Wind turbine
a wind turbine and wind power technology, applied in the direction of liquid fuel engines, renewable energy generation, greenhouse gas reduction, etc., can solve the problems of reducing the power output and energy conversion efficiency of vertical wind turbines, affecting the torque of vertical turbine blades, and rotating down
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
Embodiment Construction
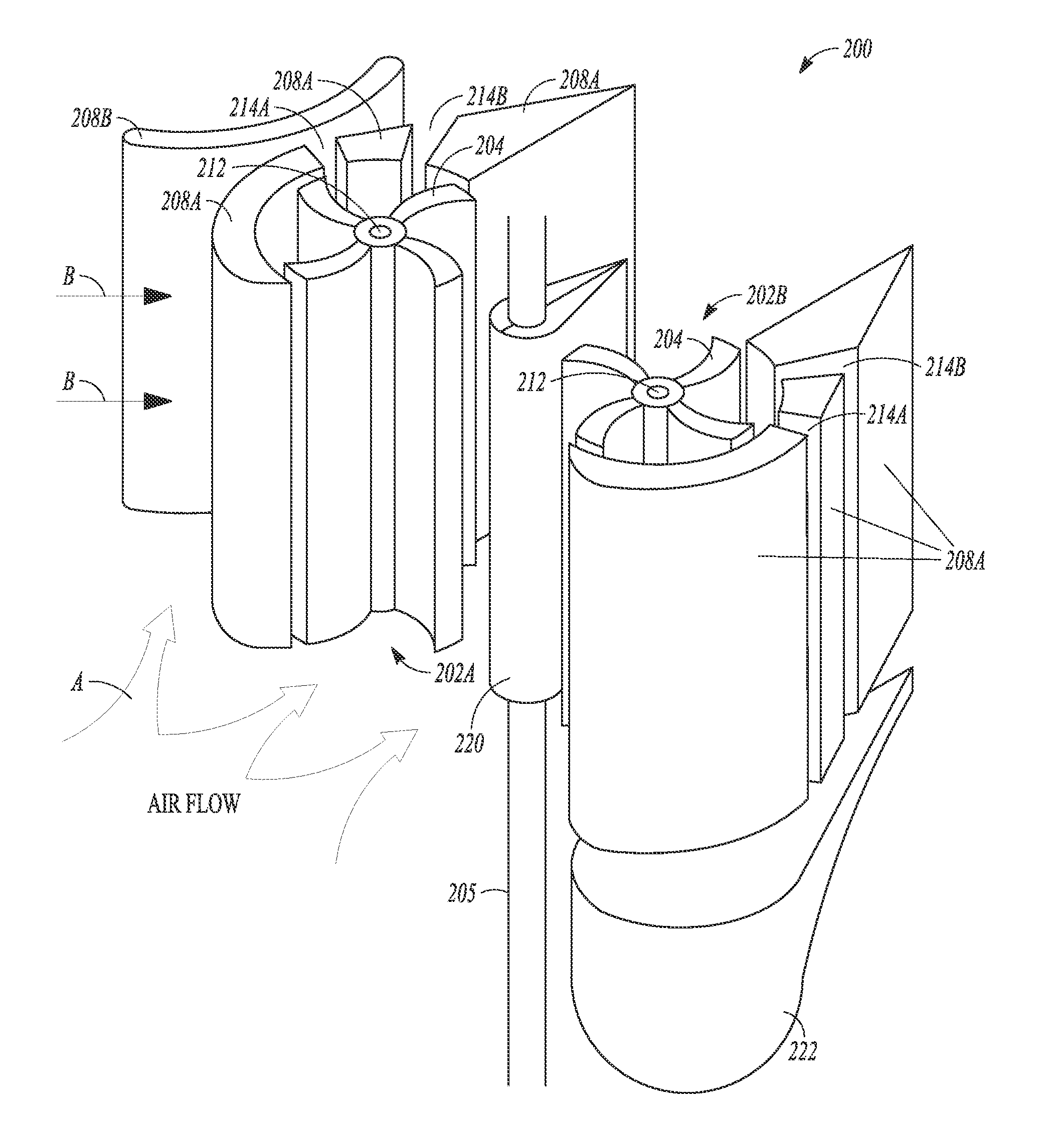
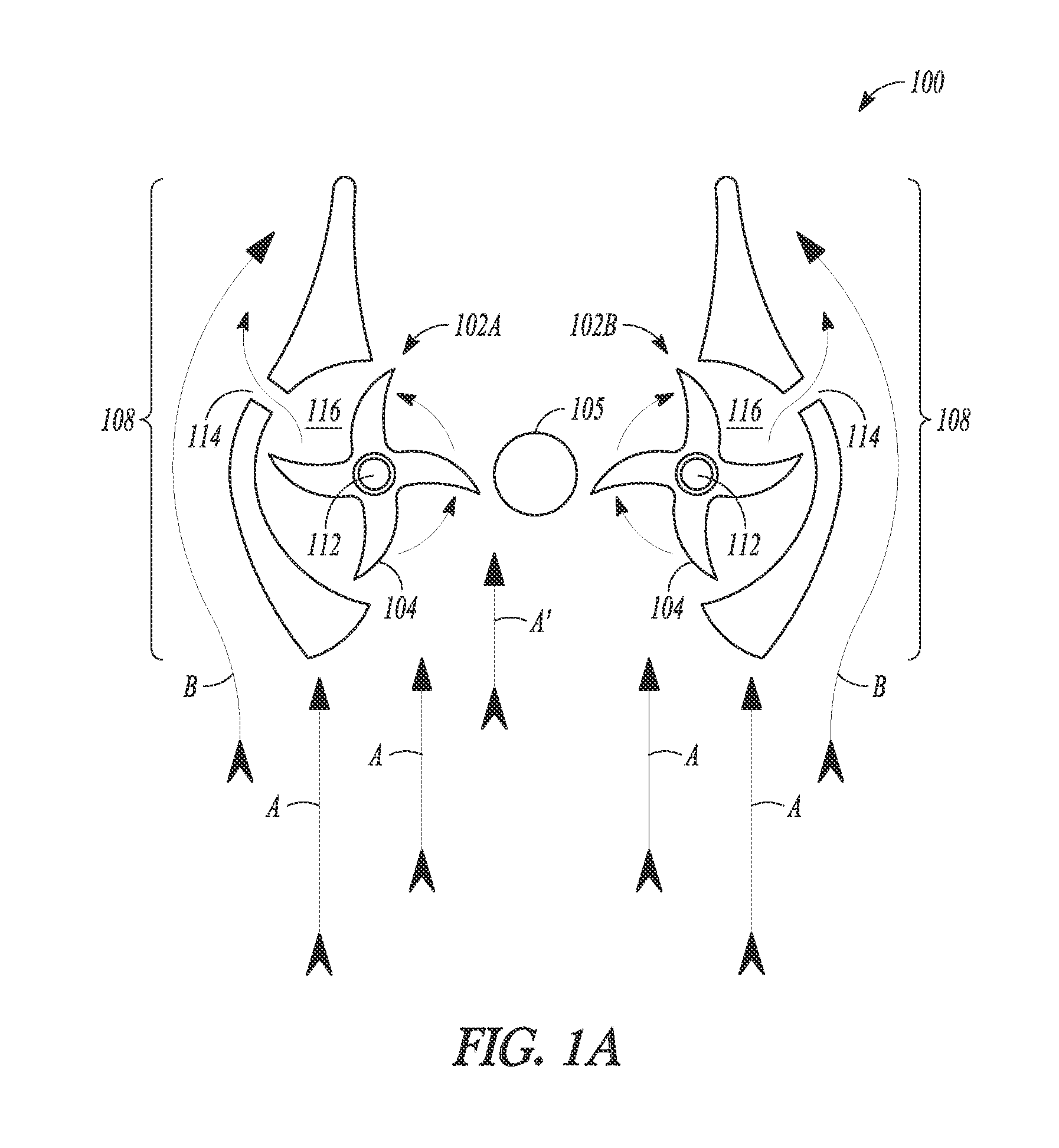
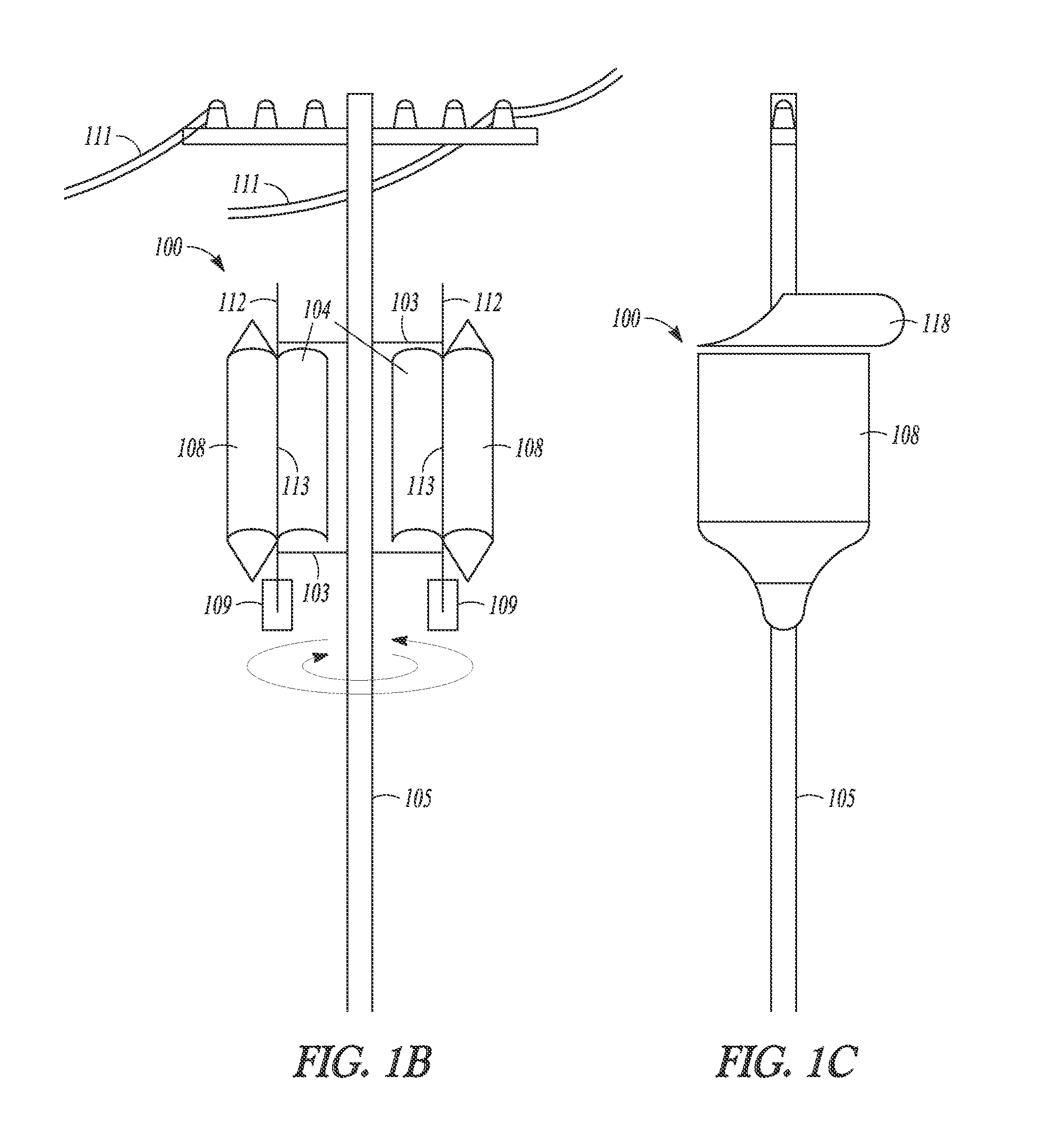
[0023]Reference is now made to FIGS. 1A-1C of the accompanying drawings which show a vertical axis wind turbine system 100 that converts wind energy into electrical or mechanical energy. Use of the word “vertical” in this specification is not intended to limit the application of the disclosure. Horizontally disposed wind turbine systems, or “vertical”-type turbines having an axis of rotation disposed at any inclined angle are within the scope of this disclosure.
[0024]The turbine system 100 comprises at least one turbine rotor 102A which has a plurality of curved blades 104 for receiving head-on wind generated airflow, as shown by arrows A in FIG. 1A. In the illustrated embodiment, two turbine rotors 102A and 102B are shown but the system could have three or more such rotors. In other embodiments, the blades could be straight or planar, relatively thick or thin in sectional thickness, and with or without a leading or trailing edge. Any blade or foil that works to drive a vertical-typ...
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com