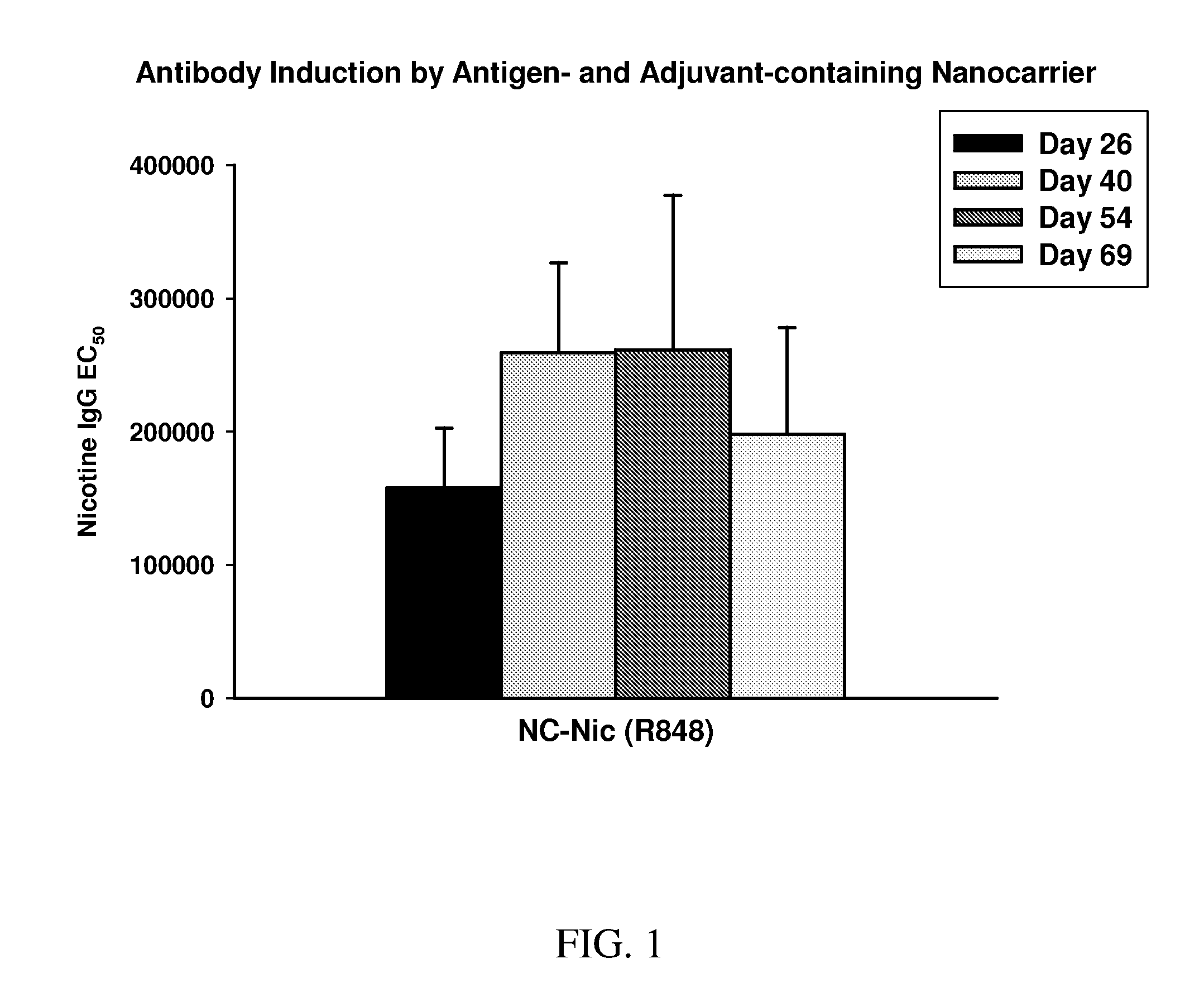
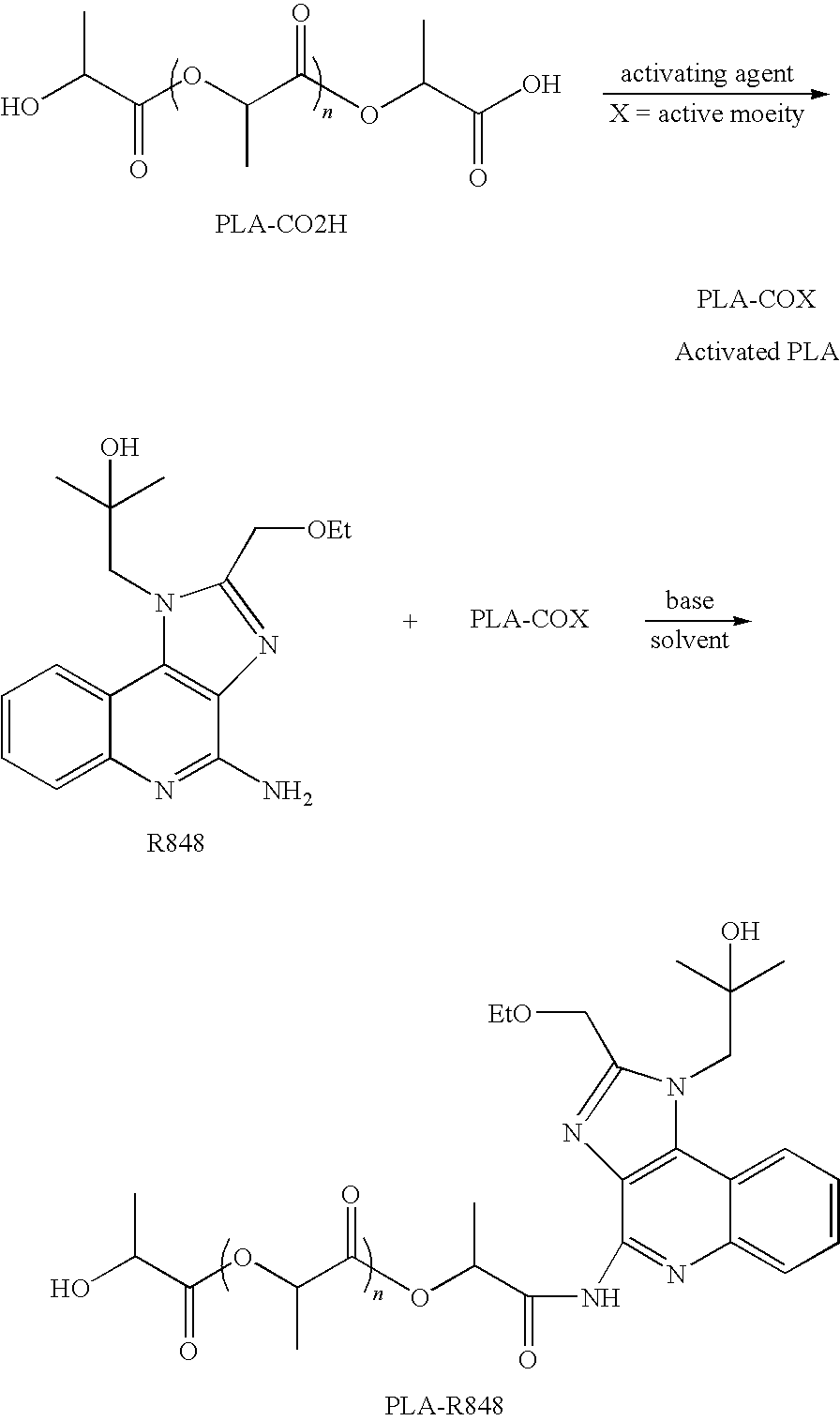
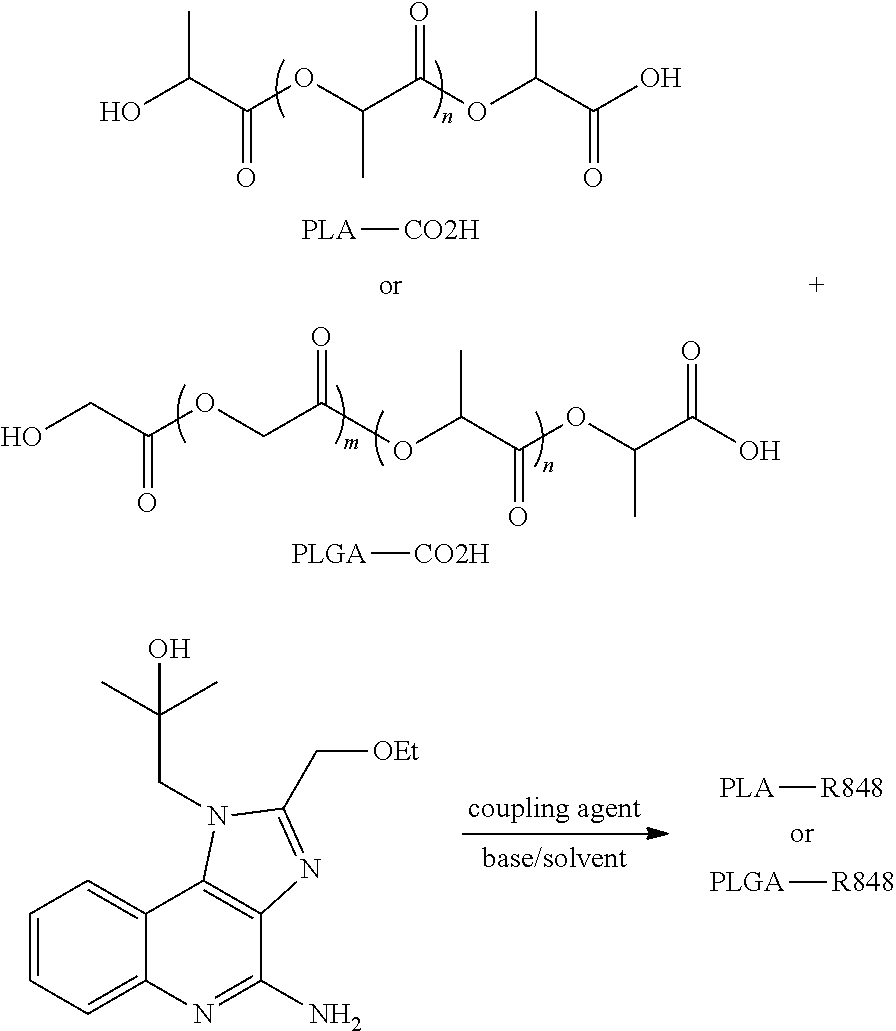
Nanocarriers possessing components with different rates of release
a technology of nanocarriers and components, applied in the field of synthetic nanocarriers, can solve the problems of insufficient information regarding the biological interplay between these two agents and the lack of control of their delivery, and achieve the effect of inducing or enhancing an immune respons
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Preparation of Activated Polymer
[0133]PLA (dl-polylactide) (Resomer R202H from Boehringer-Ingelheim, KOH equivalent acid number of 0.21 mmol / g, intrinsic viscosity (iv): 0.21 dl / g) (10 g, 2.1 mmol, 1.0 eq) was dissolved in dichloromethane (DCM) (35 mL). EDC (2.0 g, 10.5 mmol, 5 eq) and NHS (1.2 g, 10.5 mmol, 5 eq) were added. The solids were dissolved with the aid of sonication. The resulting solution was stirred at room temperature for 6 days. The solution was concentrated to remove most of DCM and the residue was added to a solution of 250 mL of diethyl ether and 5 mL of MeOH to precipitate out the activated PLA-NHS ester. The solvents were removed and the polymer was washed twice with ether (2×200 mL) and dried under vacuum to give PLA-NHS activated ester as a white foamy solid (˜8 g recovered, H NMR was used to confirm the presence of NHS ester). The PLA-NHS ester was stored under argon in a below −10 C freezer before use.
[0134]Alternatively, the reaction can be performed in DMF...
example 2
Preparation of Activated Polymer
[0136]PLA (R202H, acid number of 0.21 mmol / g) (2.0 g, 0.42 mmol, 1.0 eq) was dissolved in 10 mL of dry acetonitrile. N,N′-disuccinimidyl carbonate (DSC) (215 mg, 1.26 mmol, 3.0 eq) and catalytic amount of 4-(N,N-dimethylamino)pyridine (DMAP) were added. The resulting mixture was stirred under argon for 1 day. The resulting solution was concentrated to almost dryness. The residue was then added to 40 mL of ether to precipitate out the polymer which was washed twice with ether (2×30 mL) and dried under vacuum to give PLA-NHS activated ester (1H NMR showed the amount of NHS ester at about 80%).
example 3
Preparation of Activated Polymer
[0137]PLA (R202H) (5.0 g, 1.05 mmol) was dissolved in 25 mL of anhydrous DCM and 2.5 mL of anhydrous DMF. DCC (650 mg, 3.15 mmol, 5.0 eq) and pentafluorophenol (PFP) (580 mg, 3.15 mmol, 5.0 eq) were added. The resulting solution was stirred at room temperature for 6 days and then concentrated to remove DCM. The resulting residue was added to 250 mL of ether to precipitate out the activated PLA polymer which was washed with ether (2×100 mL) and dried under vacuum to give PLA-PFP activated ester as a white foamy solid (4.0 g).
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| weight average molecular weight | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| pH | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com