Blade mounting
a technology for mounting blades and rotor blades, which is applied in the direction of wind energy generation, motors, engine fuctions, etc., can solve the problems of difficult and risky operation of rotor blades mounted to the hub, affecting the performance of rotor blades, and unable to generally only be lifted. , to achieve the effect of fast, safe and secure method of blade mounting operation
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
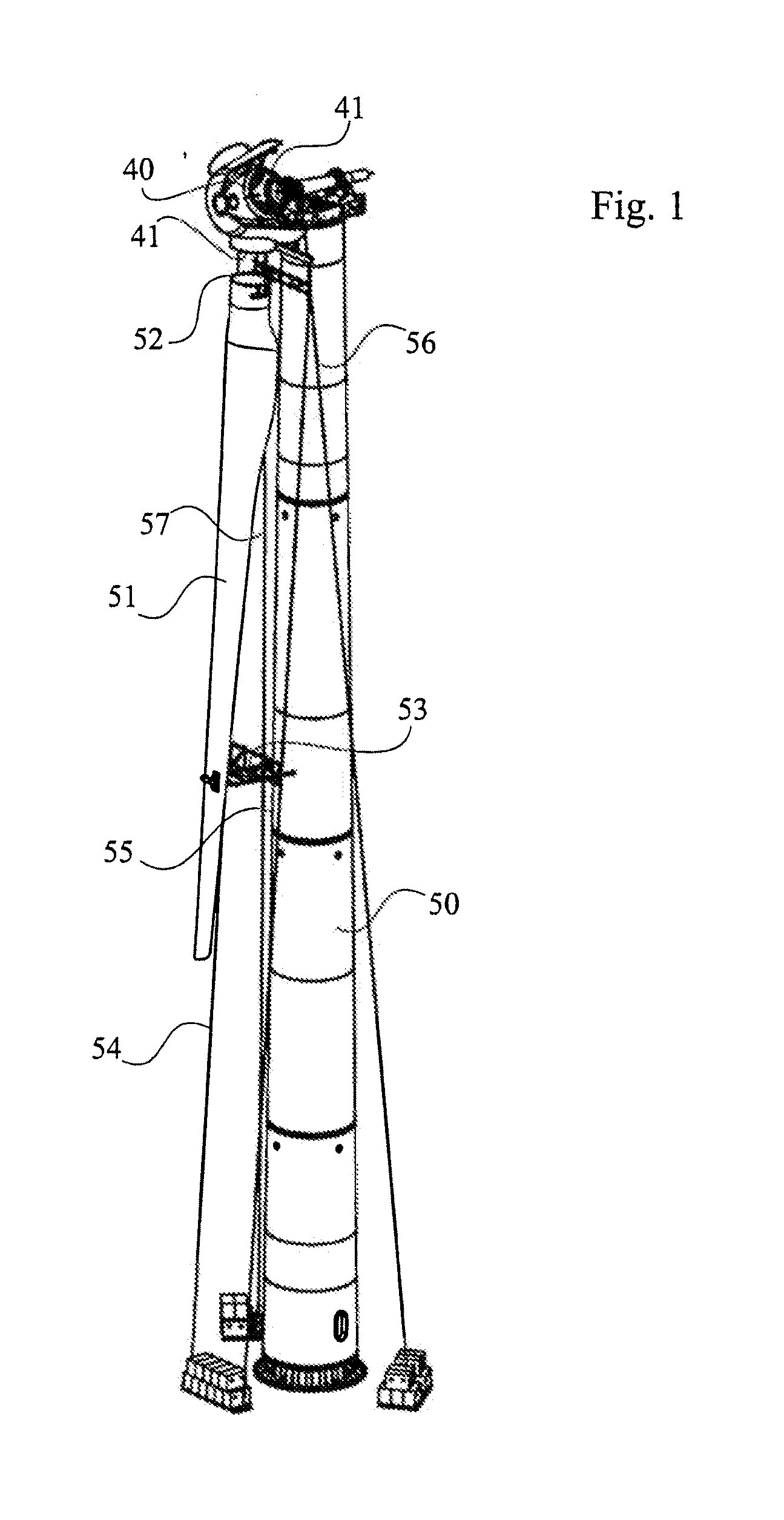
[0020]FIG. 1 is an overview of a wind power plant. A rotor blade 51 is being lifted up to the rotor hub 40 at the upper part of the tower 50 in order to be fitted with its rotor blade connection 52 to the flange 41 of the rotor hub 40, which is connected to the main shaft by means of a hub flange (shown in FIG. 2).
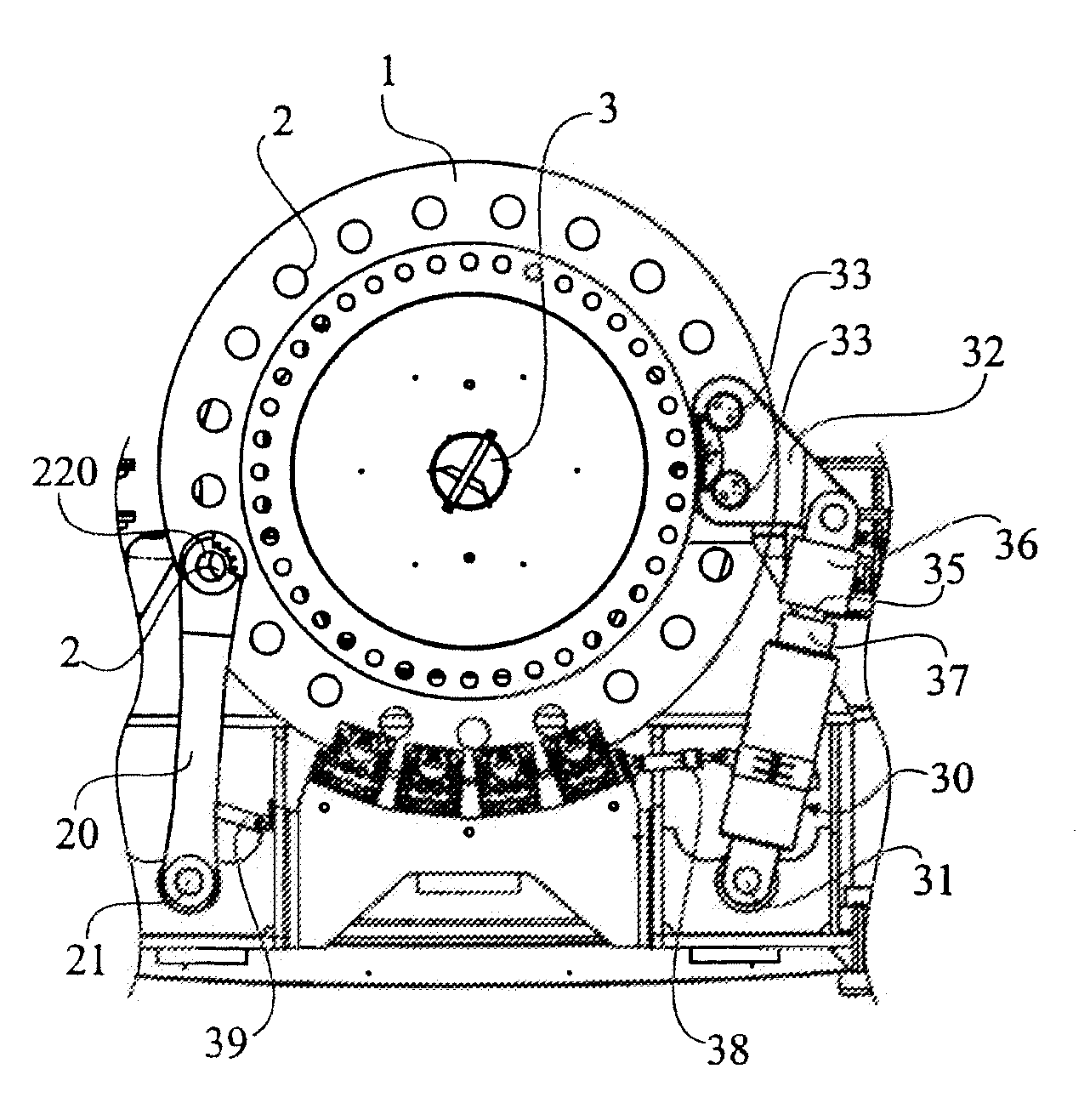
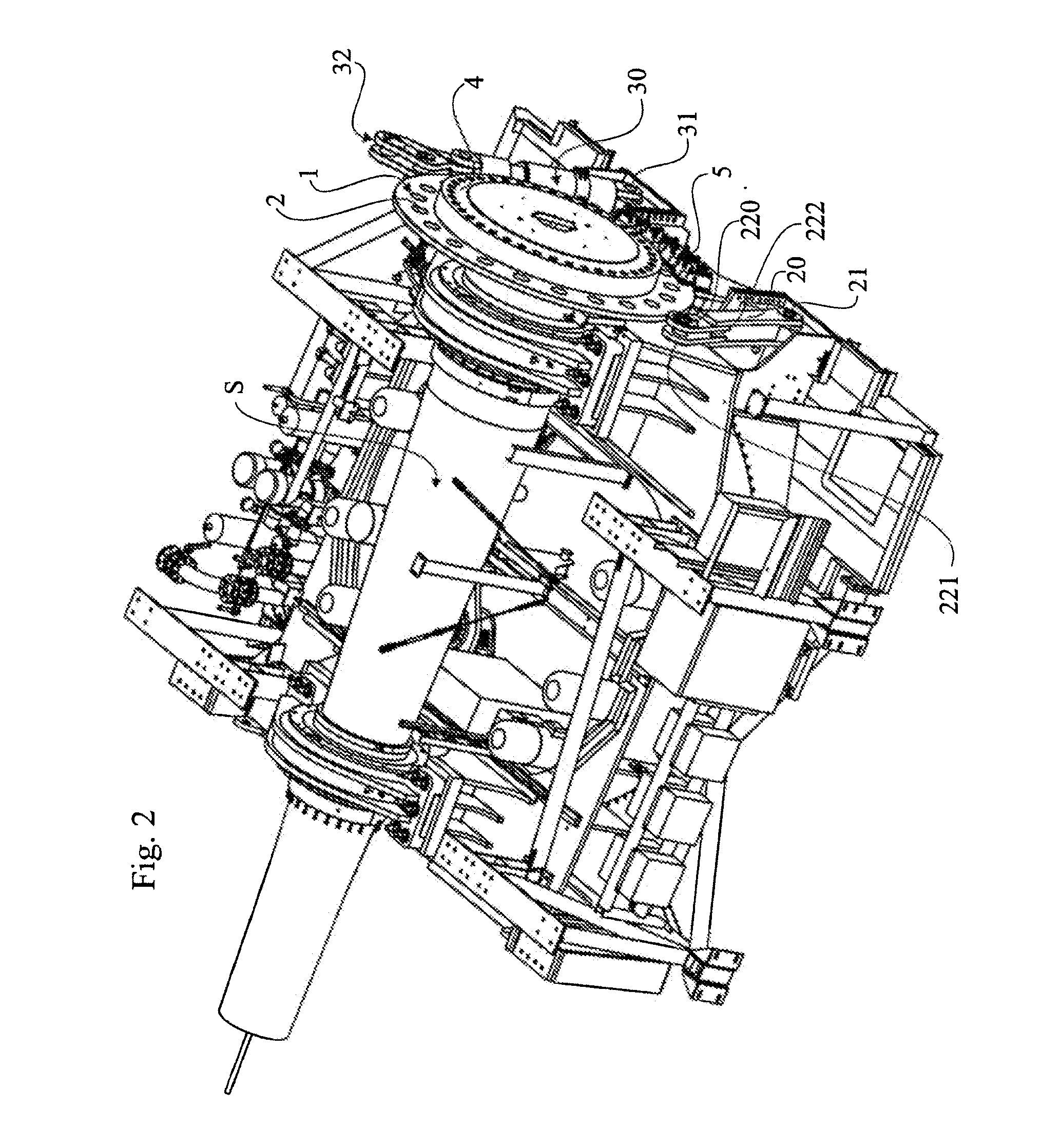
[0021]FIG. 2 is a side view of the interior of the machine housing of the wind power plant. A brake disc 1 is centrally mounted on the main shaft S of the wind turbine and has a large diameter, normally in the range of 1.5-3 meters. The brake disc 1 extends with a portion of its periphery into the gap of a number of brake units 5. The brake disc 1 is provided with a connecting means 2, consisting of a number of through bores evenly distributed on the brake disc 1 at a certain distance from the axis of the brake disc 1. The number of through holes and the degree of angles between the through holes may vary depending on the different needs. A locking device 20 is positioned ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Angle | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| Distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com