WLAN apparatus
a wireless communication and wlan technology, applied in the field of wireless communications, can solve the problems of limiting the improvement of the throughput of the wireless communication network, the ieee 802.11a communication distance is shorter than the ieee 802.11b, and the ieee 802.11n medium access control/physical layer protocol is not effective in providing a throughput of 1 gbps or more, so as to achieve the effect of high throughput and extension of the servi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
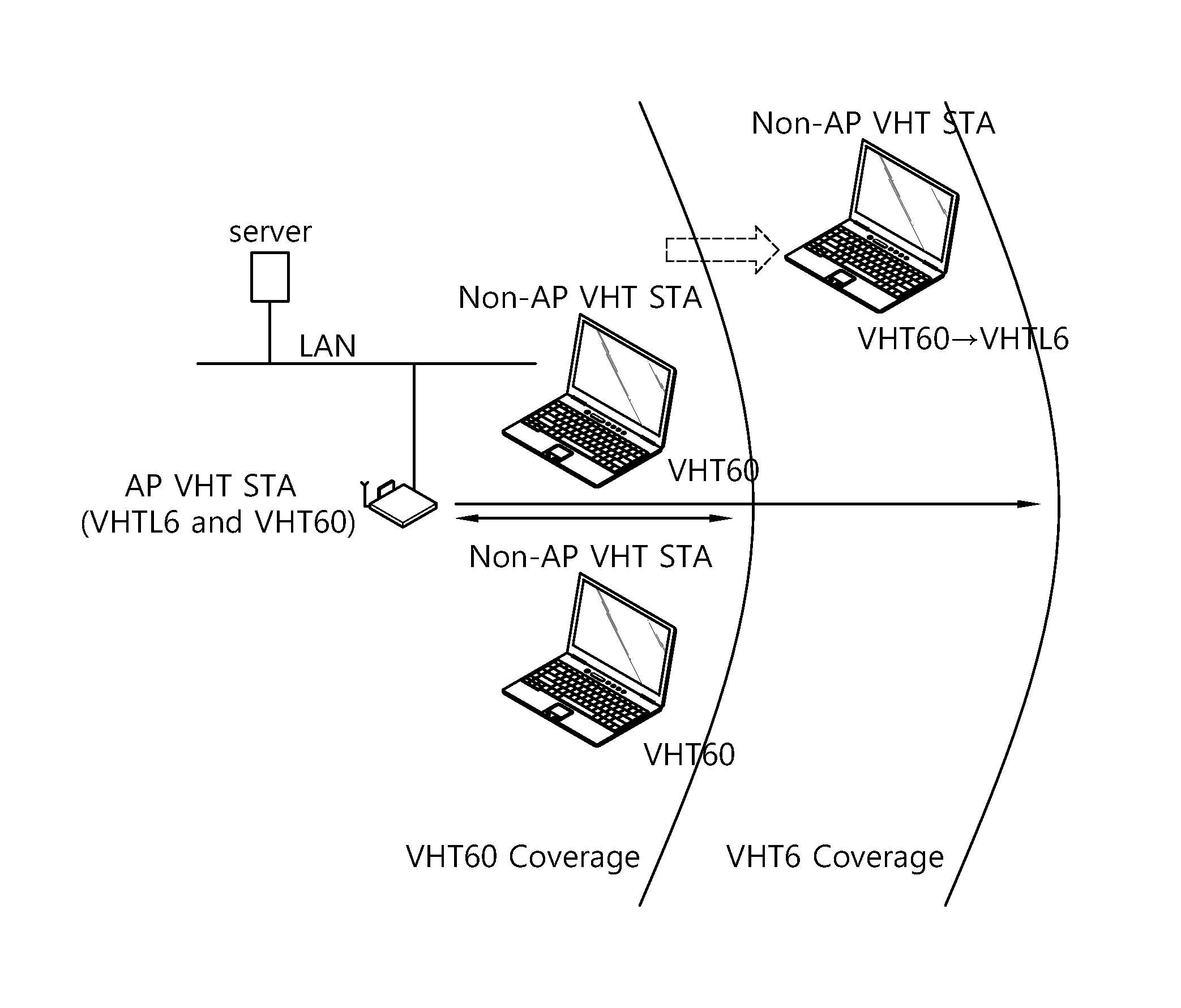
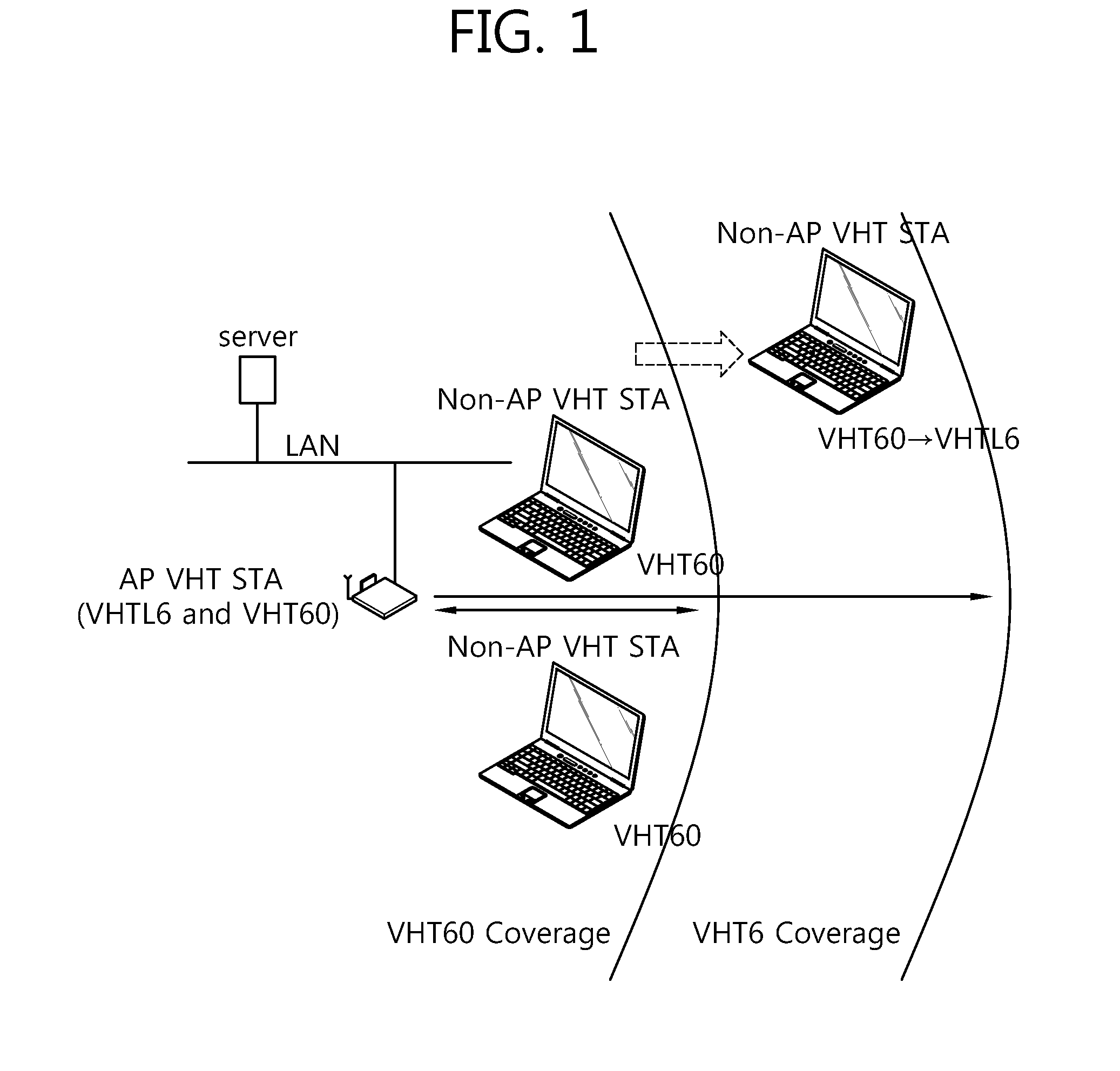
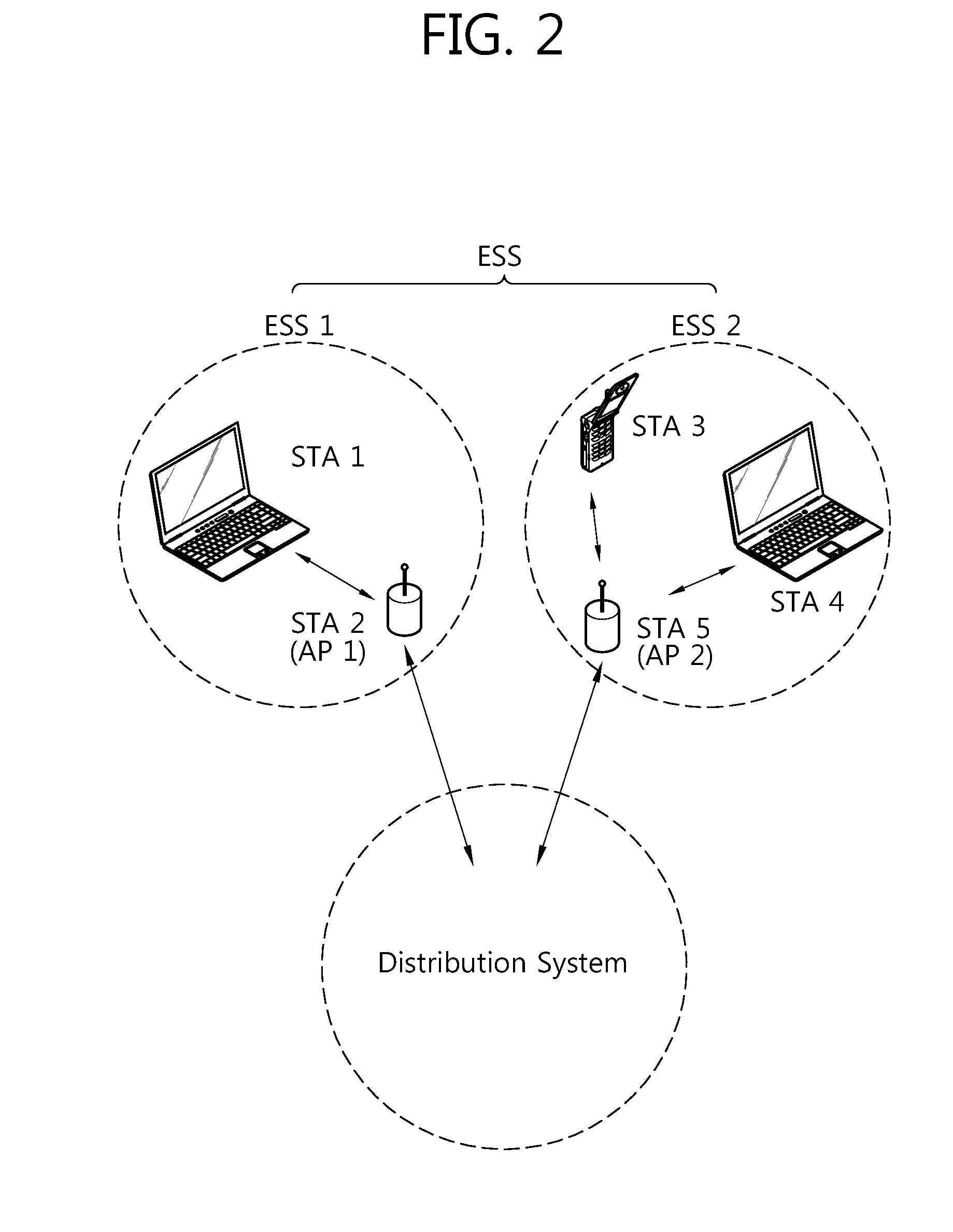
[0034]FIG. 2 schematically illustrates a configuration of an example of a very high throughput (VHT) wireless local area network (WLAN) system to which an exemplary embodiment of the present invention can be applied.
[0035]Referring to FIG. 2, a WLAN system such as the VHT WLAN system includes one or more basis service sets (BSS). The BSS is a set of stations (STA) which are successfully synchronized and capable of communicating with one another, and does not mean a specific region. In a medium access control (MAC) service access point (SAP) like the WLAN system to which an exemplary embodiment of the present invention can be applied, the BSS supporting an ultrahigh data processing rate of 1 GHz or higher will be called a very high throughput (VHT) BSS.
[0036]Further, the VHT BSS is divided into an infrastructure BSS and an independent BSS (IBSS). FIG. 2 illustrates the infrastructure BSS. The infrastructure BSS (BSS1, BSS2) includes one or more non-AP STA (non-AP STA1, non-AP STA3 an...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com