Turbine Nozzle Blade and Steam Turbine Equipment Using Same
a turbine blade and turbine technology, applied in the direction of machines/engines, stators, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the problems that the reduction effect of secondary flow loss has been unlikely to be fully brought about by the conventional technique, and achieve the effects of reducing the number of blades, reducing secondary flow loss, and improving the efficiency of the turbine stag
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
first embodiment
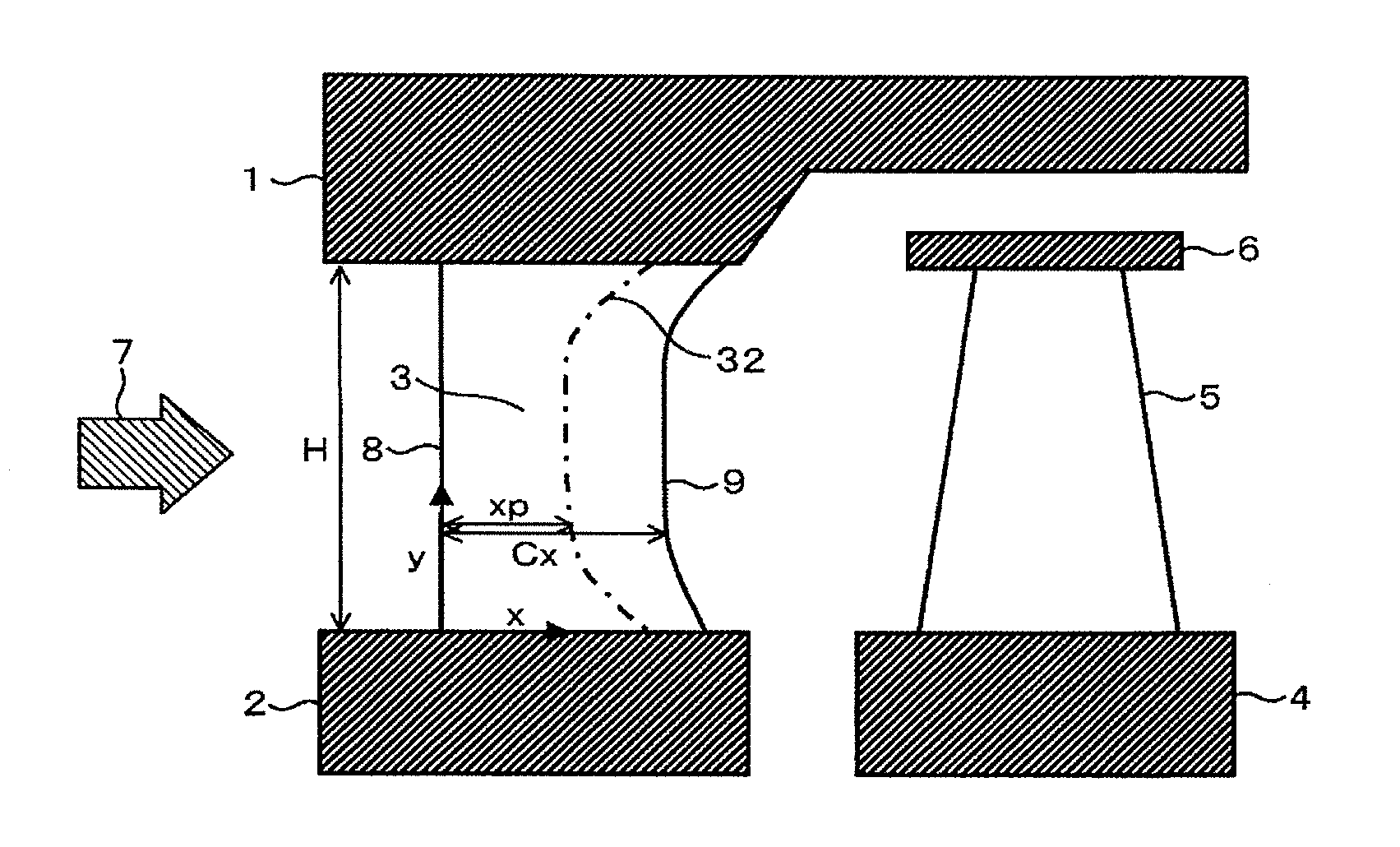
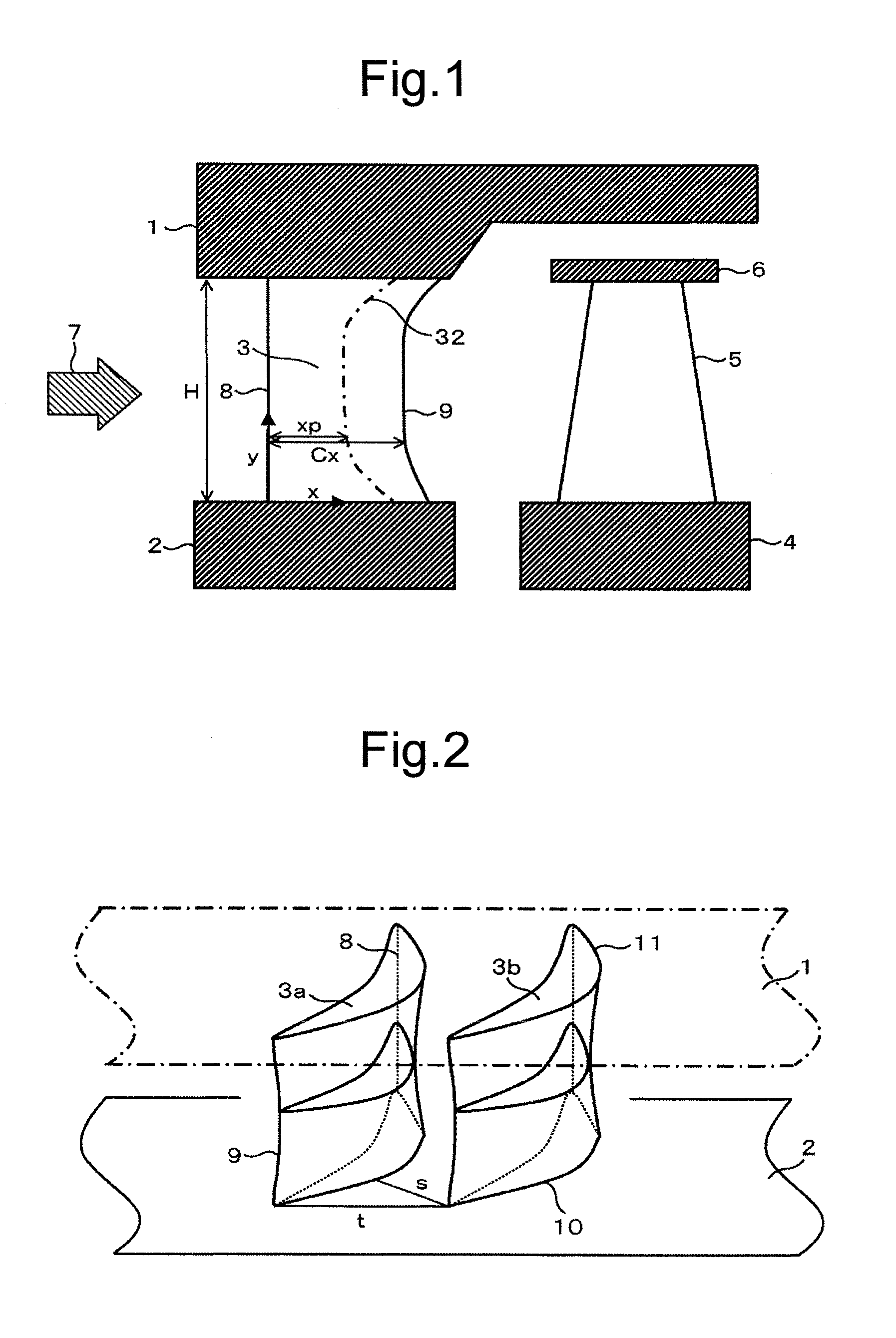
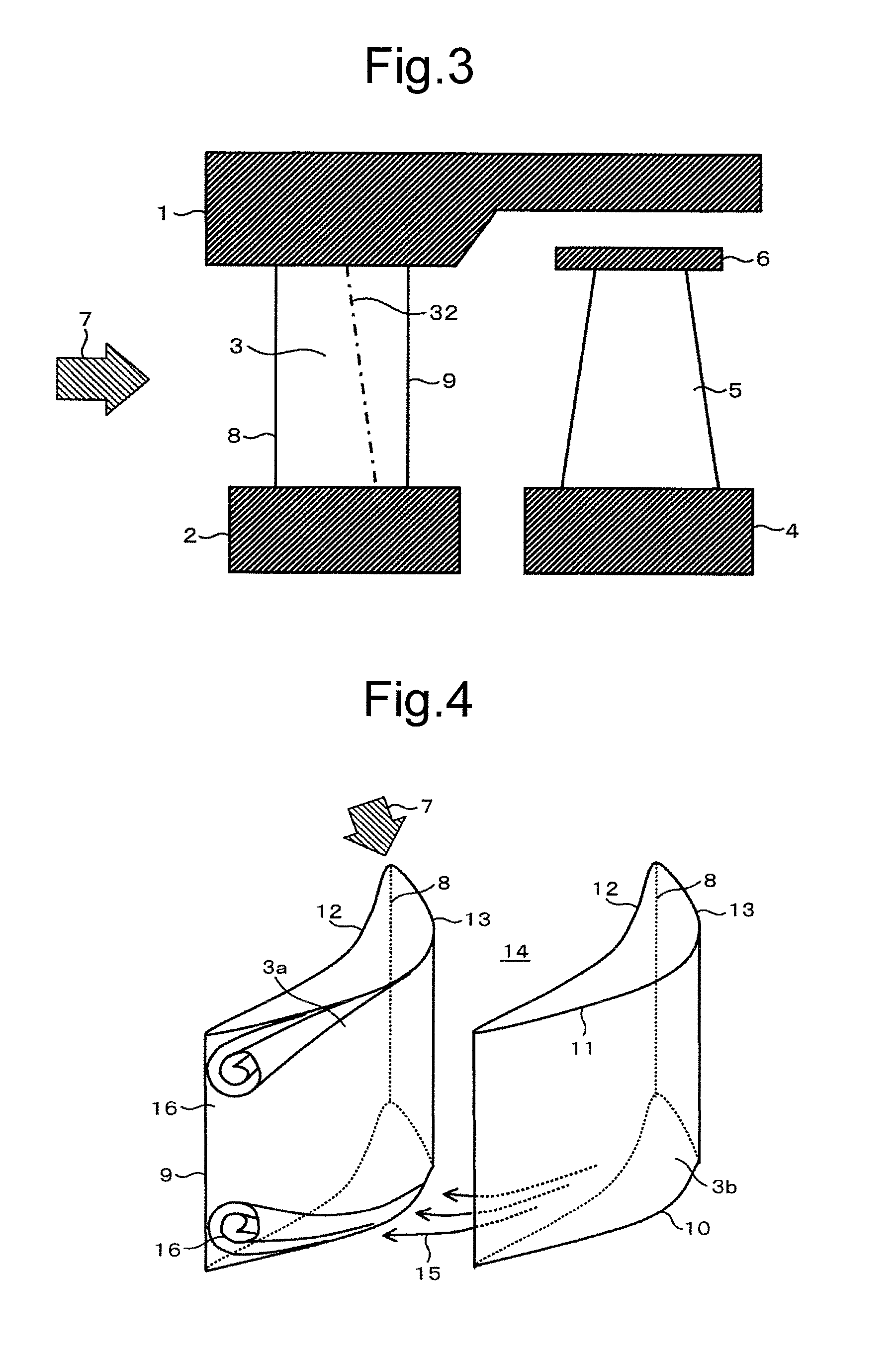
[0023]A first embodiment of the present invention is described below. FIG. 1 is a cross-sectional view showing a structure of a steam turbine stage section according to the present embodiment. As shown in FIG. 1, the steam turbine stage section according to the present embodiment includes a plurality of nozzle blades 3 each disposed in a circumferential direction of the turbine, between a diaphragm outer ring 1 and a diaphragm inner ring 2. The steam turbine stage section also includes a plurality of rotor blades 5 each disposed in a circumferential direction of a turbine rotor 4, at a downstream side of a flow direction of steam relative to one of the nozzle blades 3. The downstream side of the flow direction of steam relative to the nozzle blade 3 is hereinafter referred to simply as the downstream side. The radially outer side of the turbine is hereinafter referred to simply as the outer side. A shroud 6 is provided at a tip of each rotor blade 5, at a radially outer side of the ...
second embodiment
[0042]A second embodiment of the present invention is shown in FIG. 8. Differences from the foregoing embodiment are mainly described below.
[0043]The second embodiment relates to a blade of large H / Cx, a ratio between blade height H and axial chord length “Cx.” This cascade is equivalent to long blades having a significant difference in radius between the blade tip and hub. In this case, in order to minimize the difference in “t / Cx” (i.e., the difference in load coefficient) between the tip and hub of the blade, “Cx” has been traditionally increased according to a particular radius R. When the present invention is applied to such a case, the hub includes a portion at which, as the radius increases, “d Cx / d R” decreases relative to the distribution of “Cx” that originally has a tendency to increase, and the tip includes a portion at which, as the radius increases, “d Cx / d R” also increases more than at a mid-span position. In other words, the present embodiment is characterized in th...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com