Pmr write head with assisted magnetic layer
a write head and magnetic layer technology, applied in the field of thin magnetic film, can solve the problems of reducing the writability (magnetic field) of the writer on the magnetic recording media, limiting the achievement of a higher recording area density, and the current technology cannot enable further field gradient improvement. , to achieve the effect of improving field amplitude and field gradient, increasing bpi
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
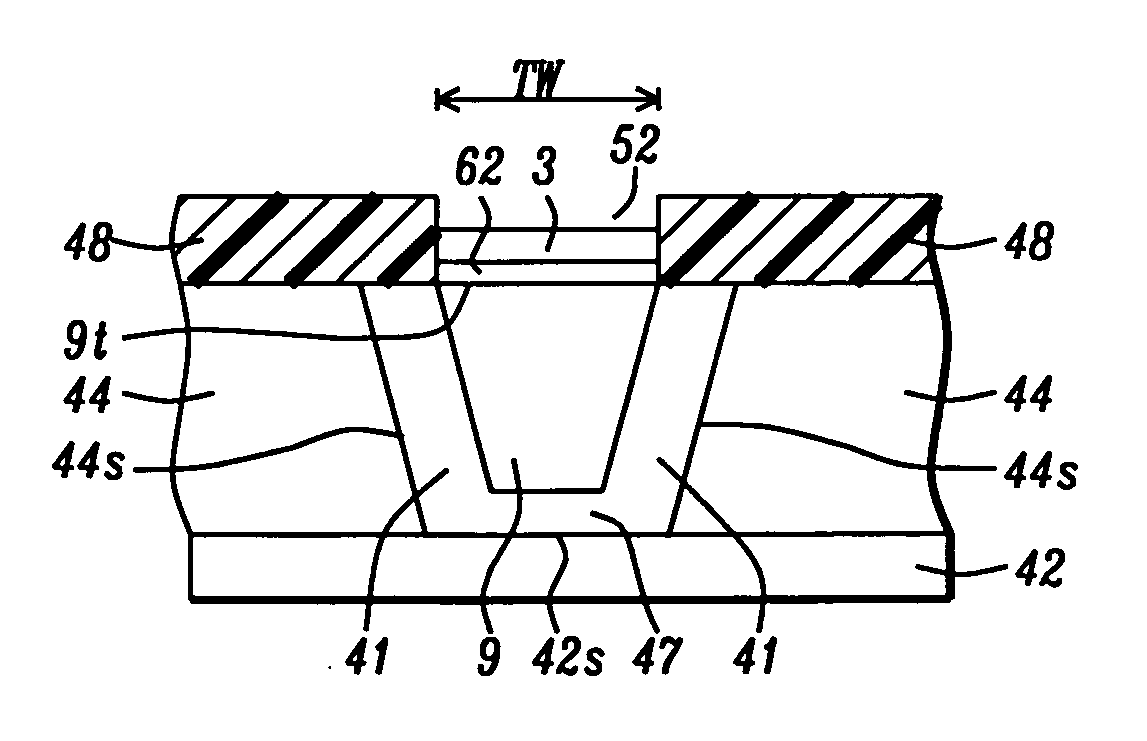
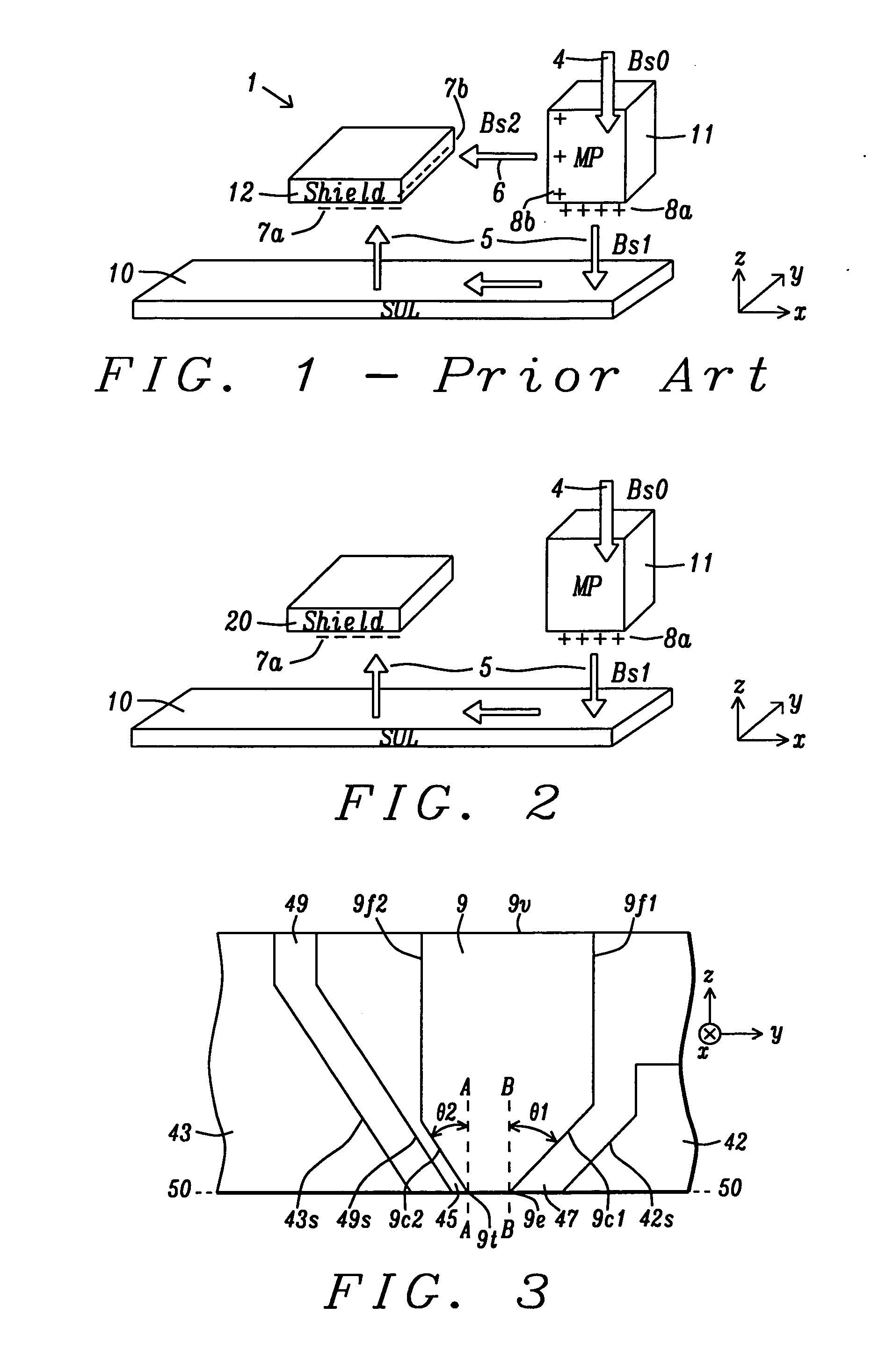
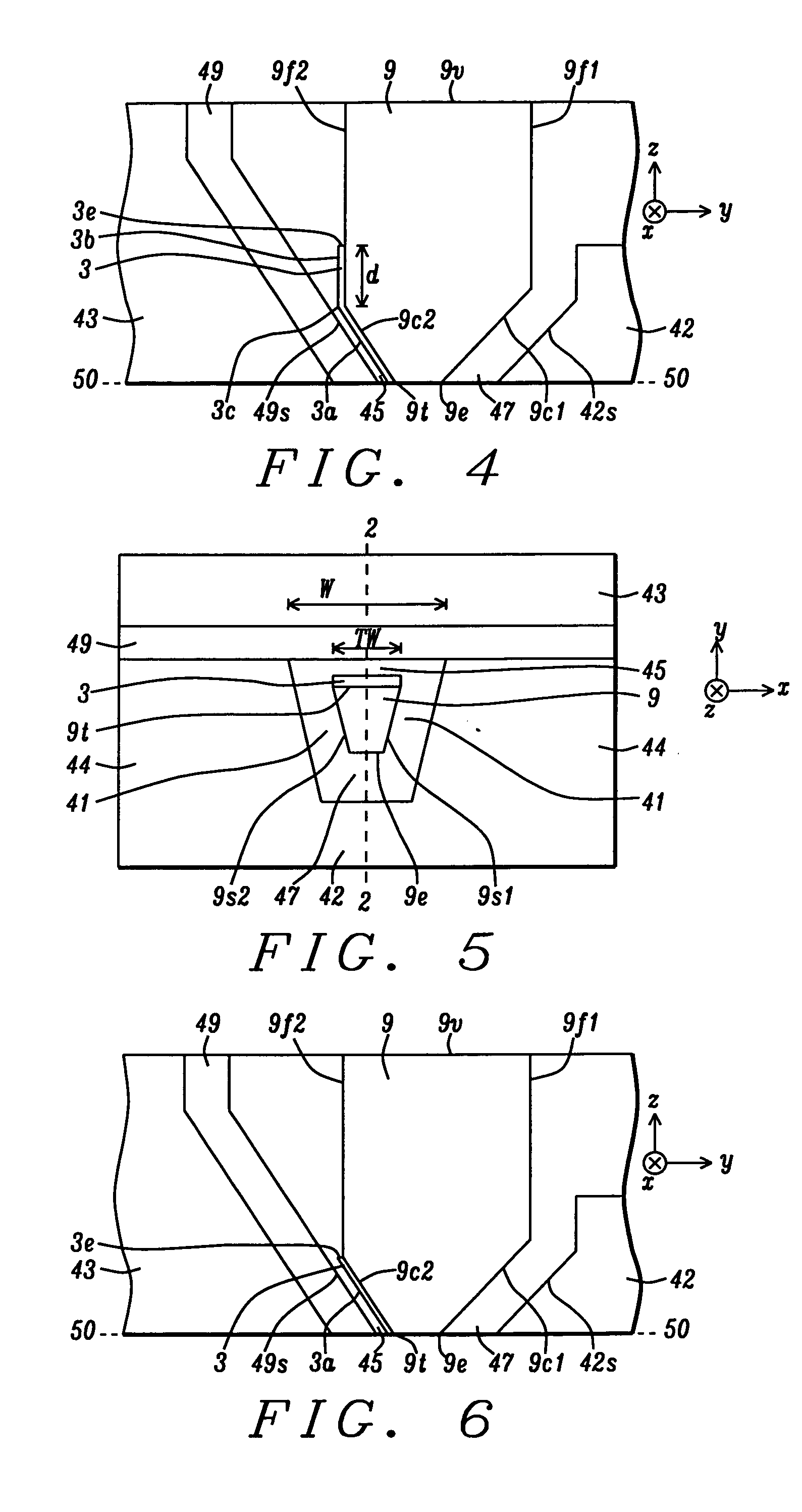
[0026]The present invention is a PMR writer design which takes advantage of the discovery that an anisotropic magnetic material may be used as a magnetic assist layer on a main pole trailing side to minimize flux loss from the main pole to a trailing shield and thereby maximize the flux field and field gradient at the main pole interface with the ABS. Although the exemplary embodiment depicts a trapezoidal shaped main pole at the ABS, the present invention also encompasses other main pole shapes. Furthermore, the main pole may have one or both of a tapered trailing edge and a tapered leading edge. Width in the context of shield structures and layers defined herein refers to a distance in a cross-track direction, and thickness or depth relates to a distance in a down-track direction. The gap layer as illustrated herein may not have a uniform thickness and the write gap portion between the main pole and trailing shield is typically thinner than the lead gap.
[0027]Referring to FIG. 2, ...
PUM
| Property | Measurement | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| thickness | aaaaa | aaaaa |
| distance | aaaaa | aaaaa |
Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com