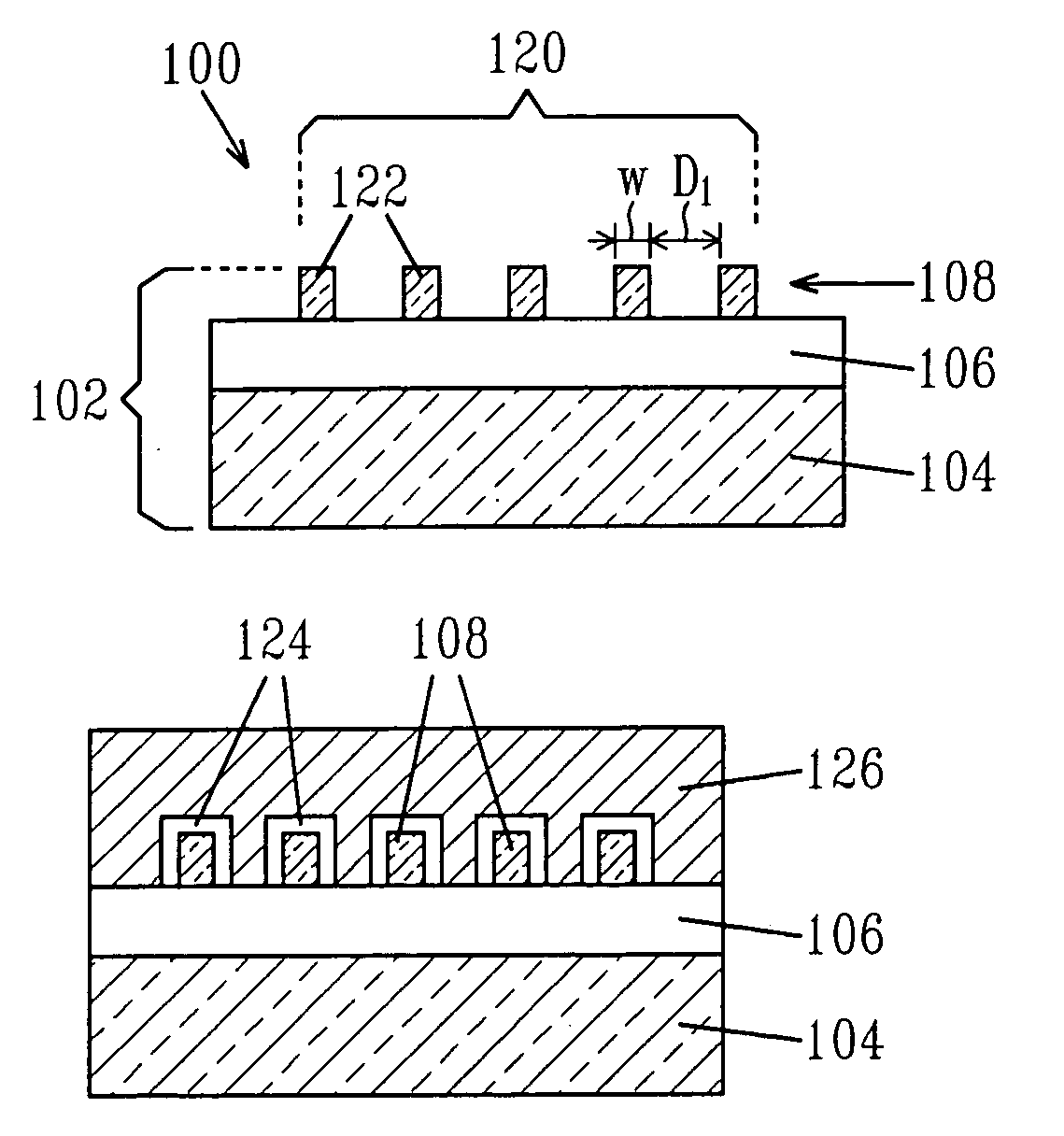
Field effect transistor device including an array of channel elements and methods for forming
a field effect transistor and array technology, applied in the field of semiconductor devices, can solve the problems of inability to achieve the same packing density limitations as previously described, and achieve the effect of optimal device structure and better control of element dimensions
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
[0079] Method 1 (Embodiment 1): This method utilizes an asymmetric A-B diblock copolymer in which block A is present as the majority component and block B is present in lesser amounts than block A. In these examples, the polymer block B is one which can be preferentially removed from the film, e.g., by exposure to UV radiation and immersion in a chemical solvent, or by exposure to ozone. When a polymer of this composition is applied to a surface containing a lithographically defined topography (FIG. 9A), a resulting line / space pattern forms in which half-cylinders of block B are embedded in a matrix of block A. The resulting pattern self aligns with the preexisting topography. Removal of block B leaves the lithographically-defined line subdivided into periods of the underlying block A matrix. This is illustrated in FIG. 9B.
embodiment 2
[0080] Method 2 (Embodiment 2): This method utilizes an asymmetric A-B diblock copolymer in which block A is present as the minority component and block B is present in a greater amount. In these examples, the polymer block B is one which can be preferentially removed from the film, e.g., by exposure to UV radiation and immersion in a chemical solvent, or by exposure to ozone. When a polymer of this composition is applied to a surface containing a lithographically defined topography (FIG. 10A), a resulting line / space pattern forms in which half-cylinders of block A are embedded in a matrix of block B. The resulting pattern self aligns with the preexisting topography. Removal of block B leaves the lithographically-defined line subdivided into periods of the underlying block A matrix. This is illustrated in FIG. 10B.
embodiment 3
[0081] Method 3 (Embodiment 3): Symmetric A-B diblock copolymer is used and is applied within an opening as discussed above. In this example, blocks A and B have substantially the same weight % in the total block copolymer and block B is a block which can be preferentially removed from the polymer film, e.g., by exposure to UV radiation and immersion in a chemical solvent, or by exposure to ozone. When a polymer of this composition is applied to a surface containing a lithographically defined topography (FIG. 11A), a resulting line / space pattern forms in which lines / spaces of block A are embedded in a matrix of block B. The resulting pattern self aligns with the preexisting topography. Removal of block B leaves the lithographically-defined line subdivided into periods of the underlying block A matrix. This is illustrated in FIG. 11 B.
[0082] After the array pattern is formed in the diblock copolymer material using any of the three above-described methods, it can be used to template t...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com