Patents
Literature
41results about How to "Reduce secondary flow loss" patented technology
Efficacy Topic
Property
Owner
Technical Advancement
Application Domain
Technology Topic
Technology Field Word
Patent Country/Region
Patent Type
Patent Status
Application Year
Inventor
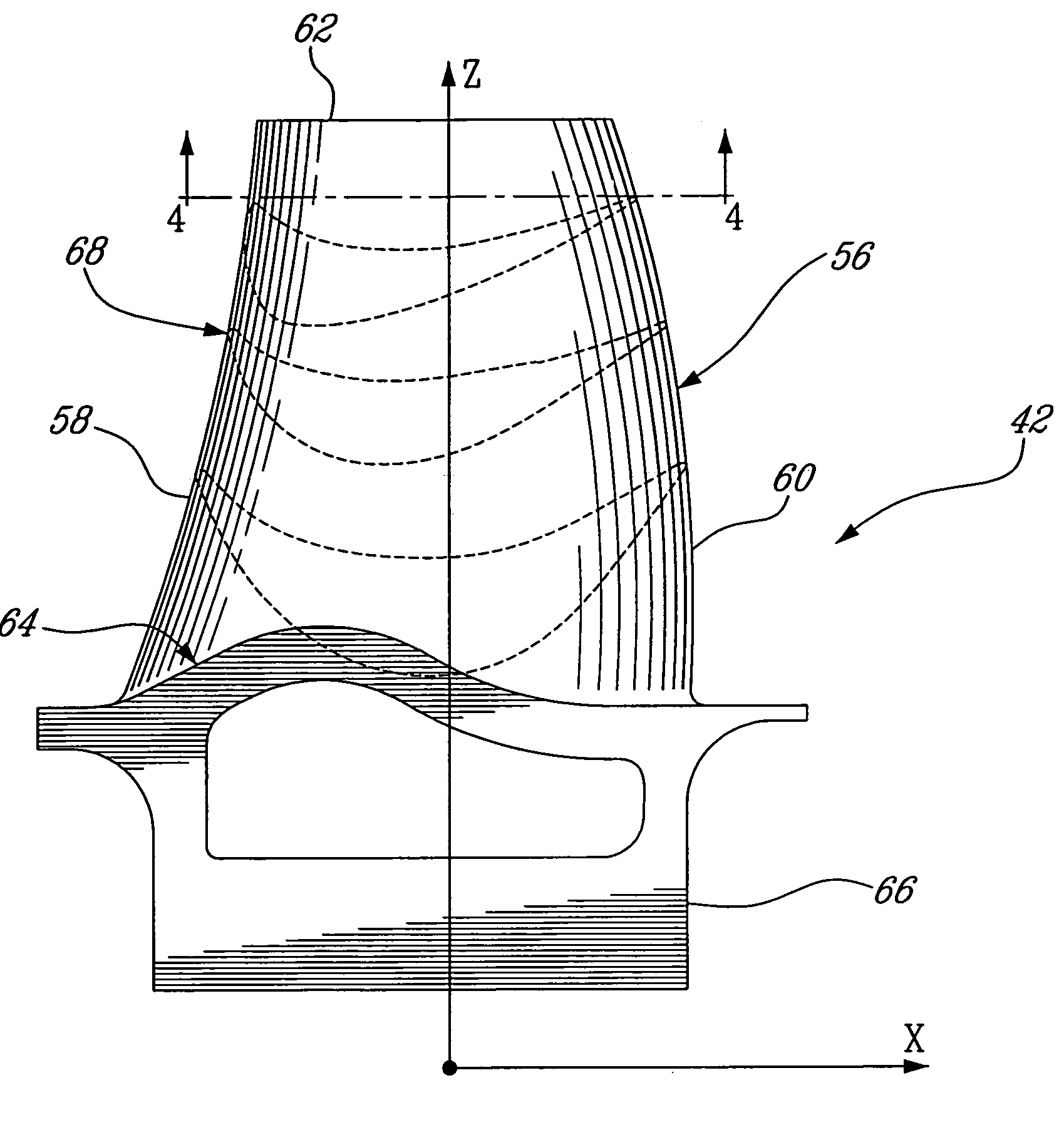
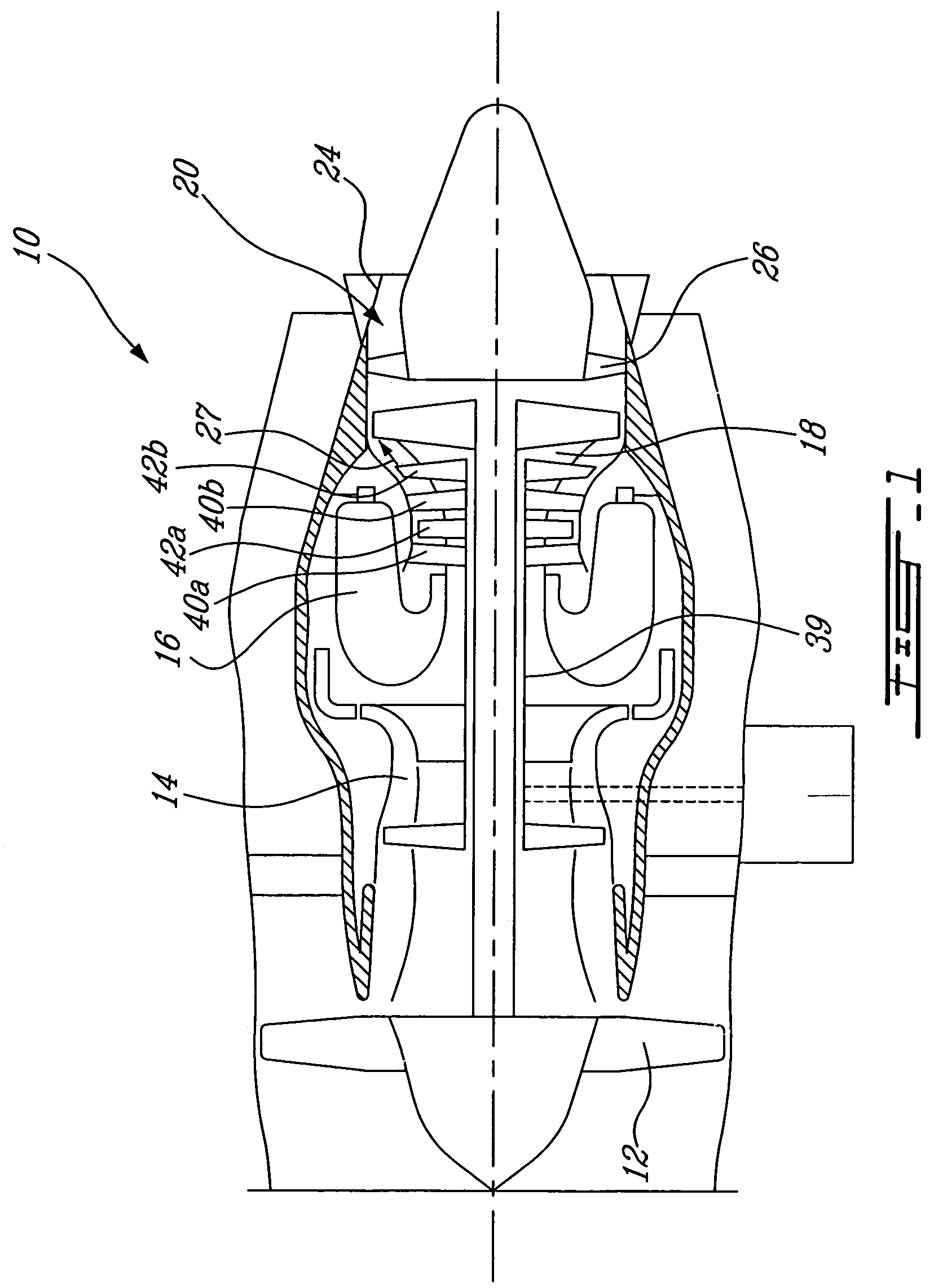
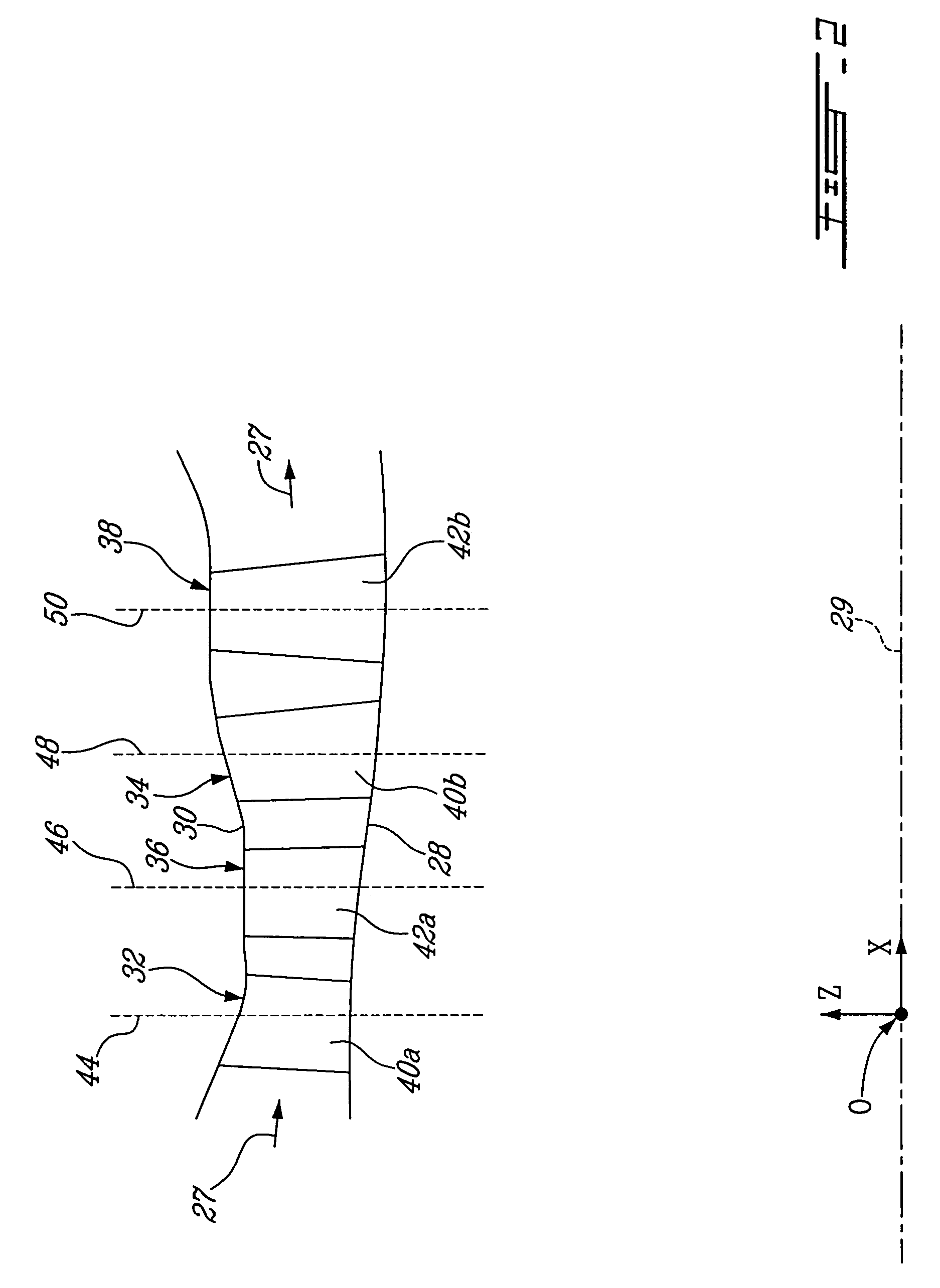
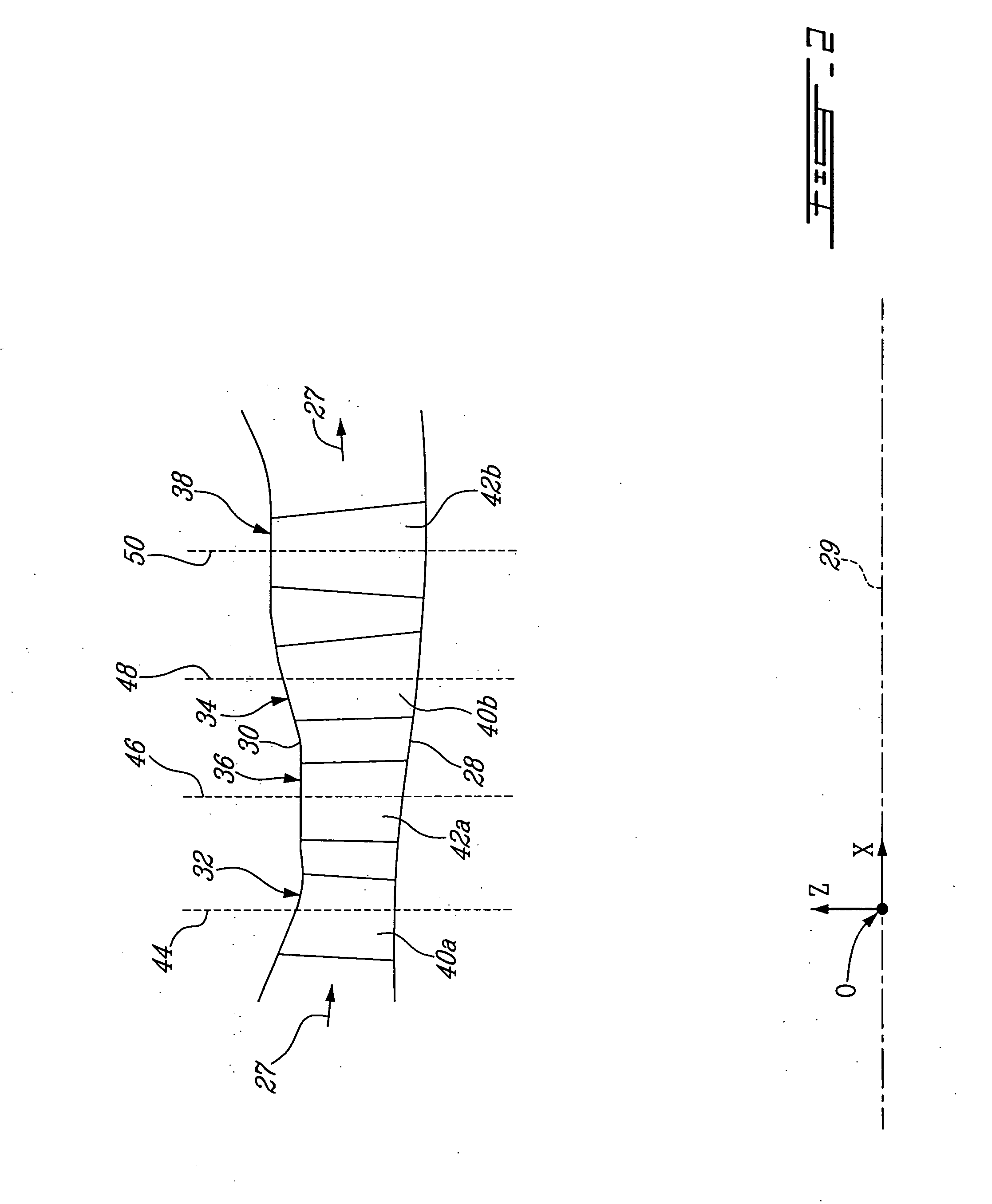
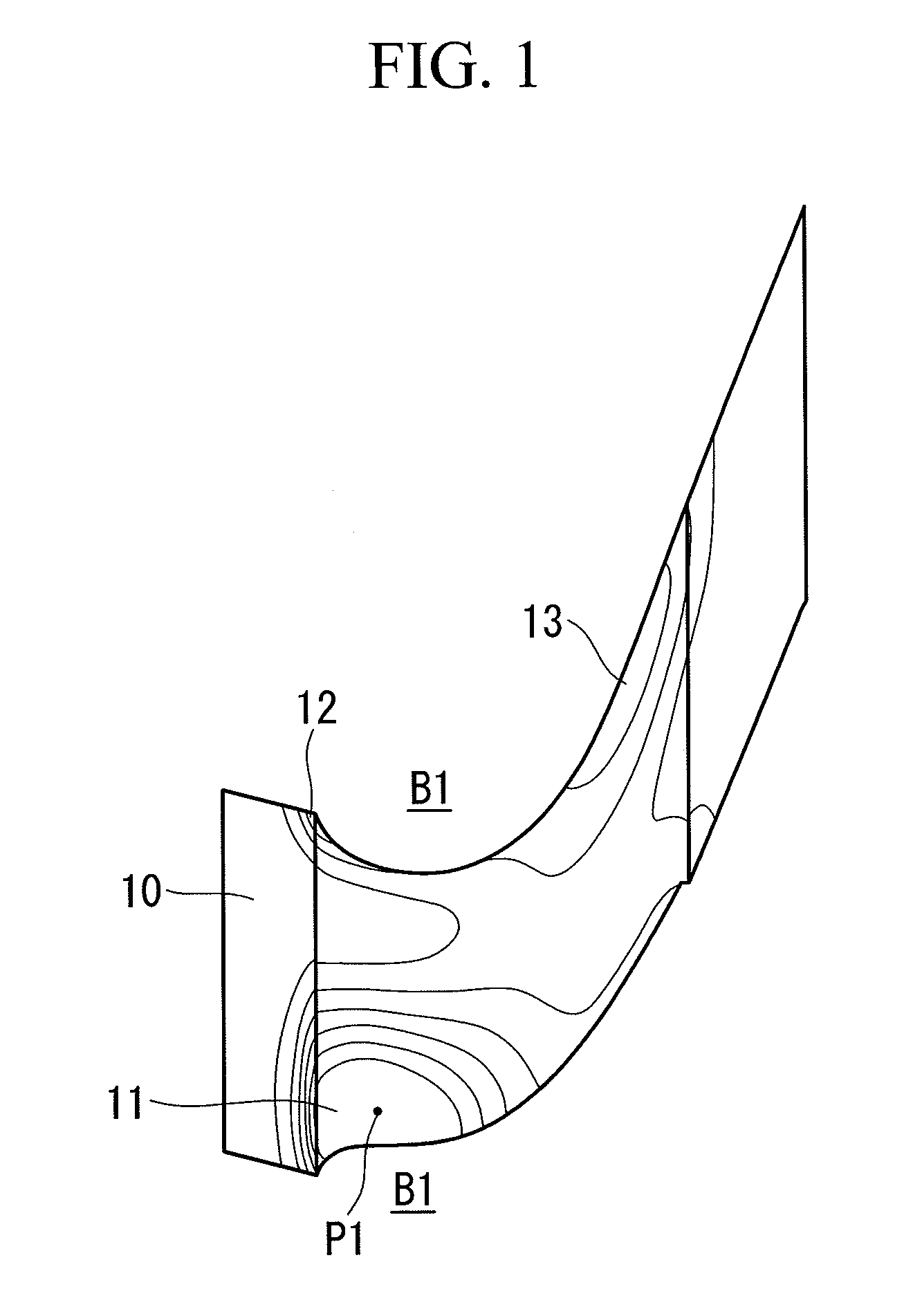
HP turbine blade airfoil profile
ActiveUS7520726B2Reduce disadvantagesReduce secondary flow lossEngine manufactureBlade accessoriesTurbine bladeHigh pressure
A first stage blade of a two-stage high pressure turbine includes an airfoil having a profile substantially in accordance with at least an intermediate portion of the Cartesian coordinate values of X, Y and Z set forth in Table 2. The X and Y values are distances, which when smoothly connected by an appropriate continuing curve, define airfoil profile sections at each distance Z. The profile sections at each distance Z are joined smoothly to one another to form a complete airfoil shape.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
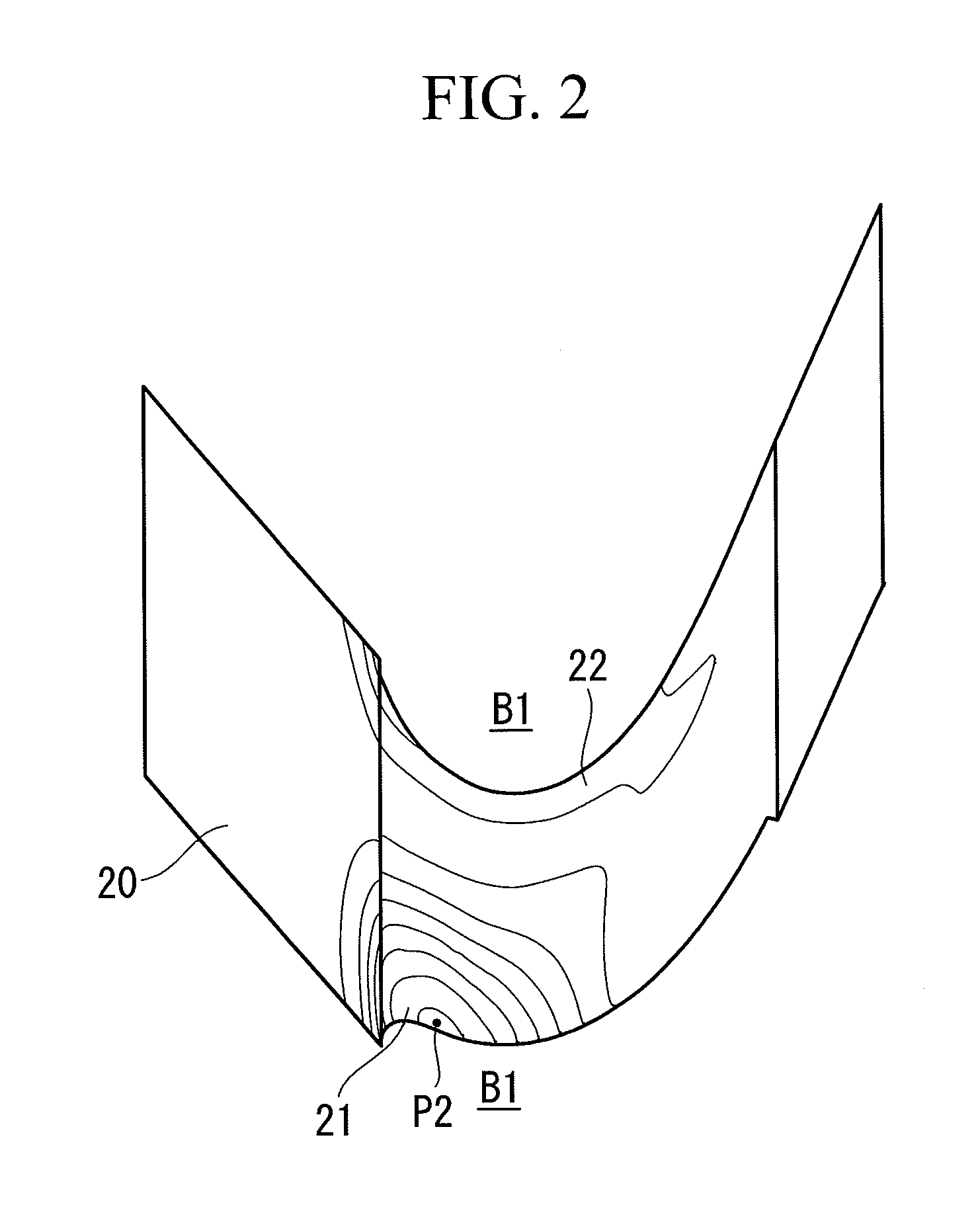
Turbine cascade structure
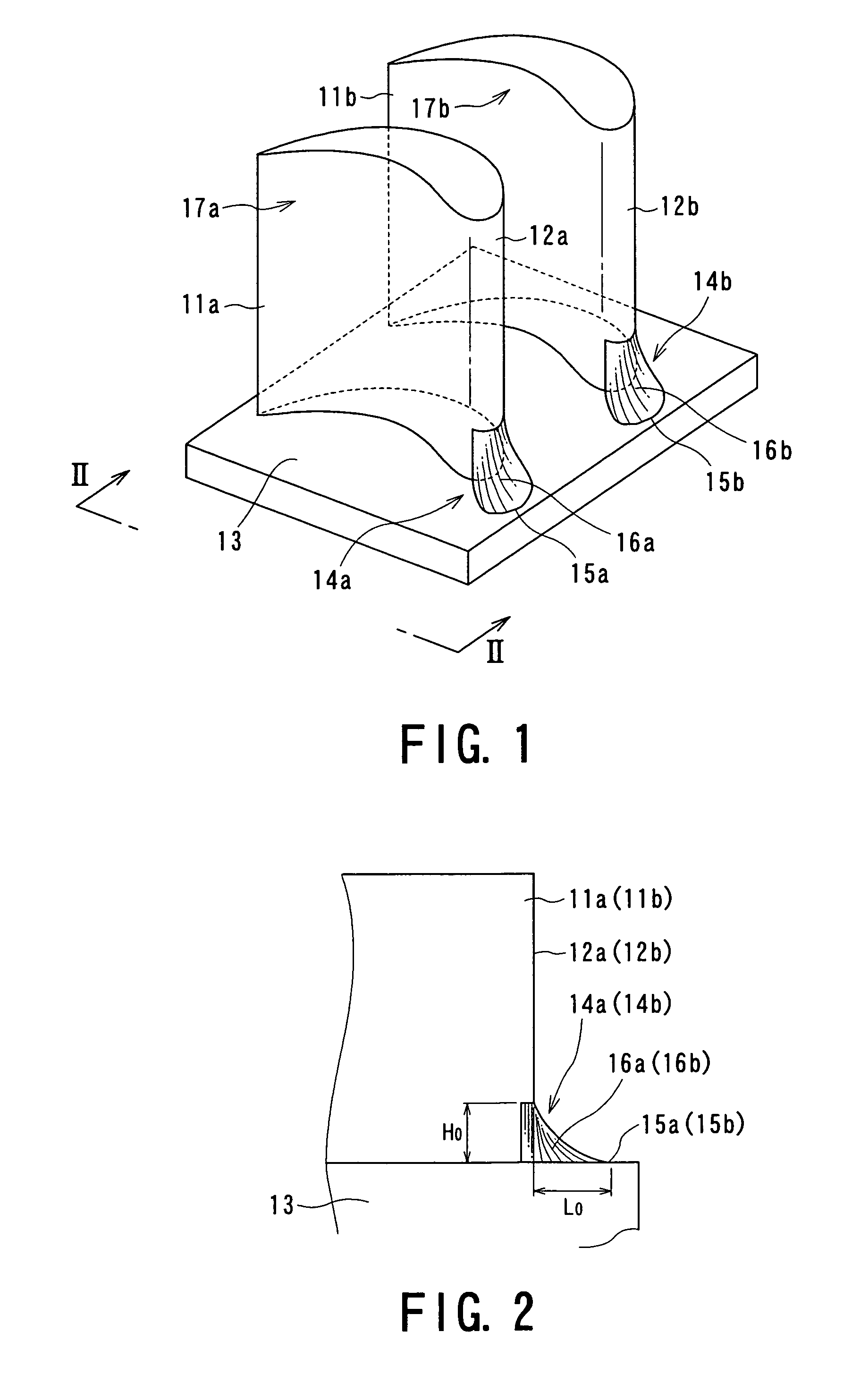
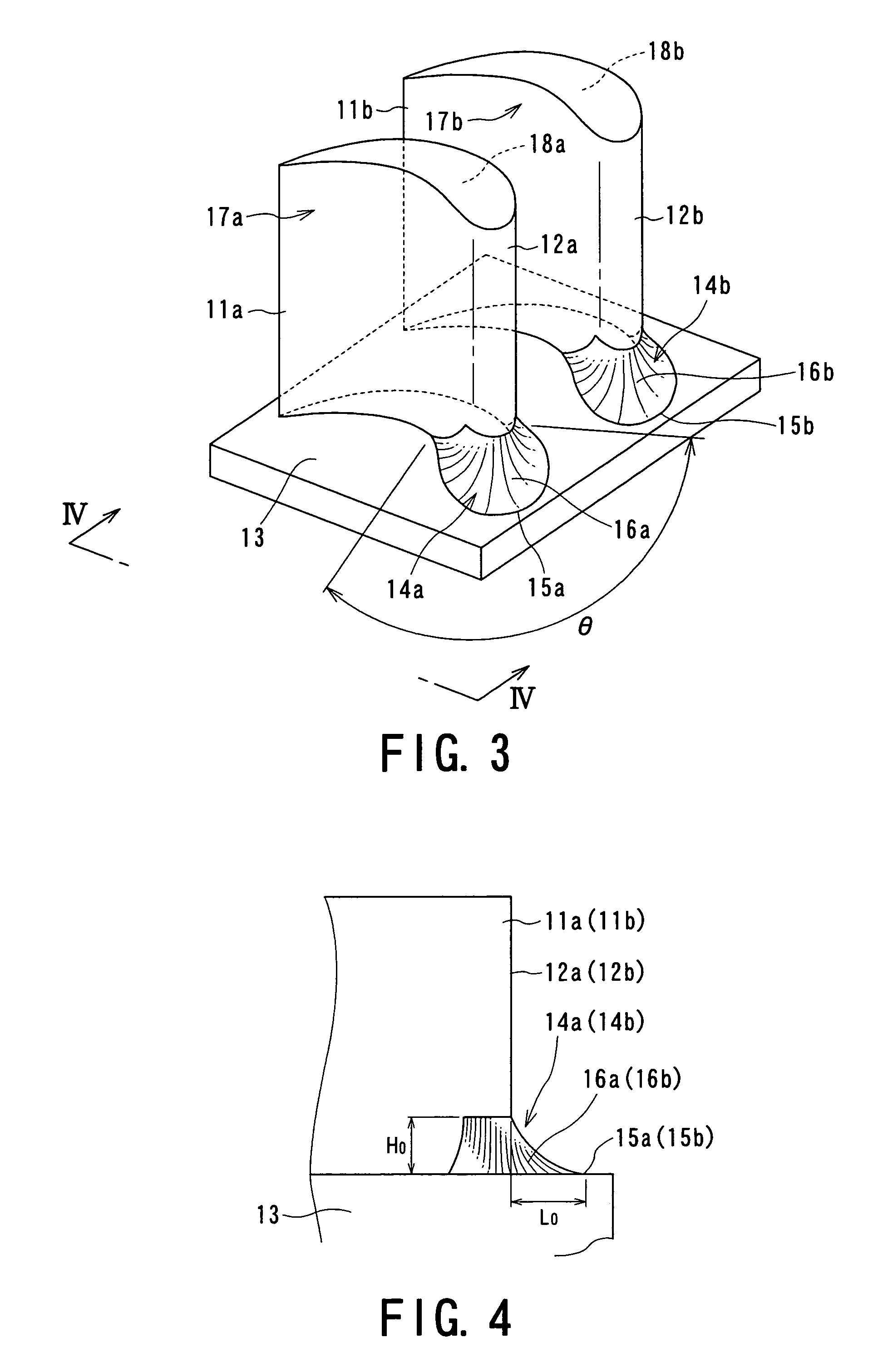
ActiveUS7625181B2Reduce secondary flow lossIncrease surface areaPropellersRotary propellersWorking fluidTurbine blade
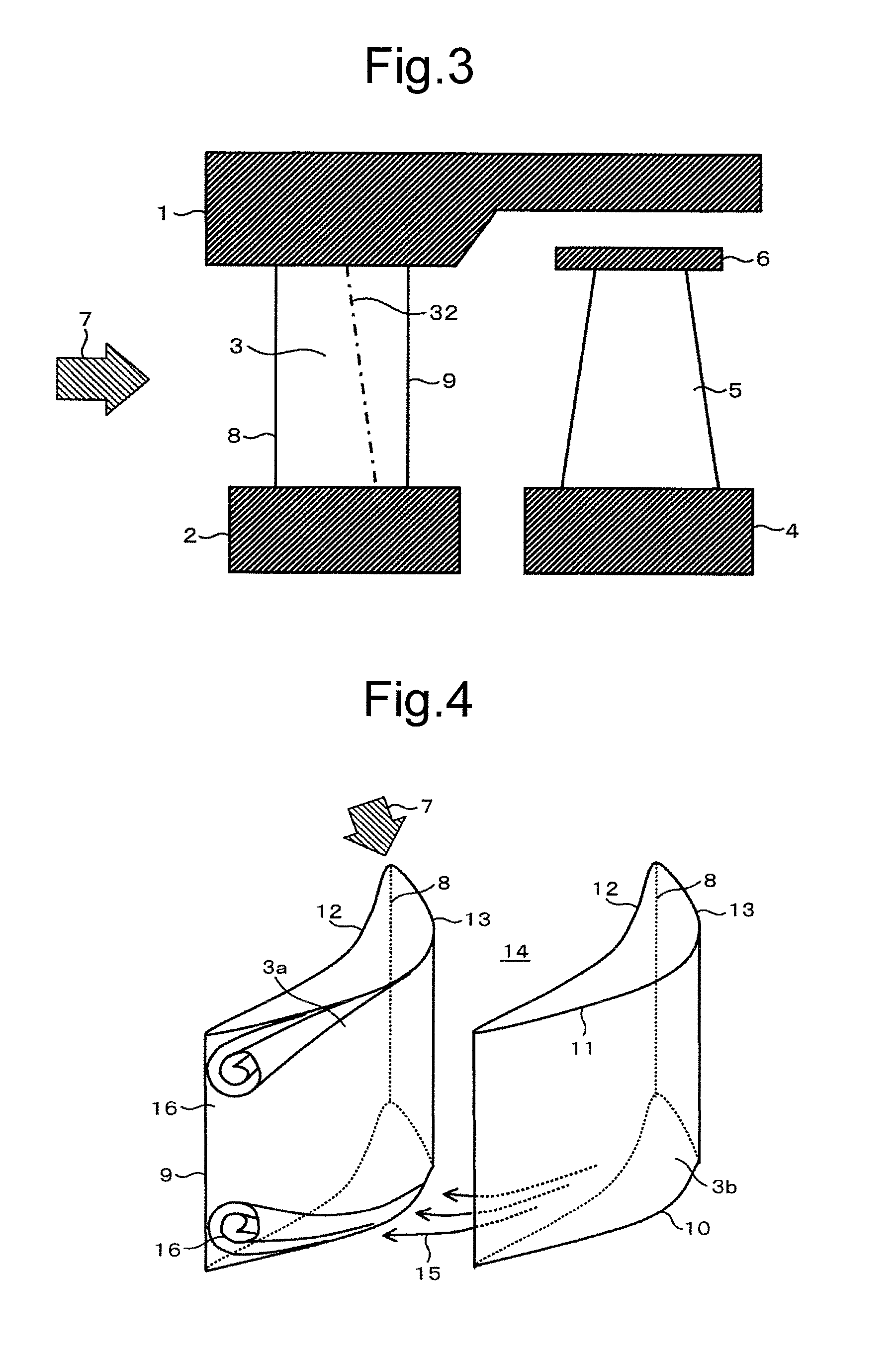
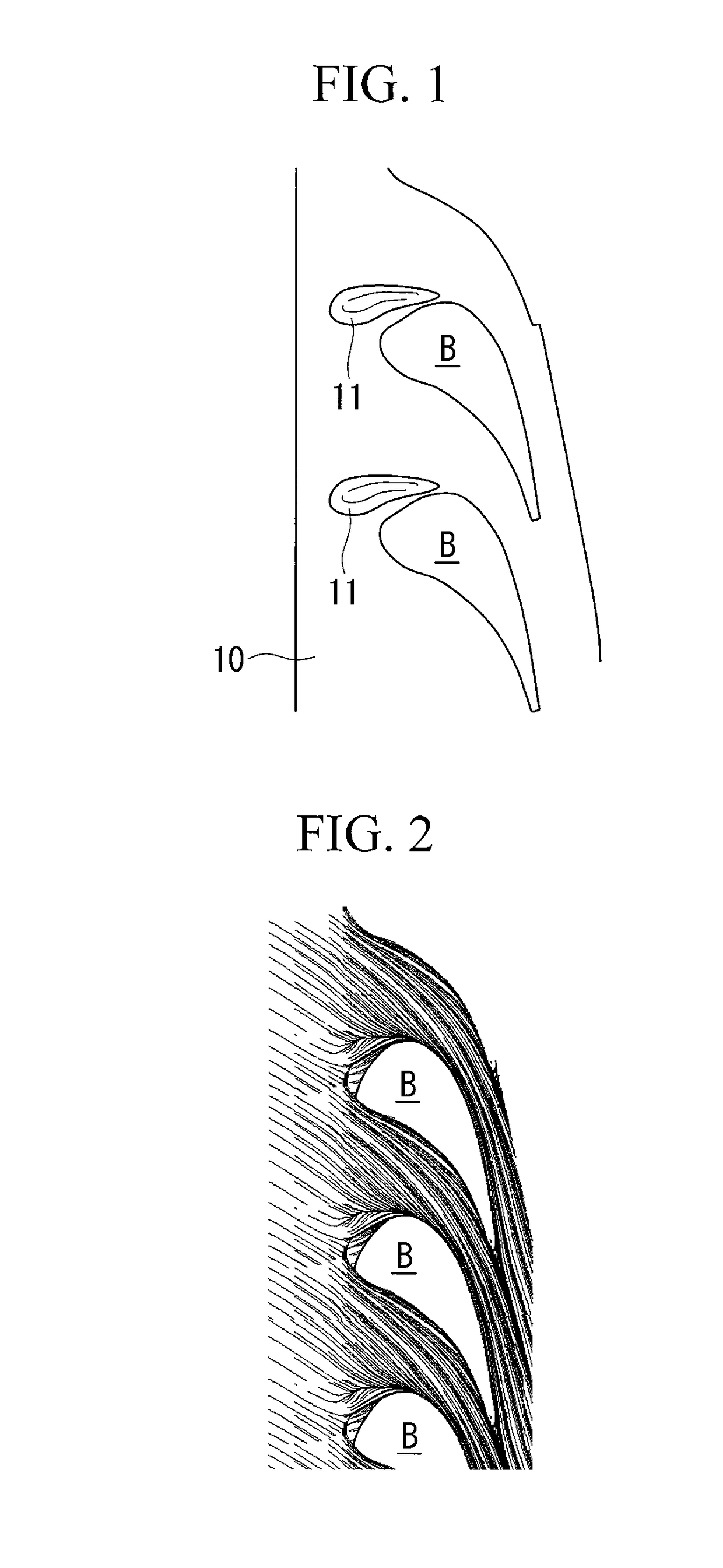
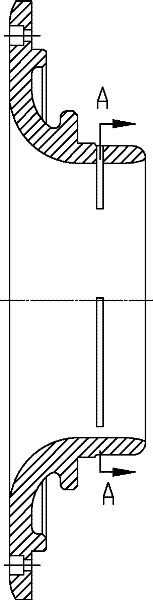
A turbine blade cascade structure includes a plurality of blades arranged in series in a circumferential direction on a wall surface, in which a corner portion defined by the wall surface and a front edge portion of each of blade bodies supported by the wall surface, to which a working fluid flows, includes a cover portion (fillet) that extends toward an upstream side of a flow of the working fluid. The turbine blade cascade structure is capable of reducing the secondary flow loss of the secondary flow in spite of the fluctuation of an incident angle of the working fluid flowing to the front edge portion of the blade body.
Owner:KK TOSHIBA
HP turbine blade airfoil profile
ActiveUS20080063530A1Minimizing flow separation disadvantageReduce secondary flow lossEngine manufactureBlade accessoriesTurbine bladeHigh pressure
A first stage blade of a two-stage high pressure turbine includes an airfoil having a profile substantially in accordance with at least an intermediate portion of the Cartesian coordinate values of X, Y and Z set forth in Table 2. The X and Y values are distances, which when smoothly connected by an appropriate continuing curve, define airfoil profile sections at each distance Z. The profile sections at each distance Z are joined smoothly to one another to form a complete airfoil shape.
Owner:PRATT & WHITNEY CANADA CORP
Turbine blade cascade endwall
ActiveUS20100196154A1Improve performanceReduce secondary flow lossEngine manufacturePump componentsSuction stressTurbine blade
Provided is a turbine blade cascade endwall that is capable of suppressing a vortex generated on a suction surface of a turbine stator blade and that is capable of reducing secondary-flow loss due to this vortex. A turbine blade cascade endwall that is positioned on a tip side of a plurality of turbine stator blades arranged in a ring form is provided with a pressure gradient alleviating part that alleviates a pressure gradient generated in the blade height direction at a suction surface of the turbine stator blades due to a clearance leakage flow, leaking out of a gap between a tip of a turbine rotor blade located on the upstream side of the turbine stator blades and a tip endwall disposed facing the tip of this turbine rotor blade.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Turbine blade cascade endwall
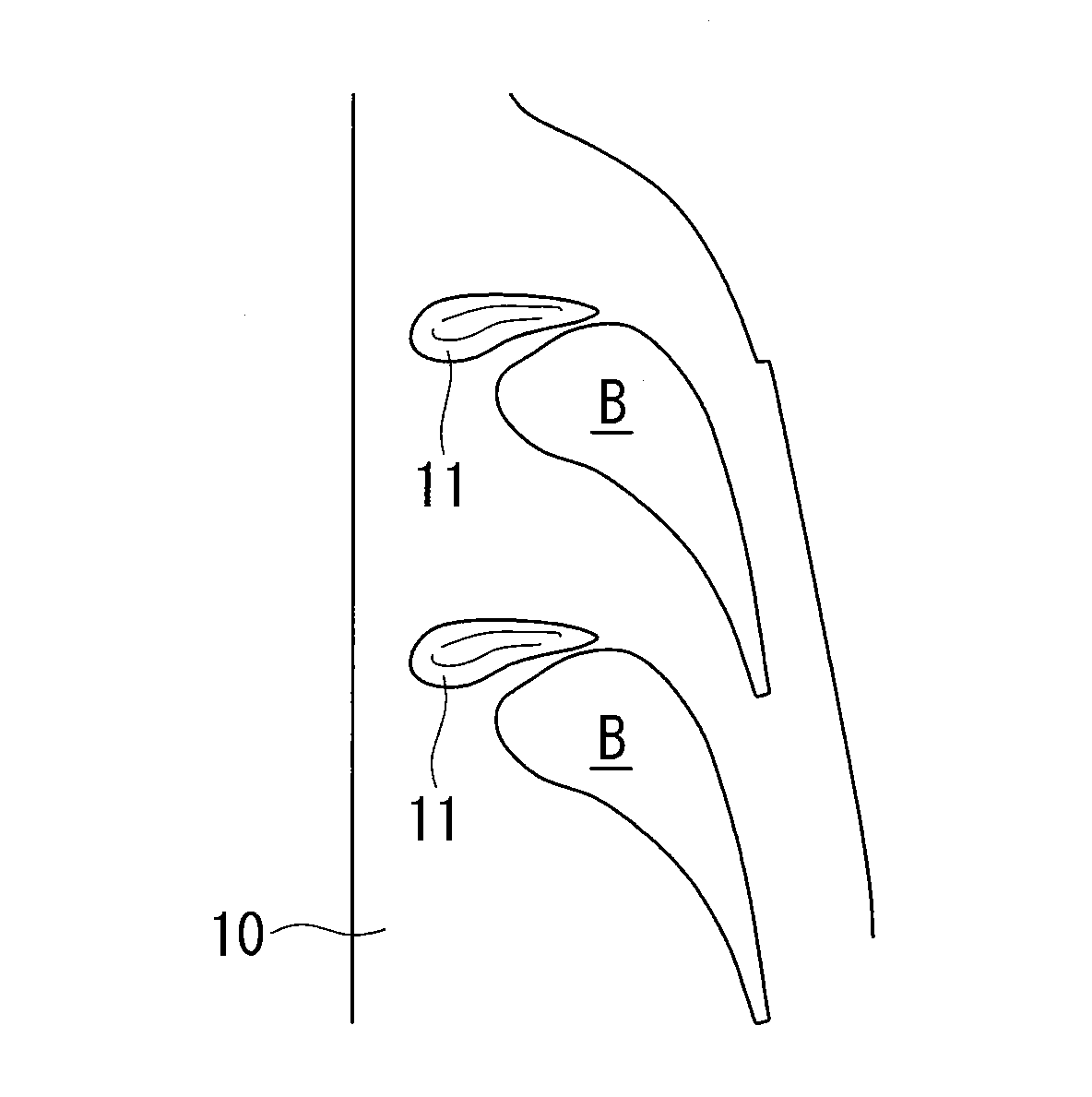
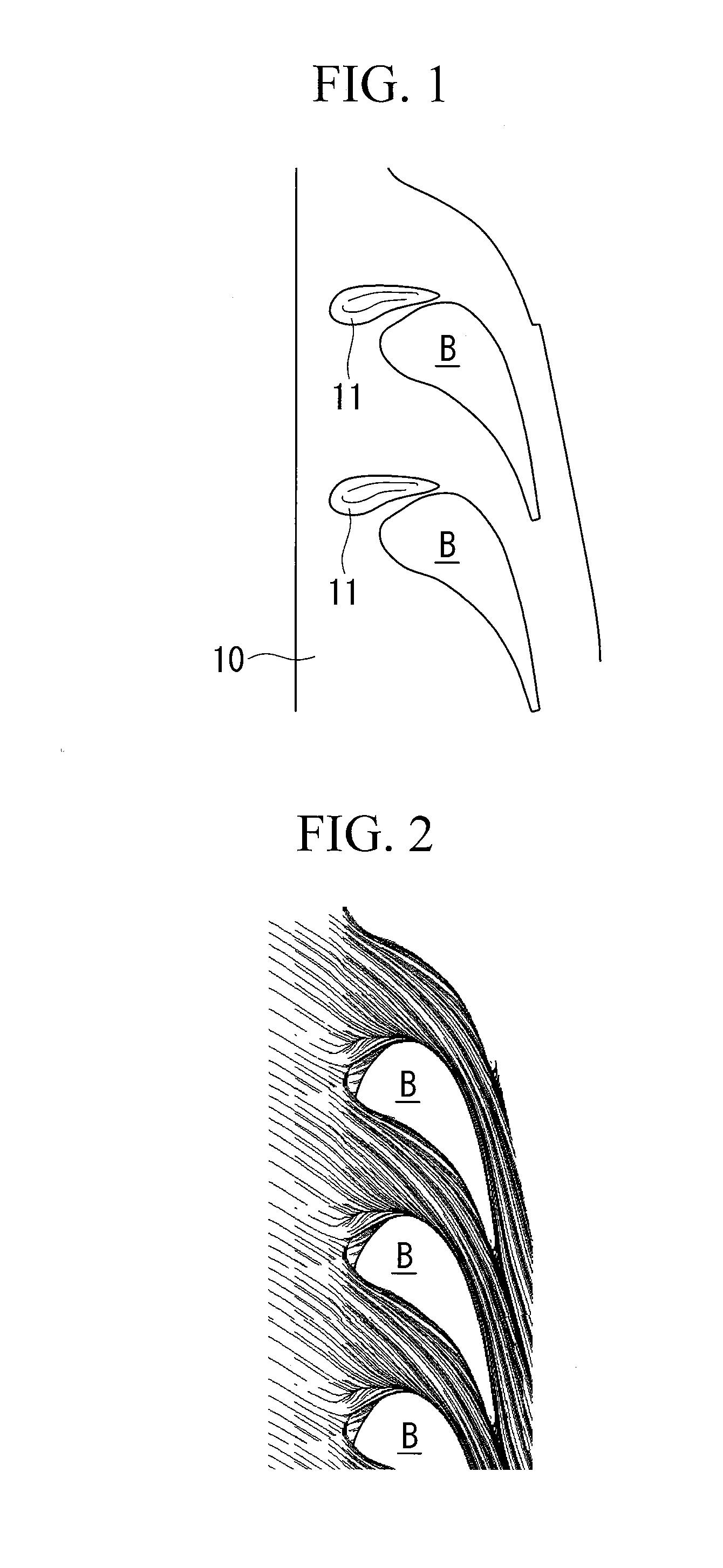
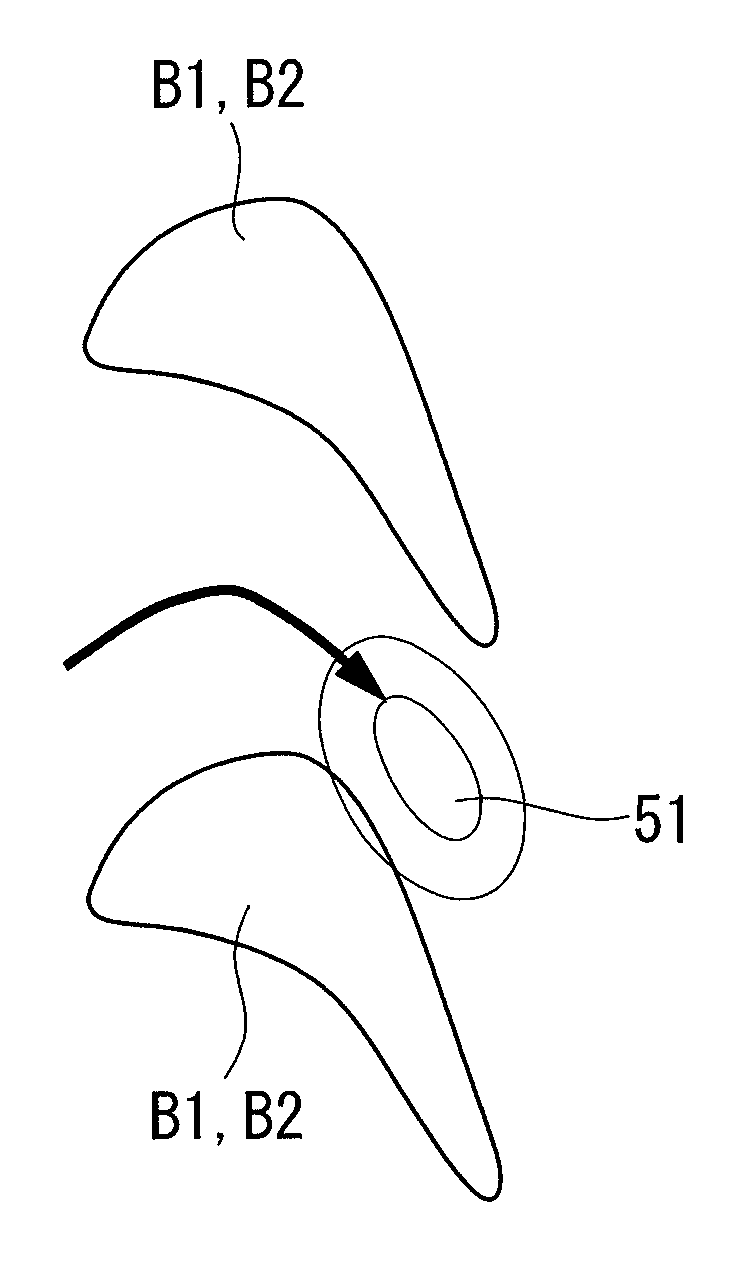
InactiveUS20100284818A1Enhanced overall turbine performanceCrossflow reducedPropellersEngine manufactureTurbine blade
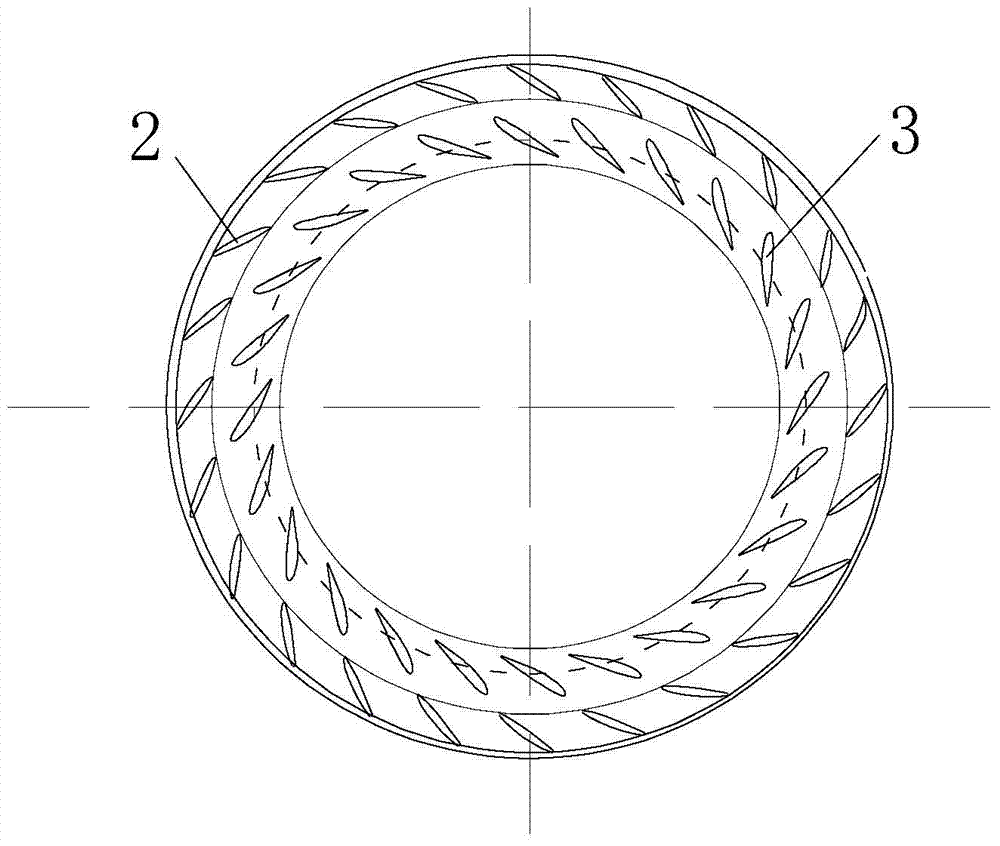
Provided is a turbine blade cascade endwall that is capable of reducing crossflow and is capable of reducing secondary-flow loss that occurs in association with the crossflow, therefore being capable of achieving enhanced turbine performance. A convex portion (11) that is gently swollen as a whole, that has an apex (P1) at a position of 0 to 20% pitch in a position of 5 to 25% Cax, that gently slopes from this apex (P1) toward a downstream side and a suction side surface of an adjacently disposed turbine stationary blade (B1) or turbine moving blade, and that slopes slightly steeply from the apex (P1) toward an upstream side is provided between one turbine stationary blade (B1) or turbine moving blade and another turbine stationary blade (B1) or turbine moving blade disposed adjacent to one turbine stationary blade (B1) or turbine moving blade.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HITACHIPOWER SYST LTD
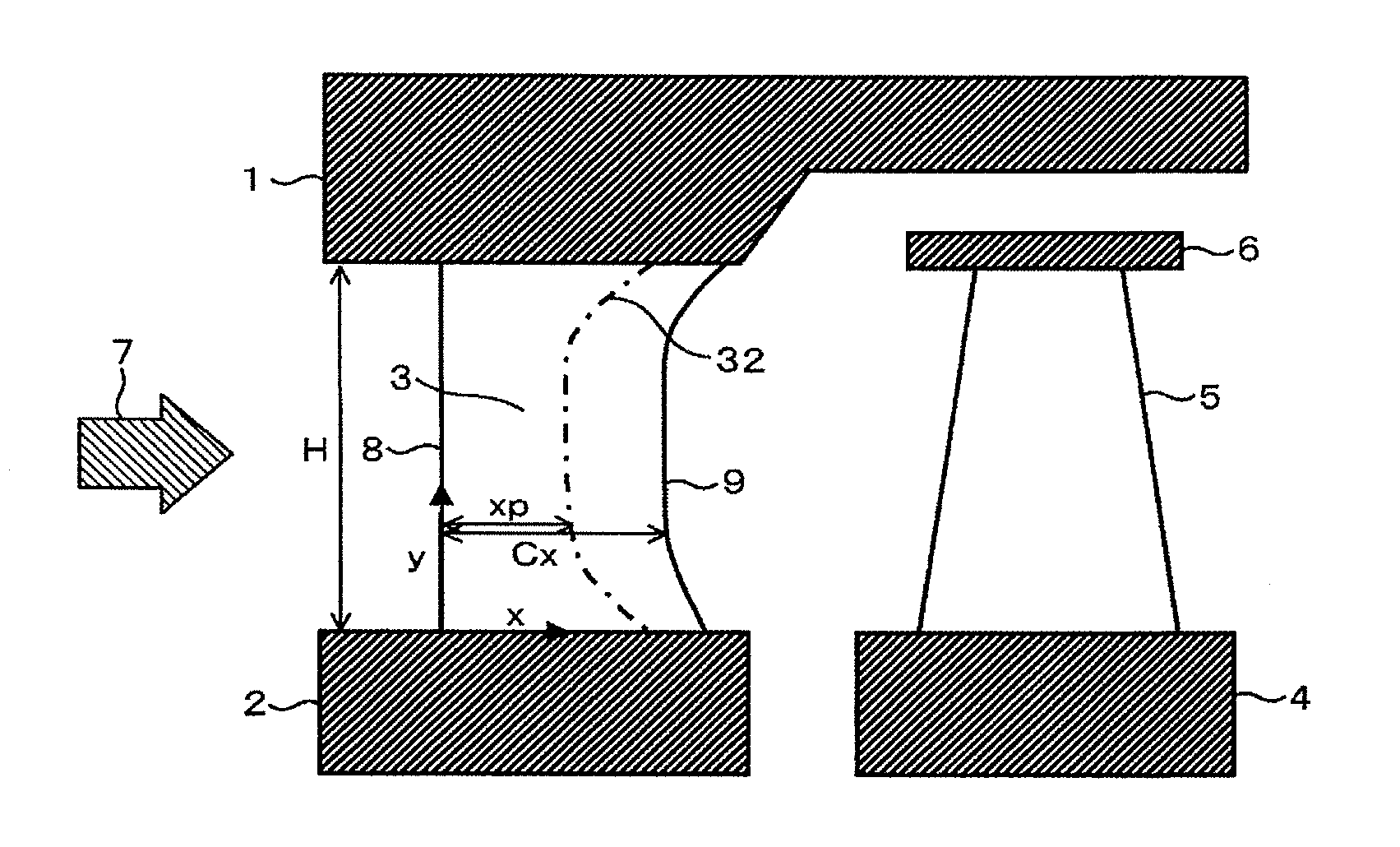
Turbine Nozzle Blade and Steam Turbine Equipment Using Same
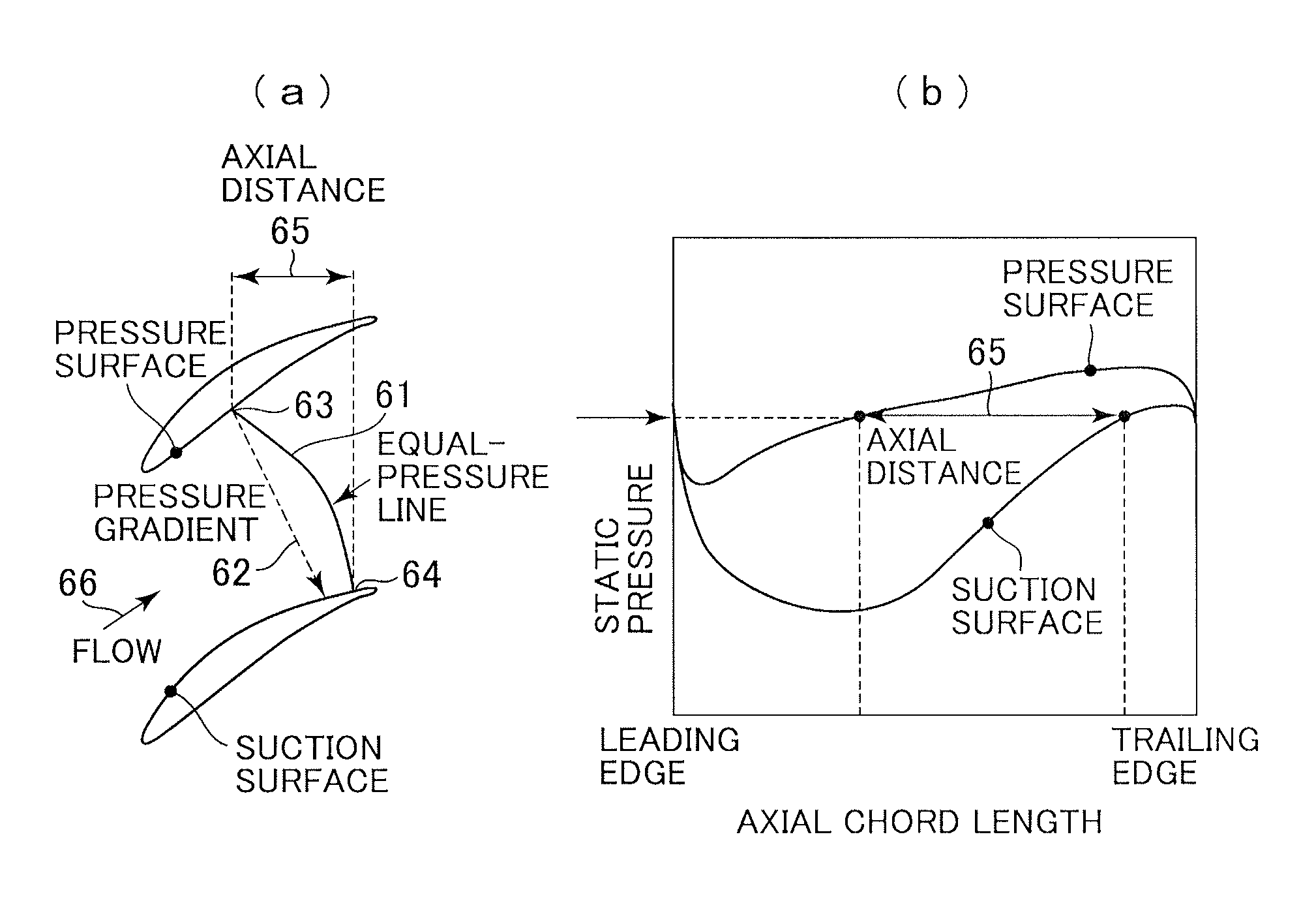
InactiveUS20120210715A1Reduce in quantityImproving turbine stage efficiencyBlade accessoriesEfficient propulsion technologiesLeading edgeDifferential pressure
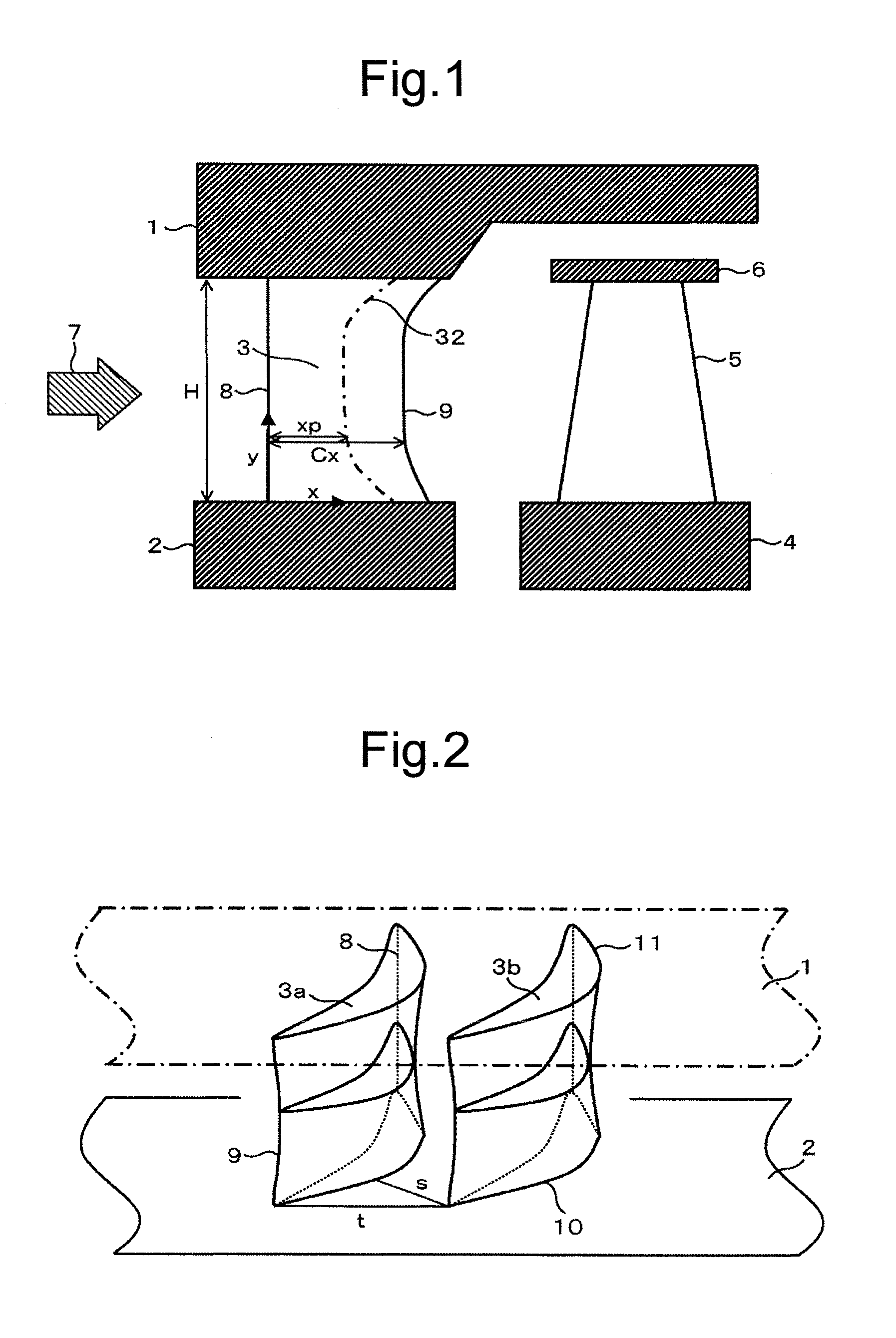
Disclosed is a highly efficient turbine nozzle blade that reduces the number of blades in an axial-flow turbine while reducing secondary-flow loss. In the nozzle blade, when a differential pressure between a pressure side and a suction side of each blade, at the same axial chord position of the blade, is defined as a load of the blade, and a ratio between axial chord length “Cx” of the blade and an axial distance “xp” from a leading edge of the blade at a maximum load position that maximizes the blade load is defined as a maximum load relative position, Cx is greater at a hub and tip than at an intermediate vertical portion, and simultaneously a maximum load relative position at the hub and tip is set to be nearer to a trailing edge thereof than a maximum load relative position of the intermediate vertical portion of the blade.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HITACHIPOWER SYST LTD
Mixed-flow type water pump turbine
InactiveCN103696895AReduce the possibility of vibrationReduce bendingHydro energy generationReaction enginesMixed flowWater pipe
The invention discloses a mixed-flow type water pump turbine. The mixed-flow type water pump turbine comprises a volute, fixed guide vanes, movable guide vanes, a turning wheel and an exhaust water pipe, wherein the turning wheel is located at the middle part inside the volute; the fixed guide vanes and the movable guide vanes are distributed inside the volute and are located near the turning wheel; the exhaust water pipe is connected to the middle part of the bottom of the volute; the turning wheel is mainly composed of an upper canopy, a lower ring and vanes; the vanes are located between the upper canopy and the lower ring and are distributed along the circumference of the lower ring in groups; each group of the vanes is composed of a long vane, an intermediate van and two short vanes; one short vane serves as a first short vane and is located between the long vane and the intermediate vane of the group of the vanes while the other short vane serves as a second short vane and is located between the intermediate vane of the group of the vanes and the long vane of the adjacent group of the vanes. The bending degree of the curve in an S region is reduced obviously, the secondary flow loss is lower, the flowing property of a flow field is improved, the running stability of a machine set is guaranteed, and the likelihood of occurrence of vibration of the machine set is reduced.
Owner:ELECTRIC POWER RES INST OF GUANGDONG POWER GRID +1
Turbine blade cascade endwall
ActiveUS8469659B2Reduce secondary flow lossSecondary-flow loss due to the vortices can be reducedEngine manufacturePump componentsTurbine bladeLeakage flow
Provided is a turbine blade cascade endwall that is capable of suppressing a vortex generated on a suction surface of a turbine stator blade and that is capable of reducing secondary-flow loss due to this vortex. A turbine blade cascade endwall that is positioned on a tip side of a plurality of turbine stator blades arranged in a ring form is provided with a pressure gradient alleviating part that alleviates a pressure gradient generated in the blade height direction at a suction surface of the turbine stator blades due to a clearance leakage flow, leaking out of a gap between a tip of a turbine rotor blade located on the upstream side of the turbine stator blades and a tip endwall disposed facing the tip of this turbine rotor blade.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
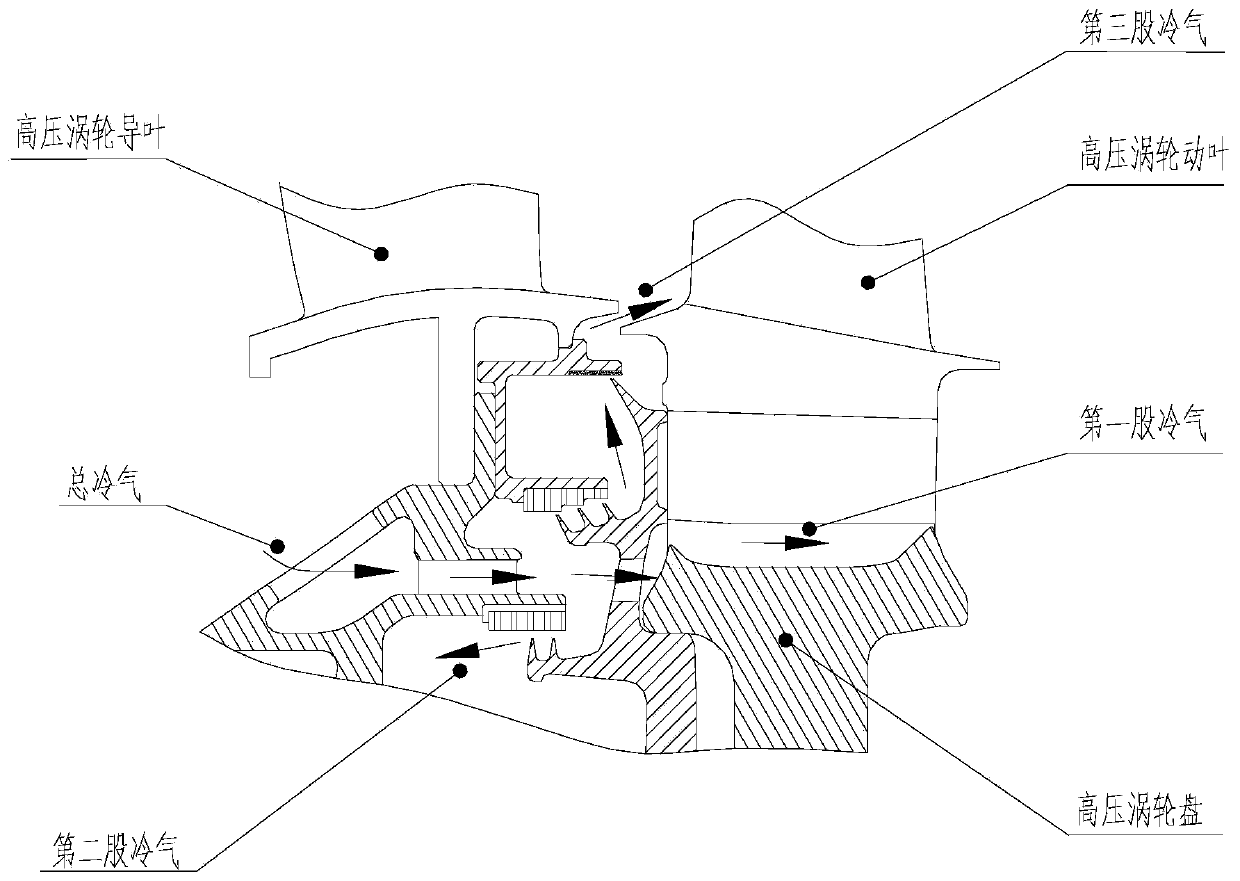
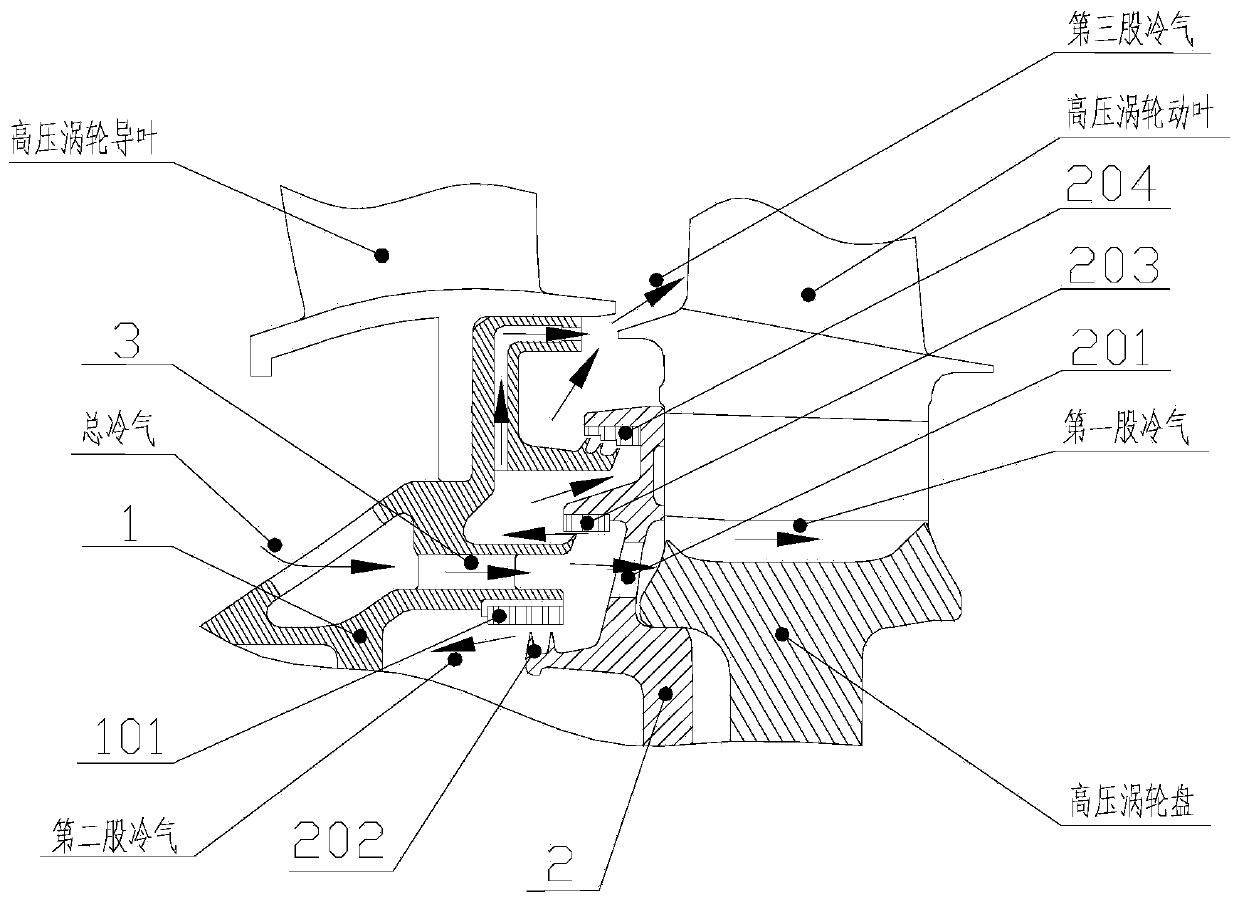
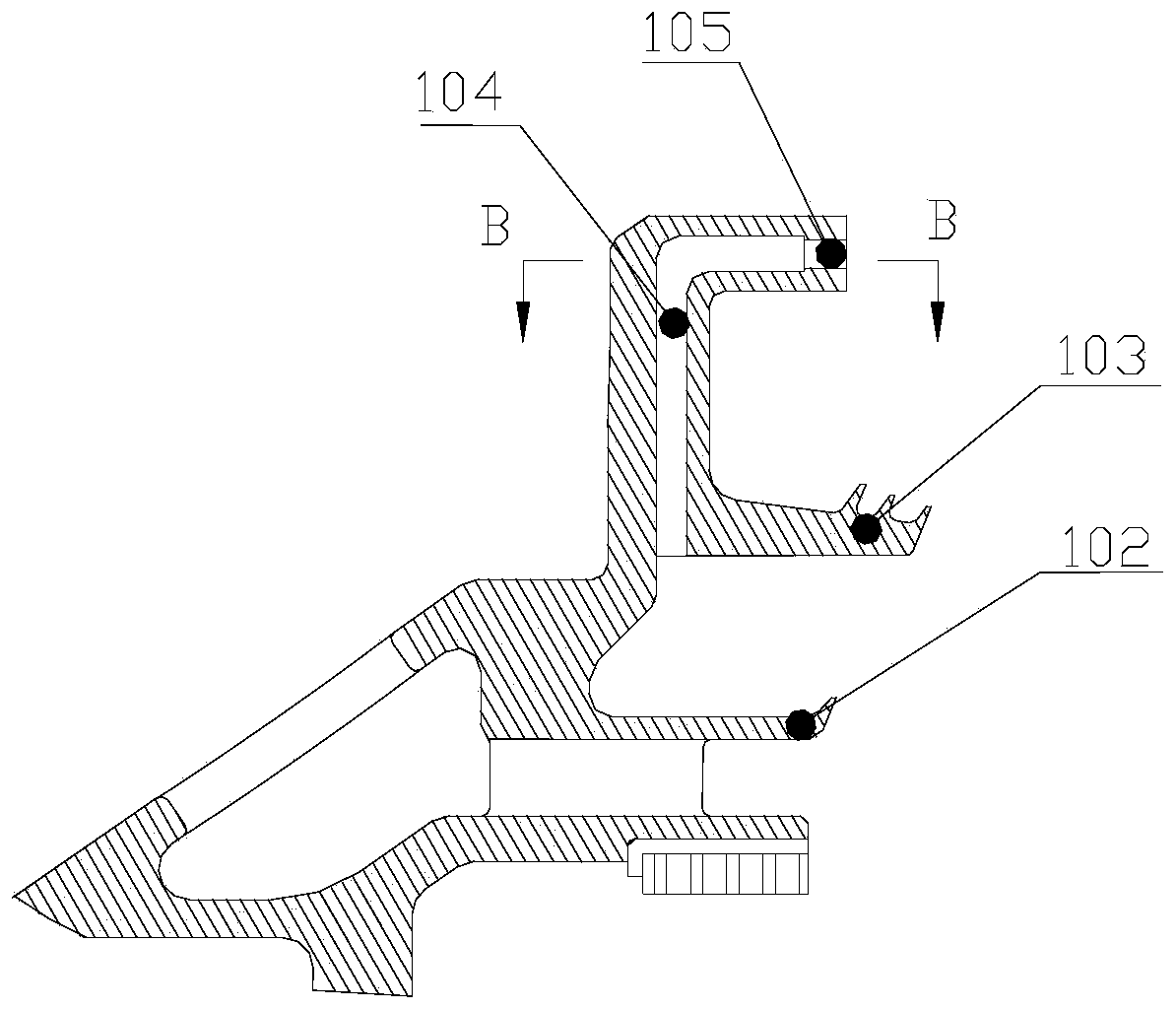
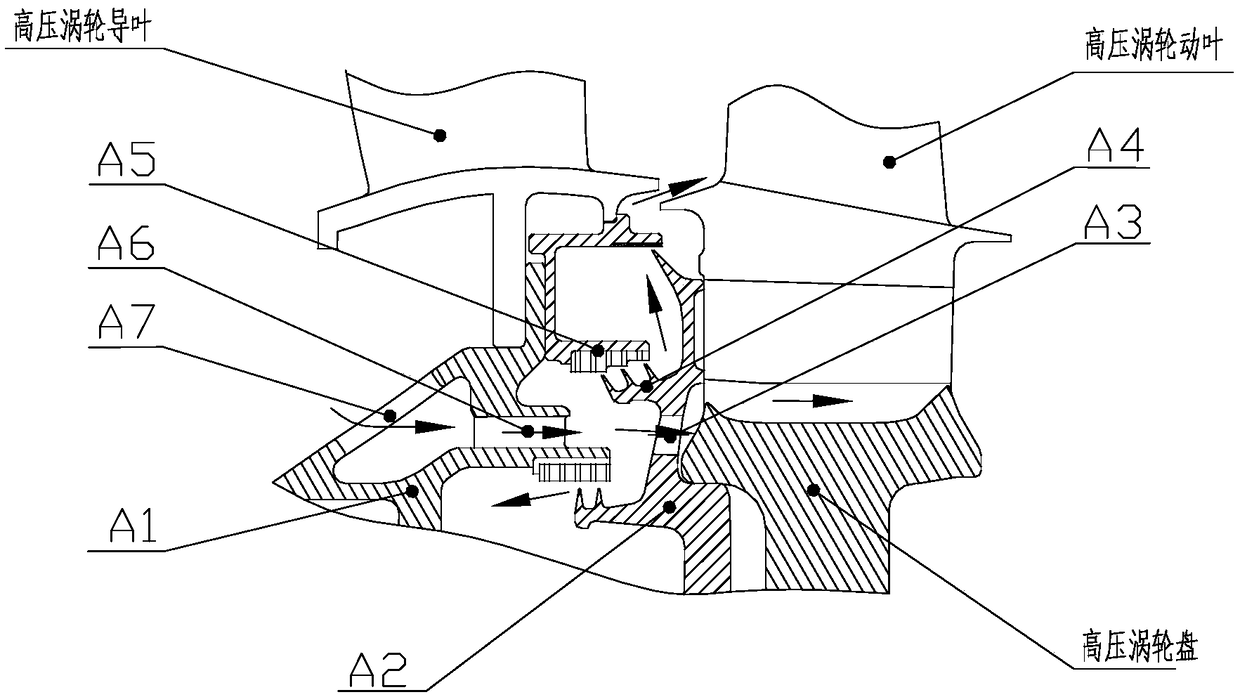
Turbine disk cavity sealing structure with bypass bleed air
InactiveCN110905606AIncrease air velocityIncrease the angleLeakage preventionMachines/enginesCold airEngineering
The invention relates to a turbine disk cavity sealing structure with bypass bleed air. The turbine disk cavity sealing structure with bypass bleed air comprises an inner support ring assembly and a front baffle assembly, wherein a bypass bleed air groove is formed in the inner support ring assembly, the bypass bleed air groove is a second flow path of a third path of cold air, and the cold air passing through the second flow path is mixed with the cold air of a first flow path at an inlet of a main flow path; the airflow speed and the pre-rotation angle of the sealed cold air outlet are increased, so that speed triangle difference with the main flow gas of a guide vane root outlet is reduced, the mixing of the sealed cold air and the main flow is reduced, the efficiency of the turbine isimproved, and a movable vane root is guaranteed to work in a design working condition.
Owner:AECC SICHUAN GAS TURBINE RES INST
Modeling method for axis-asymmetric end wall of annular blade grid of air compressor or turbine
InactiveCN102536329AImprove performanceSimple structurePump componentsBlade accessoriesAxial compressorModel method
The invention provides a modeling method for an axis-asymmetric end wall of an annular blade grid of an air compressor or a turbine. The method comprises the following steps: firstly, zoning modeling zones of a convex part structure or a concave part structure; modeling a convex part control curve or a concave part control curve in the axial direction of the blade grid or the circumferential direction of the blade grid; and finally modeling a curved surface control function in the radial direction of the blade grid. The invention particularly provides a novel convex part or concave part control function. Through the adoption of the method, the axis-asymmetric end wall of the annular blade grid of the air compressor or the turbine can be modeled conveniently and flexibly; and through the adoption of the axis-asymmetric end wall, the pressure gradient in a passage can be reduced effectively, the airflow at the exit of the passage can be more uniform, the total pressure loss coefficient in the passage can be reduced considerably, the secondary flow loss in the passage can be reduced, and further the performance of the blade grid of the air compressor or the turbine can be improved.
Owner:NORTHWESTERN POLYTECHNICAL UNIV
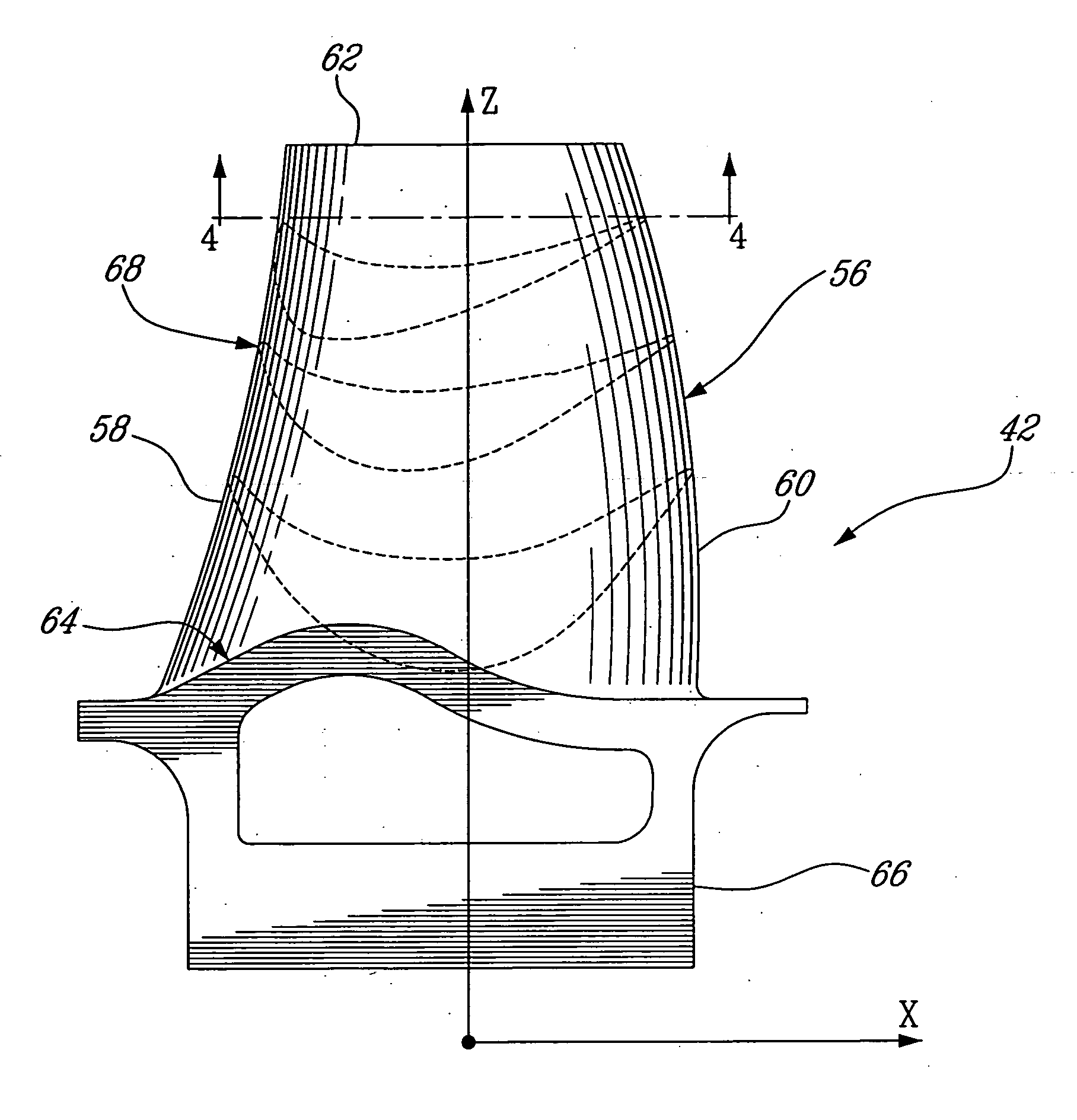
Turbine blade and turbine
InactiveUS7052237B2Increase the curvatureIncreasing the thicknessPropellersPump componentsLeading edgeTurbine blade
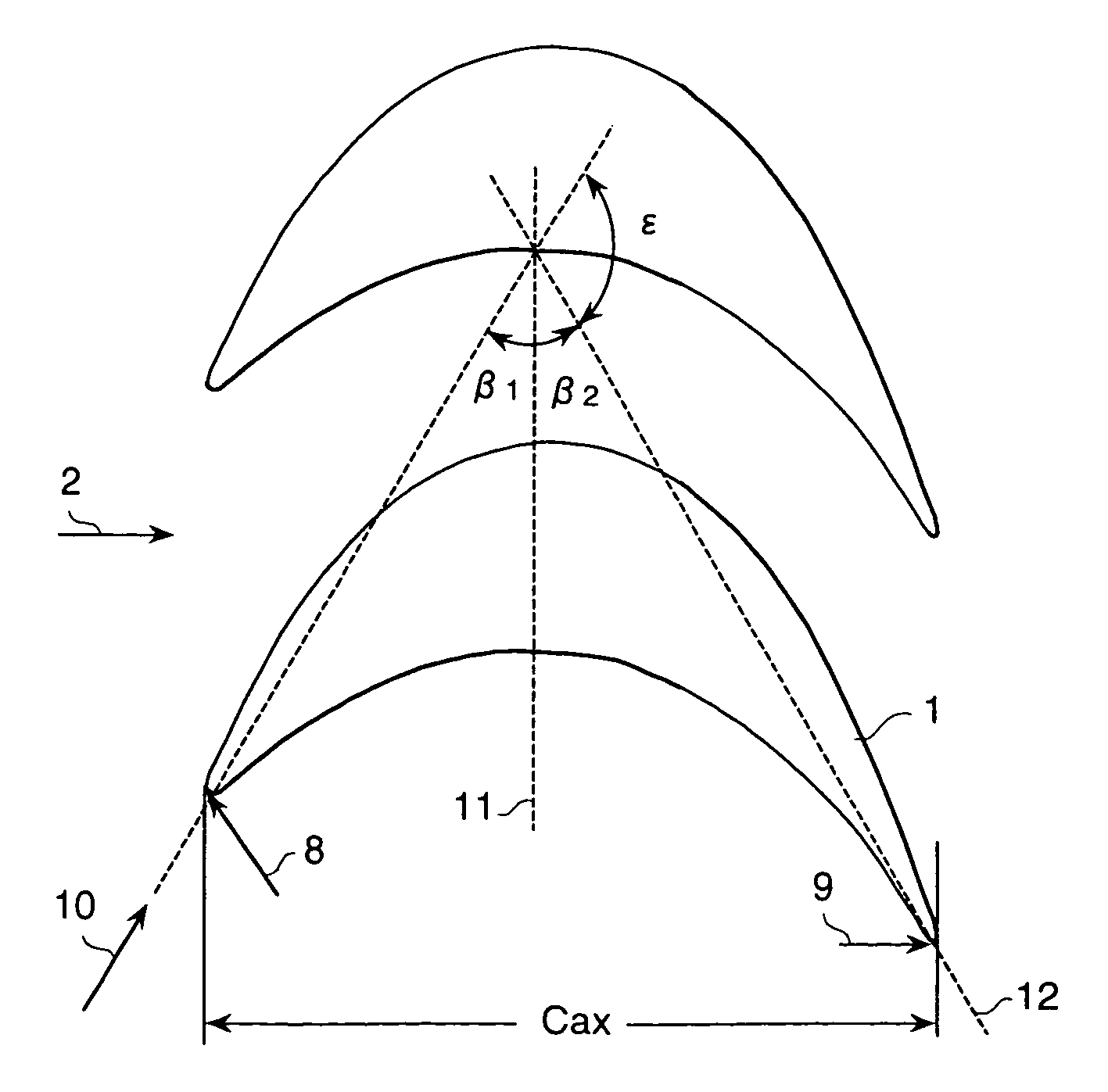
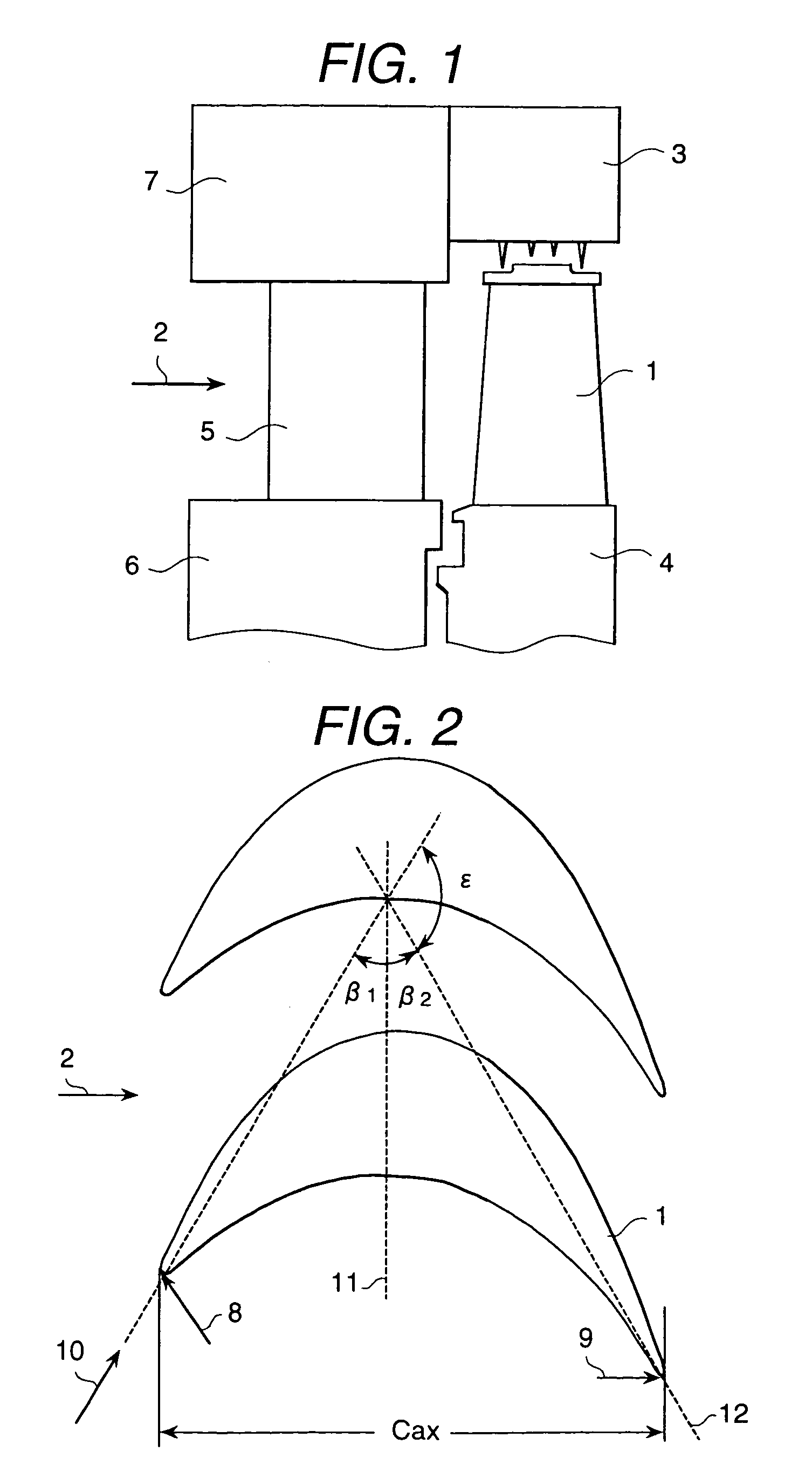
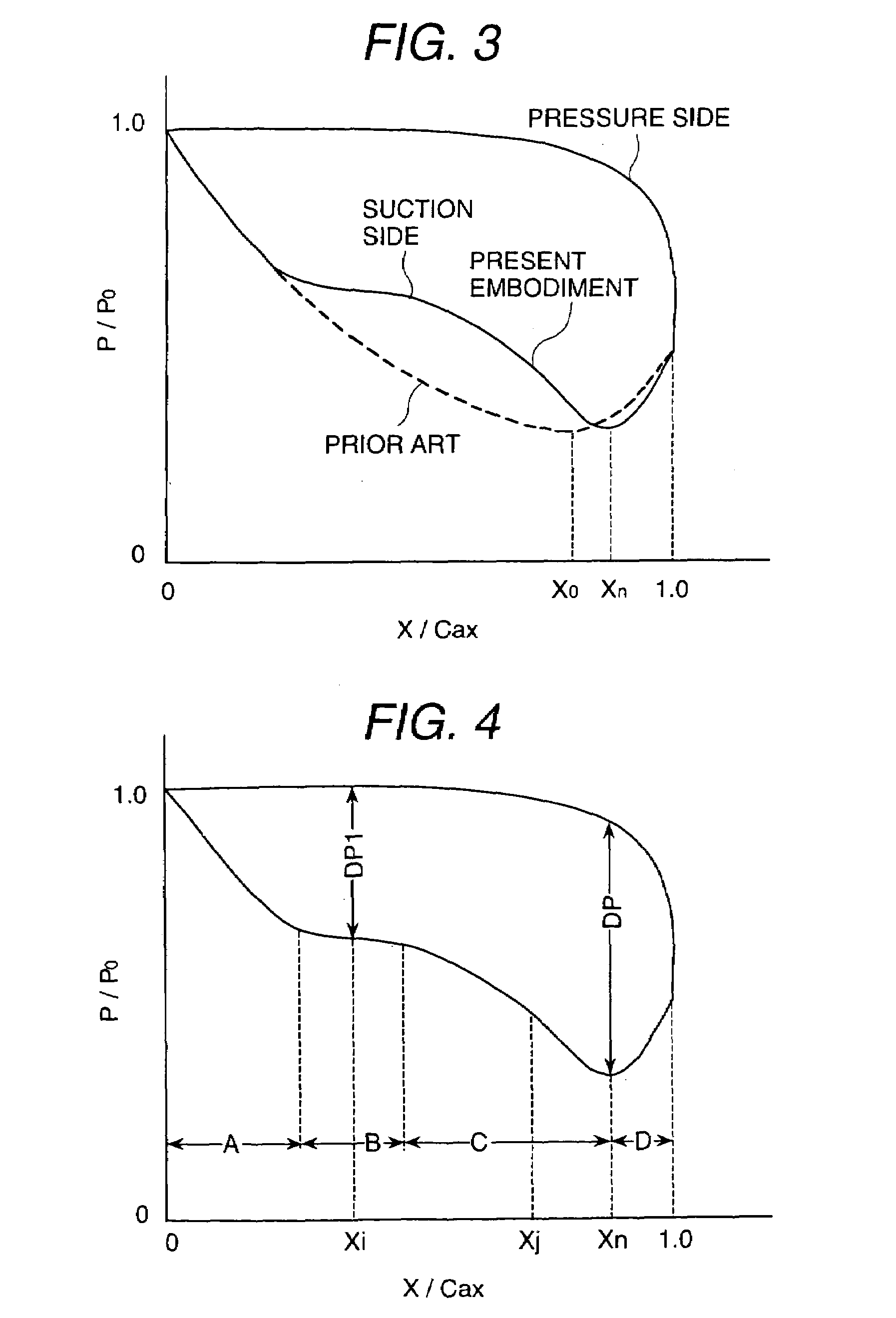
The pressure distribution curve of the blade suction-side surface excluding the leading edge portion and the trailing edge portion drops in two stages in the area from the leading edge to the minimum pressure point.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HITACHIPOWER SYST LTD
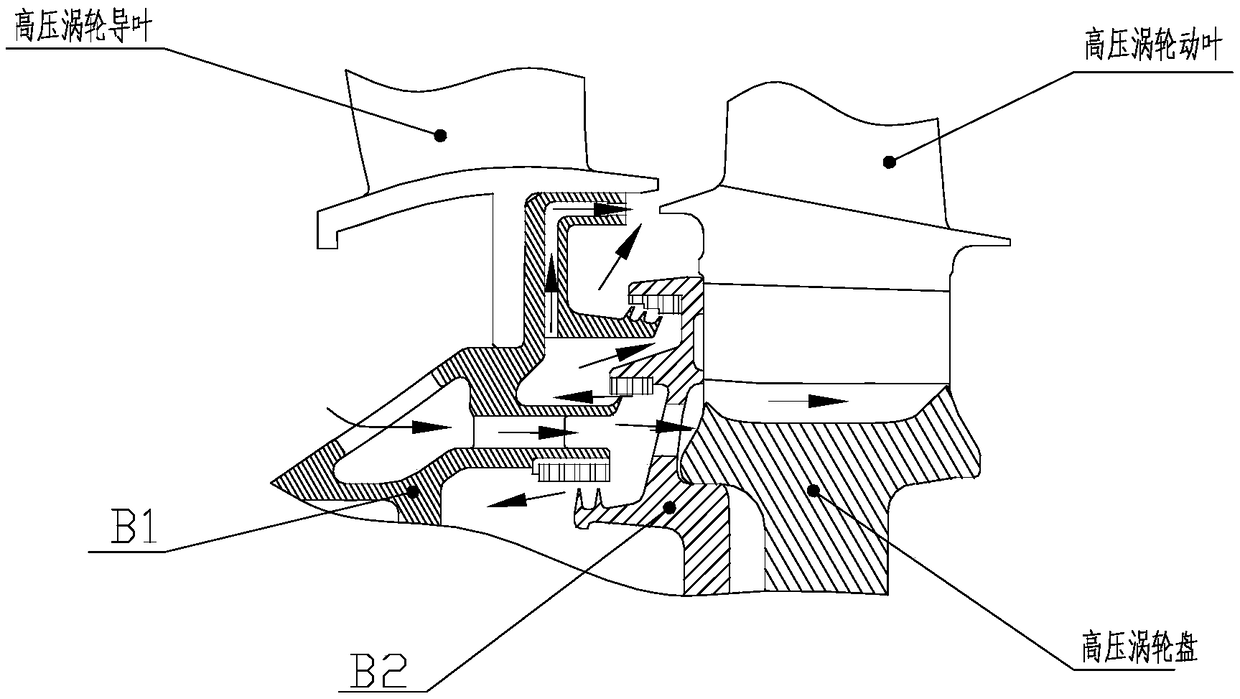
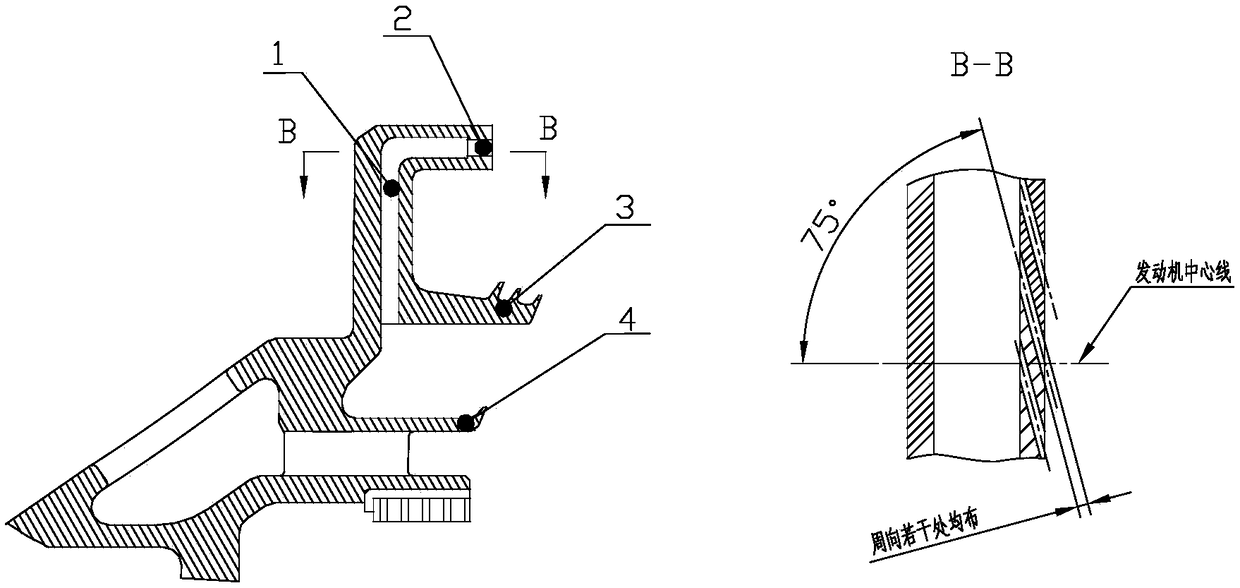
Turbine disc cavity sealing structure with prewhirl air entraining
InactiveCN109630209AReduce secondary flow lossImprove turbine efficiencyLeakage preventionMachines/enginesTurbineRealizability
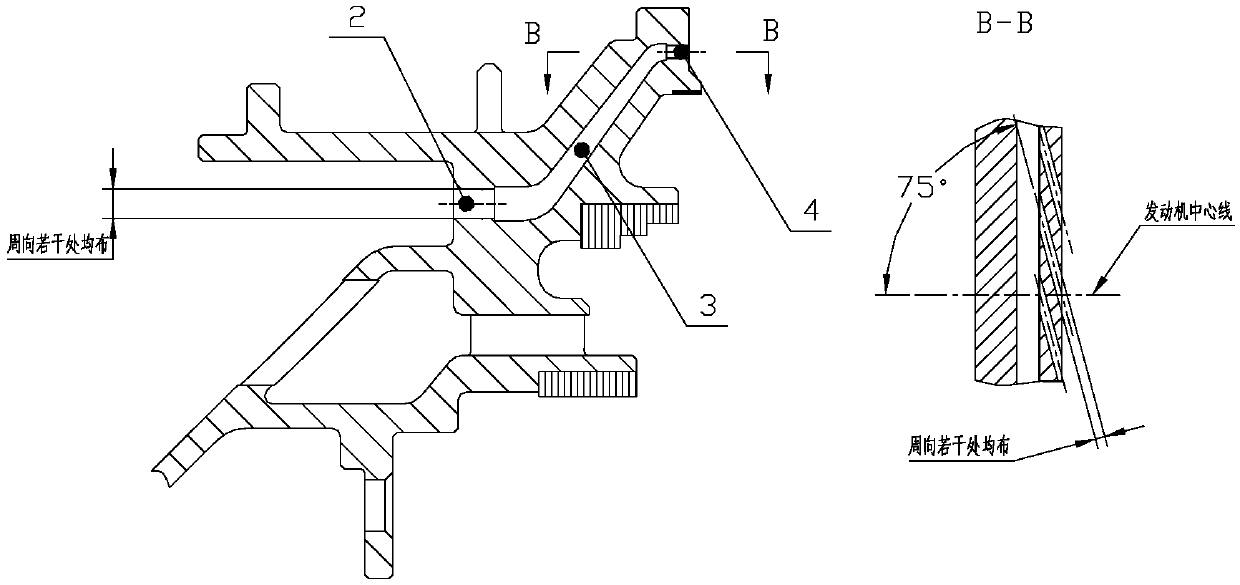
The invention discloses a turbine disc cavity sealing structure with prewhirl air entraining. An inner supporting ring 1 is provided with a plurality of prewhirl air-entraining flow paths, the prewhirl air-entraining flow paths are formed by air entraining holes 2, air collecting cavities 3 and air outlet holes 4 in sequence, wherein the air entraining holes 2 are a plurality of round holes whichare evenly arranged in the circumferential direction, the air entraining holes 2 are arranged on the end surface of an outer ring of air inlet holes of the inner supporting ring, the air collecting cavities 3 are of a hollow cavity structure, and the range of angles formed between the air outlet holes 4 and a center line of a motor is 65 to 80 degree. According to the turbine disc cavity sealing structure with prewhirl air entraining, a rotary blade root part works in design conditions, the secondary flow loss of a rotary blade passage is decreased greatly, compared with the existing disc cavity sealing structure, the efficiency of the turbine can be increased by nearly 1% after adopting the turbine disc cavity sealing structure with prewhirl air entraining, and the turbine disc cavity sealing structure with prewhirl air entraining is simple in structure, can mostly borrow the existing disc cavity sealing structure, and is good in economy and realizability.
Owner:AECC SICHUAN GAS TURBINE RES INST
Turbine blade body structure
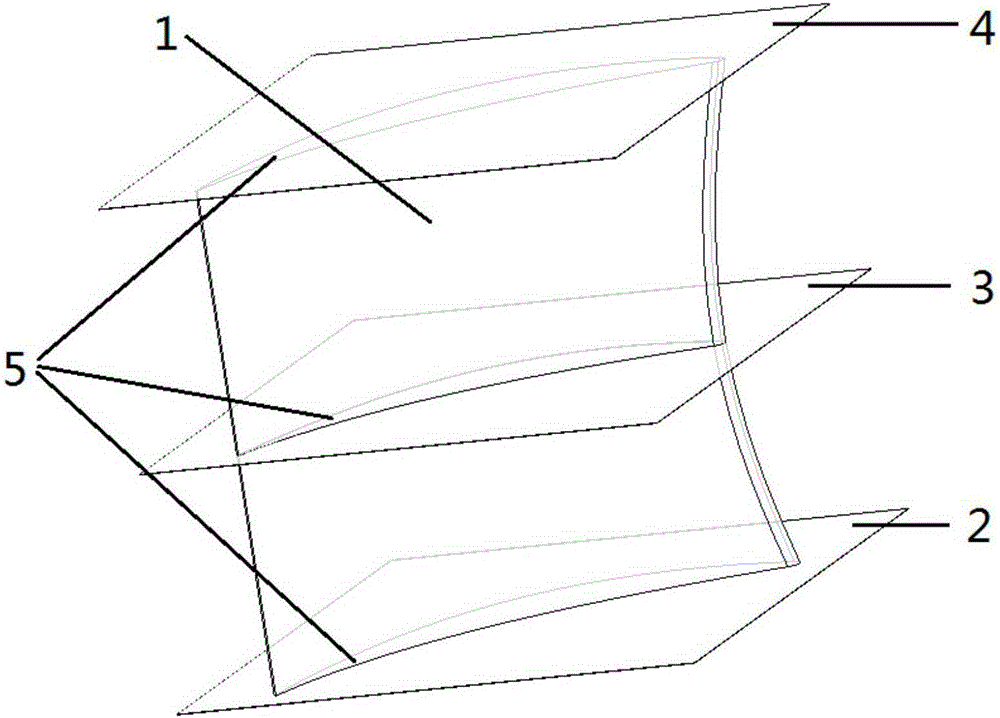
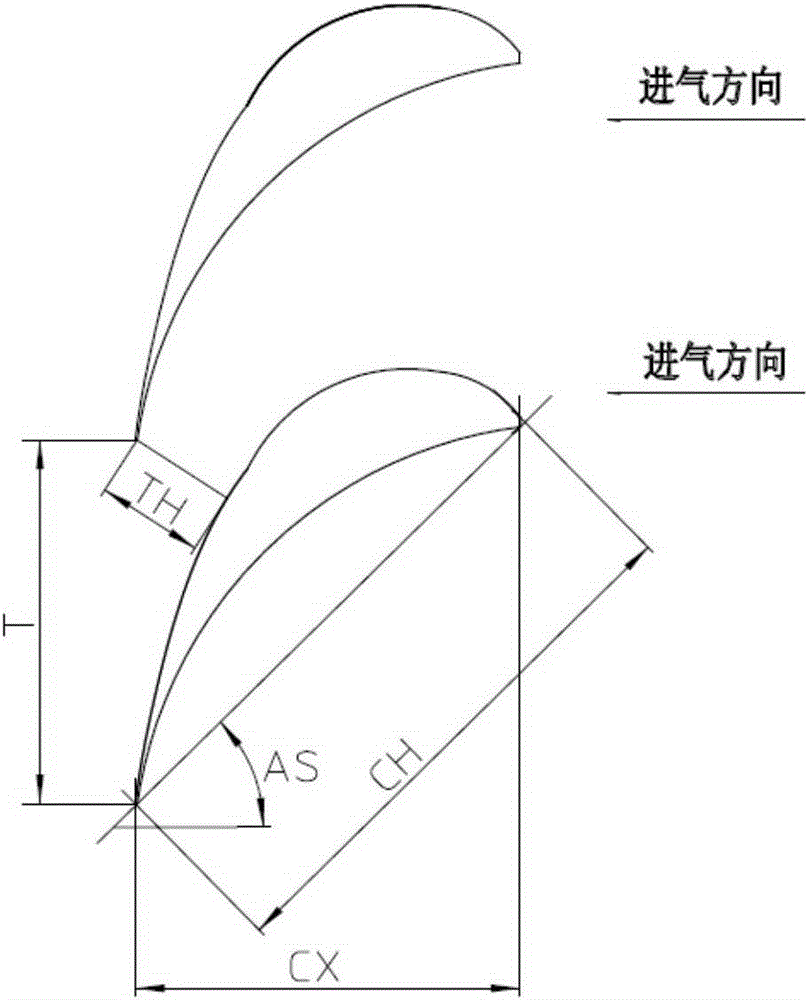
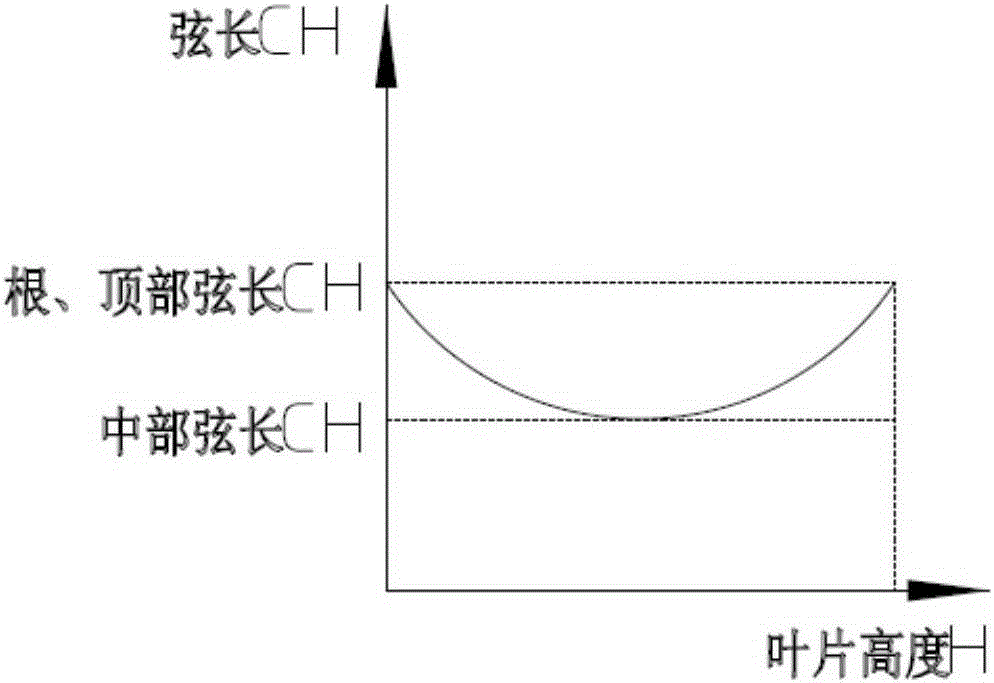
ActiveCN105298546AReduced load levelImprove aerodynamic performanceBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesTurbine bladeBody height
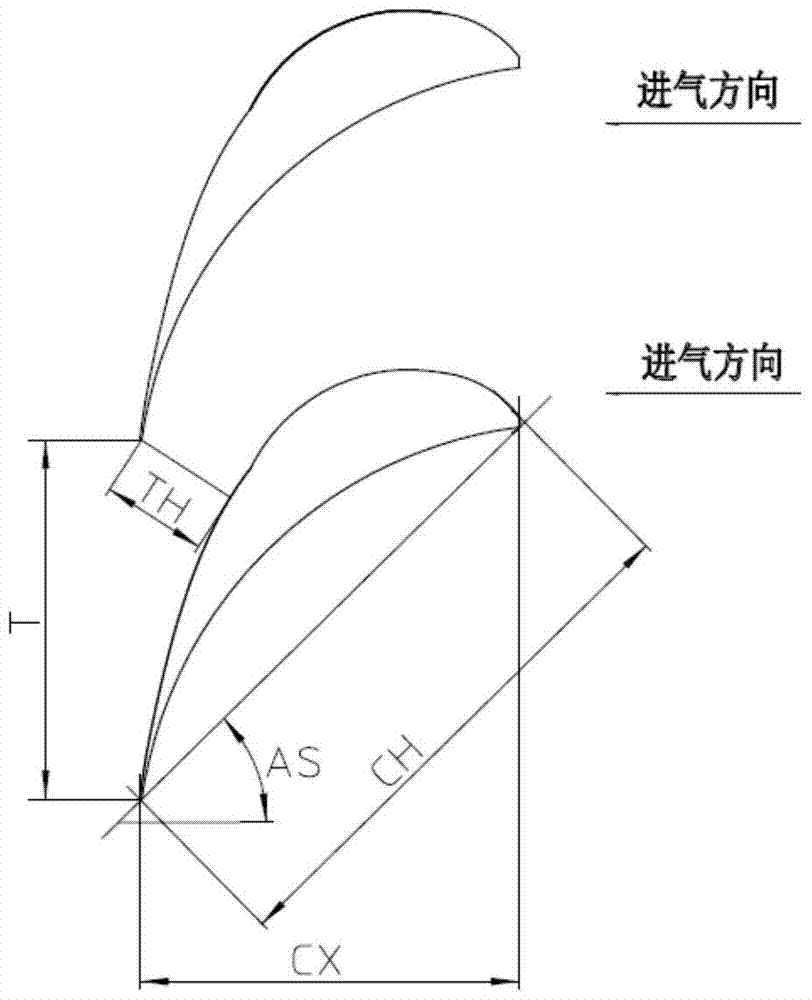
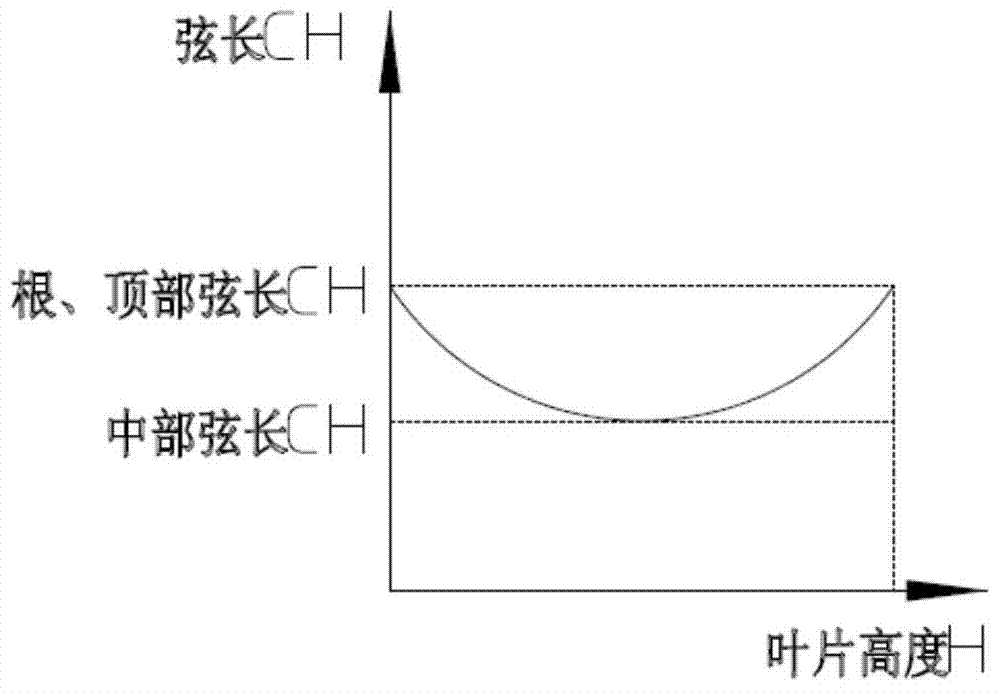
The invention discloses a turbine blade body structure. A two-dimension blade profile of a blade body is a crescent closed curve defined by an inner arc curve and a back arc curve; the blade body has a characteristic parameter chord length CH, and an axial width CX; the blade body is formed by twisting and superimposing multiple two-dimension blade profiles according to a certain rule, and has a characteristic parameter blade body height H; the chord length CH of the two-dimension blade profile accords with a parabolic distribution rule from the root area to the top area in the blade height direction; a trend is that the chord lengths of the root area and the top area of the blade body are high, and the chord length of the middle area of the blade body is low; and the axial width CX of the two-dimension blade profile substantially remains unchanged. The turbine blade body structure can allow the turbine blade to simultaneously give consideration to different main loss sources of the root area, the top area and the middle area, thereby effectively and reliably improving the aerodynamic performance of the turbine blade and reducing aerodynamic loss.
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD
Centrifugal fluid machine
ActiveCN104093988AMaintain range of motionFull strength and productionEngine manufacturePump componentsImpellerEngineering
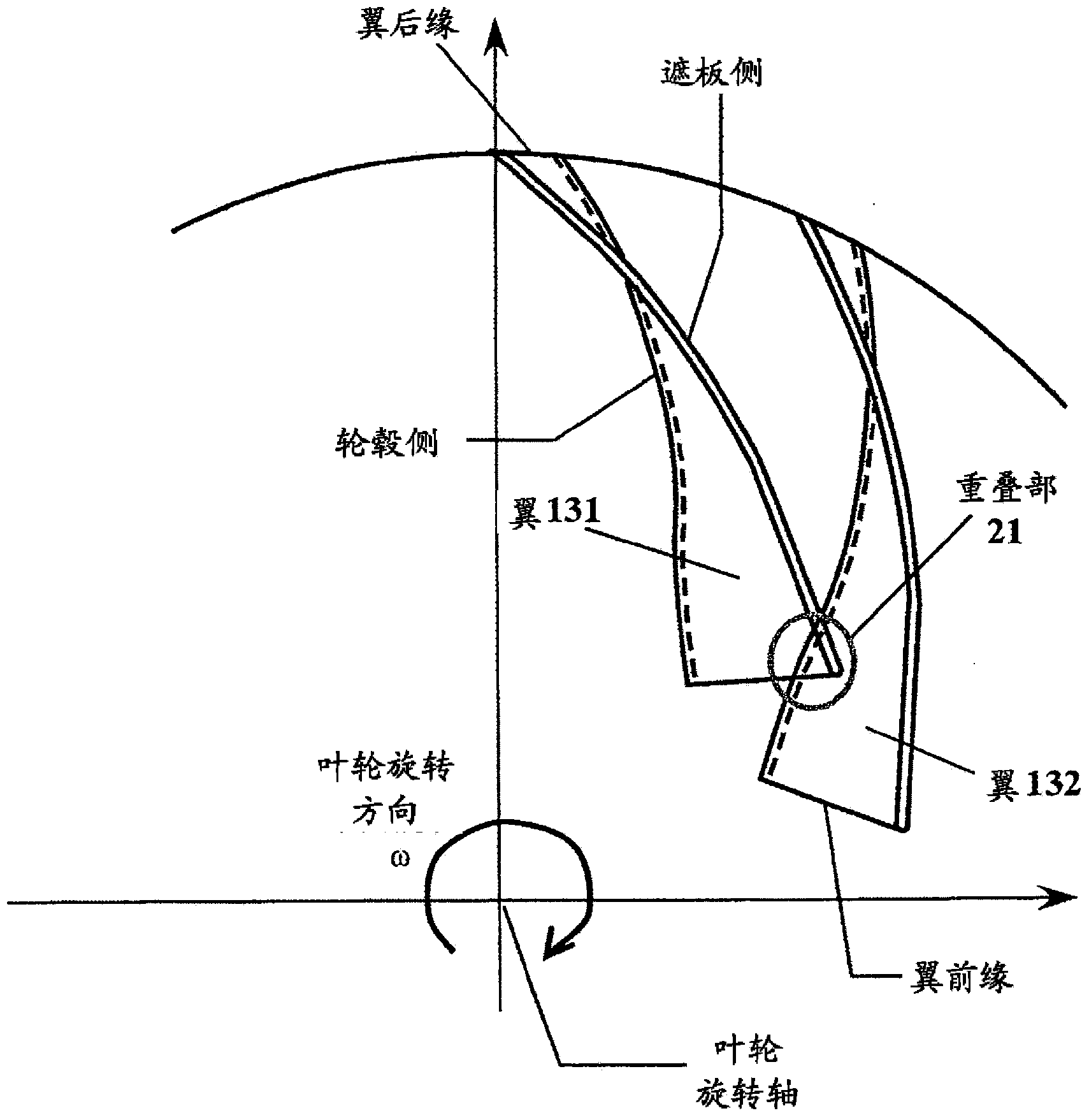
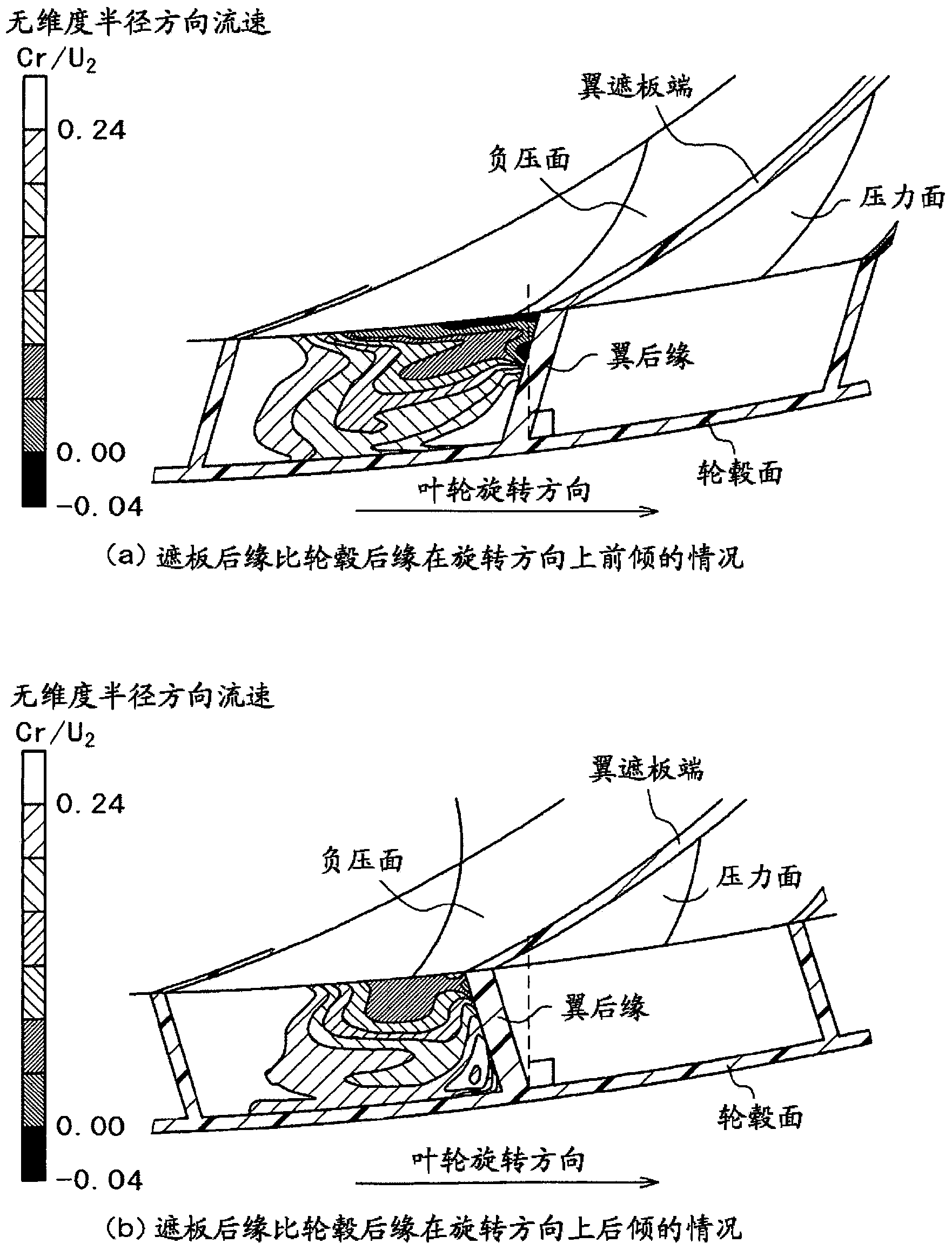
A centrifugal fluid machine is provided. In order to suppress the separation and slowdown of a flow in the vicinity of the front edge of a blade suction surface shroud of an impeller when the flow rate is reduced while reducing secondary flow loss within the impeller to thereby maintain the operating range of the impeller in a centrifugal fluid machine, the shroud side is inclined further backward with respect to a rotation direction than the hub side at the back edge of an impeller blade when the impeller is viewed from a suction direction that is the upstream direction of a rotating shaft. Moreover, in adjacent two impeller blades, the shroud side of a blade located behind in the rotation direction of the impeller overlaps, in the vicinity of the front edge of the blade, with a blade located in front in the rotation direction.
Owner:HITACHI IND PROD LTD
Low-noise device for centrifugal compressor of turbocharger
InactiveCN102588351AReduce secondary flow lossSpeed up the flowPump componentsPumpsLow noiseInlet channel
The invention discloses a low-noise device for a centrifugal compressor of a turbocharger, aiming at overcoming the defect of serious airflow turbulence after an air guide wheel air incoming re-circulating structure is adopted by a turbocharger with the lowest cost so as to lower noise and improve the efficiency of the compressor. The low-noise device has the following technical scheme that based on the prior art, a space is formed between a shell 4 of an air compressor and an air guide sleeve 3, and a flow guide cover 15 is arranged in the low-noise device so as to form secondary air inlet passages 7 and 14; and arc flow guide treatment is carried out at the turning of the channel of related parts, and the air guide sleeve 3 is provided with 3 grooves or 3-20 circular holes at the radial circumference corresponding to an impeller 1 of the air compressor. The low-noise device can be widely applied to compressors to lower the noise and has wide application prospect.
Owner:大同北方天力增压技术有限公司
Axial Compressor
ActiveUS20120093637A1Reduce lossesImprove performancePump componentsMetal-working apparatusAxial compressorMechanical engineering
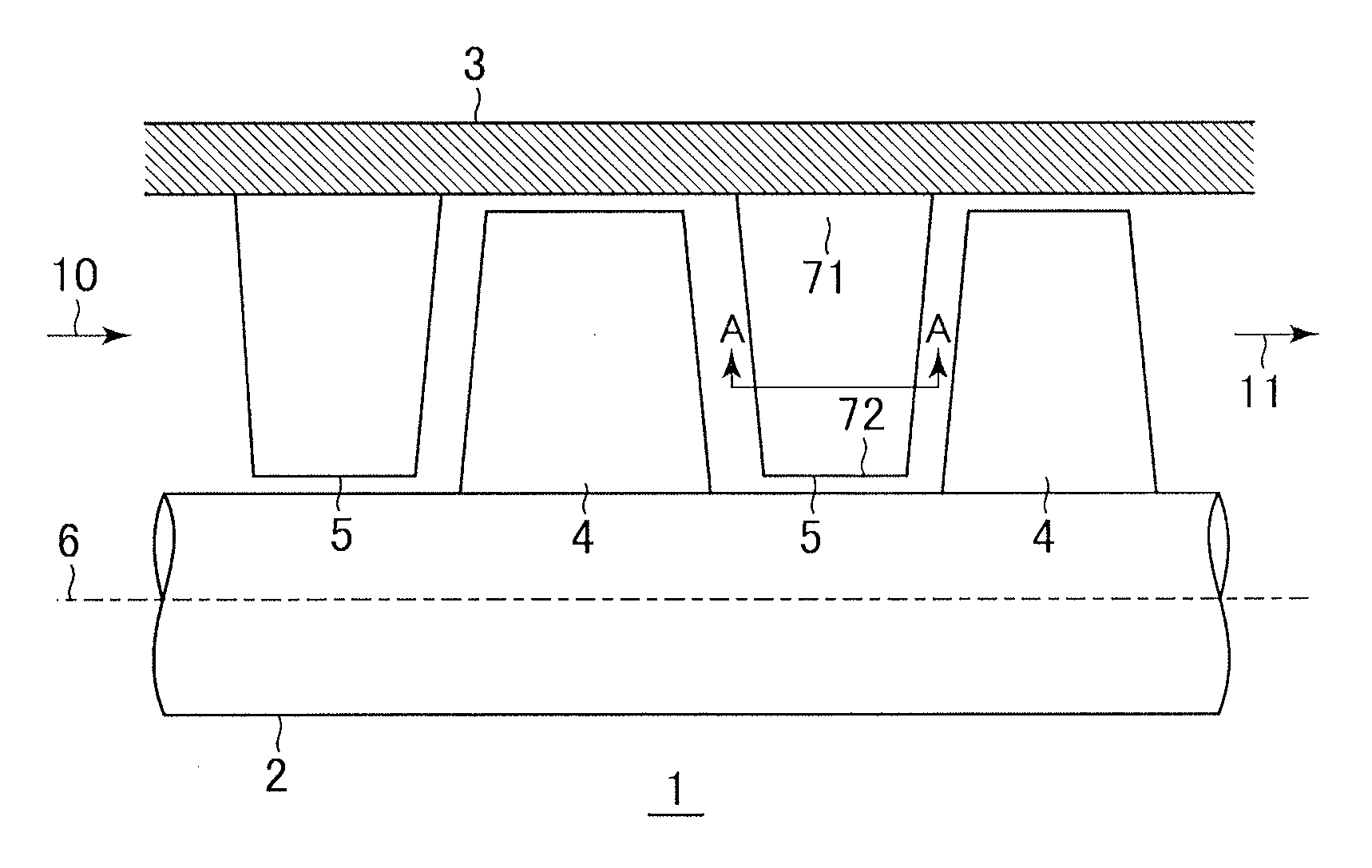
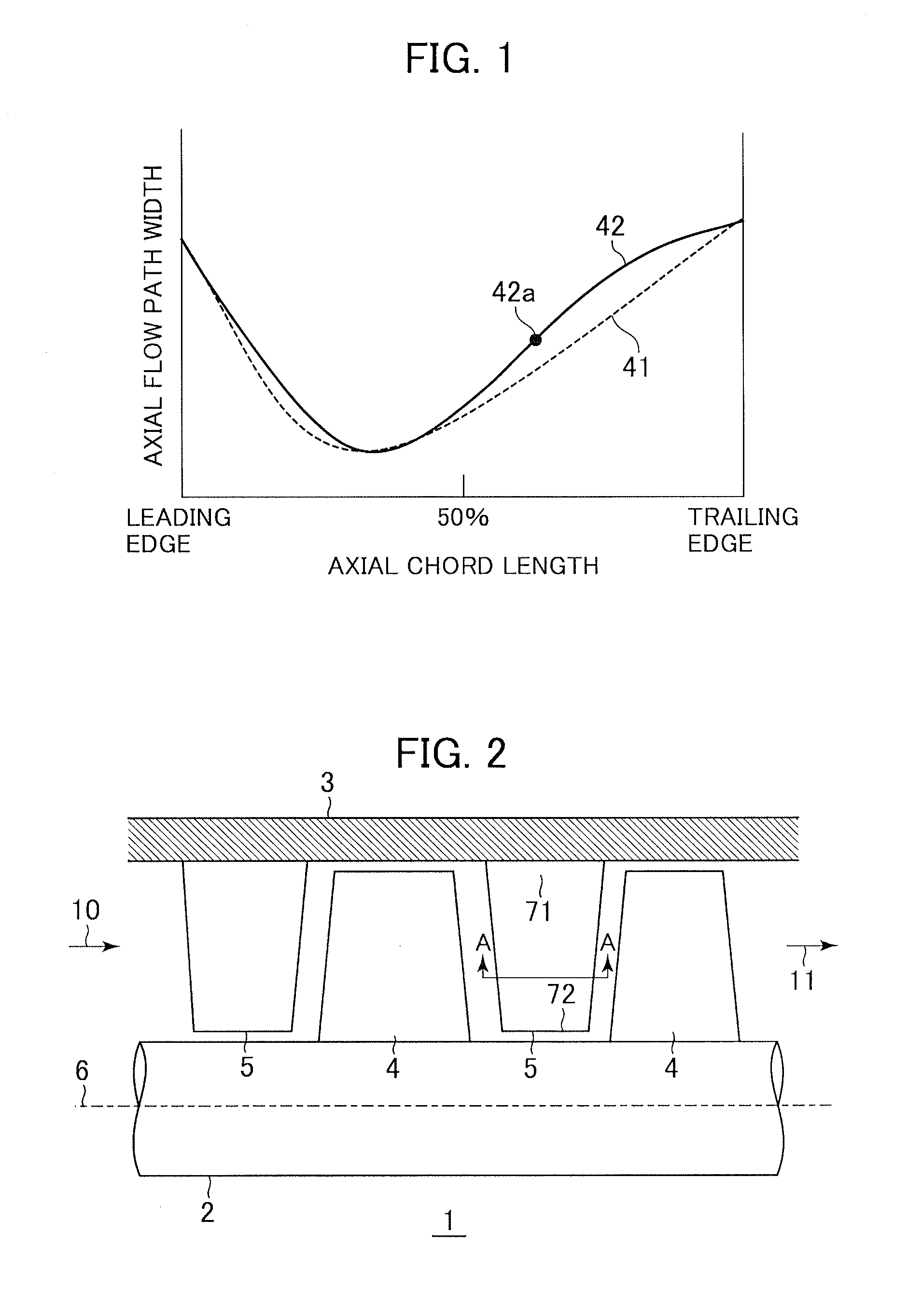
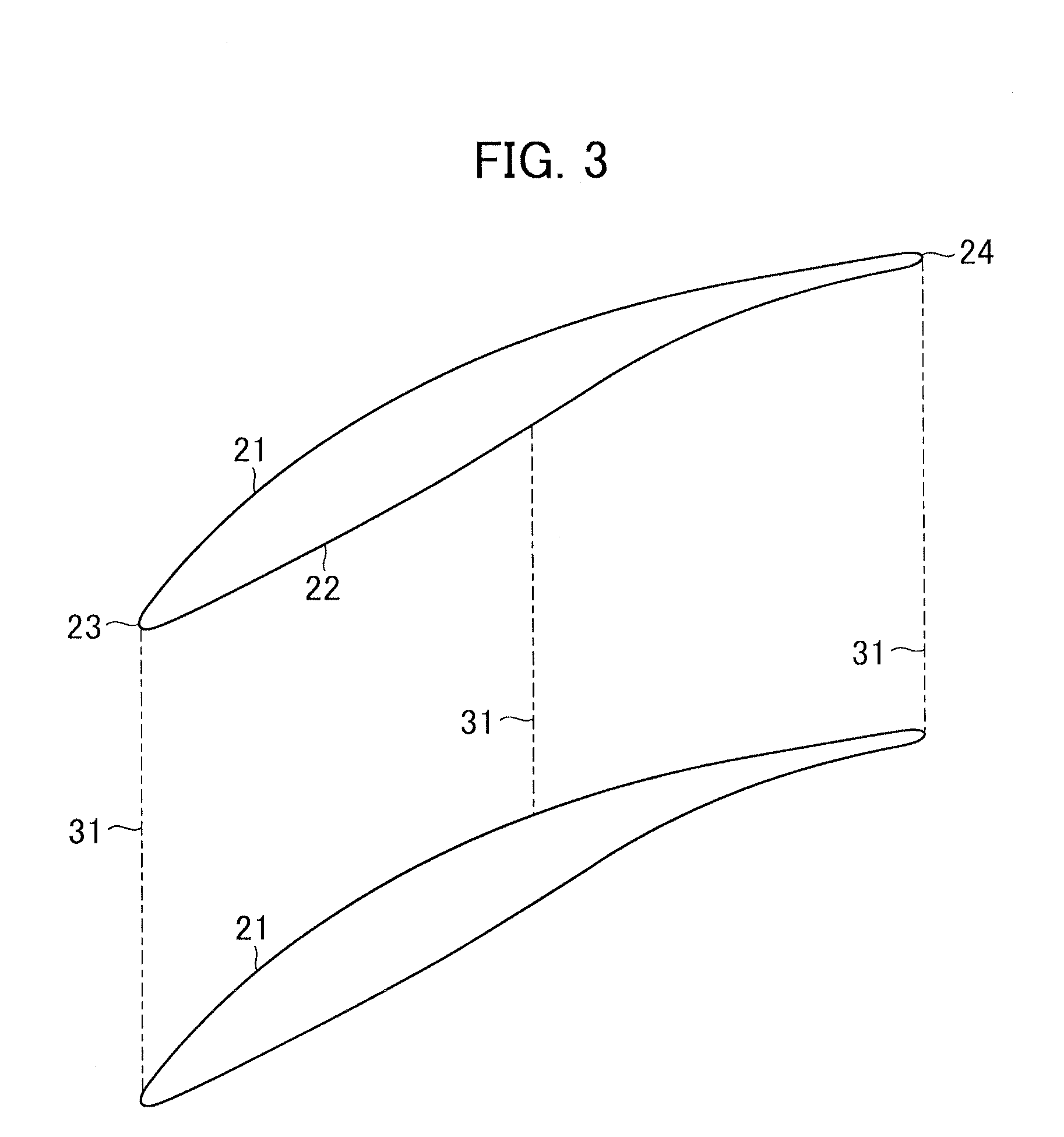
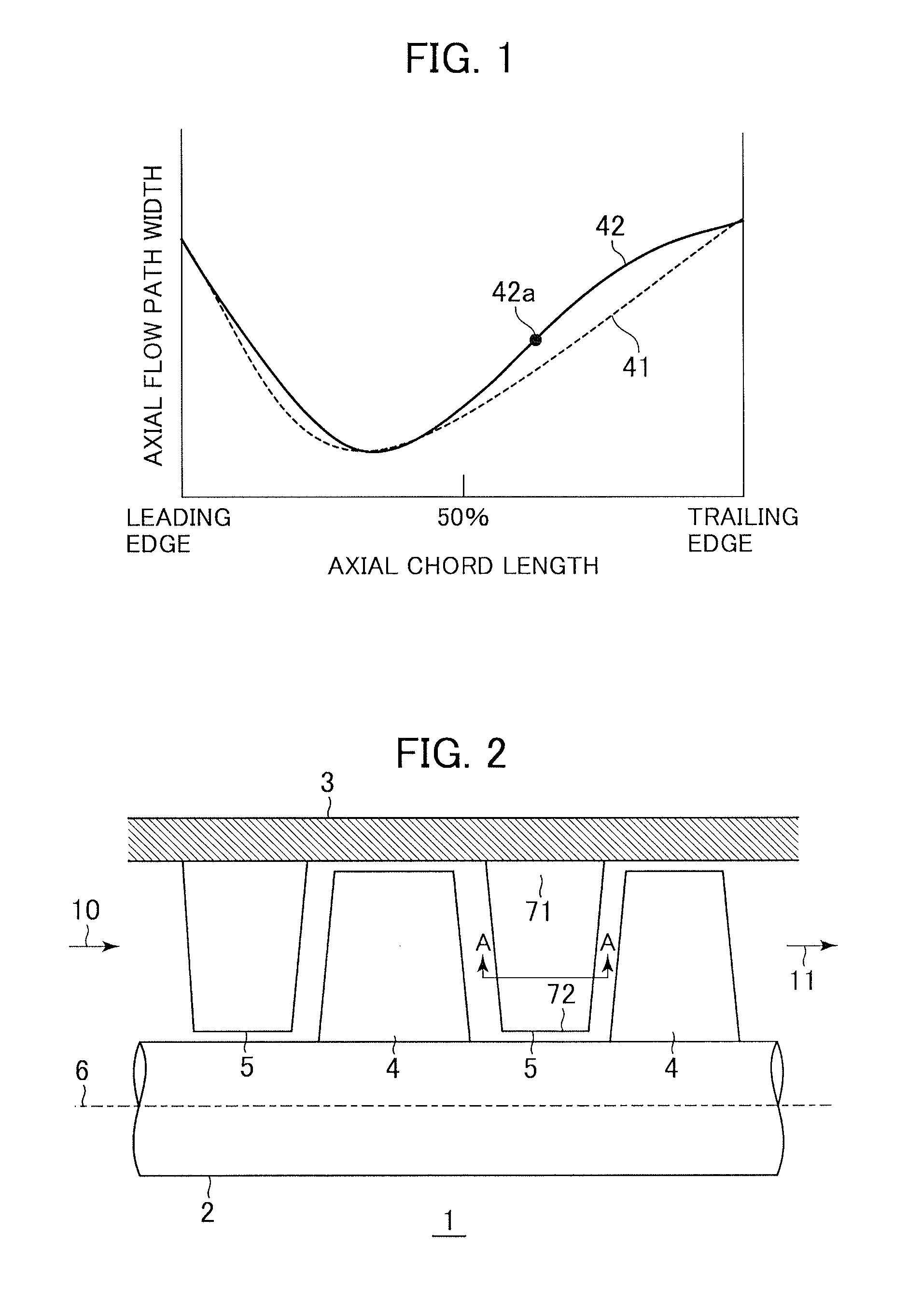
An axial compressor includes a plurality of stator vanes attached to an inner surface of a casing defining an annular flow path and a plurality of rotor blades attached to a rotating rotor defining the annular flow path. A flow path is defined between a pressure surface of a stator vane and a suction surface of a stator vane, the vanes being circumferentially adjacent to each other, or between a pressure surface of a rotor blade and a suction surface of a rotor blade, the blades being circumferentially adjacent to each other. The flow path is formed so that a throat portion at which a flow path width is minimized is provided on the upstream side of 50% of an axial chord length.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Turbine disk cavity sealing structure with bypass gas entraining
InactiveCN109458229AReduce secondary flow lossImprove turbine efficiencyLeakage preventionMachines/enginesEngineeringHigh pressure
The invention belongs to the field of gas turbine engines, and relates to a turbine disk cavity sealing structure with bypass gas entraining. The turbine disk cavity sealing structure with bypass gasentraining comprises an inner support ring assembly provided with an inner support ring gas inlet hole, a front baffle plate assembly, a pre-rotation nozzle, a first gas passage for transferring a first path of cold gas output by the pre-rotation nozzle, a second gas passage for transferring a second path of cold gas output by the pre-rotation nozzle, and a third gas passage arranged between the inner support ring assembly and the front baffle plate assembly, wherein the third gas passage comprises a first sealing device arranged between the inner support ring assembly and the front baffle plate assembly, a sub gas passage and a bypass gas entraining passage; a third path of cold gas output by the pre-rotation nozzle flows into the sub gas passage and the bypass gas entraining passage through the first sealing device; and gas output by the third gas passage flows toward a high-pressure turbine movable blade.
Owner:AECC SICHUAN GAS TURBINE RES INST
Axial compressor
ActiveUS9303656B2Reduce loadLow reliabilityPump componentsMetal-working apparatusAxial compressorEngineering
An axial compressor includes a plurality of stator vanes attached to an inner surface of a casing defining an annular flow path and a plurality of rotor blades attached to a rotating rotor defining the annular flow path. A flow path is defined between a pressure surface of a stator vane and a suction surface of a stator vane, the vanes being circumferentially adjacent to each other, or between a pressure surface of a rotor blade and a suction surface of a rotor blade, the blades being circumferentially adjacent to each other. The flow path is formed so that a throat portion at which a flow path width is minimized is provided on the upstream side of 50% of an axial chord length.
Owner:MITSUBISHI POWER LTD
Radial flow turbine guide vane structure coupled with non-axisymmetric end walls
ActiveCN110608068ADelayed formationImproves airflow uniformityStatorsMachines/enginesEngineeringPressure difference
The invention relates to a radial flow turbine guide vane structure coupled with non-axisymmetric end walls. The radial flow turbine guide vane structure aims to solve the technical problems of remarkable secondary flow of low-span chord ratio runoff guide vane end walls, relatively large channel vortex size, poor outlet air flow uniformity and the like. A non-axisymmetric concave-convex end wallstructure is adopted at each of the front end walls and the rear end walls of radial flow turbine guide vanes and can be matched with the radial flow turbine guide vanes with the three-dimensional configuration to control the flow channel secondary flow loss more effectively. According to the radial flow turbine guide vane structure, a blade lattice is modified, and specifically, the inner surfaces of the front end walls and the rear end walls are correspondingly arranged as the non-axisymmetric concave-convex end wall structures, so that the flow area of each flow channel is changed, and theair flow pressure difference between the pressure surface on one side of each flow channel and the suction surface on the other side of each flow channel is reduced, so that the secondary flow velocity distribution is affected, the formation and development of the channel vortex are delayed, the channel vortex intensity is reduced, and the reduction of the secondary flow loss is finally realized.
Owner:INST OF ENGINEERING THERMOPHYSICS - CHINESE ACAD OF SCI
1000MW steam turbine distorting yataghan blade as well as method for manufacturing the same
Disclosed are contorted saber-shaped stationary blades for high, middle and low pressure cylinders of a supercritical steam turbine of 1000MW, which are composed of a blade root, a blade profile and a shroud ring; wherein, the blade has a contorted saber-shaped cross section, which is contorted at the circumferential direction; wherein, the sections along the length direction of the blade roots of contorted saber-shaped stationary blades for high and middle pressure cylinders are T-shaped while the section along the length direction of the blade root of the contorted saber-shaped stationary blade for the low pressure cylinder is L-shaped; a blade tip is in the form of an integral shroud ring structure. The stationary blades adopt latest compound leaned technology and processing technology, and on the basis of ensuring less damage to the blade profile, the blade is contorted in the blade root and the blade tip at the circumferential direction, which causes air flow to speed up slightly when passing through the blade root and the blade tip and reduces the flowing of the airflow at the end faces of the blade root and the blade tip.
Owner:无锡润和叶片制造有限公司
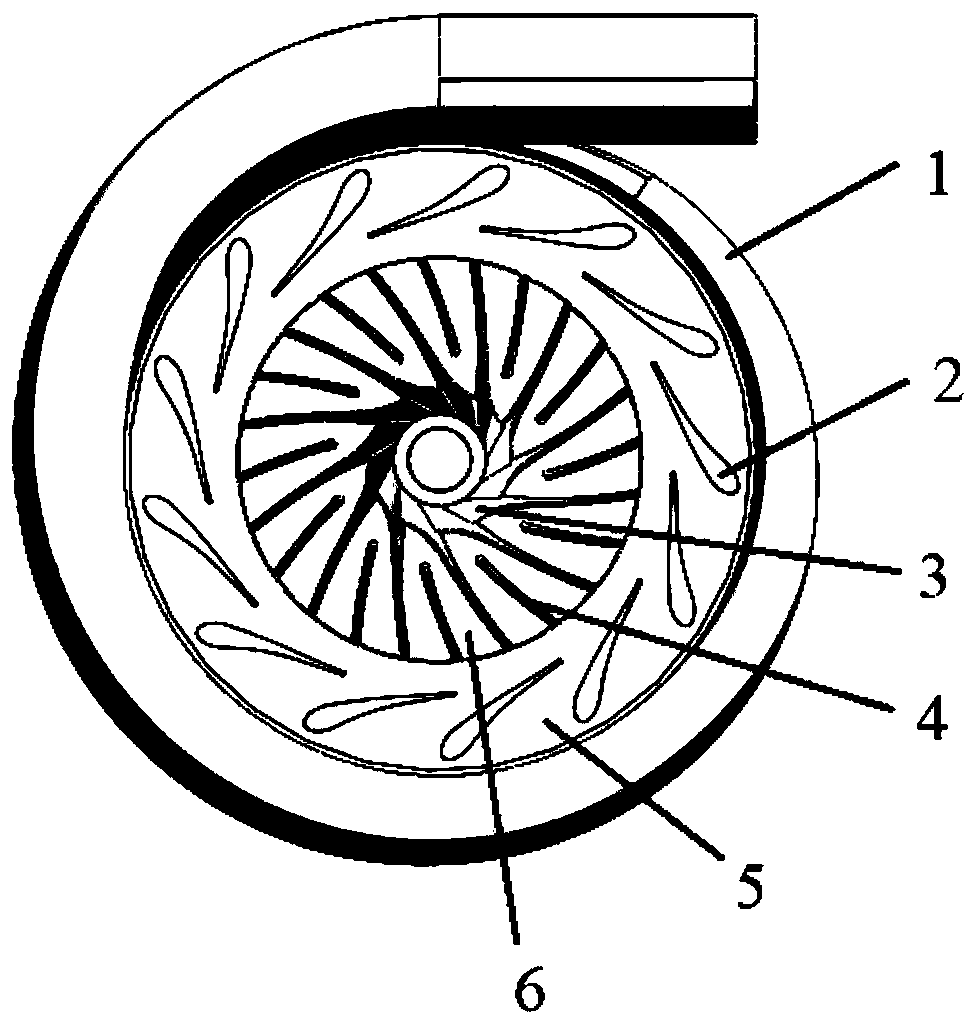
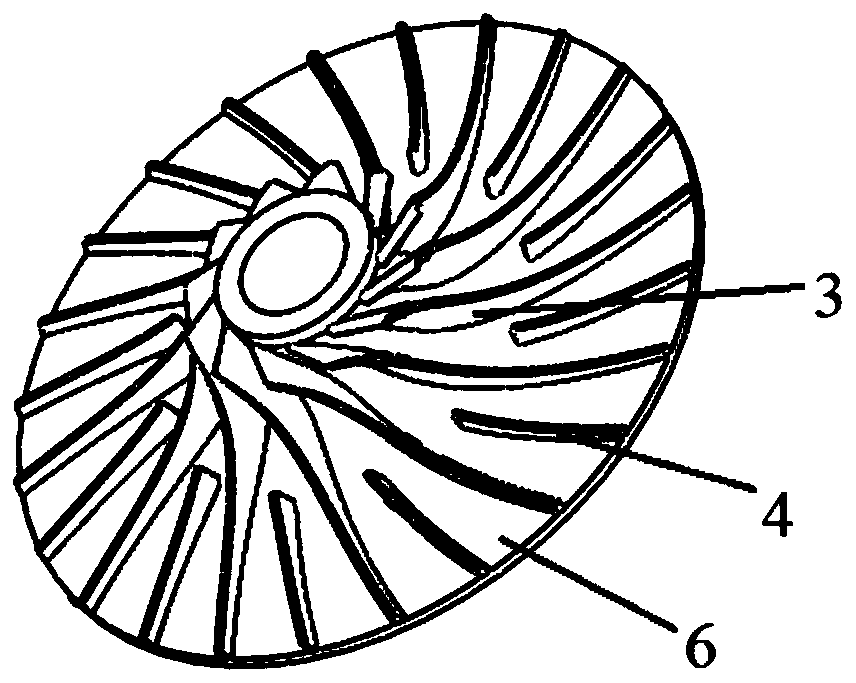
kW-grade supercritical carbon dioxide radial flow type turbine structure with flow dividing blades
The invention discloses a kW-grade supercritical carbon dioxide radial flow type turbine structure with the flow dividing blades. A volute, fixed blade grids, movable blade grids and the flow dividingblades are included, wherein the fixed blade grids, the movable blade grids and the flow dividing blades are arranged in the volute; each flow dividing blade is arranged between every two adjacent movable blade grids; each fixed blade grid flow channel is formed between every two adjacent fixed blade grids, and movable blade grid flow channels are formed between the movable blade grids and the flow dividing blades; in work, supercritical carbon dioxide work media enter the structure from the volute, the gas is uniformly allocated into the fixed blade grid flow channels by the volute, the pressure of the work media in the fixed blade grid flow channels is gradually lowered, and the flow speed is gradually increased; and then the supercritical carbon dioxide work media enter the movable blade grid flow channels, in the movable blade grid flow channels, the supercritical carbon dioxide work media push an impeller to rotate and output work, and finally discharging in the axial direction is achieved. In the kW-grade supercritical carbon dioxide radial flow type turbine structure with the flow dividing blades, due to the scheme of adding of the flow dividing blades and improvement of ageometrical angle of an impeller inlet, the pneumatic efficiency of the radial flow type turbine structure is substantially improved while the running safety is guaranteed, and important engineering significance and broad application prospects are achieved.
Owner:NO 719 RES INST CHINA SHIPBUILDING IND +1
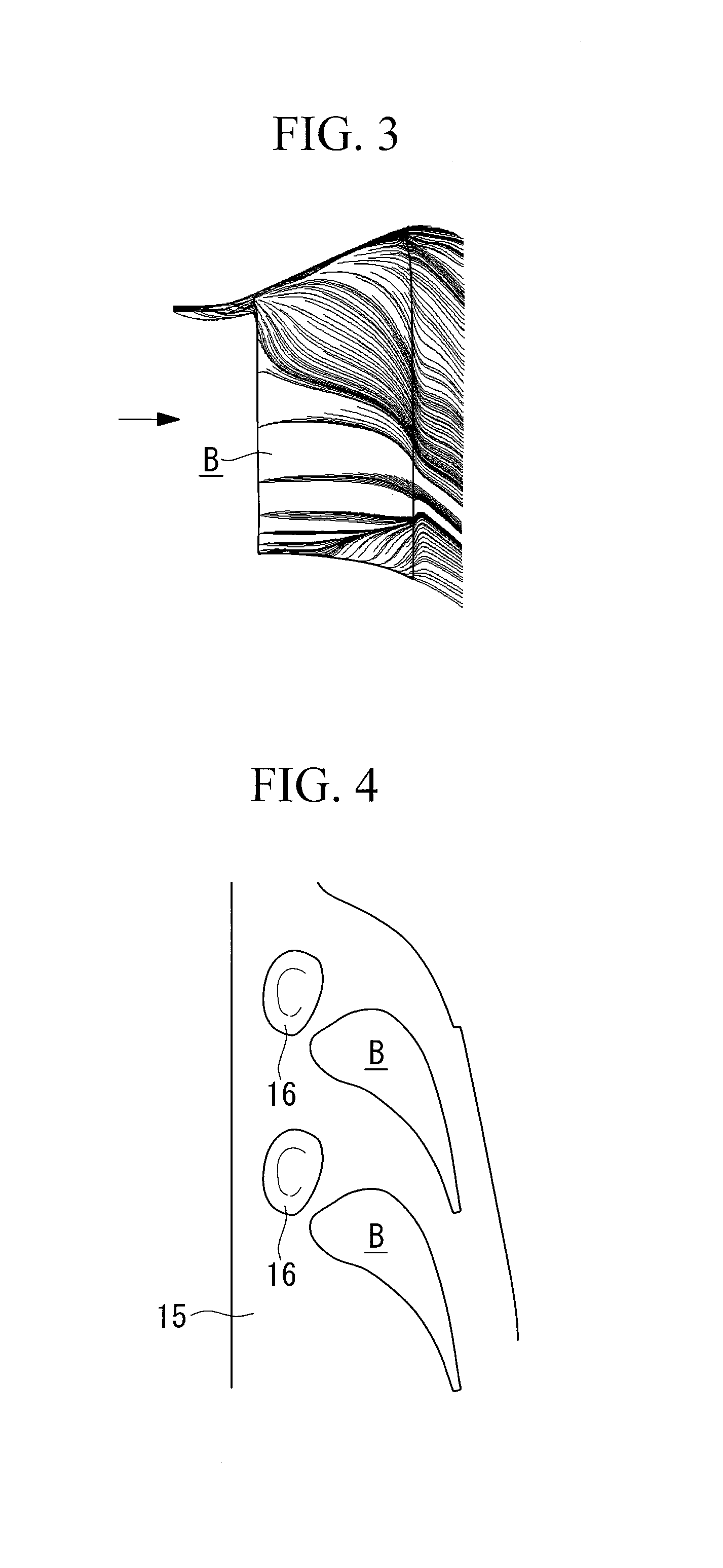
Structure and Method of Groove Loss Reduction for End Wall of New Turbine Cascade
ActiveCN104005796BReduce intensityReduced lateral pressure gradientBlade accessoriesStatorsTurbine bladeTransverse pressure
The invention provides a groove impairment structure of a novel turbine blade grid end wall. The structure is arranged on the turbine blade grid end wall, and is used for reducing secondary flow losses. The turbine blade grid end wall is located on the hub side of a plurality of turbine blades arranged in an annular mode. The invention further provides a corresponding method. The groove impairment structure of the novel turbine blade grid end wall is arranged on the turbine blade grid end wall, and is connected with the turbine blade grid end wall through a laser machining method. Transverse motion of end fluid can be obstructed, transverse pressure gradient can be reduced, and therefore the strength of a horseshoe vortex pressure side branch and a channel vortex is reduced, and the aim of reducing the secondary flow losses is achieved.
Owner:SHANGHAI JIAO TONG UNIV
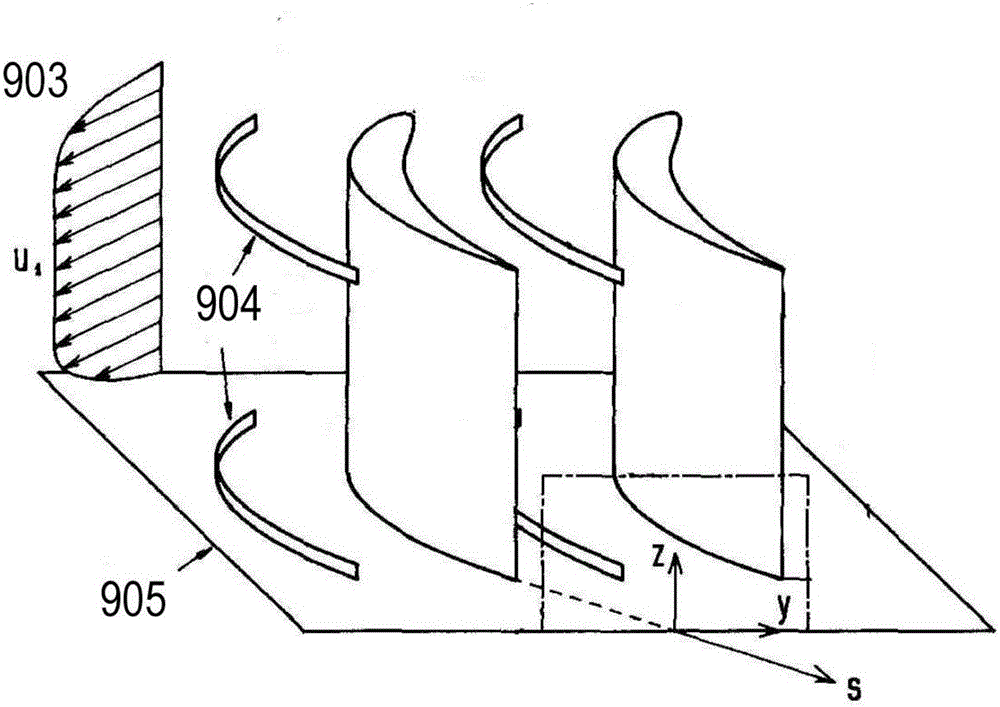
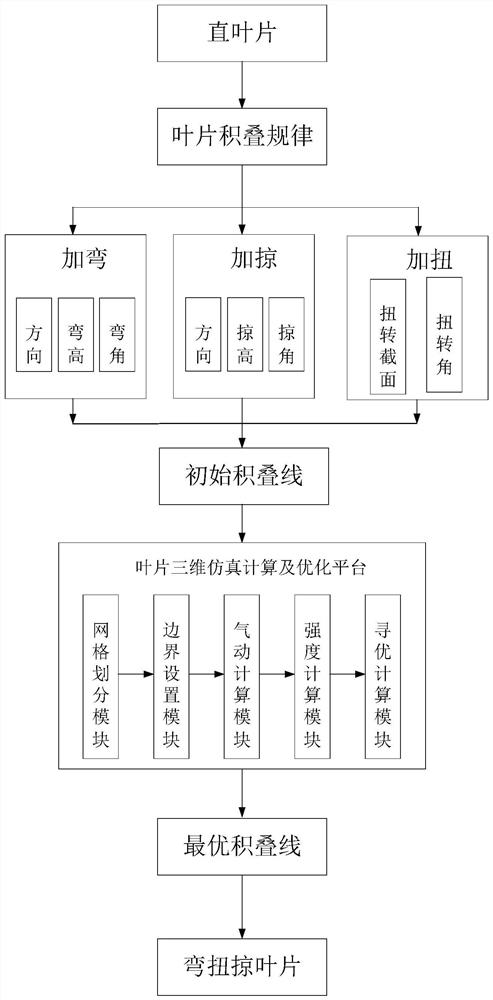
Design method of twisted swept structure stator blade for steam turbine
PendingCN114254456AReduce aerodynamic lossesAdd flow matchGeometric CADSpecial data processing applicationsDimensional simulationSteam turbine blade
The invention discloses a design method of a twisted swept structure stator blade for a steam turbine, and relates to the technical field of steam turbine blades. The invention aims to solve the problem of flow loss of low-pressure last-stage long blades of an existing steam turbine. The method comprises the steps that a blade design foundation and a stacking rule are determined, wherein the blade design foundation is a straight blade without a bending and twisting structure, and the stacking rule is stacking along the circle center of a steam outlet circle; based on the basic straight blade and the stacking rule, bending, sweeping and twisting are conducted on the blade, and the static blade of the bending, twisting and sweeping structure is obtained; an initial stacking line is determined, and a stator blade geometric entity is obtained in combination with the typical section blade profile; importing the obtained geometric entity into a blade three-dimensional simulation calculation and optimization platform, and further performing blade pneumatic calculation and blade strength calculation; and obtaining an optimal stacking line according to a calculation result, and finally stacking each typical section along the optimal stacking line to obtain the bending-twisting-sweeping blade. The method is used for designing the steam turbine stator blade.
Owner:HARBIN TURBINE +1
A blade body structure of a turbine blade
ActiveCN105298546BReduced load levelImprove aerodynamic performanceBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesTurbine bladeLength distribution
The invention discloses a blade body structure of a turbine blade. The two-dimensional blade shape of the blade body is a crescent-shaped closed curve surrounded by an inner arc curve and a back arc curve, and has characteristic parameters of chord length CH and axial width CX. The airfoil is formed by twisting and superimposing several two-dimensional airfoils according to a certain rule, and has a characteristic parameter airfoil height H; the chord length CH of the two-dimensional airfoil forms a parabolic distribution law from the root to the top along the blade height direction, The trend is that the root and top chords of the blade body grow longer, and the middle chord length is smaller; the axial width CX of the two-dimensional airfoil remains basically unchanged. The invention can make the turbine blade take into account different main loss sources in the root area, the top area and the middle area at the same time, so as to effectively and reliably improve the aerodynamic performance of the turbine blade and reduce the aerodynamic loss.
Owner:DONGFANG TURBINE CO LTD
A high pressure blower
ActiveCN112483439BIdentify non-swept featuresGood for intensity controlPump componentsPump installationsImpellerIntermediate frequency
The invention discloses a high-voltage booster, comprising an intermediate frequency motor, a moving impeller, a rectifier, an air intake cone and an air duct assembly. The rectifier is fixed on one end face of the intermediate frequency motor, and the moving impeller is installed on the motor shaft of the intermediate frequency motor. On the top, the intake cone is fixedly connected to the moving impeller, the air duct assembly includes an intake air duct and an exhaust air duct, the intake air duct is correspondingly sleeved with the intake cone and the moving impeller, and the exhaust air duct The air duct is correspondingly sleeved with the intermediate frequency motor, the moving impeller is composed of a first hub, a wheel disc and a moving blade, and the moving blade is an autonomous blade type with controllable diffusion, and the rectifier is composed of a second hub, a stationary blade and a motor The box is integrally formed, and the blade shape of the stationary blade is a curved-swept structure. The technical effect is: in this design, the basic gravity center stacking characteristics of the moving blades are not changed, so that the blade has the smallest creep amount in the long-term operation, so as to adapt to the design with small radial clearance, and the flow is controlled by static The sweep of the blades is ensured so that the impeller can maintain high efficiency characteristics.
Owner:绍兴上虞上立风机有限公司
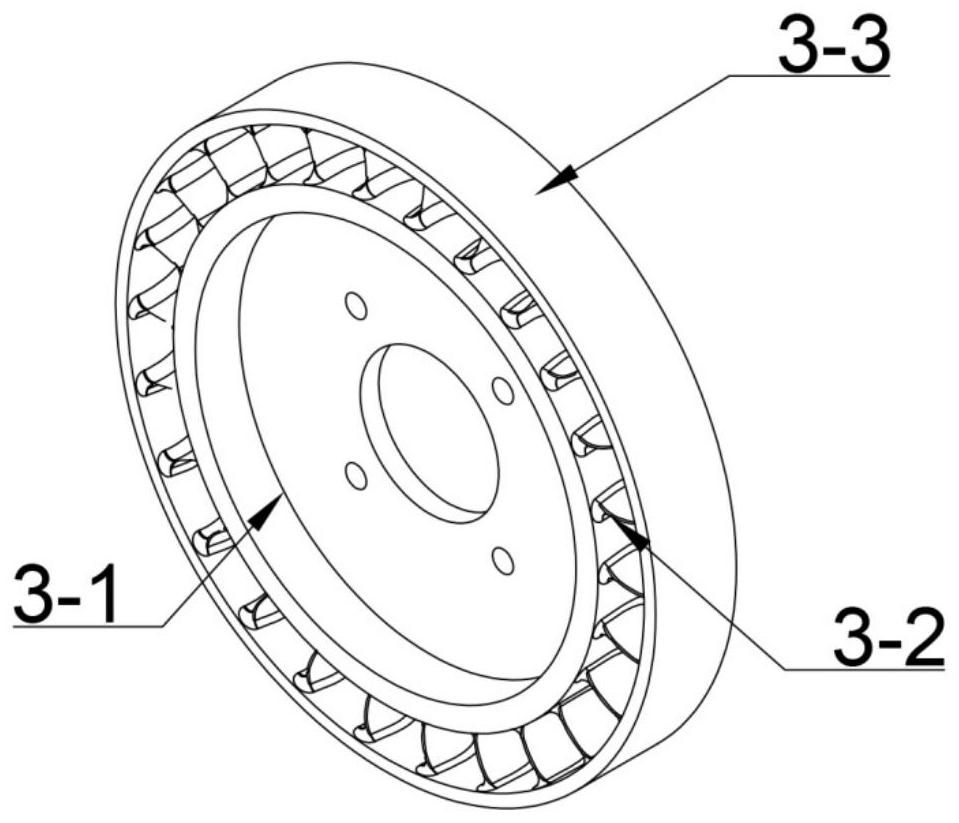
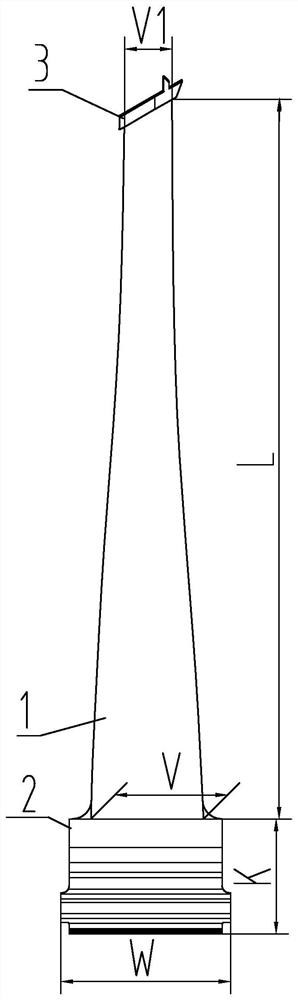
302.24 mm penultimate-stage moving blade for high-rotating-speed biomass power generation steam turbine
PendingCN113006878ASatisfy securityEnsure safetyBlade accessoriesMachines/enginesTurbineIndustrial engineering
The invention particularly discloses a 302.24 mm penultimate-stage moving blade for a high-rotating-speed biomass power generation steam turbine. The 302.24 mm penultimate-stage moving blade for the high-rotating-speed biomass power generation steam turbine solves the problems that in the prior art, the safety of a high-rotating-speed biomass generator set cannot be achieved, the pneumatic performance of a penultimate-stage blade is low, and the penultimate-stage blade cannot adapt to a high-rotating-speed biomass power generation steam turbine are solved. The 302.24 mm penultimate-stage moving blade comprises a blade working part, a blade root and a shroud ring; the blade working part, the blade root and the shroud ring are forged into a whole from top to bottom, the molded line of the blade working part is a variable cross-section twisted blade, the adjacent cross sections are twisted relatively, the cross-section areas of the blade working part are gradually reduced from the root to the top, the height L of the blade working part is 302.24 mm, the axial width V of the root of the blade working part is 47.15 mm, the diameter of the root of the blade working part is phi 960.14 mm, and the exhaust area of the blade working part is 1.20 m<2>; and the blade root is a helical tooth fir tree type blade root, and the axial width W of the blade root is 64.12 mm. The 302.24 mm penultimate-stage moving blade is used for the field of turbine moving blades.
Owner:HARBIN TURBINE +1
Compressor and compressor blades
ActiveCN112049818BImprove performanceIncrease the angle of attackPump componentsPumpsLeading edgeClassical mechanics
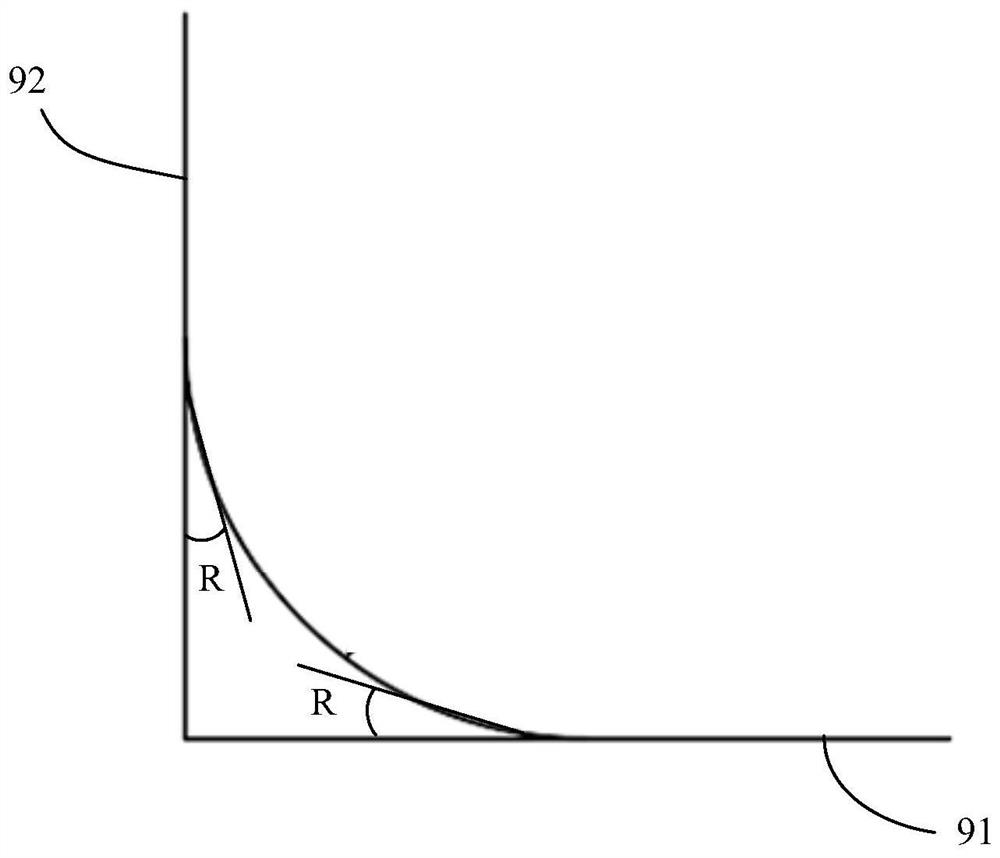
The purpose of the present invention is to provide a compressor blade, which can obtain relatively better aerodynamic performance compared with existing compressor blades. Another object of the present invention is to provide a compressor comprising the above-mentioned compressor blade. The compressor blade for achieving the aforementioned purpose comprises a blade body and an edge plate connected to the blade top or blade root of the blade body, the joint between the blade body and the edge plate is transitioned by a rounded corner, and the rounded corner A small chamfering radius is adopted at the leading edge of the airfoil, and the chamfering radius gradually increases from the leading edge of the airfoil to the trailing edge of the blade. Wherein, the fillet has a connection length L with the end wall surface of the edge plate, a height H connected with the airfoil, an included angle α formed with the end wall surface, and an included angle β formed with the surface of the airfoil, From the leading edge to the trailing edge, L, H, α, β gradually increase.
Owner:AECC COMML AIRCRAFT ENGINE CO LTD
Blade wheel structure of multiple wing type centrifugal blower fan
InactiveCN101363450BSimple shapeEasy to processPump componentsPumpsNoise levelStructural engineering
The invention discloses an impeller structure of a multi-wing centrifugal fan, comprising an impeller consisting of a plurality of aerofoil blades. The impeller structure is characterized in that: the chord length of the blade gradually reduces from the side of an impeller cover to the side of an impeller disk, or the chord length of the blade remains the same while the diameter of the impeller gradually reduces, thus leading to the result that the work capability of the blade along the side of the impeller cover to the side of the impeller disk gradually reduces. The impeller structure improved by the invention leads airflow speed of an outlet of the impeller to be more uniform distribution along the axial direction, reduces the secondary flow in a scroll casing, decreases flow losses, improves fan efficiency and reduces noise level. The impeller structure of the invention is simple in form, convenient in processing and low in manufacturing cost.
Owner:XI AN JIAOTONG UNIV
Gas compressor and gas compressor blade
ActiveCN112049818AImprove performanceIncrease the angle of attackPump componentsPumpsEngineeringFront edge
The invention aims to provide a gas compressor blade. Compared with an existing gas compressor blade, the gas compressor blade can obtain relatively better aerodynamic performance. The invention further aims to provide a gas compressor which comprises the gas compressor blade. In order to achieve the purpose, the gas compressor blade comprises a blade body and an edge plate connected with the blade top or the blade root of the blade body, the connecting position of the blade body and the edge plate is in transition through a rounded corner, the rounded corner adopts a small chamfer radius at the front edge of the blade body, and a chamfer radius is gradually increased from the front edge of the blade body to the tail edge of the blade body.
Owner:AECC COMML AIRCRAFT ENGINE CO LTD
Axial Flow Turbine
InactiveUS20200277870A1Reduce interferenceReduce secondary flow lossBlade accessoriesLeakage preventionWorking fluidEngineering
To provide an axial flow turbine that can reduce interference loss and secondary flow loss, and can reduce mixing loss. An axial flow turbine includes: stator blades provided on the inner-circumference side of a diaphragm outer ring; a diaphragm inner ring provided on the inner-circumference side of the stator blades; moving blades provided on the outer-circumference side of a rotor; a shroud provided on the outer-circumference side of the moving blades; a main flow path constituted by a flow path formed between an inner circumferential surface of the diaphragm outer ring and an outer circumferential surface of the diaphragm inner ring, and a flow path formed between an inner circumferential surface of the shroud and an outer circumferential surface of the rotor; and a cavity formed between the diaphragm inner ring and the rotor. The outer circumferential surface of the rotor has protruding portions and depressed portions. Each depressed portion extends along a relative flow direction of a working fluid passed through the stator blades in the main flow path.
Owner:MITSUBISHI HEAVY IND LTD
Features
- R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
Why Patsnap Eureka
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Social media
Patsnap Eureka Blog
Learn More Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com