Heat dissipation device and lighting device
a heat dissipation device and heat dissipation technology, which is applied in the direction of semiconductor devices for light sources, lighting and heating apparatus, fixed installations, etc., can solve the problems of poor light emission efficiency, shorten the life of leds, and difficulty in obtaining the necessary amount of light, etc., to achieve efficient transfer, small size, and high degree of freedom of layout design
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
embodiment 1
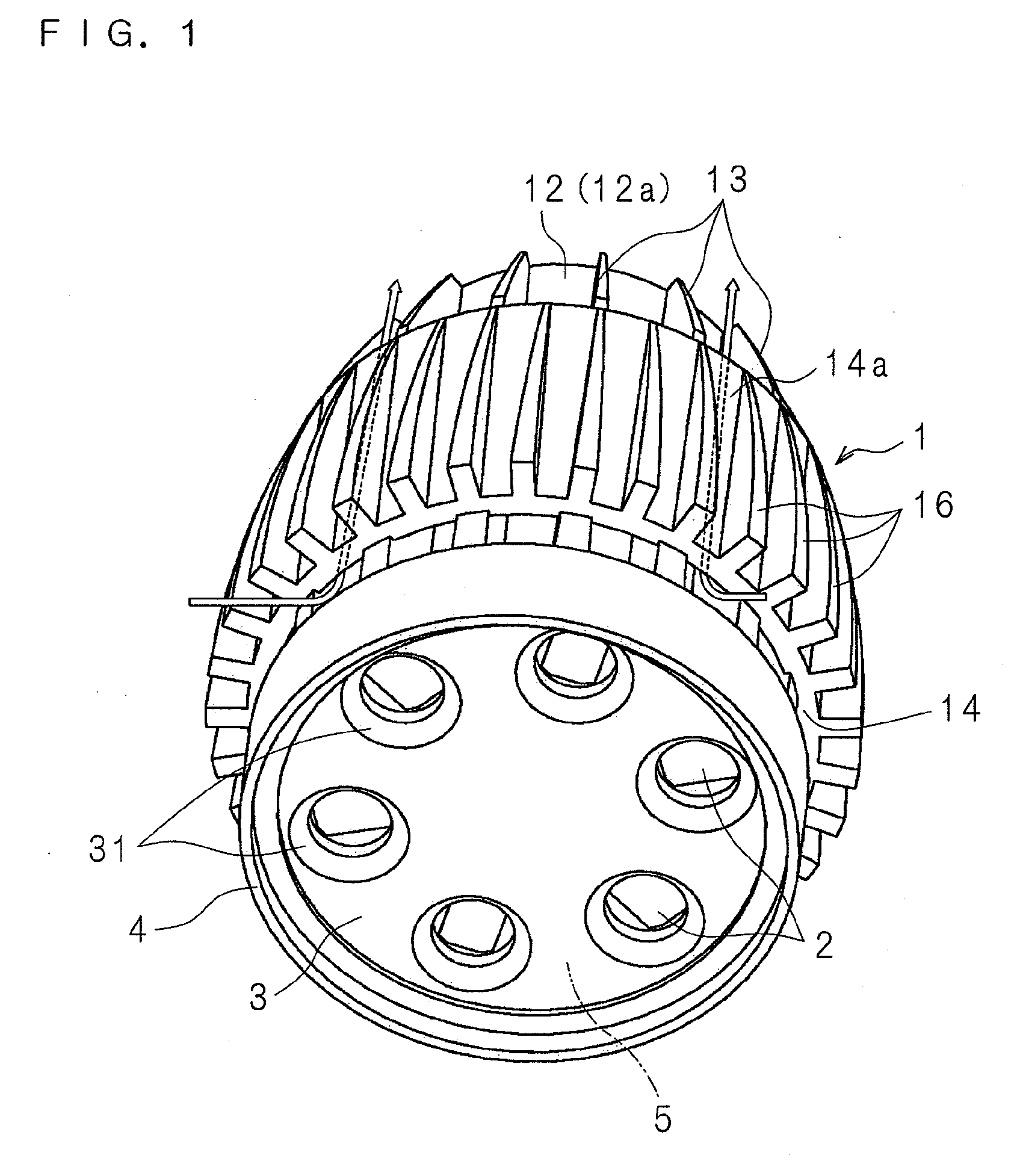
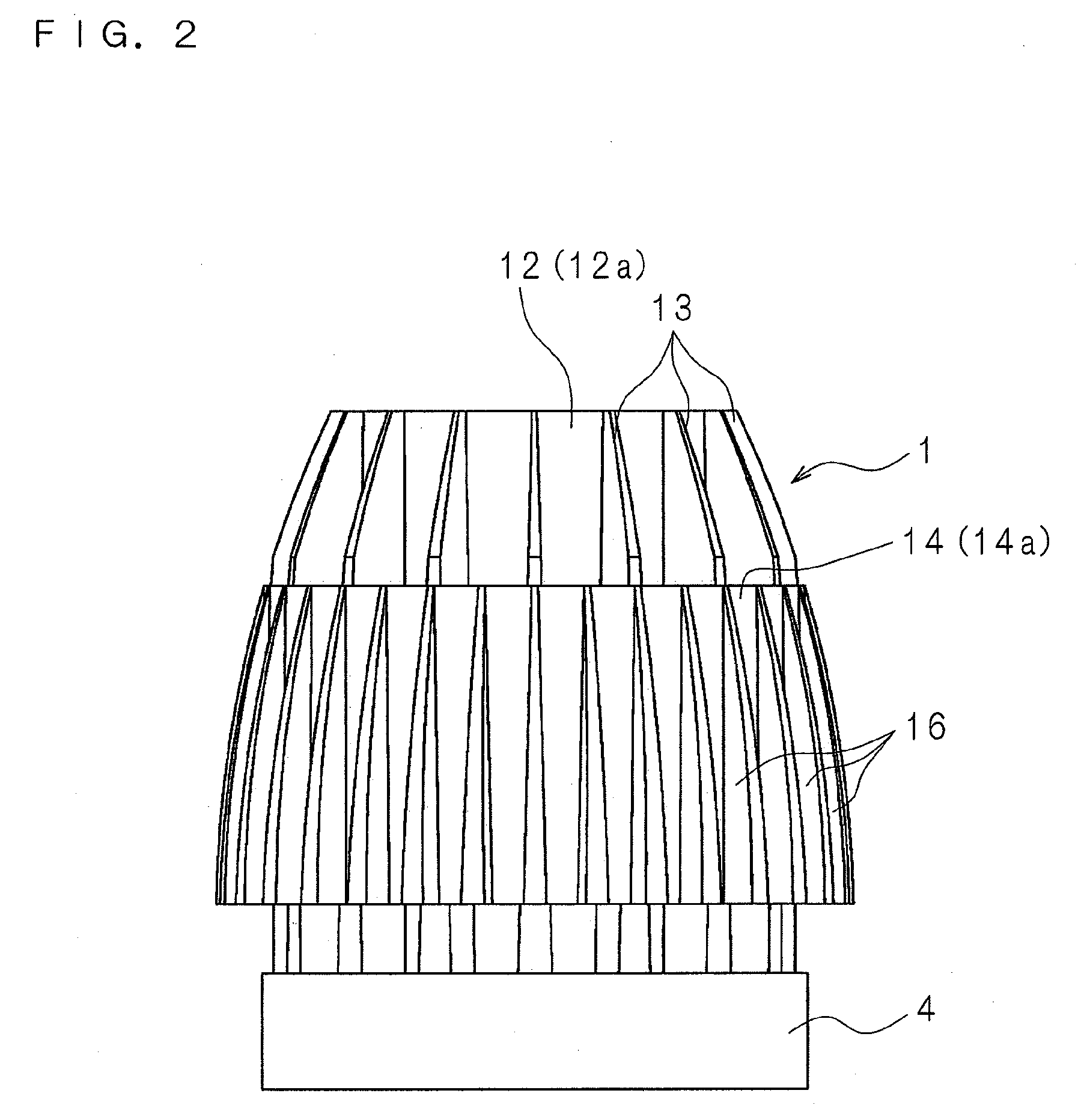
[0070]FIG. 1 is an external perspective view of a lighting device according to Embodiment 1 of the present invention. FIG. 2 is a schematic side view of the lighting device, and FIG. 3 is a schematic rear view of the lighting device. FIG. 4 is a schematic cross sectional view taken along the Iv-Iv line of FIG. 3.
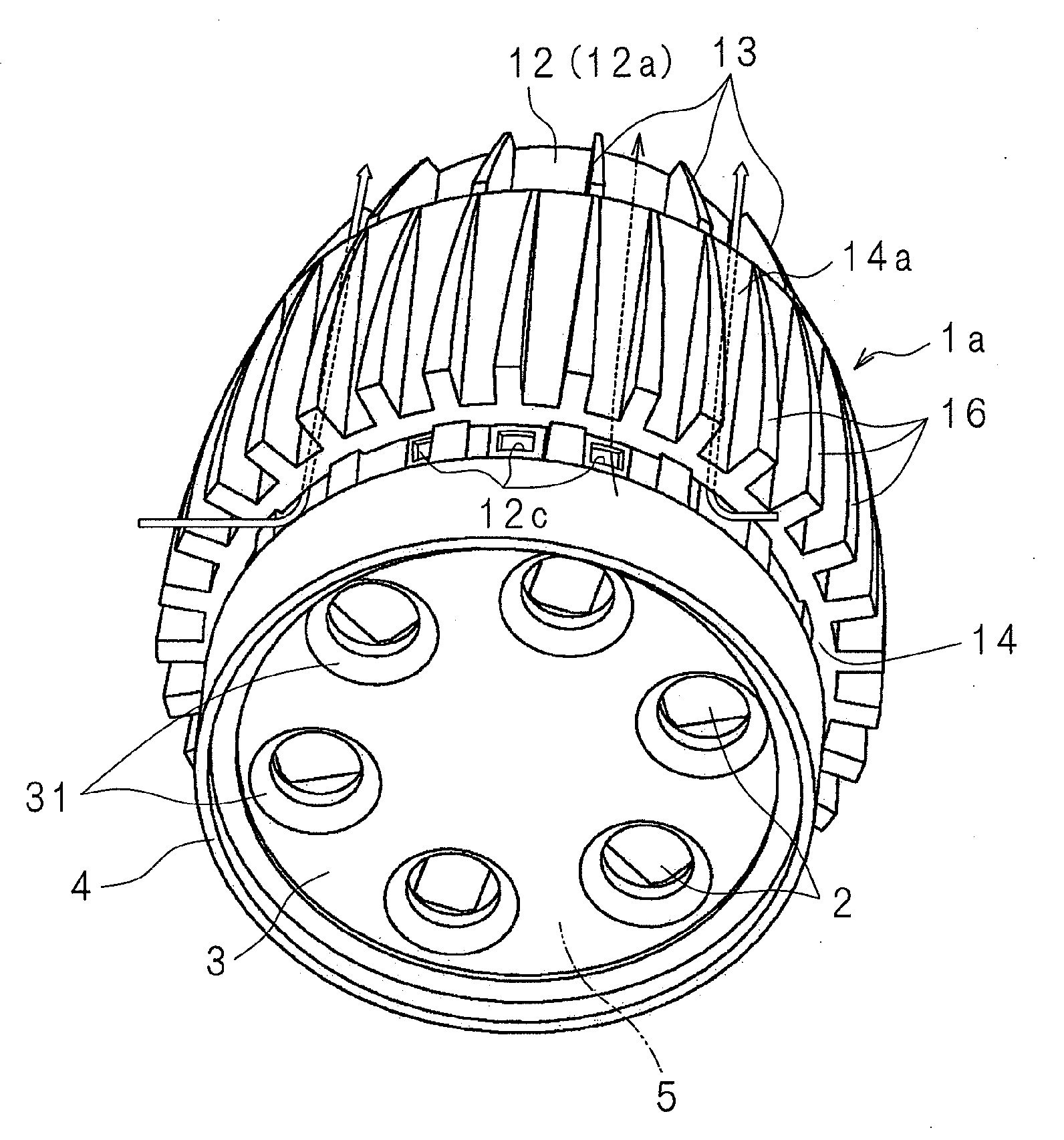
[0071]Reference numeral 1 in FIG. 1 is a heat dissipation device made of a metal, such as aluminum. The heat dissipation device 1 has the shape of a cylinder with a reduced diameter on one side in the axial direction of the cylinder, or a so-called shell-like shape.
[0072]The heat dissipation device 1 has a heat transfer plate 11 in the form of a circular plate. On one surface 11a of the heat transfer plate 11, a cylindrical inner tube 12 is disposed upright concentrically with the heat transfer plate 11. The thickness of the inner tube 12 changes successively in the axial direction so that the inner tube 12 is thicker on the side adjacent to the heat transfer plate 11 and th...
embodiment 2
[0092]FIG. 5 is an external perspective view of a lighting device according to Embodiment 2 of the present invention. On an end of the inner tube 12 of a heat dissipation device 1a on a side where the LED modules 2, 2 are mounted, rectangular vents 12c, 12c . . . are provided at equal intervals in the circumferential direction between the first fins 13, 13 . . . . Since other structures are the same as those in Embodiment 1 illustrated in FIG. 1, the corresponding component members are designated with the same reference numerals as in FIG. 1 and detailed explanations of the structures will be omitted.
[0093]By configuring the heat dissipation device 1a in the above-described manner, heat generated in the LED modules 2, 2 . . . when the LED modules 2, 2 . . . are turned on is transferred to the inner tube 12, and the air in the inner tube 12 is warmed. The warmed air flows out from the open end of the inner tube 12 as indicated by the arrows in FIG. 5, while the outside air flows in f...
embodiment 3
[0094]FIG. 6 is a schematic partial cross sectional view of a lighting device according to Embodiment 3. On the circumferential edge of one surface 11a of the heat transfer plate 11 of a heat dissipation device 1b, a turbulence promoter 11d is formed in a protruding manner over the entire circumference to face the inner tube 12. The height H of the turbulence promoter 11d is preferably determined so that the relationship with distance L between the turbulence promoter 11d and the inner tube 12 satisfies a predetermined condition (L≈10H). Since other structures are the same as those in Embodiment 1 illustrated in FIG. 4, the corresponding component members are designated with the same reference numerals as in FIG. 4, and detailed explanations of the structures will be omitted.
[0095]By configuring the heat dissipation device 1b in the above-described manner, the flow of air entering the ventilation paths 15, 15 . . . is disturbed by the turbulence promoter 11d and produces eddies, and...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| total reflectance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com