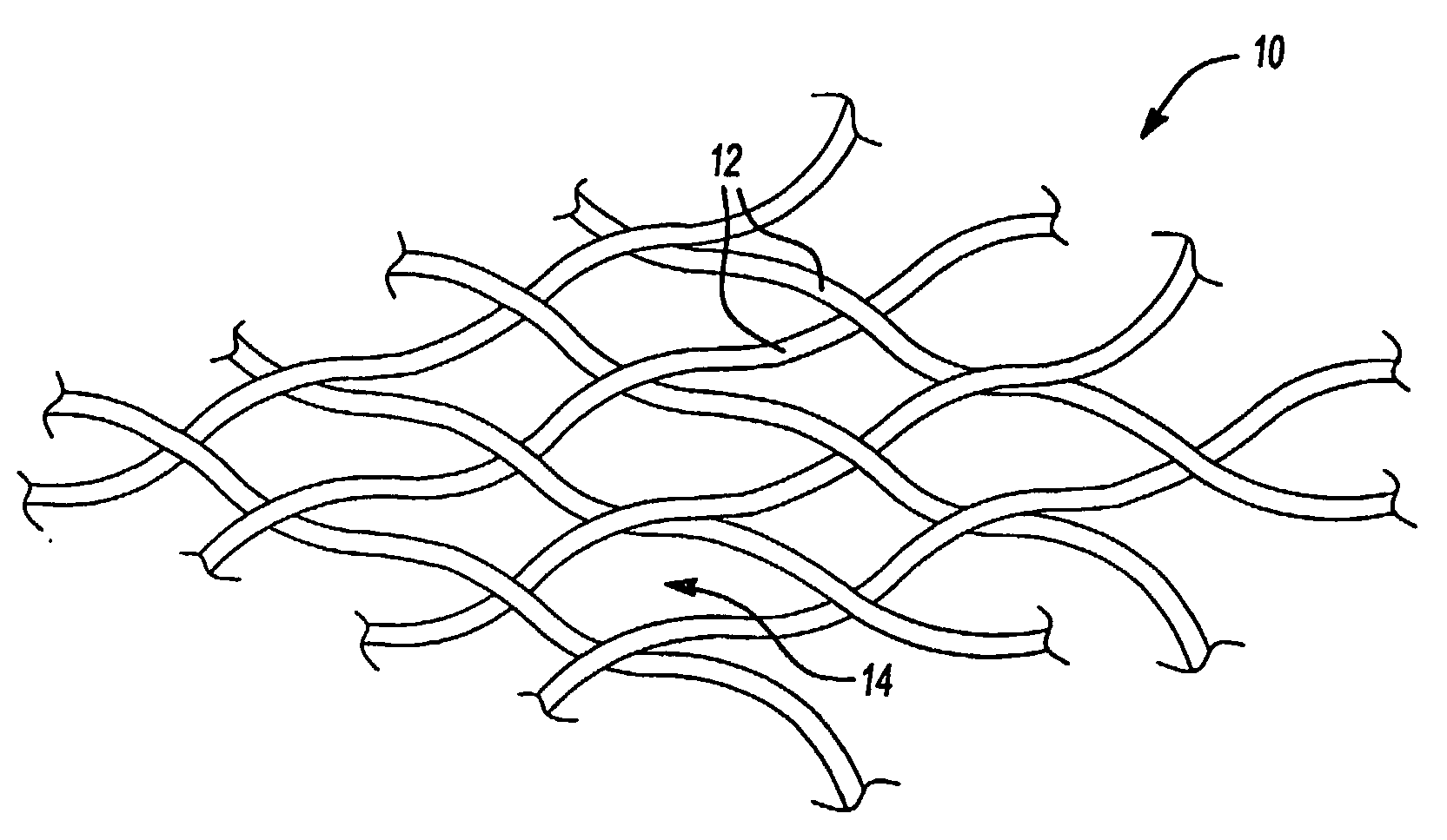
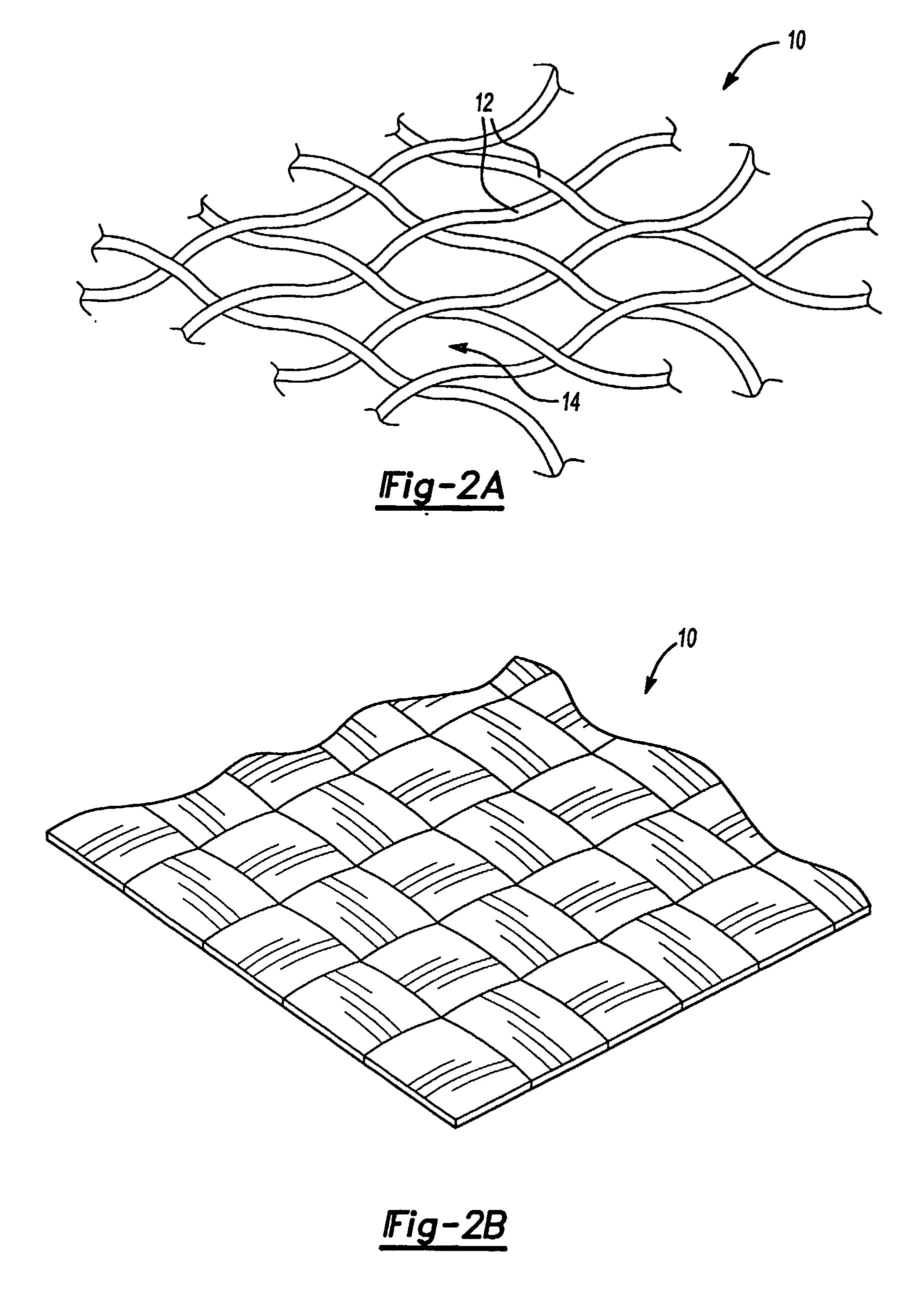
Polyolefinic Materials for Plastic Composites
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0145]Performance of a consolidated sheet (1.85 mm thickness) of coextruded tape including an propylene-ethylene copolymer co-extruded with a polypropylene homopolymer as disclosed herein (designated as Sample X) (about 0.04 mm thick by 3 mm wide) is compared with the performance of materials such as that available commercially under the designation CURV™ (denoted respectively as “Sample A” and “Sample B”) in the 1.5 and 2.2 mm thicknesses shown), using a falling dart impact test (per ISO 7765-1) at room temperature and at (−)40° C. FIGS. 5A and 5B illustrate data obtainable according to a preferred embodiment of the present invention.
example 2
[0146]A spare tire bin is injection molded with a polypropylene bulk material, along with a three layer (3 L) consolidated twill woven coextruded polypropylene tape (about 0.04 mm thick by 3 mm wide) intermediate form on one side of the polypropylene bulk material. The resulting article is ruck free and exhibits a 400% improvement as compared with a 40% long glass fiber composite with a 20% glass filled polypropylene matrix, when impacted at 8 MPH at −30° C. A complete ductile break is observed without shattering; i.e., no flying pieces are observed during impact.
example 3
[0147]Example 2 is repeated but the intermediate form is placed on both sides of the polypropylene bulk material, exhibiting enhanced stiffness and impact resistance relative to the Example 2 composite.
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Fraction | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com