Apparatus, system and method for tracking drugs during a repackaging and administering process
a drug and repackaging technology, applied in the field of apparatus, system and method for tracking drugs, can solve the problems of increasing the risk that a user will mistake one drug for another, affecting the safety of users, and causing catastrophic consequences, so as to reduce certain kinds of errors
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
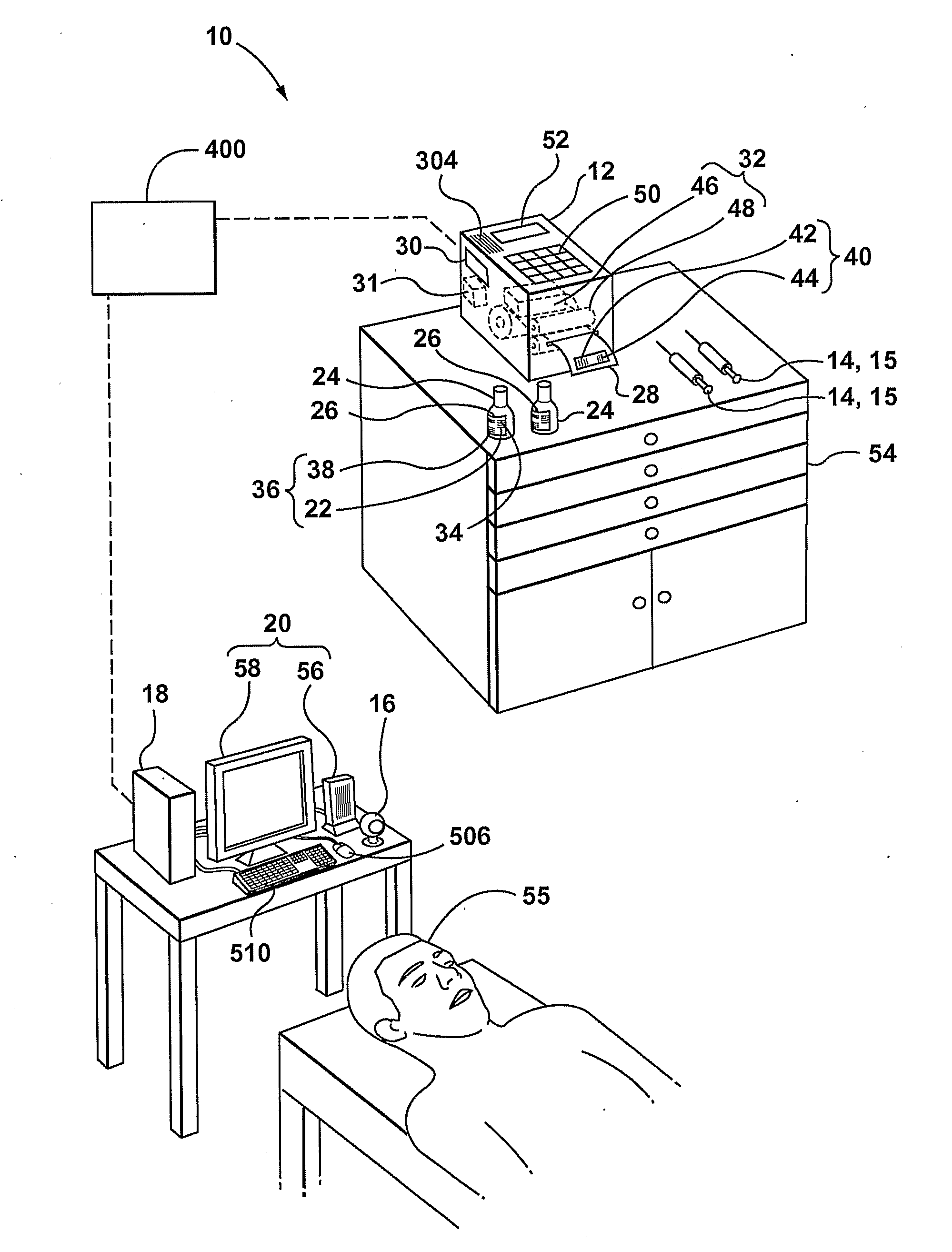
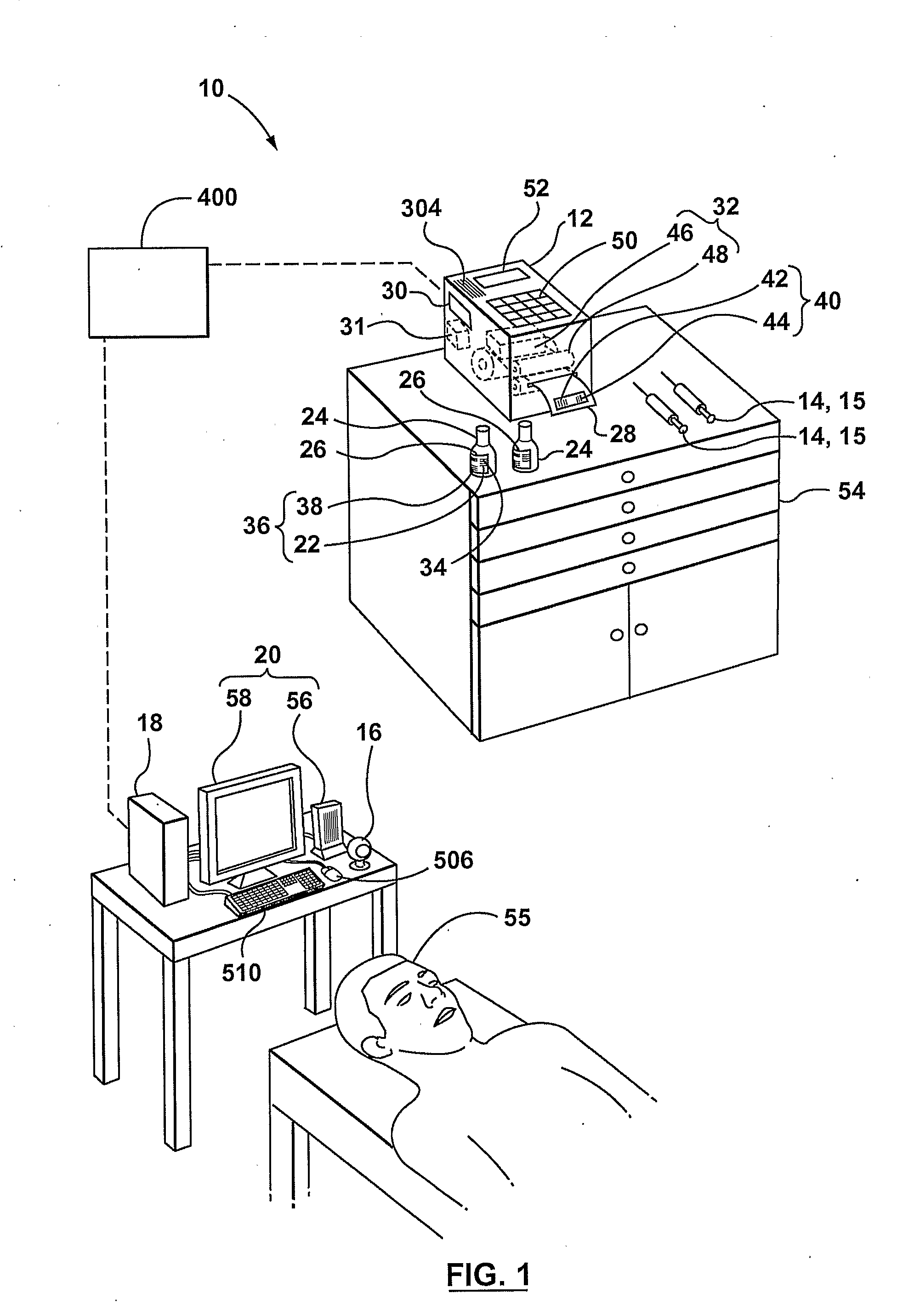
[0042]Reference is made to FIG. 1, which shows a system 10 for tracking drugs during a drug transfer and administering process in accordance with an embodiment of the present invention. Drug transfer may also be referred to as drug repackaging.
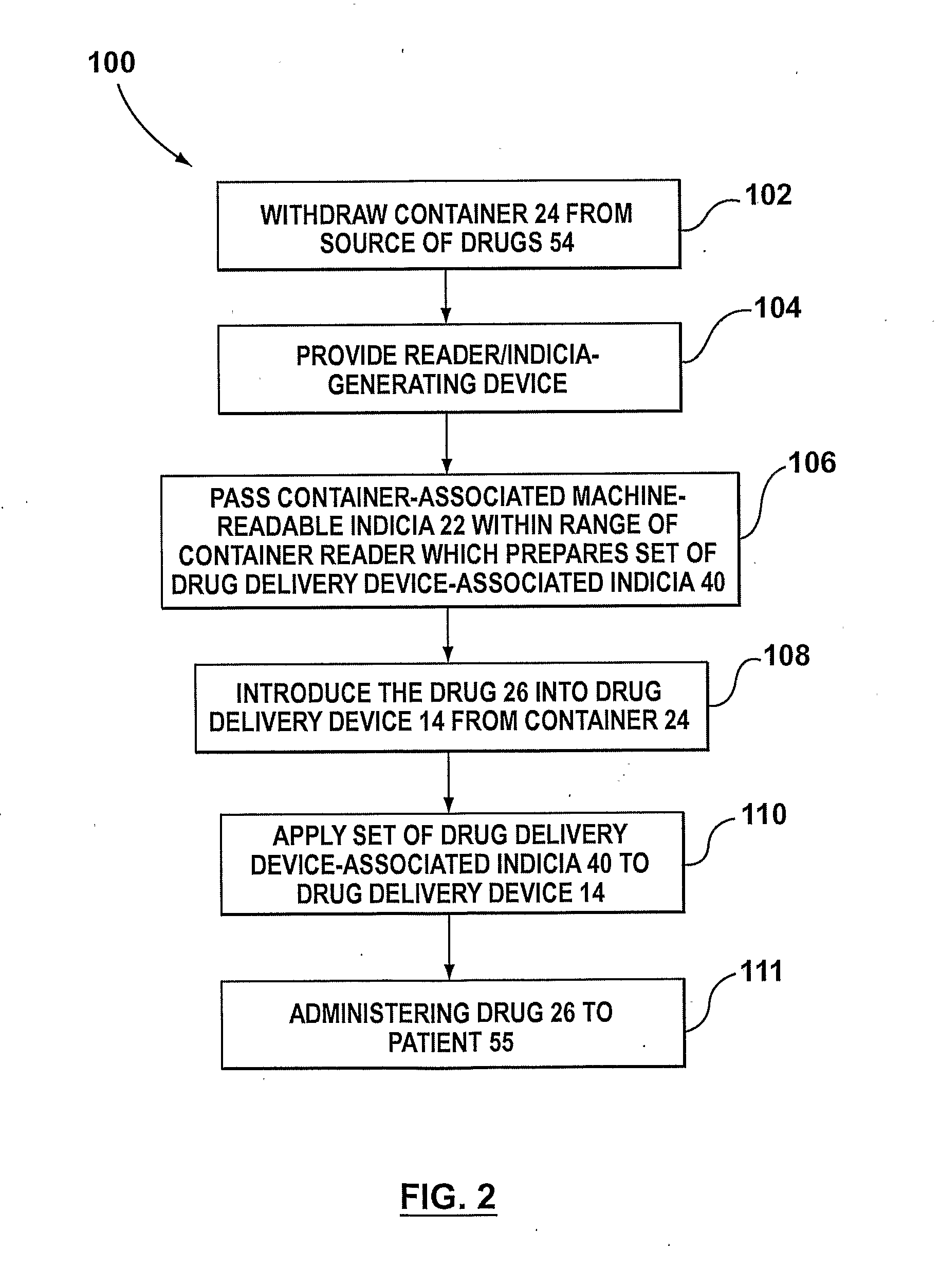
[0043]In many environments, such as an operating room, a recovery room and a critical care room, a drug 26 is transferred from a storage container 24 to a drug delivery container 14, such as a syringe 15. The system 10 permits the applying of a set of one or more drug identification indicia 40 on the drug delivery container 14 with a reduced degree of error over some prior art systems and methods.
[0044]The system 10 includes a reader / indicia-generating device 12 and optionally further includes a drug delivery container reader 16, a processing unit 18, and an output device 20. The reader / indicia-generating device 12 is used to read a set of one or more storage-container-associated machine-readable indicia 22 that are present on the drug storage...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com