Articles Comprising Nanoscale Patterns With Reduced Edge Roughness and Methods of Making Same
a nanoscale pattern and edge roughness technology, applied in the field of articles comprising nanoscale patterns with reduced edge roughness and methods of making same, can solve the problems of affecting the performance of bio-analytical and microfluidic systems, and affecting the efficiency of nanoscale wires
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0037]The following detailed description illustrates the invention by way of example and not by way of limitation. The description enables one skilled in the art to make and use the present disclosure, and describes several embodiments, adaptations, variations, alternatives, and uses of the present disclosure, including what is presently believed to be the best mode of carrying out the present disclosure.
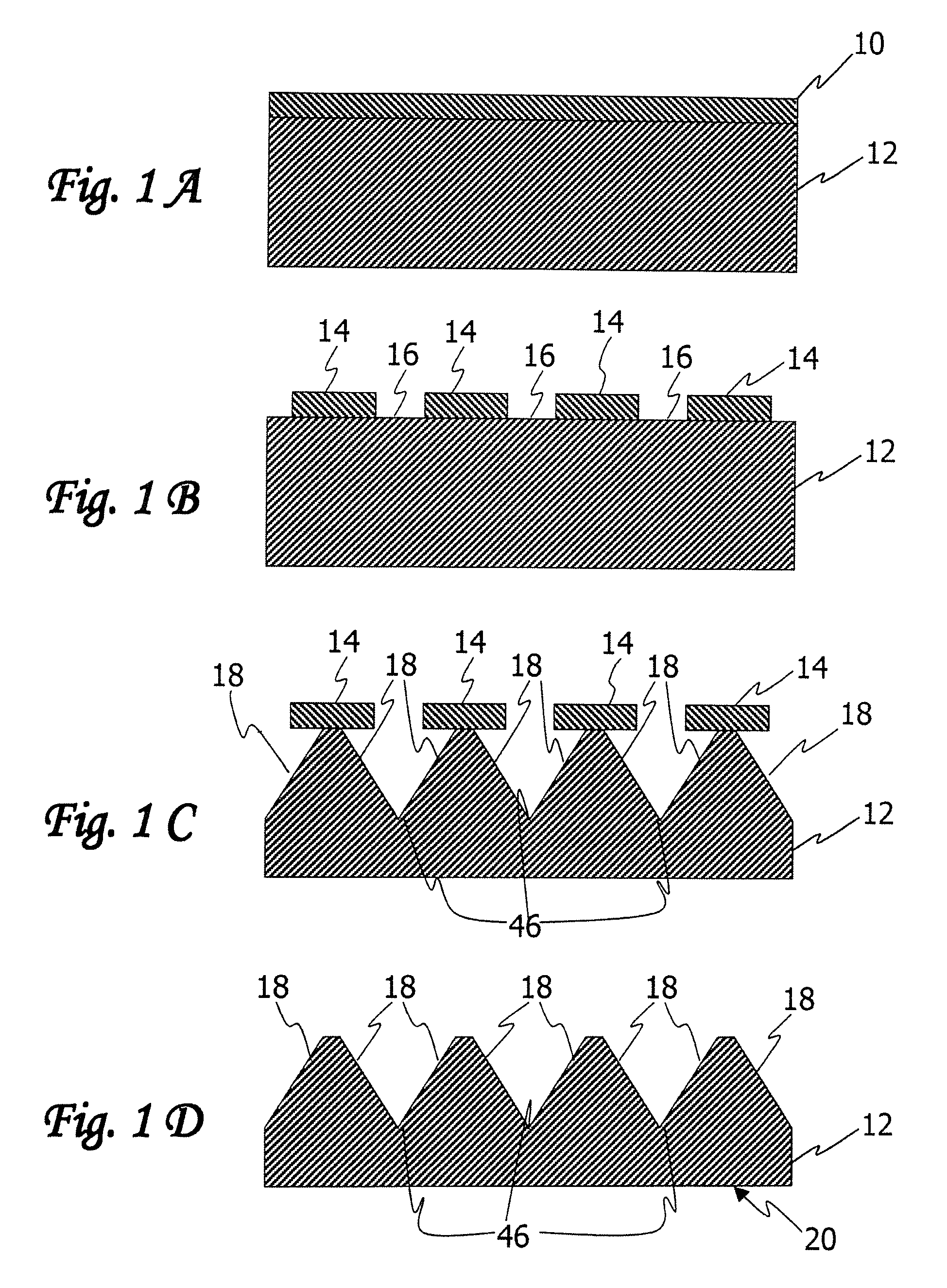
[0038]The description is divided into four parts. Part I describes an exemplary article having a nanoscale pattern with smooth edges and / or sidewalls, and Parts II, III and IV describe approaches for making such articles.
[0039]I. Exemplary Article
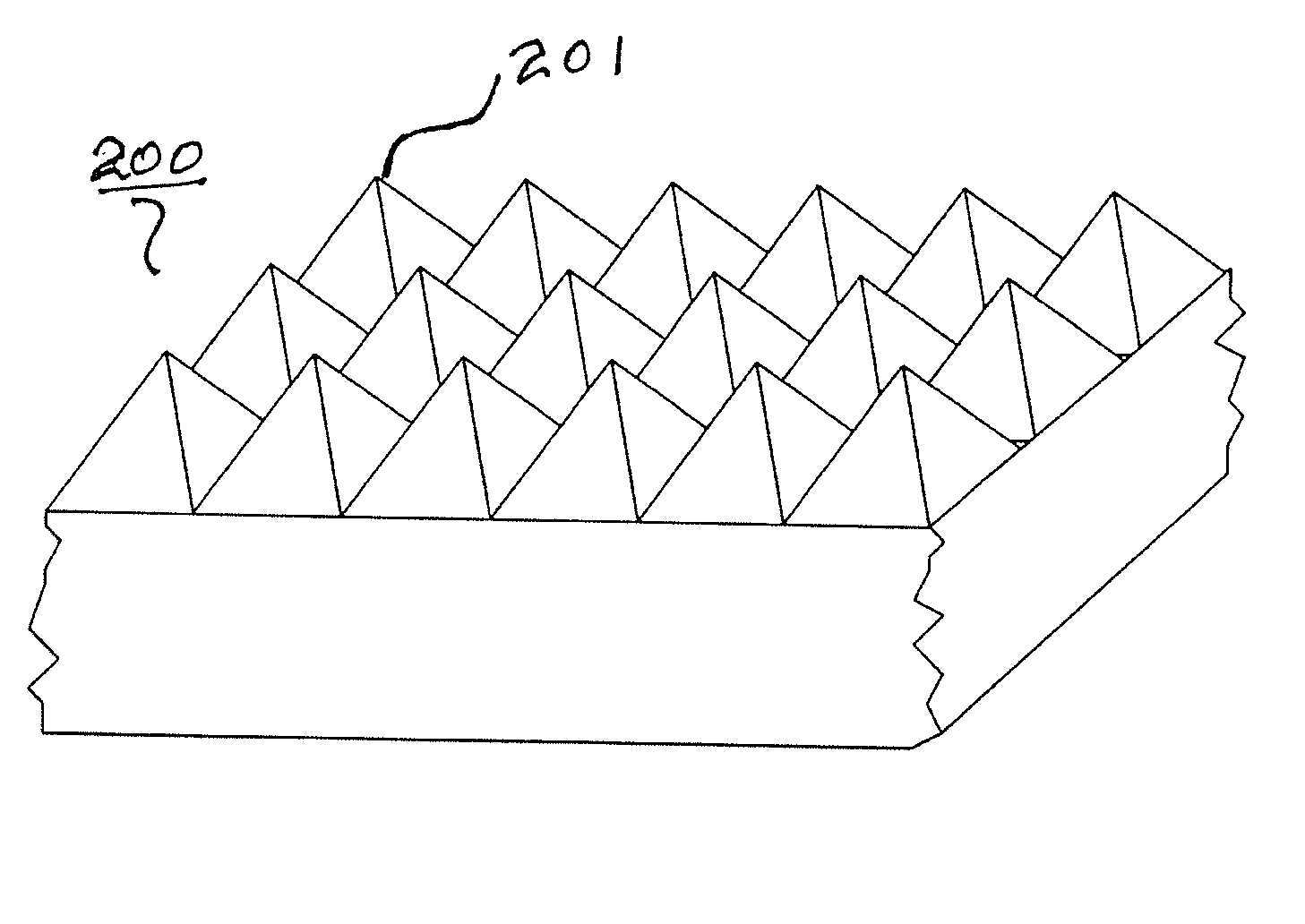
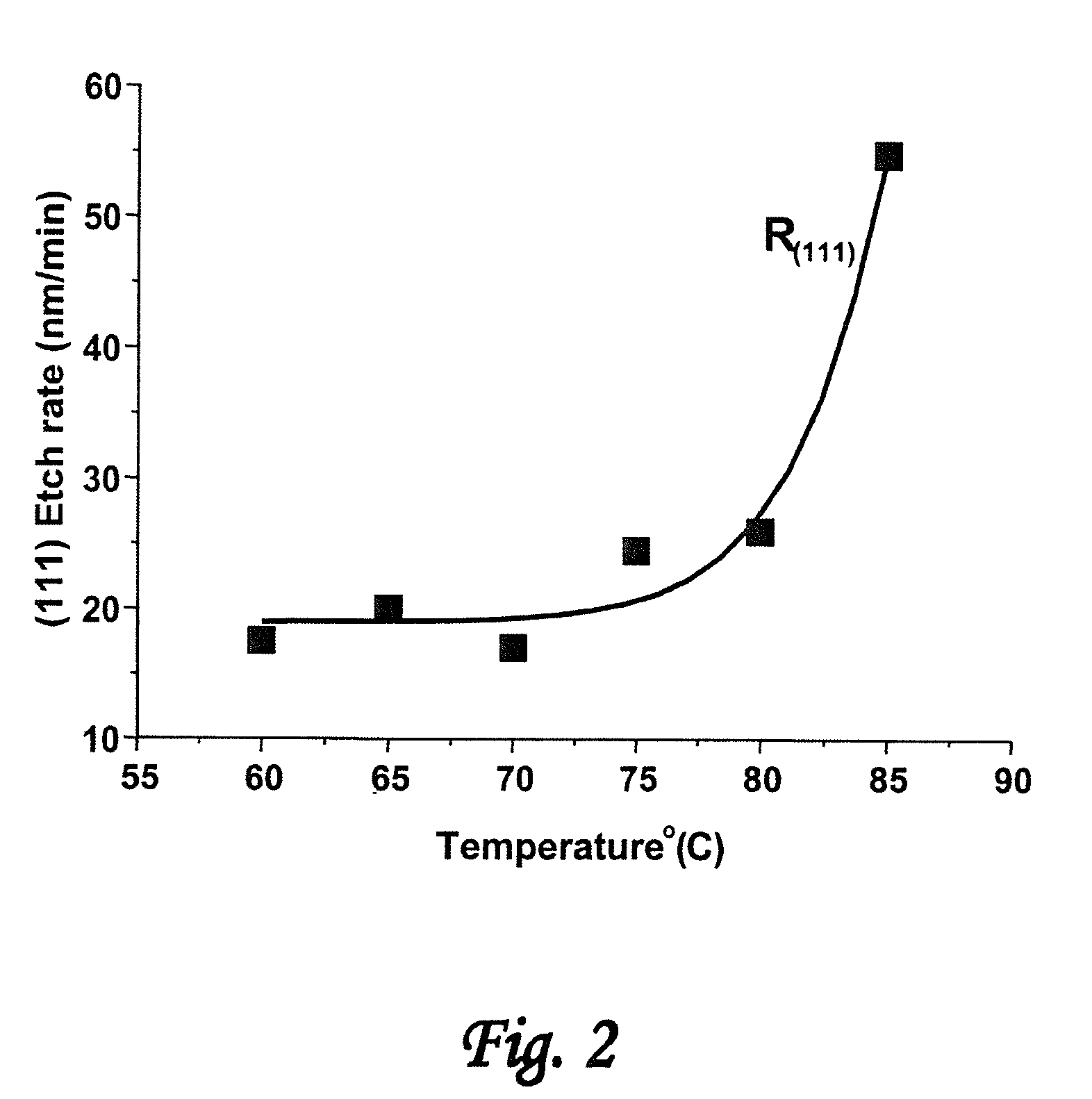
[0040]Referring to the drawings, FIG. 20 is a schematic top view of an exemplary article 100 comprising a nanoscale patterned surface 101. Typical useful nanoscale surface patterns 101 are comprised of a plurality of protruding features 102 and one or more recessed features 103 having at least one protruding feature with a minimum lateral d...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Electrical resistance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com