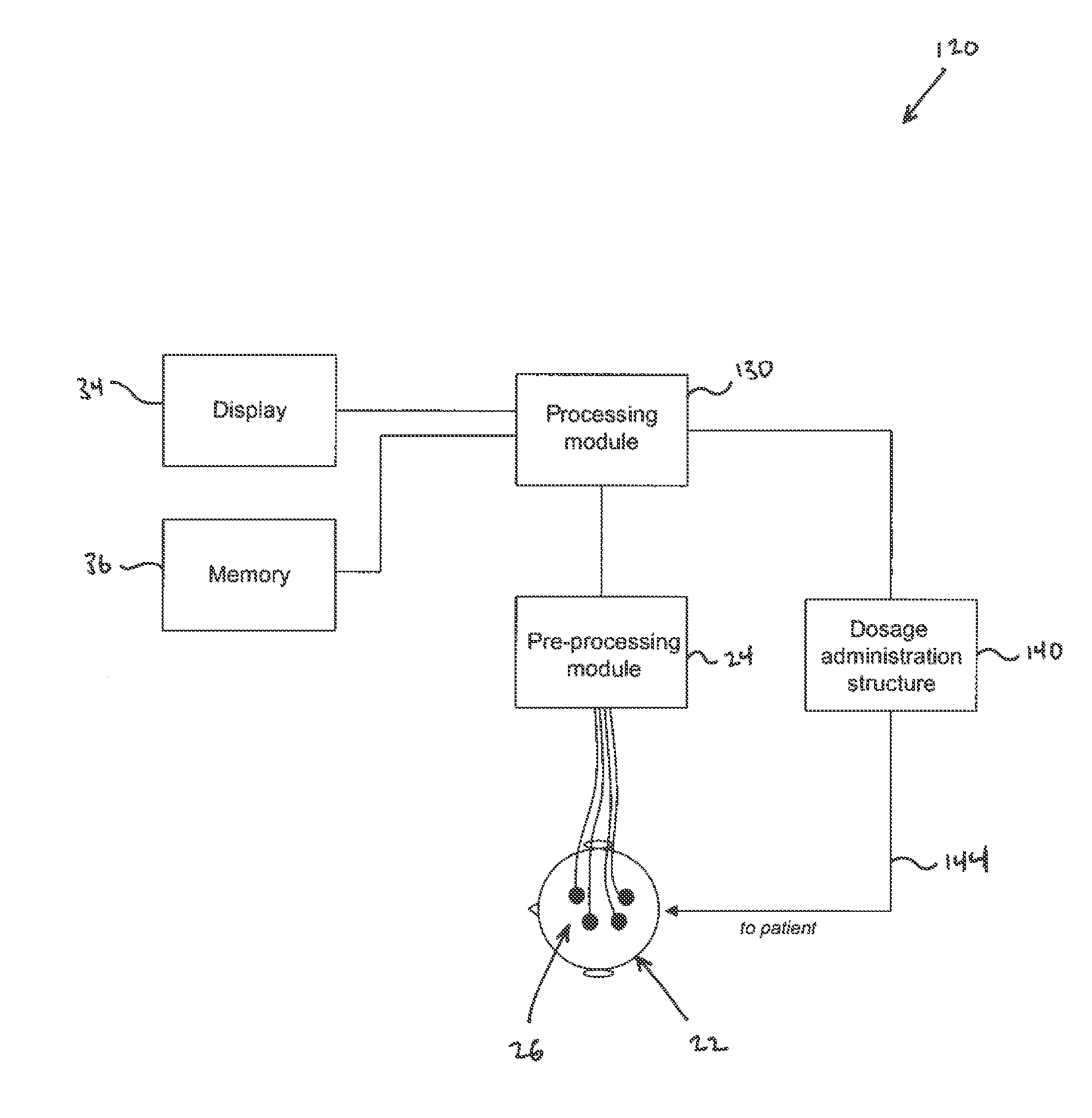
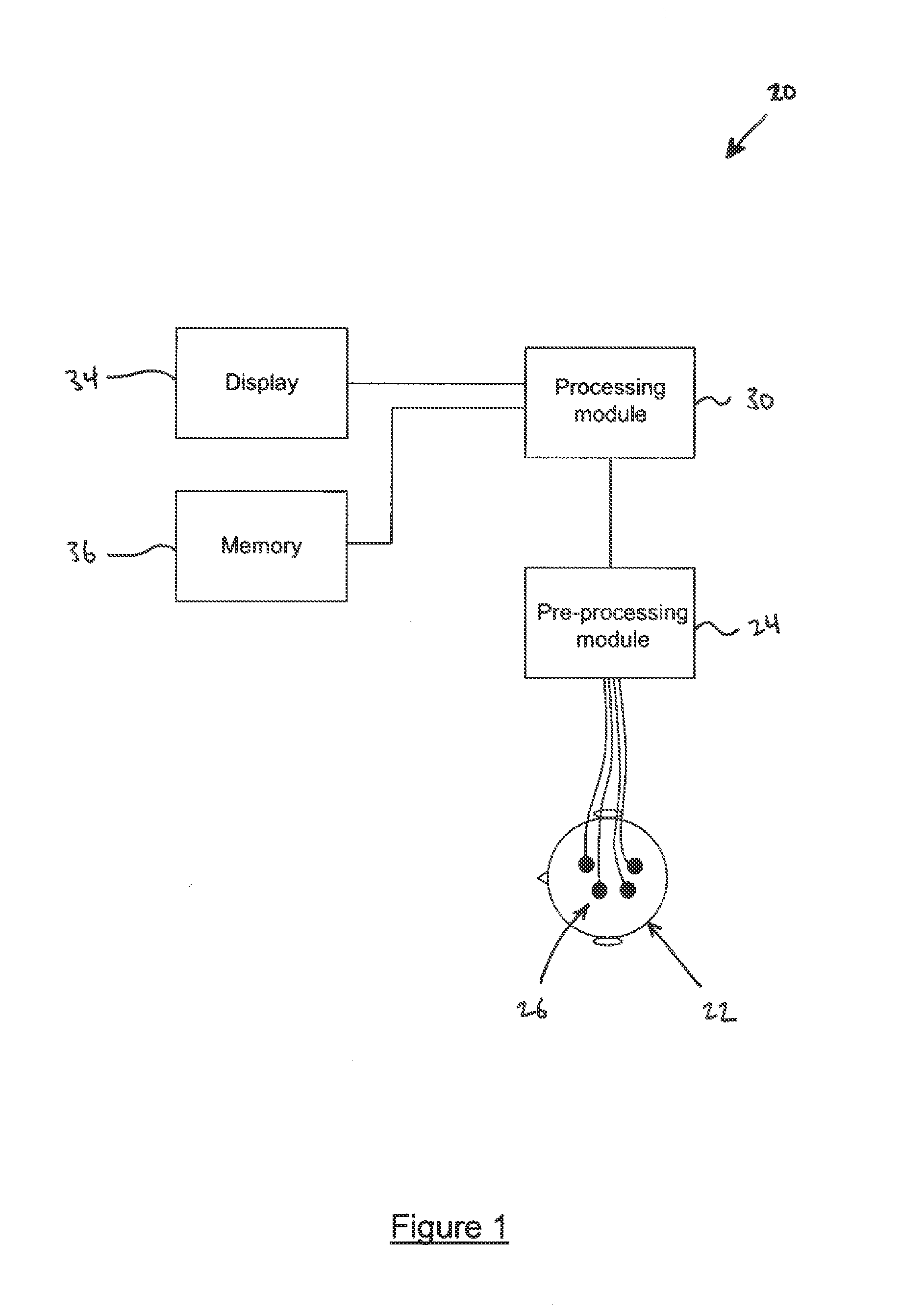
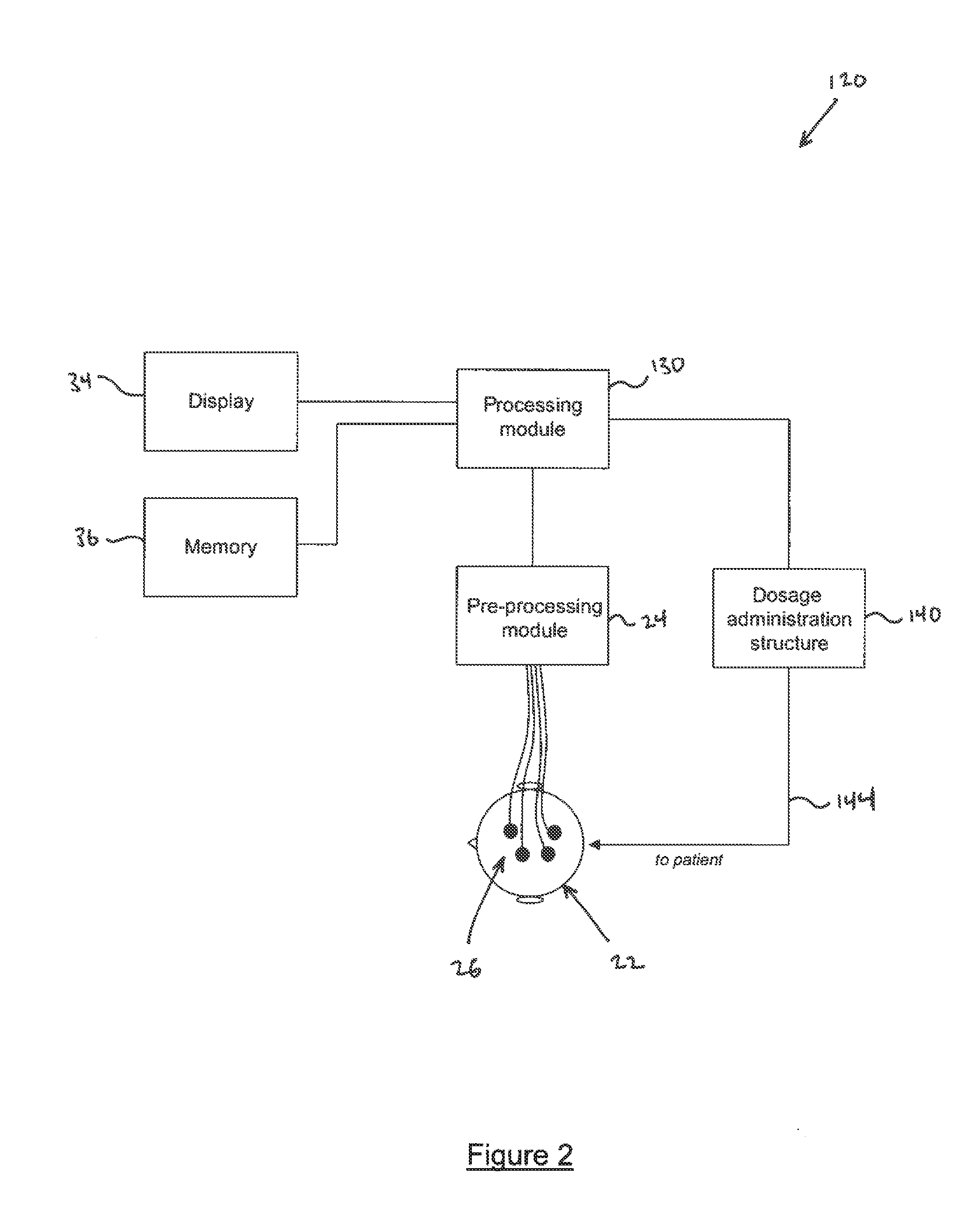
Method of monitoring depth of anesthesia and apparatus for same
a technology of depth monitoring and anesthesia, applied in the field of anesthesia, can solve the problems of prolonging the post-anesthesia recovery period and undesirable administration of anesthesia in excess
- Summary
- Abstract
- Description
- Claims
- Application Information
AI Technical Summary
Benefits of technology
Problems solved by technology
Method used
Image
Examples
example
[0062]Digitized scalp EEG signals were sampled at 1024 Hz using disposable silver / silver-chloride electrodes, 9 mm in diameter (XLTEK, Oakville, Ontario, Canada). Electrode placement followed the international standard 10-20 system recommended by the International Federation of Societies for Electroencephalography and Clinical Neurophysiology (IFSECN), and as shown in FIG. 3. A common reference electrode was positioned between Cz and Fz. EEG signals were recorded from six (6) patients undergoing surgical procedures requiring general anesthesia and having a duration of approximately 1 hour. The patients were screened such that they were not being prescribed central nervous system (CNS) medications and did not have any diagnosed CNS pathology. EEG signals were recorded continuously just prior to and during anesthesia and surgery, and during the emergence period following anesthesia and surgery. The bispectral index (BIS™) was simultaneously recorded using a BIS™ monitor (Aspect, Mass....
PUM
 Login to View More
Login to View More Abstract
Description
Claims
Application Information
 Login to View More
Login to View More - R&D
- Intellectual Property
- Life Sciences
- Materials
- Tech Scout
- Unparalleled Data Quality
- Higher Quality Content
- 60% Fewer Hallucinations
Browse by: Latest US Patents, China's latest patents, Technical Efficacy Thesaurus, Application Domain, Technology Topic, Popular Technical Reports.
© 2025 PatSnap. All rights reserved.Legal|Privacy policy|Modern Slavery Act Transparency Statement|Sitemap|About US| Contact US: help@patsnap.com