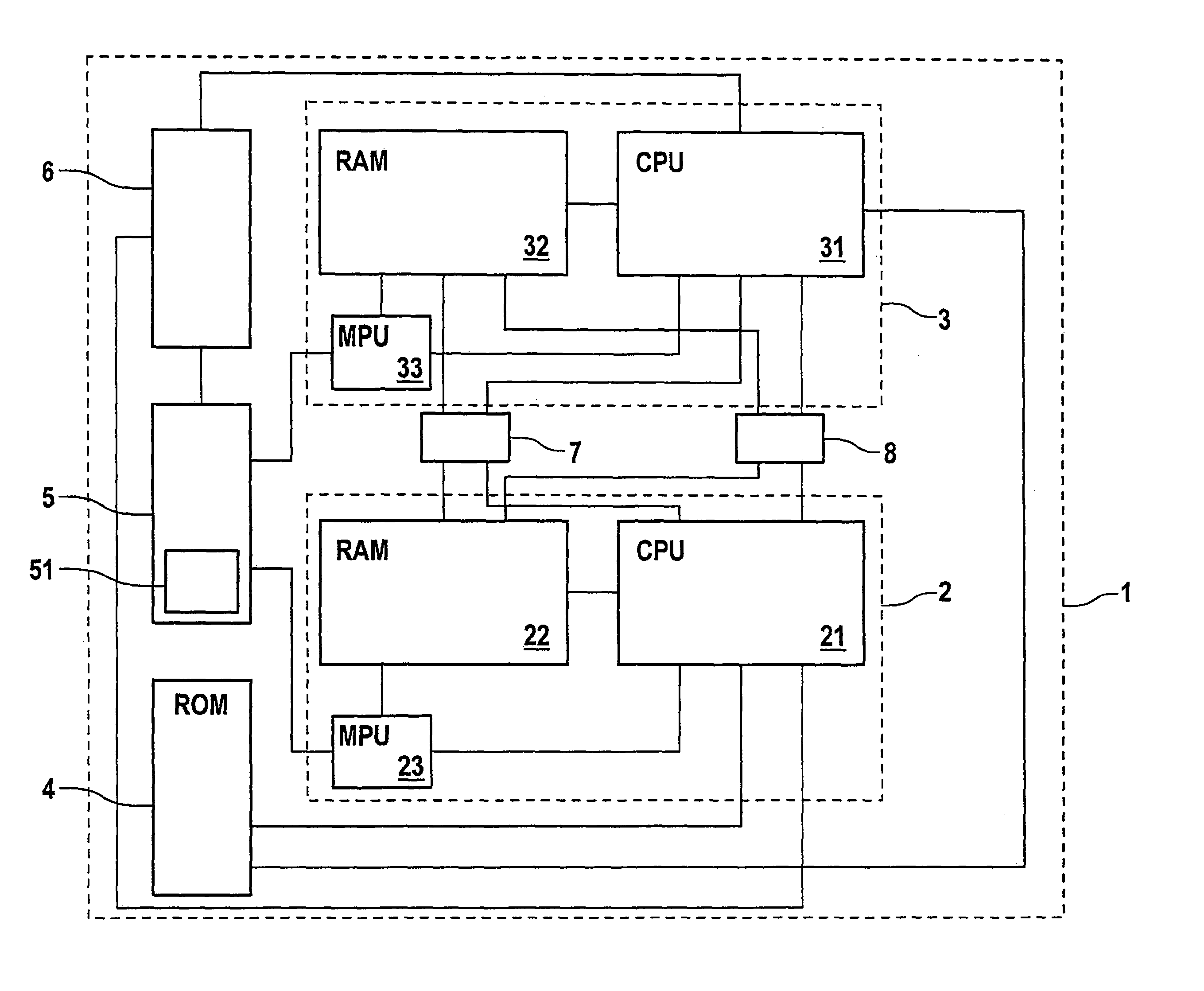
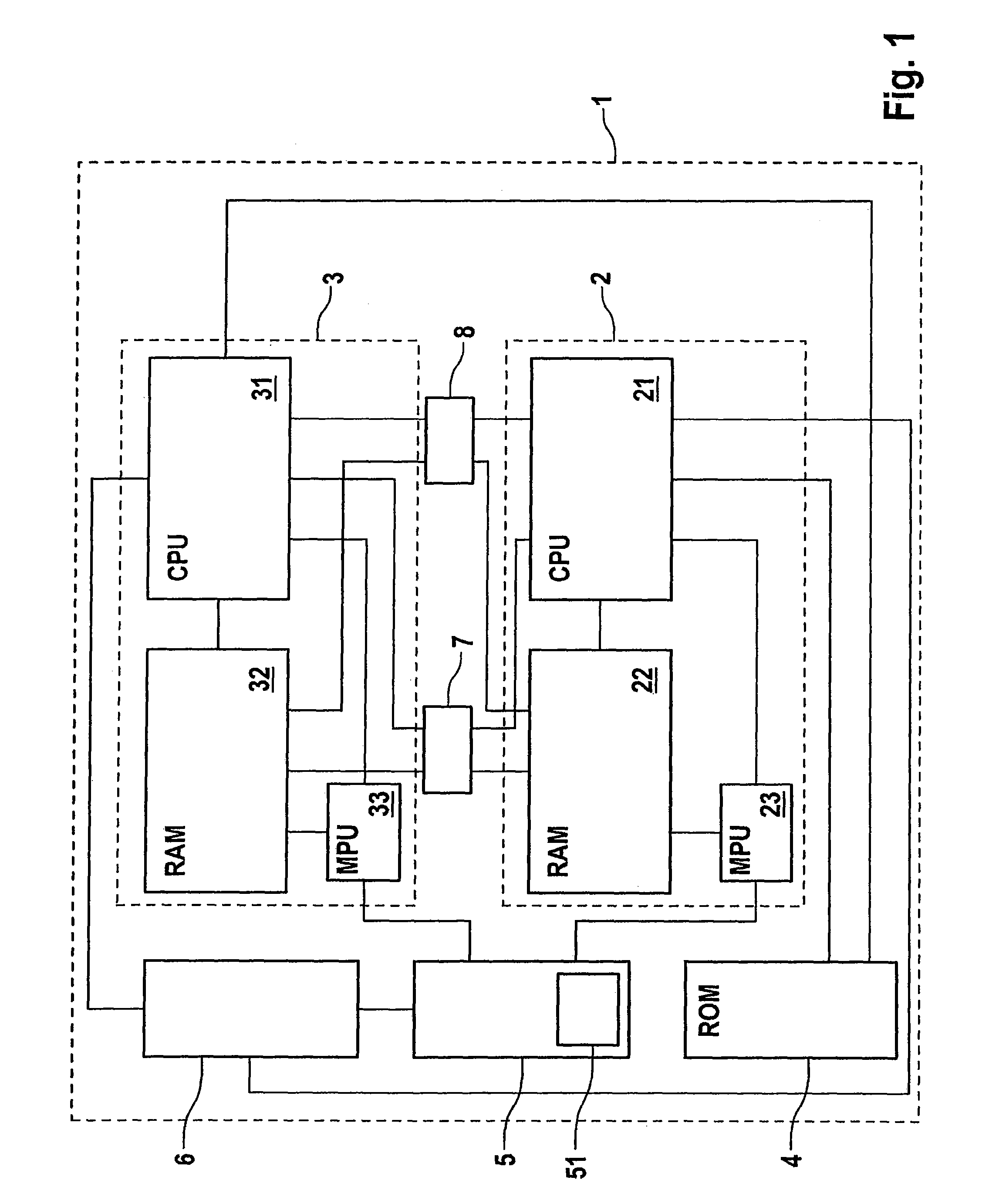
Integrated microprocessor system for safety-critical control systems
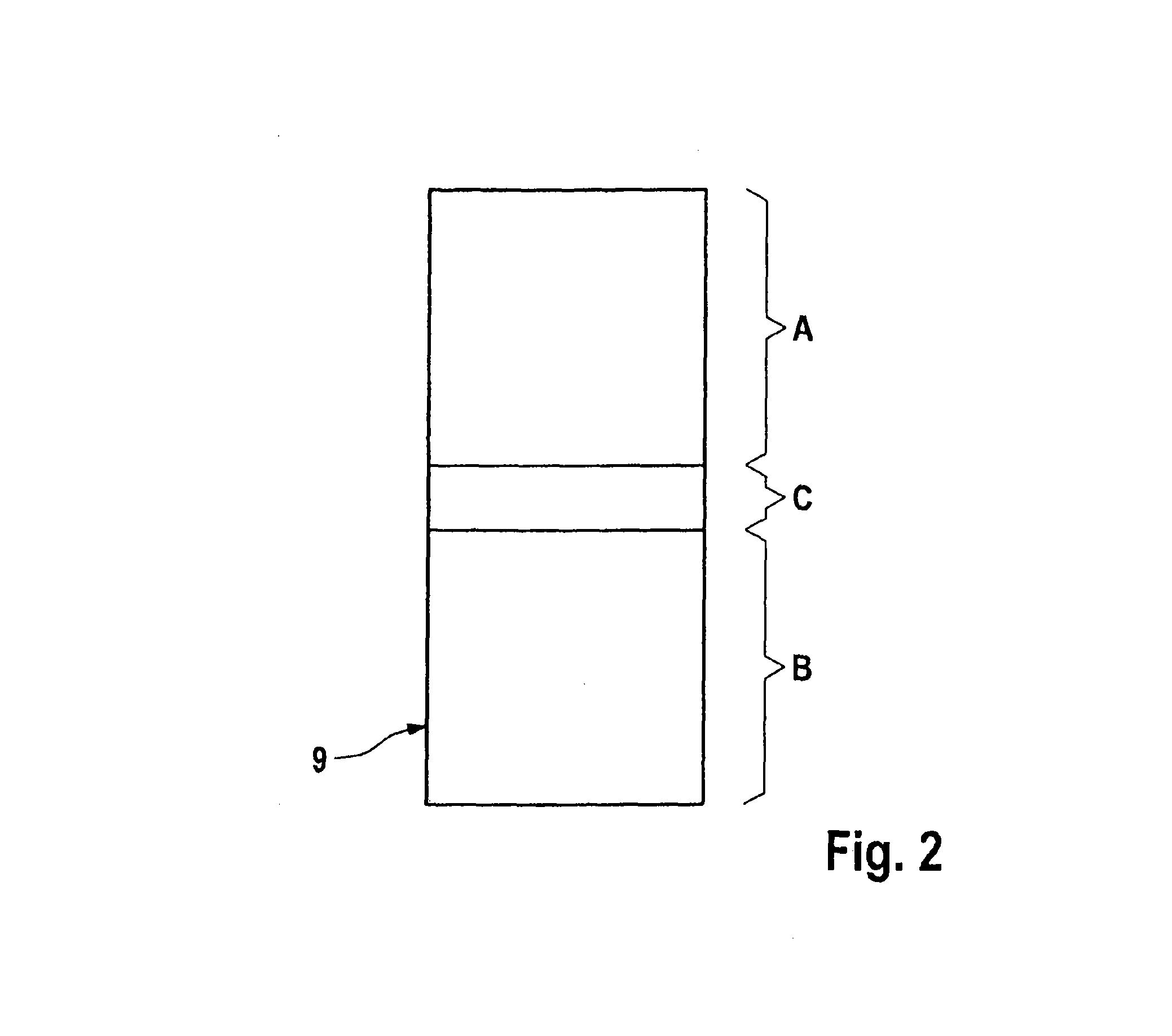
ActiveUS20100306601A1Strict requirementsCost-effectiveProgramme controlUnauthorized memory use protectionControl systemRead-only memory
An integrated microprocessor system for safety-critical control systems, comprising at least two microprocessor system modules each comprising at least one processor core, a read / write memory and a memory protection unit, and a read-only memory which is jointly assigned to the processor cores of the microprocessor system modules. Each of the microprocessor system modules executes a main program and a monitoring program which may comprise a plurality of subprograms. If the memory protection unit detects unauthorized operations by one of the programs for accessing a separate address area (A, B) of another program, then the respective memory protection unit assigns a separate address area (A, B) of the read / write memory to the main program and to the monitoring program.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
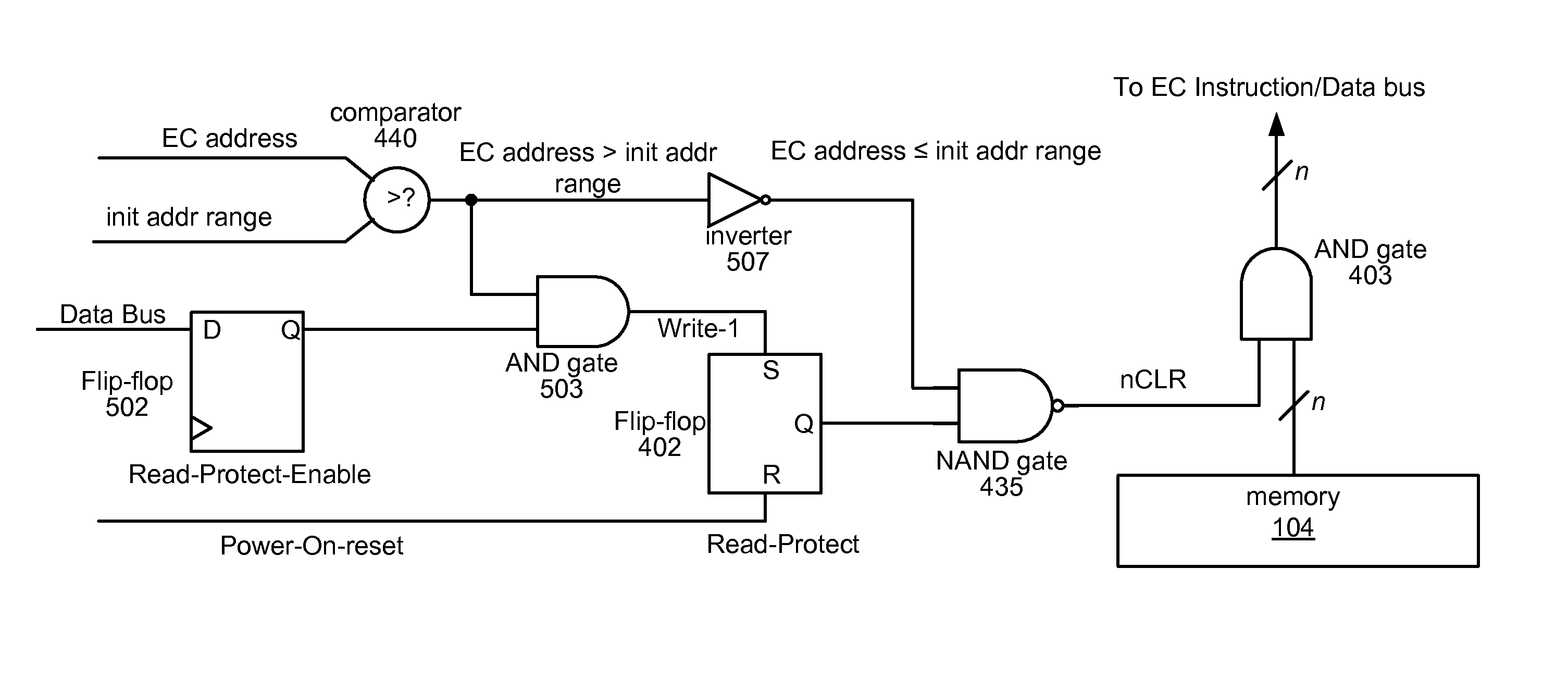
Memory protection for embedded controllers
ActiveUS7917716B2Avoid dataImprove protectionDigital computer detailsUnauthorized memory use protectionPower-on resetTerm memory
Owner:MICROCHIP TECH INC
Integrated microprocessor system for safety-critical control systems including a main program and a monitoring program stored in a memory device
ActiveUS8549352B2Cost-effectiveStrict requirementsProgramme controlRedundant hardware error correctionControl systemComputer module
An integrated microprocessor system for safety-critical control systems, comprising at least two microprocessor system modules each comprising at least one processor core, a read / write memory and a memory protection unit, and a read-only memory which is jointly assigned to the processor cores of the microprocessor system modules. Each of the microprocessor system modules executes a main program and a monitoring program which may comprise a plurality of subprograms. If the memory protection unit detects unauthorized operations by one of the programs for accessing a separate address area (A, B) of another program, then the respective memory protection unit assigns a separate address area (A, B) of the read / write memory to the main program and to the monitoring program.
Owner:CONTINENTAL TEVES AG & CO OHG
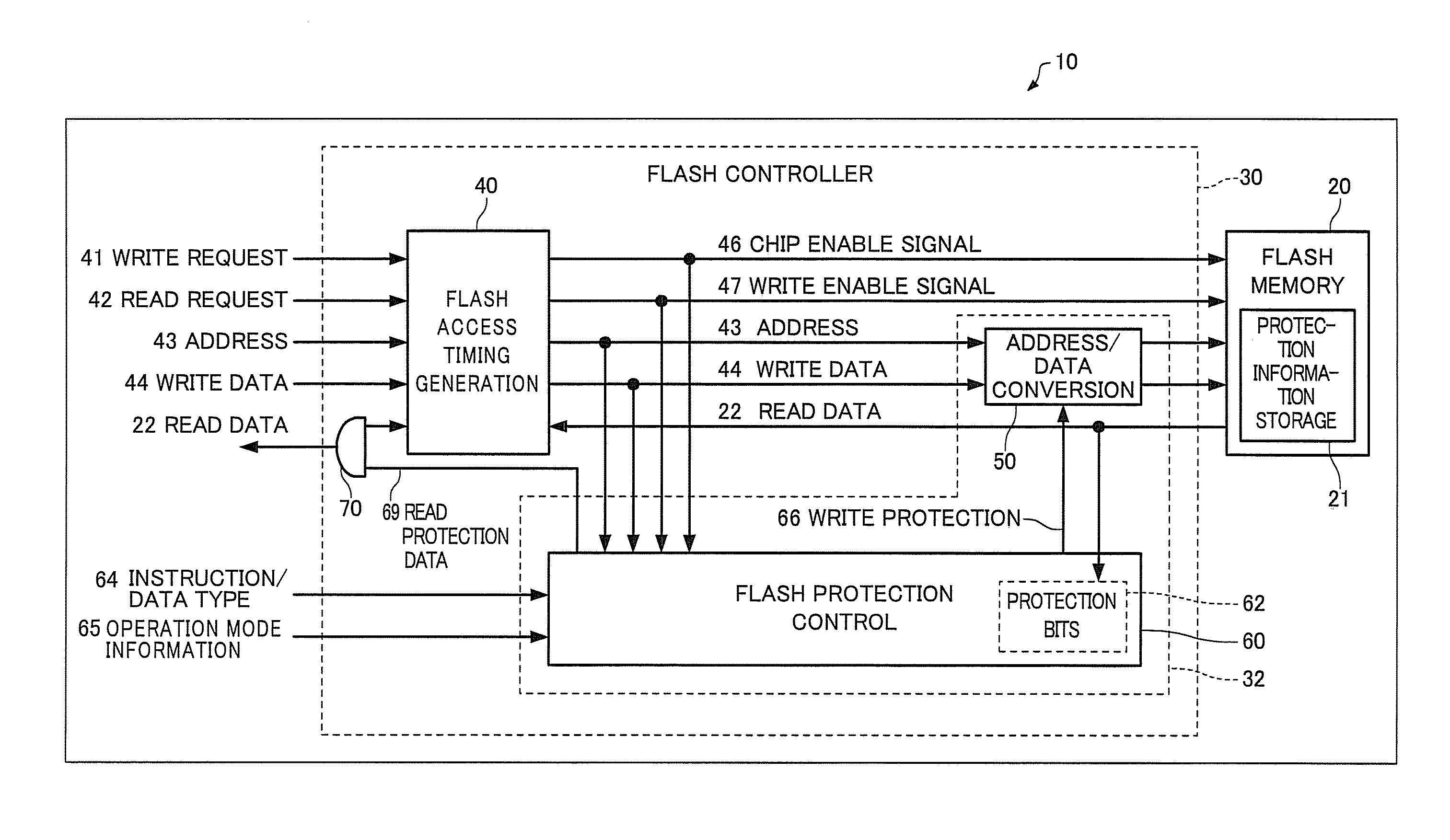
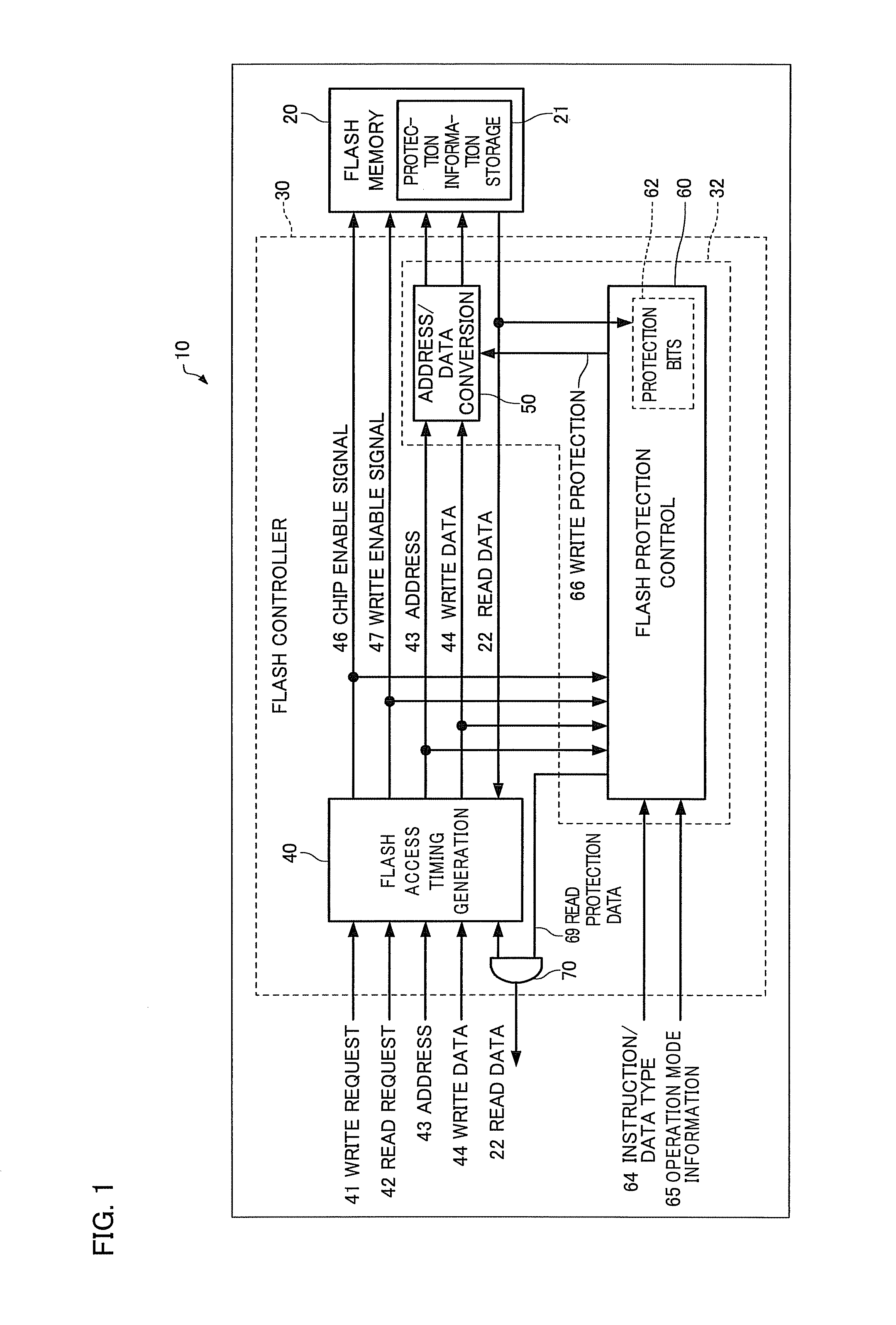
Microcomputer, electronic instrument, and flash memory protection method
ActiveUS20080256288A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationEnergy efficient ICTMicrocomputerElectronic instrument
A microcomputer includes a flash memory and a flash controller that controls access to the flash memory, the flash memory including a protection information storage section that stores protection information, the protection information indicating whether or not access to a given area of the flash memory is available; the flash controller including a flash protection section that performs a protection process relating to access to a given area of the flash memory based on the protection information; and the flash protection section performing the protection process relating to access to the flash memory when an access target is data.
Owner:SEIKO EPSON CORP
Memory consistency protection in a multiprocessor computing system
InactiveUS7895407B2Low-cost and effectiveImprove consistencyResource allocationMemory adressing/allocation/relocationMulti processorObject code
A method and apparatus to protect memory consistency in a multiprocessor computing system are described, in particular relating to program code conversion such as dynamic binary translation. The exemplary system provides a memory, processors and a controller / translator unit (CTU) arranged to convert subject code into at least first and second target code portions executable on the processors. The CTU comprises an address space allocation unit to provide virtual address space regions and direct the target code portions to access the memory therethough; a shared memory detection unit to detect a request to access a shared memory area, accessible by both target code portions, and to identify at least one group of instructions in the first target code portion which access the shared memory area; and a memory protection unit to selectively apply memory consistency protection in relation to accesses to the shared memory area by the identified group of instructions.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
Method and computer system for providing remote direct memory access
InactiveUS7921177B2Simple methodCostly adaptationMultiple digital computer combinationsTransmissionDirect memory accessComputerized system
A method for providing remote direct memory access (RDMA) between two computers, preferably between central processing units (CPUs) and a functional subsystem of a computer system as part of their network communication, e.g. using TCP / IP. Tasks of analyzing network protocol data and the actual RDMA operations can be offloaded to the functional subsystem with this method. Further, the functional subsystem cannot compromise the status of the first computer system as only access to certain allowed memory locations is granted by a memory protection unit during phases of actual data transfer between the functional subsystem and the CPUs.
Owner:INT BUSINESS MASCH CORP
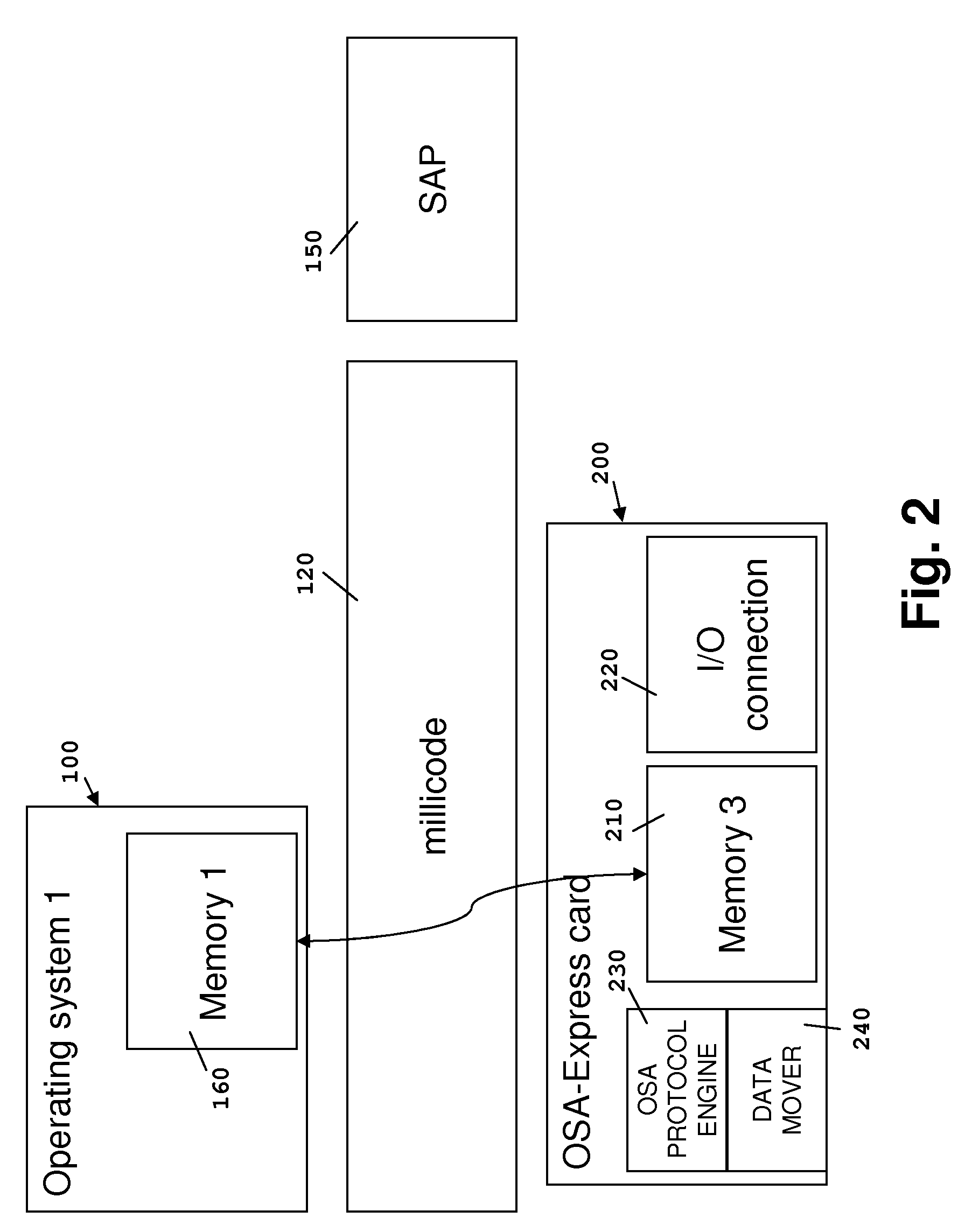
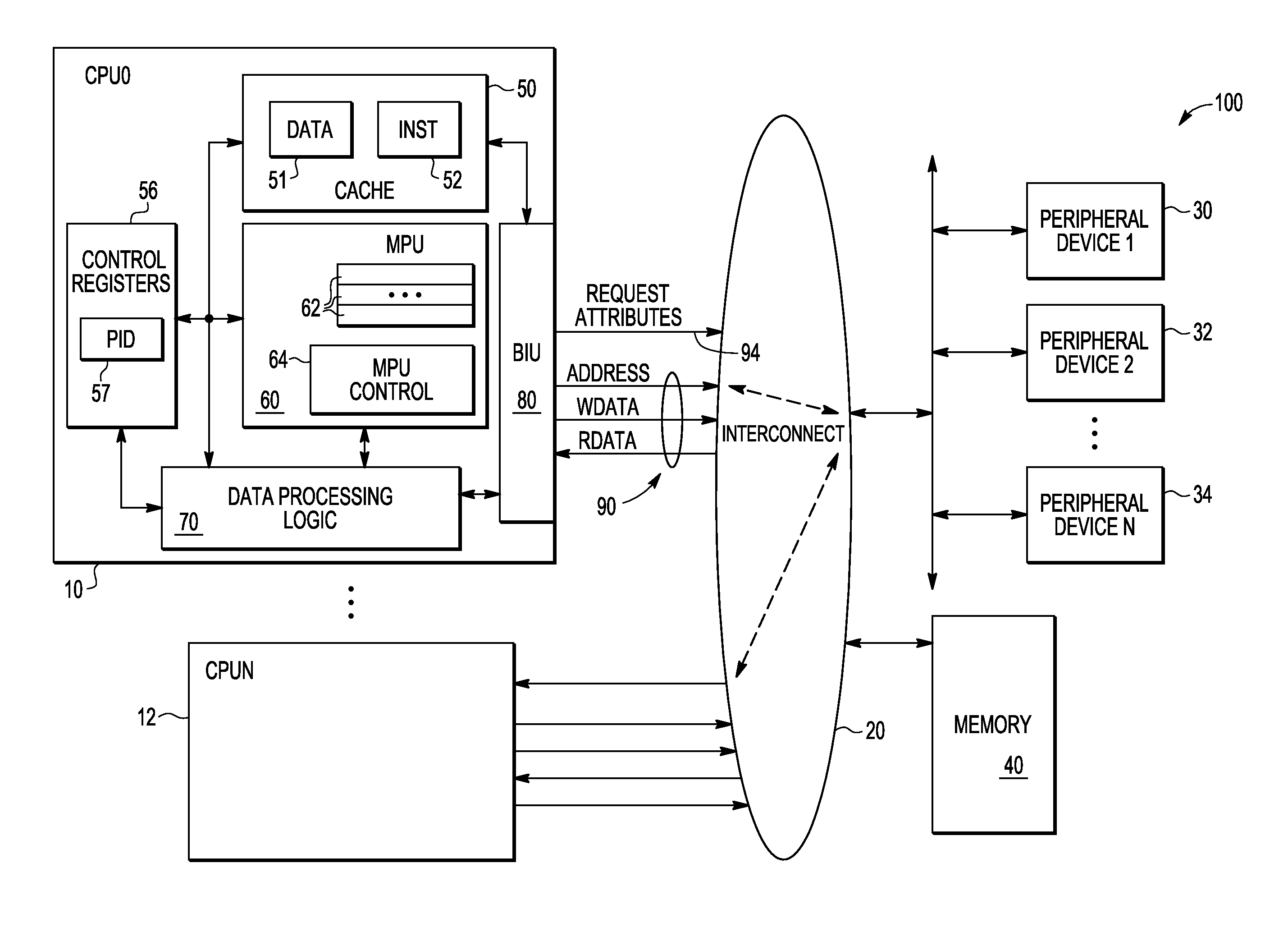
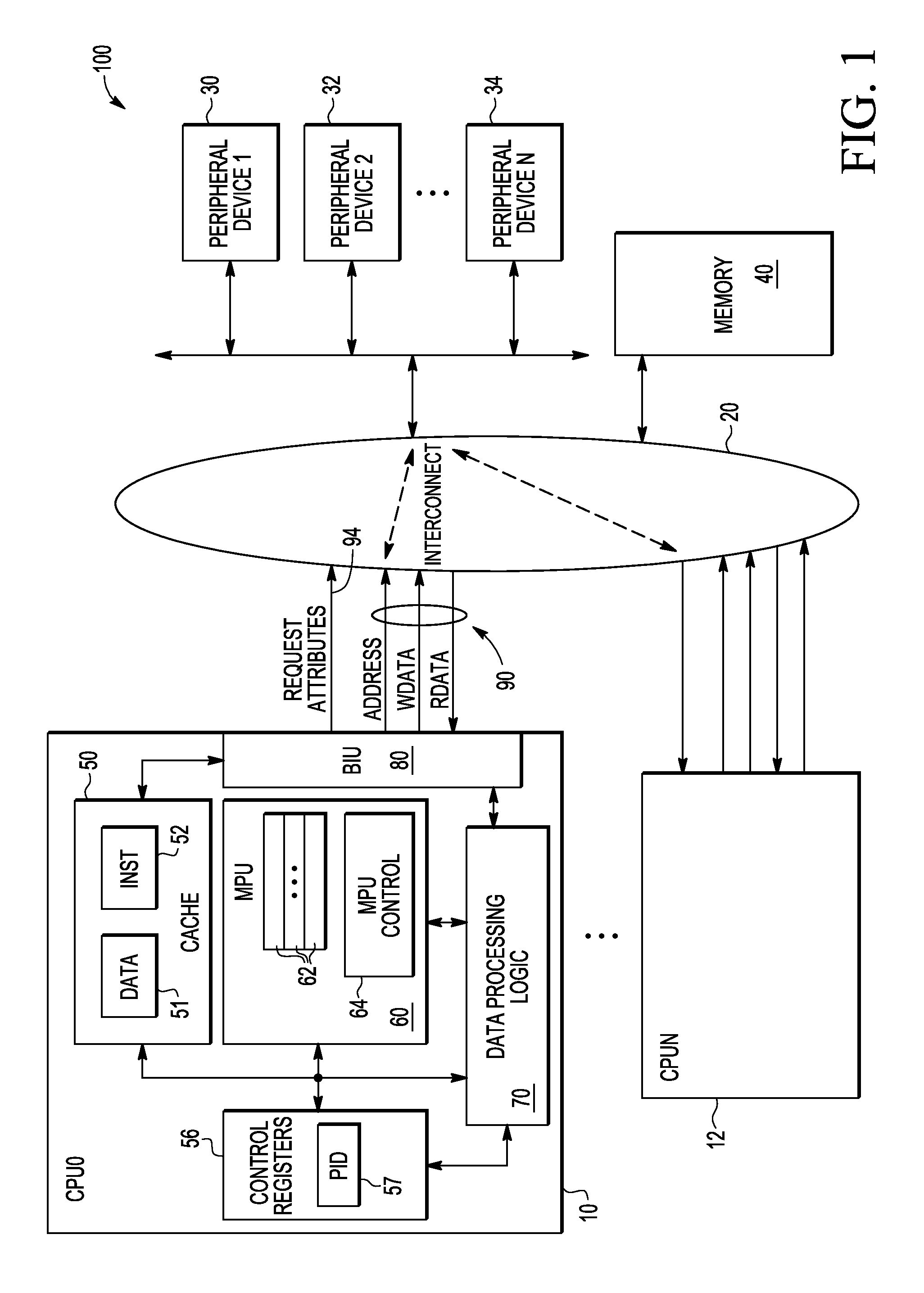
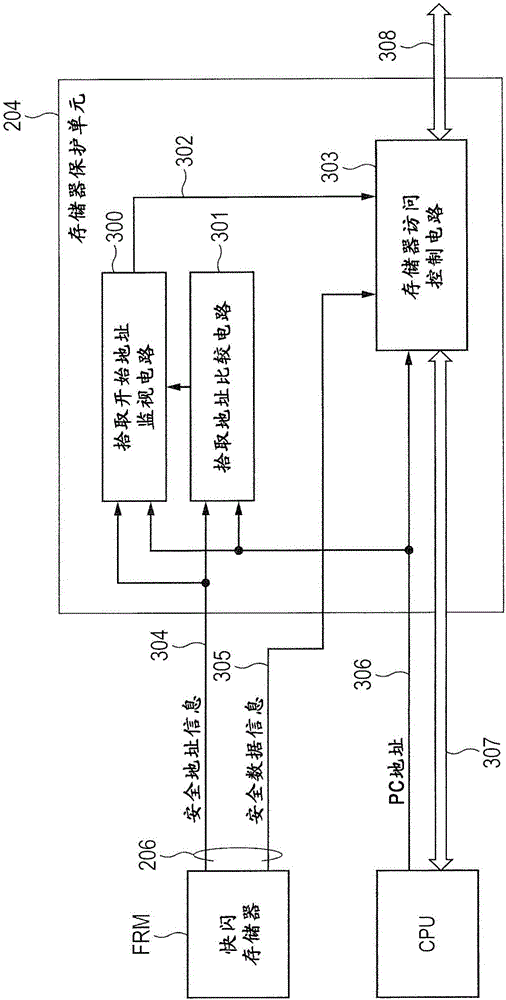
Memory protection unit, memory protection method, and computer-readable record medium in which memory protection program is recorded
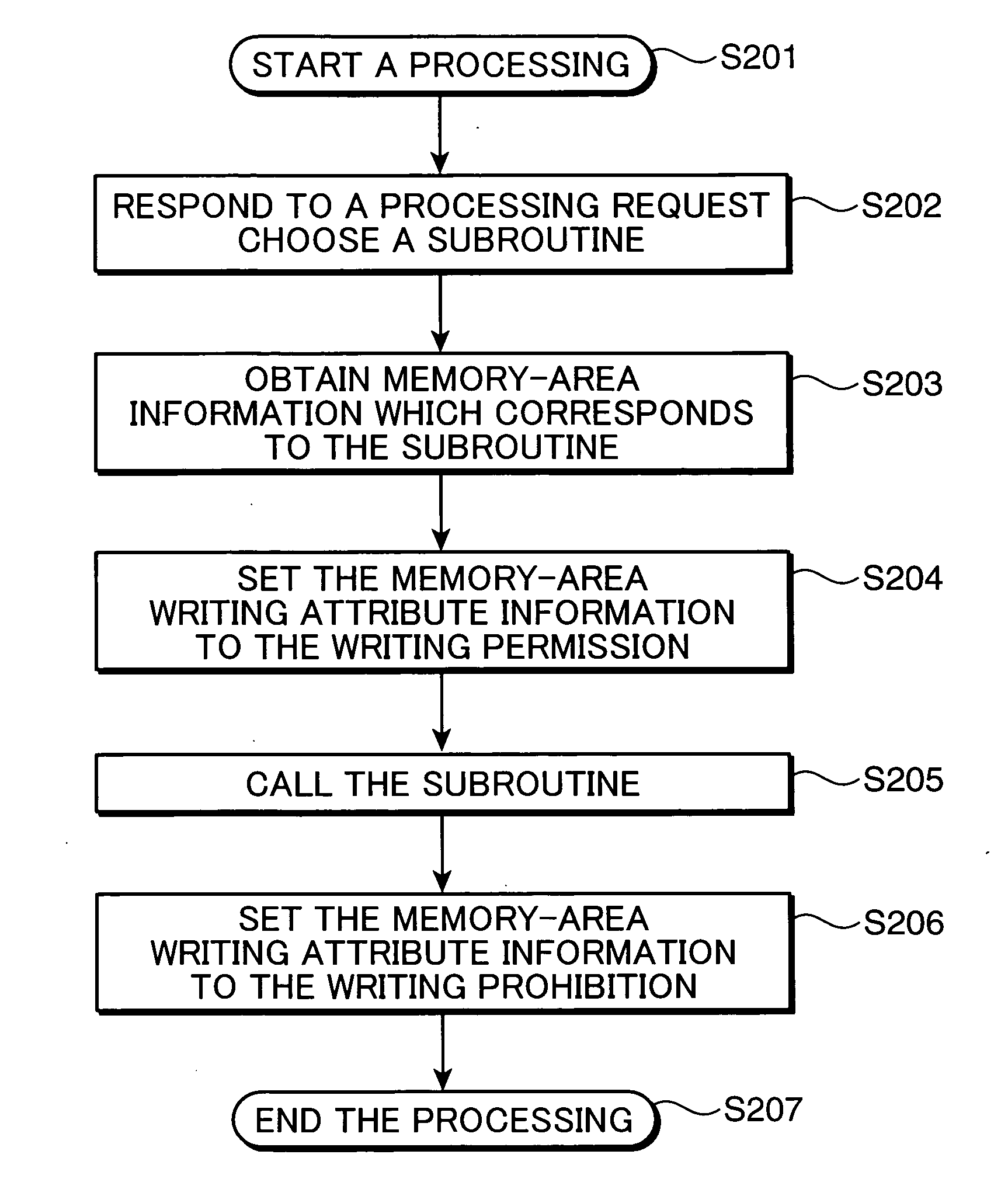
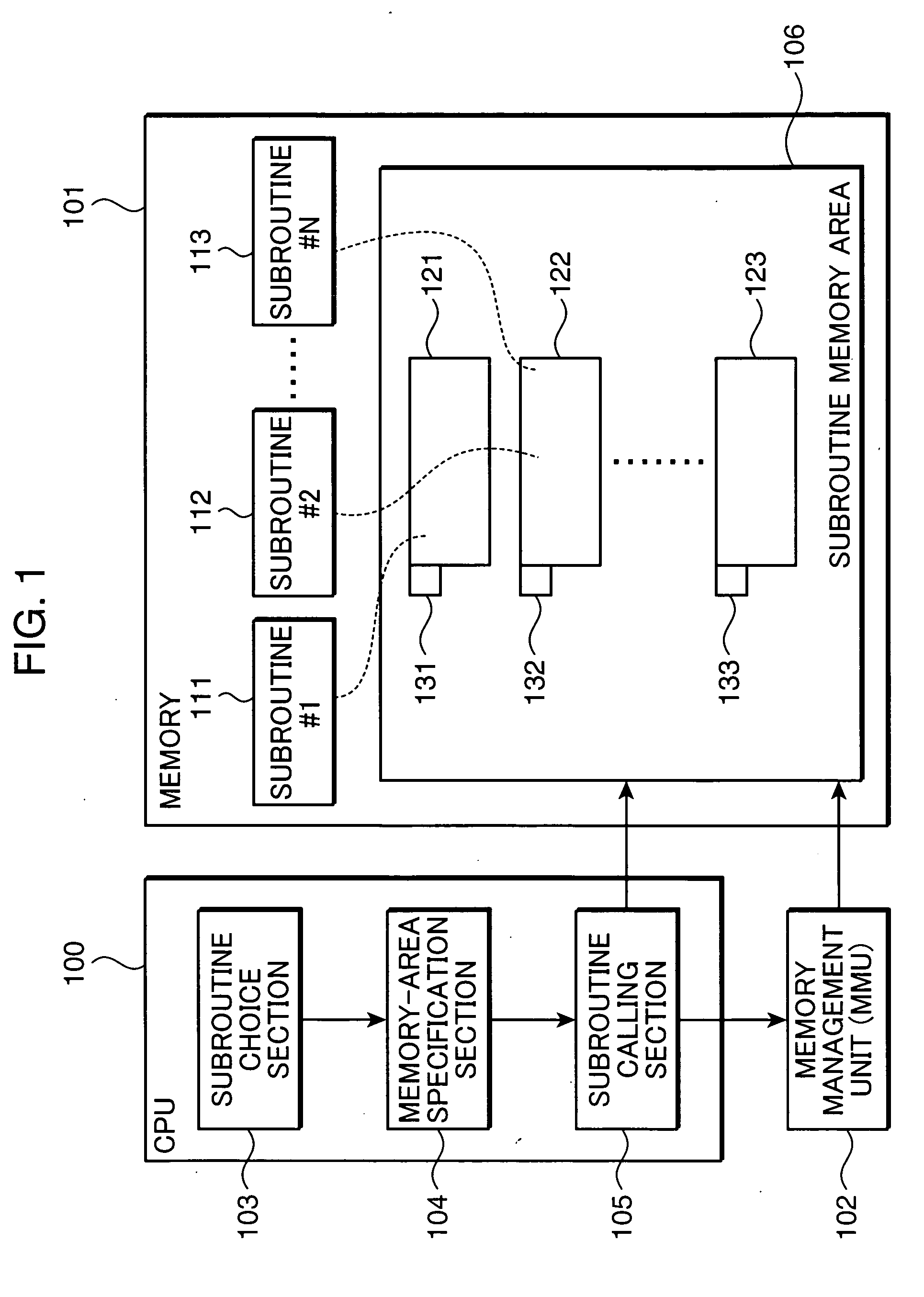
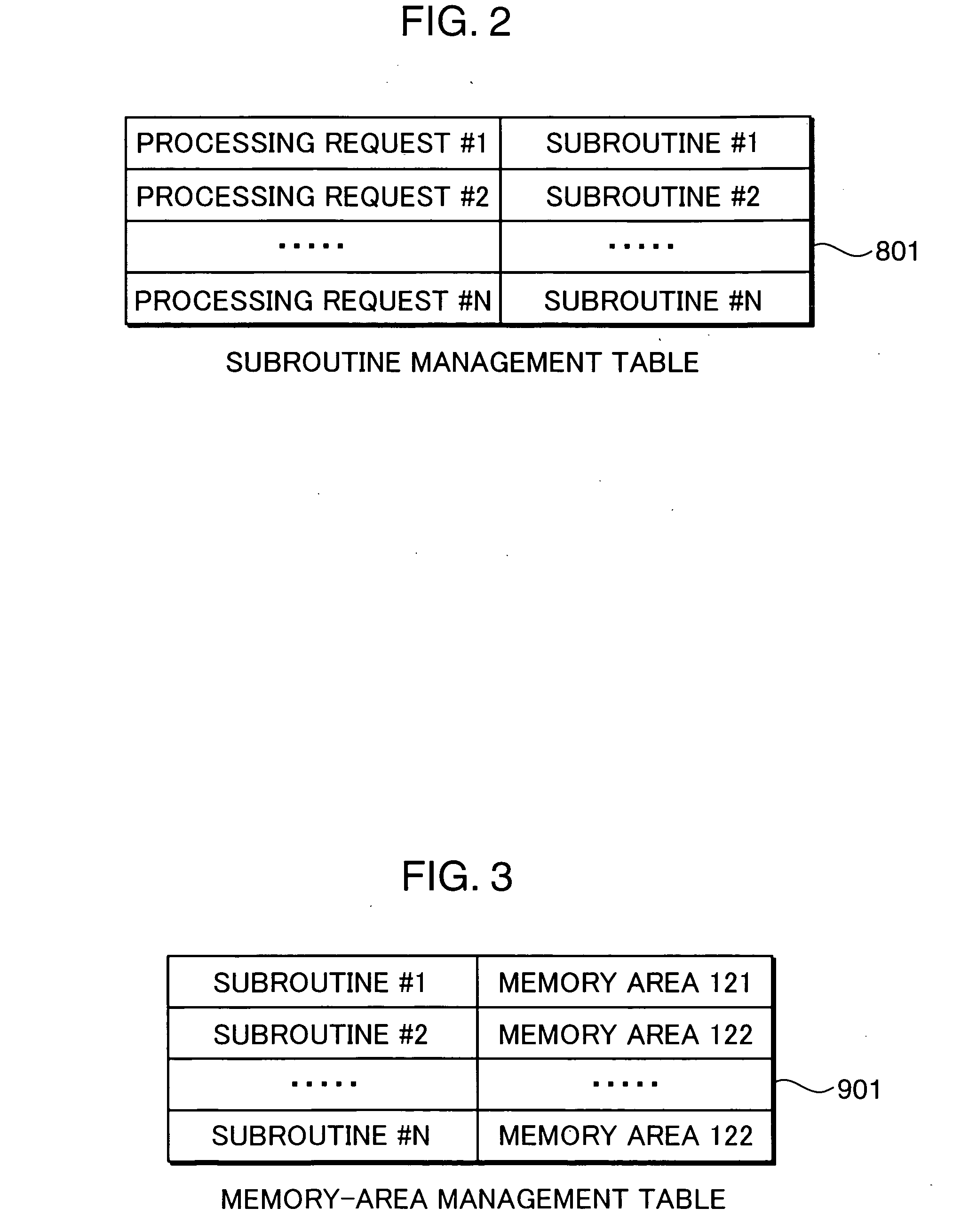
InactiveUS20050144408A1Preventing a memory from being improperly rewrittenUnauthorized memory use protectionPlatform integrity maintainanceComputer hardwareMemory protection unit
A memory protection unit, a memory protection method and a computer-readable record medium in which a memory protection program is recorded is provided which are capable of preventing a memory from being improperly rewritten by a malfunction in a subroutine. This memory protection unit includes: a memory which has at least one memory area that is used by at least one subroutine, and in which a writing attribute that shows a writing permission or a writing prohibition can be set for every memory area; a subroutine choice section which chooses a subroutine that executes a processing request; a memory-area specification section which specifies a memory area that is used by the subroutine; and a subroutine calling section which sets, to the writing permission, the writing attribute of the specified memory area, calls the chosen subroutine, and sets, to the writing prohibition, the writing attribute of the memory area after completing the execution of the subroutine.
Owner:PANASONIC CORP
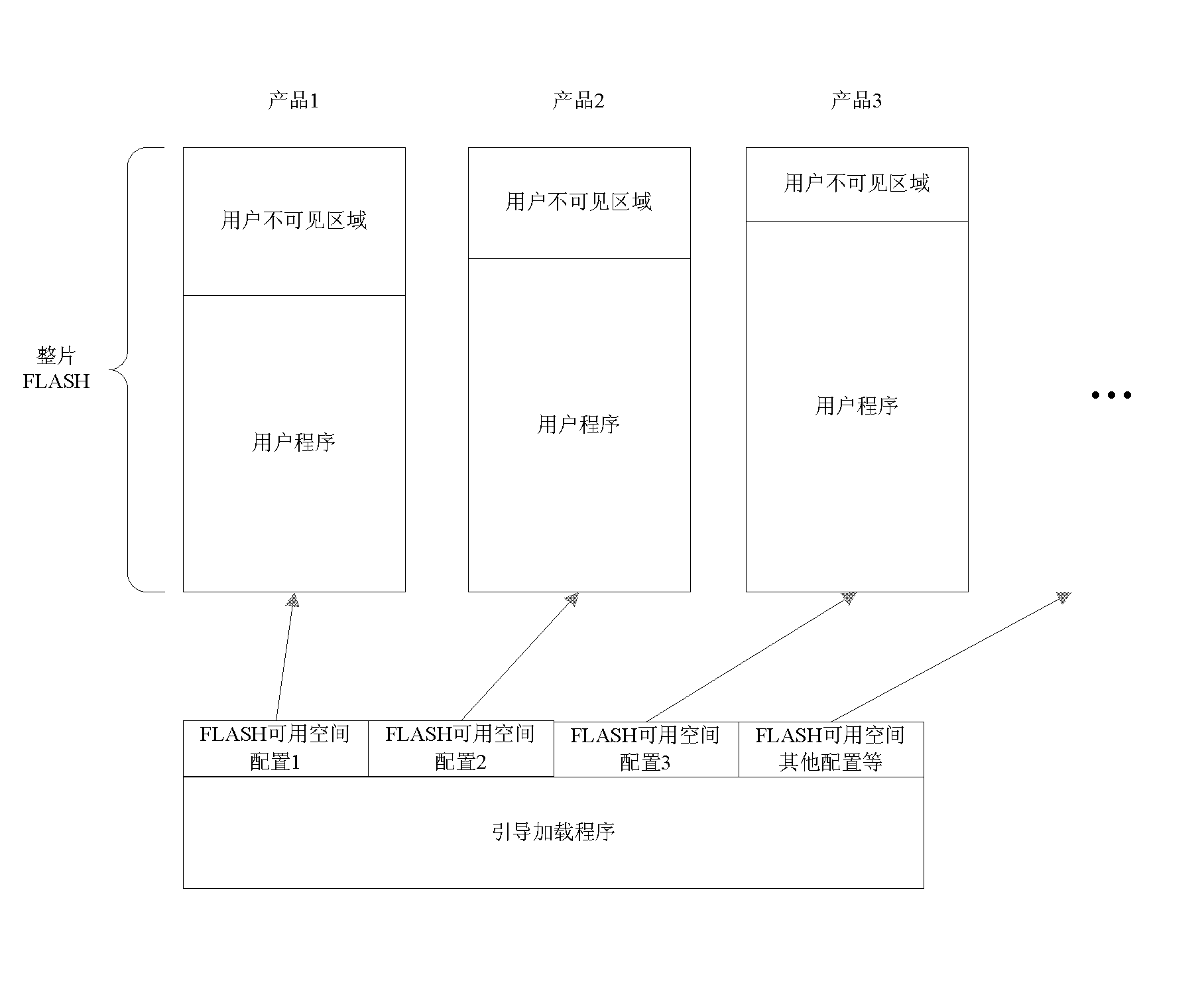
Method for controlling space size of smart card FLASH
ActiveCN102736983ALow costIncrease flexibilityMemory adressing/allocation/relocationUnauthorized memory use protectionSmart cardControl space
The invention discloses a method for controlling space size of a smart card FLASH, comprising the steps of 1. dividing a space of the flash memory FLASH in a boot loader according to different application requirements of different users; dividing the flash memory FLASH into a needed area and a non-needed area according to the user requirement; performing authorization settings for different areas; 2. switching the operating mode of ARM (advanced RISC machines) in the boot loader; switching the operating mode of the ARM to a user mode from a privileged mode so as to ensure that the user can not modify previous setup by memory protection unit MPU (microprocessor unit) in the user mode; 3. repeating the steps, developing the boot loader of space size of different flash memories FLASH so as to satisfy different user requirements. According to the method, the FLASH space can be controlled by a software method, so that the development cost of the smart card hardware is lowered and the configuration flexibility of the product is improved by repeatable modification performance of the boot loader.
Owner:SHANGHAI HUAHONG INTEGRATED CIRCUIT
Memory management unit (MMU) having region descriptor globalization controls and method of operation
ActiveUS20130073827A1Memory architecture accessing/allocationUnauthorized memory use protectionManagement unitParallel computing
Embodiments of computer processing systems and methods are provided that include a memory protection unit (MPU), and a plurality of region descriptors associated with the MPU. The region descriptors include address range and translation identifier values for a respective region of memory. Control logic determines whether a translation identifier control indicator is in a first state, and if the translation identifier control indicator is in the first state, the control logic allows a first process being executed by the processing system to access a memory region allocated to a second process being executed by the processing system.
Owner:NXP USA INC
Memory management unit (MMU) having region descriptor globalization controls and method of operation
ActiveUS8572345B2Memory architecture accessing/allocationMemory systemsParallel computingMemory management unit
Embodiments of computer processing systems and methods are provided that include a memory protection unit (MPU), and a plurality of region descriptors associated with the MPU. The region descriptors include address range and translation identifier values for a respective region of memory. Control logic determines whether a translation identifier control indicator is in a first state, and if the translation identifier control indicator is in the first state, the control logic allows a first process being executed by the processing system to access a memory region allocated to a second process being executed by the processing system.
Owner:NXP USA INC
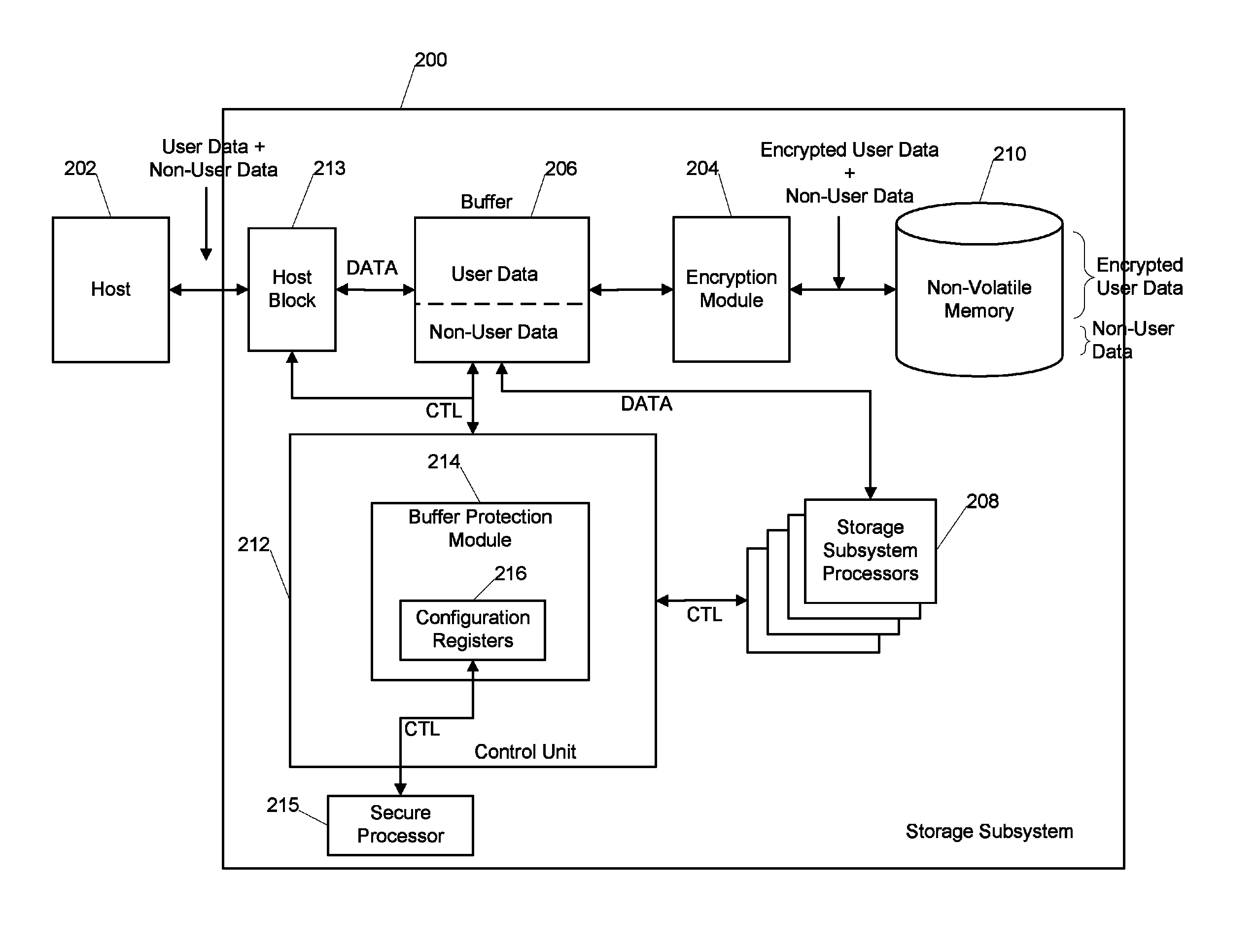
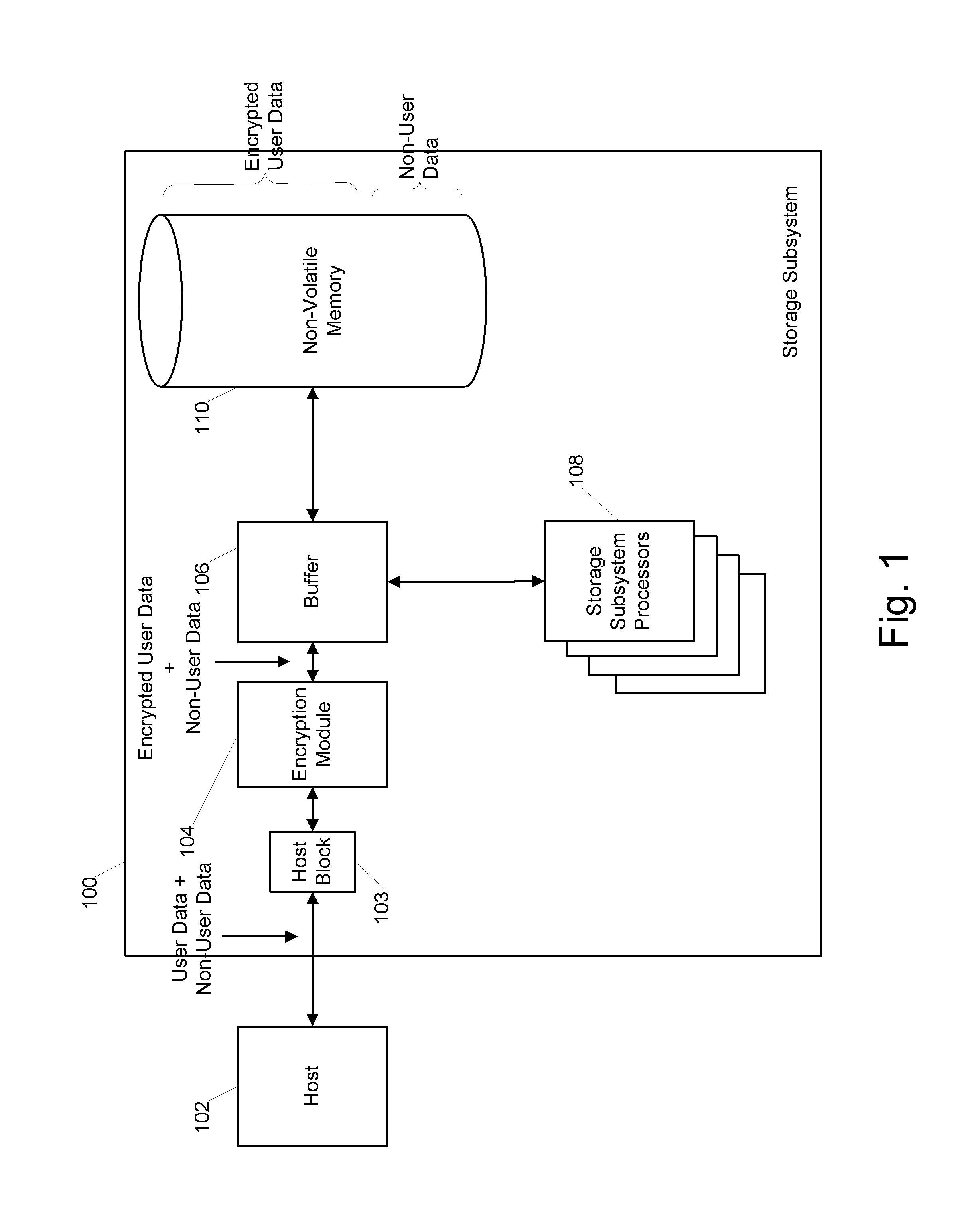
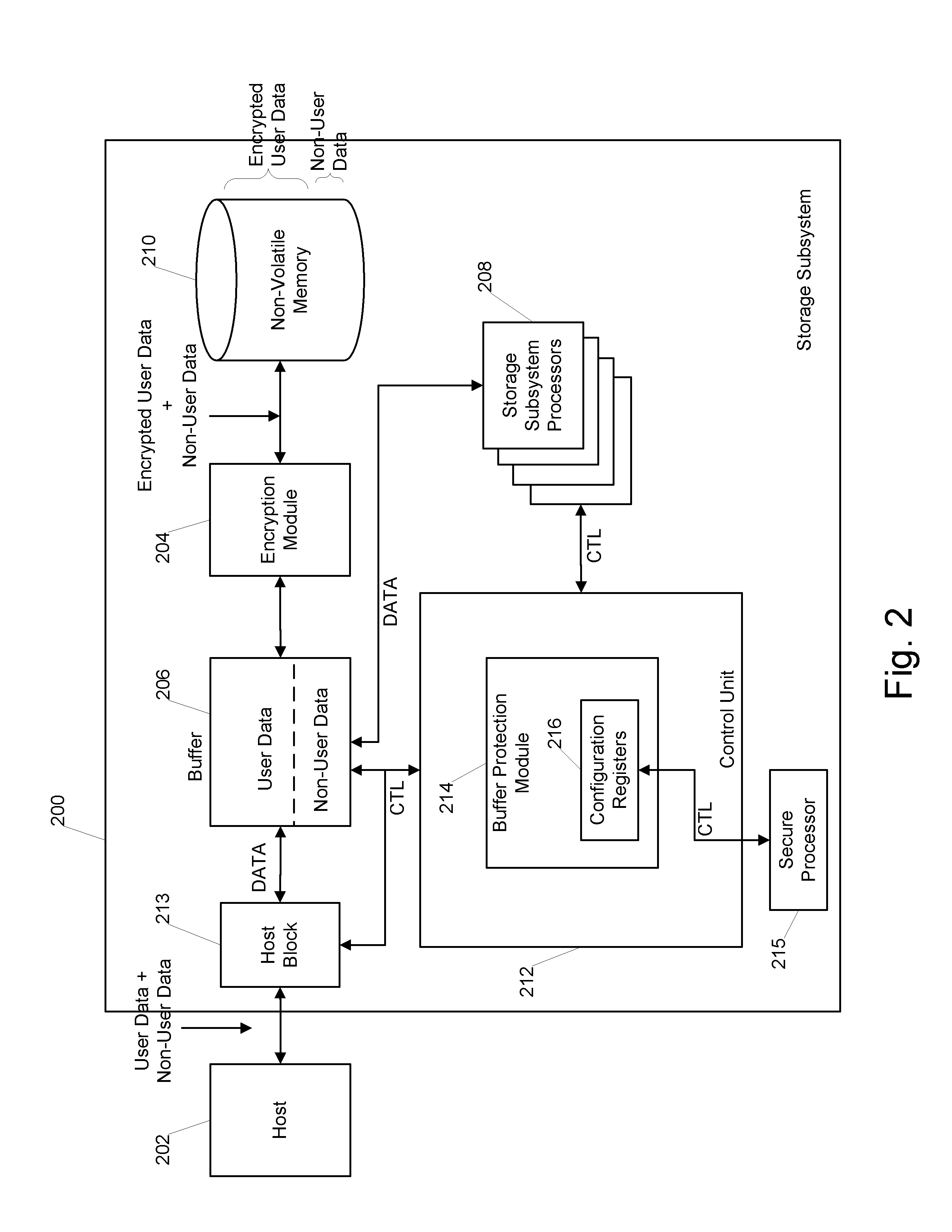
Buffer memory protection unit
ActiveUS9305142B1Unauthorized memory use protectionDigital data protectionOperating systemMemory protection unit
Owner:WESTERN DIGITAL TECH INC
Memory protection unit (MPU) having a shared portion and method of operation
In a disclosed embodiment, a data processing system comprises a memory protection unit (MPU); and a plurality of region descriptors associated with the MPU. Each region descriptor is associated with one of multiple subsets of the region descriptors and includes an address range, protection settings, and attributes for a respective region of memory. The subsets include data-only region descriptors, instruction-only region descriptors, and shared region descriptors. The shared region descriptors are used to access memory regions for data and instruction memory requests.
Owner:NXP USA INC
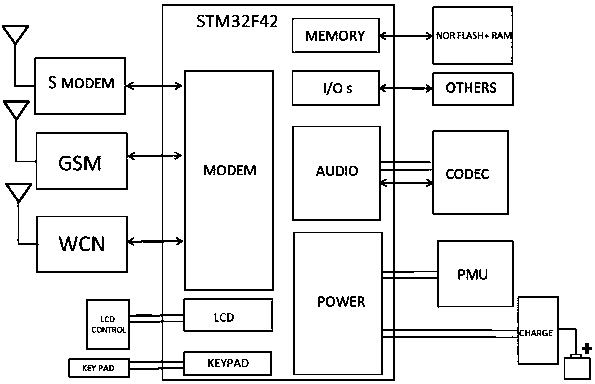
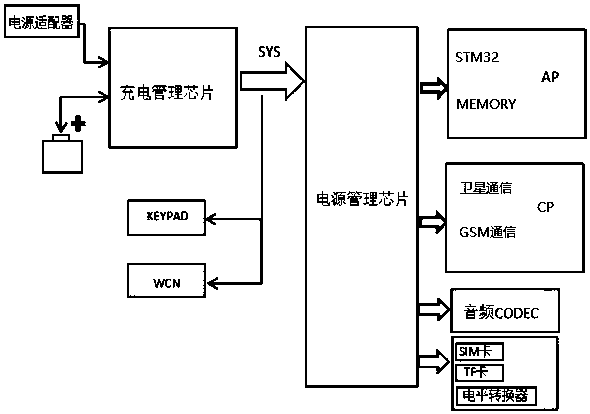
Mobile phone satellite communication method based on STM32 platform
ActiveCN108200230AImprove securityEasy to switchRadio transmissionTelephone set constructionsDigital signal processingSTM32
The invention relates to a mobile phone satellite communication method based on an STM32 platform. An STM32F427 chip platform design is adopted, and an STM32F427 chip terminal body integrates a storage system, a power supply network, an audio system, a core module, a BT / WIFI module, a key module, an LCD module, an SIM card module and a level conversion module, which are in communication connectionwith each other; by adoption of the mobile phone satellite communication method, a complete set of digital signal processing instructions (DSP) and memory protection unit (MPU) is achieved, and the security of a mobile phone satellite communication application is improved; and a handheld terminal system based on the STM32 platform realizes the mobile phone communication function and supports thefree switching of the satellite communication mode and the traditional GSM mobile communication module.
Owner:CHENGDU FOURIER ELECTRONICS TECH +2
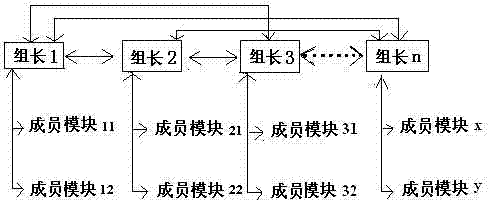
A Reconfigurable Feeder Termination System
InactiveCN102270881AEasy and flexible operationShorten the timeCircuit arrangementsGroup controllerCommunication unit
The invention discloses a reconfigurable feeder terminal system, which includes a plurality of identical feeder modules, each feeder module correspondingly controls a circuit breaker; a plurality of feeder modules are grouped according to different line sections, and each group includes a group leader feeder module and multiple member feeder modules; in each group, any feeder module can be used as the group leader feeder module; the group leader feeder module receives the feeder information of each member feeder module in the group; the group leader feeder module of multiple groups Each feeder module includes a control unit, a real-time measurement unit connected to the control unit, a storage unit including a protection limit storage part, a logic operation unit including a load calculation part, and a communication unit. The present invention uses the control mode of the team leader management system to control the circuit breaker on the line section according to the real-time measurement parameters, and realizes the automatic reconstruction of the distribution network system while rapidly isolating the fault, shortening the recovery time of the line in the non-fault section. time.
Owner:NANJING INTELLIGENT DISTRIBUTION AUTOMATION EQUIP
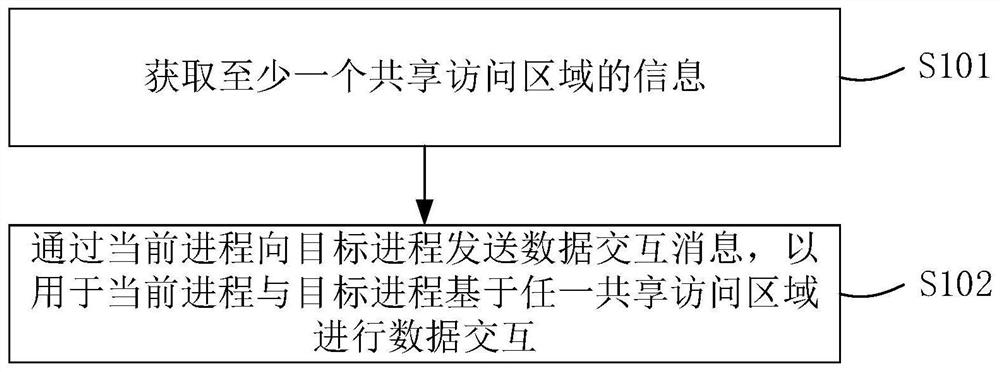
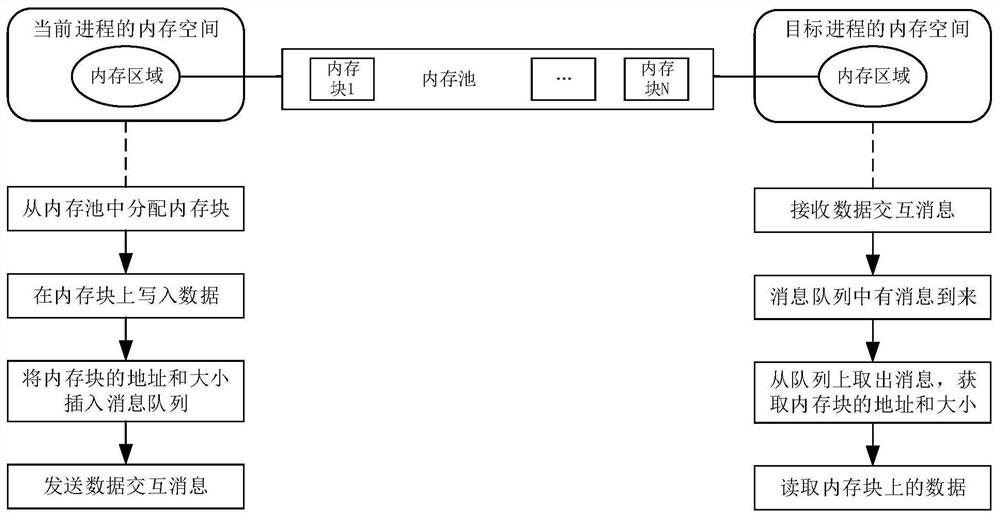
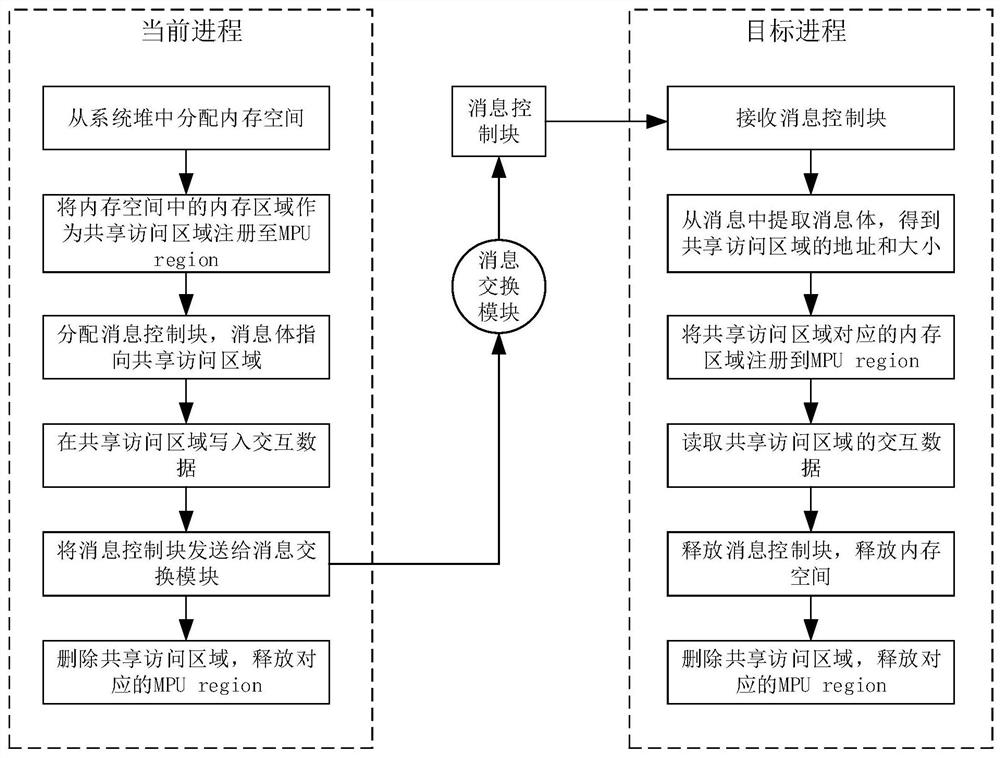
Inter-process communication method and device, electronic equipment and computer readable storage medium
PendingCN112256460AEnable secure communicationInterprogram communicationComputer hardwareSecure communication
The embodiment of the invention provides an inter-process communication method, a device, electronic equipment and a computer readable storage medium, and relates to the field of process communication. The method comprises the steps that information of at least one shared access area is acquired, a data interaction message is sent to a target process through a current process, and the data interaction message at least comprises information of all the shared access areas so that the current process and the target process can conduct data interaction based on any shared access area. According tothe method, the information of at least one shared access area pre-registered to the memory protection unit is acquired, and the data interaction message containing the information of the shared access area is sent to the target process, so that at least two processes perform data interaction by accessing the registered memory space; therefore, the process except the interactive process cannot access the shared access area, and safe communication between the processes is realized.
Owner:BEIJING YUANXIN SCI & TECH
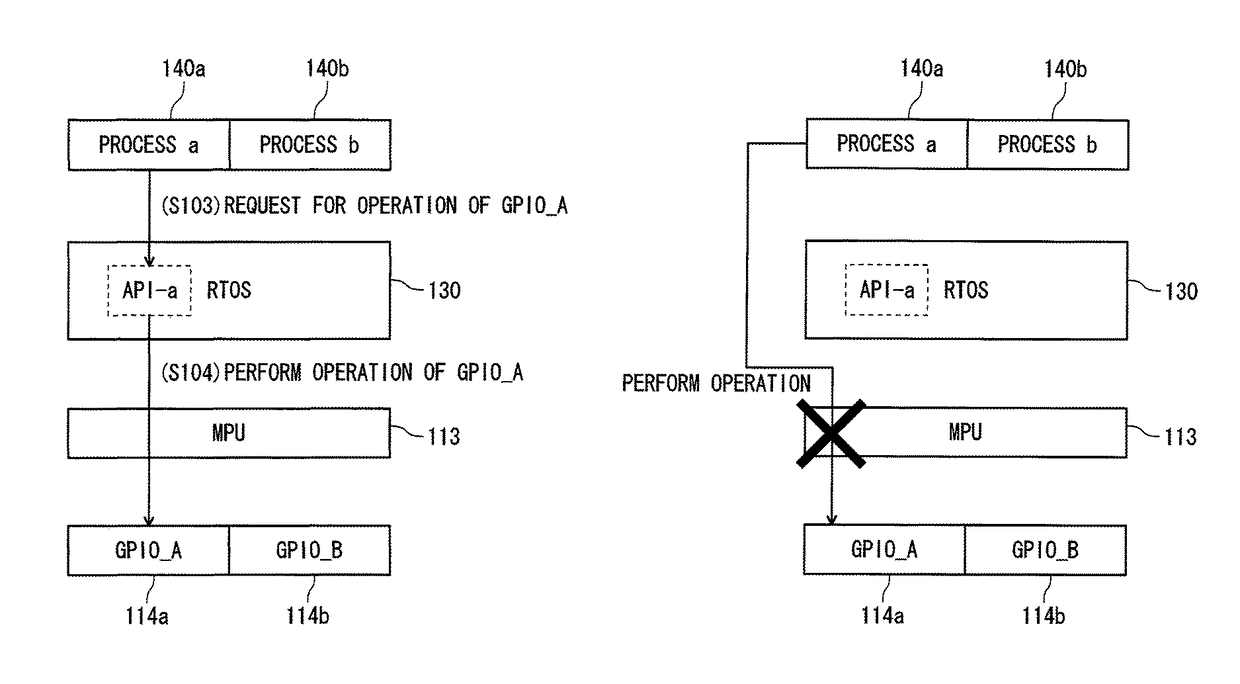
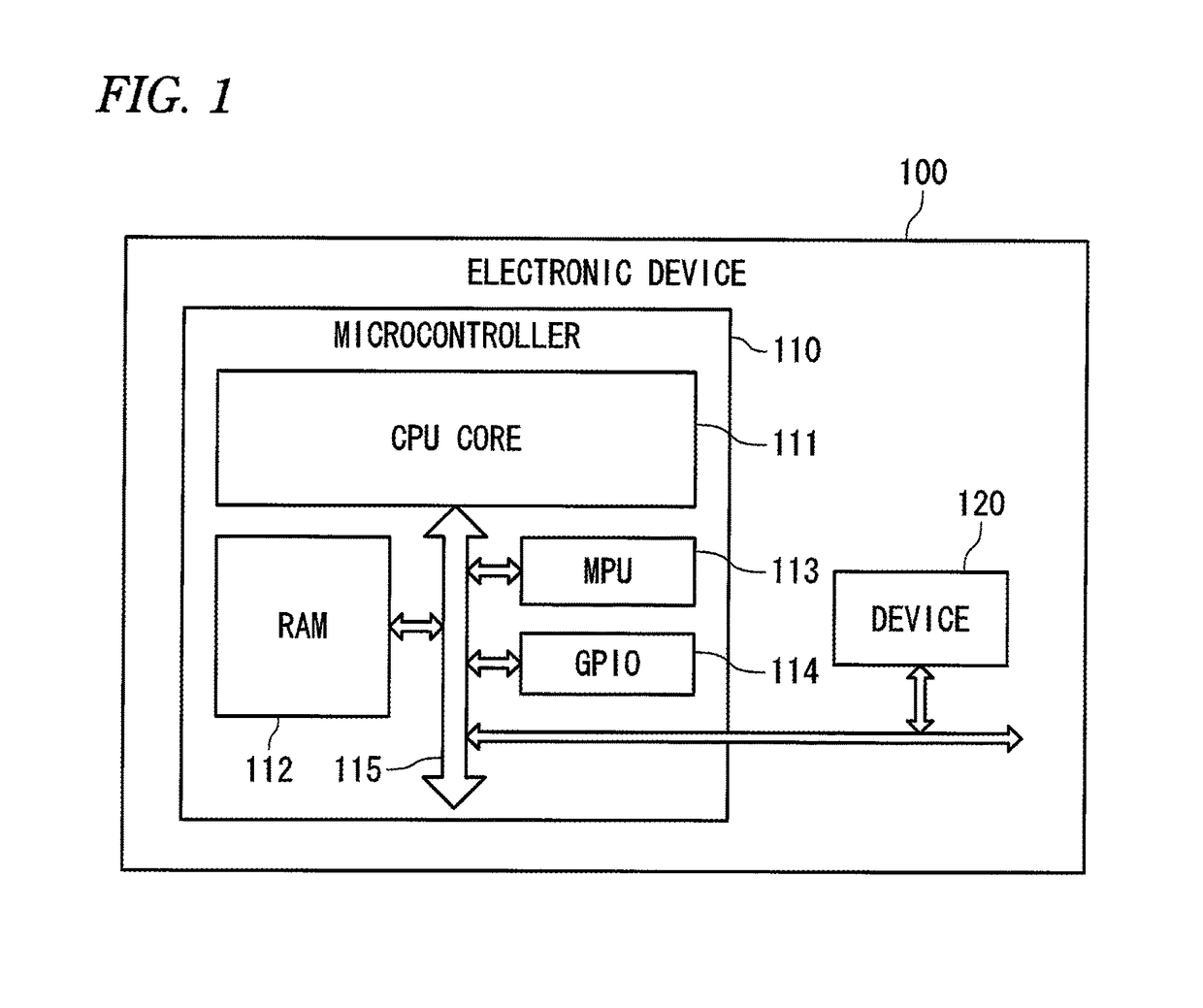
Electronic device, operating system and access control method for protection of a register through an application programming interface
ActiveUS9898420B2Increase freedomUnauthorized memory use protectionPlatform integrity maintainanceApplication programming interfaceProcessor register
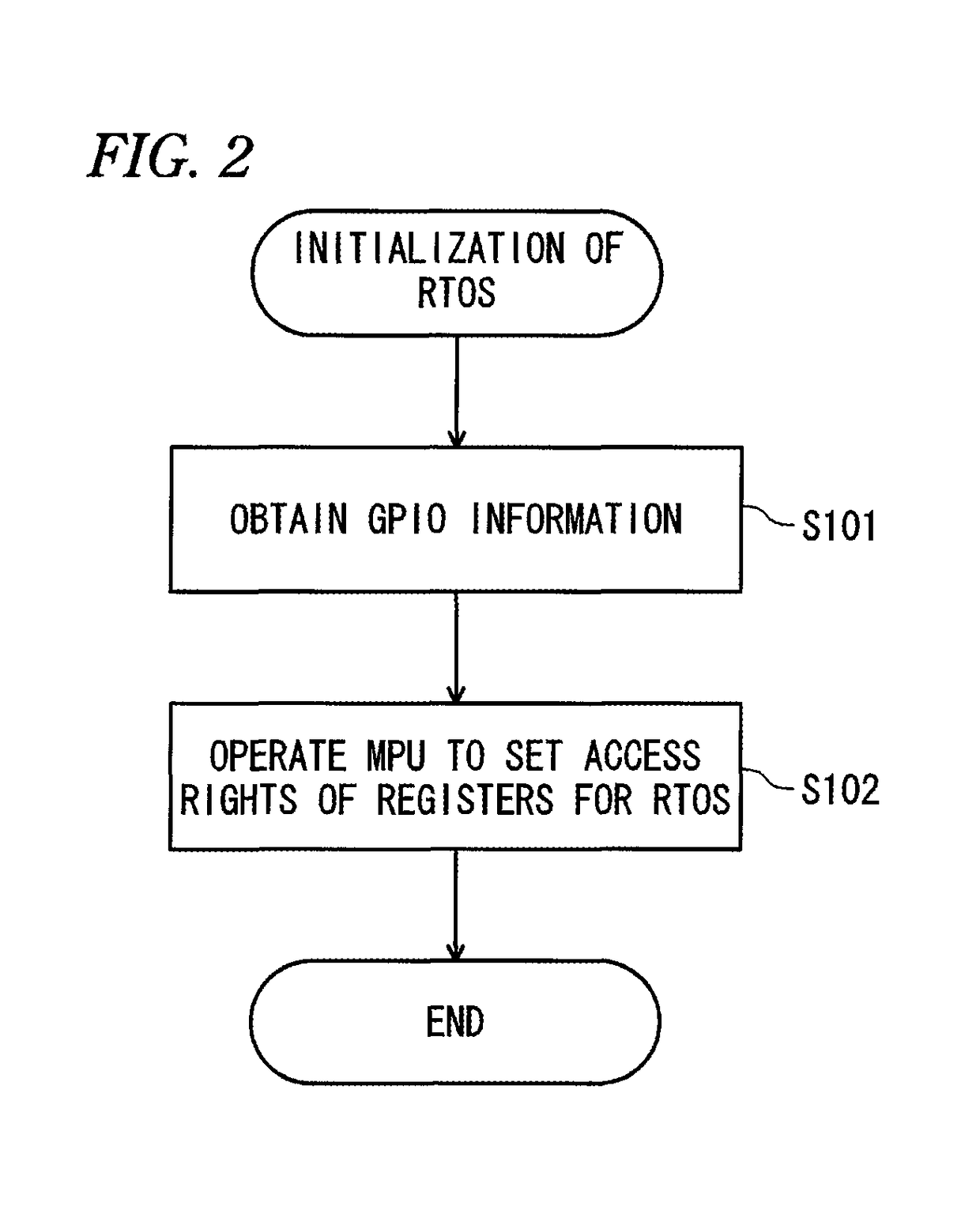
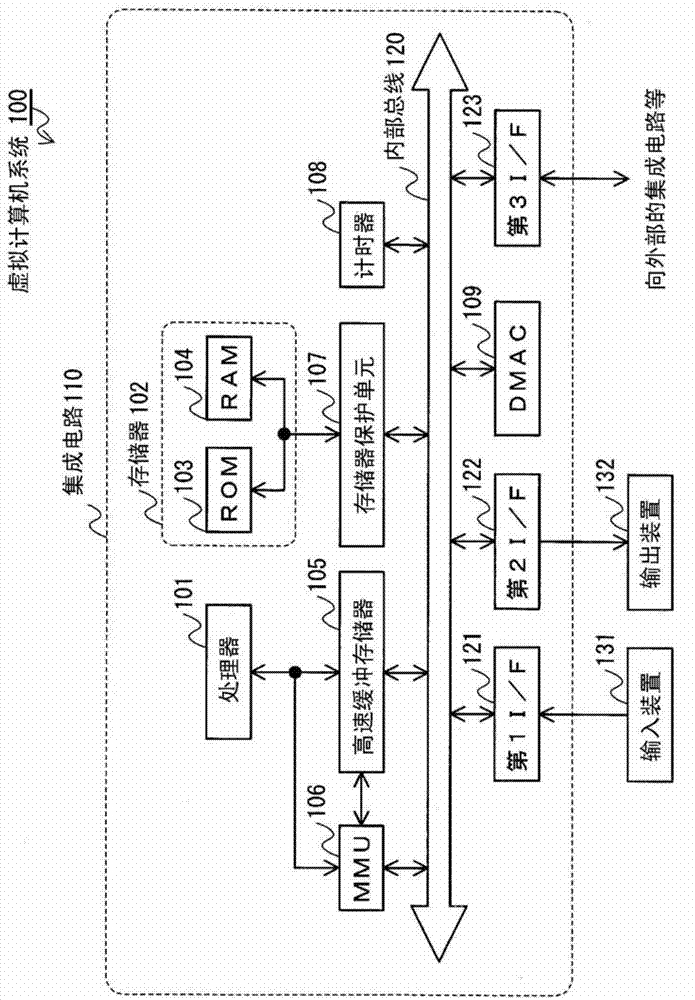
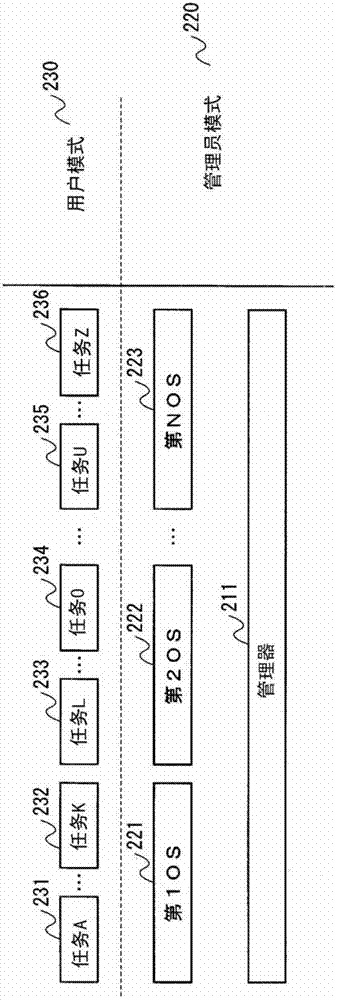
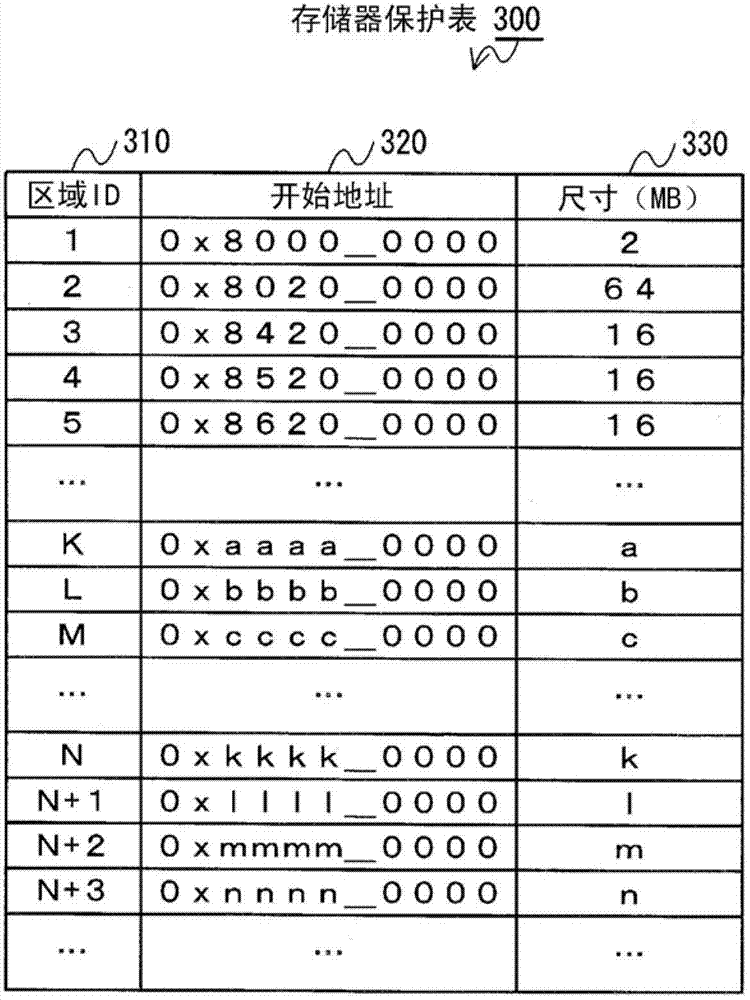
An electronic device includes a memory protection unit configured to protect an access to a register of a device arranged in an address space. An operating system sets an access right to the register by using the memory protection unit. A process requests the operating system to operate the device when the process operates the device, and the operating system makes an access to the corresponding register in accordance with the request for the operation to operate the device.
Owner:YOKOGAWA ELECTRIC CORP
Virtual computer system, virtual computer control method, virtual computer control program, and semiconductor integrated circuit
ActiveCN102859502AAvoid attackPrevent theftMemory architecture accessing/allocationResource allocationVirtual computingMemory protection unit
This invention is provided with a memory protection unit for controlling access to a memory region from virtual computers. The memory protection unit and a hypervisor executed by a processor operate in coordination with each other, whereby access to a memory storage region is controlled for the virtual computers so that access to a predetermined region is prohibited in a corresponding manner. Each of the virtual computers is thereby prevented from accessing programs, data, and other information recorded in the region to which access is prohibited.
Owner:SUN PATENT TRUST
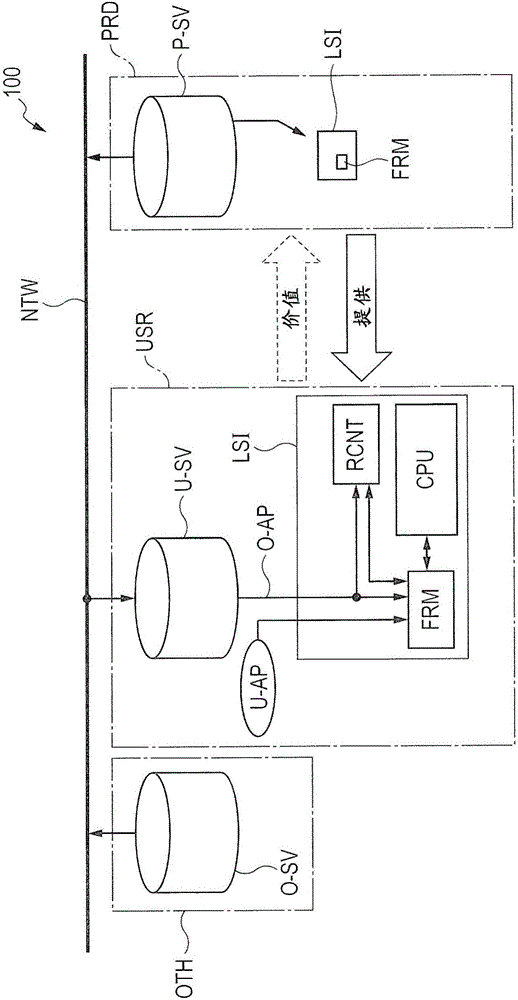
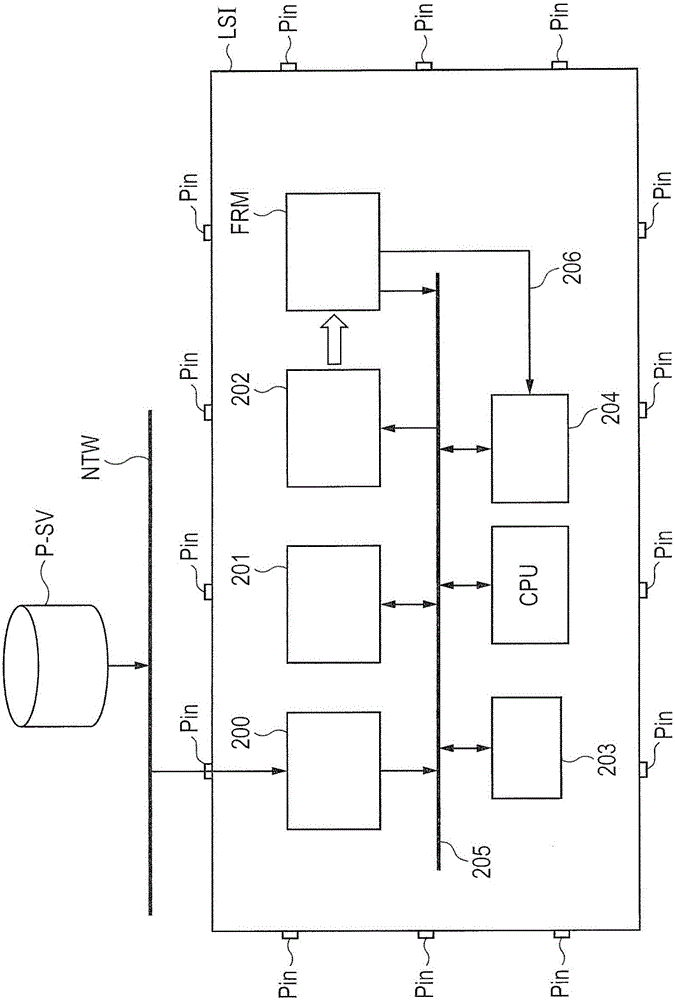
Semiconductor device
ActiveCN106529300AArbitrary operationMemory architecture accessing/allocationInternal/peripheral component protectionDevice materialBranch
A semiconductor device capable of arbitrarily operating a microprocessor while protecting a secure program is provided. The semiconductor device includes a memory equipped with a first program area in which an arbitrary program is stored, and a second program area in which a secure program is stored, a microprocessor which outputs an address designating an instruction in a program, and a memory protection unit which controls access to the memory based on the address outputted from the microprocessor. When the address outputted from the microprocessor by executing the program in the first program area designates a branch allowable area in the second program area, the memory protection unit permits access to the memory. When the address designates a branch prohibition area, the memory protection unit inhibits access to the memory.
Owner:RENESAS ELECTRONICS CORP
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com