Expandable clip for tissue repair
a tissue flap and expandable technology, applied in the field of tissue flaps and expandable clips, can solve the problems of tissue flaps not healing to permanently occlude the foreman ovale, other septal defects can be more serious, undesirable to continue having blood flow, etc., and achieve the effect of effectively treating and treating an opening
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0064]The invention is an apparatus, system, and method for treating a patent foramen ovale (PFO) to cause closure thereof. More specifically, the invention provides for percutaneous or other minimally-invasive application of suture to PFO to cause closure of the PFO.
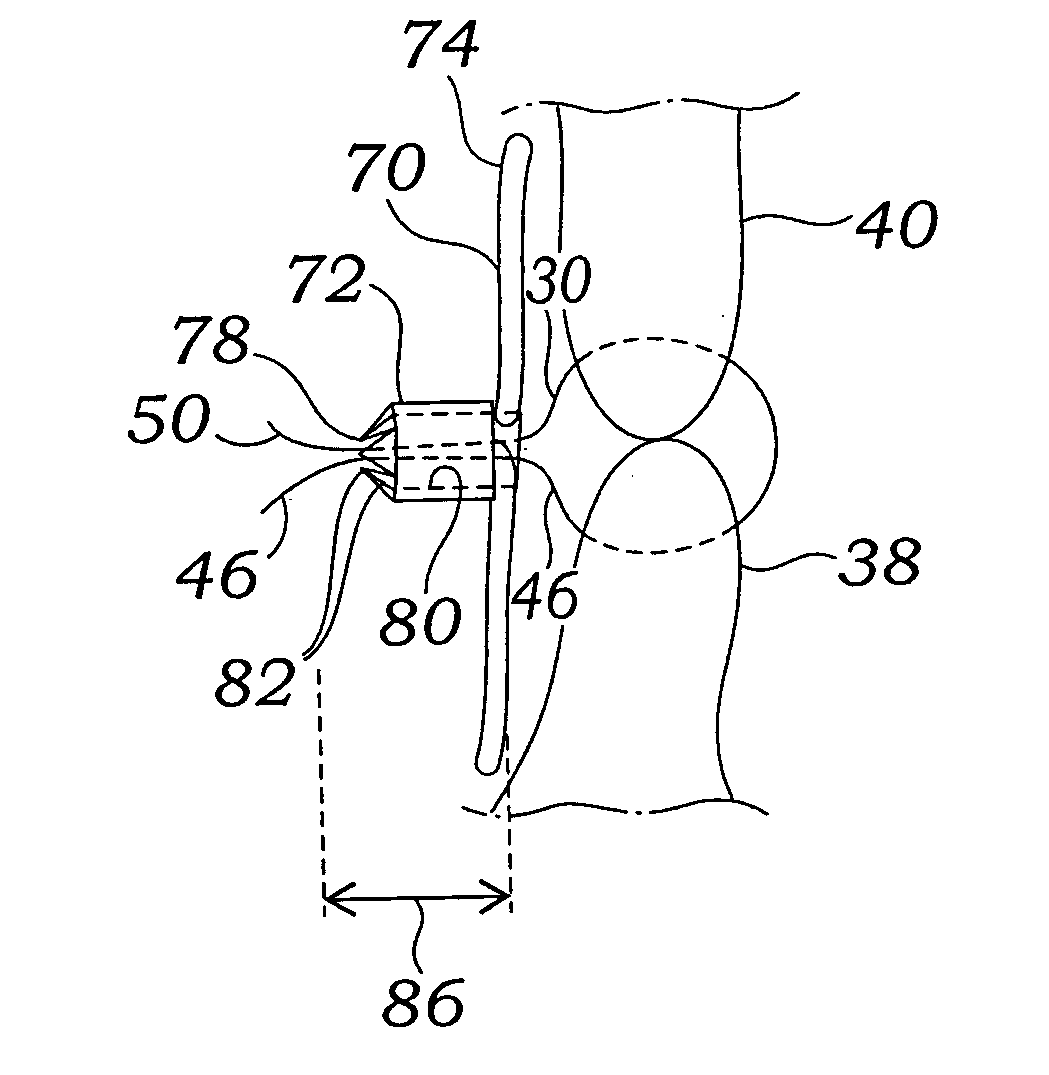
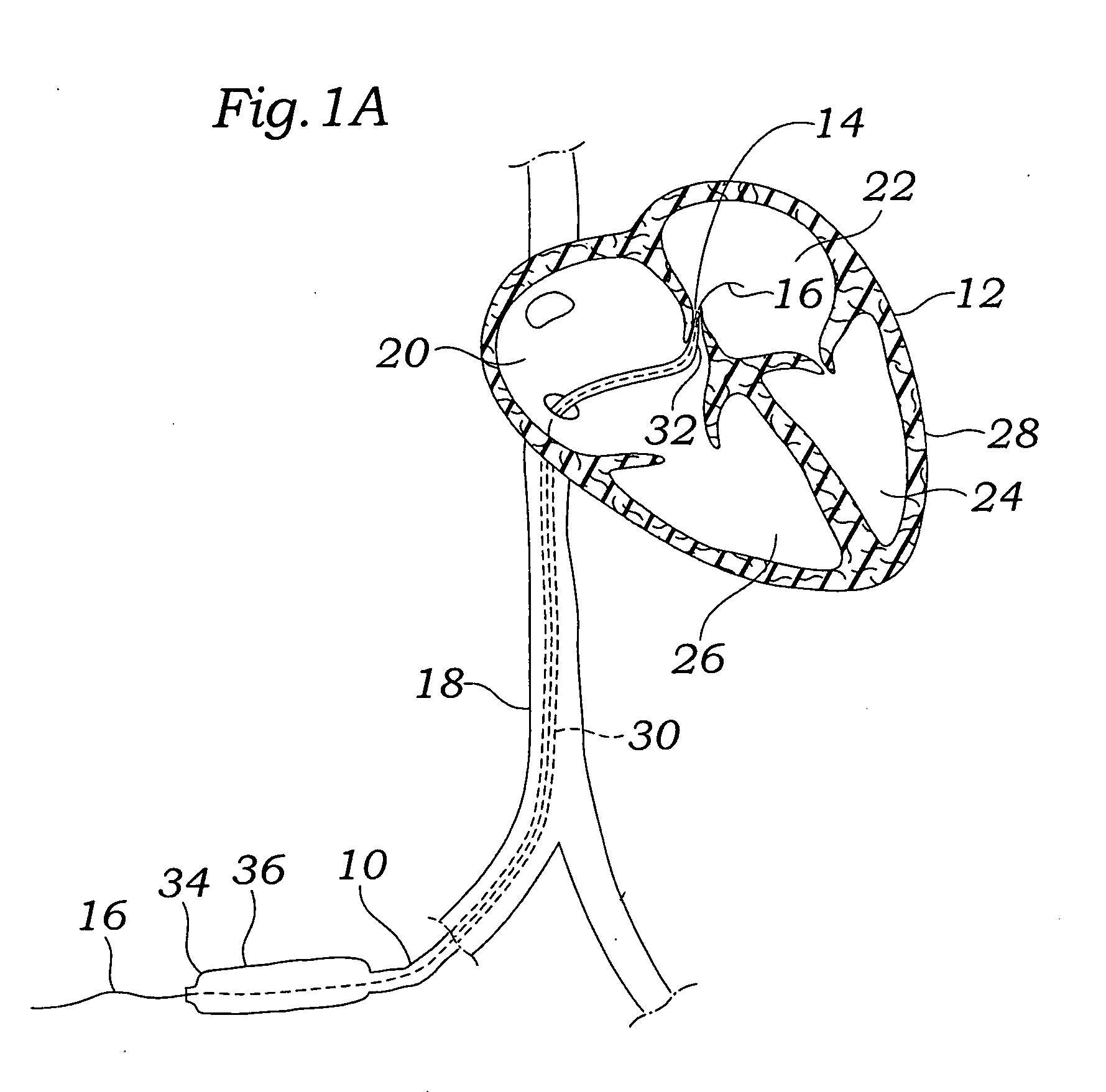
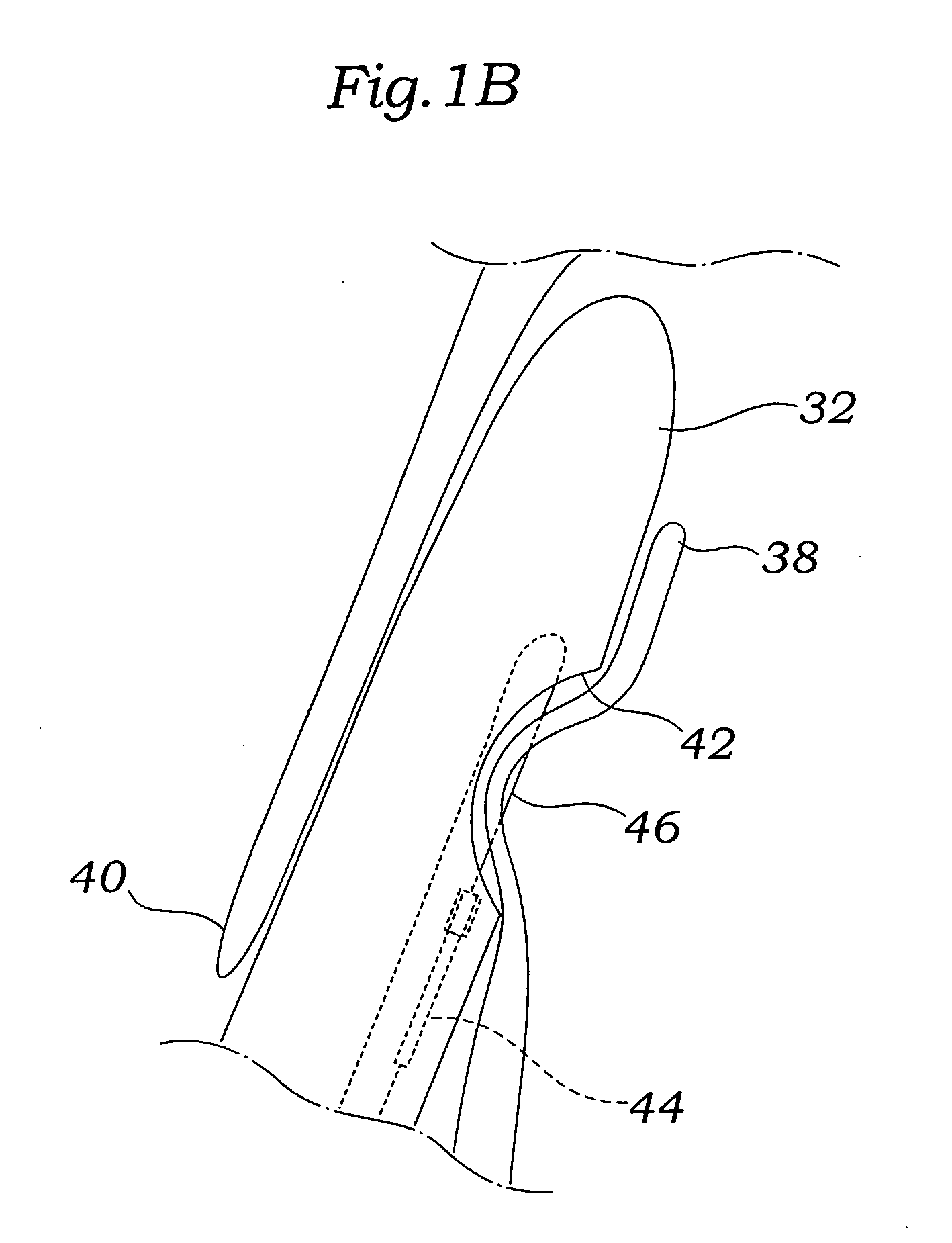
[0065]FIG. 1A depicts a suture-deploying treatment catheter 10 according to the invention being advanced through a patient's vasculature to a heart 12 and into a PFO 14. A guidewire 16 has previously been advanced through the vasculature by passing up the inferior vena cava 18, through the right atrium 20, and through the PFO 14 and into the left atrium 22. Note that other introductory routes, including other percutaneous and minimally invasive routes, are also within the scope of the invention. For example, the guidewire and device could be introduced through heart vessels leading to the left ventricle 24 or right ventricle 26, and then on to access the PFO 14 through either the right atrium 20 or left atrium 22. Depen...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com