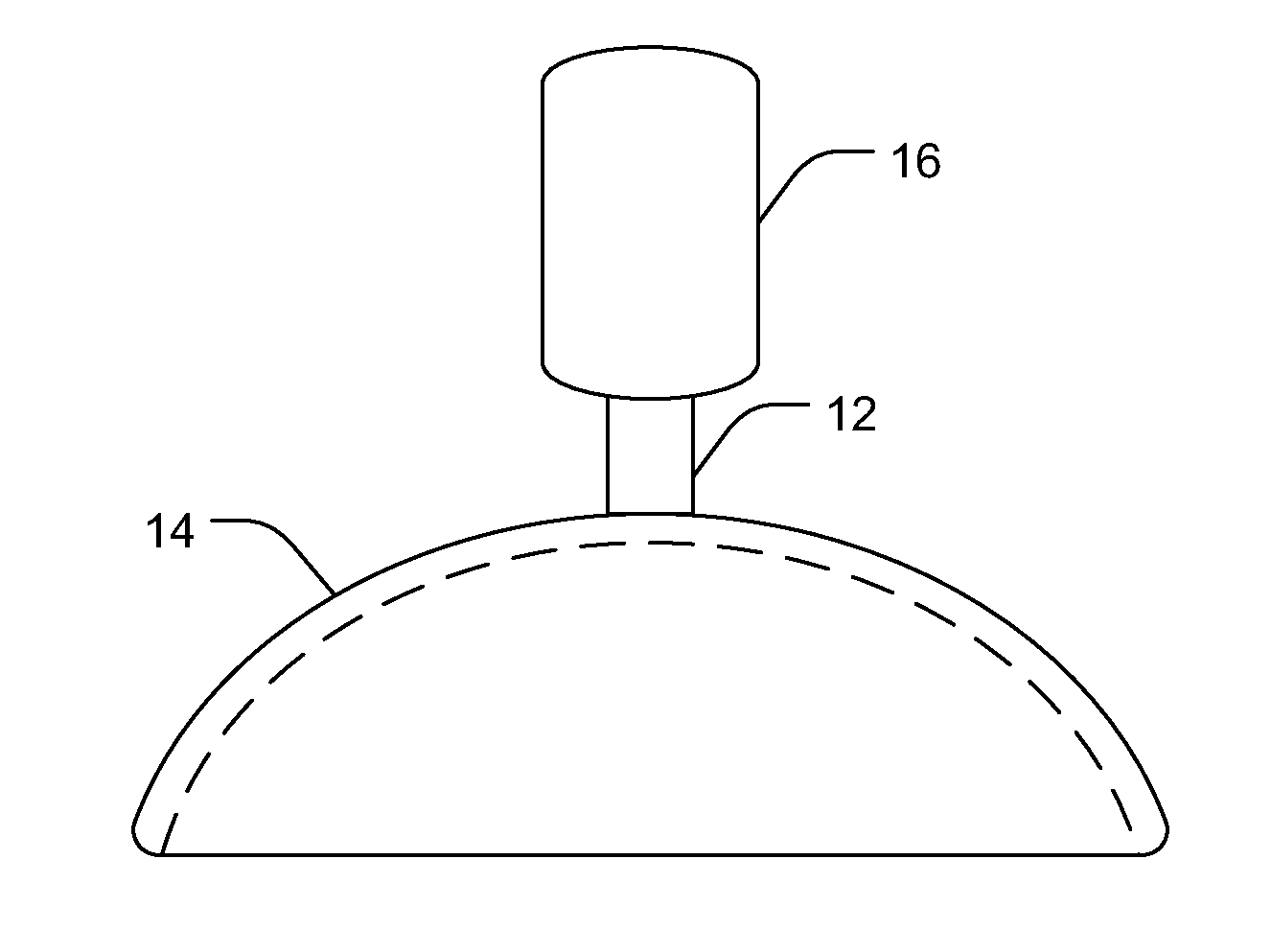
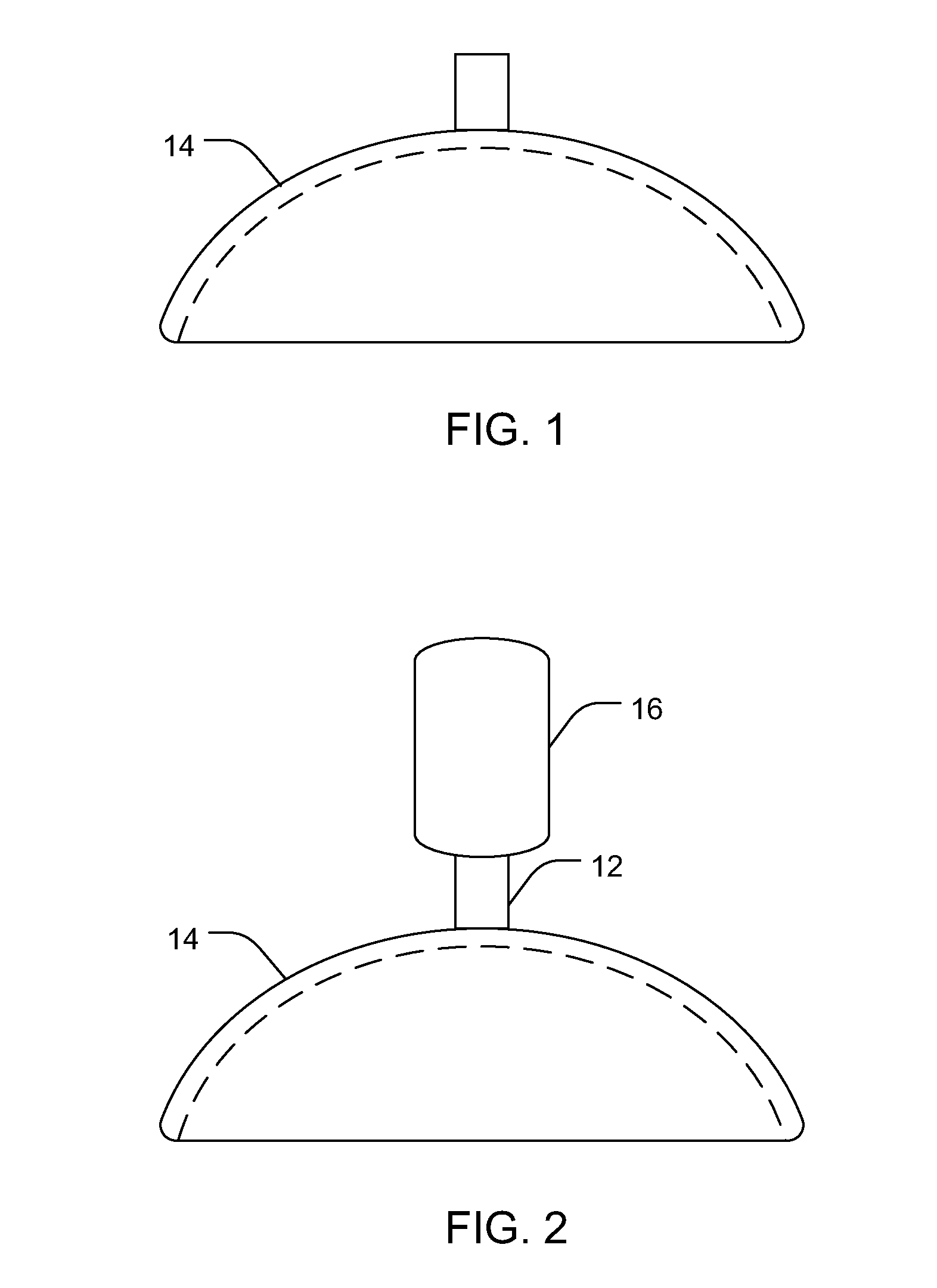
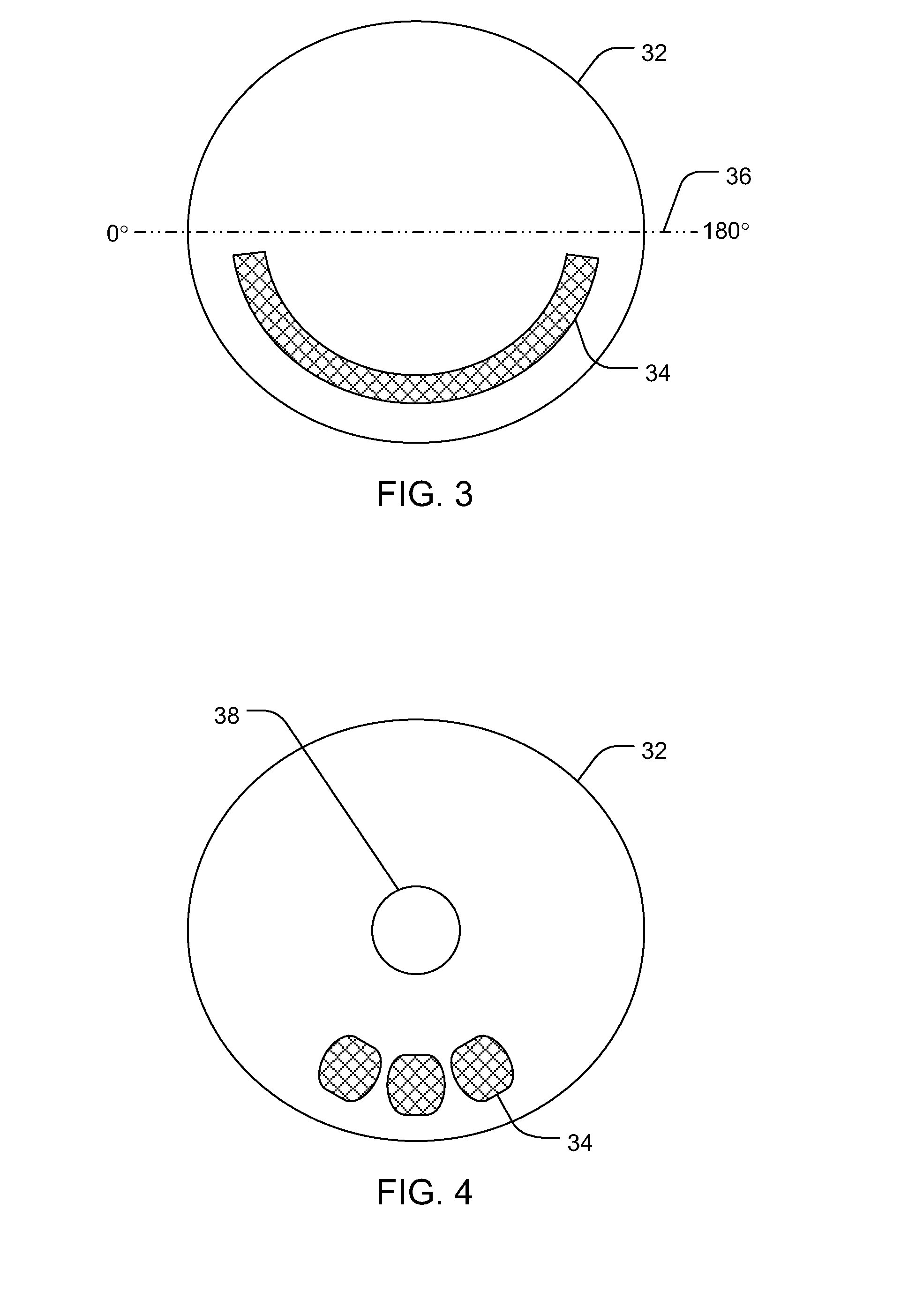
Intraocular iontophoretic device and associated methods
a technology of ionophoretic devices and ocular ion channels, which is applied in the field of ophthalmology, can solve the problems of spatial misalignment between the delivery region and the reservoir, affecting the efficiency of the delivery of active agents, and difficulty in maintaining spatial correspondence with the reservoir, so as to achieve convenient and effective non-invasive delivery and maintain alignmen
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
[0094]A handheld ocular iontophoretic device is constructed from a plastic tube, wherein one end is shaped to conform to the eye of a rabbit. An electroplated AgAgCl electrode is positioned in one end of the plastic tube and a hydrogel is inserted into the tube so that one side of the hydrogel contacts the electrode, while the opposite side is configured to contact the eye. The hydrogel has been previously loaded with 1.0M Mn++. The iontophoretic device is coupled to a power source and placed against the surface of an eye of a rabbit, partially within the cul-de-sac in a dorsal location. A return electrode is attached to the ear of the rabbit, and finger pressure is used to seal the device against the eye. 2 mA of current is applied to the iontophoretic device for 20 minutes to deliver the Mn++ from the hydrogel and into the eye. Distribution of the Mn++ within the eye of the rabbit is analyzed using a 3 Tesla Siemens MRI system as is shown in FIG. 7. As can be seen in this figure, ...
example 2
[0095]An iontophoretic scleral lens device is configured to conform to the eye of a rabbit. An electroplated AgAgCl electrode coupled to a 1.0M Mn++ filled hydrogel is located within a reservoir structure along the contact surface of the scleral lens. The iontophoretic device is coupled to a power source and positioned on an eye of a rabbit, such that the reservoir is located partially within the cul-de-sac in a dorsal region of the eye. A return electrode is attached to the ear of the rabbit, and suction is applied to the scleral lens to preclude movement of the lens relative to the eye surface. 3 mA of current is applied to the scleral lens device for 20 minutes to deliver the Mn++ from the hydrogel and into the eye. Distribution of the Mn++ within the eye of the rabbit is analyzed using a 3 Tesla Siemens MRI system as is shown in FIG. 8. As can be seen in this figure, Mn++ ions (white contrast) were delivered primarily into the eye tissues. Additionally, the black region along th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com