Polypeptide having activity of aminoacyl-tRNA synthetase and use thereof
a technology of aminoacyltrna and polypeptide, which is applied in the field of polypeptides having aminoacyltrna synthetase activity, can solve the problem of insufficient specificity of the substrate of such an aars mutant to an unnatural amino acid, and achieve the effect of high specificity to an amino acid
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Construction of Editing Reaction Peptide Expression Plasmids
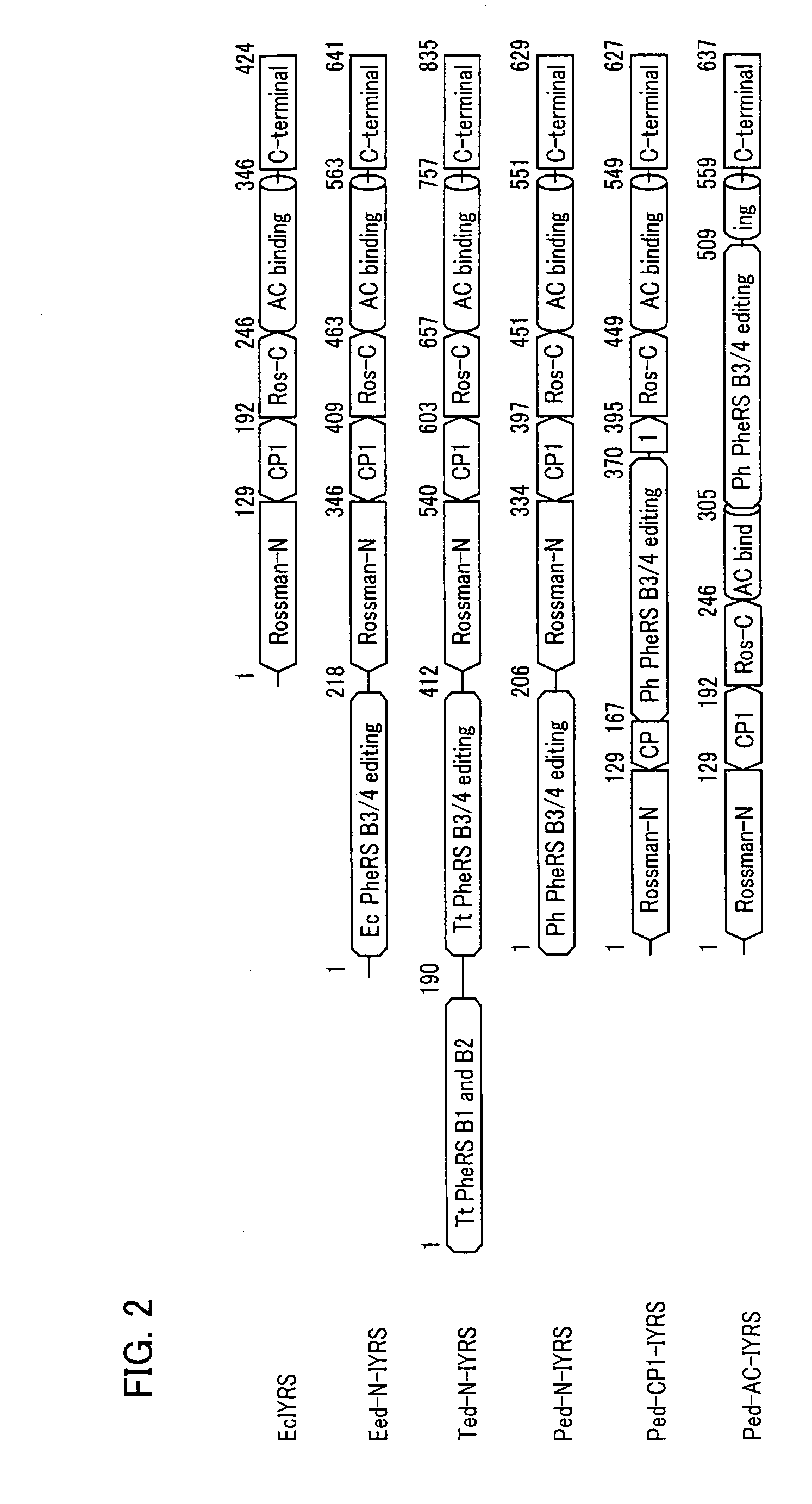
[0125]As mentioned above, the beta-subunit of PheRS consists of B1, B2, B3 / 4, B5, B6 / 7, and B8 domains, and the B3 / 4 domain is an editing reaction domain.
[0126]In the beta-subunit of PheRS, the B6 / 7 and B8 domains is placed separately from the B3 / 4 domain because of the three-dimensional structure. Further, it is believed that there is no fixed structure formed between the B5 domain and the B6 / 7 domain.
[0127]In view of this, the present example uses, as an editing polypeptide, a polypeptide fragment (hereinafter referred to as “editing reaction peptide”) including the B3 / 4 domain, and as such, does not include the B6 / 7 domain and the B8 domain.
[0128]With use of the genome DNA of E. coli, the genome DNA of T. thermophilus, and the genome DNA of P. horikoshii as templates, a DNA fragment coding for the BH to B5 domains (B1-B5) of the beta-subunit of PheRS of each living organism, a DNA fragment coding for the BH to B3 / 4 domai...
example 2
Expression and Purification of Editing Reaction Peptides
[0137]With use of each of the expression plasmids thus cloned, Escherichia coli BL21 Star (DE3) (Invitrogen Corporation) was transformed, and then cultured at 37° C. in an LB medium containing 50 μg / ml of kanamycin. At the point of time where the O.D. 600 of the culture fluid took on a value of 0.4 to 0.6, IPTG was added so that the final concentration was 1 mM. After the addition of IPTG, the culture temperature was lowered to 20° C. In this manner, the expression of each editing reaction peptide was induced. Twenty hours after the start of induction, the bacteria were harvested.
[0138]Next, the editing reaction peptide was extracted from the bacteria thus harvested, and purified. A lytic buffer solution was prepared by adding a grain of a protease inhibitor Complete (Roche) to 200 ml of a buffer solution A (20 mM Tris-Cl (ph 8.0), 300 mM NaCl, 30 mM imidazole, 5 mM 2-mercaptoethenol). The harvested bacteria were suspended in t...
example 3
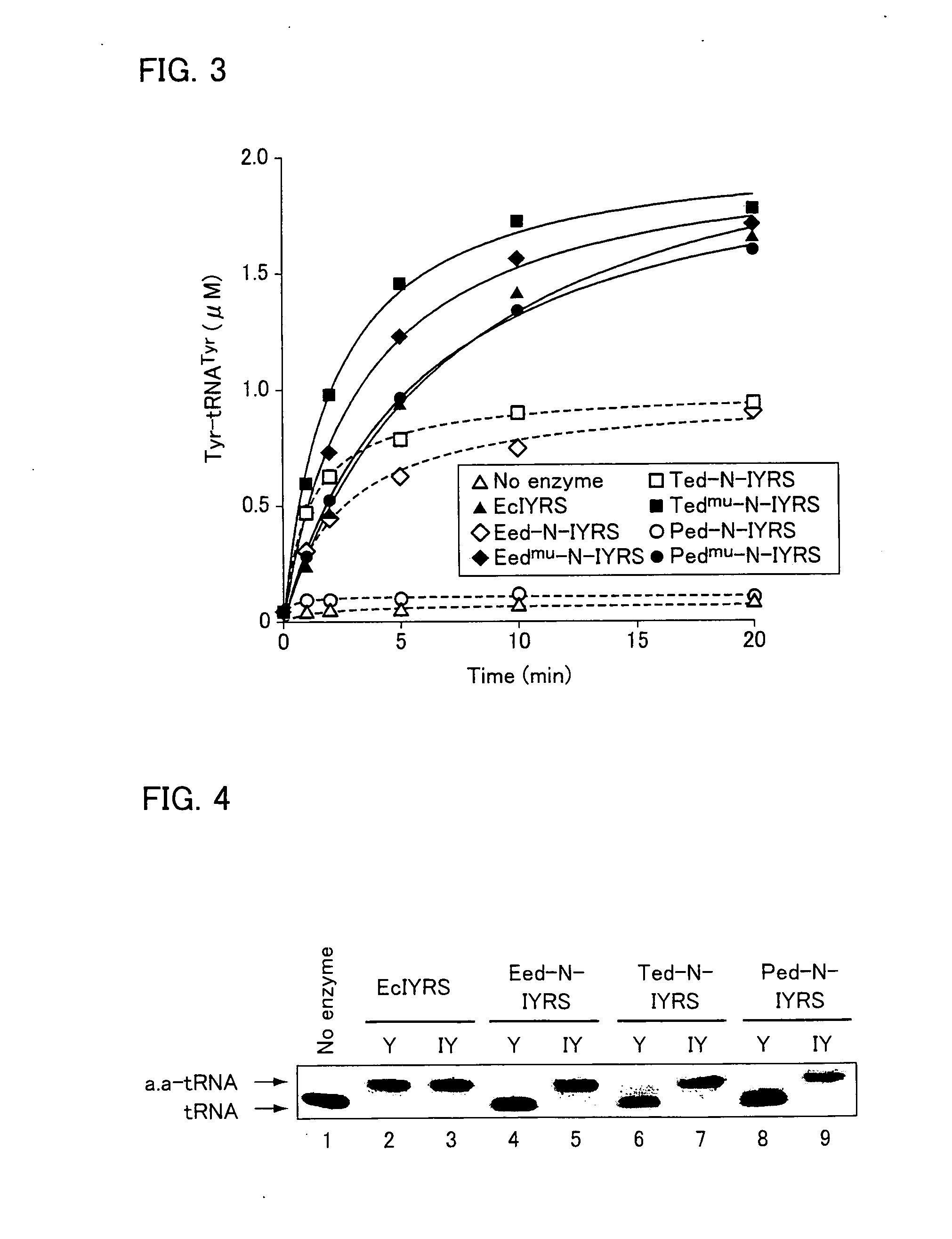
Hydrolysis Activity of the Editing Reaction Peptides
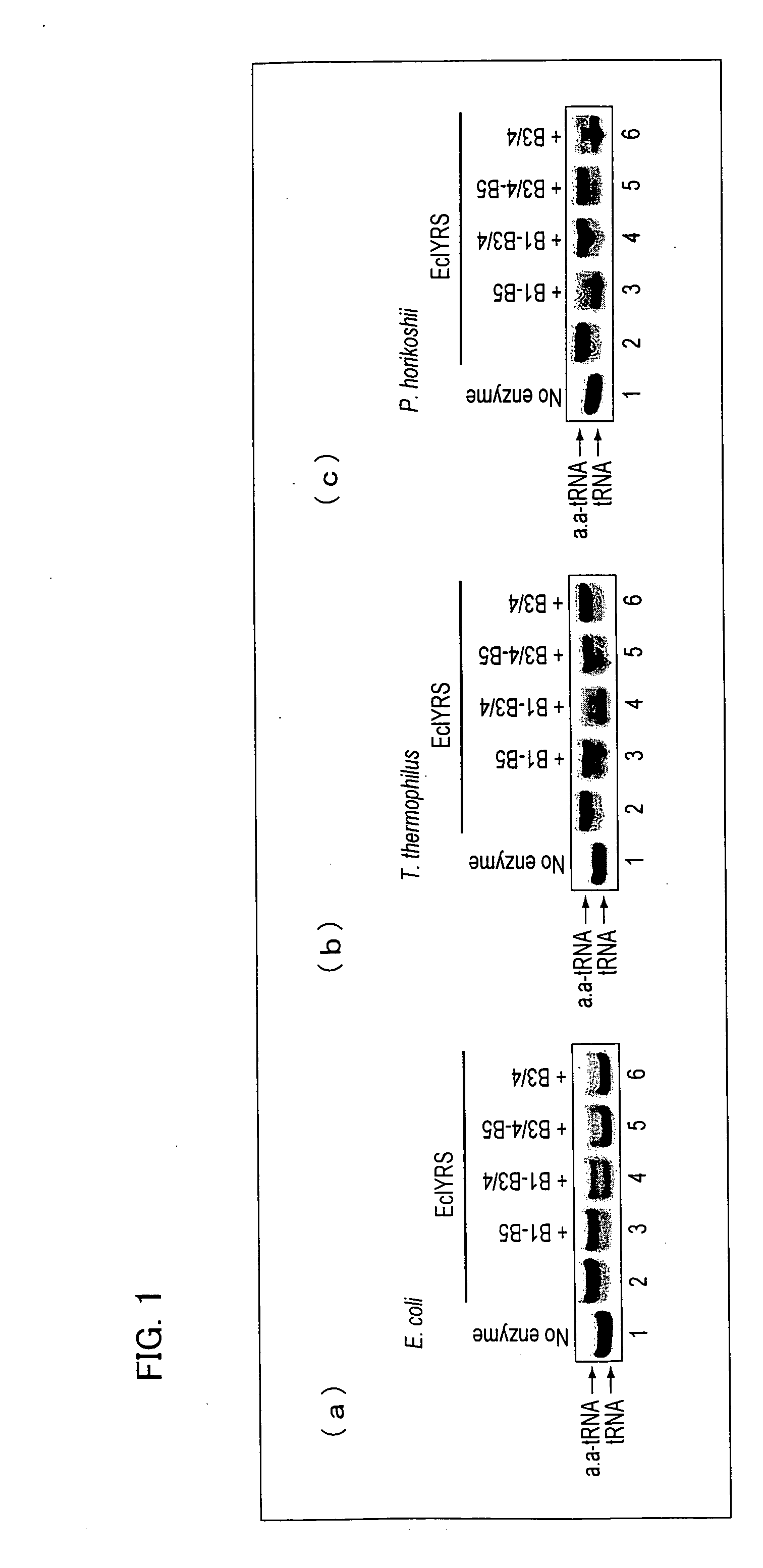
[0141]Next, the hydrolysis activity of each of the editing reaction peptides was measured. The measurement of the hydrolysis activity of each of the editing reaction peptides was performed by measuring the extent to which tyrosylation of tRNATyr by EcIYRS was inhibited, instead of directly measuring hydrolysis in tyrosyl tRNATyr. EcIYRS was obtained in the following manner. That is, a pET-26b-derived plasmid (donated from Dr. Kobayashi of RIKEN) cloned so that His-tag sticks to the C terminal of EcIYRS was used to transform Escherichia coli BL21 Star (DE3) (Invitrogen Corporation) The subsequent operations were performed in the same manner as in the aforementioned expression and purification of editing reaction peptides.
[0142]It should be noted that the base sequence of EcIYRS is represented by SEQ. ID. NO: 4. It should also be noted that the amino-acid sequence of EcIYRS is an amino-acid sequence represented by the aforementioned ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Molar density | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com