System to establish trust between policy systems and users
a technology of policy systems and users, applied in the field of policy-based computing systems, can solve the problems of insufficient trust between users and policy systems, insufficient traditional approaches to the implementation of policy-based systems, and complex requirements, and achieve the effect of increasing the trust of users
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
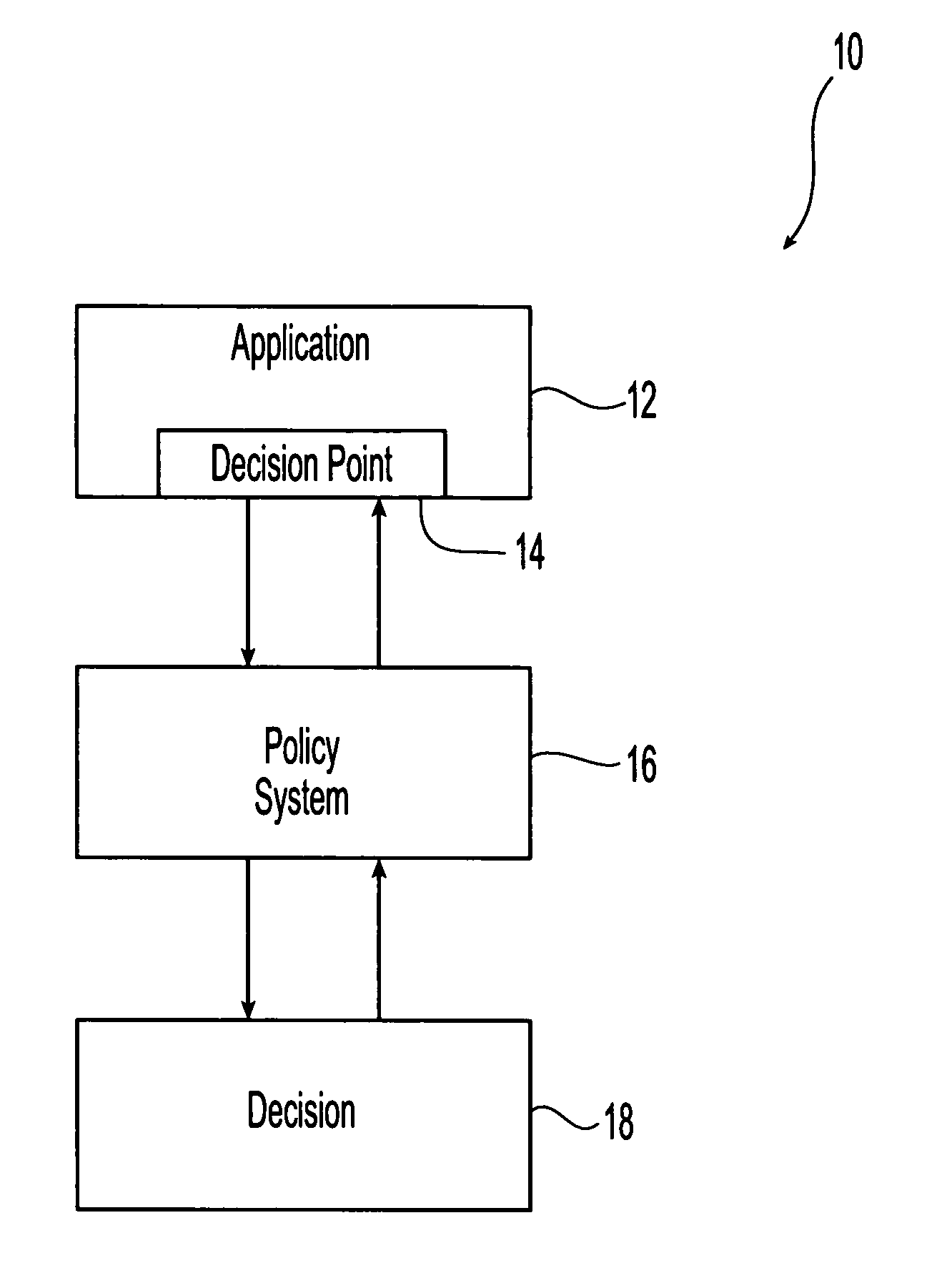
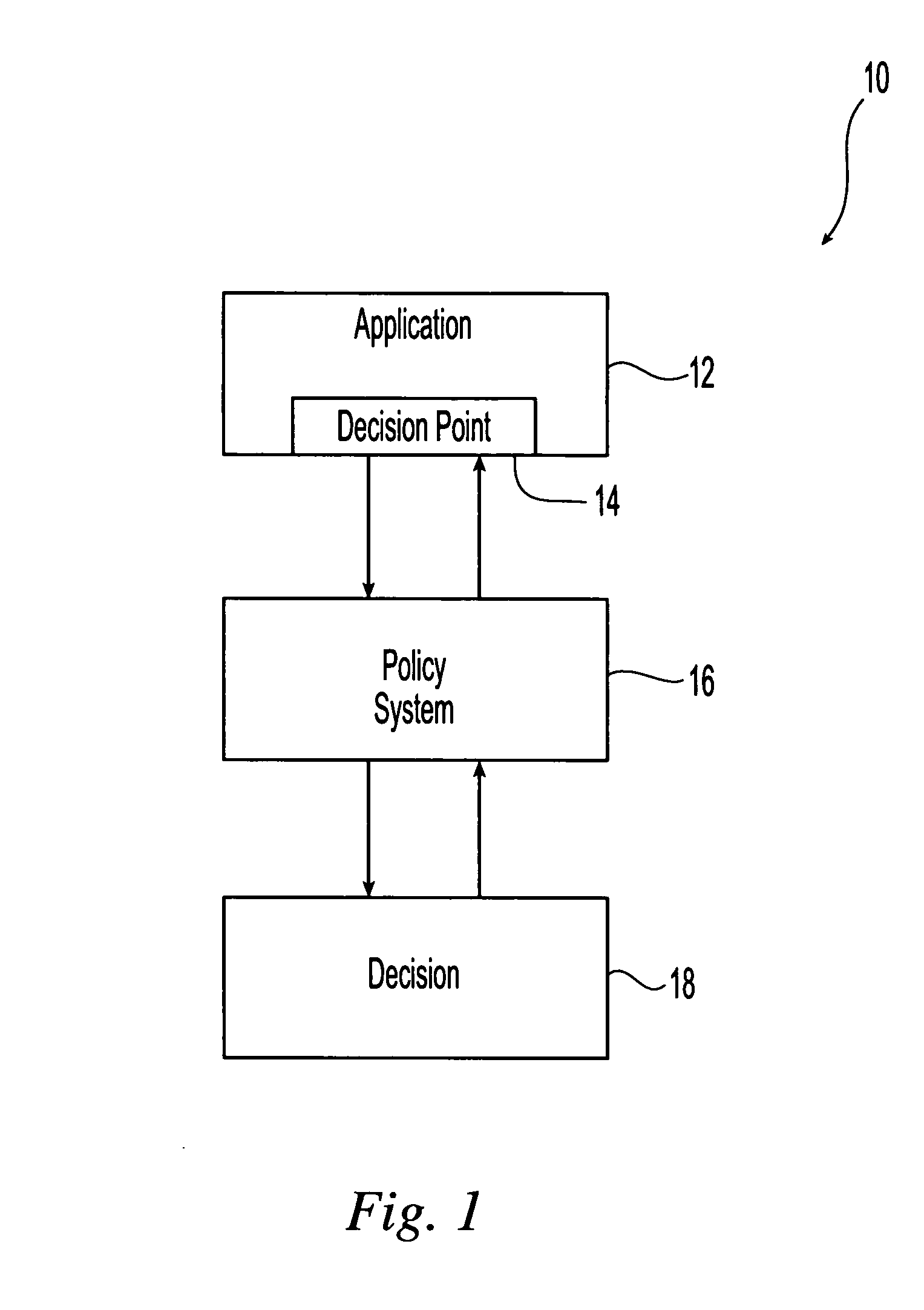
[0016] Referring initially to FIG. 1, an exemplary embodiment of a policy or policy-based system for use with trust building tools 10 in accordance with the present invention is illustrated. As illustrated an application 12 is interfaced with a policy implementation and enforcement system 16 that provides for the automated implementation of rules and policies to control or to modify the application. The policy system monitors decision points 14 within the application and uses these decision points to develop decisions 18 regarding actions to be taken within the application to implement pre-determined and user-inputted policies contained within the policy system. A user or system administrator is responsible for the operation of the application. However, implementation of the actions decided upon by the policy system affect the operation of the application, and the policy system is constructed to operate autonomously and without the need for user input or oversight. Therefore, the re...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com