BMP-2 variants with improved properties
a technology of bmp-2 and variants, which is applied in the direction of osteogenic factors, peptide/protein ingredients, drug compositions, etc., can solve the problems of limiting the development and use of bmp therapeutics, hampering development and production, and poor bmp expression yields, etc., to achieve improved expression yield, increase solubility, and improve the effect of properties
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Structural Modeling
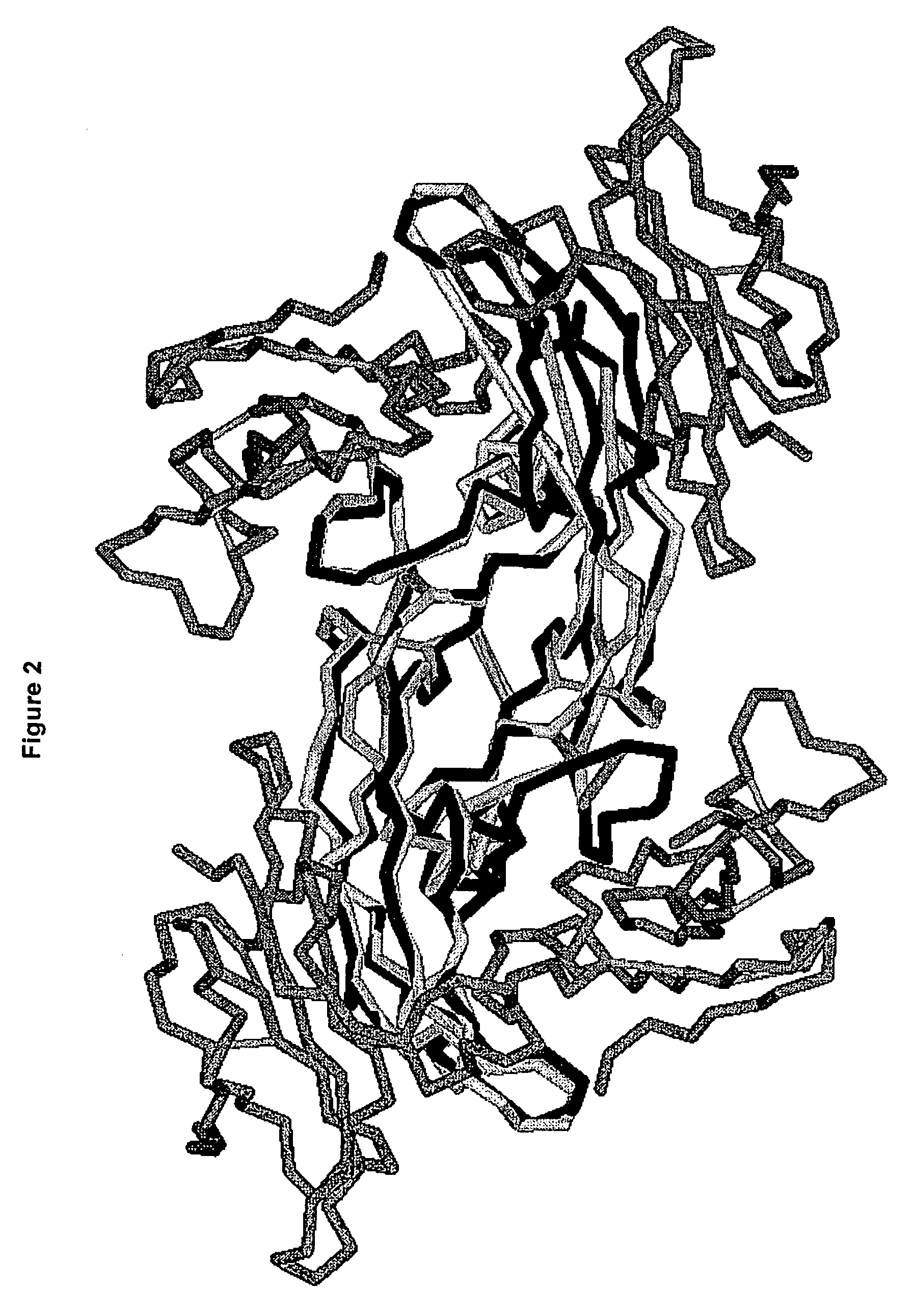
[0165] Hexameric complexes comprising a BMP-7 dimer or a BMP-2 dimer bound to two ALK-3 receptors and two ActRIIa receptors was constructed using the structure of BMP-7 bound to ActRIIa (PDB code 1LX5) and the structure of BMP-2 bound to ALK-3 (PDB code 1ES7). Using InsightII (Accelrys), the BMP structures were superimposed as follows: BMP-2 residues 22-32 superimposed with BMP-7 residues 47-56, BMP-2 residues 49-71 superimposed with BMP-7 residues 73-95, and BMP-2 residues 101-106 superimposed with BMP-7 residues 126-131. This yielded a backbone atom RMSD of 0.77 Å. The superposition was repeated so that chain A in the BMP-7 structure was superimposed onto chains A and C of the BMP-2 structure. The sequence alignment between BMP-2 and BMP-7 is shown in FIG. 3 and the structure of the hexameric complex is shown in FIG. 2.
[0166] Homology modeling was used to generate structures of additional BMP receptors bound to BMP-2 and BMP-7. As shown in FIG. 5, the sequence...
example 2
Identification of Exposed Hydrophobic Residues in BMPs
[0167] Structures of BMP-7 dimer (“dimer”) and BMP-7 dimer bound to ALK-3 and ActRIIa “hexamer”) were analyzed to identify solvent-exposed hydrophobic residues. The absolute and fractional solvent-exposed hydrophobic surface area of each residue was calculated using the method of Lee and Richards (J. Mol. Biol. 55: 379-400 (1971)) using an add-on radius of 1.4 Å (Angstroms). Each residue was also classified as core, boundary, or surface (see Dahiyat and Mayo Science 278: 82-87 (1997)).
[0168] Solvent exposed hydrophobic residues in BMP-7 were defined to be hydrophobic residues with at least 50 Å2 (square Angstroms) exposed hydrophobic surface area in the BMP-7 dimer (PDB code 1LX5, chain A, plus symmetry-related BMP-7 molecule). Exposed hydrophobic surface area was also measured in the context of the BMP-7 / ALK-2 / ActRIIa hexamer and RESCLASS was run to categorize each position as core, boundary, or surface.
TABLE 1Exposed hydrop...
example 3
Identification of Receptor and Inhibitor Interface Residues in BMP-7
[0169] Potential sites of interactions between BMP-7 and ALK-3, BMP-7 and ActRIIa, and BMP-7 and noggin were identified by examining the structure of the hexameric structure described in Example 1 and the co-crystal structure of BMP-7 and noggin (PDB code 1M4U). Next, distance measurements were used to identify residues that may participate in intermolecular interactions. Residues in BMP-7 that are within 5 Å (Angstroms) of the ALK-3, ActRIIa, or noggin interfaces (as measured by CA-CA distances) are shown below, along with the receptor or inhibitor positions that are contacted. Next, the receptor sequence alignments used for homology modeling were analyzed for polymorphisms. Information about receptor polymorphisms was used to design receptor-specific variants, described below. If the receptor positions are polymorphic, it is noted in Table 2; “na” indicates that the receptor positions were not sufficiently well-a...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| wavelength | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com