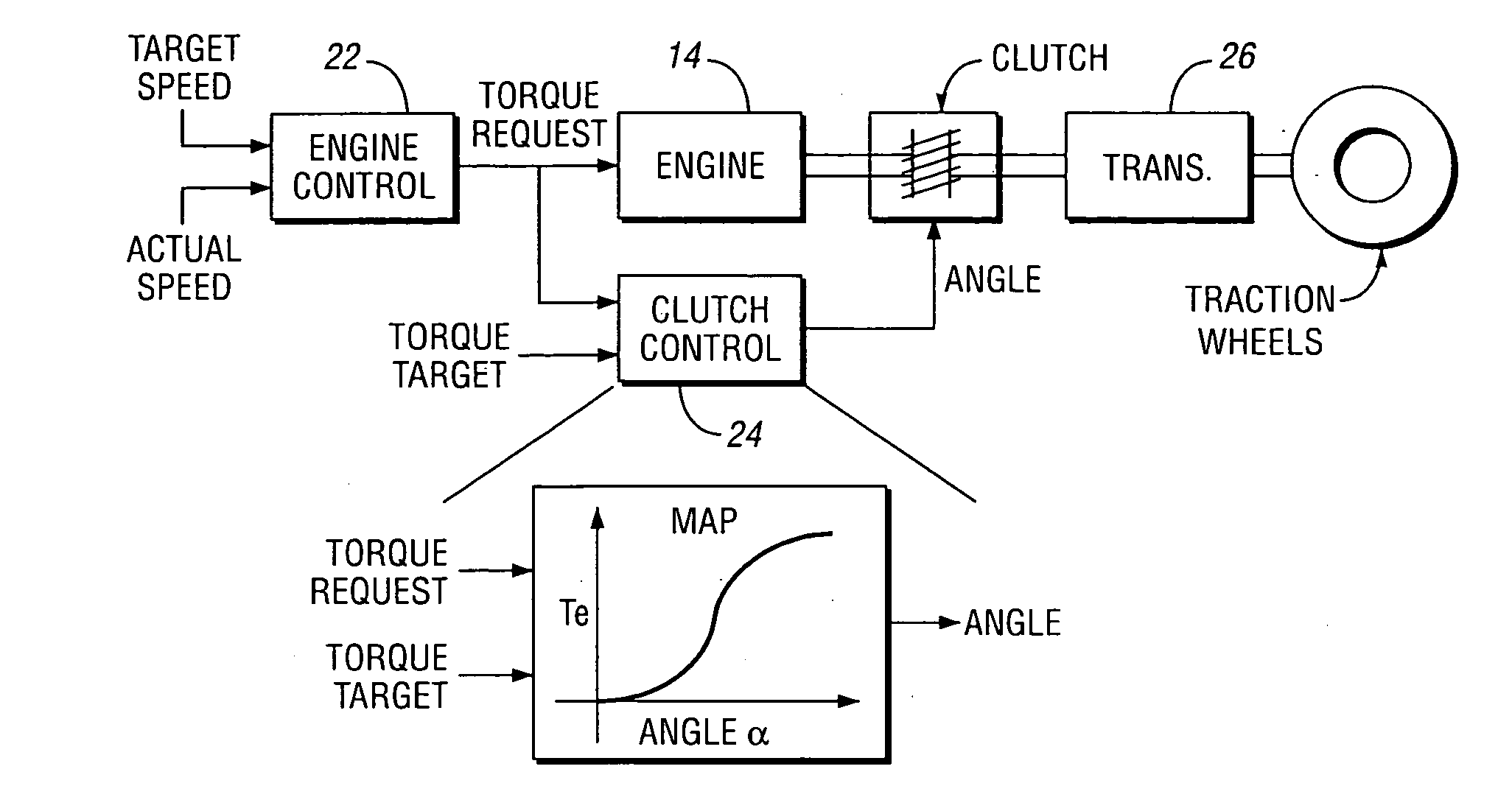
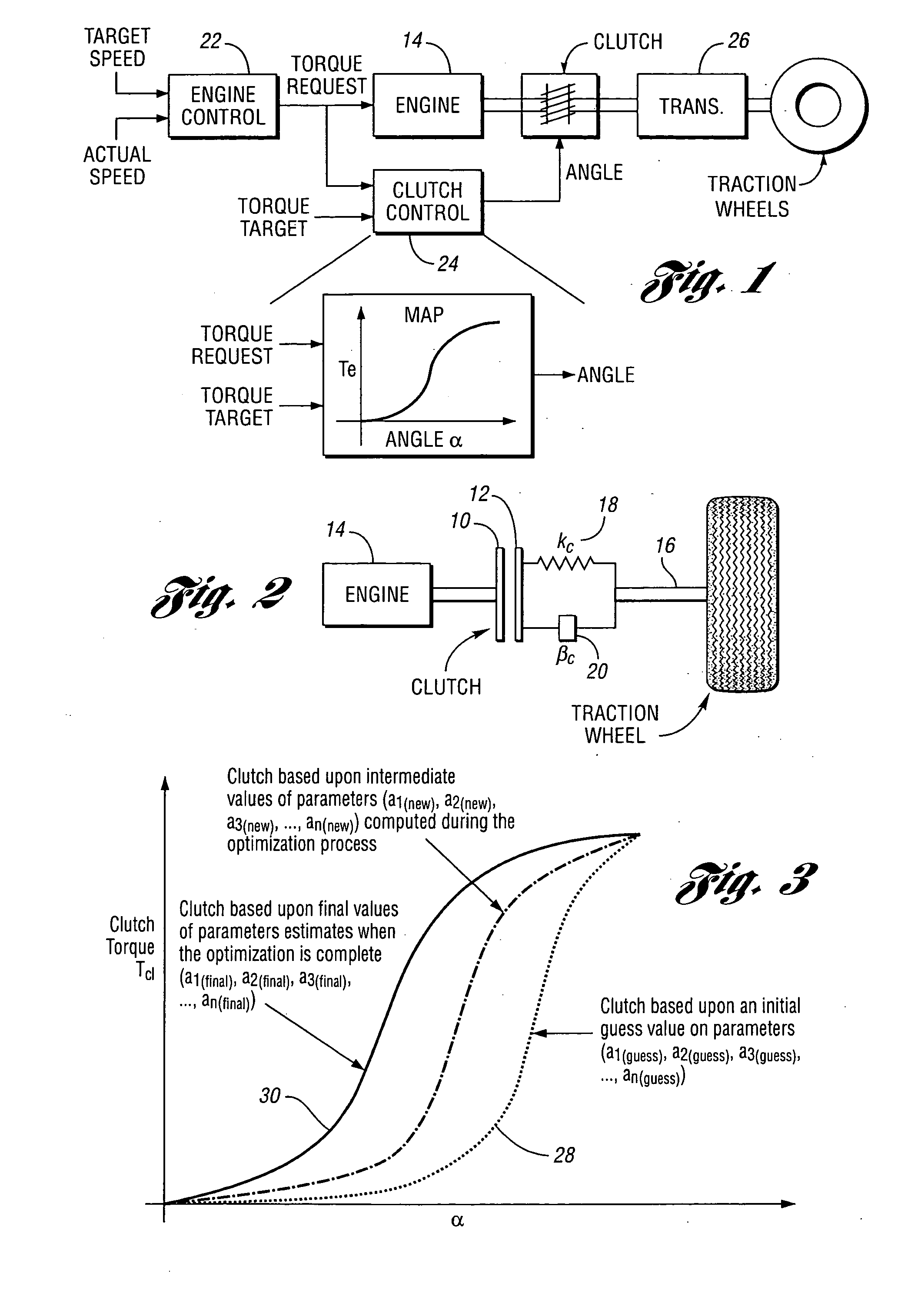
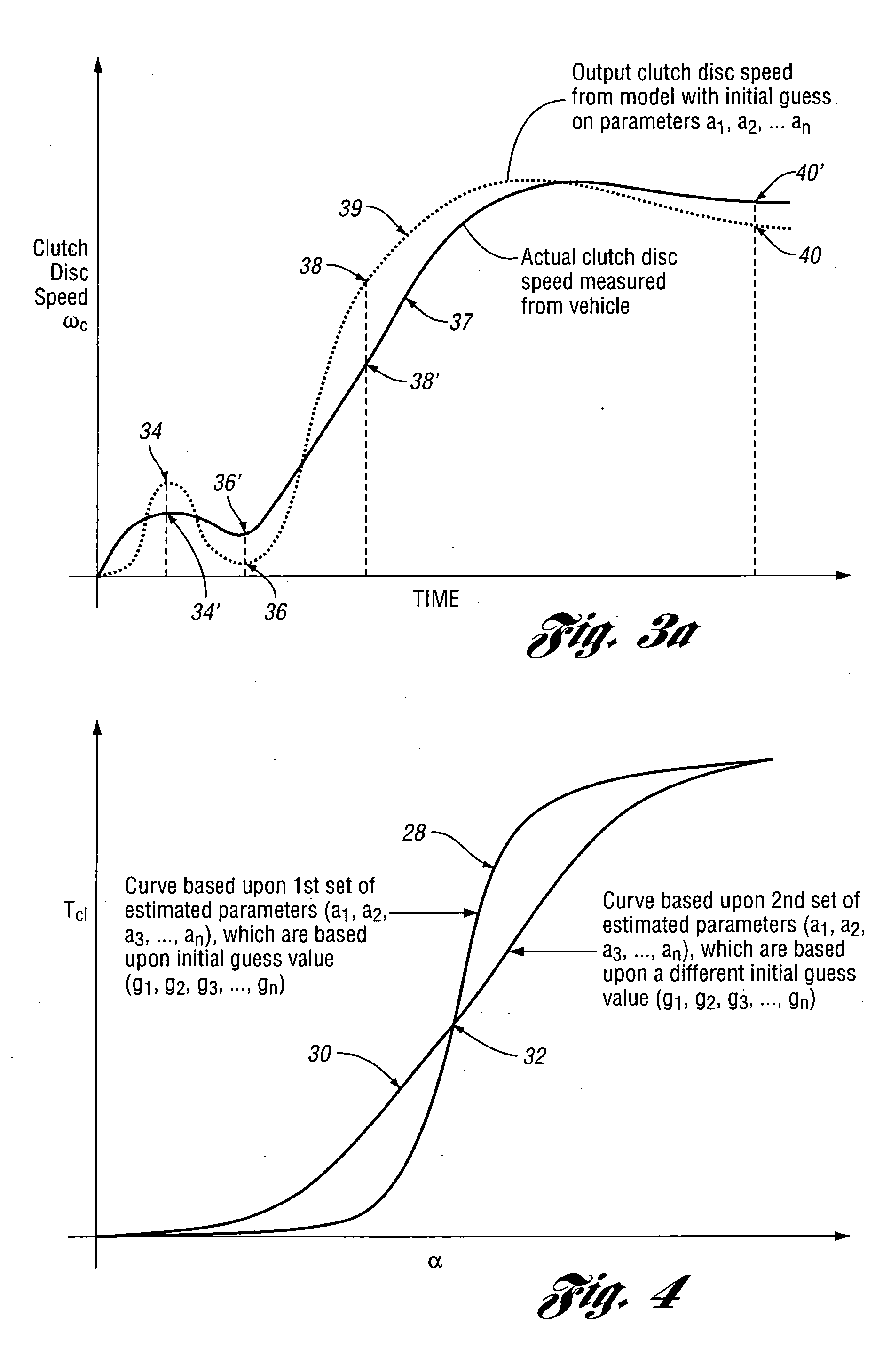
Method for estimating clutch engagement parameters in a strategy for clutch management in a vehicle powertrain
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0024]In the schematic diagram of FIG. 2, the clutch input friction disk is shown at 10 and the clutch output friction disk is shown at 12. Disk 10 is drivably connected to engine 14. The clutch output disk is drivably connected to a transmission mainshaft or a driveline driveshaft 16. Driveline elasticity is schematically represented by a spring constant 18 (Kc), and a vibration damper constant is schematically represented by at 20 (βc). During upshifts and downshifts of the transmission, or during vehicle launch, torque delivery from the engine is interrupted as the clutch disks 10 and 12 are opened. A dynamic model of the entire system can be found by applying a torque equilibrium condition at various nodes in the structure. The dynamic equations for the driveline shown in FIG. 2, when the clutch is slipping in an engagement mode, are indicated as follows:
ω.e=-βeJeωc-1JeTcl+1JeTe(1)ω.c=-βcJcωc-1JcTl+1JcTcl(2)Tcl=F(α,α0,α1,α2,…,αn)(3)
[0025]where:
[0026]ωe=Engine speed, measured on ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com