Blends of lubricant basestocks with polyol esters
a technology of lubricant basestocks and esters, applied in the direction of base materials, lubricant compositions, additives, etc., can solve the problem that the arrhenius equation is not applicable to the case of associated solutions such as methanol and water
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
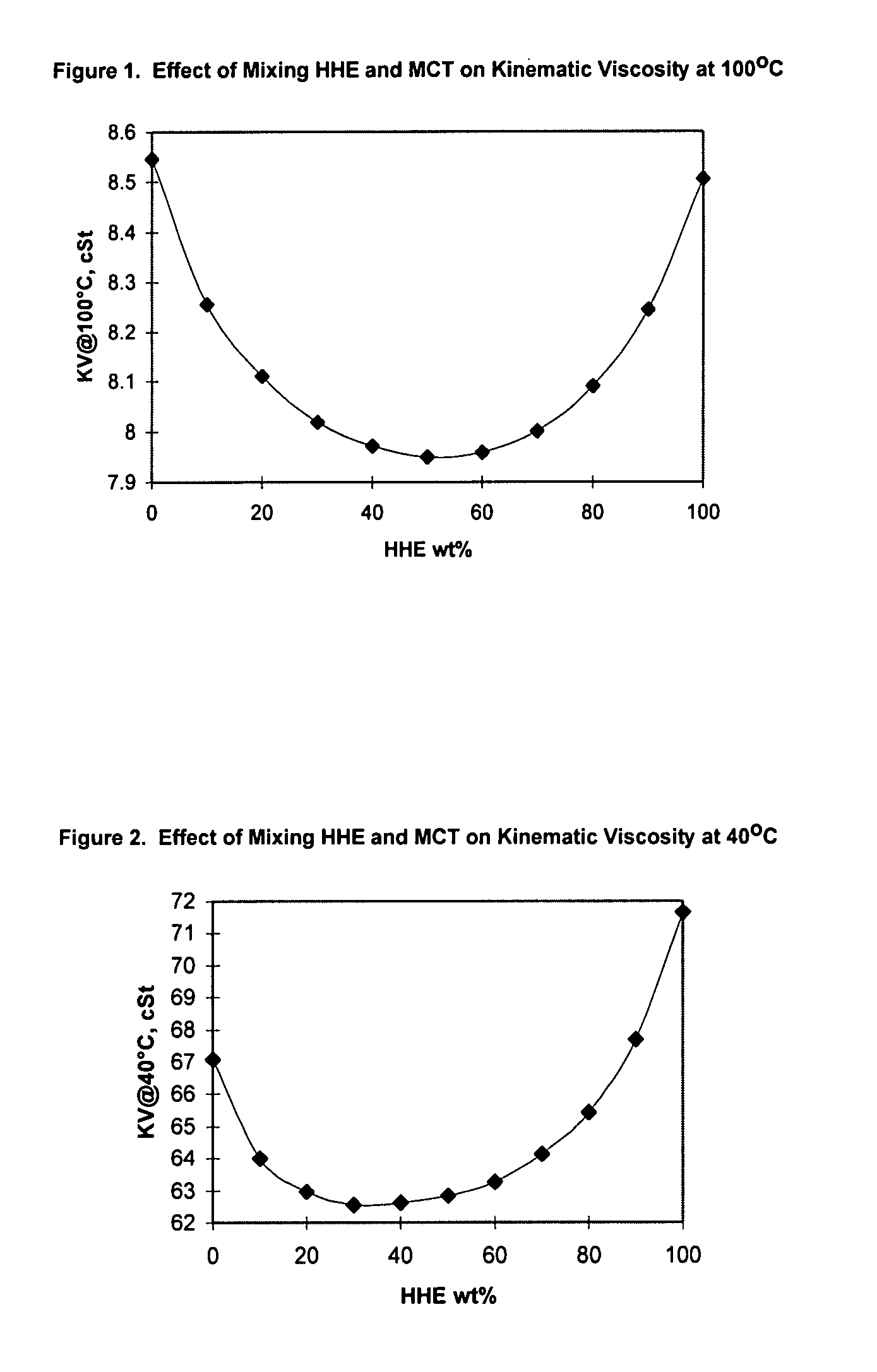
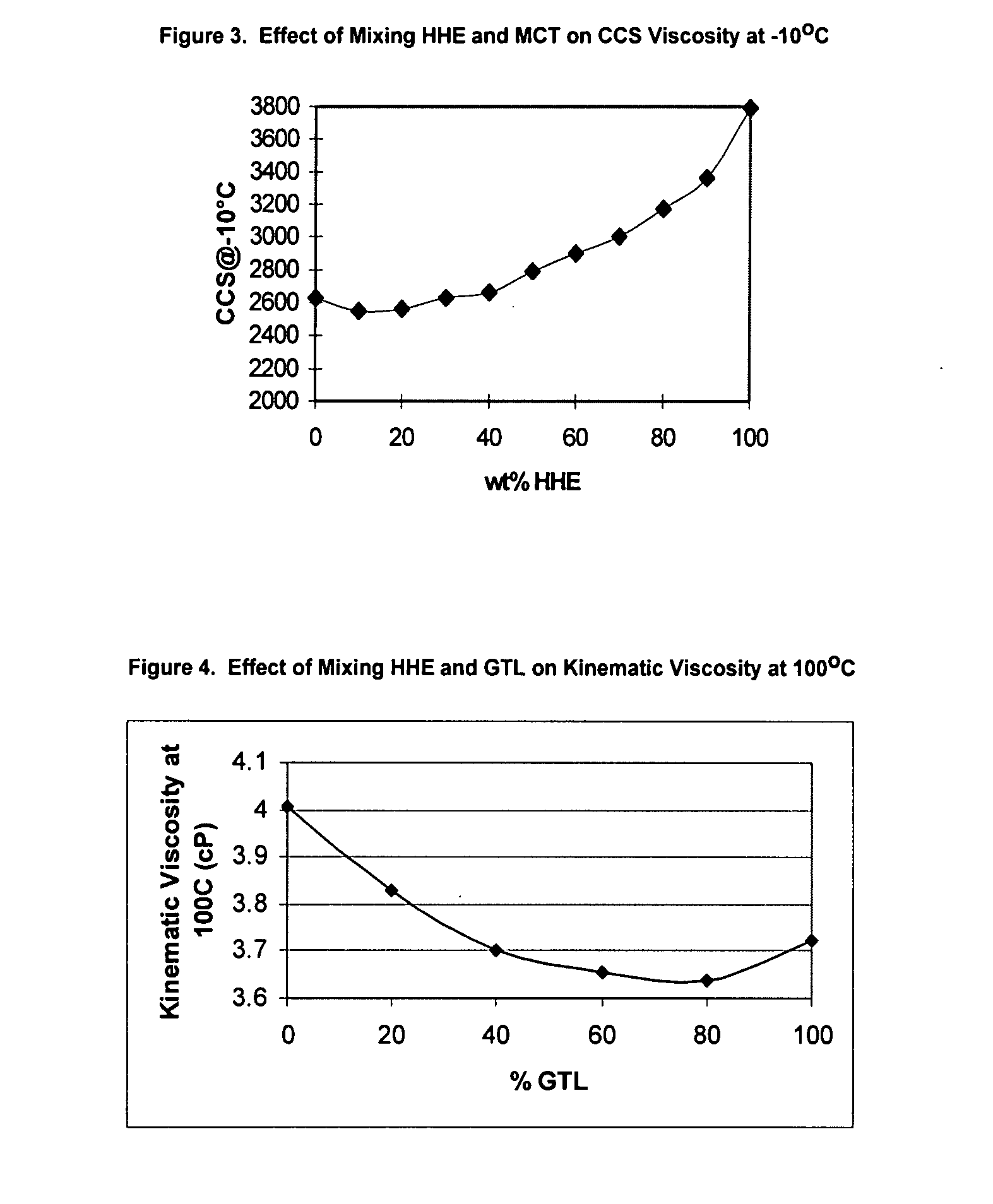
[0074]In this example a series of lubricating compositions were prepared from a polyol ester and a mixture of mineral oils. The polyol ester was a high hydroxyl ester (HHE) obtained from Exxon Chemical Co., Houston, Tex. and had about 1 hydroxyl group per molecule (corresponding to approximately 105 mg KOH / gram). The mineral oil was a mixture of MCT 10 and MCT 30, sold by Imperial Oil Co., Calgary, Canada, and the ratio was adjusted to give a similar viscosity to the HHE ester. The kinematic viscosity of the ester at 100° C. was 8.506 cSt and the kinematic viscosity at 100° C. of the MCT mixture was 8.547 cSt. The kinematic viscosity of the mixtures were determined at 100° C. and at 40° C. The results are presented in FIGS. 1 and 2. The Cold Cranking Simulator (CCS) viscosity at −10° C. was also determined (ASTM Test D5293), and the results are presented in FIG. 3. The data are also shown in Table 1.
TABLE 1Kinematic Viscosity and CCS Viscosity Data of HHE and MCT BlendsMCTHHEkV @kV ...
example 2
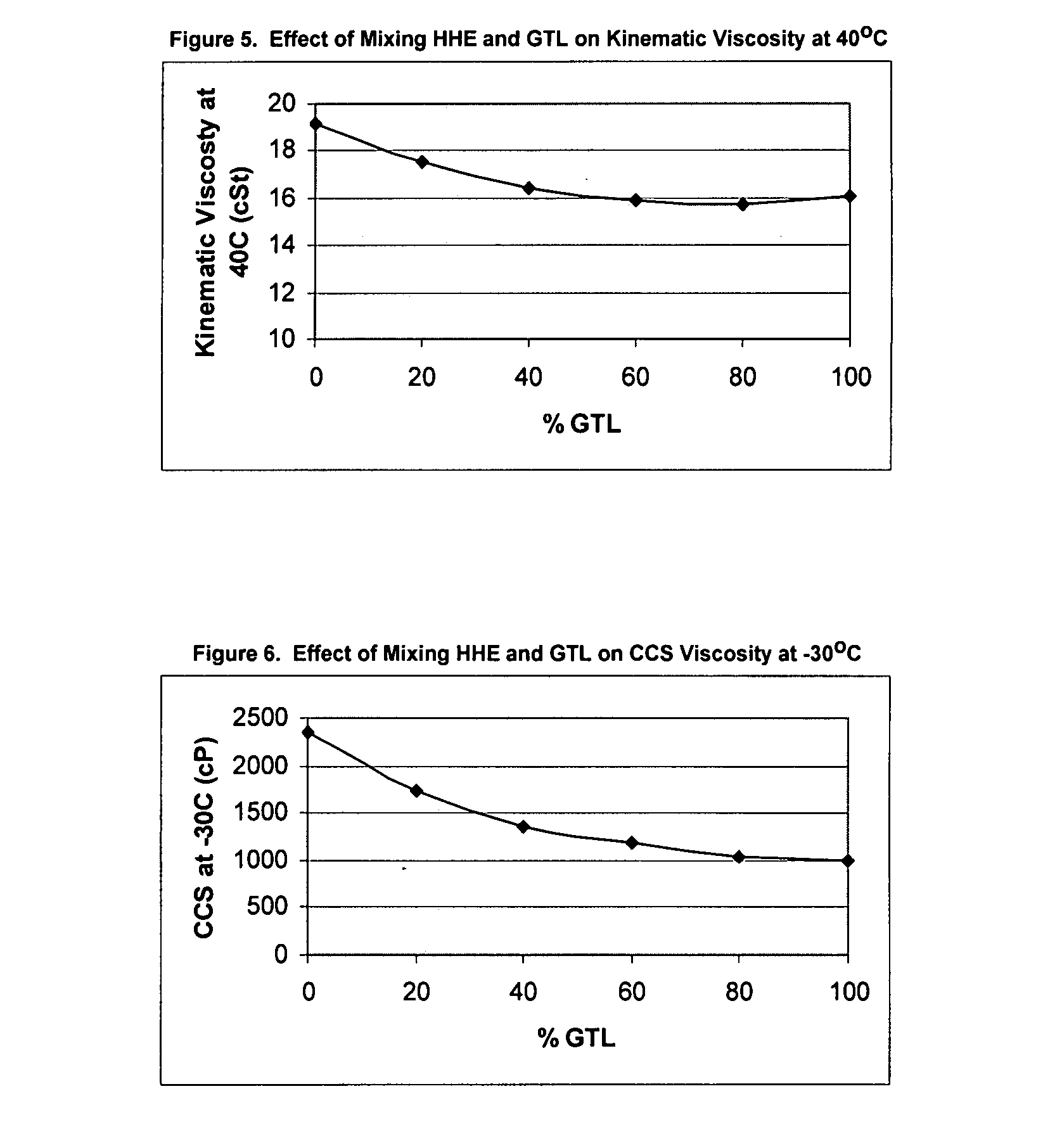
[0075]The procedure of Example 1 was followed except that the polyol had a kinematic viscosity at 100° C. of 4.008 cSt, and the oil was a GTL oil that had a kinematic viscosity of 3.724 cSt at 100° C.
[0076]The viscosity and cold cranking properties of the compositions and components are given in FIGS. 4 to 6. The data are shown in Table 2.
TABLE 2Kinematic Viscosity and CCS Viscosity Data of HHE and GTL BlendsOil03-3328903-3329003-3329103-3329203-3329303-33294Componentwt %wt %wt %wt %wt %wt %HHE10080604020GTL20406080100KV at 100 C., cSt4.0083.8273.7003.6533.6383.724KV at 40 C., cSt19.11817.52216.44615.9415.69416.07CCS at −30, cSt23531732135911971038992
example 3
[0077]The procedure of Example 1 was followed except that the ester was a polyol ester with a mixed alkyl groups ranging from C2 to C24, with no free hydroxyl groups and a Kv at 100° C. of 5.004. Also, the oil was a GTL oil having a Kv at 100° C. of 4.240. The viscosity properties of the components and blends are given in FIGS. 7 and 8.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com