Methods for breast cancer risk assessment
a breast cancer and risk assessment technology, applied in the field of methods for breast cancer risk assessment, can solve the problem that the gene linkage study has not identified any further links
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example 1
Evaluation of a SNP Panel for Breast Cancer Risk Assessment in a Nested Case-Control Study from the Women's Health Initiative
Rationale
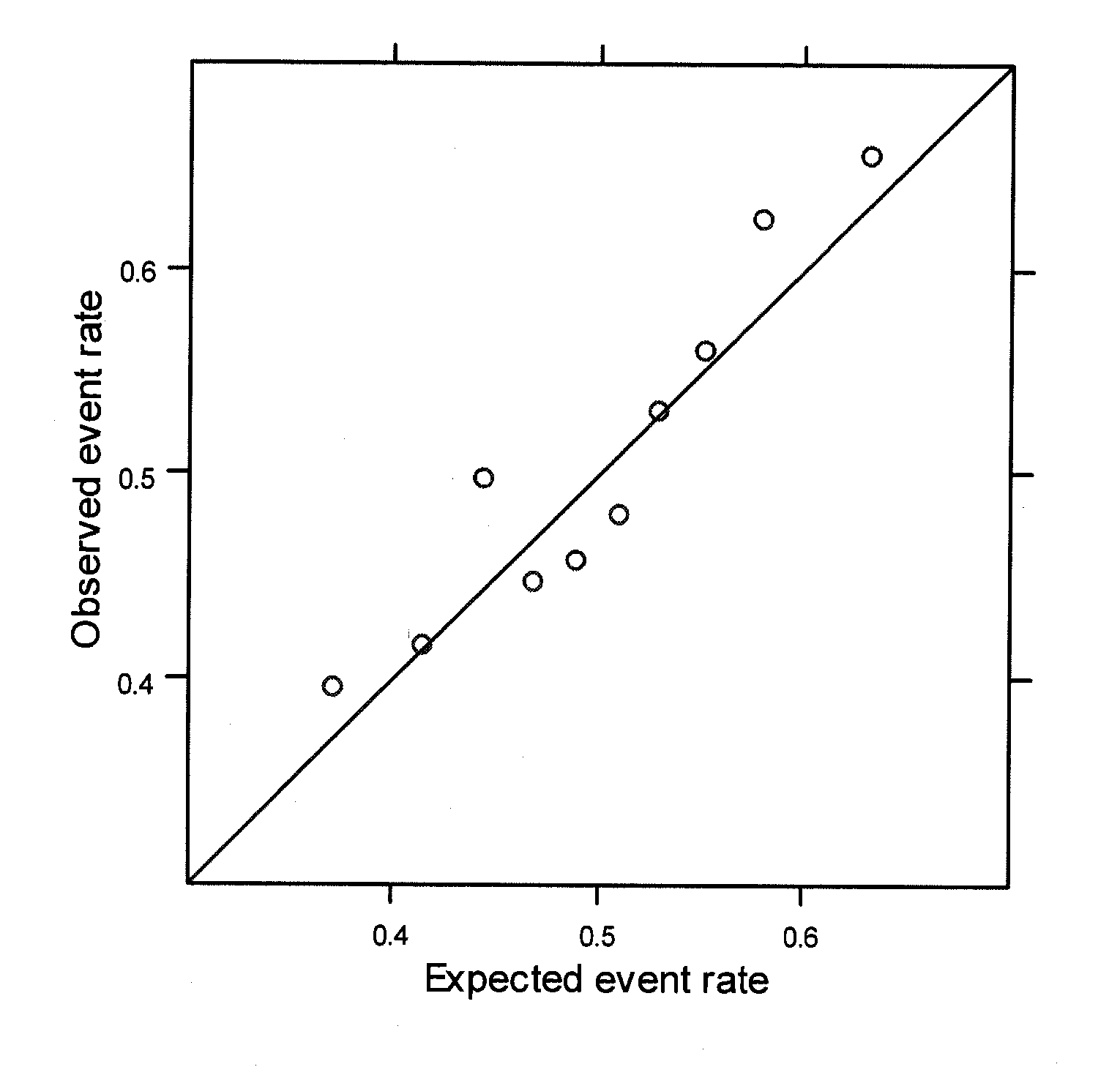
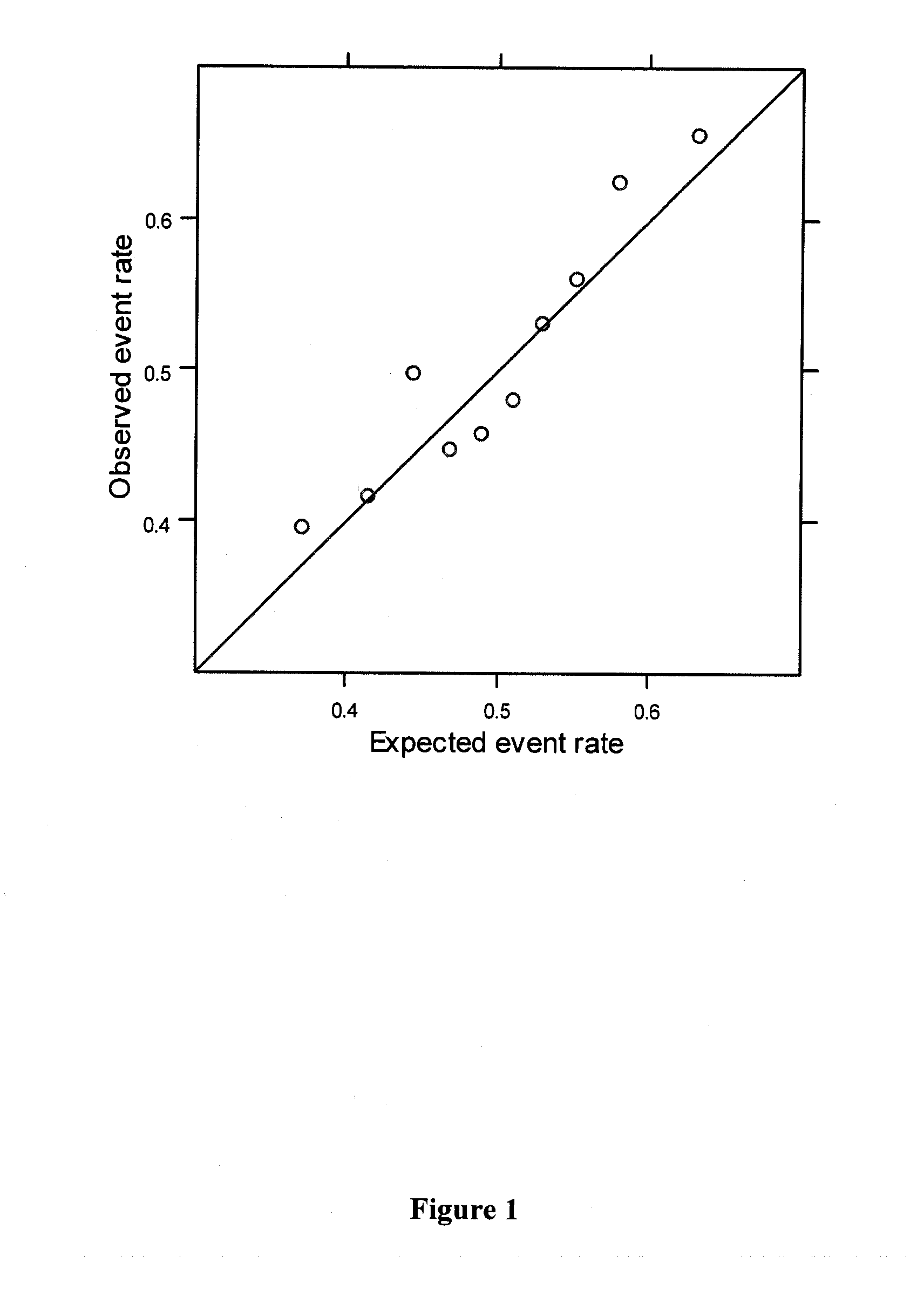
[0151]The extent to which recently discovered breast cancer (BCa)-associated genetic variation can assist in BCa risk assessment is unclear. The effect of the addition of risk information from a panel of 7 BCa-associated SNPs on risk stratification offered by the Gail Model was assessed.
Methods
[0152]1664 women who developed BCa after randomization in the WHI Clinical Trial and 1636 matched BCa-free controls were examined. Controls were matched on the basis of baseline age, self-reported ethnicity, clinical trial participation, years since randomization, and hysterectomy status. Seven SNPs from the published literature meeting rigorous criteria for genome-wide significance and replication were chosen to be genotyped (7-SNP Panel). To model SNP risk across the 7 selected panel SNPs, previously reported effect size estimates were used along with a multip...
example 2
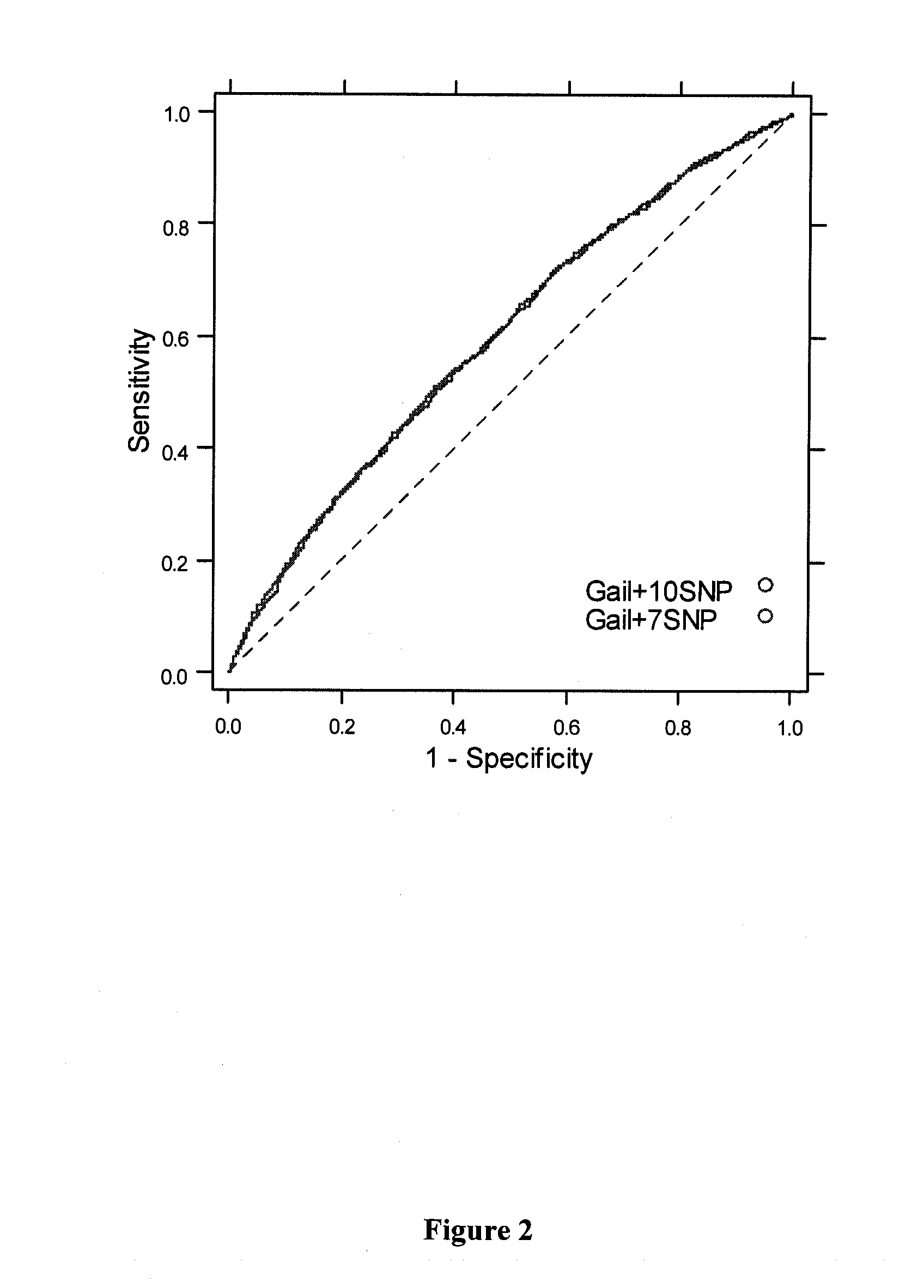
Use of SNPs for Breast Cancer Risk Assessment: 10-SNP Model SNP Genotyping
[0159]Ten (10) SNPs that have been reported to be associated with breast cancer with high statistical significance across multiple large sample sets were identified and are shown in Table 9.
[0160]Genotyping of 7 of the 10 SNPs is described in Example 1. The remaining 3 SNPs (rs4973768, rs6504950, rs11249433) were genotyped on the Sequenom MassArray platform. Two assays were designed in opposing orientations for each of the SNPs. Two of these SNPs (rs6504950 and rs11249433) had previously been genotyped on the same samples on oligonucleotide arrays. Samples that had performed poorly in previous Sequenom genotyping also performed poorly in this dataset, with agreement of less than 90% on these two SNPs, compared to 99.9% for the other samples. As a result, data for this same set of problematic samples was excluded.
[0161]Table 10 summarizes genotyping results for the 10 breast cancer associated SNPs.
TABLE 9Replic...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| residual familial risk | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| physical | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com