Method of starting a steam turbine
a steam turbine and steam technology, applied in the direction of steam engine plants, engine starters, machines/engines, etc., can solve the problems of insufficient steam temperature reduction and degrading of the material properties of the rotor
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
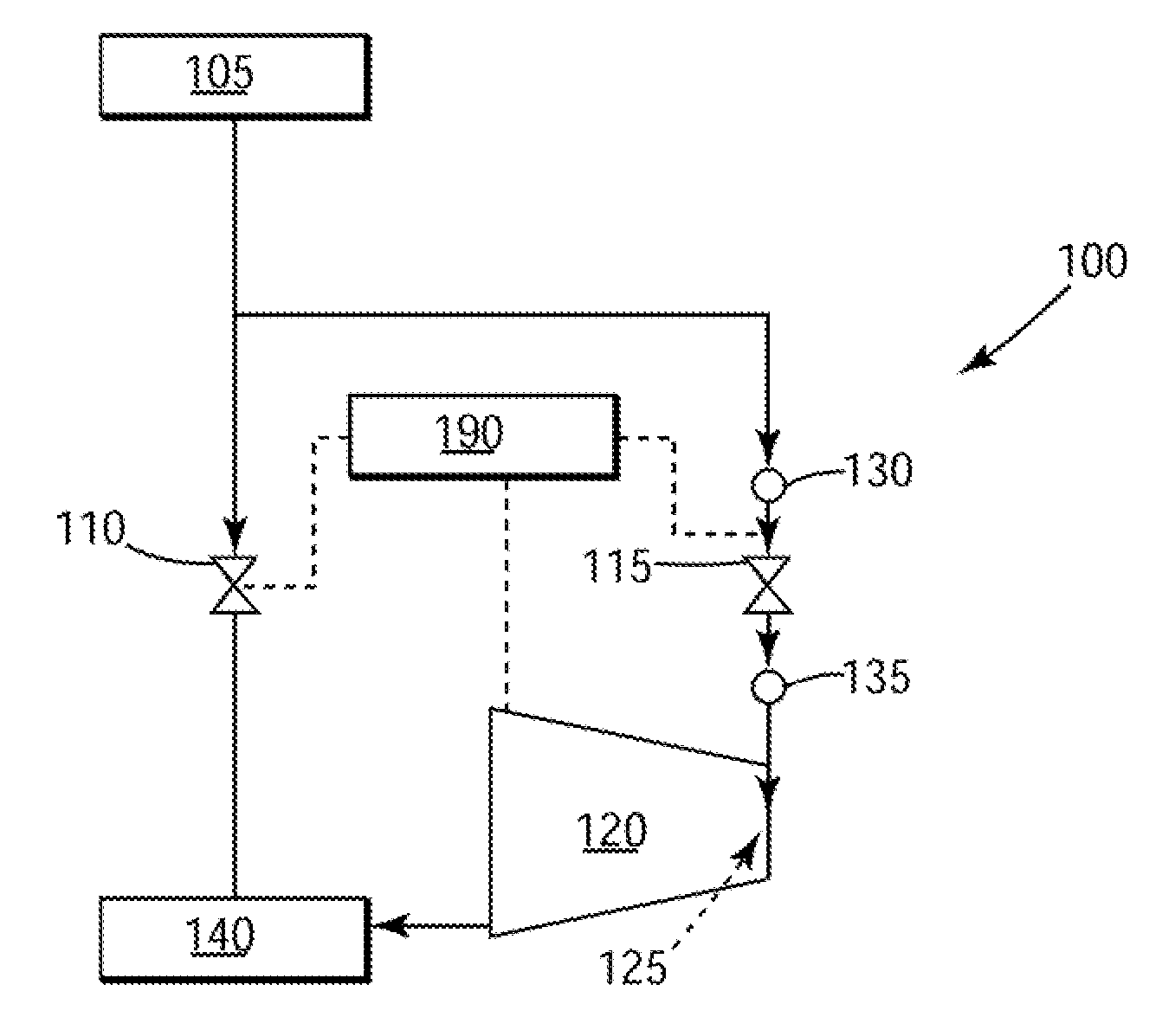
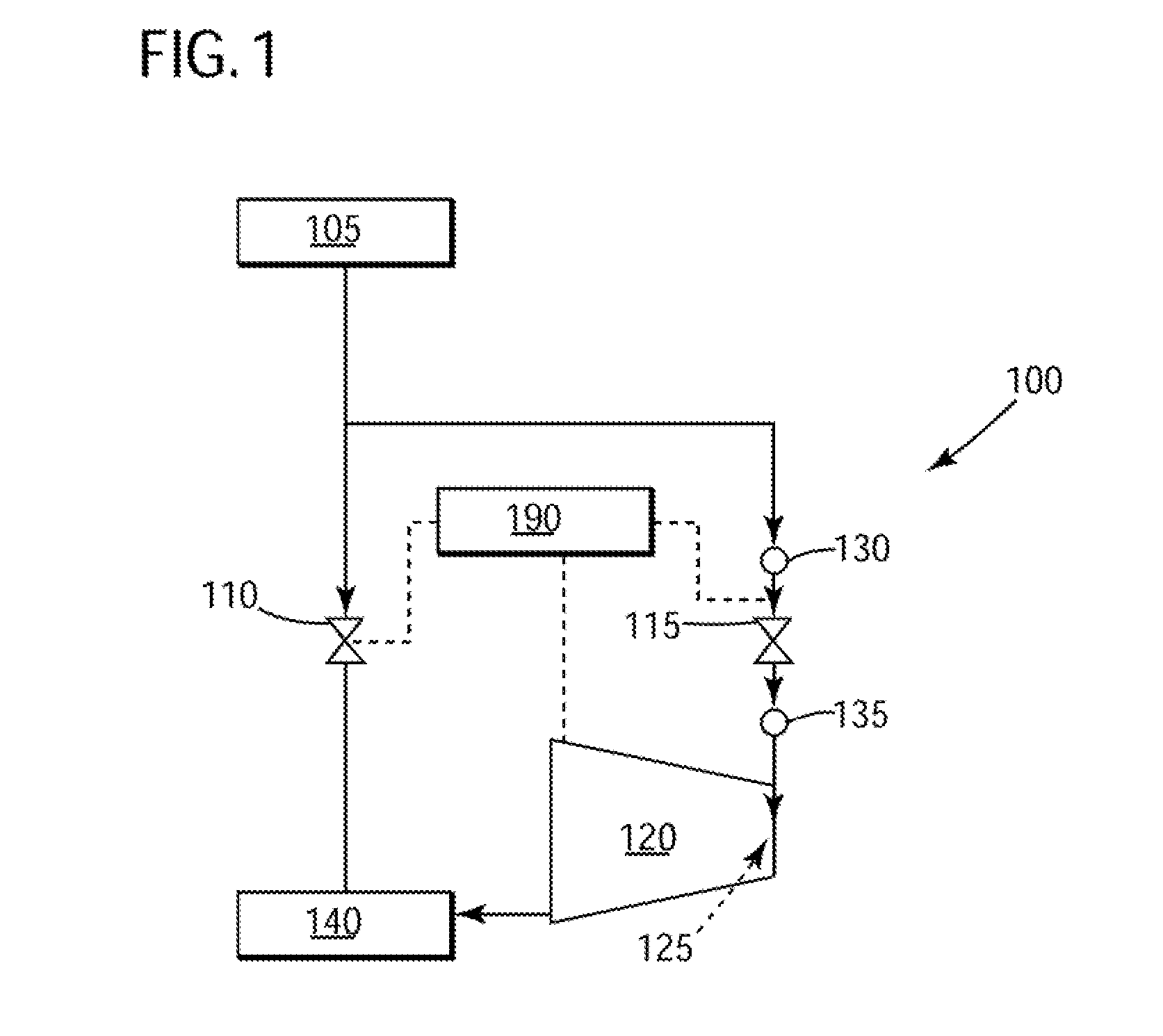
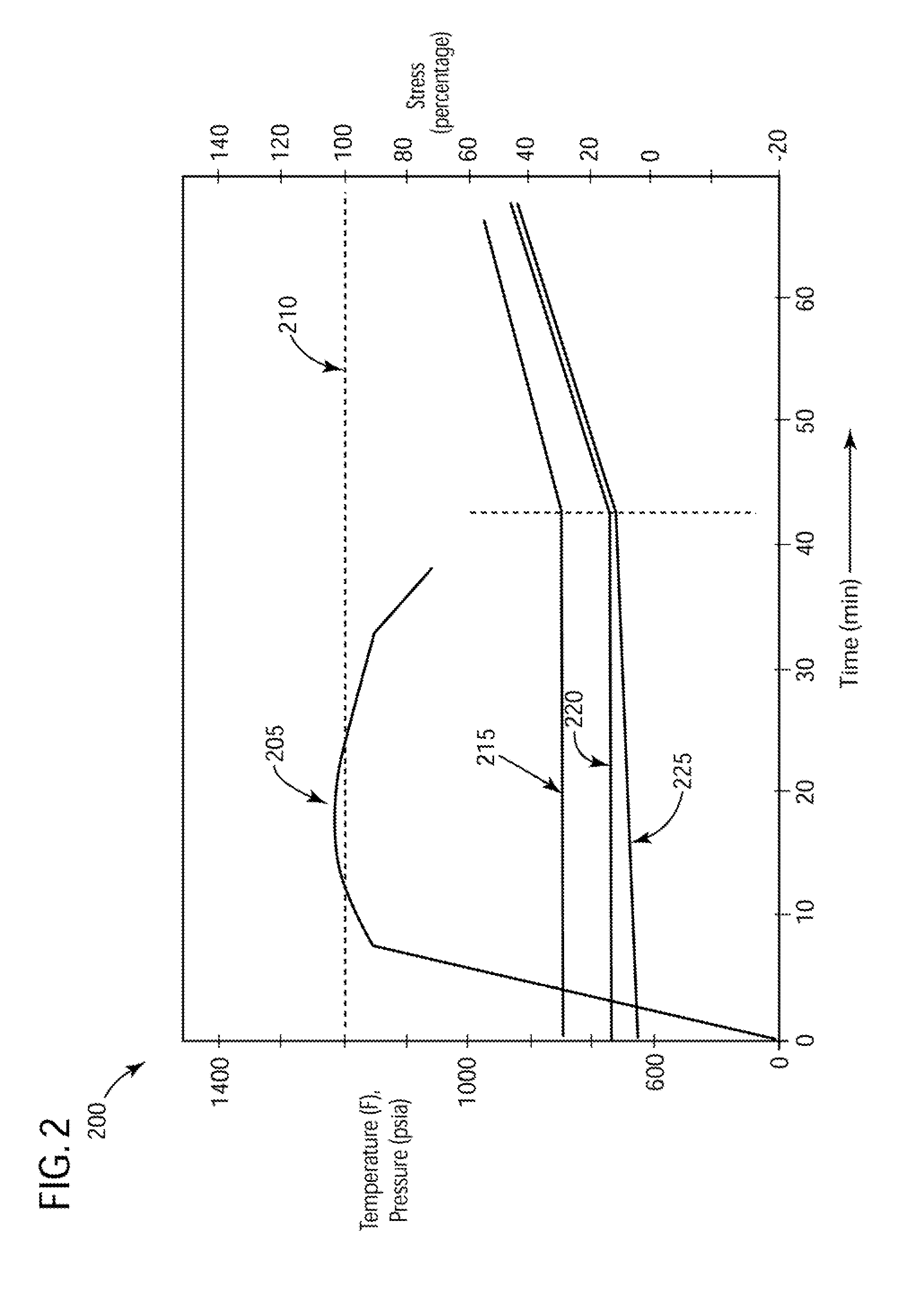
[0014]The present invention has the technical effect of reducing the start-up time associated with starting a steam turbine. Embodiments of the present invention provide a new methodology for reducing the steam-to-metal temperature mismatch present during the start-up of a steam turbine. Essentially, embodiments of the invention may raise the pressure of the steam upstream of an admission valve associated with a High Pressure (HP) section of a steam turbine. The initial high pressure of the steam may reduce the enthalpy of steam, thus reducing temperature of the steam admitted to the HP section.
[0015]Detailed example embodiments are disclosed herein. However, specific structural and functional details disclosed herein are merely representative for purposes of describing example embodiments. Example embodiments may, however, be embodied in many alternate forms, and should not be construed as limited to only the embodiments set forth herein.
[0016]Accordingly, while example embodiments...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com