Methods for writing non-volatile memories for increased endurance
a non-volatile memory and endurance technology, applied in the field of mass digital data storage systems, can solve the problems of affecting the life of memory cells, affecting the longevity and being subjected to full amount of wear, so as to prolong the lifetime of memory storing such frequently updated data and wear memory cells more quickly
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
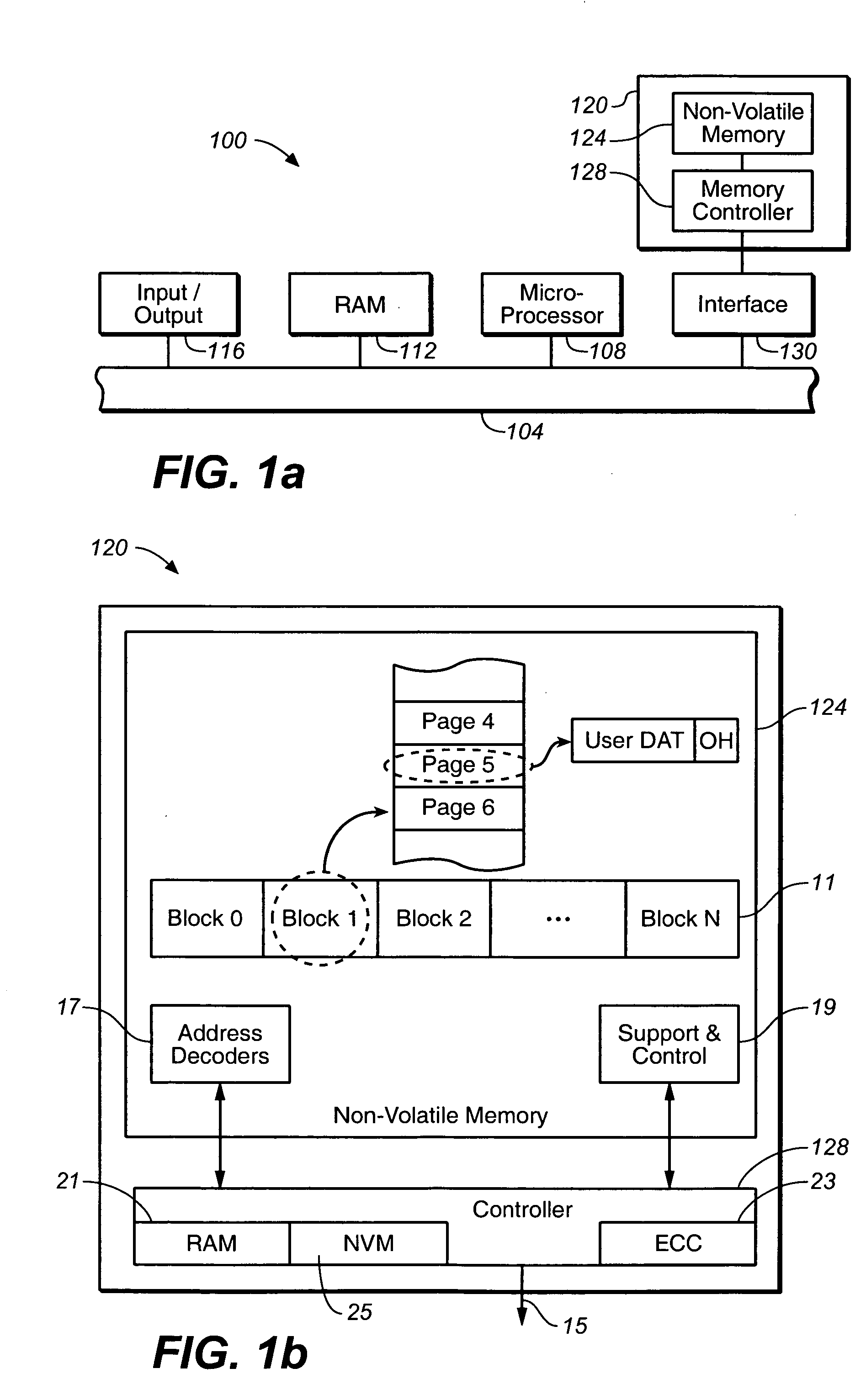
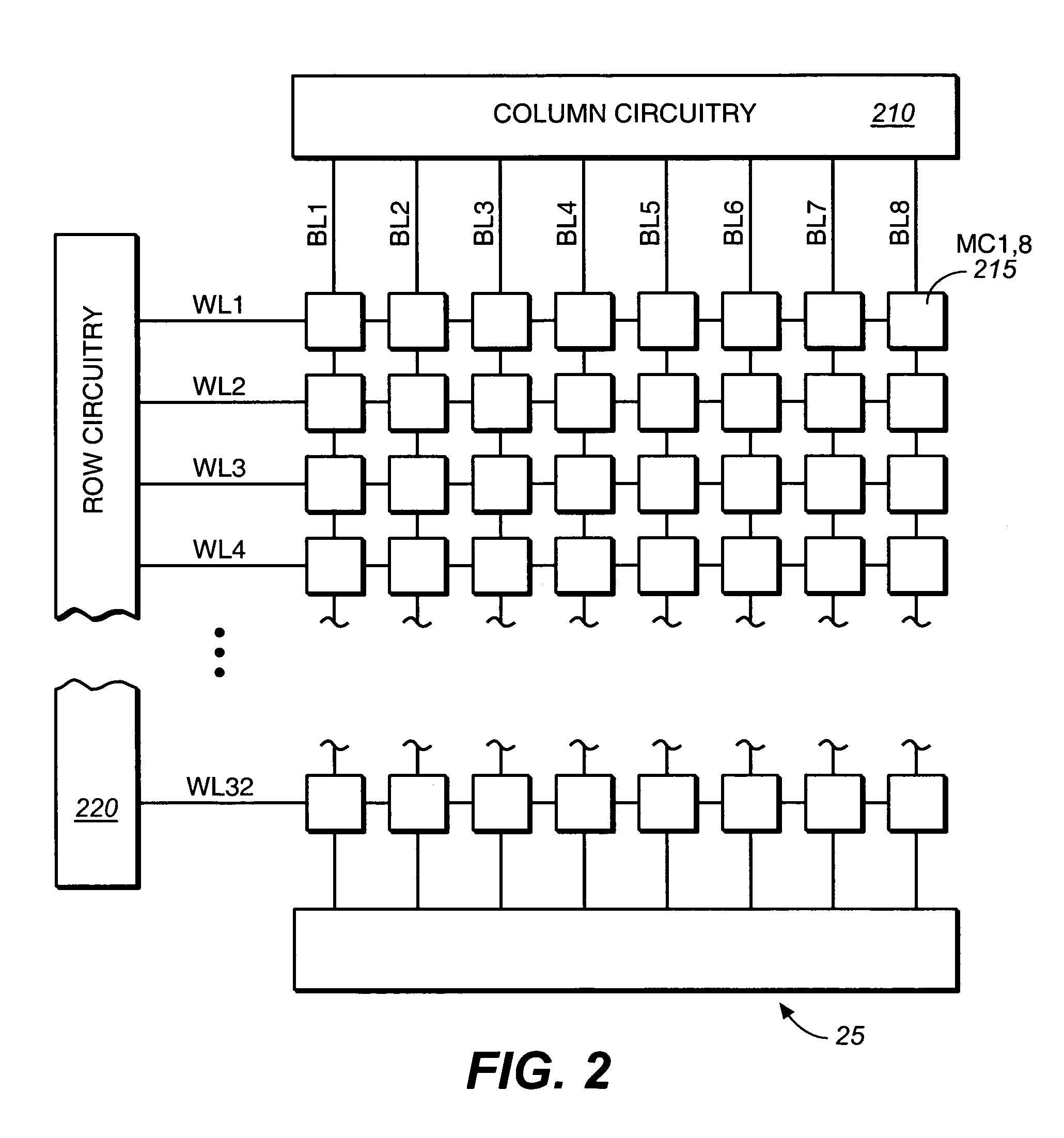
A. Memory Organization and Basic Definitions
[0017] The present inventions are related to increasing endurance in memory systems that are capable of deteriorating in performance over time as the number of erase and write cycles increases. While the embodiments described herein describe non-volatile EEPROM-based memory systems, the various aspects of the present inventions are applicable to any type of storage medium susceptible to“wear”. For example, an emerging type of non-volatile memory technology is phase-change memory. Information is stored by changing the phase of a given material. A number of other examples of such systems are given in U.S. patent application Ser. No. 10 / 841,379. Such systems also may be prone to“wear”, where the storage medium is less capable of storing information as the number of times the medium has been cycled increases. The present inventions can be readily applied to such technologies.
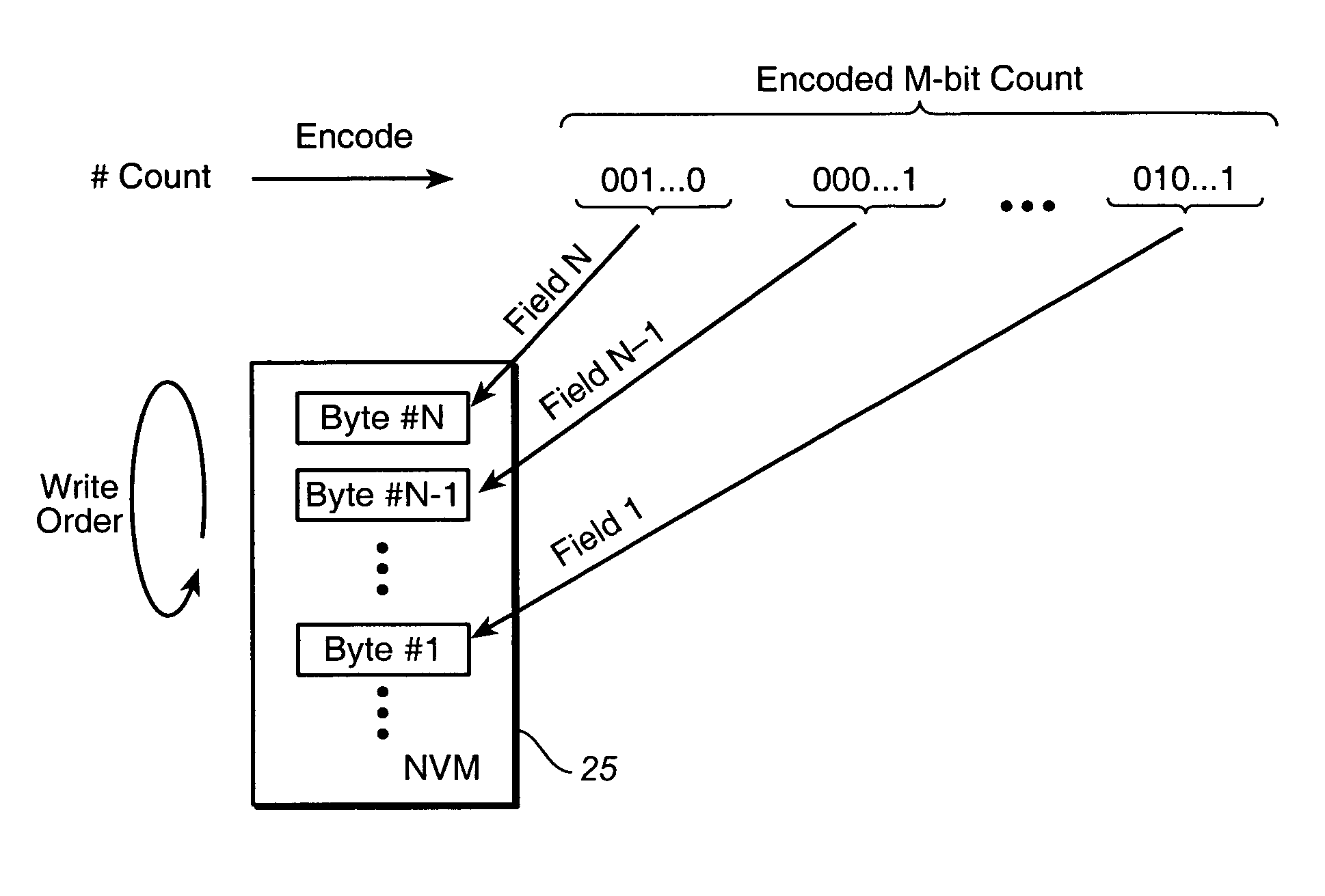
[0018] In one embodiment, non-volatile memory storage cells within f...
PUM
 Login to view more
Login to view more Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to view more
Login to view more - R&D Engineer
- R&D Manager
- IP Professional
- Industry Leading Data Capabilities
- Powerful AI technology
- Patent DNA Extraction
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic.
© 2024 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap