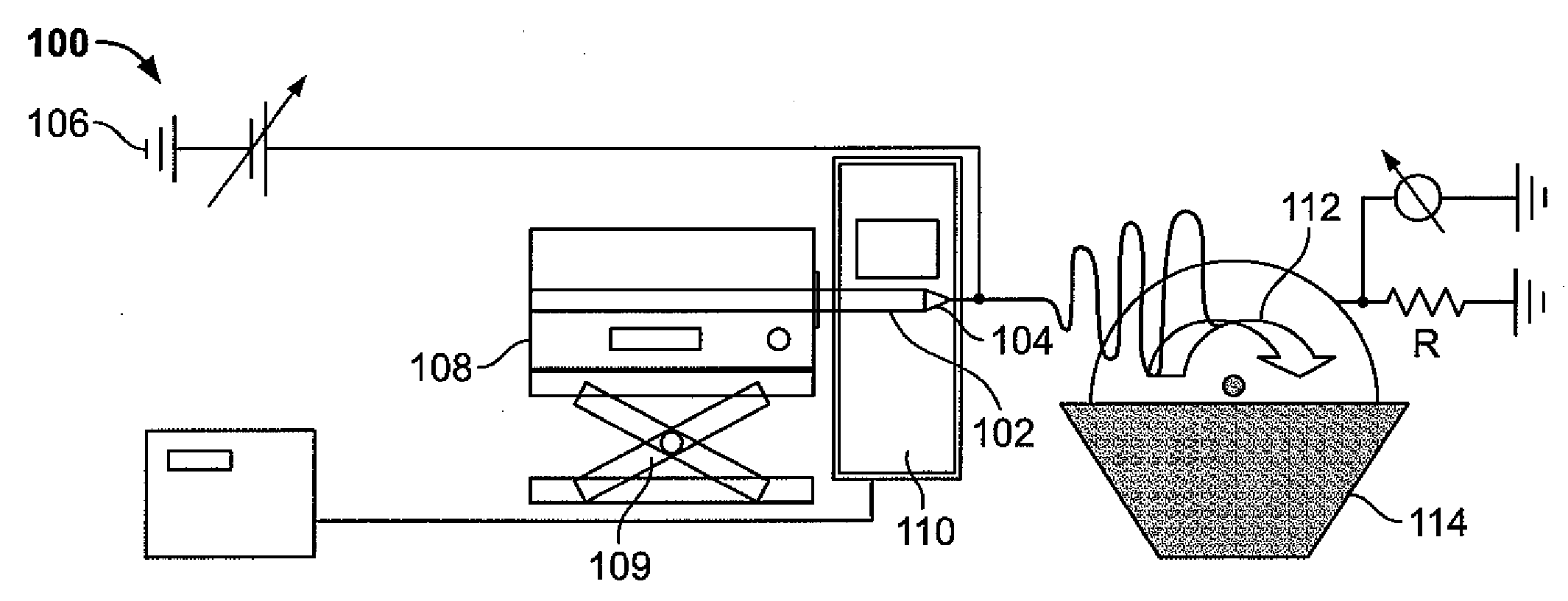
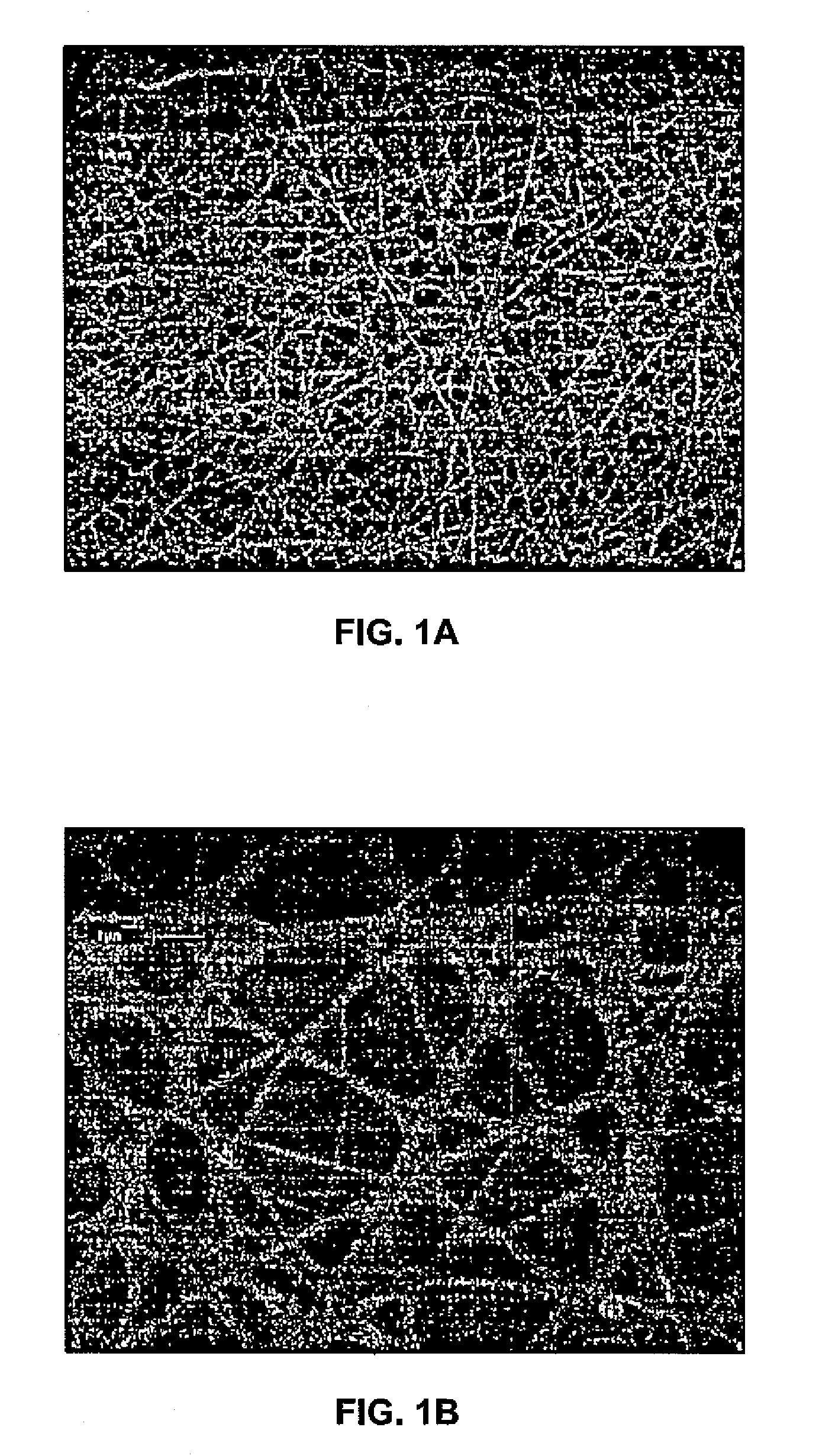
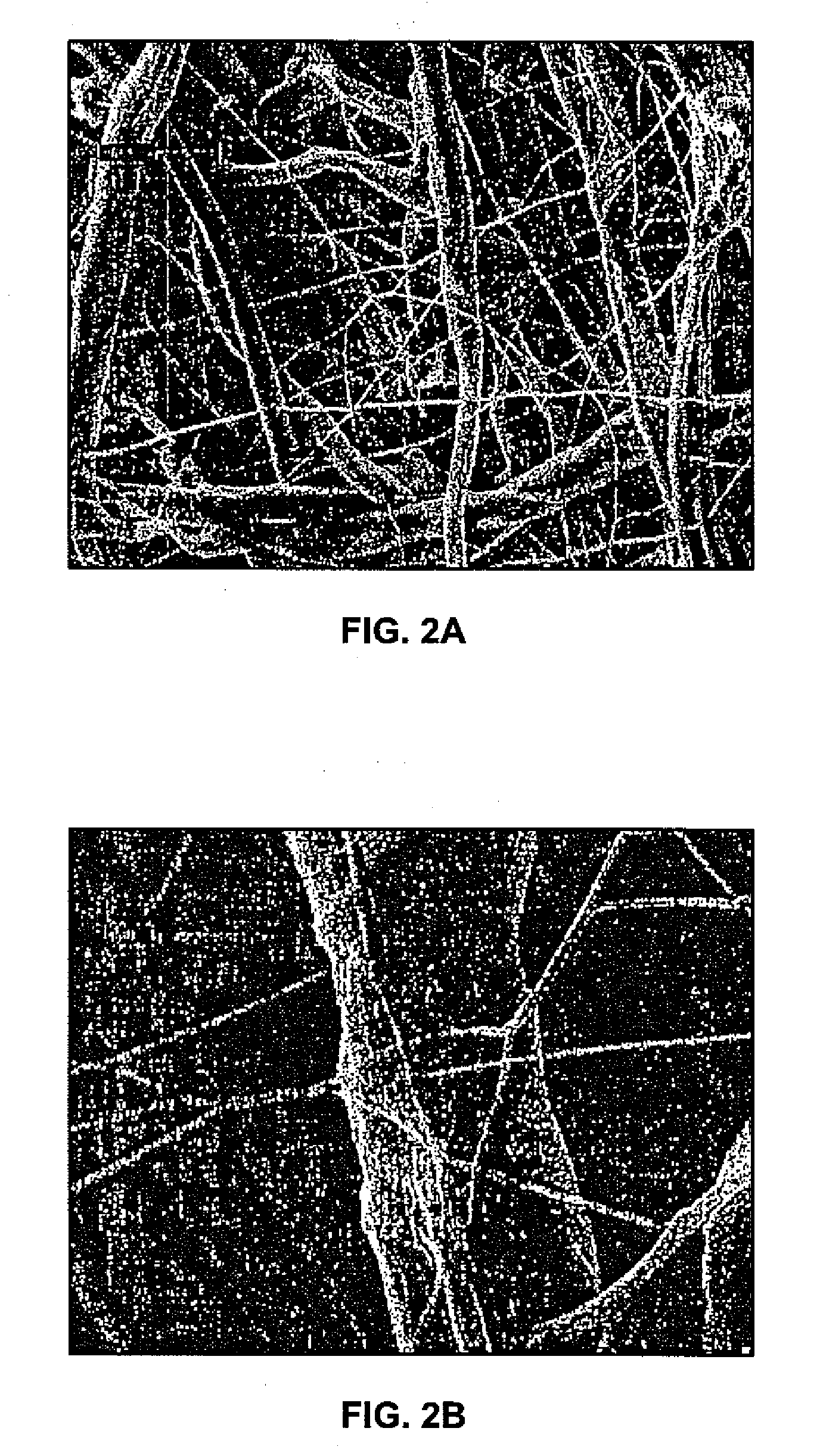
Apparatus and Method for Producing Electrospun Fibers
a technology of electrospun fibers and apparatuses, applied in the field of fibers, can solve the problems of cellulose being difficult to transform into fibers, and substantially insoluble in common solvents
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
[0018]The nanofibers of the present invention may be made from organic polymeric starting materials. These organic polymeric starting materials are typically mixed with a solvent comprising a relatively high volatility (i.e., the readiness with which a material vaporizes), and then subjected to an electrospinning process. Ideally, the solvent is sufficiently volatile to substantially dissolve during the electrospinning process.
[0019]Nanofibers made in accordance with the present invention comprise an organic polymer, and typically exhibit fiber diameters between about 50.0 nm and 1.0 micron, more particularly between about 100.0 nm and 300.0 nm and still more particularly between about 100.0 nm and 200.0 mm. The nanofibers may be relatively amorphous, comprising a degree of crystallinity less than about 60% and more particularly between about 1.0% and 50.0% and still more particularly between about 1.0% and 40.0%. The degree of crystallinity is determined through X-ray diffraction p...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Temperature | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Time | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com