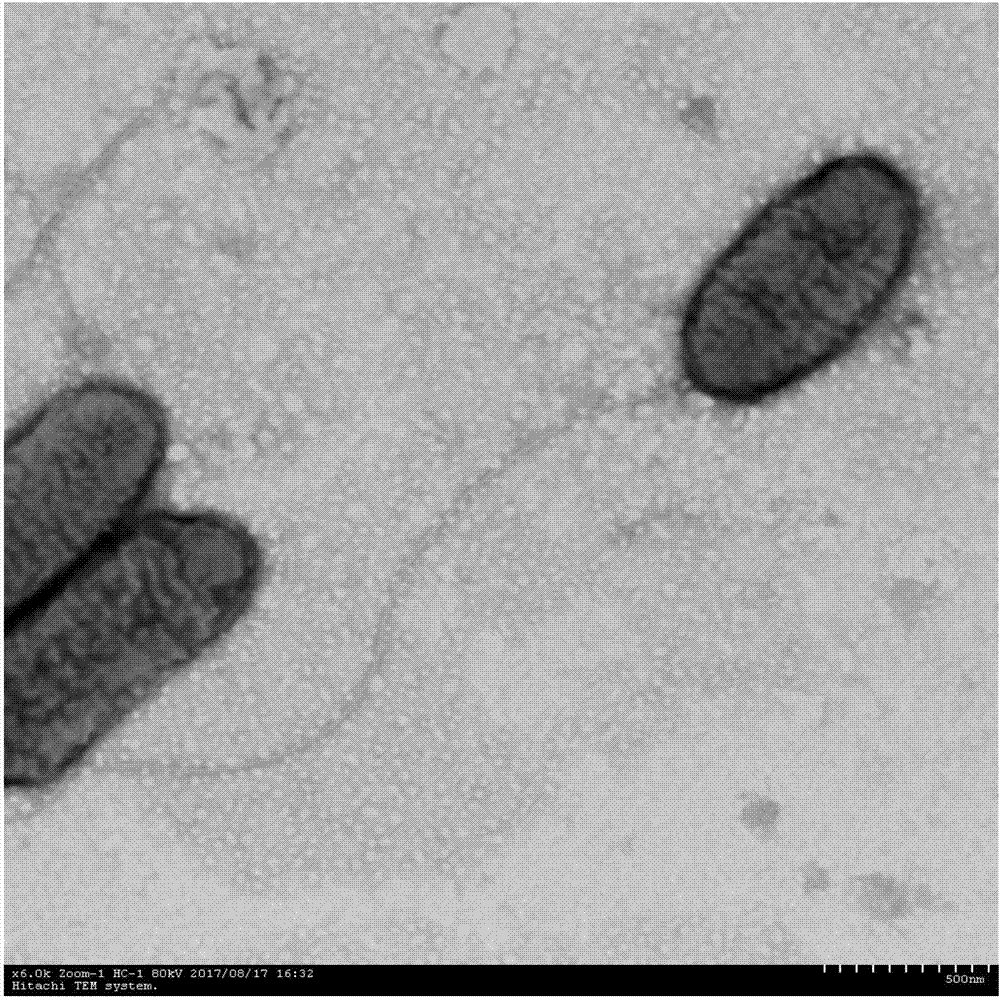
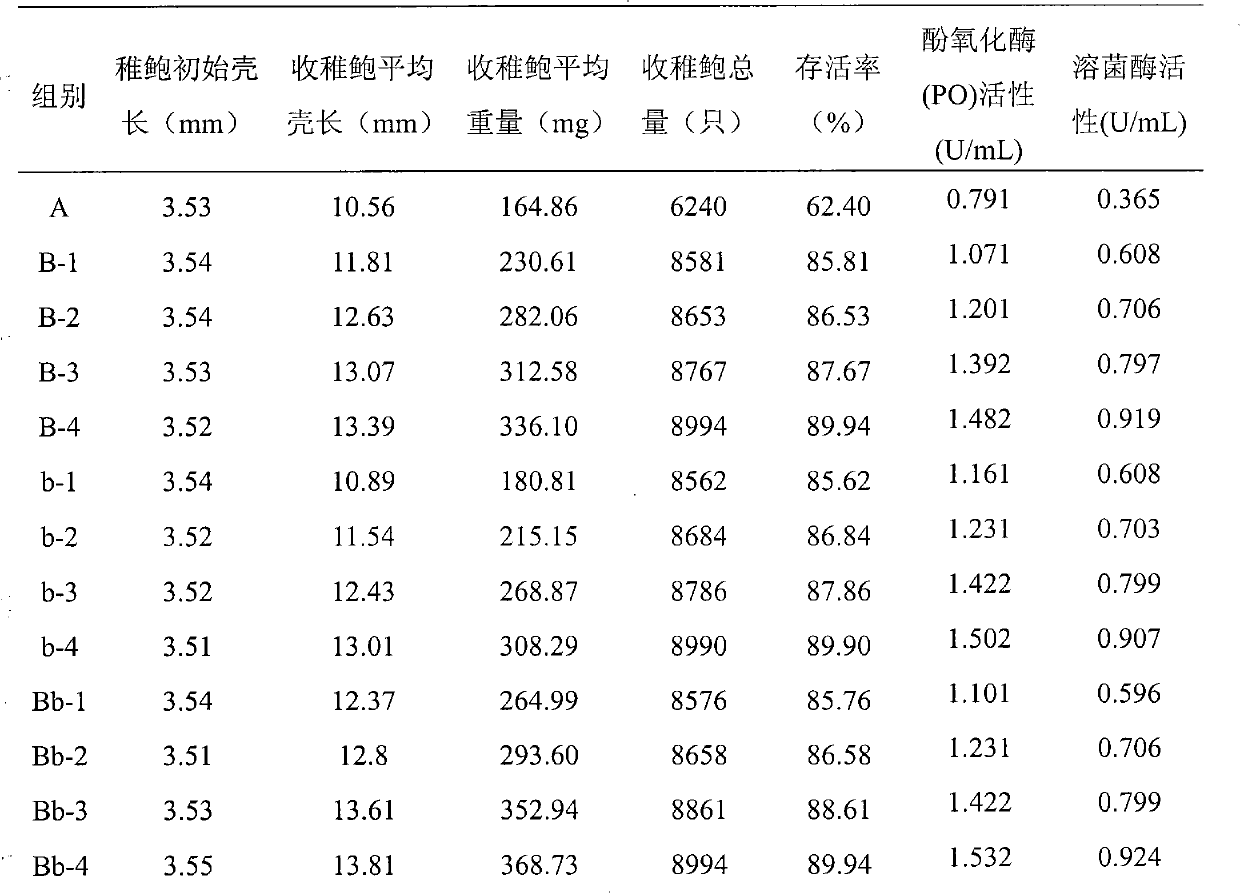
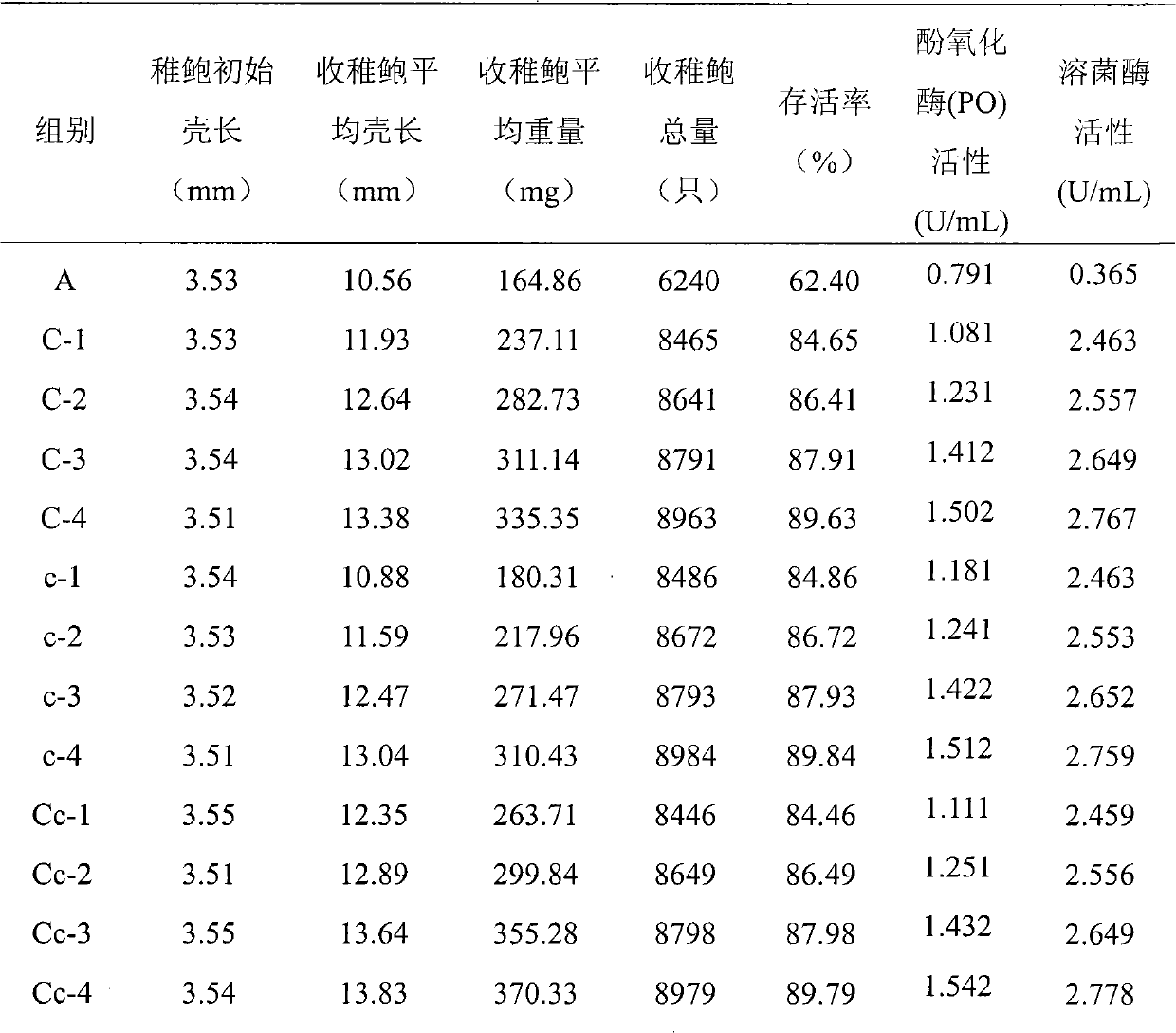
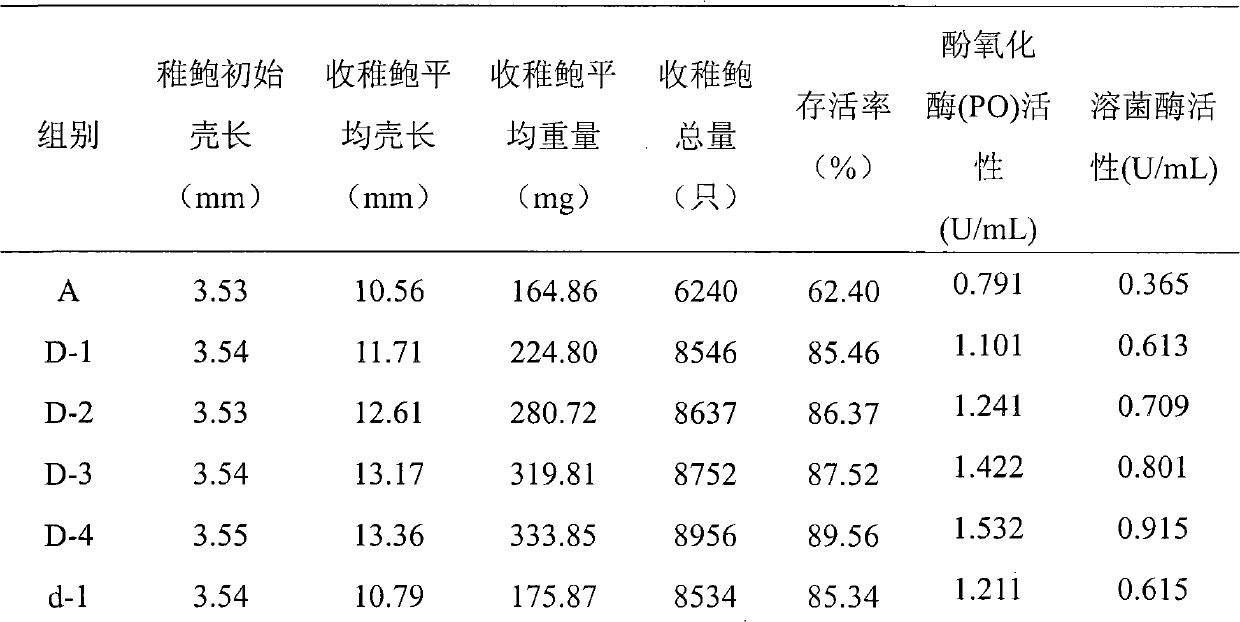
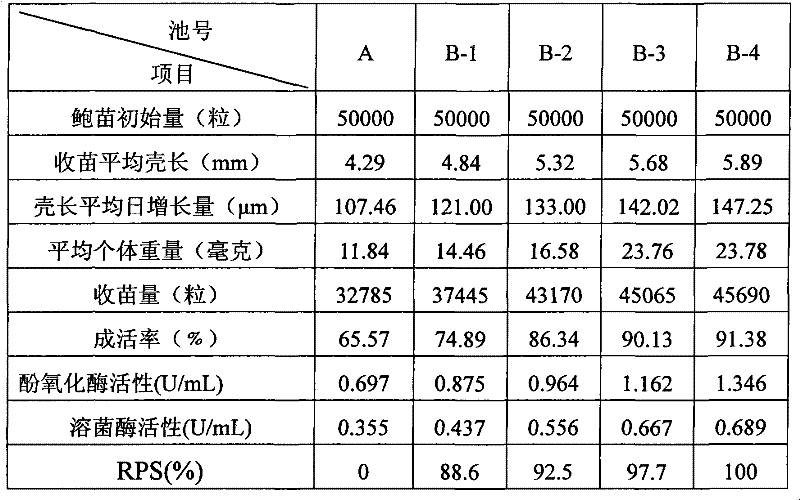
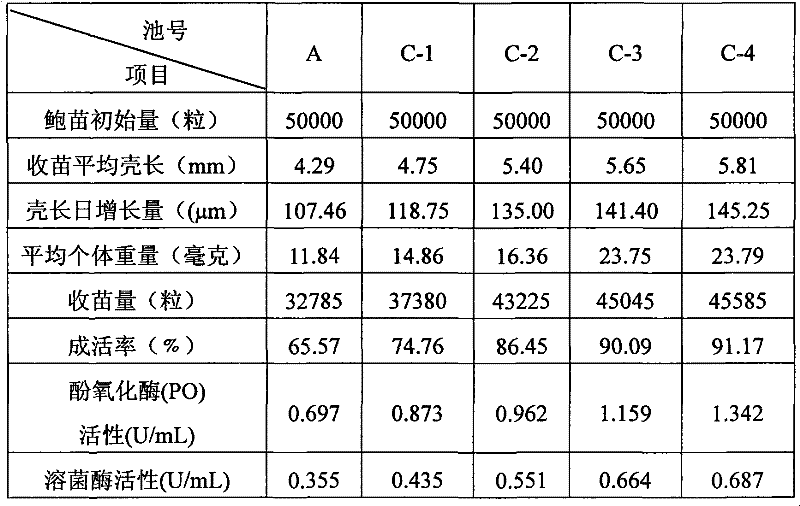
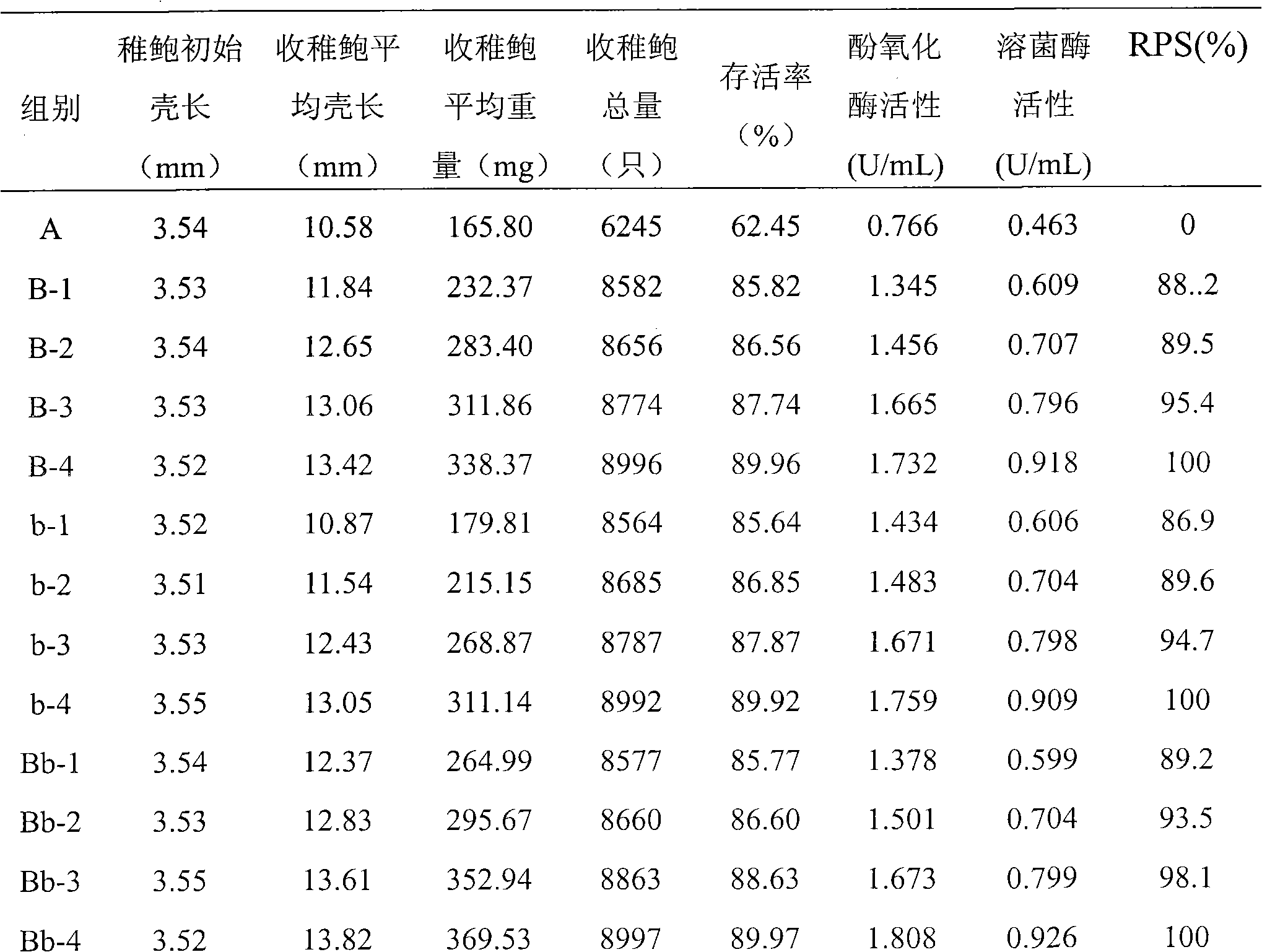
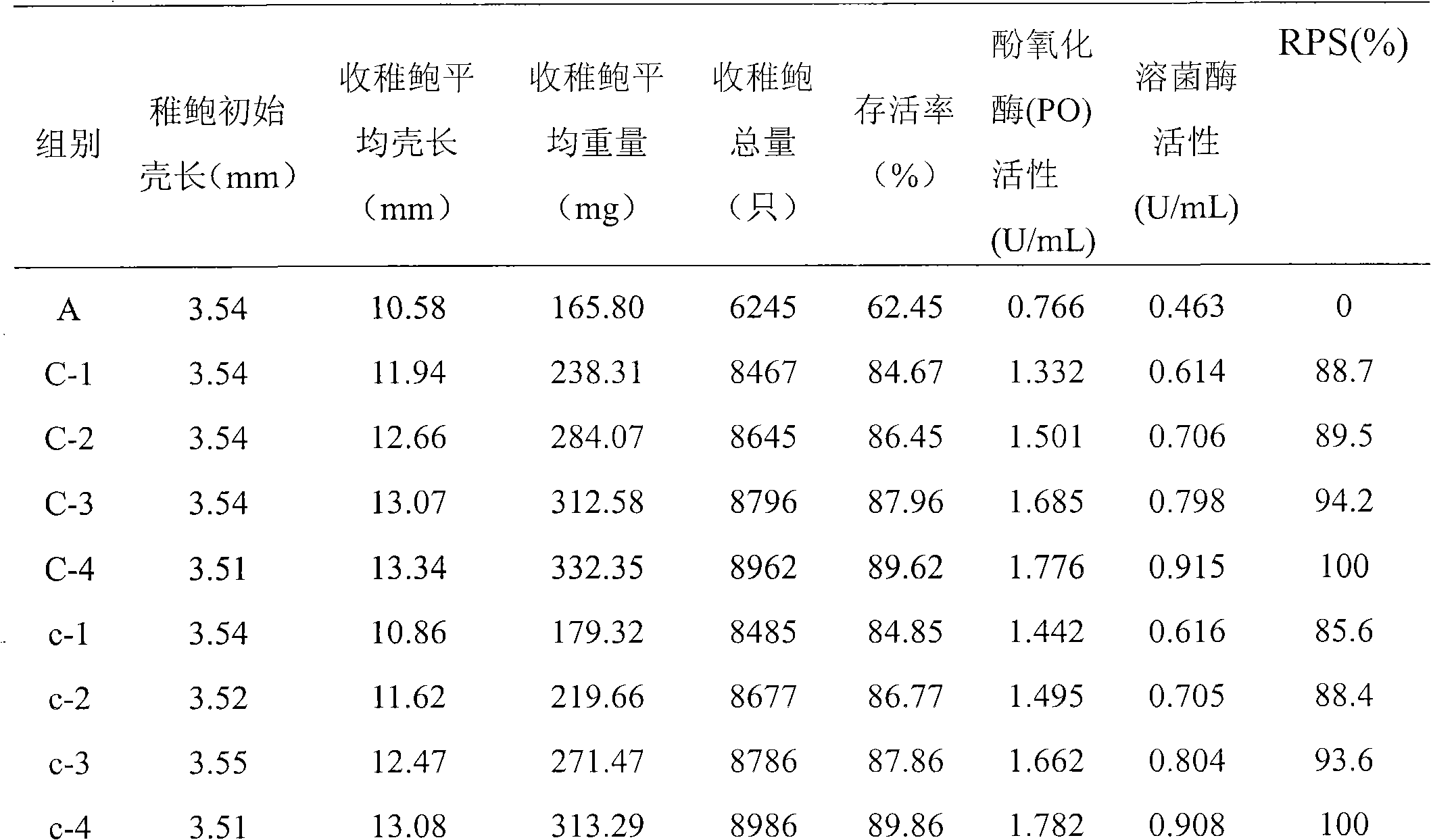
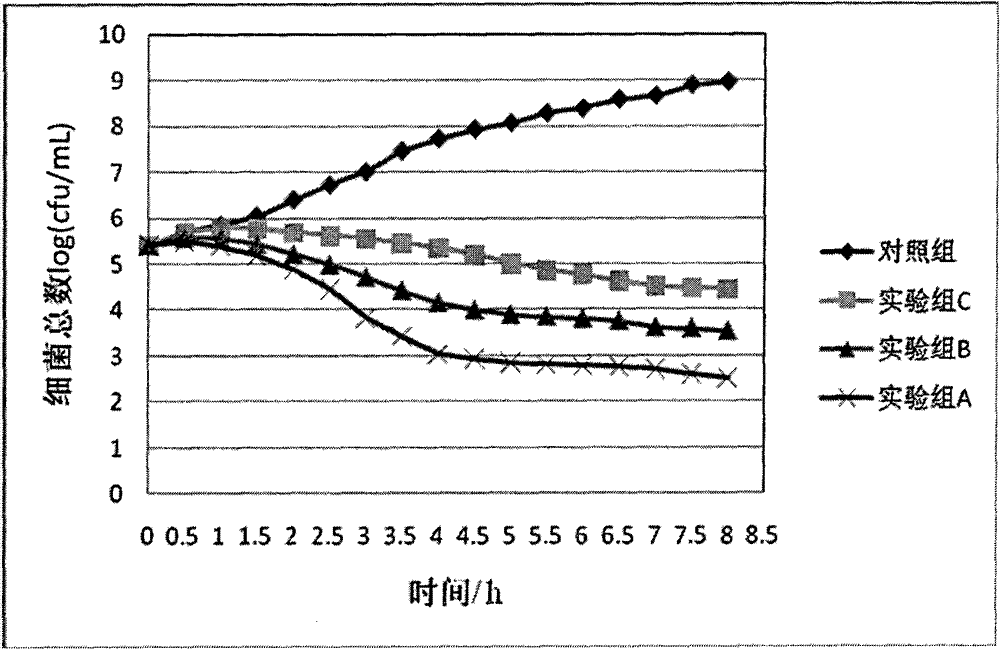
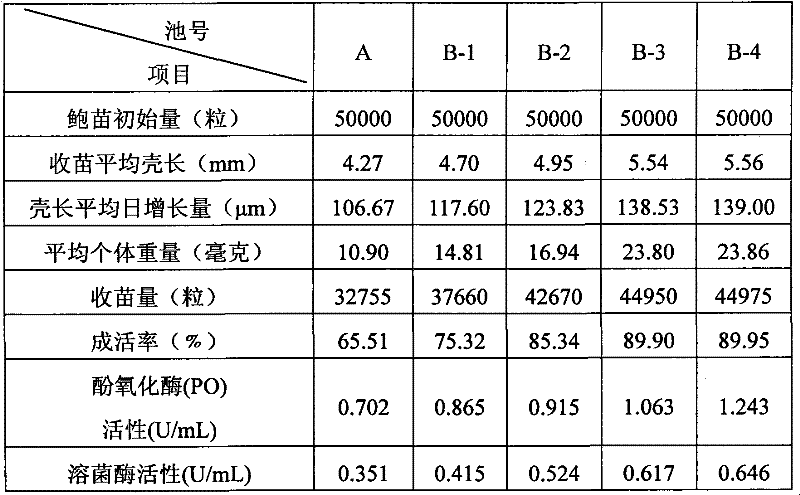
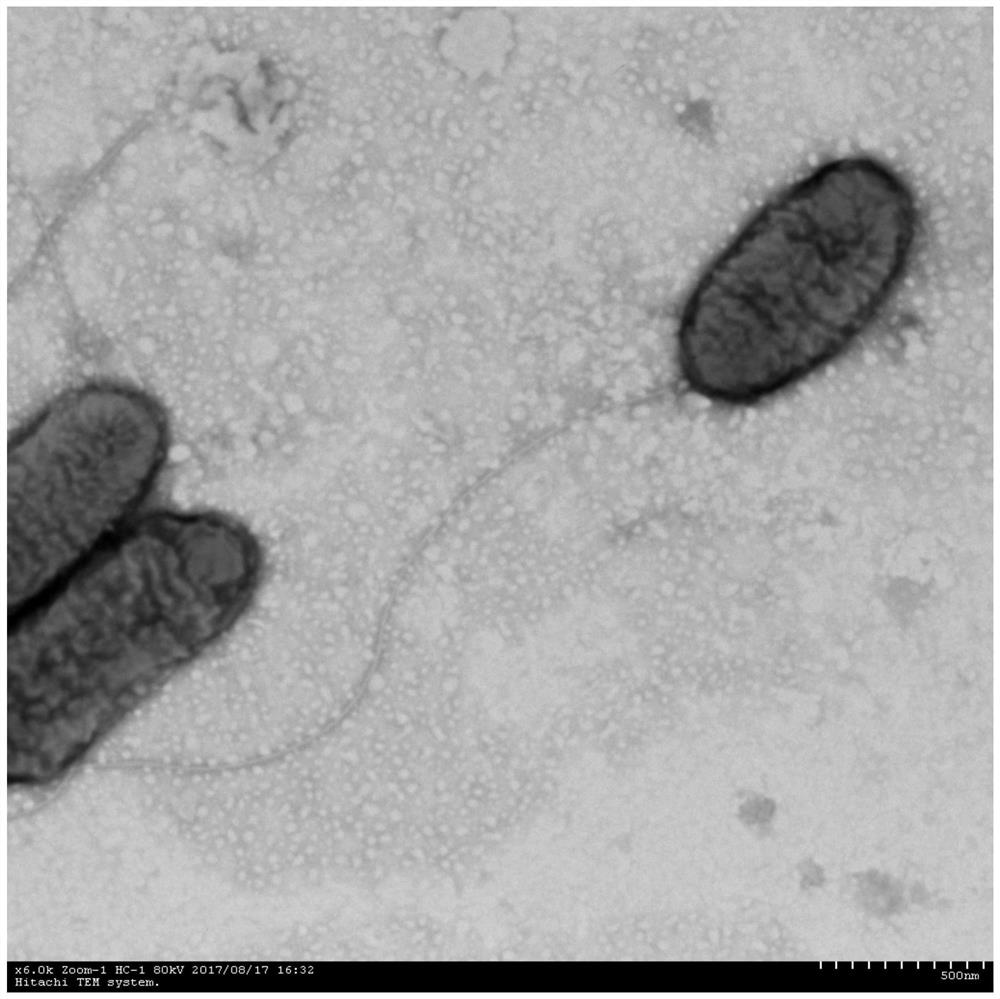
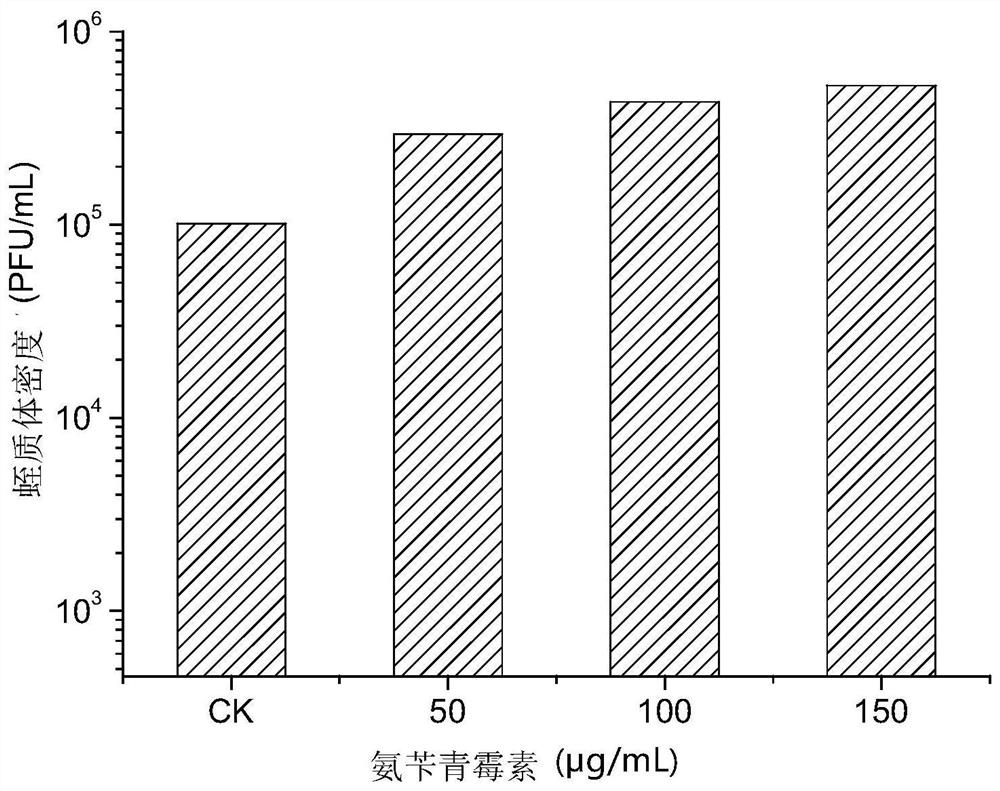
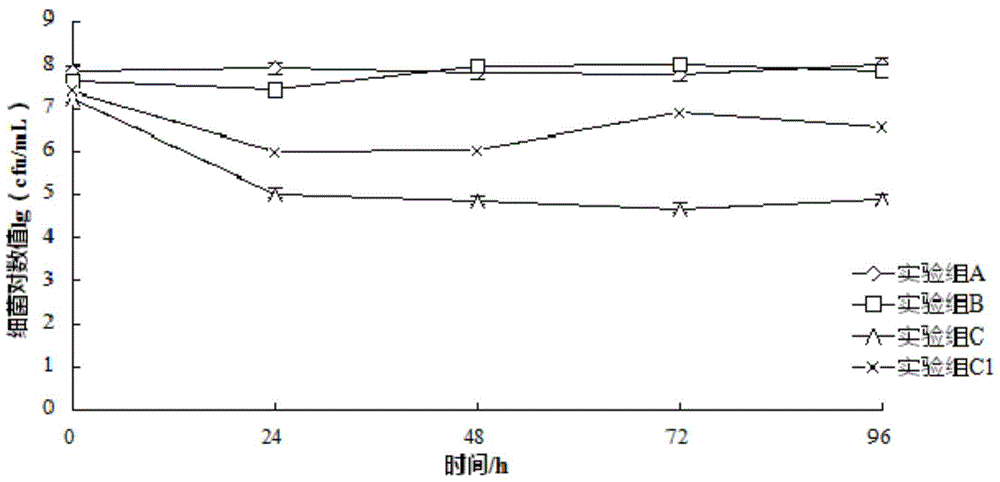
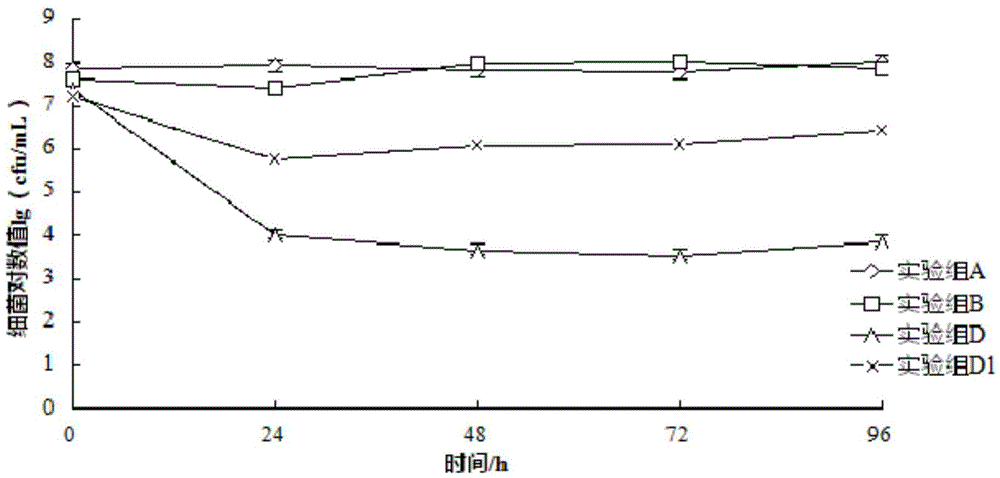
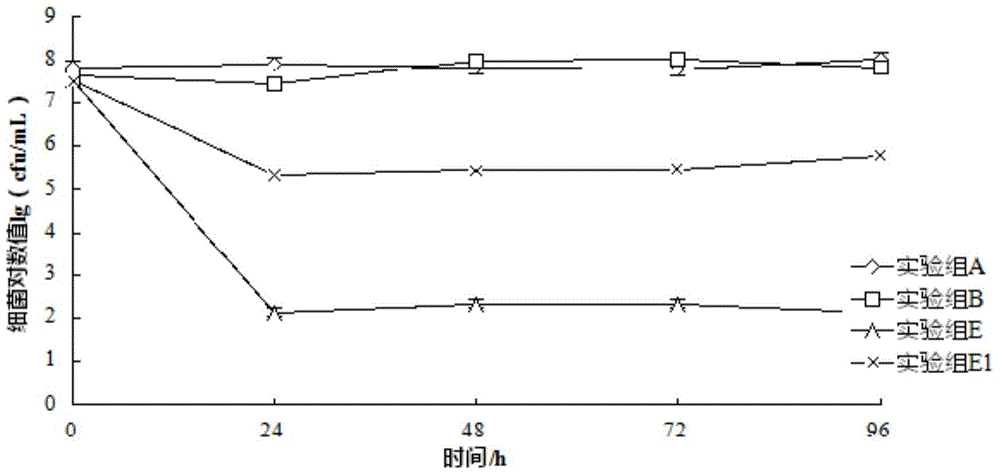
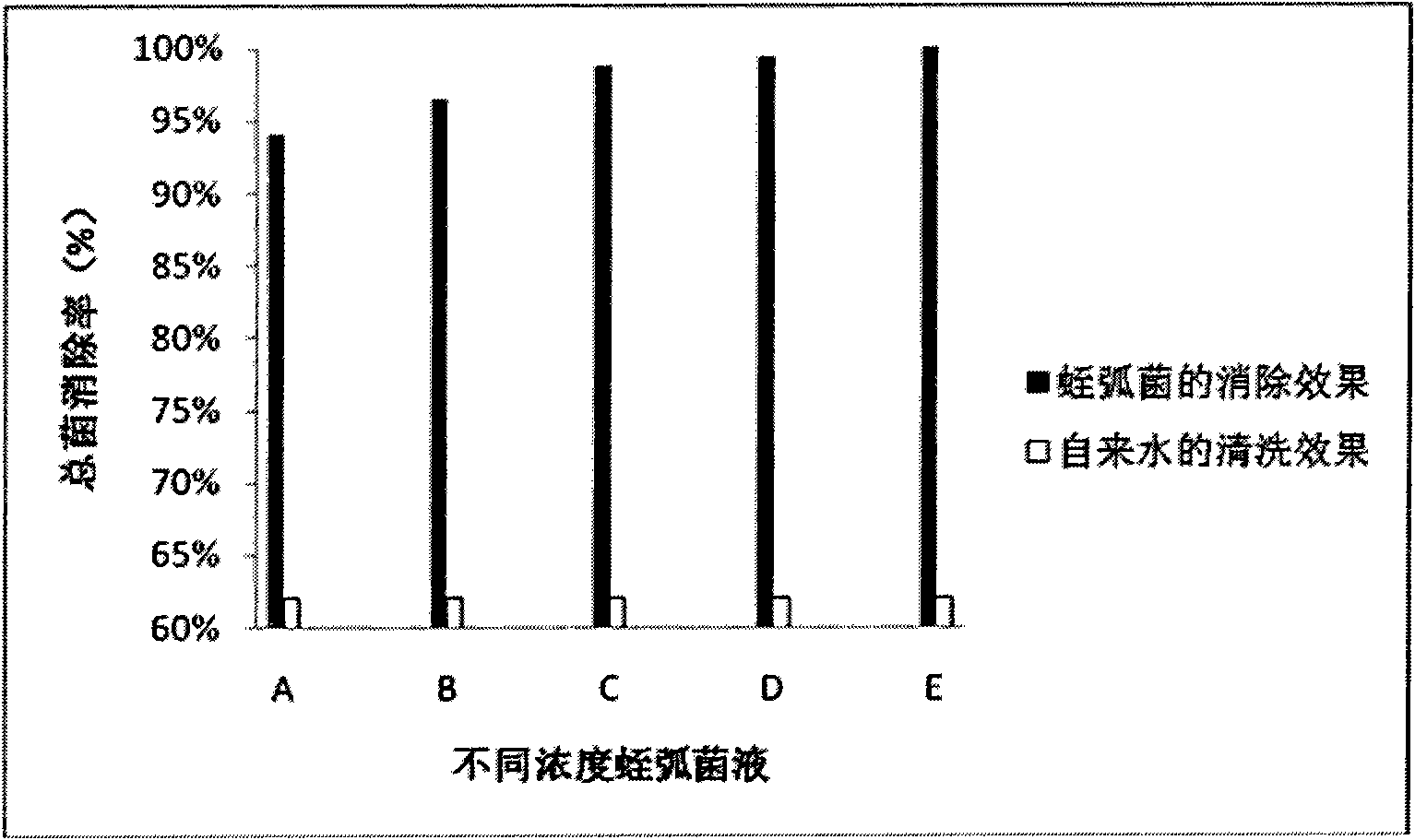
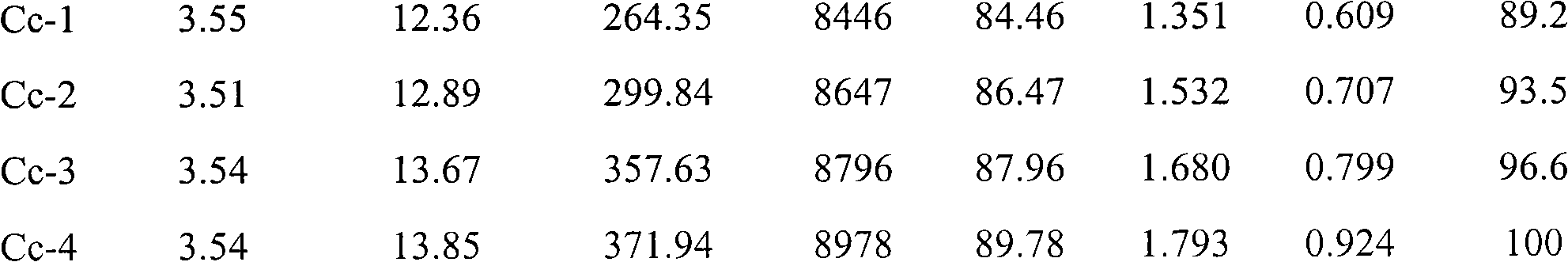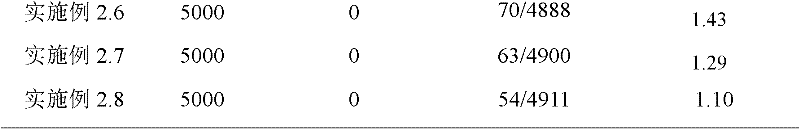Patents
Literature
46 results about "Bdellovibrio sp." patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
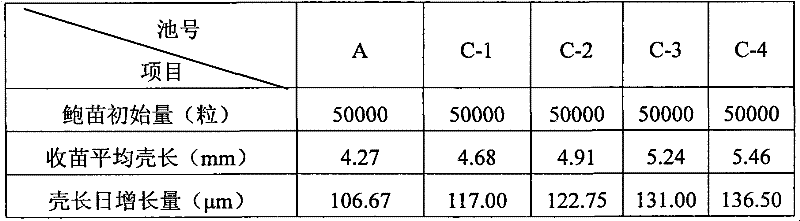
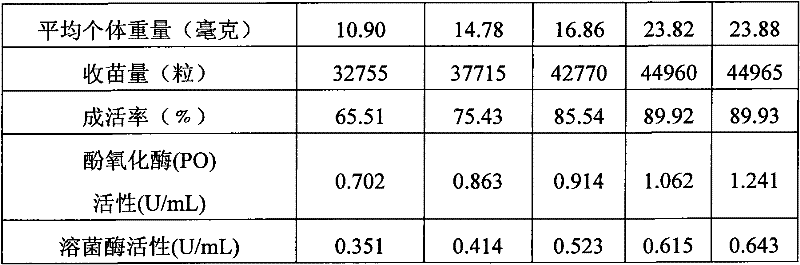
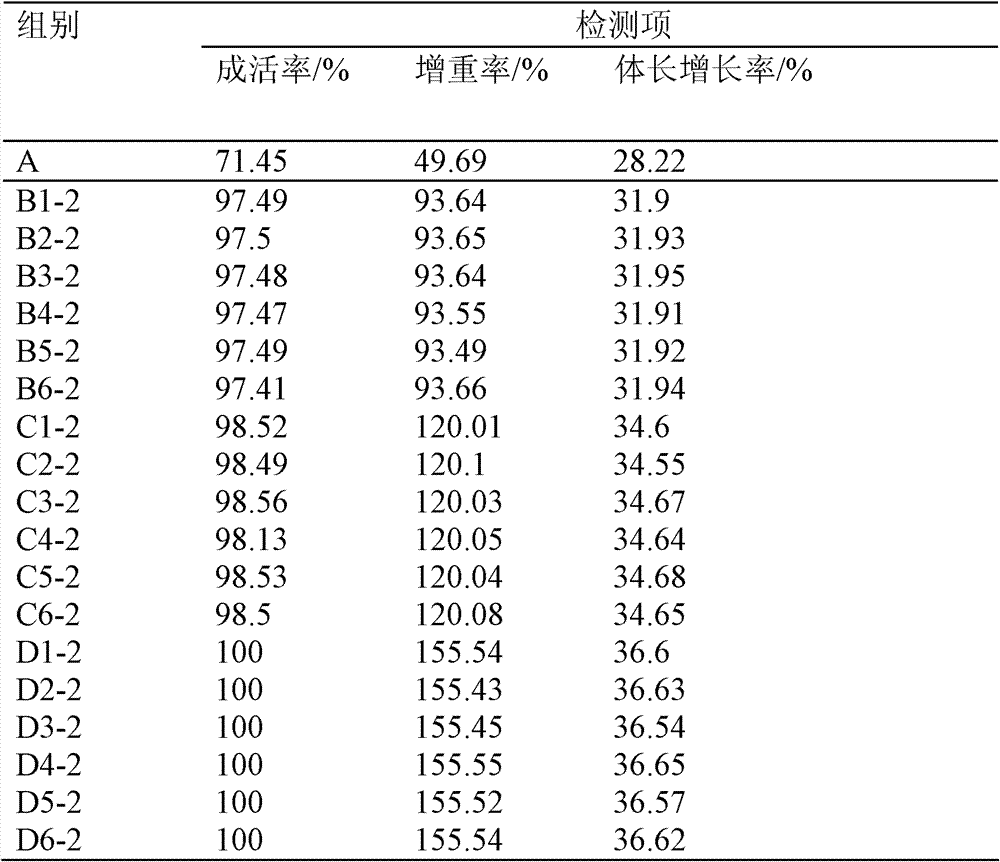
Phagocytosing type bacterium and application thereof in reducing sludge
ActiveCN105969690AImprove dehydration and weight loss performanceImprove biodegradabilityBacteriaSpecific water treatment objectivesMicroorganismEcological safety
The invention discloses a phagocytosing type bacterium. The phagocytosing type bacterium is identified to be a bdellovibrio organism, called bdellovibrio for short and classified and named as Bdellovibrio sp., the strain is preserved in the China General Microbiological Culture Collection Center on May 12th, 2016, and the preservation serial number is CGMCC No.11671. The invention further discloses application of the phagocytosing type bacterium in reducing sludge, and further discloses a bacterium extract. The strain is obtained through screening in sludge of a secondary sedimentation tank of a municipal wastewater treatment plant and meets the biosafety regulations; the strain serves as the phagocytosing type bacterium to be applied in sludge cell disruption dewatering, and the sludge dewatering and reducing performance is greatly improved by phagocytosing suspension bacteria and splitting sludge flocs, so that the operation cost of the wastewater treatment plant is reduced, both ecological safety and sanitary safety are considered, and the ecological civilization construction of the environment is promoted.
Owner:SOUTHEAST UNIV
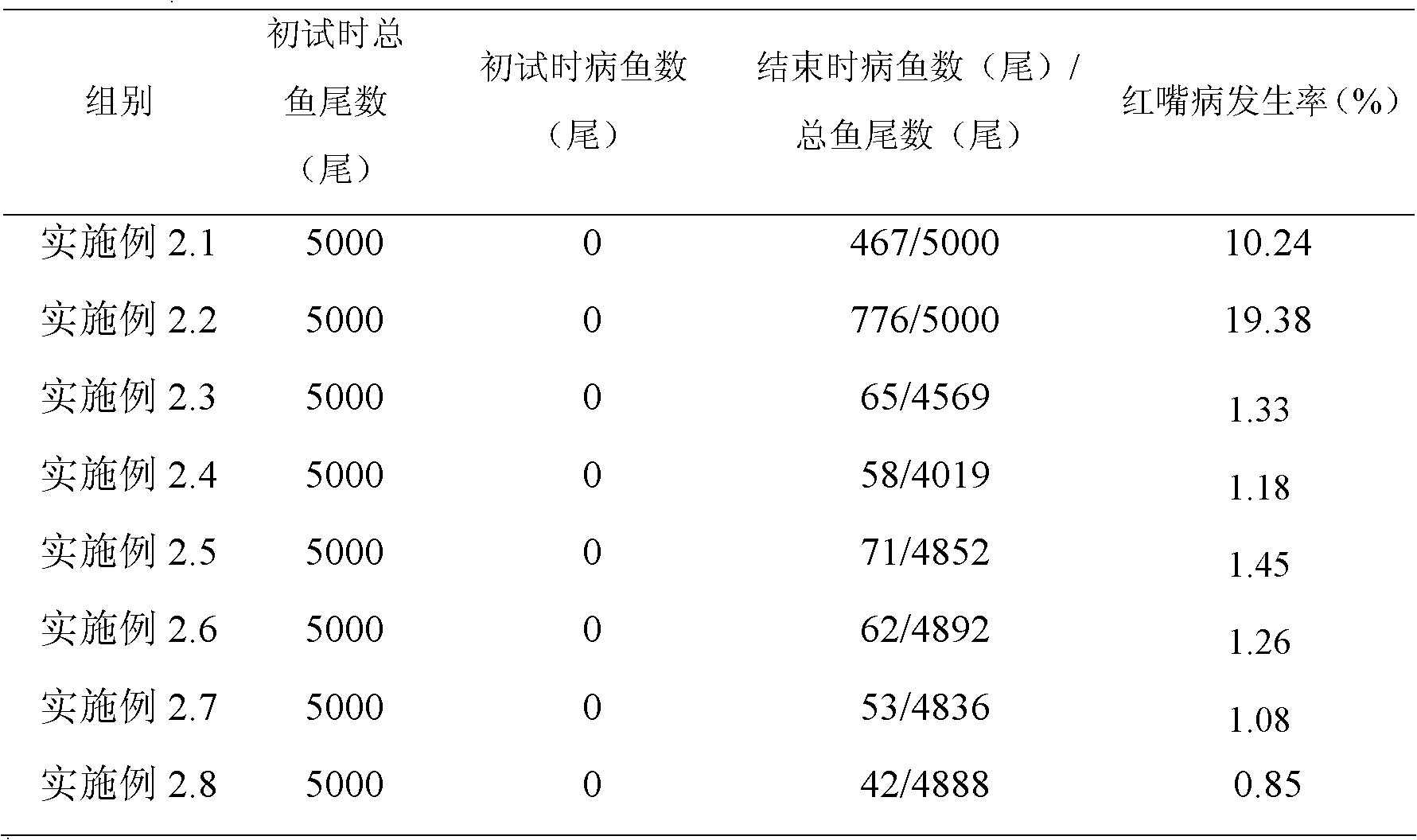
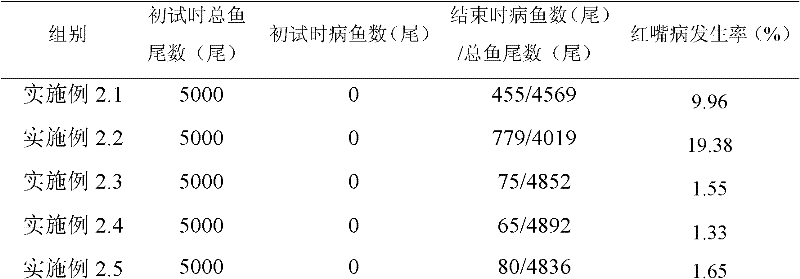
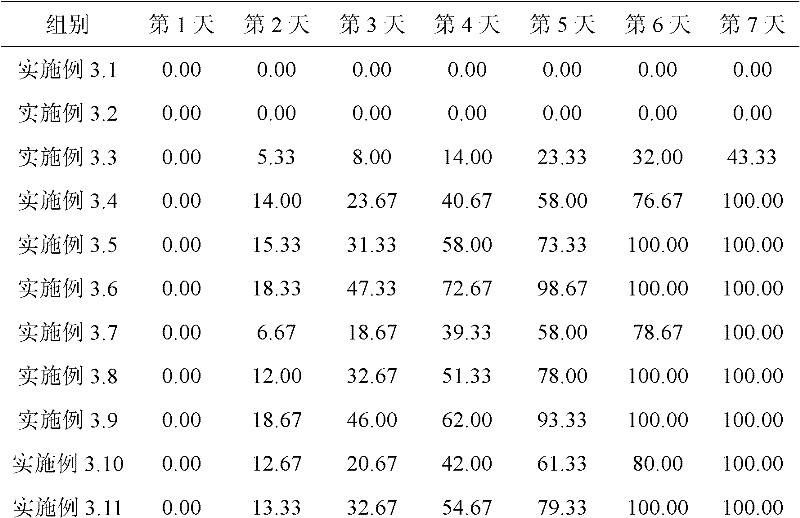
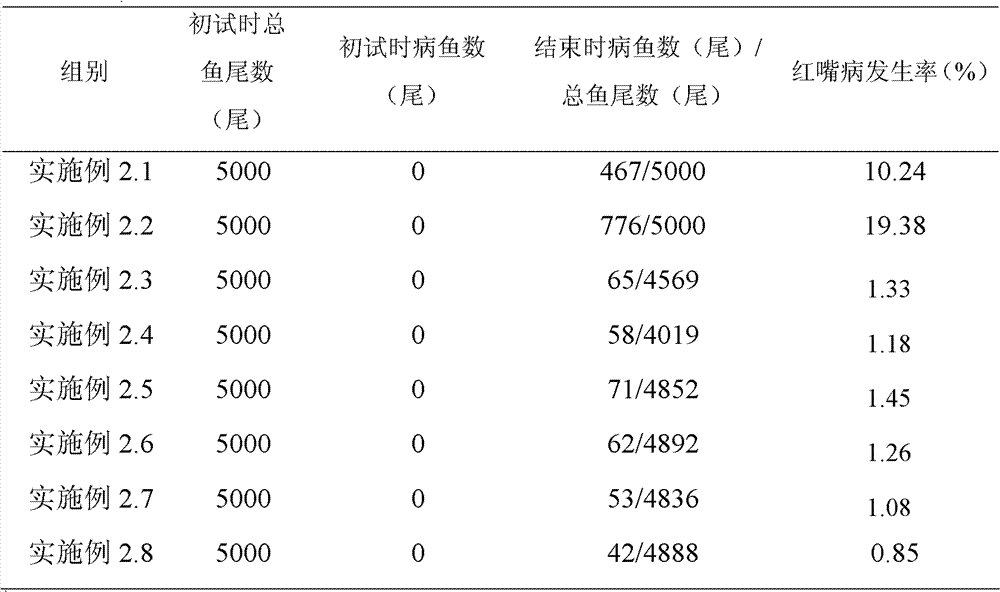
Application of bdellovibrio bdelloplast in preparing bacterial agent for preventing and controlling red mouth disease of scophthalmus maximus
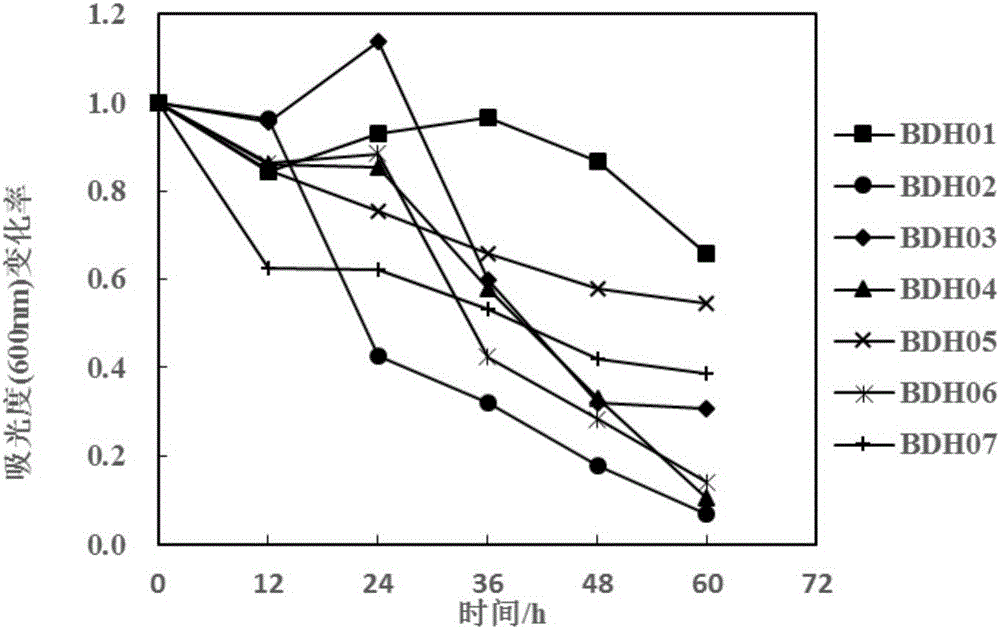
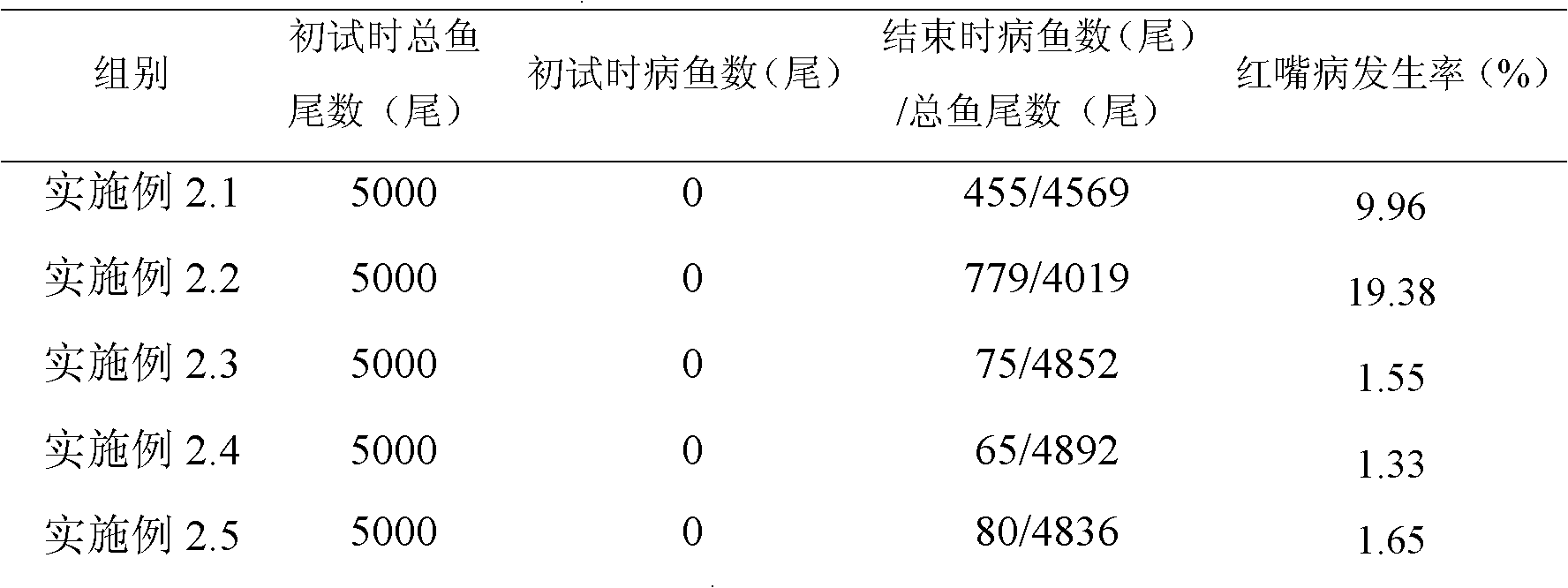
The invention discloses application of bdellovibrio bdelloplast in preparing a bacterial agent for preventing and controlling red mouth disease of scophthalmus maximus. The bdellovibrio is (Bdellovibrio sp.) BDM01. The application method for the bacterial agent comprises that: the bacterial agent is put into water body to prevent and control the red mouth disease of scophthalmus maximus to ensure that the final concentration of the bdellovibrio bdelloplast in the water body is 10-10<7>pfu / mL, or a feed is soaked by the bacterial agent for controlling the red mouth disease of scophthalmus maximus for 15 to 45 minutes, and the concentration of the bdellovibrio bdelloplast in the bacterial agent is 10-10<7>pfu / mL. When the bdellovibrio bdelloplast is applied to preparing the bacterial agent for preventing and controlling the red mouth disease of scophthalmus maximus, the bacterial agent can effectively prevent and control the red mouth disease of scophthalmus maximus, has high safety when applied to aquaculture, is environment-friendly, does not cause pathogenic bacteria resistance, and has good application prospect.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for improving shelf life of bdellovibrio sp. microbial prepartion
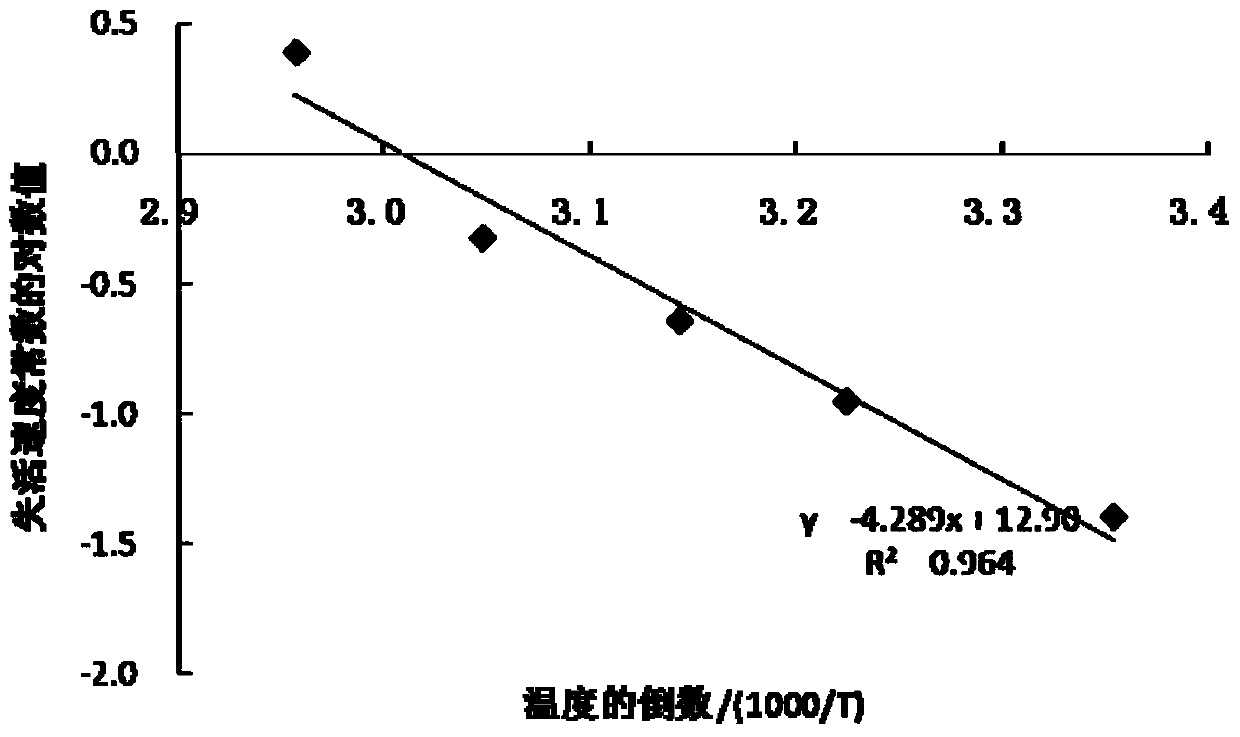
InactiveCN103952309AExtended decay timeExtended shelf lifeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyMonosodium glutamate
The invention discloses a method for improving shelf life of a bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation. The method comprises the following steps: preparing the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation, mixing the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation with a protection agent belonging to different kinds and / or with different concentration, then filling with a DNB medium, so as to obtain a mixed solution; placing the mixed solution at 25 DEG C, 37 DEG C, 45 DEG C, 55 DEG C and 65 DEG C to perform accelerated testing; sampling regularly, and detecting the bdellovibrio sp. concentration in the mixed solution; utilizing Arrhenius equation and recorded data to calculated out the shelf life of the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation; and determining the effect of the protection agent by comparing the shelf life. The protection agent is at least one of monosodium glutamate, cane sugar, internal-compensation inositol, melitose, glucose and glycerin. By employing the method, the attenuation time of a high-concentration bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation is obviously prolonged, and the shelf life of the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation is improved; and by comparing the quality-guaranteeing effect of different protection agents, an optimum quality-guaranteeing method is screened out.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for improving shelf life of saltwater-freshwater bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation
InactiveCN103952308AExtended shelf lifeKeep activeMicrobiological testing/measurementMicroorganism based processesFresh water organismMicrobiology
The invention discloses a method for improving shelf life of a saltwater-freshwater bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation. The method comprises the following steps: preparing the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation; mixing the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation with a protection agent belonging to different kinds and / or with different concentration, so as to obtain a mixed solution; placing the mixed solution at different temperature to perform accelerated testing; sampling regularly, and detecting the live bacteria concentration of the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation in the mixed solution; and utilizing Arrhenius equation and recorded data to calculate out the shelf life of the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation, and determining the effect of the protection agent by comparing the shelf life. According to the method, by comparing the quality-guaranteeing effect of different protection agents on the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation, a protection agent with best quality-guaranteeing effect is screened out, and the shelf life of the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation is obviously prolonged; and also the activity of thalline in the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation can be effectively kept for a long time. The provided protection agent is wide in raw material selection scope and cheap in price, and is suitable for popularization and usage.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Application of bdellovibrio sp. leech plasmid bacterium solution in cultivating penaeus monodon
InactiveCN102037917AStrong disease resistanceImprove intestinal environmentBacteriaClimate change adaptationWater qualityHuman health
The invention in particular relates to an application of a bdellovibrio sp. leech plasmid in cultivating marine products such as penaeus monodon, and the like. The invention is realized by adding a bdellovibrio sp. leech plasmid to the water body and the feeds. The invention is realized specifically based on cultivation pond conditions, preparation before stocking, shrimp postlarvae selecting andstocking, feeding management and water environment management in the cultivation period. The invention is characterized by adding a bdellovibrio sp. leech plasmid bacterium solution to the water bodyand ensuring the concentration of the bdellovibrio sp. leech plasmid in the water body to be 101-107pfu / mL, simultaneously soaking the feeds in the bdellovibrio sp. leech plasmid bacterium solution with the concentration of 101-107pfu / mL for 30 minutes and changing water once every 30 days in the cultivation period. The invention provides a method for cultivating organisms. The method has the advantages of environment friendliness, safety, no pollution, obvious effect and capabilities of improving the water quality, promoting growth of penaeus monodon, improving the immunity and improving thesurvival rate, thus having wonderful development prospect. The invention has very important significance in improving the economic benefits and eating safety and guaranteeing human health.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Energy-saving and emission-reducing abalone fry culture method
InactiveCN101933479AEliminate pathogenic bacteriaStrong toleranceBacteriaClimate change adaptationSide effectMicrobiology
The invention discloses an energy-saving and emission-reducing abalone fry culture method. An abalone fry culture process comprises the following steps of: (1) cultivating algae; (2) cultivating the abalone fry, namely adding the mixed bacterial liquid of bdellovibrio nectophore and leech plastid in the abalone fry culture process until the concentration of the mixed bacteria in water reaches at least 10 pfu / mL, wherein the bdellovibrio strain is bdellovibrio sp. BDFM05 and is collected by China Center for Type Culture Collection; and the collection number is CCTCC NO:M 209172 and collection date is 2009-08-07; (3) changing water, namely changer water every 5 to 30 days after egg distribution and adding the bdellovibrio mixed bacterial liquid once changing water; and (4) harvesting. The bdellovibrio mixed bacterial liquid has a strong effect for eliminating the common bacteria under the culture environment. The bdellovibrio mixed bacterial liquid has no toxic and side effect on the abalones, so the method has the advantages of suitability for large-scale industrial cultivation of the abalones and capacity of increasing abalone culture survival rate.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
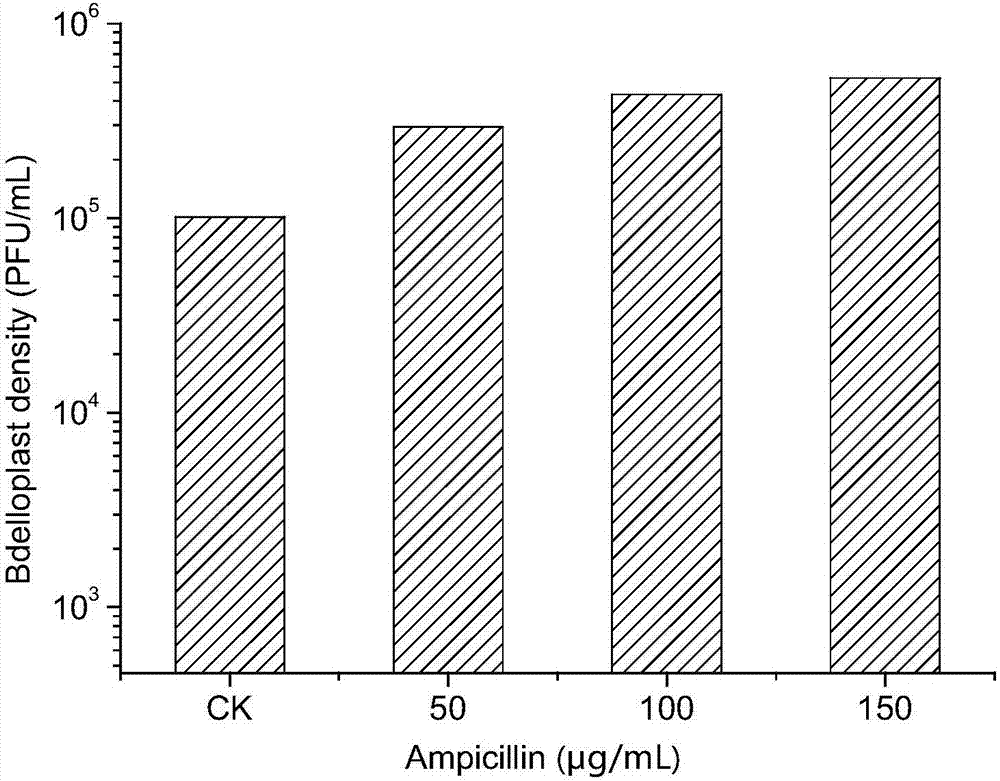
Marine bdellovibrio and application thereof in promoting formation of bdelloplast under existence of ampicillin
ActiveCN107974418AThe cultivation method is simplePromote formationBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyAquaculture industry
The invention discloses marine bdellovibrio and application thereof in promoting the formation of bdelloplast under existence of ampicillin, and belongs to the technical field of bdellovibrio. The marine bdellovibrio is (Bdellovibrio sp.) BDN-1, and was preserved into Guangdong Microorganism Center for Culture Collection in Guandong Microorganism Research Institute (No.5 Floor, No.59 Building, No.100 Central Xian Lie Middle Road, Guangzhou City) on November 27th, 2017, and the preservation number is GDMCC NO:60291. The marine bdellovibrio has the advantages that the factors for promoting the formation of the bdelloplast by the bdellovibrio, such as ampicillin or ampicillin and calcium and magnesium ions, are utilized, and the formation of the bdelloplast by the bdellovibrio BND-1 is promoted; the effect of obviously extending the quality warranty period of the bdellovibrio microorganism preparation is verified; the activity of the bacteria in the bdellovibrio microorganism preparationis effectively maintained for a long time; the culture method for promoting the formation of the bdelloplast is simple and feasible, and is suitable for being popularized and applied, and the contribution is expected to be made to the disease and pest controlling in the aquaculture industry.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Abalone breeding method capable of saving energy and reducing emissions
InactiveCN101999325AEnhance physical fitnessImprove immunityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaSide effectBacilli
The invention discloses an abalone breeding method capable of saving energy and reducing emissions, comprising the following steps of: (1) cultivating algae; (2) breeding seedlings: adding bdellovibrio bacteriovorus leech plastid bacterial liquid during breeding so that the concentration of the leech plastid in water body is at least up to 10pfu / mL, wherein the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus strain is Bdellovibrio sp. BDFM05 which is preserved by China Center for Type Culture Collection on August 7th, 2009, with preservation number of CCTCC NO: M 209172; (3) exchanging water: exchanging the water every 5-30 days after egg distribution, and immediately adding the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus leech plastid bacterial liquid after exchanging water; (4) collecting products. The bdellovibrio bacteriovorus leech plastid has strong effect of eliminating common bacteria in cultivating environment. Since the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus leech plastid has no toxic and side effect to the abalone, the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus leech plastid is adaptable for industrial breeding of abalone in large scales and is capable of improving survival rate of the abalone during breeding.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Marine bdellovibrio sp. and application of marine bdellovibrio sp. to facilitation of formation of leech plastid in presence of ampicillin
ActiveCN107988136ABroad cracking spectrumCracking performance is not reducedAntibacterial agentsBacteriaHigh concentrationMicroorganism
The invention discloses marine bdellovibrio sp. and application of the marine bdellovibrio sp. to facilitation of formation of leech plastid in the presence of ampicillin. The bacterial strain is bdellovibrio sp. (BED-1) which is collected in Guangdong Microbiological Culture Collection Center of Guangdong Institute of Microbiology which is located at 5th floor, building 59, No. 100 Courtyard, Xianlie Middle Road, Guangzhou on November 27, 2017 with the collection number GDMCC NO:60292. The formation of high-density leech plastid of the bdellovibrio sp. BDE-1 is facilitated with the ampicillinserving as a factor for facilitating the formation of the leech plastid of the bdellovibrio sp., so that high-concentration leech plastid of the bdellovibrio sp. BDE-1 is provided. As found by the research, the ampicillin plays a role in remarkably facilitating the formation of the leech plastid of the bdellovibrio sp., and the cracking performance of the leech plastid does not decrease; comparedwith a control group, the shelf life of the high-density leech plastid is prolonged remarkably; the method for culturing the leech plastid is simple and feasible, and can be popularized and used.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for cultivating juvenile abalones
InactiveCN101999324AImprove juvenile abalone's physiqueImprove immunityBacteriaClimate change adaptationBrickPathogenic bacteria
The invention discloses a method for cultivating juvenile abalones. The method comprises the following steps of: 1. paving bricks in a cultivating pond, and filling sea water; 2. putting juvenile abalones in the pond, and carrying out aeration simultaneously, 3. periodically feeding bait, adding a bdellovibrio telotroch bacterium liquid to the cultivating water and / or the fed bait, and changing water every 5-30 days by one measuring range every time; and 4. harvesting the juvenile abalones when the length of the juvenile abalones is 1.0-1.6cm. In the method, the bdellovibrio stain is Bdellovibrio sp. BDFM05, which is collected by China Center for Type Culture Collection, the collection number is CCTCC NO: M209172, and the collection date is August 7th, 2009. The invention has the advantages of saving energy, reducing emission reducing and being more environmental friendly; the effect of the bdellovibrio telotroch on controlling and eliminating pathogenic bacteria of the juvenile abalones is quick, and the activity is high; and the method can obviously improve the quality of the juvenile abalones and enhance the immunity.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Application of Bdellovibrio nectophore in preparing bactericide for controlling red mouth disease of scophthalmus maximus
InactiveCN102007941AEffective preventionEffective therapeuticAntibacterial agentsBiocideDiseaseScophthalmus
The invention discloses an application of Bdellovibrio nectophore in preparing a bactericide for controlling the red mouth disease of a scophthalmus maximus. Bdellovibrio is Bdellovibrio sp. BDM01. In the application method of the bactericide, the bactericide for controlling the scophthalmus maximus red mouth disease is splashed into a water body to cause the final concentration of the Bdellovibrio nectophore in the water body to be 10-107pfu / mL, or feeds are soaked by the bactericide for controlling the scophthalmus maximus red mouth disease for 15-45min to cause the concentration of the Bdellovibrio nectophore in the bactericide to be 10-107pfu / mL. The application of the Bdellovibrio nectophore in preparing the bactericide for controlling the scophthalmus maximus red mouth disease can effectively control and treat the red mouth disease of the scophthalmus maximus and has high safety, environmental protection and good application prospect and does not generate pathogenic bacteria resistance in the application of aquatic animal culture.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for controlling total number of bacteria in fresh milk
The invention discloses a method for controlling the total number of bacteria in fresh milk. Bdellovibrio is utilized for controlling the total number of bacteria, and the Bdellovibrio strain is a Bdellovibrio (Bdellovibrio sp.) BDFM05 and collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection (CCTCC for short) with the collection number of M209172 on August 7, 2009. The method comprises the following specific steps of: (1) preparing the Bdellovibrio to Bdellovibrio swimming body bacterial liquid; and (2) adding the Bdellovibrio swimming body bacterial liquid prepared in the step (1) to the fresh milk, and standing or stirring for 1 to 8 hours, wherein the concentration of Bdellovibrio swimming body is at least 102 pfu / ml. The invention can effectively control the growth of the bacteria in the fresh milk, and is beneficial to keeping the original flavor and quality of cowmilk, improving rating number of the fresh milk in acquisition and reducing waste of raw milk caused by excessively rapid growth of the bacteria.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Young abalone culture method
InactiveCN101953315AImprove juvenile abalone's physiqueImprove immunityBacteriaClimate change adaptationBrickSeawater
The invention discloses a young abalone culture method, which comprises the following steps of: (1) paving bricks in a culture pond, and injecting seawater; (2) putting young abalone into the pond, and simultaneously beginning aeration; (3) regularly feeding bait, adding Bdellovibro mixed bacterial liquid into culture water body and / or the fed bait, and changing water every 5-30 days, wherein the water changing quantity each time is a span; and (4) when the young abalone grows to reach 1.0-1.6cm, harvesting the young abalone, wherein the Bdellovibro strain is (Bdellovibrio sp.)BDFM05, which has been preserved by China Center for Type Culture Collection on Aug 7, 2009 with the collection number of CCTCC NO:M209172. The young abalone culture method has the advantages that: (1) the young abalone culture method can save energy and reduce emission, and is more environment-friendly; (2) the Bdellovibro mixed bacterial liquid has the advantages of quick response, strong activity, convenient preparation and long sterilizing time; and (3) the young abalone culture method can obviously improve the physique of the young abalone and enhance the immunity.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
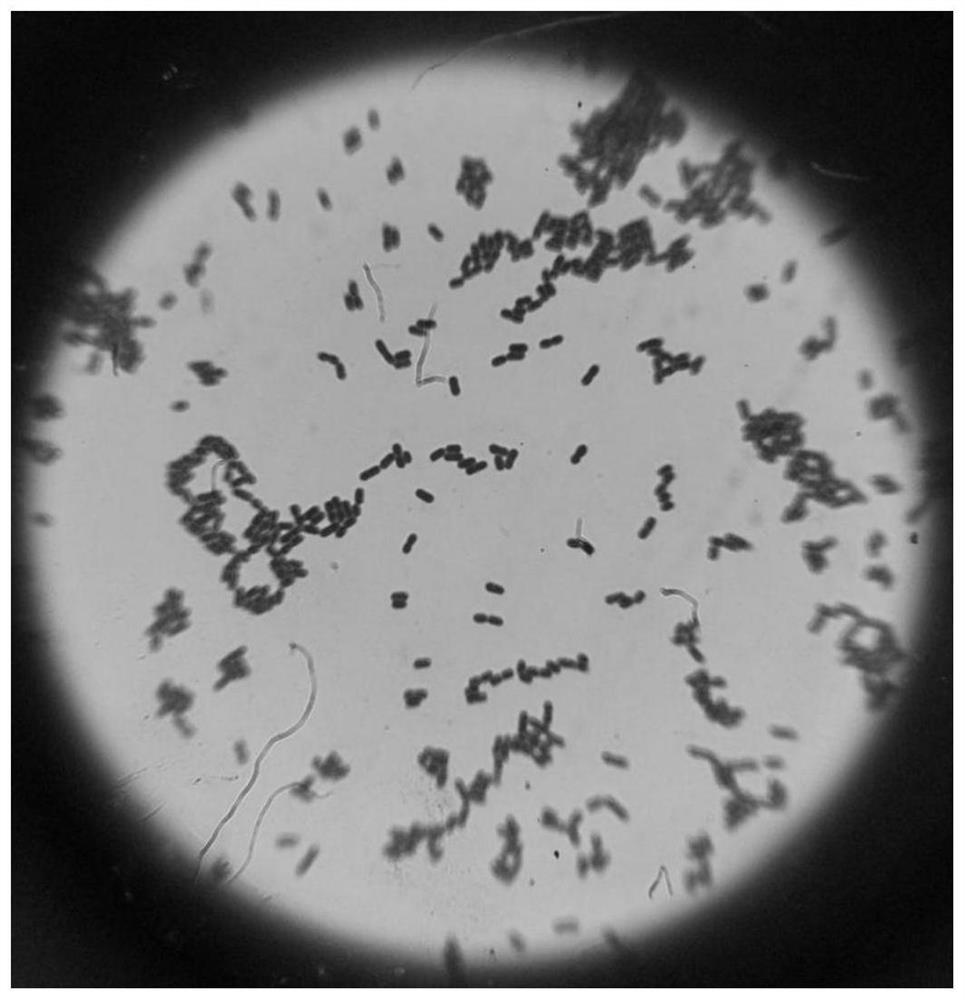
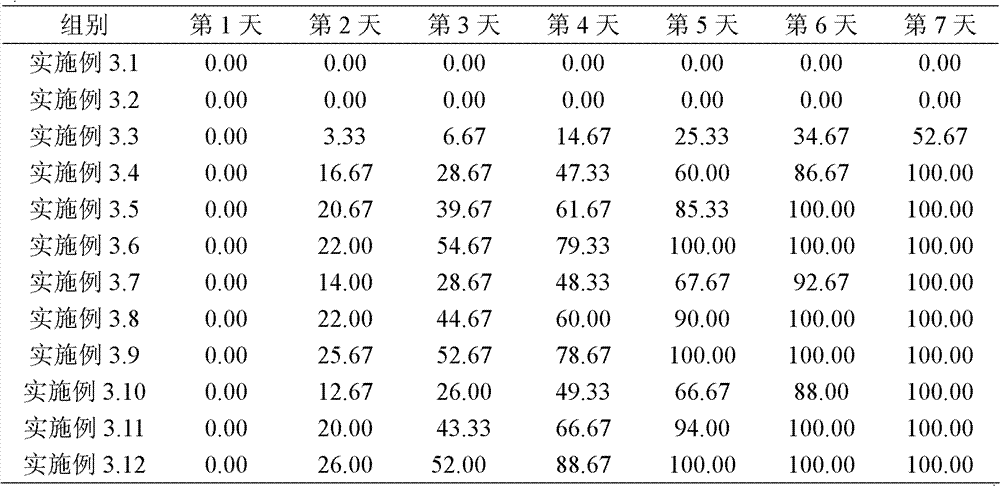
Bdellovibrio sp. induced mutation strain with strong cracking performance and application thereof
ActiveCN111363690AStrong cracking abilityImprove cracking capacityAntibacterial agentsBacteriaBiotechnologyMicroorganism
The present invention discloses a bdellovibrio sp. induced mutation strain with the strong cracking performance and an application thereof, and belongs to the technical field of microorganism inducedmutation breeding. The bdellovibrio sp. induced mutation strain is Bdellovibrio sp. BDN-1F2, which is collected in the Guangdong Microbial Culture Collection center in June 11, 2018 and has the collection number of GDMCC NO:60385. The cracking performance of bdellovibrio sp. is enhanced by a Co60 irradiation induced mutation method, so that the cracking capability of the bdellovibrio sp. to gram-negative and positive pathogenic bacteria is effectively improved, the application range of the bdellovibrio sp. is expanded, and the requirements of production practice are met. The cracking performance of the bdellovibrio sp. induced mutation strain is checked to prove that two strains of bdellovibrio sp. which cannot be cracked can be cracked, and the cracking capability of the gram-positive bacteria is enhanced, so that a method basis is provided for separation and performance enhancement of more bdellovibrio sp. with the positive bacteria as hosts.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Energy-saving and emission-reducing abalone fry culture method
InactiveCN101933479BEliminate pathogenic bacteriaStrong toleranceBacteriaClimate change adaptationMicrobiologyEcology
The invention discloses an energy-saving and emission-reducing abalone fry culture method. An abalone fry culture process comprises the following steps of: (1) cultivating algae; (2) cultivating the abalone fry, namely adding the mixed bacterial liquid of bdellovibrio nectophore and leech plastid in the abalone fry culture process until the concentration of the mixed bacteria in water reaches at least 10 pfu / mL, wherein the bdellovibrio strain is bdellovibrio sp. BDFM05 and is collected by China Center for Type Culture Collection; and the collection number is CCTCC NO:M 209172 and collection date is 2009-08-07; (3) changing water, namely changer water every 5 to 30 days after egg distribution and adding the bdellovibrio mixed bacterial liquid once changing water; and (4) harvesting. The bdellovibrio mixed bacterial liquid has a strong effect for eliminating the common bacteria under the culture environment. The bdellovibrio mixed bacterial liquid has no toxic and side effect on the abalones, so the method has the advantages of suitability for large-scale industrial cultivation of the abalones and capacity of increasing abalone culture survival rate.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Water-saving method for culturing young abalones
InactiveCN101982070AImprove juvenile abalone's physiqueImprove immunityBacteriaClimate change adaptationWater savingBrick
The invention discloses a water-saving method for culturing young abalones, comprising the following steps: (1) paving bricks in a culture pond and then pouring seawater into the culture pond; (2) putting the young abalones into the culture pond and starting to carry out aeration; (3) regularly feeding bait and adding a bdellovibro plastid bacterial liquid to a culture water body and / or the fed bait; changing water every 5-30 days with the volume of changed water each time as a measuring range; and (4) collecting the young abalones when the young abalones grow to a length of 1.0-1.6cm, wherein the bacterial strain is Bdellovibrio sp. BDFM05, and preserved in China Center for Preserving Type Culture Collection with the preservation number of CCTCC NO: M209172 on 7th, August 2009. The method provided by the invention has the following advantages: (1) saving energy and reducing emission and being more environment-friendly; (2) enjoying more convenient preparation and preservation of leech plastid, good tolerance and longer bactericidal action; and (3) being capable of invigorating health and enhancing immunity of the young abalones.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for controlling total number of bacteria in fresh milk
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
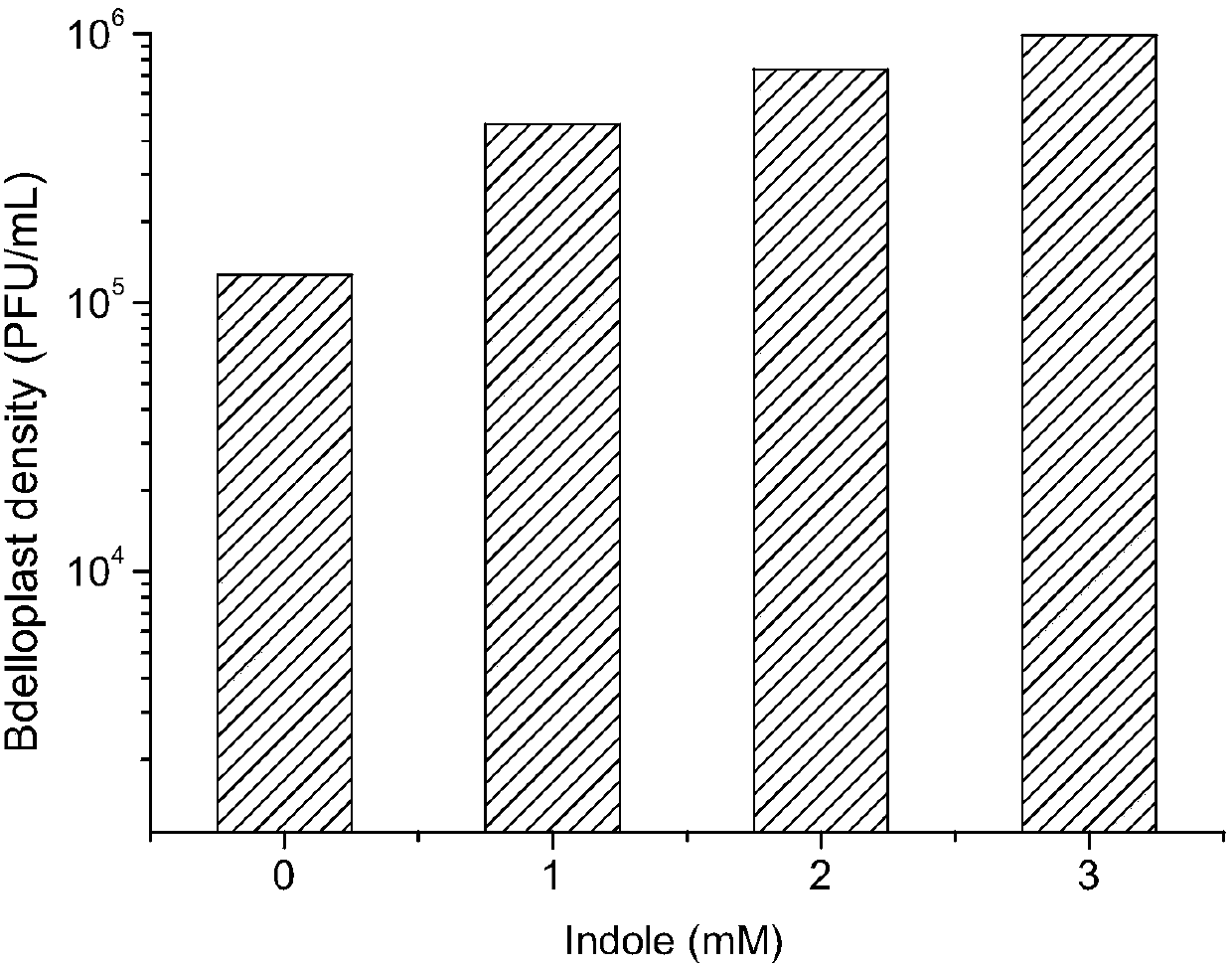
Application of indole in promoting formation of marine Bdellovibrio sp. BDE-1 bdelloplast
ActiveCN108102999ACracking performance is not reducedPromote formationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDiseaseFood borne
The invention discloses application of indole in promoting formation of a marine Bdellovibrio sp. BDE-1 bdelloplast, and belongs to the technical field of Bdellovibrio sp. BDE-1. According to the application of the indole in promoting the formation of the marine Bdellovibrio sp. BDE-1 bdelloplast, a factor, namely, the indole, is formed by utilizing a Bdellovibrio sp. BDE-1 promoting bdelloplast,so that the formation of high-density bdelloplast of the Bdellovibrio sp. BDE-1 is promoted; the research discovers that the indole has an obvious promoting effect on the formation of the bdelloplastof the Bdellovibrio sp. BDE-1; the cracking performance of the bdelloplast is not reduced; compared with a control group, the quality guarantee period of a high-density bdelloplast group is obviouslyprolonged; the high-density bdelloplast provided by the invention can inhibit vibrios which can cause human infection and food poisoning and can also inhibit the vibrios which can cause biological diseases in aquaculture, has a very good inhibiting effect on other food-borne pathogenic bacteria, and has wide cracking spectrum; the cracking effect of the bdelloplast is unchanged as compared with that of a BDE-1 mixture; and a bdelloplast promoting culturing method disclosed by the invention is simple and feasible, and can be popularized and used.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Energy-saving and emission reducing method for raising abalone seedlings
InactiveCN101999326BEliminate pathogenic bacteriaStrong elimination abilityBacteriaClimate change adaptationSide effectCulture environment
The invention discloses an energy-saving and emission reducing method for raising abalone seedlings, which comprises the following steps of: (1) culturing algae; (2) raising the seedlings, namely adding concentrated solution of bdellovibrio swim body in the process of raising the seedlings, so that the concentration of a swim body in a water body at least reaches 10 pfu / mL finally, wherein bdellovibrio is Bdellovibrio sp. BDFM05 and was collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection in 7th August, 2009 with the collection number of CCTCC NO: M 209172; (3) changing water, namely changing the water every 5 to 30 days after ovum laying, and adding the concentrated solution of bdellovibrio swim body immediately after water refreshing; and (4) harvesting. The bdellovibrio swim body has the strong effect of eliminating common bacteria in culture environment. The bdellovibrio swim body has no toxic or side effect on abalone, so the bdellovibrio swim body is suitable for large-scale factory cultivation of the abalone, and the culturing survival rate of the abalone can be improved.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Application of indol or indol and calcium-magnesium ions in promoting formation of marine bdellovibrio sp. leech plastid
ActiveCN107937330APromote formationExtended shelf lifeBacteriaMicroorganism based processesDiseaseAquaculture industry
The invention discloses application of indol or indol and calcium-magnesium ions to promotion of the formation of marine bdellovibrio sp. leech plastid, belonging to the technical field of bdellovibrio sp.. In the application, the indol or the indol and calcium-magnesium ions are utilized to promote the formation of bdellovibrio sp. BND-1 leech plastid; The indol or the indol and calcium-magnesiumions are determined to have an obvious effect with respect to prolonging the expiration date of a bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation; and the indol or the indol and calcium-magnesium ions can beused for maintaining the vitality of thalluses in the bdellovibrio sp. microbial preparation. The high-density leech plastid provided by the invention can be used for inhibiting vibrioes capable of triggering biological diseases in aquaculture and has broad lysis spectrum performance, and the splitting action of the leech plastid is more excellent compared with that of a bdellovibrio sp. BDN-1 mixture (containing both the leech plastid and swinging bodies). The cultivating method for promoting the leech plastid is simple and feasible, suitable for promotion and application, and is expected tomake a contribution to preventing diseases in the aquaculture industry.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Application of Indole in Promoting the Formation of Marine Bdellovibrio Bacteroids
ActiveCN108102999BCracking performance is not reducedPromote formationBacteriaMicroorganism based processesBiotechnologyHigh density
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A mutant strain of Bdellovibrio with strong lytic performance and wide lytic spectrum and its application
ActiveCN111363689BStrong cracking abilityImprove cracking capacityBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMutagenesis
The invention discloses a leech vibrio mutant strain with strong lysis performance and wide lysis spectrum and its application. The leechvibrio mutant strain is Bdellovibrio sp.BDE-1F2, which was deposited in the Guangdong Provincial Microbial Culture Collection Center on November 22, 2018, with the deposit number: GDMCC NO: 60491. The present invention utilizes Co 60 Irradiation-induced mutation method to enhance the lysis performance of Hirudovibrio, effectively improve the lytic ability of Hirudovibrio against Gram-negative and positive pathogenic bacteria and / or potential pathogenic bacteria, and broaden the application scope of Hirudovibrio , to better meet the needs of production practice. The lysis performance of the leech vibrio mutant strain of the present invention is tested to confirm that it can lyse four gram-negative bacteria that cannot be lysed by the original, so that the total lysis rate of 28 indicator bacteria reaches 100%, and the lysis of Gram-negative bacteria is enhanced. The lysis ability of positive bacteria provides a method basis for the enhancement of the lysis performance of Hirudovibrio.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Application of bdellovibrio bdelloplast in preparing bacterial agent for preventing and controlling red mouth disease of scophthalmus maximus
InactiveCN102038714BReduce the probability of suffering from red mouth diseaseGood effectAntibacterial agentsBacteriaDiseaseScophthalmus
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
A strain of marine Bdellovibrio and its application to promote the formation of hiruplasma under ampicillin
ActiveCN107974418BThe cultivation method is simplePromote formationBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyAquaculture industry
The invention discloses a strain of marine bdellovibrio and the application of promoting the formation of bdellovibrio under ampicillin, and belongs to the technical field of bdellovibrio. The strain is Bdellovibrio sp. BDN‑1, which was preserved on November 27, 2017 at the Guangdong Provincial Microbiological Culture Collection Center, 5th Floor, Building 59, Compound 59, No. 100 Xianlie Middle Road, Guangzhou City , deposit number: GDMCC NO: 60291. The present invention utilizes ampicillin or ampicillin and calcium and magnesium ions to promote the formation of the Bdellovibrio Bdellovibrio Bideloplasts; it has been confirmed that it has the effect of significantly prolonging the shelf life of Bdellovibrio microbial preparations effect; and can effectively maintain the vitality of the bacterium in the Bdellovibrio microbial preparation for a long time. The method for promoting leech plastid cultivation provided by the invention is simple and feasible, is suitable for popularization and use, and is expected to contribute to the prevention and control of diseases in the aquaculture industry.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Method for controlling total count of bacteria carried by copepoda
ActiveCN104126529AMaintain lytic activityDoes not cause deathAntibacterial agentsBacteriaSaccharumSide effect
The invention discloses a method for controlling the total count of bacteria carried by copepoda. The method comprises the following steps: preparing a Bdellovibrio sp. diluent of which the concentration is 2*10<2>-2*10<5>PFU / mL, and mixing the Bdellovibrio sp. diluent with a mixed solution of sodium glutamate and cane sugar in the volume ratio 1:1 to obtain a Bdellovibrio sp. preparation; and mixing the Bdellovibrio sp. preparation with a pretreated copepoda-containing water sample. The method provided by the invention is simple and feasible, and is suitable for industrial batch production. The contained sodium glutamate and cane sugar do not have toxic or side effects on water bodies and the copepoda, and do not cause pollution to the water bodies or death of beneficial aquatic plankton such as the copepoda. Through the method disclosed by the invention, the total count of the bacteria carried by the copepoda can be effectively controlled within 103cfu / mL in 24 hours, and the regeneration of the bacteria is slowed down for a long period of time.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Bdellovibrio induced strain with strong cracking performance and wide cracking spectrum and application of bdellovibrio induced strain
ActiveCN111363689AStrong cracking abilityImprove cracking capacityBiocideBacteriaBiotechnologyMicrobiological culture
The invention discloses a bdellovibrio induced strain with strong cracking performance and a wide cracking spectrum and application of the bdellovibrio induced strain. The bdellovibrio induced strainis Bdellovibrio sp.BDE-1F2, is preserved on November 22, 2018 in Guangdong Microbiological Culture Collection Center and has a preservation number of GDMCC NO:60491. The cracking performance of bdellovibrio is enhanced by virtue of a Co60 irradiation induced mutation method, so that the cracking capability of the bdellovibrio to Gram negative and positive pathogenic bacteria and / or potential pathogenic bacteria, the application range of the bdellovibrio is broadened, and demands on production practice are better satisfied. Verification on the cracking performance of the bdellovibrio induced strain proves that four Gram negative bacteria which cannot be cracked in the past can be cracked, and the total cracking rate of the bdellovibrio to 28 indicator bacteria reaches up to 100%, the cracking capability of the bdellovibrio to the Gram negative bacteria is enhanced, and a method foundation is provided for enhancement of the cracking capability of the bdellovibrio.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
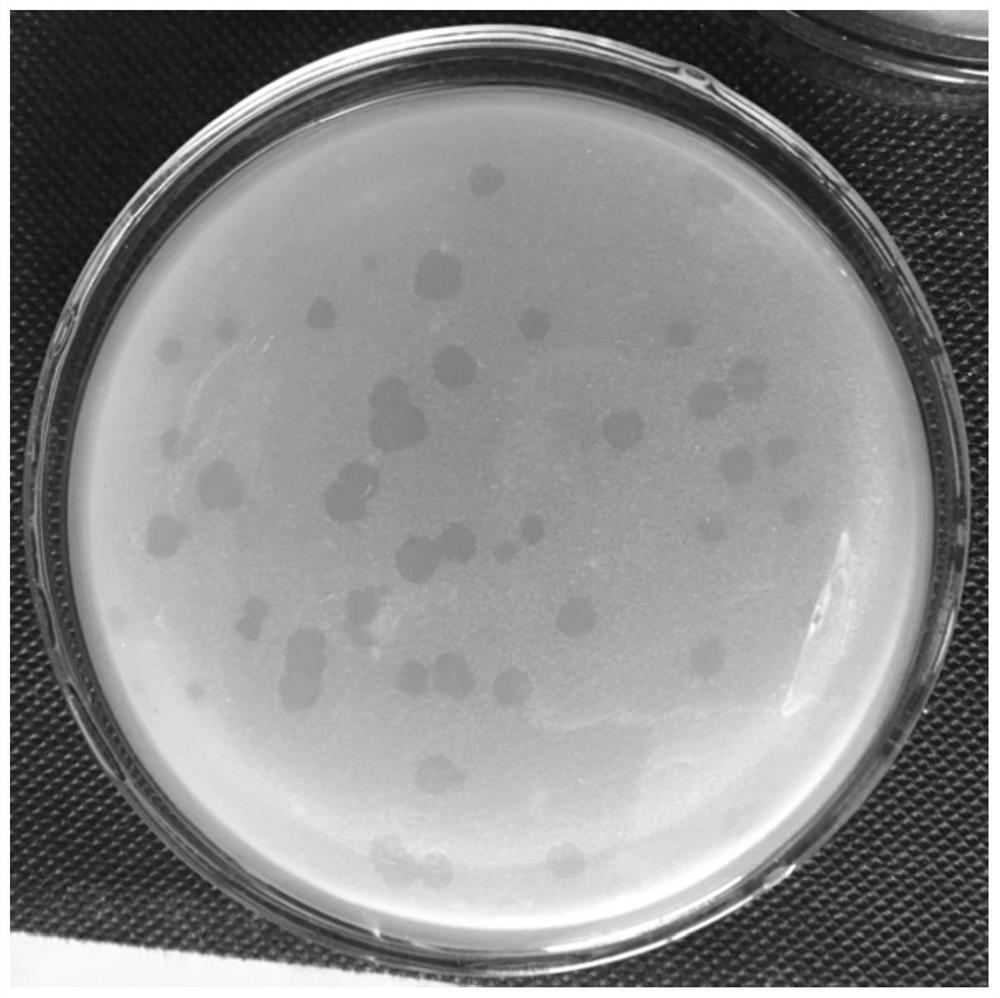
Use of bdellovibrio bacteriovorus bdelloplast as bacteria remover in fruit cleaning
InactiveCN101961083AGood effectImprove securityBacteriaMicroorganism based processesMicrobiologyCommon disease
The invention discloses the use of bdellovibrio bacteriovorus bdelloplast as a bacteria remover in fruit cleaning. The use is characterized in that: bdellovibrio bacteriovorus bdelloplast liquid is added into cleaning water as the bacteria remover for cleaning the fruits; or the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus bdelloplast liquid is sprayed into processing environment for cleaning the processing environment; and the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus is bdellovibrio bacteriovorus (Bdellovibrio sp.)BDM01, and was collected in the China Center for Type Culture Collection on April 28th, 2008 with the collection number of CCTCC No.M208066. The bdellovibrio bacteriovorus bdelloplast has strong effect of eliminating common disease germs on the fruit surface, the disease germ eliminating rate of the bdellovibrio bacteriovorus bdelloplast reaches over 93 percent, and the bdelloplast has the advantages that: the preparation and collection of the bdelloplast are more convenient; the environmental resistance of the bdelloplast is higher; the sterilizing effect of the bdelloplast lasts for a longer time; and the like.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Application of bdellovibrio sp. leech plasmid bacterium solution in cultivating penaeus monodon
InactiveCN102037917BStrong disease resistanceImprove intestinal environmentBacteriaClimate change adaptationWater qualityHuman health
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Application of Bdellovibrio nectophore in preparing bactericide for controlling red mouth disease of scophthalmus maximus
InactiveCN102007941BReduce the probability of suffering from red mouth diseaseGood effectBacteriaBacteria material medical ingredientsBiotechnologyAquatic animal
The invention discloses an application of Bdellovibrio nectophore in preparing a bactericide for controlling the red mouth disease of a scophthalmus maximus. Bdellovibrio is Bdellovibrio sp. BDM01. In the application method of the bactericide, the bactericide for controlling the scophthalmus maximus red mouth disease is splashed into a water body to cause the final concentration of the Bdellovibrio nectophore in the water body to be 10-107pfu / mL, or feeds are soaked by the bactericide for controlling the scophthalmus maximus red mouth disease for 15-45min to cause the concentration of the Bdellovibrio nectophore in the bactericide to be 10-107pfu / mL. The application of the Bdellovibrio nectophore in preparing the bactericide for controlling the scophthalmus maximus red mouth disease can effectively control and treat the red mouth disease of the scophthalmus maximus and has high safety, environmental protection and good application prospect and does not generate pathogenic bacteria resistance in the application of aquatic animal culture.
Owner:SOUTH CHINA UNIV OF TECH
Saprospira sp. and its application
A Saprospira sp. PdY3 (CGMCC No.1043) is disclosed. It can dissolve the blue algae, such as Anabaena, so it can be used in conjunction with other alga-dissolving factors, such as Bdellovibrio sp. S-23 (CGMCC No.1045) to improve the water quality of lake.
Owner:PEKING UNIV
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com