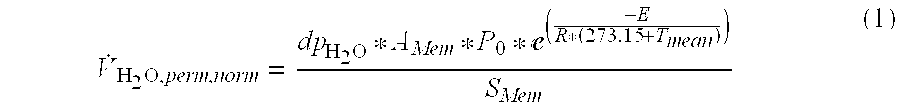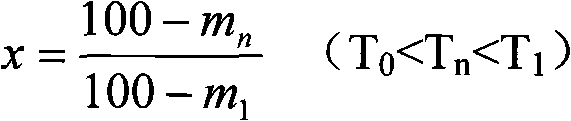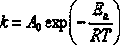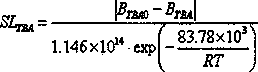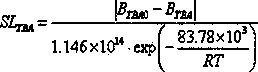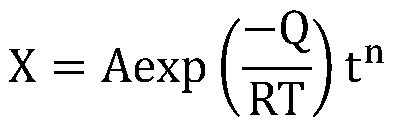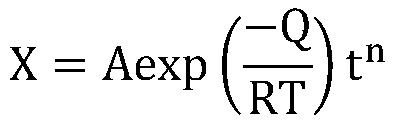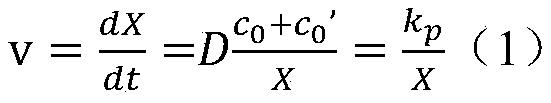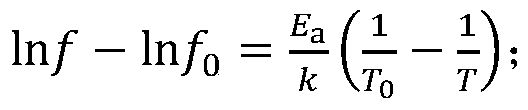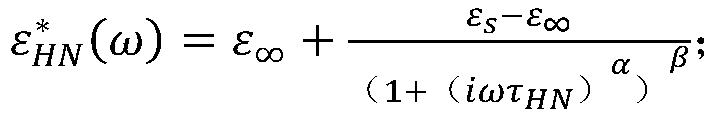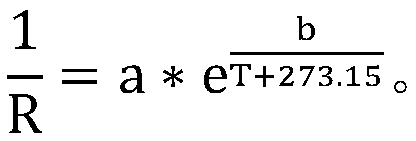Patents
Literature
54 results about "Arrhenius equation" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
In physical chemistry, the Arrhenius equation is a formula for the temperature dependence of reaction rates. The equation was proposed by Svante Arrhenius in 1889, based on the work of Dutch chemist Jacobus Henricus van 't Hoff who had noted in 1884 that van 't Hoff equation for the temperature dependence of equilibrium constants suggests such a formula for the rates of both forward and reverse reactions. This equation has a vast and important application in determining rate of chemical reactions and for calculation of energy of activation. Arrhenius provided a physical justification and interpretation for the formula. Currently, it is best seen as an empirical relationship. It can be used to model the temperature variation of diffusion coefficients, population of crystal vacancies, creep rates, and many other thermally-induced processes/reactions. The Eyring equation, developed in 1935, also expresses the relationship between rate and energy.
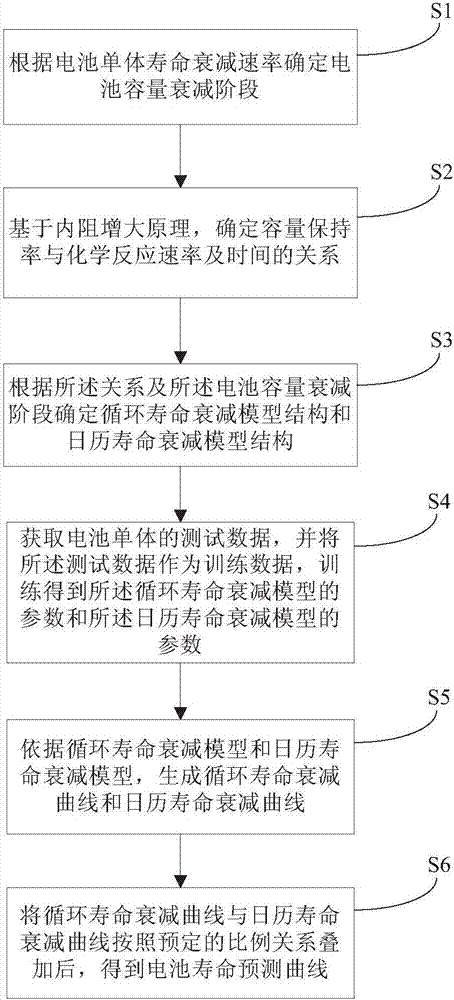
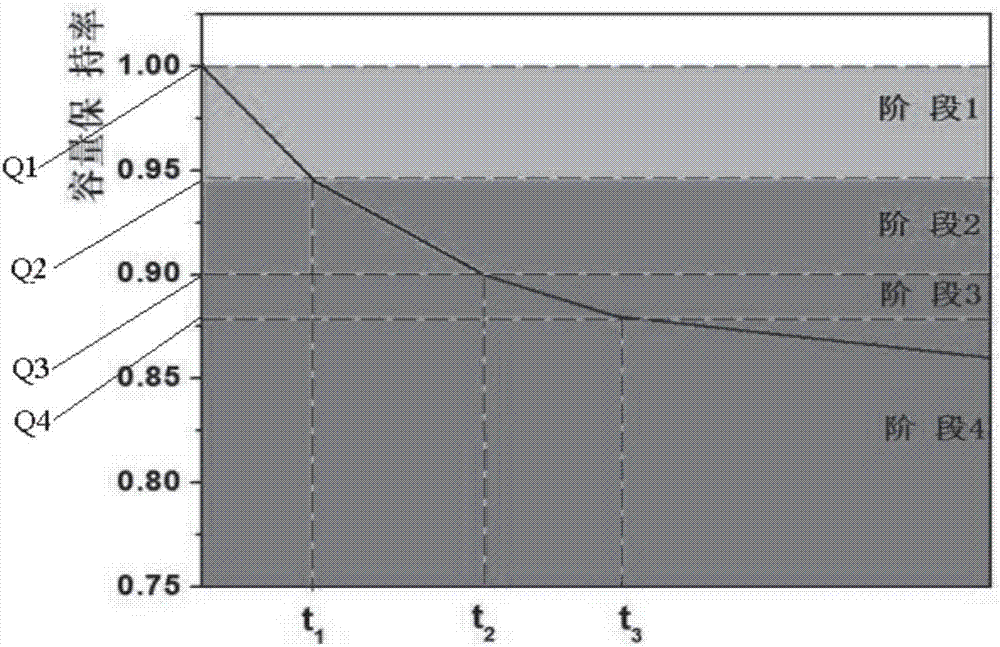
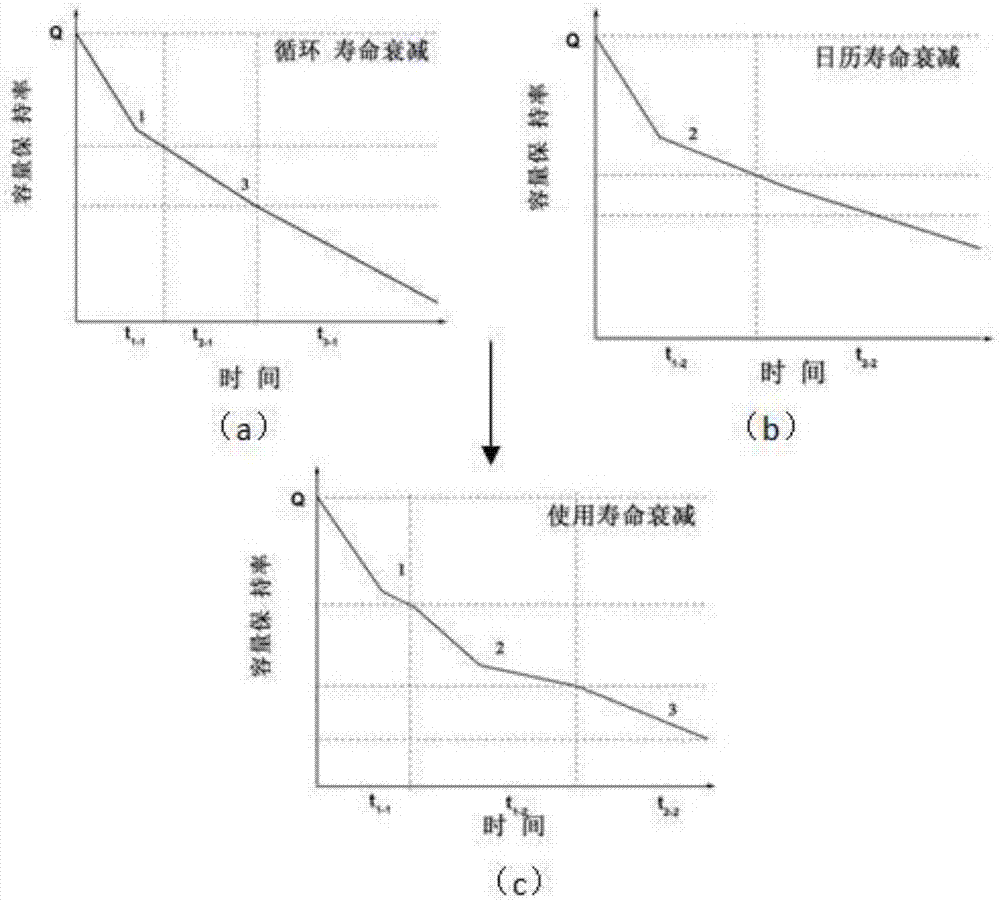
Power battery life prediction method
InactiveCN107202960AImprove accuracyAvoid forecast errorsElectrical testingChemical reactionReaction rate
The invention discloses a power battery life prediction method. The power battery life prediction method comprises the following steps: determining battery capacity fading stages according to battery cell life decay rate; establishing a capacity fading model for capacity retention rate with chemical reaction rate and time; obtaining a cycle life decay module and a calendar life decay module in combination with the battery capacity fading stages; training the cycle life decay module and the calendar life decay module on the basis of battery cell test data and determining parameters in the models; generating a cycle life decay curve and a calendar life decay curve according to the cycle life decay module and the calendar life decay module; superposing the two curves in a predetermined ratio to obtain a battery life prediction curve. On the basis of Arrhenius equation an internal resistance increase principle, multiple variables are provided for comprehensive consideration, and the battery life prediction curve bettering meeting the actual use conditions of a battery is obtained, so that larger prediction errors are effectively avoided, and the accuracy of a prediction model is improved substantially.
Owner:ANHUI JIANGHUAI AUTOMOBILE GRP CORP LTD
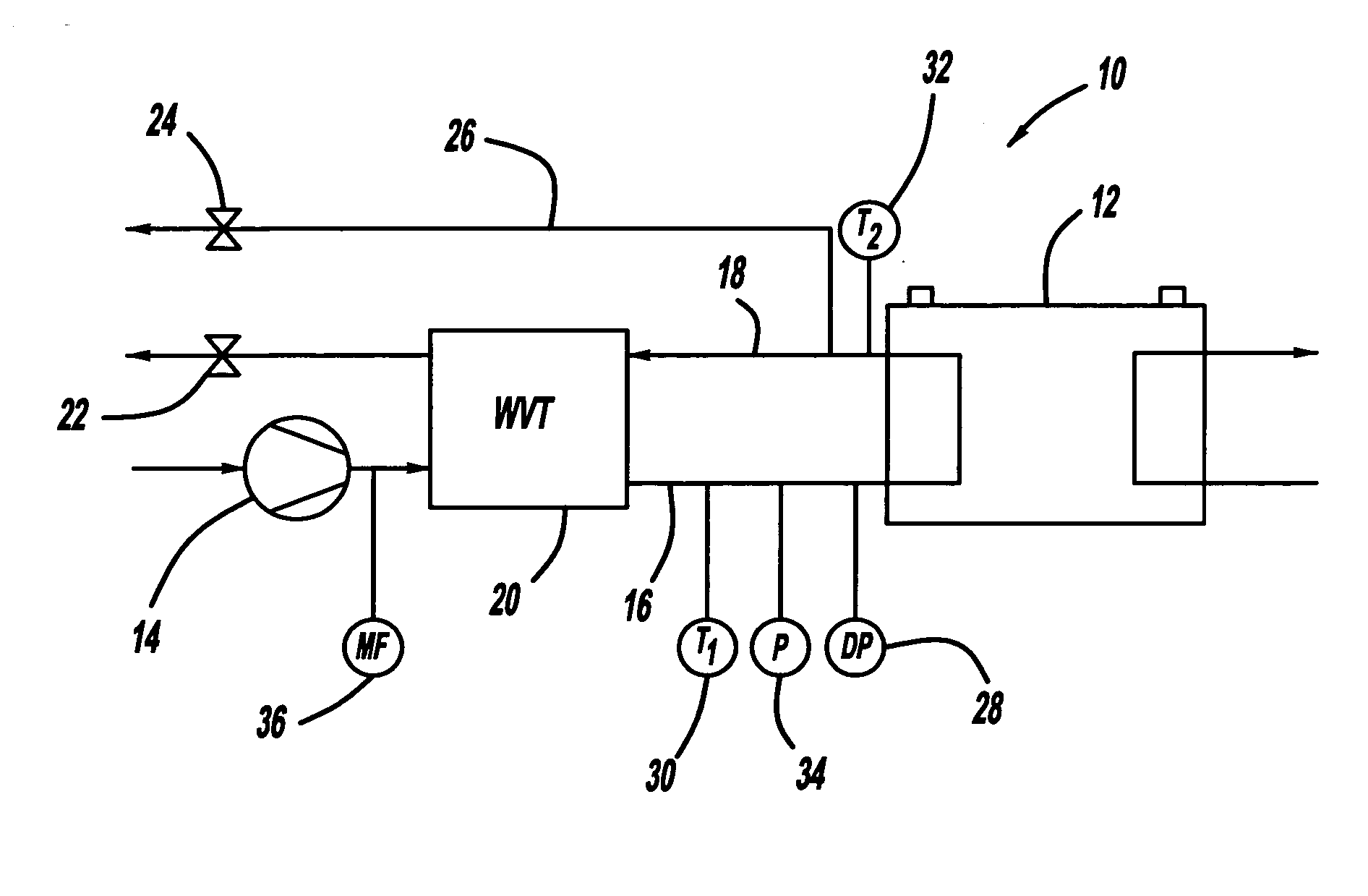
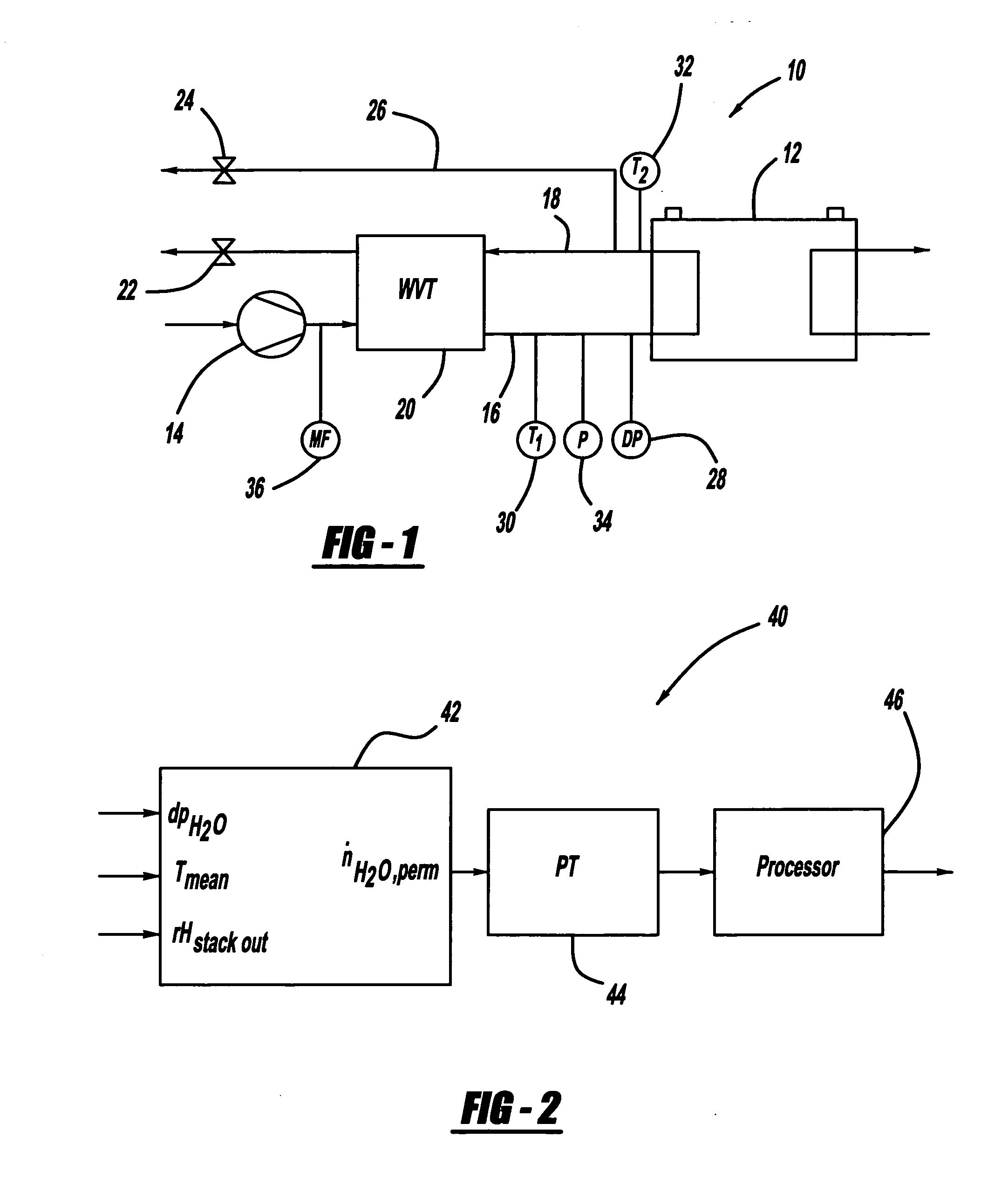
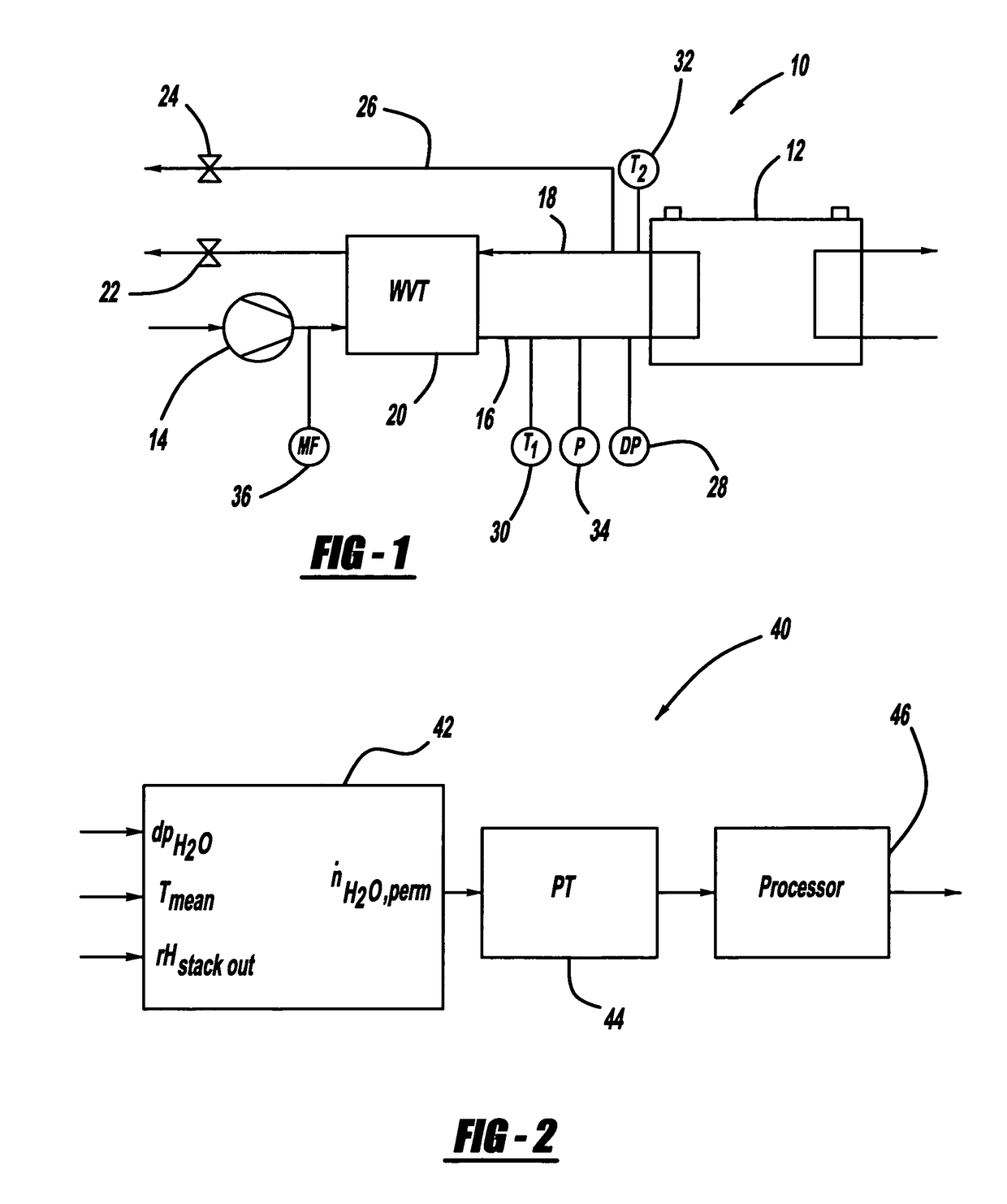
Sensorless relative humidity control in a fuel cell application
InactiveUS20070141412A1Eliminate needControlling ratio of multiple fluid flowsFuel cells groupingFuel cellsWater volume
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
Self-ignition fatalness decision method of coal
InactiveCN101271053AImprove effectivenessImprove economyWeighing by removing componentFuel testingSpontaneous combustionTemperature control
The invention belongs to a spontaneous combustion easiness judgment method of coal, in particular to a spontaneous combustion danger judgment method of the coal. The method includes the following steps: 1. sampling: a coal sample is collected on a coal working face, sealed and then taken back to a laboratory; the coal sample is ground to be below 50 mesh in the laboratory and put into a dry and clean jar which is labeled; the label will indicate the sampling place and the coal sample preparation time; the jar is sealed by a rubber sleeve; 2. testing: an experiment is taken by a thermogravimetric analyzer; during the experiment, temperature control and data collection are completed by the thermogravimetric analyzer; 3. operation and calculation: calculation of the reaction activation energy is according to an Arrhenius equation; the judgment method is to judge the spontaneous combustion easiness of the coal by the ''ignition activation energy'' in oxidation spontaneous combustion reaction between the coal and the oxygen, without need of a lot of equipments and instruments; the analysis and judgment can be conducted only by one thermogravimetric analyzer; the judging reliability is high.
Owner:LIAONING TECHNICAL UNIVERSITY
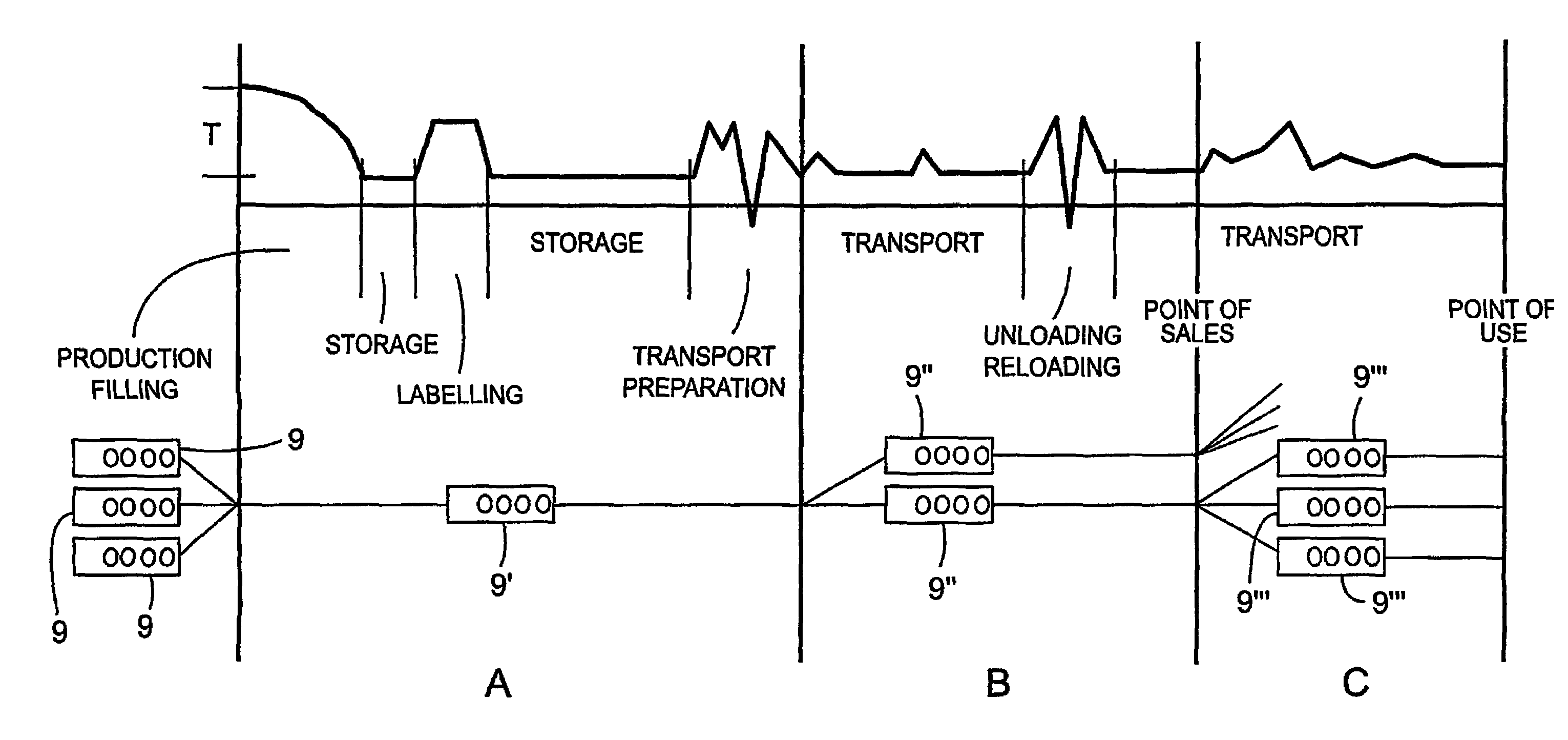
Environmental parameter indicator for perishable goods
InactiveUS20050021279A1Accurate expiry dataImprove quality controlThermometer detailsElectric/magnetic detection for well-loggingData interfaceComputer science
An electronic device is proposed for accompanying a perishable good during one period to monitor the exposure of the good to an environmental parameter, such as temperature. The device includes a data interface for receiving data representing the exposure of the good to the environmental parameter during an immediately preceding period. It further includes a sensor for measuring the environmental parameter. Also, the device includes a processor for using a relationship specific to the good (such an Arrhenius equation for that good) to compute a characteristic of the good at the end of the one period using the received data and the output of the sensor. The device further includes a memory for recording the output of the sensor. To economise on memory usage, data is stored at a faster rate during periods when the data is of most significant (e.g. it indicates a high temperature). A switch is provided for indicating that data should not be taken into account in the computation, during a short interval, in which for example the device may be being handled.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
Calculation method for remaining shelf life of fruits and vegetables
InactiveCN104749329AEffectively predict storage timeImprove storage and transportation valueTesting foodChemical reaction kineticsArrhenius equation
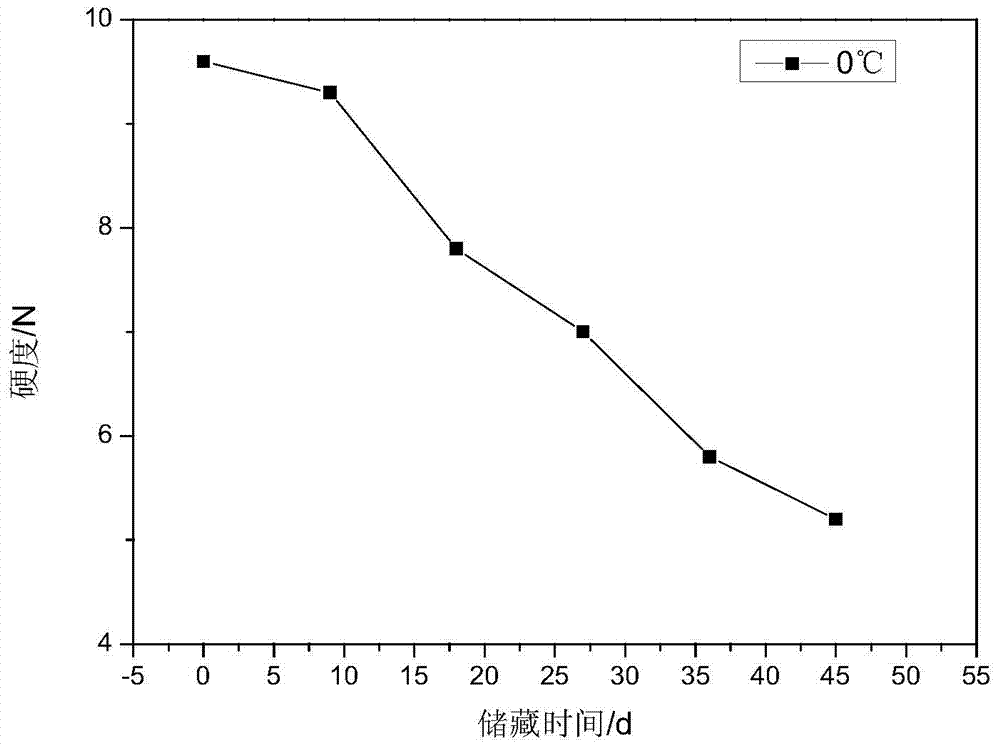
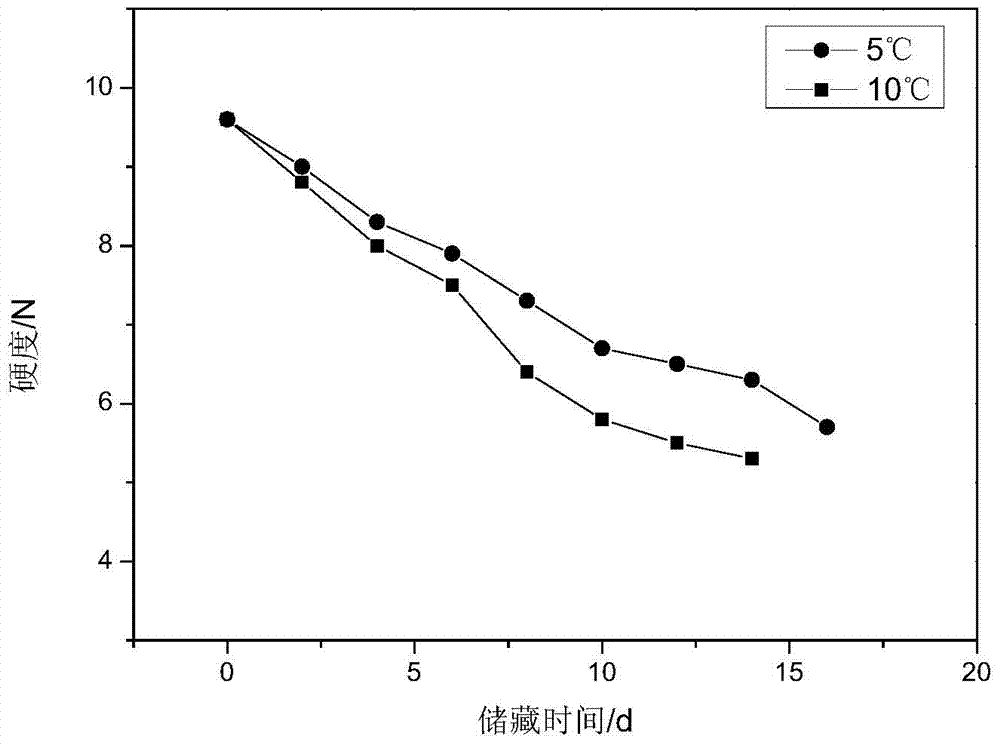
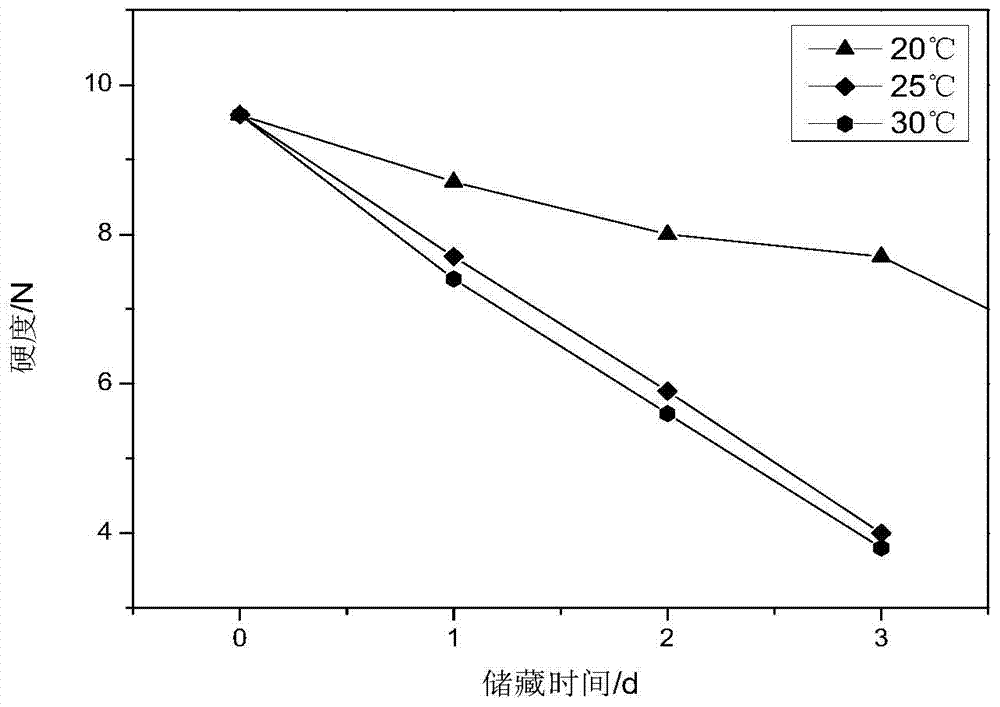
The invention discloses a calculation method for the remaining shelf life of fruits and vegetables and provides a calculation method for determining the remaining shelf life of fruits and vegetables by the hardness index. The calculation method comprises the following steps: firstly measuring an initial hardness value Q of the fruits and the vegetables, and simultaneously measuring a transformation relation of the hardness of the fruits and the vegetables with time under different temperatures; establishing a dynamic model of the fruits and the vegetables by adopting a first-order chemical reaction dynamic equation InAt=lnA0-kt, carrying out linear regression fitting on a hardness and time relation of the step, and thus obtaining a hardness-change rate constant ki of the fruits and the vegetables under different temperatures; applying an Arrhenius equation shown in the specification and combining the hardness-change rate constant ki of the fruits and the vegetables under different temperatures and a fitting-equation determination coefficient to obtain a relation curve graph shown in the specification of the fruits and the vegetables, obtaining a curve fitting equation from the obtained relation curve graph and determining the inclination and the intercept of the fitting line, wherein the mass equation of the fresh-eating fruits and vegetables is shown as the specification, the equivalent transformation is shown in the specification, and then the shelf life t of the fruits and the vegetables under the ambient temperature can be calculated.
Owner:TIANJIN UNIV OF COMMERCE
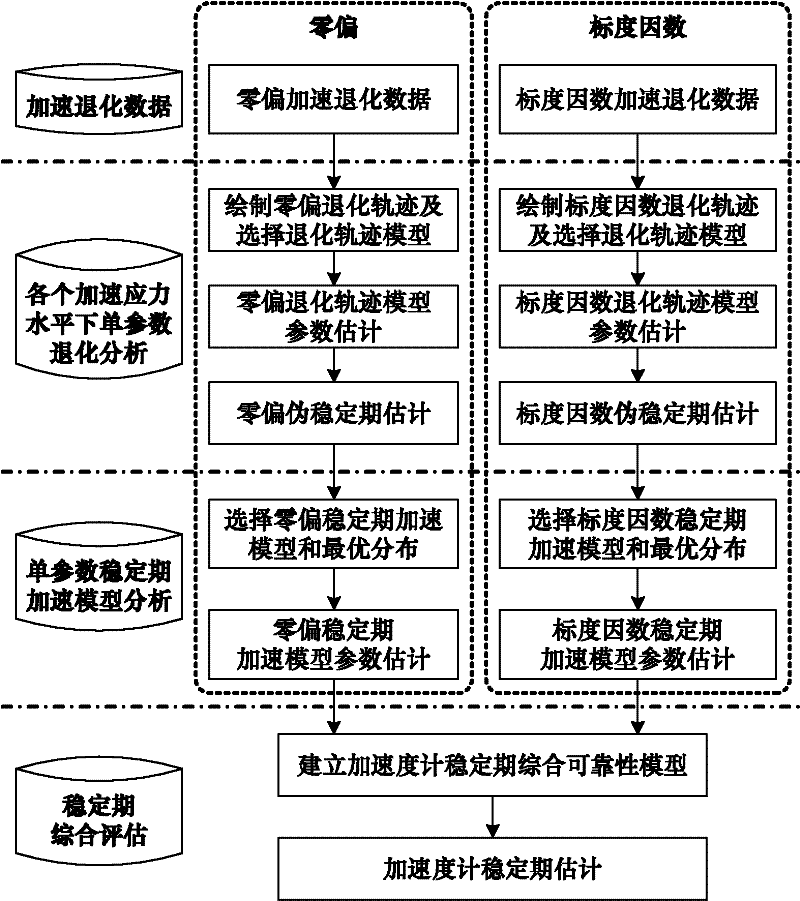
Method for determining stationary phase of accelerometer based on dual-parameter accelerated degradation data
InactiveCN102253242ADescribe wellRapid assessmentTesting/calibration of speed/acceleration/shock measurement devicesStationary phaseAccelerometer
The invention provides a method for determining the stationary phase of an accelerometer based on dual-parameter accelerated degradation data. The method is based on the assumption that the zero deviation and scale factors of the accelerometer degrade commonly and meet a power degradation law, the assumption that a high-temperature accelerated degradation test of the accelerometer meets the consistency condition of a failure mechanism, and the assumption that an accelerated model is an Arrhenius equation. The method comprises the following steps of: 1, establishing a degradation track model of the zero deviation and the scale factors; 2, estimating the pseudo-stationary phase of the zero deviation and the scale factors; 3, establishing a stationary phase accelerated model of the zero deviation and the scale factors; and 4, establishing a comprehensive reliable model of the stationary phase of the accelerometer, and determining the stationary phase of the accelerometer under the reliability. In the method, the influence of the zero-deviation degradation and the scale factors on the stationary phase of the accelerometer is taken into consideration simultaneously, horizontal information among different test temperatures is utilized fully by an integral maximum likelihood estimation process, so that the condition of the stationary phase of the accelerometer can be better describedunder the condition of dual-parameter common degradation, and the estimation accuracy is improved effectively.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
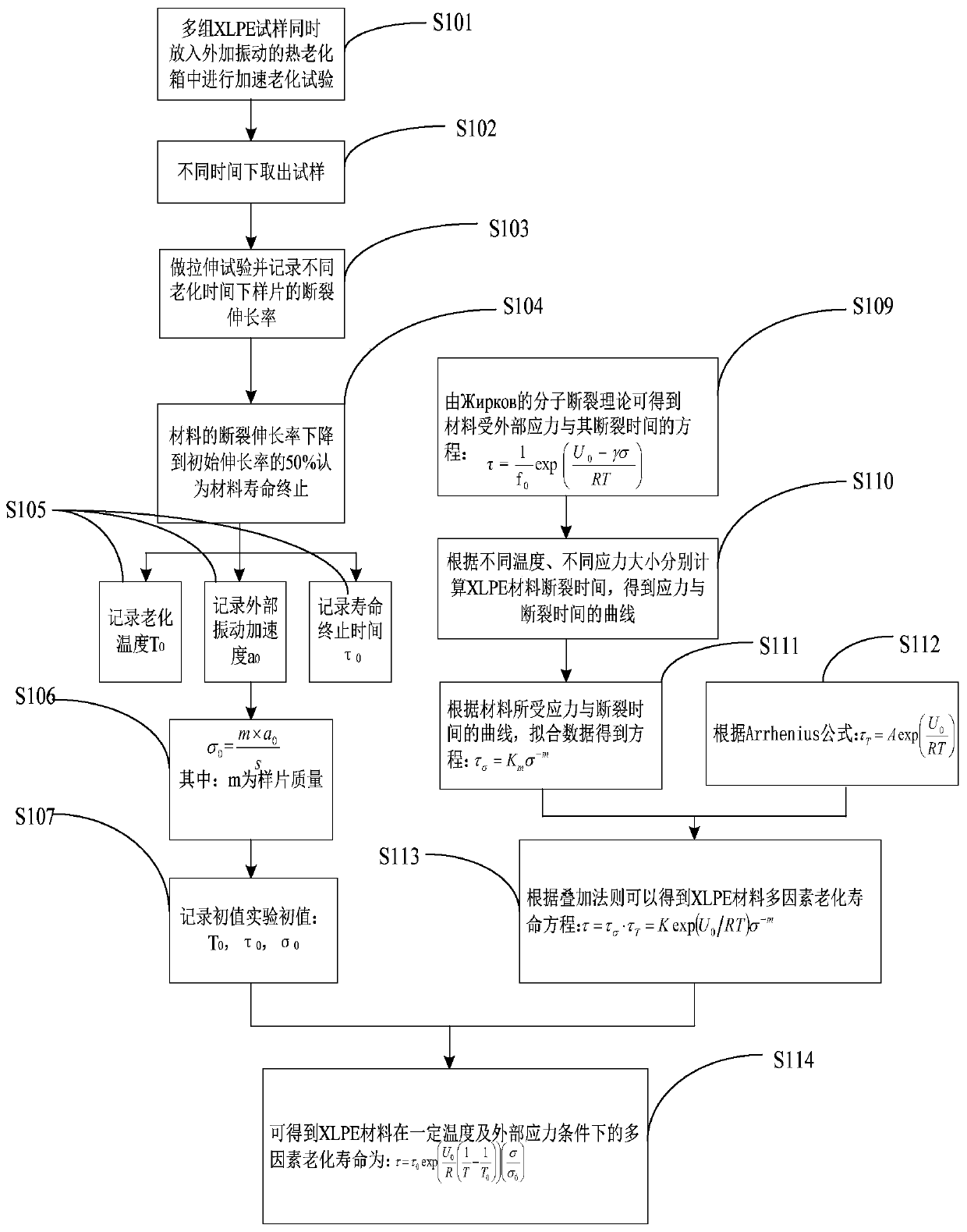
XLPE cable insulation material aging service life prediction method
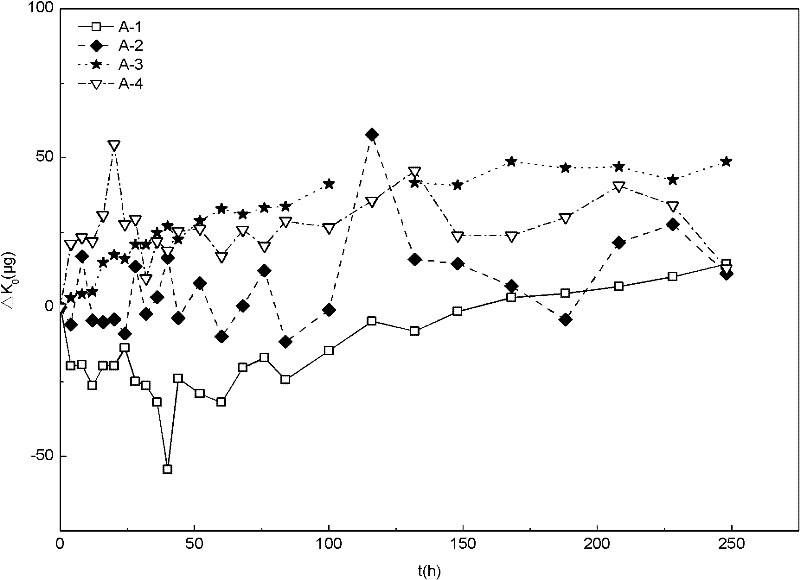
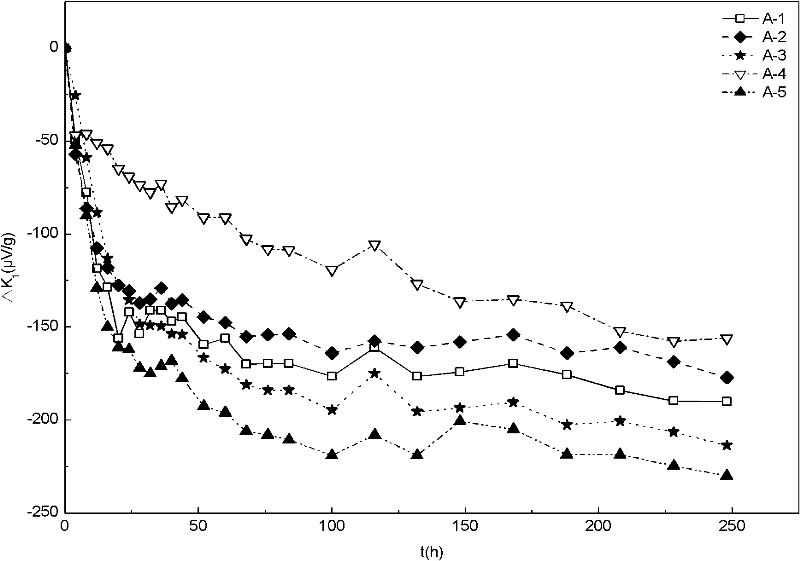
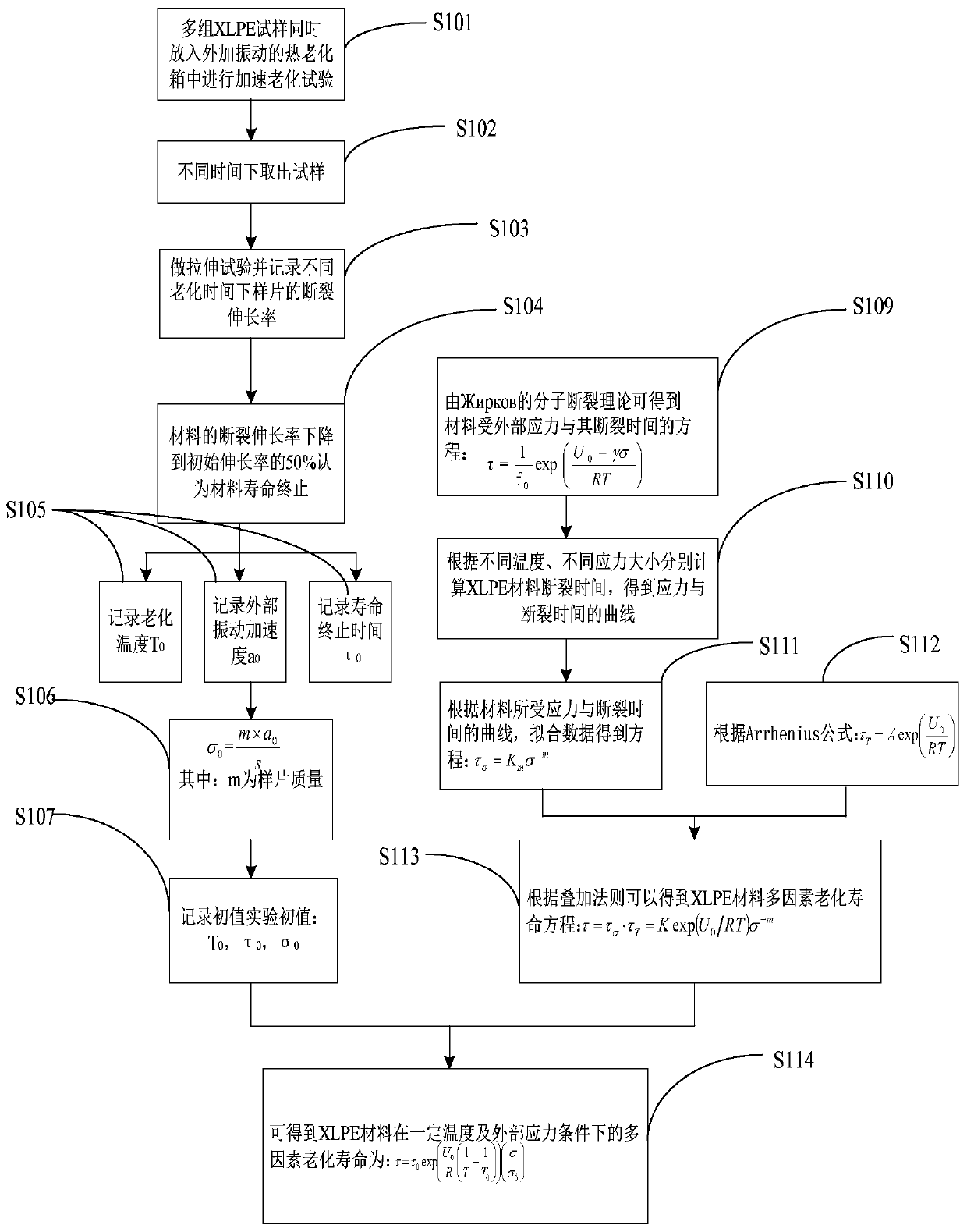
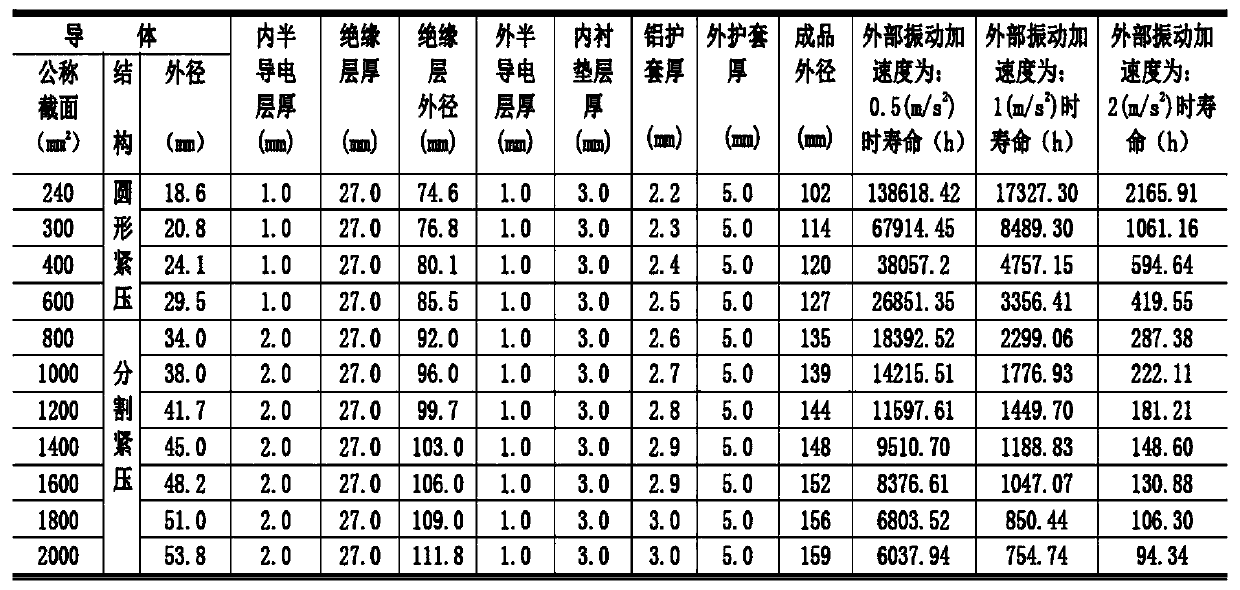
ActiveCN109917251ACalculation method is simpleShort test cycleTesting dielectric strengthMaterial strength using tensile/compressive forcesVibration accelerationAccelerated aging
The invention discloses an XLPE cable insulation material aging service life prediction method. The method includes the following steps that: a material to be tested is acquired; the working environmental temperature of the material to be tested is measured, and a vibration acceleration is applied to the material to be tested; and the service life of the material to be tested is predicted according to a prediction equation. The service life, temperature and other parameters of the LPE cable insulation material under an acceleration and aging combined condition are obtained and are adopted as initial conditions, so that the service life equation of the XLPE cable insulation material under different temperature and self-vibration stress is obtained on the basis of the Yierkefu molecular fracture theory equation, the Arrhenius equation, an inverse power law and a superposition rule. The calculation method of the invention has the advantages of simplicity, short test period, times-saving and cost-saving performance, and high reliability in life prediction.
Owner:STATE GRID JIANGSU ELECTRIC POWER CO ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +3
Determination of acceleration parameter range in vacuum fluorescent display device accelerated life test
InactiveCN101329219ALife EstimationFind out exactlyOptical apparatus testingFluorescenceDisplay device
The invention relates to the determination of acceleration parameter range in the acceleration service life test of vacuum fluorescent displays (VFD) and discloses a method that comprises the following steps: (1) the service life of the VFD is described by applying the Weibell distribution function; (2) a shape parameter m and a size parameter Eta of the Weibell distribution are estimated by adopting the maximum likelihood method; (3) the range of an acceleration parameter Beta in the acceleration service life test of the vacuum fluorescent display is calculated by combining Arrhenius equation and the least square method. The method calculates the range of the acceleration parameter Beta in the acceleration service life test of the vacuum fluorescent display based on the maximum likelihood method, thus estimating the service life of the VFD in a short time, saving time for the service life test and lowering service life prediction cost.
Owner:SHANGHAI UNIVERSITY OF ELECTRIC POWER
Component level-based asphalt thermal decomposition behavior researching method
InactiveCN103472091AImprove traffic safetyIncreased durabilityMaterial heat developmentColor/spectral properties measurementsAdditive ingredientSpectroscopy
The invention relates to a new method for researching the asphalt thermal decomposition behavior by deepening into the asphalt component level, belongs to the field of fire disaster safety and solves the problem that the current asphalt thermal decomposition behavior research is difficultly thorough. The method comprises the steps of: firstly, preparing component test samples, determining component content, testing the thermal decomposition property of asphalt and four components thereof by adopting differential scanning calorimetry-infrared spectroscopy technology, acquiring the thermal decomposition test data of all components in the asphalt, analyzing the thermal decomposition gradient distribution character of all the component and producing smoke ingredient and release rule; secondly, calculating the thermal analysis kinetic parameters of all the components according to the Arrhenius equation, and establishing a thermal decomposition kinetic model; finally, testing the microstructure, components and content of residues of the thermally-decomposed components by adopting a transmission electron microscope and aphotoelectron spectroscopy instrument, researching the thermal decomposition behavior of all the components in asphalt, and comparing with the asphalt test sample test results, and revealing the asphalt thermal decomposition mechanism. The method can fundamentally reveal the thermal decomposition behavior of asphalt under the high-temperature environment.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Leaf spring normal-temperature and high-temperature stress relaxation life predicting method
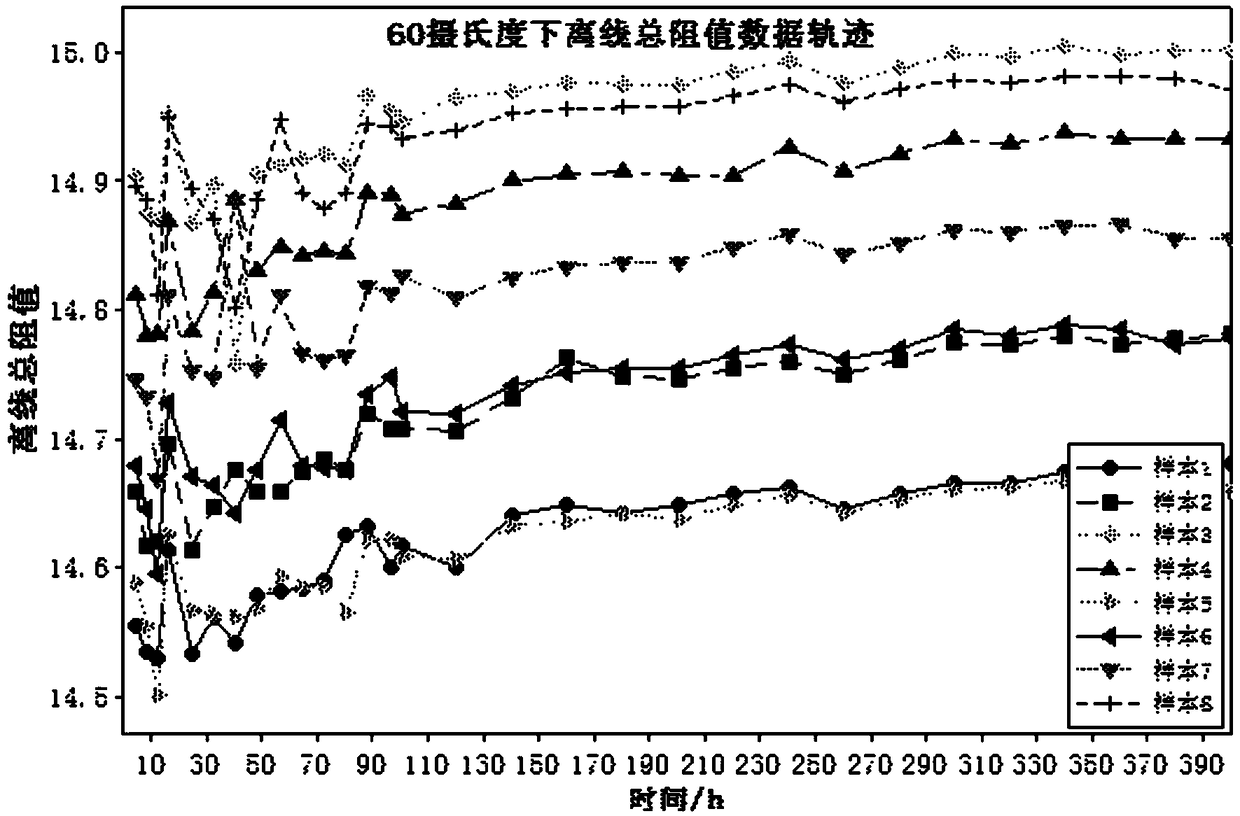
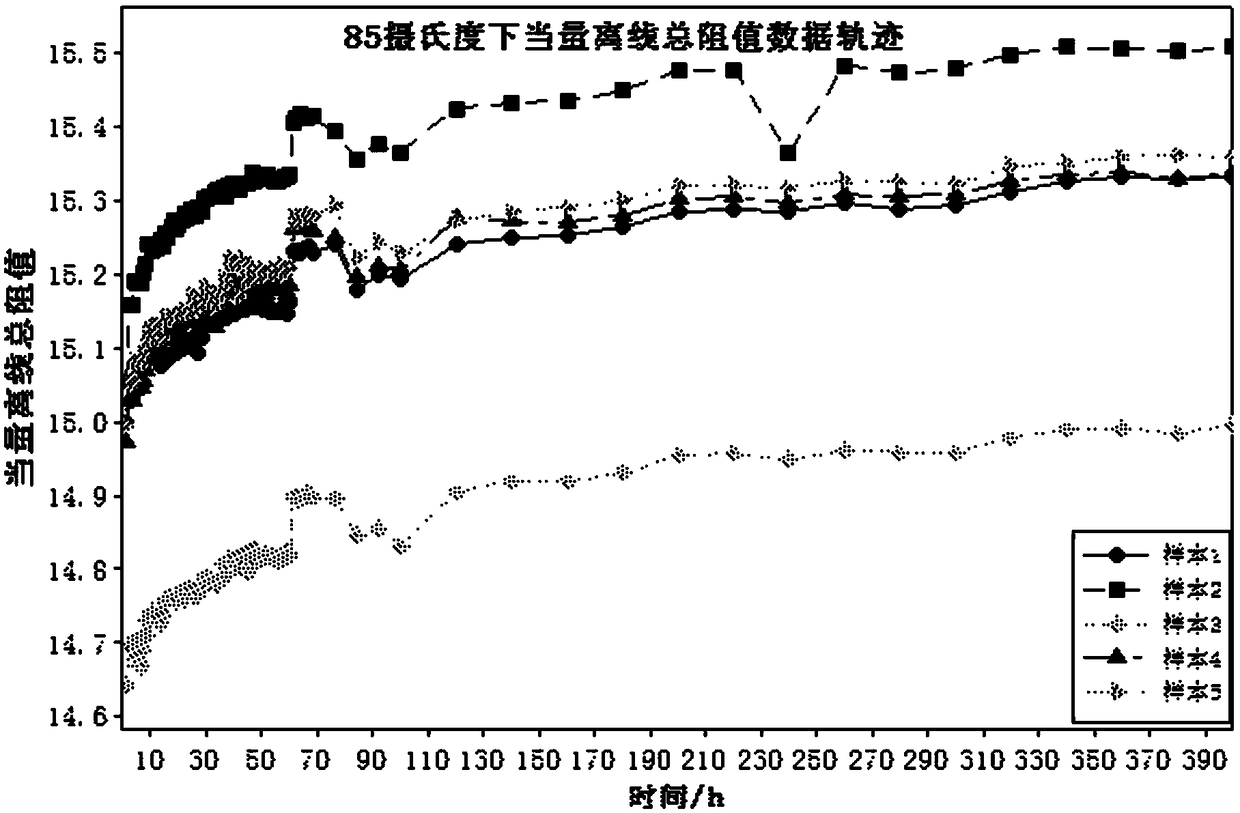
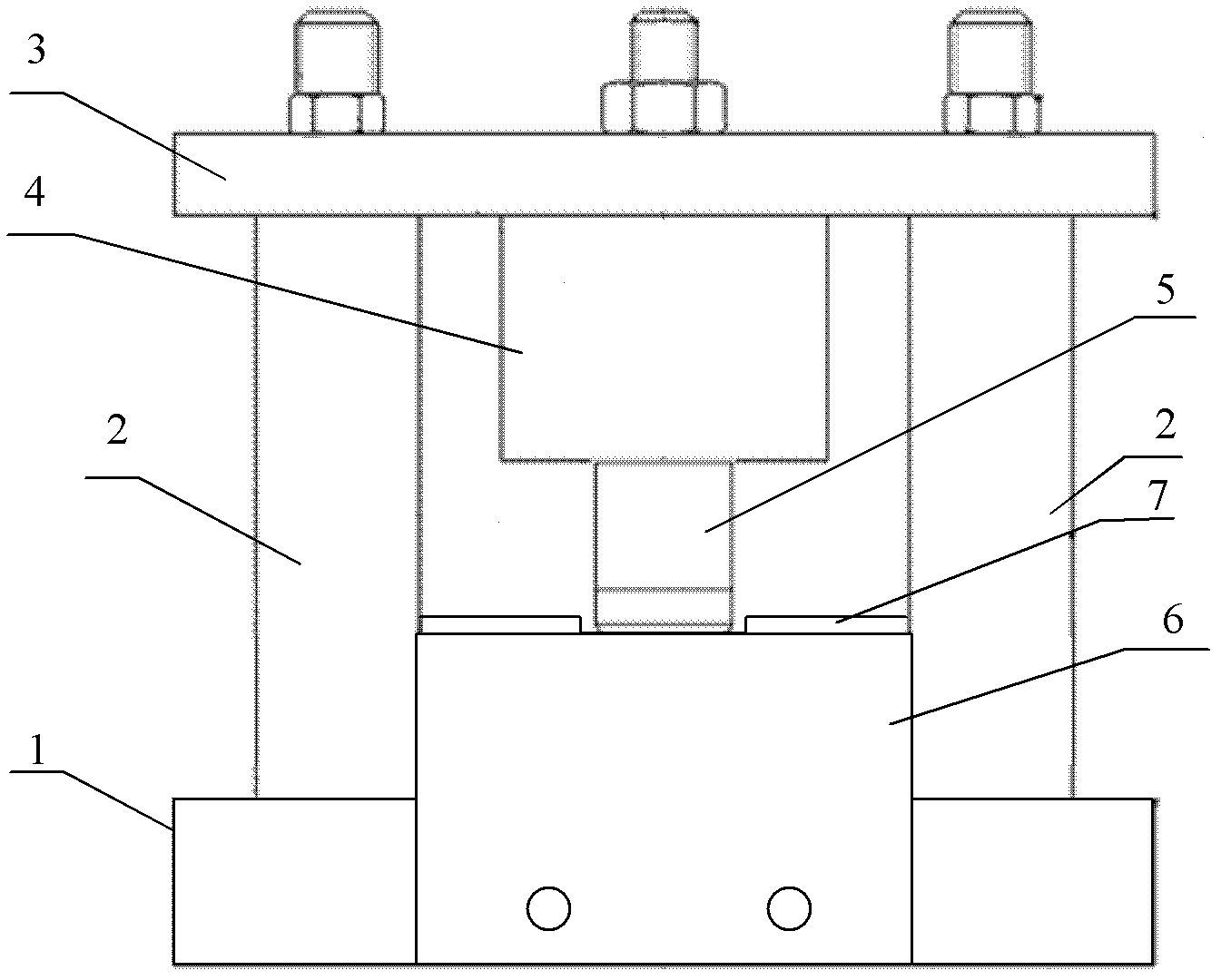
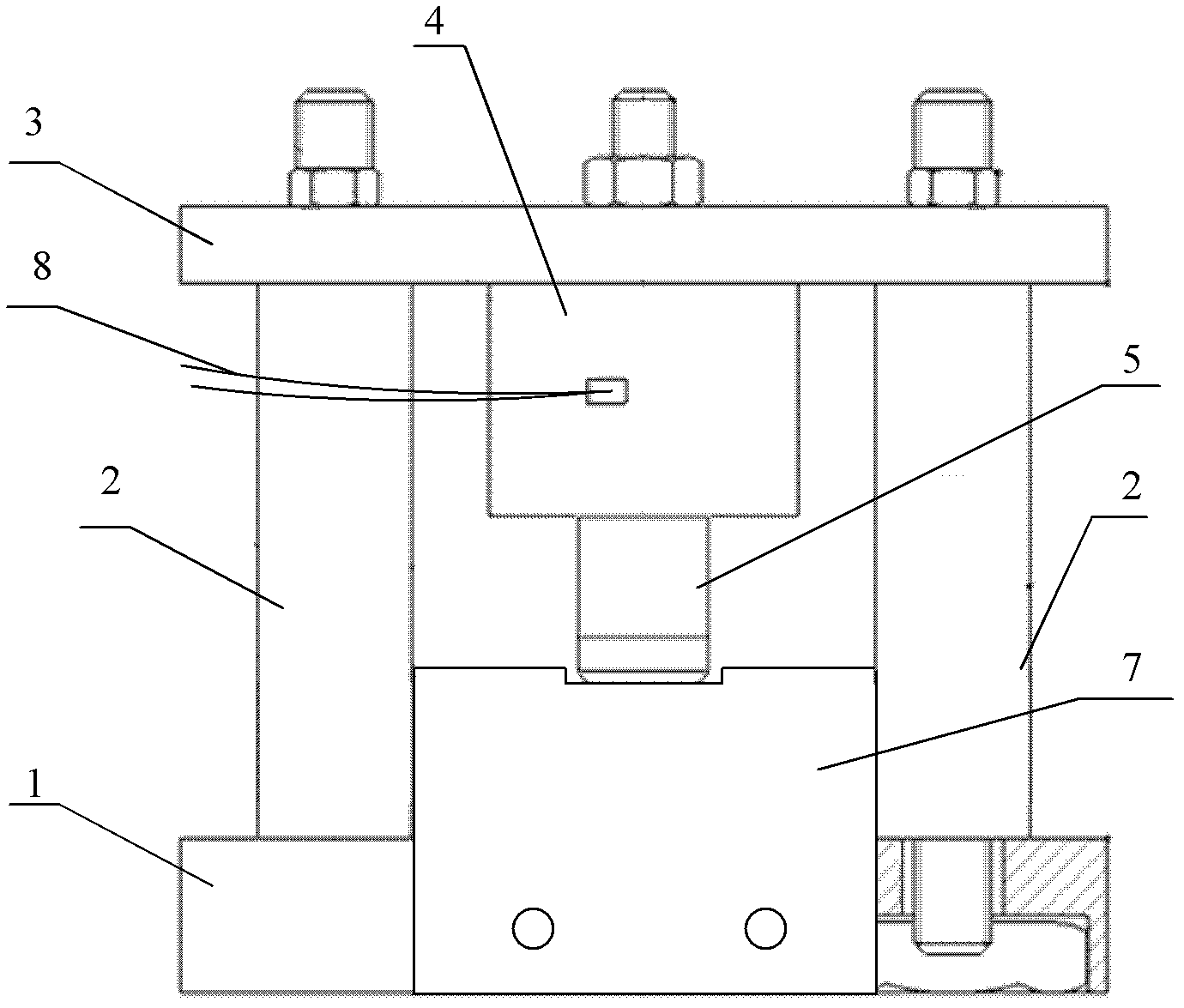
InactiveCN102650582AGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed repeatabilityInvestigating material hardnessTemperature stressRoom temperature
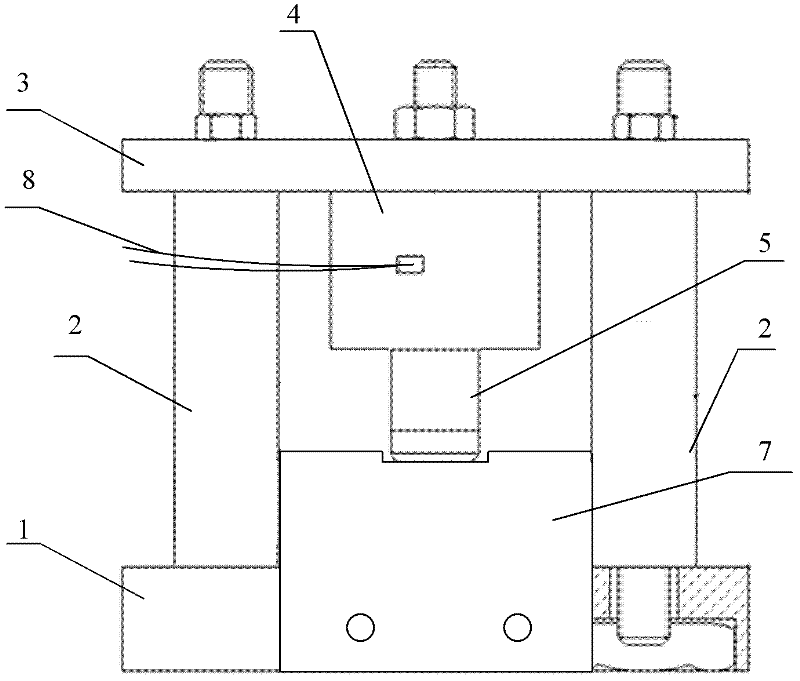
The invention provides a leaf spring normal-temperature and high-temperature stress relaxation life predicting method. Firstly, a spring sample to be tested is prepared, and the prepared spring sample to be tested is an equal stress sample; then a test device is arranged, side plates are fixed at the front part and the rear part of a base of the test device, two ends of the sample are respectively arranged on the side plates, the base and an upper plate are fixed together through limiters, a pressure sensor is arranged on the upper plate, and a pressure head arranged at the lower end of the pressure sensor applies pressure on the sample; and then a spring stress relaxation experiment is carried out, stress values at different time are acquired to determine the stress relaxation loss condition of a sample material after the regulated experiment time is up, test data is selected according to failure criteria, the data is processed by an empirical formula and an Arrhenius equation, and finally the life of the sample at the normal temperature is determined. According to the method disclosed by the invention, sample bending deflection which is not easy to measure is converted into an electrical signal which is easy to measure, the work efficiency is improved, the method is simple, and the obtained life prediction result is accurate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Method for establishing river carp shelf life prediction model by using TBA
InactiveCN104200068AAccurate predictionAdapt to sales method requirementsCommerceSpecial data processing applicationsChemical reaction kineticsCarp
A method for establishing a river carp shelf life prediction model by using TBA is that the river carp shelf life prediction model is established by researching sensory evaluation on river carps at different temperatures and change of the TBA with storage time prolonging and utilizing an Arrhenius equation according to the TBA. The method is novel, operation is simple, the river carp shelf life prediction model can be obtained through substitution of a simple formula and calculation, a relative error of an obtained shelf life prediction value is within a range from -5% to +5%, and the accuracy is high. The zero-level chemical reaction kinetic is confirmed and selected by measuring the TBA change of the river carps at the different temperatures to reflect a river carp TBA change rule, and the method has sufficient reasonability and persuasion. Therefore, the method can be used for accurately predicting the remaining river carp shelf life and mastering and learning the quality condition and freshness of the river carps.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
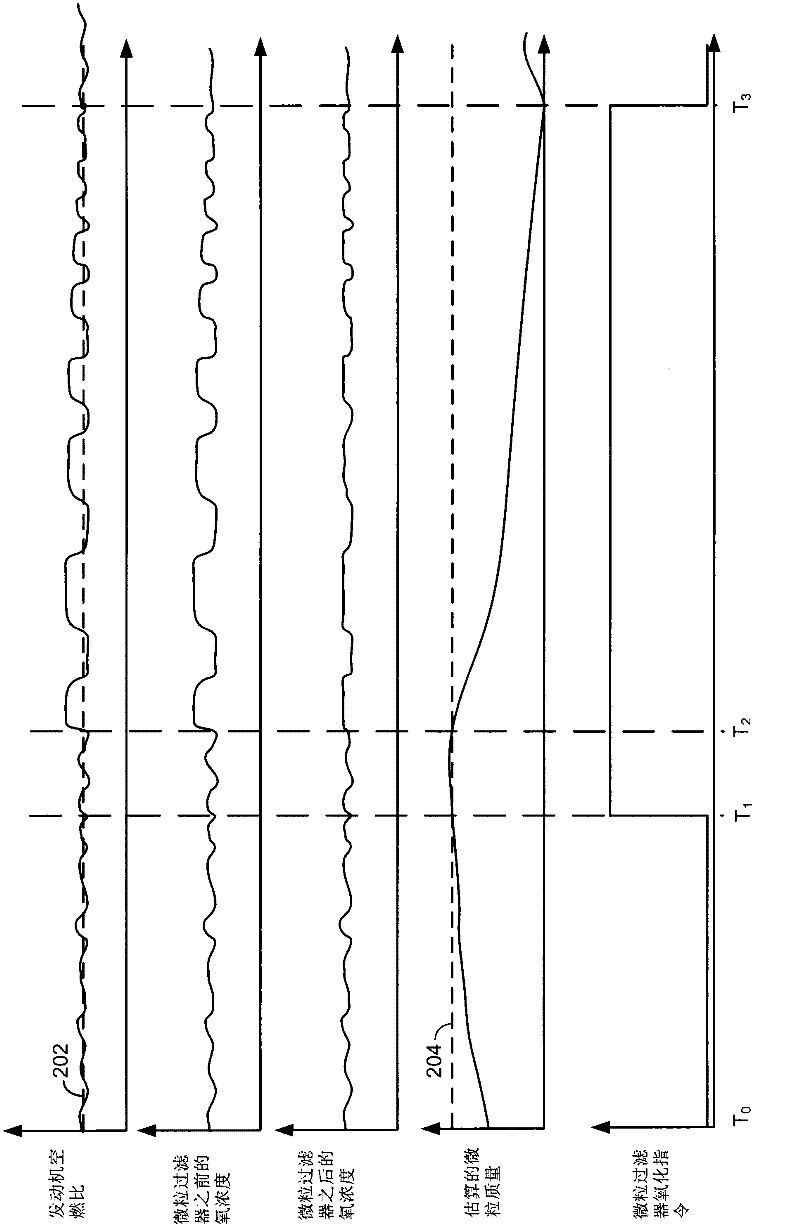
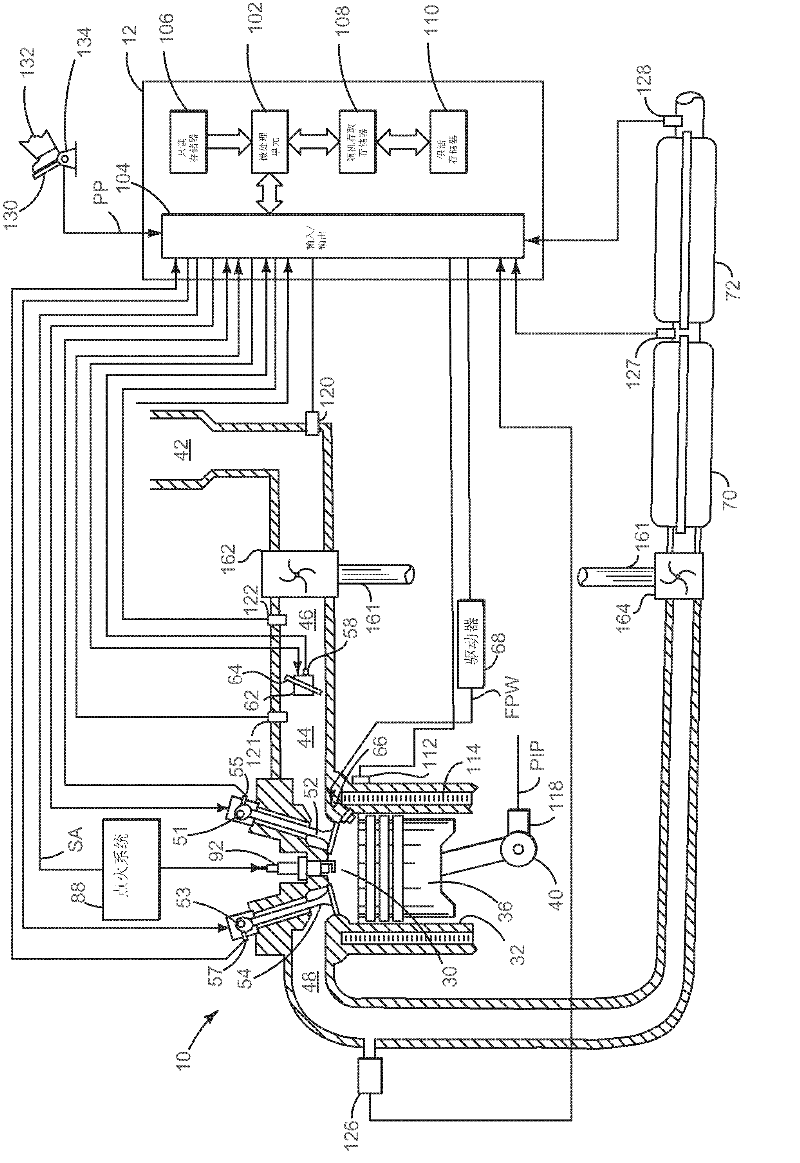
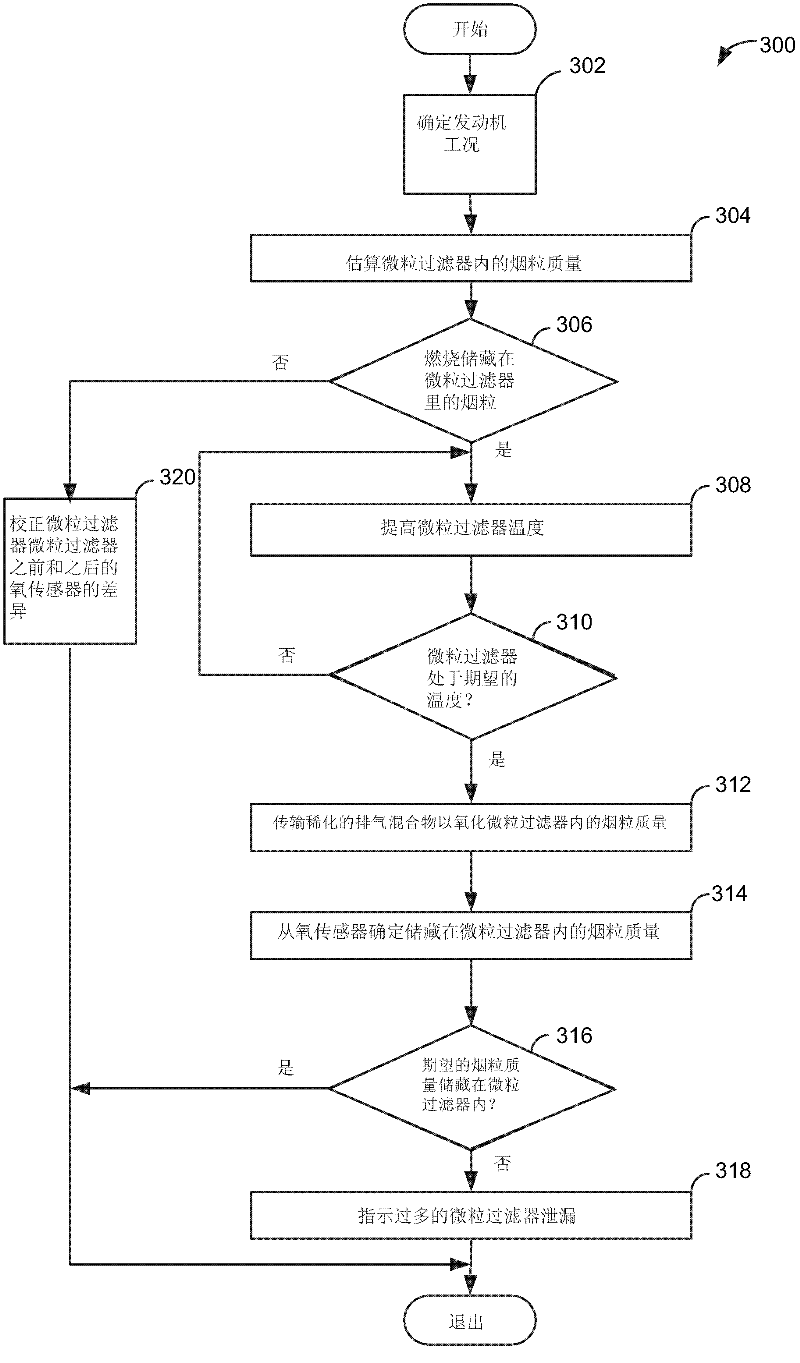
Method for determining soot mass stored with a particulate filter
A method for determining soot mass oxidized during a particulate filter oxidation procedure is disclosed. In one example, soot mass is determined via an Arrhenius equation. The approach may provide cost savings and reliability improvements as compared to other ways of determining soot mass.
Owner:FORD GLOBAL TECH LLC
Environmental parameter indicator for perishable goods
InactiveUS7392150B2Accurate dataImprove quality controlThermometer detailsTemperature control without auxillary powerData interfaceComputer science
An electronic device is proposed for accompanying a perishable good during one period to monitor the exposure of the good to an environmental parameter, such as temperature. The device includes a data interface for receiving data representing the exposure of the good to the environmental parameter during an immediately preceding period. It further includes a sensor for measuring the environmental parameter. Also, the device includes a processor for using a relationship specific to the good (such an Arrhenius equation for that good) to compute a characteristic of the good at the end of the one period using the received data and the output of the sensor. The device further includes a memory for recording the output of the sensor. To economise on memory usage, data is stored at a faster rate during periods when the data is of most significant (e.g. it indicates a high temperature). A switch is provided for indicating that data should not be taken into account in the computation, during a short interval, in which for example the device may be being handled.
Owner:3M INNOVATIVE PROPERTIES CO
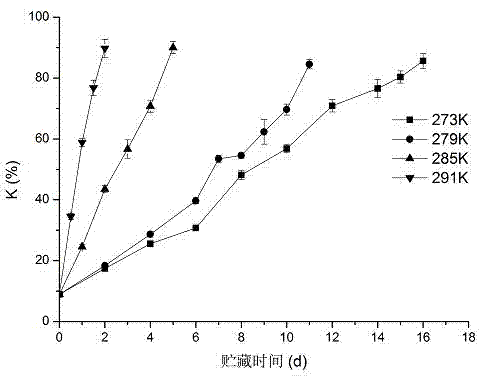
River crucian crucian carp shelf life prediction method
InactiveCN104297440AGrasp and understand the quality statusGrasp and understand freshnessTesting foodChemical reaction kineticsZoology
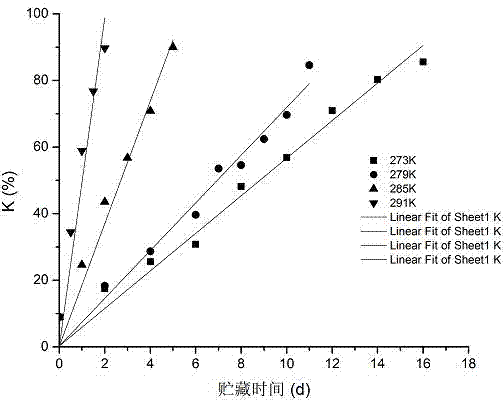
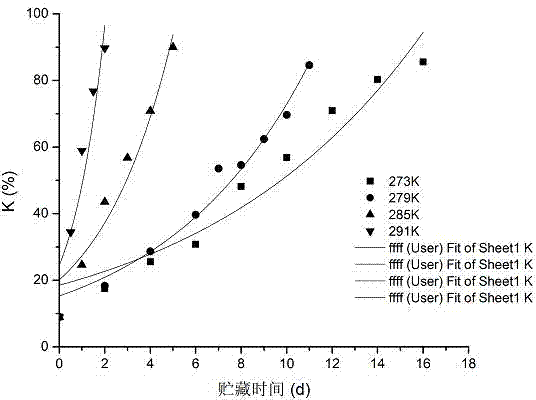
The invention discloses a river crucian carp shelf life prediction method, by researches on sensory evaluation and K value change along with the extension of storage time of river crucian carp at different temperatures, a river crucian carp shelf life prediction model is established according to K value by use of Arrhenius equation, the method is novel and simple in operation, the river crucian carp shelf life prediction value can be calculated by substitution into a simple formula, the obtained the relative error of the river crucian carp shelf life prediction value is within + / -5%, and the accuracy is high. By measuring the K value change of the river crucian carp at different temperatures, corresponding quality energy level functions are analyzed, zero order chemical reaction kinetic is more suitable for reflecting the river crucian carp K value change rule, and is fully reasonable and persuasive, so that the method can be used to accurately predict the river crucian carp remaining shelf life, master and know the river crucian carp quality state and fresh degree.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
Asphalt aging performance prediction method based on isothermal thermal analysis kinetics
ActiveCN107576587AReduce adhesionReduced service lifeMaterial weighingChemical structurePerformance index
The invention discloses an asphalt aging performance prediction method based on isothermal thermal analysis kinetics, belongs to the technical field of road asphalt pavement durability, and solves problems that an asphalt aging process cannot be predicted accurately and more practical asphalt aging performance prediction cannot be provided for pavement management and maintenance work when attenuation of a macroscopic performance index of the asphalt is adopted to speculate a pavement performance degradation degree at present. The asphalt aging performance prediction method provided by the invention comprises the following steps: firstly, selecting an asphalt sample, testing with a thermal analyzer, simulating thermal-oxidative aging of the asphalt to obtain TG and DTG data and a char yieldof the asphalt; secondly, selecting a reaction mechanism function corresponding to the asphalt aging process according to a chemical structure, a functional group and thermal stability change of theasphalt aging process to establish an isothermal thermal analysis kinetics model of the asphalt; finally, using an aging-time equivalence principle to analyze equivalence of the asphalt aging processand time, calculating an isothermal aging shift factor by an Arrhenius equation to predict the asphalt aging performance, thereby providing a basis for decision-making of an asphalt pavement maintenance scheme.
Owner:NANJING FORESTRY UNIV
Method of predicting shelf life of sauce ducks
InactiveCN108399467ATimely processingPrediction is fast and accurateForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationEscherichia coliColony number
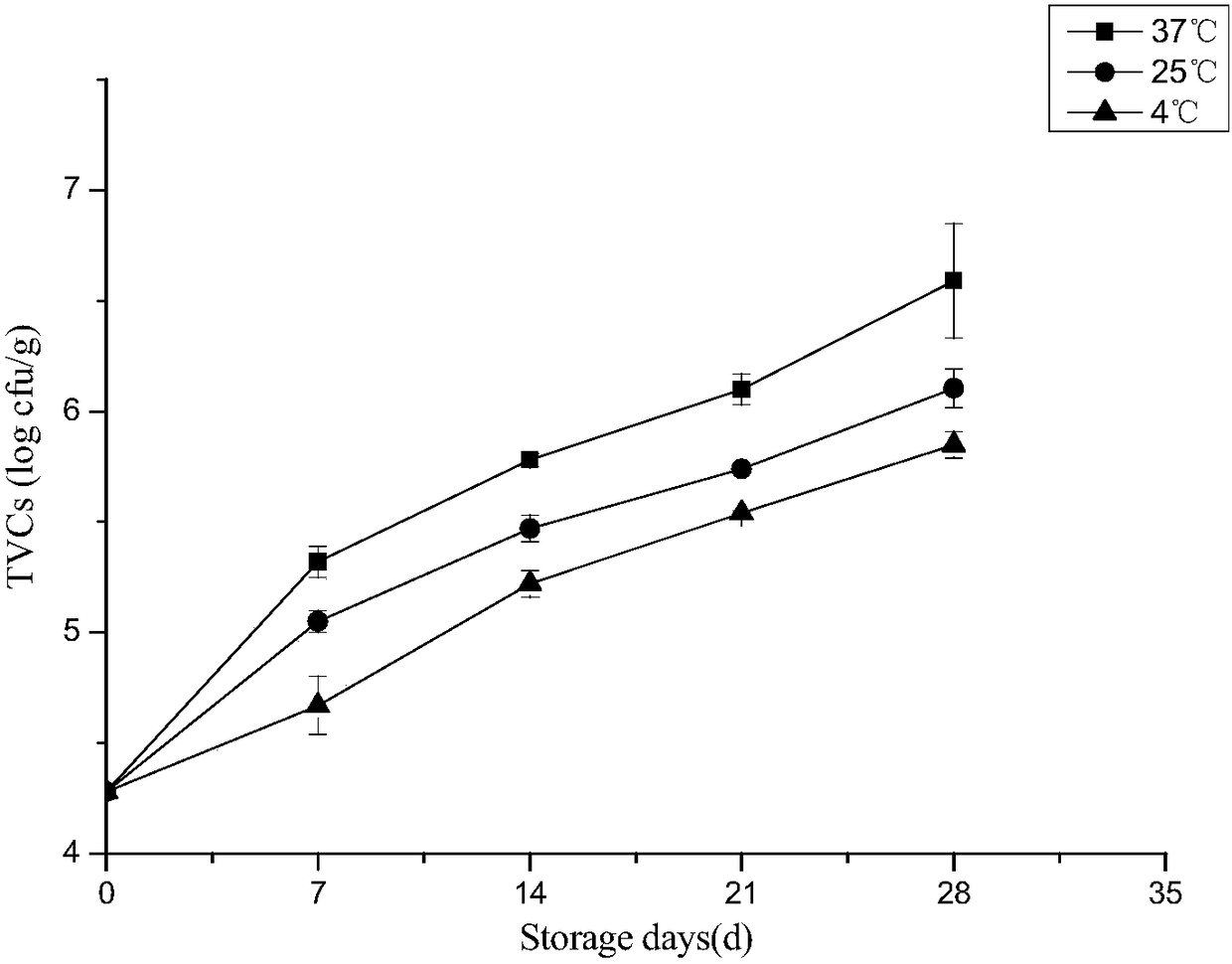
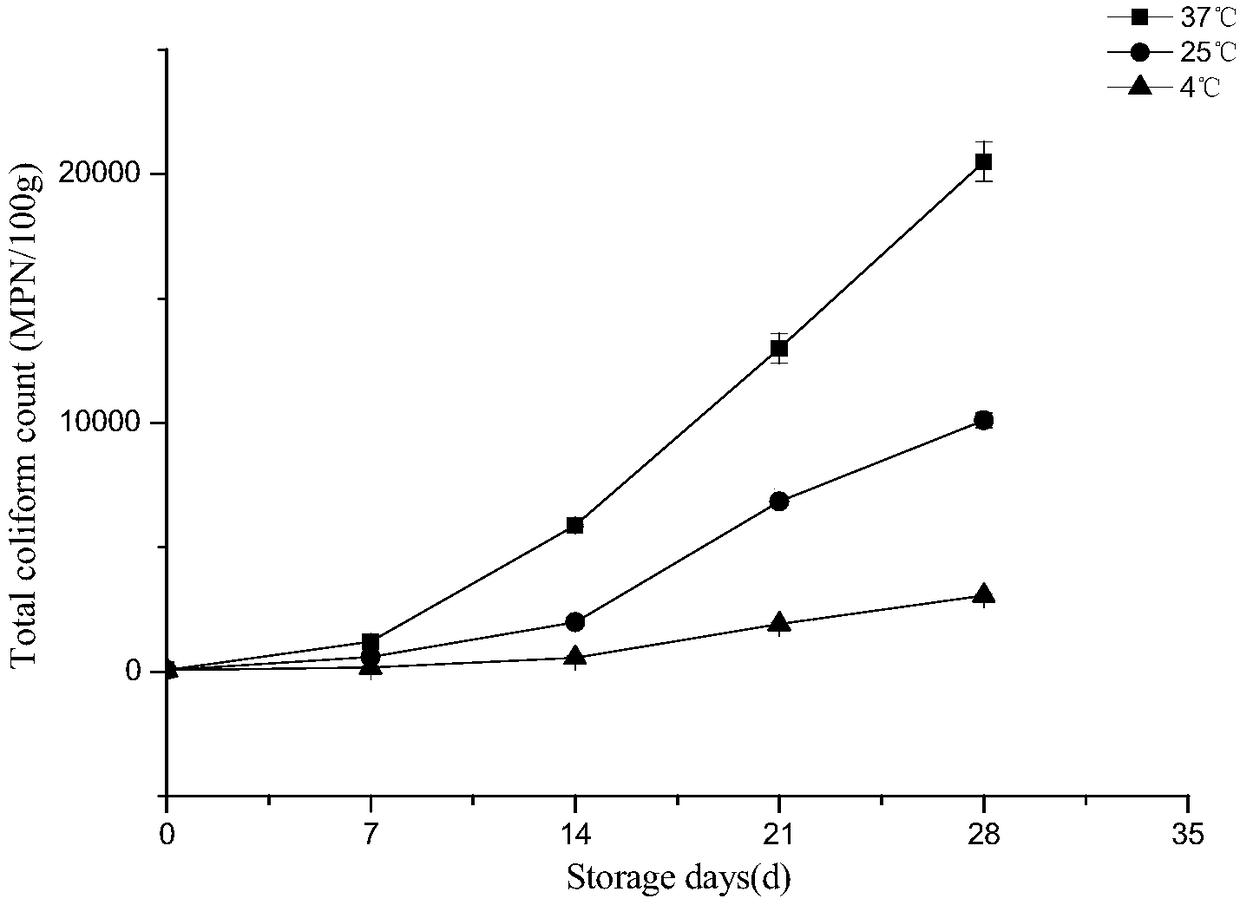
The invention discloses a method of predicting shelf life of sauce ducks. Quality indexes of sauce-duck products stored under different temperatures are studied, a kinetic model of sauce-duck qualitychanges is determined through determining, by measurement, laws of changes of total colony numbers of the sauce ducks, escherichia coli, mould, acid values, peroxide values, thiobarbituric acid reactive substances (TBARS) and sensory quality with time, then quality change key-indexes of the mould and the TBARS in a sauce-duck storage period are screened out according to Pearson correlation analysis, and the change laws accord with a zero-order kinetic-model. An Arrhenius equation is combined to establish a shelf-life prediction model of the sauce ducks according to mould and TBARS values of the sauce-duck quality indexes. According to the method, remaining shelf life of sauce ducks in a temperature range of 0-40 DEG C can be quickly and effectively predicted, guidance can be provided for storage, transportation and sales processes to facilitate correspondingly processing sauce-duck products of different freshness in time, and costs can be saved.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV OF TECH
Method for calculating thickness of oxide film of martensite heat-resistant steel under supercritical high-temperature steam
ActiveCN111161806AGuaranteed safe operationEasy to calculateMeasurement devicesChemical processes analysis/designPipeMartensite
The invention relates to a method for calculating the thickness of an oxide film of martensitic heat-resistant steel under supercritical high-temperature steam. The method is particularly suitable for9% Cr martensitic heat-resistant steel. According to the method, a parabola model of metal oxidation kinetics is utilized; mathematical correction is carried out on the Arrhenius equation on the basis of the parabola model; a large number of actual operation results of a power plant and simulation experiment data are comprehensively taken into consideration; an oxide film thickness calculation formula of the 9% Cr martensitic heat-resistant steel in a high-temperature steam environment with a temperature of 23-35MPa is obtained by using a step-by-step linear fitting method and a function curve fitting method; and according to the formula, the influence of time and temperature on the thickness of the oxide film is comprehensively taken into consideration, and the thickness of the oxide film of the 9% Cr martensite heat-resistant steel under the condition can be calculated by substituting steam temperature and running time into the formula. The formula breaks through the limitation thatmost oxidation kinetic models only consider the influence of a single factor, and overcomes the defects that traditional oxide skin thickness measurement method is long in test period, high in cost,complex in operation and unstable in precision, or need to cut a steel pipe and the like.
Owner:GUODIAN SCI & TECH RES INST +1
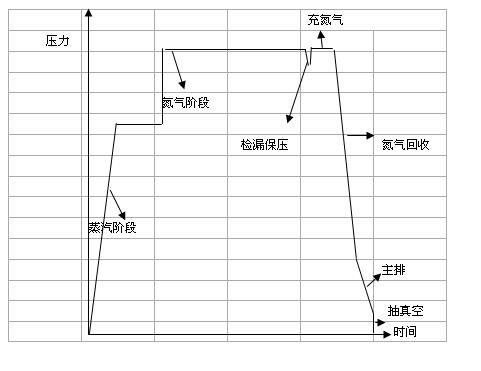
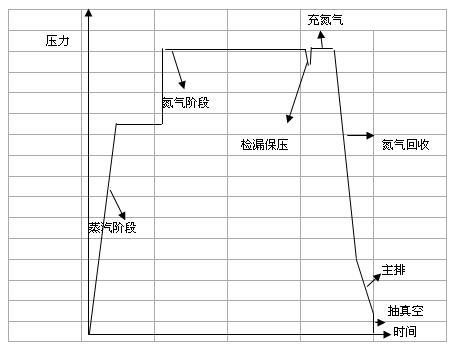
Method for rubber vulcanization of semisteel tire
The invention discloses a method for rubber vulcanization of a semisteel tire. The method comprises the steps of: a, filling saturated steam for 1.5minutes, and filling saturated steam with the temperature being 206-214 DEG C and the pressure being 1.7-1.9Mpa into a vulcanized bag; b, filling saturated steam according to the specification of the tire, and calculating the proper steam filling time by utilizing the Arrhenius equation according to the tire temperature data measured by a thermocouple; c, filling nitrogen with the temperature being 15-35 DEG C and the pressure being 2.4-2.6Mpa according to the specification of the tire; d, detecting the leakage and retaining the pressure for 1minute, releasing the tire normally if the initial pressure of the nitrogen in the vulcanized bag is 2.4-2.6Mpa and is more than 2.3Mpa after 1minute, abandoning the tire after the vulcanization is completed if the pressure is less than 2.0Mpa, and conducting the nitrogen filling step and automatic delay vulcanization if the pressure is between 2.0 Mpa and 2.3Mpa; e, filling nitrogen for 1minute; f, recovering the nitrogen for 0.3minute; g, discharging the residual mixed water and steam, and the setting the steam discharging time as 0.1minute; and h, vacuuming the vulcanized bag for 0.4minute, and then demolding the vulcanized tire.
Owner:TRIANGLE TIRE
Sensorless relative humidity control in a fuel cell application
Owner:GM GLOBAL TECH OPERATIONS LLC
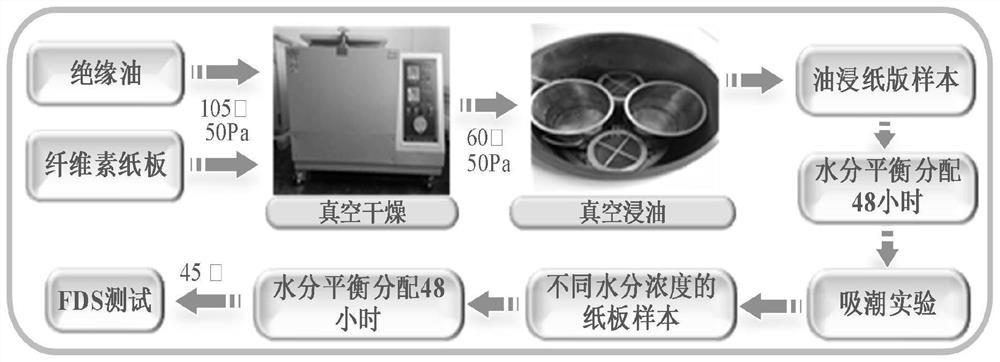
Bushing insulation oil paper temperature correction and activation energy prediction method based on dielectric modulus
ActiveCN112883536AHelp identify potential risksGuaranteed uptimeDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsDielectricEngineering
The invention relates to the technical field of electrical equipment fault diagnosis, and discloses a bushing insulation oil paper temperature correction and activation energy prediction method based on dielectric modulus, comprising the following steps: obtaining an expression of a dielectric model M (omega); preparing experimental samples with different moisture contents, and performing frequency domain dielectric spectrum testing on the samples at different temperatures to obtain an FDS curve corresponding to a complex dielectric constant; converting the FDS curve corresponding to the complex dielectric constant imaginary part to obtain an FDS curve corresponding to M ''(omega); positioning the peak frequency fp of the FDS curve corresponding to the M "(omega) by using a least square method, and obtaining the change rule of the fp along with the temperature and the moisture; defining a translation factor, and obtaining a rule that the translation factor changes along with temperature and moisture; introducing a classical Arrhenius equation into activation energy calculation, and obtaining an activation energy calculation formula related to the translation factor; and establishing an activation energy prediction model. According to the invention, the influence of temperature and moisture in the oil-paper insulation system on activation energy is considered, and the method is of great significance to aging evaluation of on-site bushings.
Owner:GUANGXI UNIV
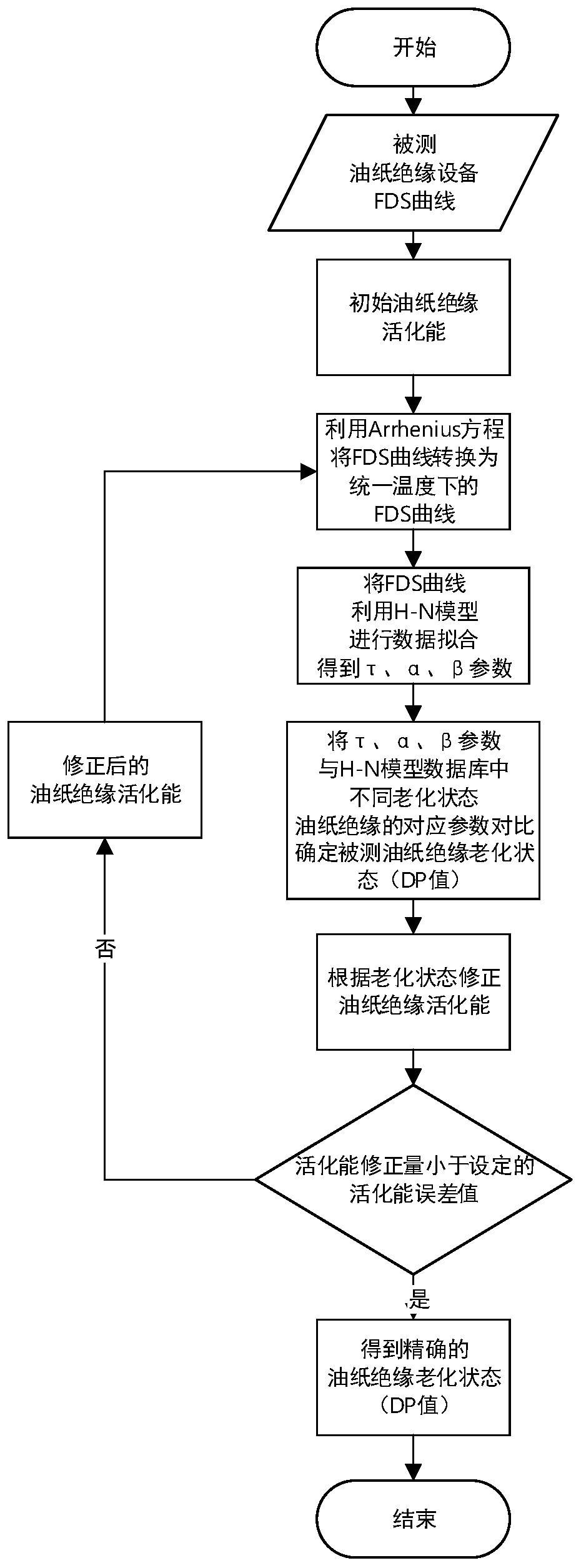
Oil paper insulation aging state evaluation method and system based on activation energy iterative correction
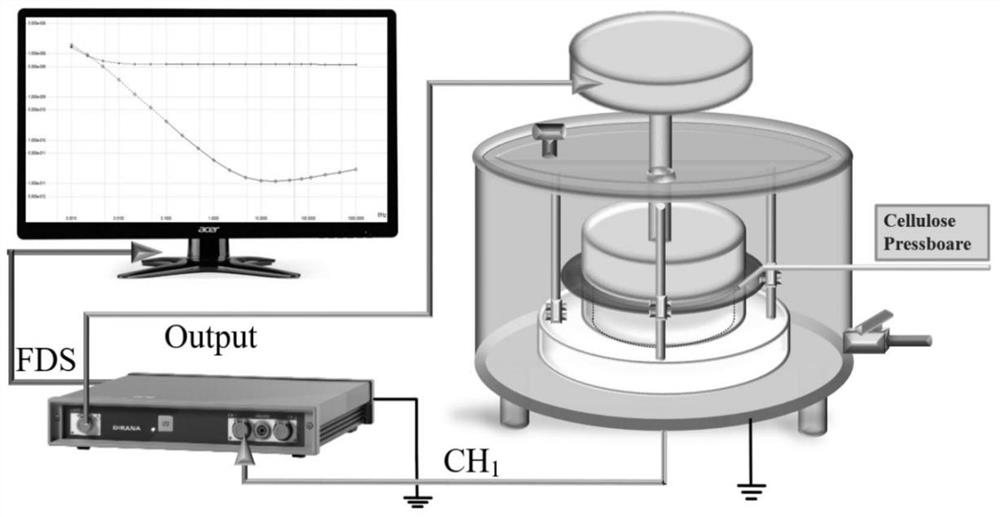
ActiveCN109870635AStandardization of aging state assessment processHigh precisionTesting dielectric strengthDielectricSpectral curve
The invention discloses an oil paper insulation aging state evaluation method and system based on activation energy iterative correction. By utilizing an iterative algorithm, activation energy is continuously corrected in an oil paper insulation aging state evaluation iteration process, so that the activation energy error is reduced and the accuracy of a temperature normalization process is improved. The method comprises the steps of carrying out temperature normalization processing on a frequency domain dielectric spectral curve of tested oil paper insulation equipment by utilizing an Arrhenius equation; carrying out curve fitting on the frequency domain dielectric spectral curve subjected to the temperature normalization processing and an H-N model to obtain characteristic parameters tau, alpha and beta of the H-N model; and matching the characteristic parameters with a database of oil paper insulation H-N models with different aging states to determine an oil paper insulation agingstate. An evaluation result has relatively high accuracy and reliability.
Owner:STATE GRID SHAANXI ELECTRIC POWER RES INST +2
Method for accurately forecasting quality change of quickly-frozen lotus root slices
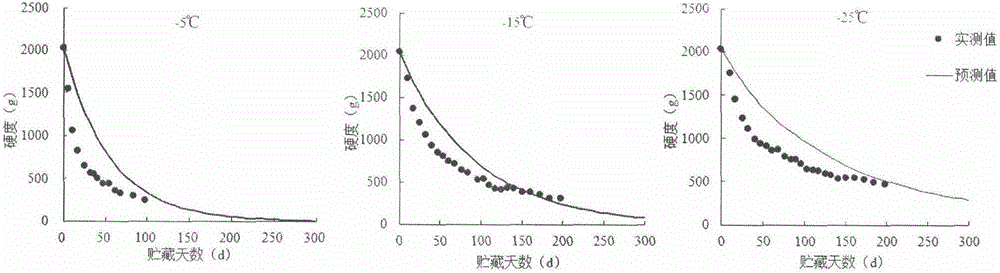
InactiveCN106093324AAccurate prediction of quality changesTesting starch susbtancesChemical analysis using titrationHardnessBusiness forecasting
The invention discloses a method for accurately forecasting the quality change of quickly-frozen lotus root slices, and belongs to the field of agricultural product processing and storage. According to the method, respective quality change kinetic models are constructed according to the change-with-time rules of the VC, the color and the hardness of the quickly-frozen lotus root slices under different temperature storage conditions (-5 DEG C, -15 DEG C and -25 DEG C); all indexes are fitted by adopting the Arrhenius equation, thus determining quality change forecasting models of the quickly-frozen lotus root slices, i.e.: FORMULA I and FORMULA II respectively, wherein f(t) represents a quality index value of a sample at the time t, f(t0) represents an initial quality index value of the sample, t represents the storage duration (d), and T represents the absolute temperature (K). An experiment shows that the relative errors between actually measured values and forecast values of each index at different temperatures are less than 8 percent, and the accuracy is higher; furthermore, the relevant coefficients are all greater than 0.9, and the relevancy is good. The models can accurately forecast the quality of the quickly-frozen lotus root slices in a storage process, so that a basis is provided for actual production and application.
Owner:JIANGSU ACADEMY OF AGRICULTURAL SCIENCES
Method for improving shelf life of saltwater-freshwater bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation
InactiveCN103952308AExtended shelf lifeKeep activeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFresh water organismMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method for improving shelf life of a saltwater-freshwater bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation. The method comprises the following steps: preparing the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation; mixing the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation with a protection agent belonging to different kinds and / or with different concentration, so as to obtain a mixed solution; placing the mixed solution at different temperature to perform accelerated testing; sampling regularly, and detecting the live bacteria concentration of the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation in the mixed solution; and utilizing Arrhenius equation and recorded data to calculate out the shelf life of the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation, and determining the effect of the protection agent by comparing the shelf life. According to the method, by comparing the quality-guaranteeing effect of different protection agents on the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation, a protection agent with best quality-guaranteeing effect is screened out, and the shelf life of the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation is obviously prolonged; and also the activity of thalline in the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation can be effectively kept for a long time. The provided protection agent is wide in raw material selection scope and cheap in price, and is suitable for popularization and usage.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
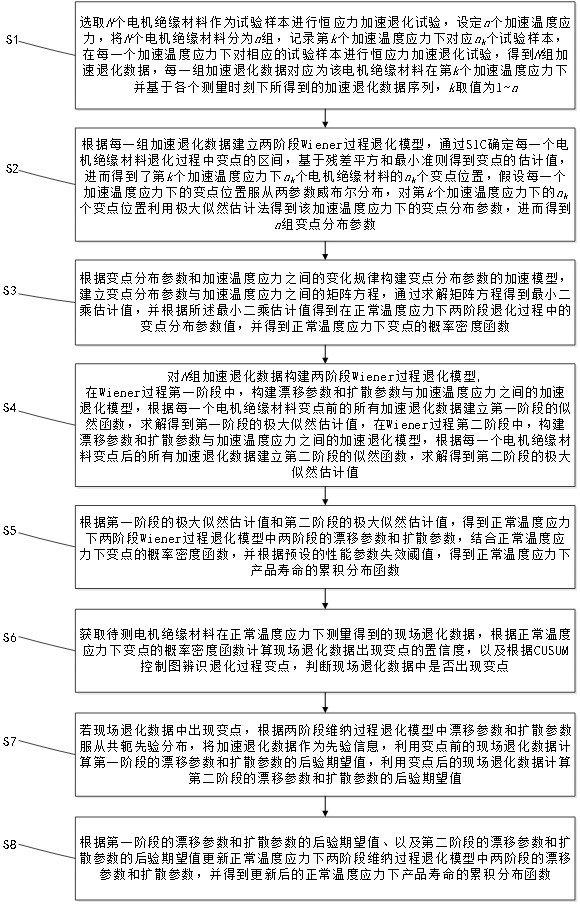
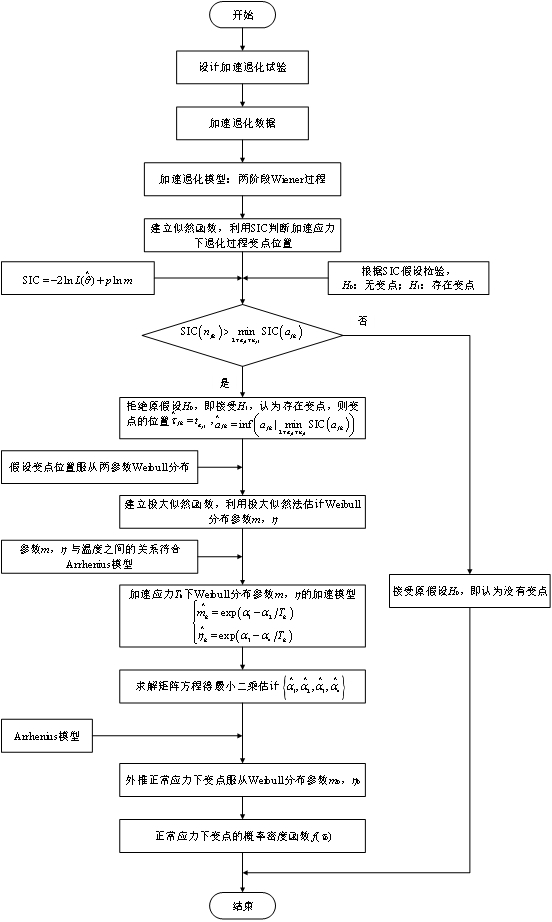
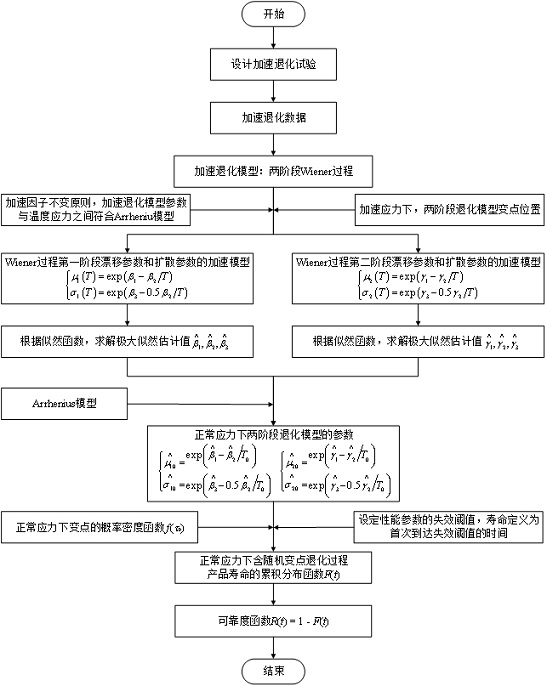
Life prediction method fusing field data and two-stage accelerated degradation data
ActiveCN114091790AAchieve Life PredictionImprove test efficiencyForecastingDesign optimisation/simulationMotor insulationArrhenius equation
The invention discloses a life prediction method fusing field data and two-stage accelerated degradation data, and the method comprises the steps: determining a transformation point position of a degradation process according to the accelerated degradation data of a motor insulation material test sample under different thermal stresses through SIC and a residual sum of squares minimum criterion; constructing a motor insulation performance degradation model based on a two-stage random process under the action of thermal stress, obtaining a relationship between a model parameter and a change point distribution parameter and a temperature according to an Arrhenius equation, and extrapolating a probability density function and a model parameter of a change point position of a product in a degradation process at a normal temperature; utilizing on-site degradation data of a to-be-tested motor insulating material, using a CUSUM control chart for identifying a change point, and determining the probability of occurrence of the change point in combination with a probability density function of the change point; and taking the accelerated degradation data as prior information of model parameters, obtaining a posterior estimation value of the model parameters based on a Bayes method according to the field degradation data, obtaining a cumulative distribution function of product life under the sense of first arrival time, and realizing real-time life prediction of motor insulation.
Owner:ZHEJIANG UNIV
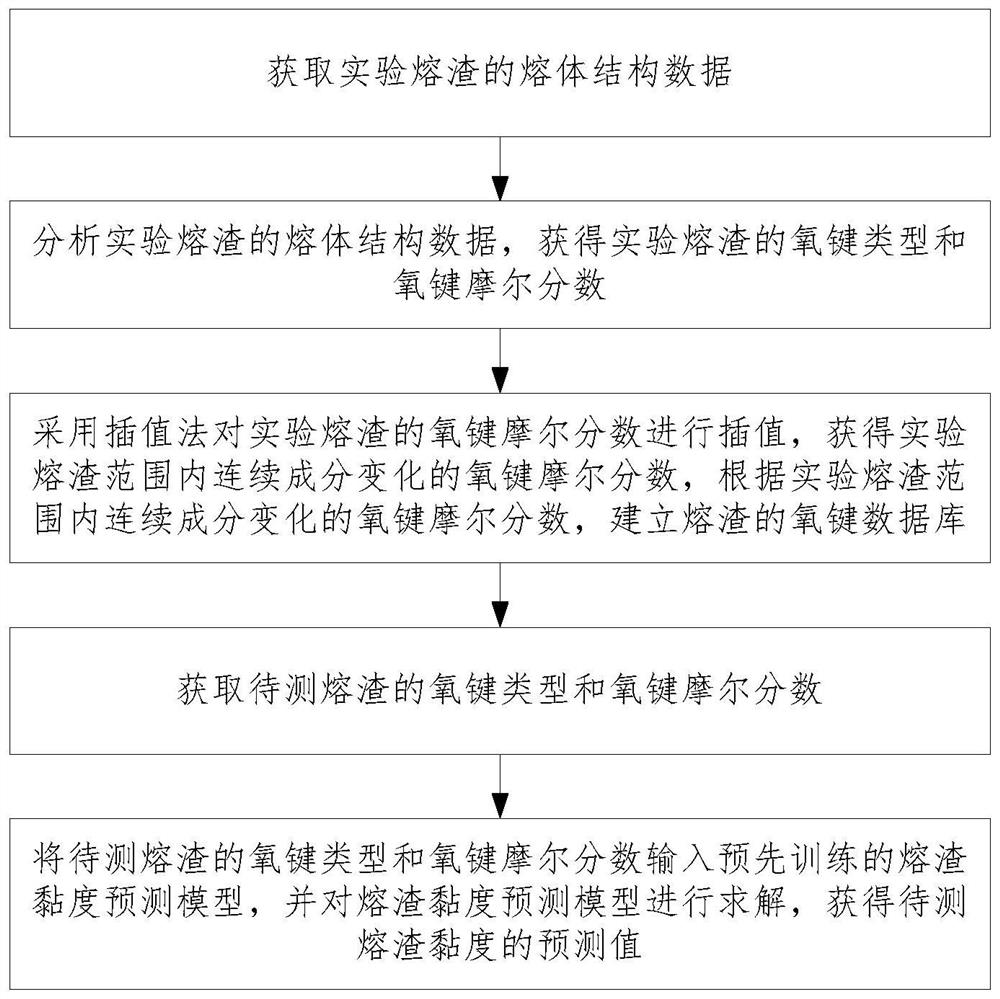
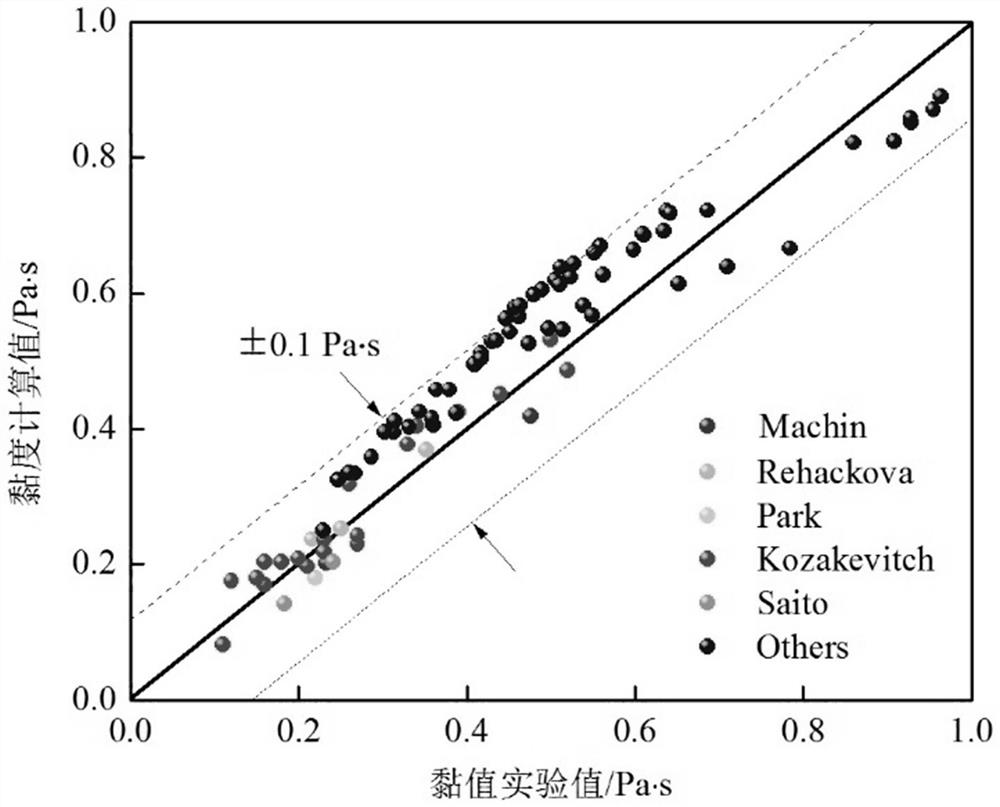
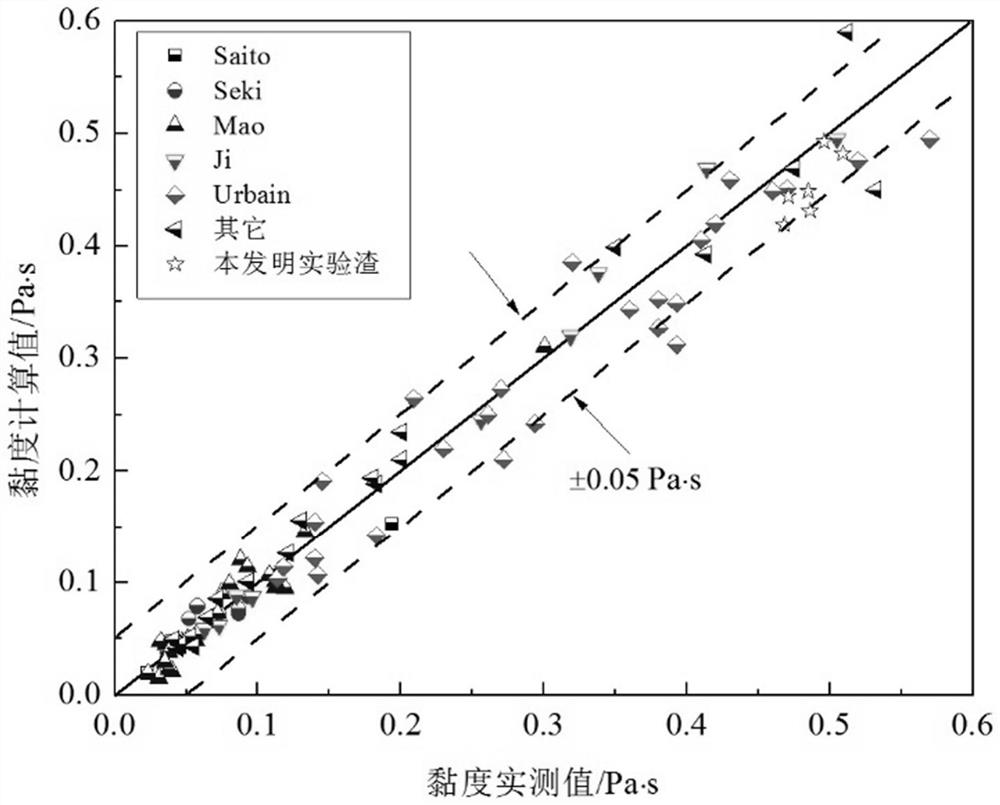
Molten slag viscosity prediction method based on melt structure analysis
PendingCN112561182ASolution implementationViscosity Prediction RealizedFlow propertiesForecastingStructure analysisNetwork structure
The invention provides a molten slag viscosity prediction method based on melt structure analysis. The molten slag viscosity prediction method comprises the steps of S1, obtaining the oxygen bond typeand the oxygen bond mole fraction of molten slag to be measured; s2, inputting the oxygen bond type and the oxygen bond molar fraction into a pre-trained molten slag viscosity prediction model, and solving the molten slag viscosity prediction model to obtain a predicted value of the viscosity of the molten slag to be measured, wherein the molten slag viscosity prediction model comprises a moltenslag viscosity prediction equation constructed by considering a flow mechanism of a silicate network structure and combining an oxygen bond type and an oxygen bond molar fraction of molten slag according to an Arrhenius equation. The applicability is wide, and the prediction precision and stability of the slag viscosity are improved.
Owner:NORTHEASTERN UNIV
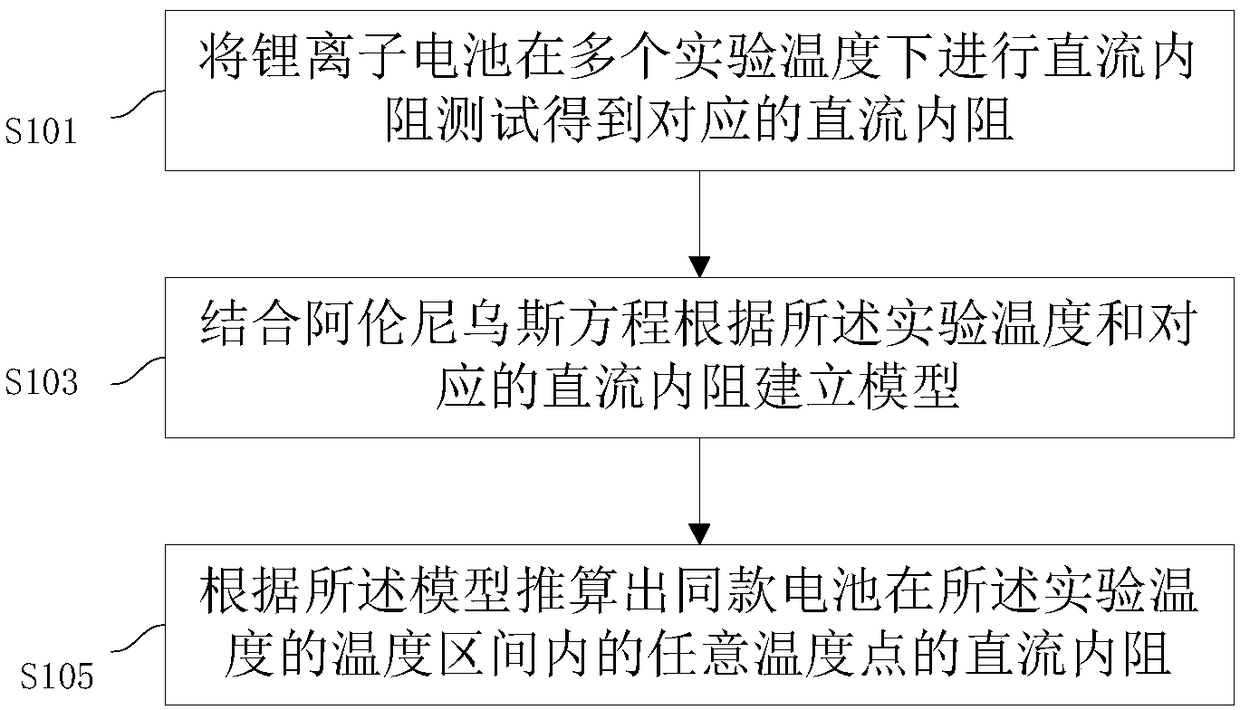
Calculation method and system for direct-current internal resistance of lithium-ion battery
The invention discloses a calculation method and system for the direct-current internal resistance of a lithium-ion battery which are used for solving the problem that only several limited points of the internal resistance temperature of a battery can be tested in the prior art. The calculation method comprises the steps that the lithium-ion battery is subjected to direct-current internal resistance test at multiple experimental temperatures to obtain corresponding direct-current internal resistance; by combining with an Arrhenius equation, a model is established according to the experimentaltemperatures and the corresponding direct-current internal resistance; and the direct-current internal resistance of the same type of battery at any temperature point in the temperature interval of the experimental temperatures is calculated according to the model. By establishing the model of the temperature and the direct-current internal resistance, a direct-current internal resistance value atany temperature point can be tested, and practicability is high.
Owner:台州钱江新能源研究院有限公司
Method for evaluating aging degree of basin-type insulator
InactiveCN109142422AAging degree reflectsReliable assessmentMaterial thermal analysisBiologyArrhenius equation
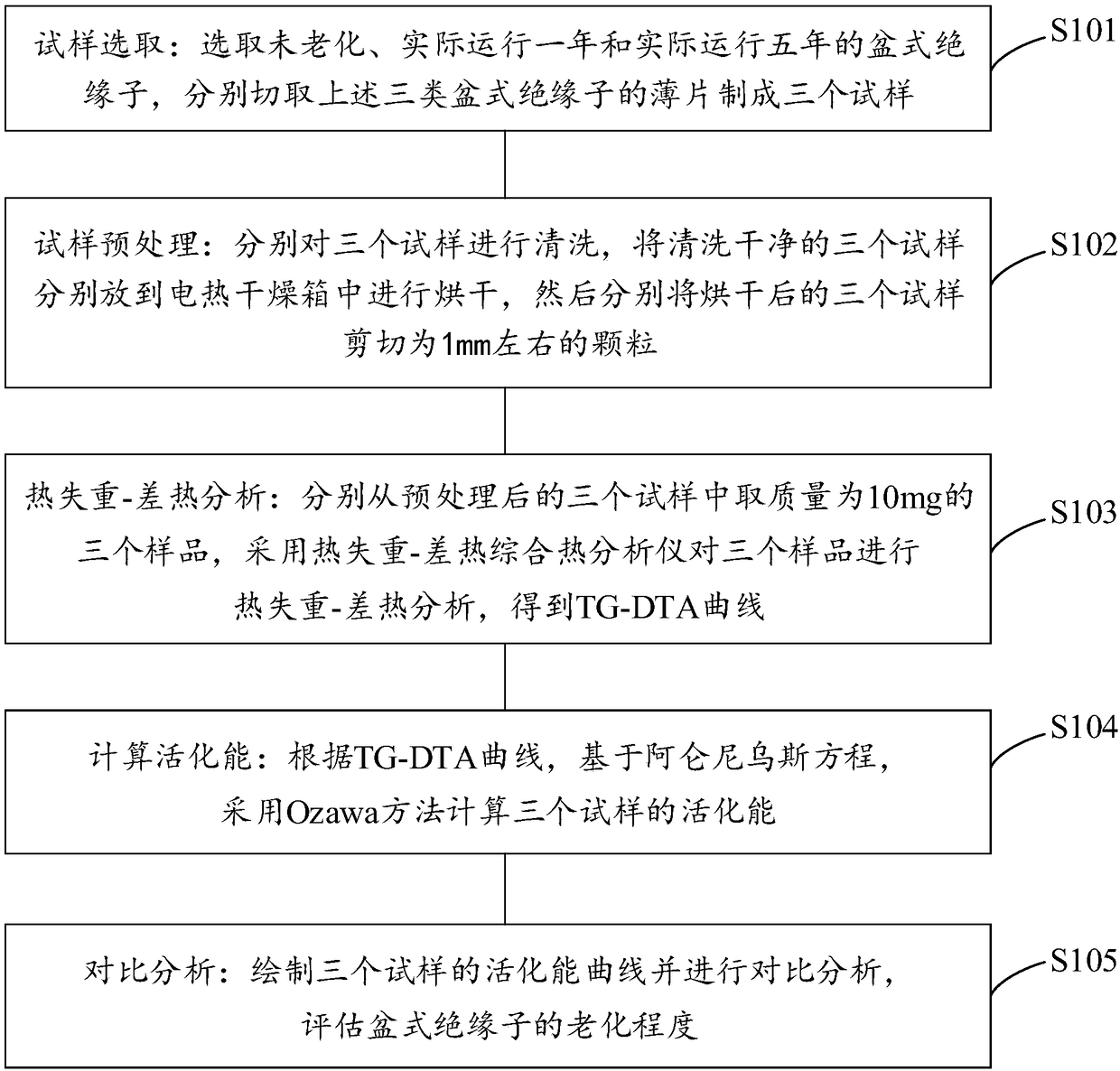
The invention discloses a method for evaluating the aging degree of a basin-type insulator. The method comprises the following steps: sample selecting: selecting un-aged insulators, insulators runningfor one year and insulators running for five years, selecting three samples from the three types of basin-type insulators respectively; sample pretreating: washing and drying the three samples respectively; thermal weight loss-differential thermal analysis: using a thermal weight loss-differential thermal comprehensive thermal analyzer to carry out thermal weight loss-differential thermal analysis on the three pretreated samples respectively to obtain a TG-DTA curve. Activation energy calculating: according to the TG-DTA curve, using an Ozawa method to calculate the activation energy of the three samples based on the Arrhenius equation; comparing and analyzing: plotting the activation energy curves of the three samples and carrying out comparison and analysis to evaluate the aging degreeof the basin-type insulators. According to the embodiment of the invention, the aging degree of the basin-type insulators can be directly reflected, and the aging degree of the basin-type insulators can be accurately and reliably evaluated.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RESEARCH INSTITUTE, CHINA SOUTHERN POWER GRID CO LTD +2
Fresh-cut lettuce shelf life prediction model
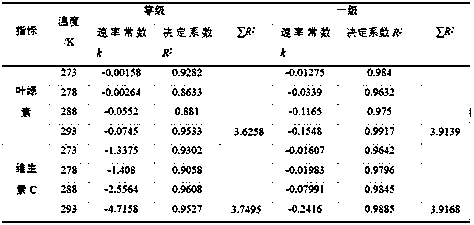
PendingCN108982883APrediction and Validation AccuracyDetect quality changesDesign optimisation/simulationBiological testingVitamin CArrhenius equation
The invention provides a fresh-cut lettuce shelf life prediction model. According to the fresh-cut lettuce shelf life prediction model, the changes of the content of vitamin C and the content of chlorophyll of the fresh-cut lettuce at different temperatures caused along with the extension of the storage time are studied, modeling is carried out on the vitamin C and the chlorophyll separately by utilizing an Arrhenius equation, and the obtained shelf life prediction model comprises a chlorophyll content shelf life prediction model body: SLchlo=ln(C / C0) / (-1.16*10<14>*e<(-83100 / 8.314T)>) and a vitamin C content shelf life prediction model body: SLvc=ln(V / V0) / (-2.39*10<15>*e<(-90300 / 8.314T)>); and the accuracy of the prediction model bodies is verified separately with a shelf life measured value at 283 K temperature, the predicted values and relative errors of the two shelf life model bodies are compared, modeling is carried out by taking the vitamin C as the characteristic index, and therefore the shelf life of the fresh-cut lettuce within the temperature range of 0-20 DEG C can be monitored in real time.
Owner:SHANGHAI OCEAN UNIV
A method for predicting that storage life of a data product
PendingCN109359375AIncrease the amount of information availableImproving the Accuracy of Pseudo-Failure Life EstimationDesign optimisation/simulationSpecial data processing applicationsStress levelProduct base
A method for predict that storage life of a data product is provided. The accelerated degradation data of the product under various stress levels obtained from on-line and off-line tests. A storage life evaluation method of data products based on on-line data and off-line data is proposed. The pseudo-life of the data products under various accelerated stress levels is obtained by this method, andthe storage life of the data products under normal stress is evaluated by combining the temperature accelerated model. Making full use of on-line test data and adopting equivalent off-line performanceparameter data to effectively increase the amount of available information in the process of pseudo-failure life estimation and improve the precision of pseudo-failure life estimation. The temperature factor is introduced to transform the on-line test data into equivalent off-line data effectively, and the product life assessment can be completed more effectively by making full use of the data obtained from the test. The linear activation energy theory is introduced to make the selection of acceleration model more reasonable. The modified three-parameter Arrhenius equation is selected as acceleration model.
Owner:BEIJING INST OF STRUCTURE & ENVIRONMENT ENG +1
Leaf spring normal-temperature and high-temperature stress relaxation life predicting method
InactiveCN102650582BGuaranteed accuracyGuaranteed repeatabilityInvestigating material hardnessTemperature stressRoom temperature
The invention provides a leaf spring normal-temperature and high-temperature stress relaxation life predicting method. Firstly, a spring sample to be tested is prepared, and the prepared spring sample to be tested is an equal stress sample; then a test device is arranged, side plates are fixed at the front part and the rear part of a base of the test device, two ends of the sample are respectively arranged on the side plates, the base and an upper plate are fixed together through limiters, a pressure sensor is arranged on the upper plate, and a pressure head arranged at the lower end of the pressure sensor applies pressure on the sample; and then a spring stress relaxation experiment is carried out, stress values at different time are acquired to determine the stress relaxation loss condition of a sample material after the regulated experiment time is up, test data is selected according to failure criteria, the data is processed by an empirical formula and an Arrhenius equation, and finally the life of the sample at the normal temperature is determined. According to the method disclosed by the invention, sample bending deflection which is not easy to measure is converted into an electrical signal which is easy to measure, the work efficiency is improved, the method is simple, and the obtained life prediction result is accurate.
Owner:BEIHANG UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com