Network protection using network coding
a network protection and network coding technology, applied in the field of network protection, can solve the problems of node failure, network maintenance failure, node failure is more damaging than link or system failure, etc., and achieve the effect of reducing the cost and effect of failur
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
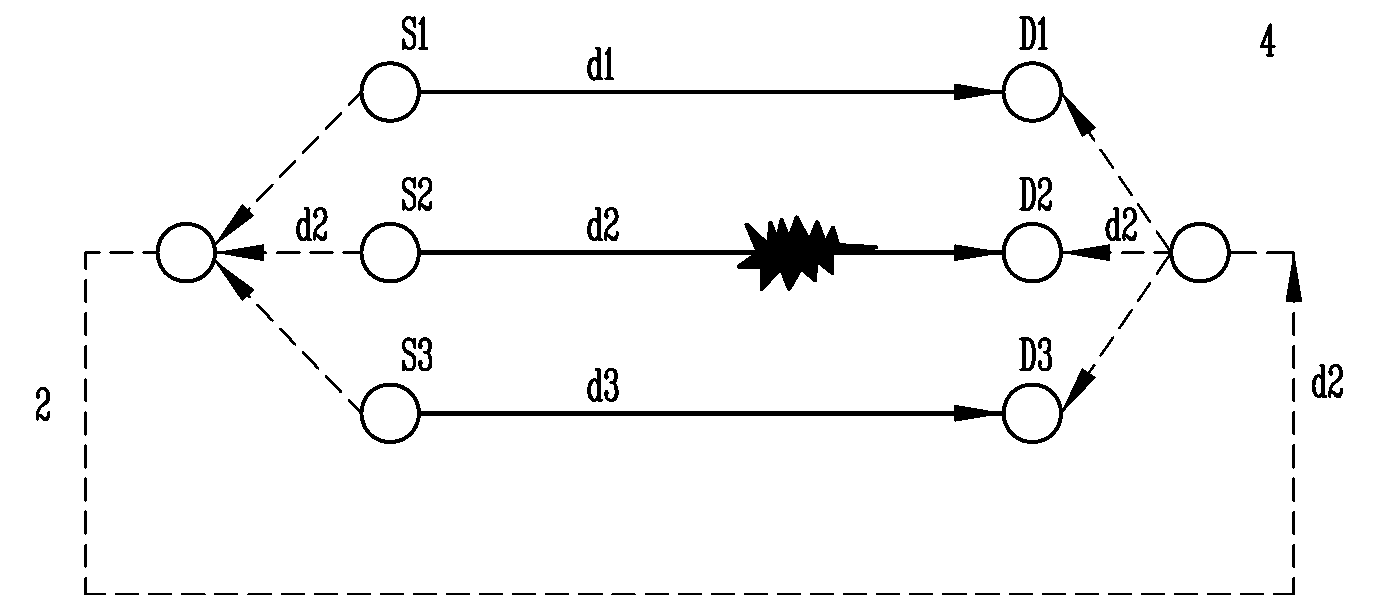
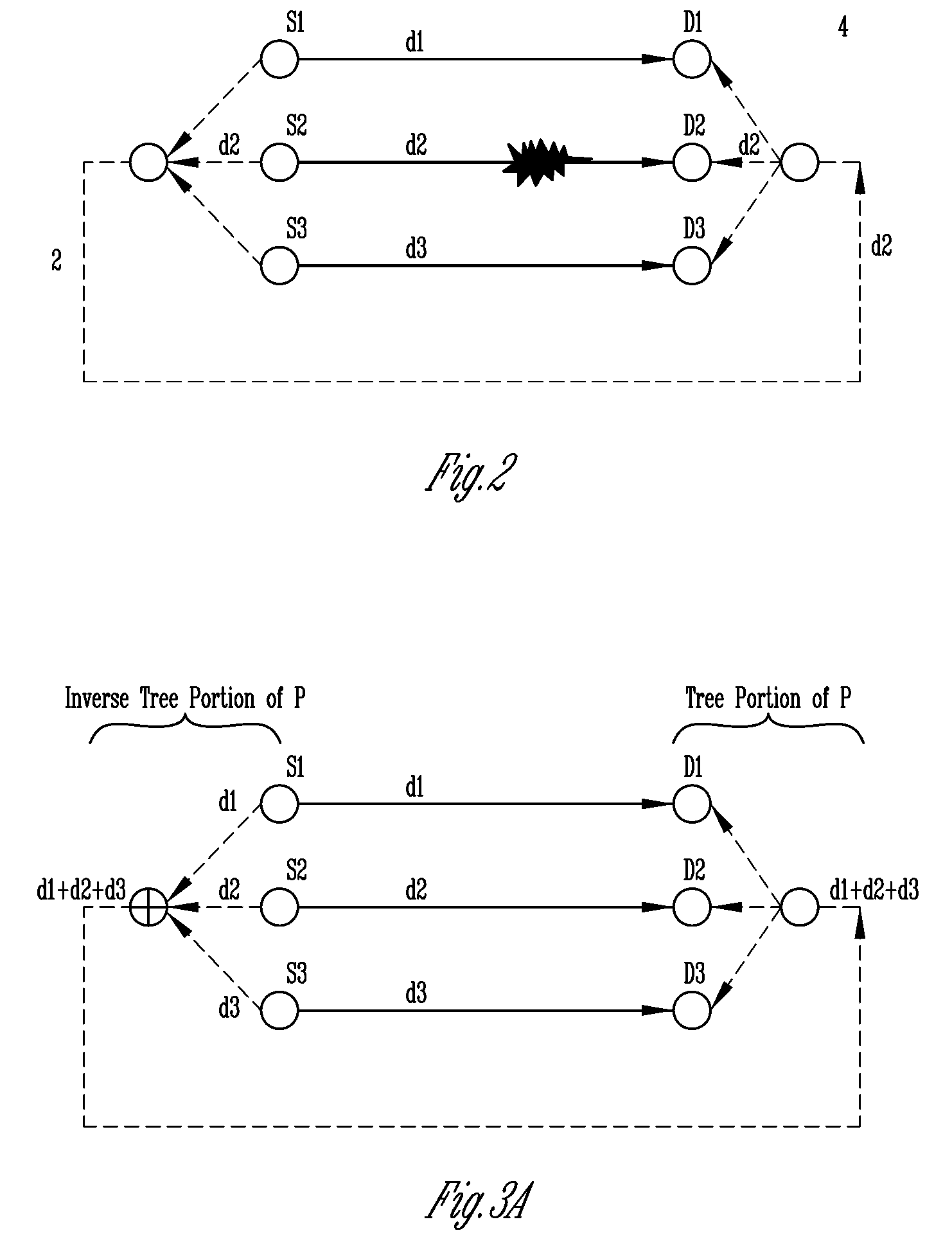
[0026]The present invention includes a number of different strategies relating to network protection against various types of failures. In a first embodiment, discussed primarily in section 1, a methodology for providing 1+N protection is described. In this section, network coding is used to combine a number of signals on one protection circuit. This method can be used to provide 100 percent 1+N protection against single link failures. The single protection circuit or backup circuit is shared between N sessions by applying a network coding technique to the data. The use of the network coding technique uses the same resources required by a 1:N technique, but at the speed of the 1+1 method.
second embodiment
[0027]In a second embodiment, discussed primarily in section 2, a modified 1+N protection is described, which is a modification of the strategy of section 1. The modified strategy may result in the requirement of fewer network resources for protection, at the expense of requiring one of the network nodes, that is not necessarily a transmitter or a receiver, to play a special role to facilitate the protection.
third embodiment
[0028]In a third embodiment, discussed primarily in section 3, a methodology is provided for protecting against a single link failure in optical networks. Network coding and reduced capacity are used on the working paths to provide a backup protection that will carry encoded data from all sources. In addition, implementation aspects are provided regarding how to deploy the method in the case of an optical network with n disjoint working paths.
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com