Heat exchanger
a heat exchanger and heat exchanger technology, applied in the direction of heat exchange apparatus, heat exchanger conduits, corrosion prevention, etc., can solve the problem of promoting turbulence in the heat exchanger
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
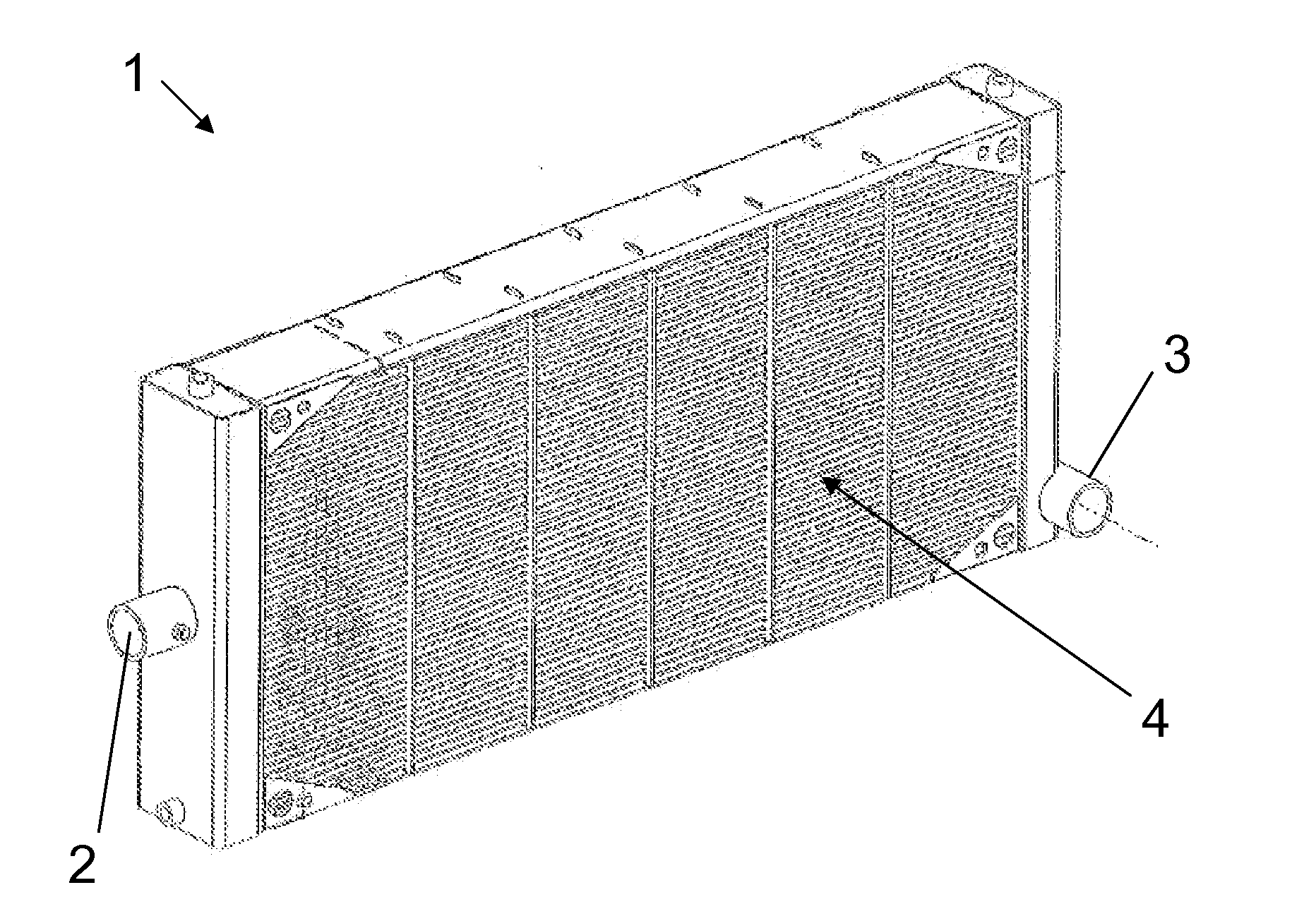
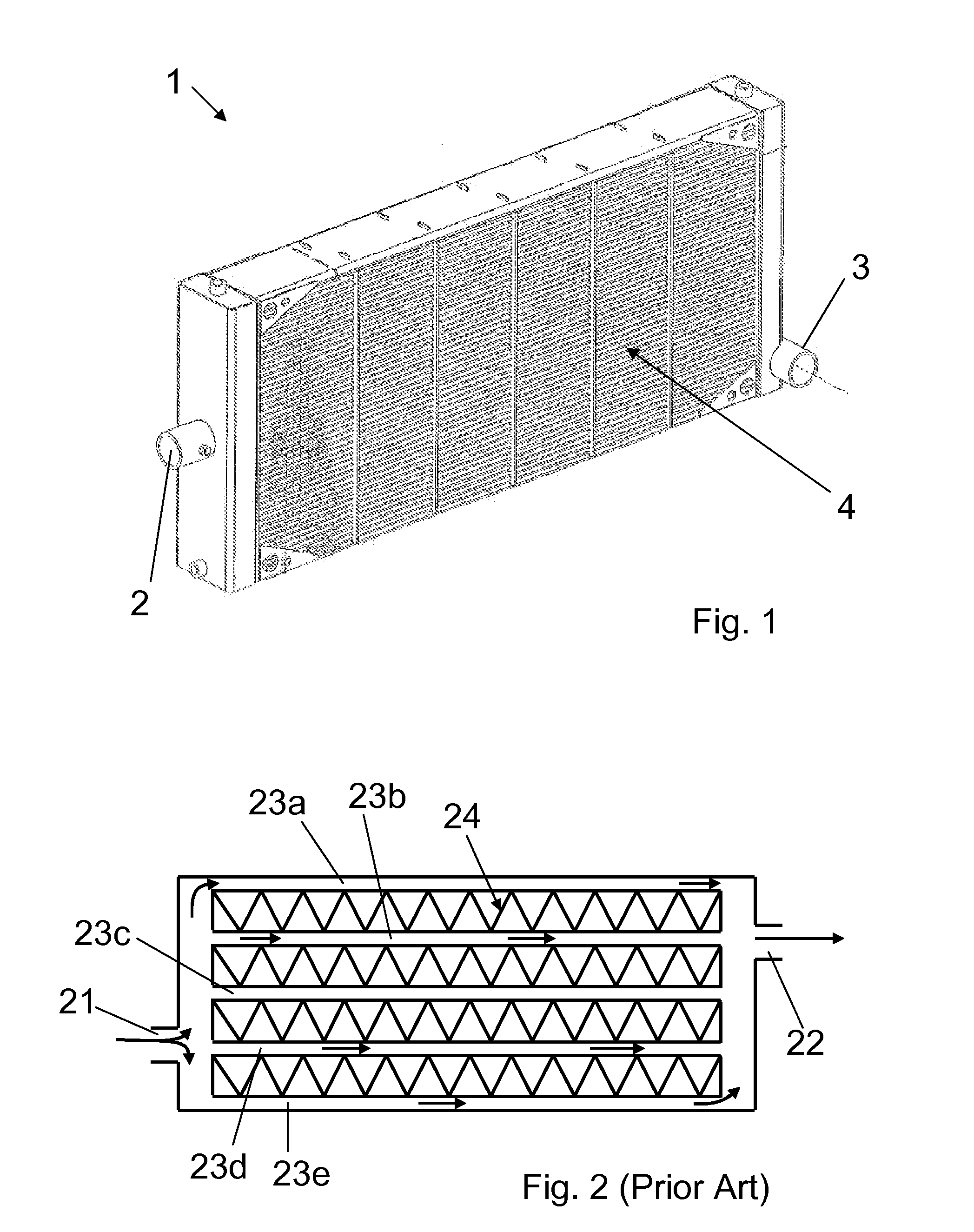
[0023]The heat exchanger of the embodiment shown in FIG. 1 is specifically a radiator 1 for cooling a train diesel engine. A heat transfer fluid, which in this embodiment is a water based coolant, is pumped through the engine to absorb the heat generated thereby. The radiator 1 is mounted at the side of the train perpendicular to the direction of travel. A fan is used to cause atmospheric air, which is the heat removal fluid, to flow through the radiator to remove the heat to atmosphere.
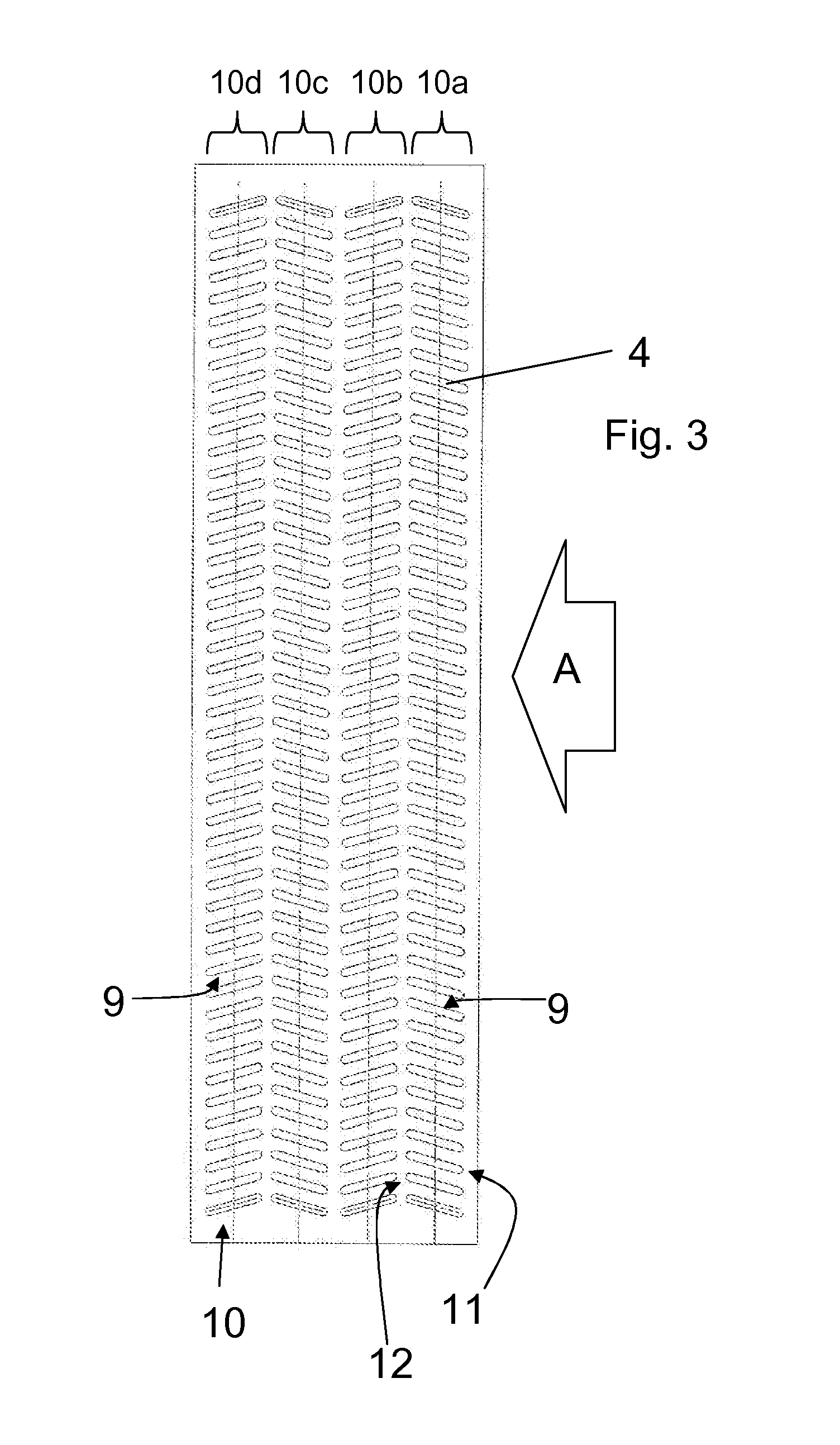
[0024]The radiator 1 comprises an inlet 2 to receive the coolant from the engine. An outlet 3 returns the coolant, once cooled by its passage through the radiator 1, to the engine water jackets and pipework for recirculation. The radiator 1 includes a plurality of heat transfer tubes 4 that connect the inlet 2 and outlet 3. Thus, the coolant received at the inlet 2 passes through a distributor or inlet header, which distributes the coolant into the heat transfer tubes 4. The coolant flows through the...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com