Design method of twisted swept structure stator blade for steam turbine
A design method and technology of static vanes, applied in special data processing applications, instruments, electrical digital data processing, etc., can solve the problems of flow loss in the last few stages of low pressure and long vanes, and achieve enhanced dynamic and static flow matching, reduce aerodynamic losses, improve Intake flow field effect
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
specific Embodiment approach 1
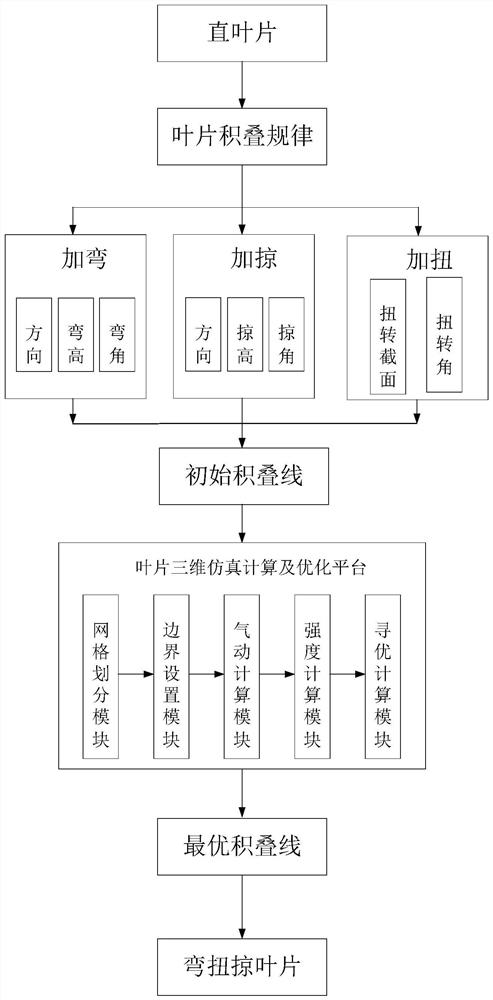
[0026] Specific implementation mode one: combine figure 1 To illustrate this embodiment, a method for designing a stator blade with a twisted and swept structure for a steam turbine described in this embodiment includes the following steps:
[0027] Step 1: Determine the blade design basis and stacking law: the blade design basis is straight blades, without bending and torsion-sweeping structure, and the stacking law is stacking along the center of the steam outlet circle. The structural parameters of the basic straight blades include the total blade height L, The top axial width of the working part of the blade is V, and the diameter of the blade root is The exhaust area of the working part of the blade is A;
[0028] Step 2: Based on the basic straight blades and stacking rules, add bending, sweeping, and twisting to the blades to obtain stationary blades with curved, twisted, and swept structures;
[0029] Step 3: Determine the initial stacking line, and obtain the geo...
specific Embodiment approach 2
[0038] Specific implementation mode two: combination figure 1 Describe this embodiment. In the second step of this embodiment, the blade bending includes parameter determination of the bending direction, bending height and bending angle, wherein the bending direction adopts positive bending, and the bending area is located at the root of the blade. The height is 10% to 15% of the total height L of the blade, and the bending angle is an included angle with the vertical direction, which is controlled between 10° and 45°. The undisclosed technical features in this embodiment are the same as those in the first embodiment.
[0039] The bending direction is divided into positive bending and reverse bending. The positive bending means that the pressure surface bends to the suction surface, and the reverse bending means that the suction surface bends to the pressure surface. In this embodiment, positive bending is selected.
specific Embodiment approach 3
[0040] Specific implementation mode three: combination figure 1To illustrate this embodiment, in the second step of this embodiment, blade sweeping includes parameter determination of sweeping direction, sweeping height and sweeping angle. , the sweeping area is on the top of the blade, the shapes of two adjacent sections during the sweeping process are exactly the same, only the axial position changes, the sweeping height is less than or equal to 10% of the height of the working part of the blade, and the sweeping angle is the distance between the vertical direction The angle is controlled between 20° and 40°. The undisclosed technical features in this embodiment are the same as those in the second embodiment.
[0041] The direction of adding and sweeping is the axial direction, which can be divided into two types: steam inlet sweeping toward outlet and steam outlet sweeping toward inlet. This embodiment adopts steam inlet toward outlet, which can control the aerodynamic los...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com