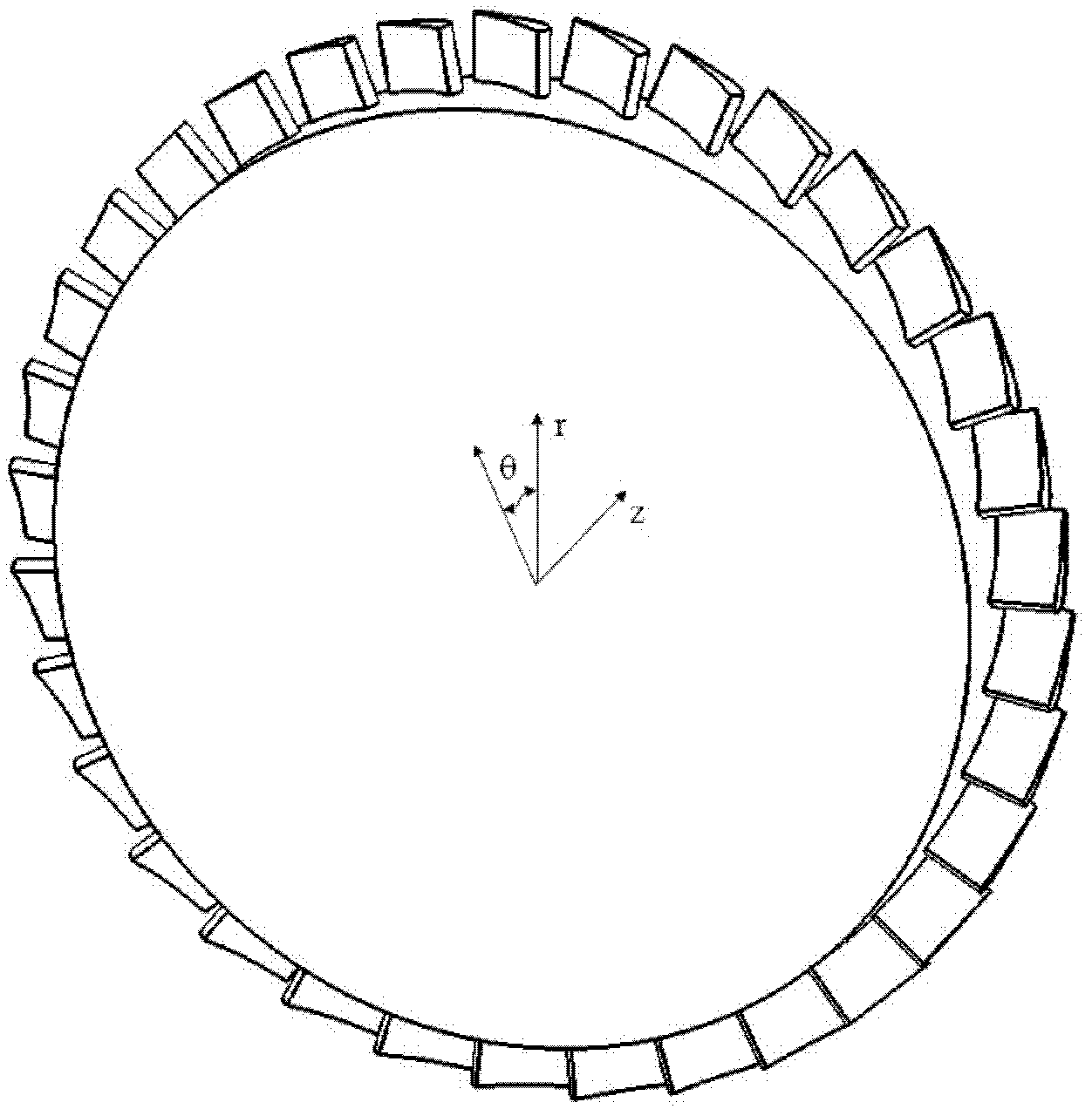
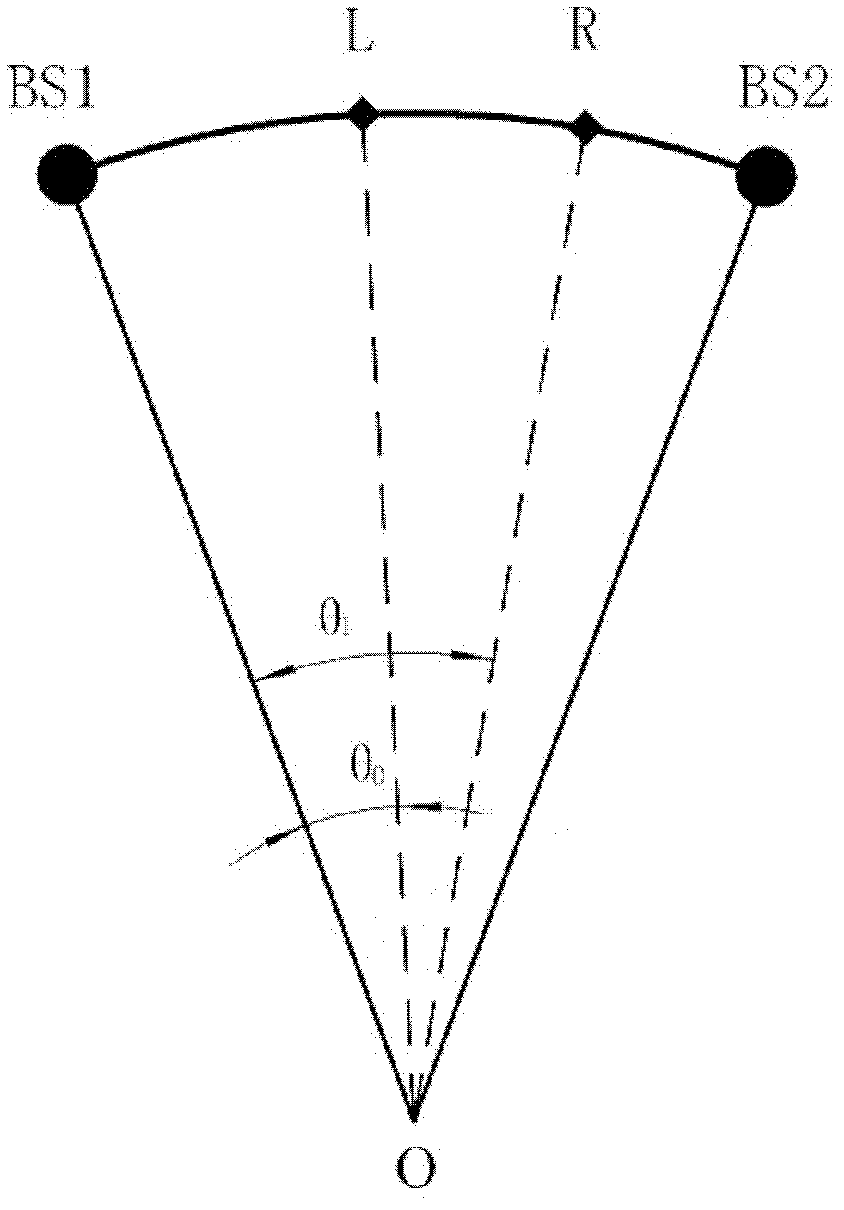
Modeling method for axis-asymmetric end wall of annular blade grid of air compressor or turbine
A non-axisymmetric, annular blade cascade technology, applied in the direction of machine/engine, blade supporting element, mechanical equipment, etc., can solve the secondary flow loss and improve the efficiency, the effect is not significant, and the end wall structure cannot be flexibly constructed, Unable to give full play to problems such as non-axisymmetric end walls
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment 1
[0022] This embodiment is to construct a non-axisymmetric end wall of a turbine annular cascade, wherein the shape of the end walls between all adjacent blades on the turbine annular cascade is the same, and the end walls between adjacent blades are used as a shaped end wall cycle, there are several convex and / or concave structures in one molding end wall cycle, and the non-axisymmetric end wall with only one convex structure is constructed in this embodiment.
[0023] For a convex or concave structure follow the steps below:
[0024] Step 1: In a molding end wall cycle, at -10%C ax , 110%C ax , 0% grid pitch, and 100% grid pitch surround the end wall area as the modeling area of the non-axisymmetric end wall, of which 0%C ax Indicates the position of the leading edge of the blade along the axial direction of the cascade, 100%C ax Indicates the position of the trailing edge of the blade along the axial direction of the cascade, 0% grid pitch indicates the position of the ...
Embodiment 2
[0031] This embodiment is to construct a non-axisymmetric end wall of a turbine annular cascade, wherein the shape of the end walls between all adjacent blades on the turbine annular cascade is the same, and the end walls between adjacent blades are used as a shaped end wall cycle, there are several convex and / or concave structures in one molding end wall cycle, and the non-axisymmetric end wall with only one concave structure is constructed in this embodiment.
[0032] For a convex or concave structure follow the steps below:
[0033] Step 1: In a molding end wall cycle, at -10%C ax , 110%C ax , 0% grid pitch, and 100% grid pitch surround the end wall area as the modeling area of the non-axisymmetric end wall, of which 0%C ax Indicates the position of the leading edge of the blade along the axial direction of the cascade, 100%C ax Indicates the position of the trailing edge of the blade along the axial direction of the cascade, 0% grid pitch indicates the position of the...
Embodiment 3
[0040] This embodiment is to construct a non-axisymmetric end wall of a turbine annular cascade, wherein the shape of the end walls between all adjacent blades on the turbine annular cascade is the same, and the end walls between adjacent blades are used as a shaped end wall cycle, there are several convex and / or concave structures in one cycle of the shaped end wall, and the non-axisymmetric end wall with one concave structure and one convex structure is constructed in this embodiment.
[0041] For a convex or concave structure follow the steps below:
[0042] Step 1: In a molding end wall cycle, at -10%C ax , 110%C ax , 0% grid pitch, and 100% grid pitch surround the end wall area as the modeling area of the non-axisymmetric end wall, of which 0%C ax Indicates the position of the leading edge of the blade along the axial direction of the cascade, 100%C ax Indicates the position of the trailing edge of the blade along the axial direction of the cascade, 0% grid pitch ind...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com